Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleA new approach to the synthesis of legionaminic acid analogues†
James R. Carter and
Milton J. Kiefel *
*
Institute for Glycomics, Griffith University Gold Coast Campus, Southport, QLD 4222, Australia. E-mail: m.kiefel@griffith.edu.au
First published on 19th October 2018
Abstract
Legionaminic acid is a member of the nonulosonic acids, which are a class of sugars considered to be a virulence factor within a wide variety of pathogenic bacteria. We have developed a synthetic pathway towards C-7 analogues of legionaminic acid starting from Neu5Ac, resulting in the complete synthesis of both legionaminic acid, and its C-7 epimer, from a common precurser. Our approach involves the late-stage introduction of the requisite C-7 nitrogen functionality, thus making our strategy amenable to the introduction of a range of different amide groups at C-7 of legionaminic acid.
Introduction
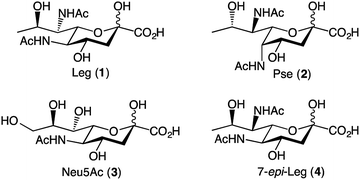
The nonulosonic acid class of sugars consists of 9-carbon α-keto acid carbohydrate monomers. Unique to bacterial species are the recently identified 5,7-diamino-3,5,7,9-tetradeoxy-nonulosonate derivatives, which are an important sub-class of nonulosonic acids.1 There appear to be two predominant parent compounds: legionaminic acid (Leg, 1) and pseudaminic acid (Pse, 2) (Fig. 1).1 Both Pse and Leg occur naturally as several derivatives, notably with changes in the nature of the amide groups attached to carbon-5 and carbon-7, or in the case of Leg, also as epimers at C-4 and C-8. Legionaminic acid was first reported in 1994, where it was discovered as an α-(2,4)-linked homopolymer component of the Legionella pneumophila serotype 1, O-chain LPS.2 L. pneumophila is the causative agent of Legionnaires' disease, and as it is understood that the LPS of serotype 1 is the key determinant for the development of the disease, studies have shown that Leg is important to the virulence capabilities of L. pneumophila.3 Other pathogenic species from which legionaminic acid and its derivatives have been isolated include Acinetobacter,4–7 Pseudomonas,4,8,9 Salmonella,10 Campylobacter,11,12 Escherichia,13–15 and Vibrio.4,16–19Given the importance of these nonulosonic acids within a range of human pathogenic bacteria, there is much interest in better understanding their role in pathogenesis and recognition events. However, the structural complexity of these sugars that makes them such attractive biological probes, also makes the synthesis of these sugars quite difficult. Towards this end, a pivotal piece of work by Tsvetkov and colleagues in 2001, describes the synthesis of nine of the possible fifteen stereoisomers of pseudaminic acid.20 This work resulted in the absolute stereochemistry of Pse and Leg being confirmed, as well as the confirmation of the natural stereoisomers 4-epi-Leg and 8-epi-Leg. The key step in the Tsvetkov synthesis to gain access to the nine-carbon sugars was an aldol condensation between a series of previously prepared hexose sugars and oxaloacetic acid, although the chemical yield for this aldol condensation was below 5% in all cases.20 In 2015, Matthies et al. published a synthesis of five legionaminic acid analogues, via a strategy that commenced with D-threonine, and involved a series of chelation-controlled organometallic additions and a Petasis multicomponent reaction.21 Importantly this work provided a route to legionaminic acid derivatives that could be effectively attached to solid surfaces, thus facilitating serological studies into human pathogens that contain legionaminic acid.21 In 2017, a complete synthesis of disaccharides of legionaminic acid was published by the Crich group, and involved converting commercially available N-acetylneuraminic acid (Neu5Ac, 3) into a legionaminic acid glycosyl donor via a fifteen-step synthetic route with an overall yield of 17%.22 A chemoenzymatic approach to legionaminic acid synthesis has recently been reported, by Santra et al.,23 wherein D-fucose was converted through 9 synthetic steps (44% overall yield) into a trideoxy mannose derivative that was subsequently condensed with sodium pyruvate in the presence of the sialic acid aldolase from Pasteurella multocida to give 1.23
Despite the important contribution of all these nonulosonic acid syntheses, to date there does not exist a synthetic pathway towards C-7 analogues of Leg. The C-7 functionality of Leg is vital to its role in the bacteria, which can be seen from the fact that there are multiple naturally occurring C-7 analogues of legionaminic acid,4,5,12,13,18 as well as the fact that there are multiple steps in the biosynthetic pathway dedicated to introducing the amide functionality at this position.24 Our approach towards legionaminic acid synthesis was therefore designed to synthesise a range of C-7 analogues of Leg, including the C-7 epimer (4) and a variety of nitrogenous C-7 functionalities; generating all of these analogues from a common, commercially accessible precursor; and keeping the C-7 functionalisation step as late in the synthesis as possible to avoid different functionalities interfering in later reactions.
Results and discussion
We based our approach towards legionaminic acid synthesis on our earlier efforts in synthesising 8-epi-Pse.25 Our approach towards 8-epi-Pse was achieved in 8 steps and 35% yield from KDN, and involved a halogenation–hydrogenation approach to deoxygenate C-9, and an activation-azide displacement approach to achieve the introduction of the nitrogen functionalities at C-5 and C-7.25 Based on the experience we gained during our synthesis of 8-epi-Pse, our proposed approach towards C-7 modified legionaminic acids is shown in retrosynthetic terms in Fig. 2. Commencing with Neu5Ac (3), after esterification and methyl glycoside introduction, our plan was to deoxygenate at C-9, and then selectively protect the C-4 and C-8 hydroxyls to give 5, such that the C-7 hydroxyl is available for either activation and displacement with azide thereby leading to 7-epi-legionaminic acids (e.g. 4). Alternatively, the C-7 stereochemistry in 5 could be inverted to give 6, which would then afford legionaminic acids via activation of the inverted C-7 hydroxyl and subsequent displacement with azide and elaboration into C-7 amides.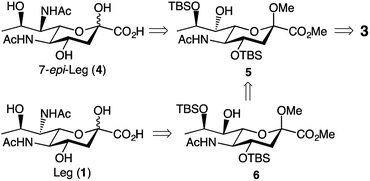 | ||
| Fig. 2 Our retrosynthetic approach towards legionaminic acids (e.g. 1) and 7-epi-legionaminic acids (e.g. 4). | ||
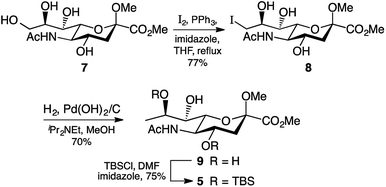
During some preliminary investigations into legionaminic acid synthesis we found that C-9 deoxygenation late in the synthesis gave a complex mixture of products, and so we opted to perform this step as early in the synthesis as possible. Accordingly, C-9 of the methyl ester methyl glycoside derivative 7 of Neu5Ac was iodinated under Garegg–Samuelsson conditions,26 which involved refluxing 7 in THF with imidazole, triphenylphosphine, and iodine chips, to furnish 8 in 77% yield after chromatography (Scheme 1). The presence of the iodine at carbon nine was clearly observed by examination of the 13C NMR spectra, notably by the change in chemical shift of the C-9 peak from δ 60 ppm in 7 to δ 17 ppm in 8. It should be noted that triphenylphosphine oxide salts were particularly difficult to separate from the product 8 and required extensive column chromatography using different solvent systems to obtain 8 pure. Reductive removal of the iodo group in 8 was first attempted using the same conditions as we had developed for the 8-epi-Pse synthesis,25 which involved exposure of a methanolic solution of 8 to Pd(OH)2/C catalyst, N,N-diisopropylethylamine, under hydrogen gas at atmospheric pressure. Unfortunately, while the reaction gave us good yields of the 9-deoxy derivative 9, it proceeded very slowly, returning ∼60% unreacted 8 after 3 days. However, changing from a hydrogen atmosphere at atmospheric pressure to 300 kPa on the Parr hydrogenator meant the reaction proceeded more quickly, and afforded the desired 9-deoxy derivative 9 in 70% yield (Scheme 1), with only limited amounts of unreacted 8 being recovered. The 9-deoxy product 9 was identified by examination of the 1H NMR spectrum which showed a characteristic doublet at δ 1.3 ppm integrating to 3H indicating the C-9 methyl group, as well as the change in multiplicity of H-8 from a doublet of doublets of doublets in 8 to a quartet of doublets in 9.
The final step before we could begin work on modification of the C-7 was the selective protection of the hydroxyl groups attached to C-4 and C-8. As the silyl ether protecting group had served us well at carbon four in our 8-epi-Pse synthesis,25 we elected to attempt to use this protecting group again. Exposure of the triol 9 to 2.4 molar equivalents of TBSCl and 5 molar equivalents of imidazole overnight at room temperature gave the 4,8-bis-silyl derivative 5 in reasonable yield (75%). The lack of any product with a silyl group at C-7 was expected, based on the pattern of selective protection of sialic acids.27
In order to synthesise legionaminic acid with the natural stereochemistry at C-7, an inversion of stereochemistry at C-7 in 5 would be required prior to introduction of the nitrogen-based functionality. We initially explored two approaches towards this: the displacement of a leaving group with a nitrite nucleophile based on the work of Dong et al.,28 and the displacement with an acetate nucleophile based on the work of Battistini et al.29 While the former did successfully produce the 7-epi-Neu5Ac derivative 6, the yield over the two reactions was poor (18%). The latter method gave even poorer results, with none of the desired 7-epi-acetoxy derivative formed at all.
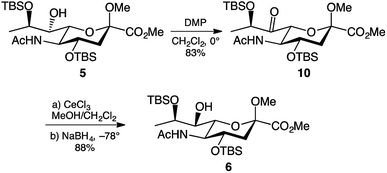
Another approach towards inversion of C-7 stereochemistry is the oxidation-reduction approach. This is the approach used by the Crich group for the inversion of C-7 stereochemistry in their legionaminic acid synthesis.22 The approach uses Dess–Martin periodinane30 to oxidise the C-7 hydroxyl to a ketone, followed by reduction to regenerate the hydroxyl functionality. Accordingly, treatment of 5 with 1.5 molar equivalents of Dess–Martin periodinane in dichloromethane afforded the 7-keto derivative 10 in an 83% yield after two hours at 0 °C (Scheme 2). Extensive purification through column chromatography was required to remove the iodinane by-product produced during the reaction. The presence of the ketone in 10 was evident by the shift of the C-7 signal in the 13C NMR spectrum, changing from δ 74 ppm in 5 to δ 207 ppm in 10. Following the successful C-7 oxidation, the next step was to reduce the ketone to the hydroxyl. Following the conditions reported by the Crich group22 cerium(III) chloride in methanol was added to a solution of the 7-keto derivative 10 in dichloromethane at −78 °C. After one hour, sodium borohydride was added to form Luche's reagent,31 and after another hour visualisation on TLC showed that the starting material had been completely consumed. To our delight, this reduction gave the desired 7-epi-hydroxy derivative 6 in 88% yield, with no formation of 5 detectable. Obtaining a single stereoisomer from reduction of the keto group in 10 was particularly pleasing, since in the work reported by the Crich group22 gave a 6![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 preference of the inverted stereoisomer over the original C-7 stereochemistry.
1 preference of the inverted stereoisomer over the original C-7 stereochemistry.
Due to our prior success in the introduction of nitrogen functionality via the azide displacement of a triflate group,25 we believed that the most viable approach towards our target legionaminic acid derivatives would be to once again explore this avenue. After considerable experimentation, it was found that the conditions that gave the greatest yield of the triflate derivatives 11 and 12 was using N,N-dimethylaminopyridine as base, and leaving the reaction overnight at 4 °C. In this way the triflates 11 and 12 could be obtained from 5 and 6 in 74% and 68% yield, respectively (Scheme 3). The presence of the triflate groups in both 11 and 12 could be determined by a quartet peak centred at δ 120 ppm in the respective 13C NMR spectra, due to the fluorine atoms of the triflate group splitting the methyl carbon. To introduce the desired nitrogen functionality at C-7, the triflates 11 and 12 were exposed to an excess of sodium azide in N,N-DMF overnight at 4 °C, and gave the azide derivatives 13 and 14 in 57% and 59% yields, respectively. The use of alternative sources of azide, e.g. trimethylsilyl azide, or altering the reaction conditions, failed to improve the yield of the desired C-7 azide derivatives. The presence of the azide group in 13 and 14 was confirmed by IR spectroscopy, with a sharp peak around 2100 cm−1.
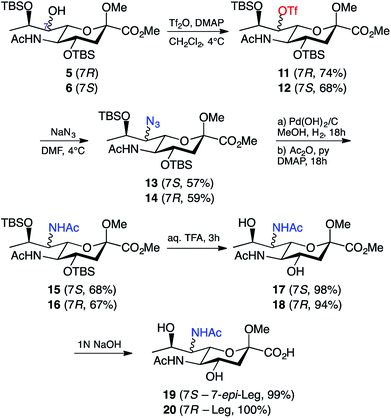 | ||
| Scheme 3 Synthesis of legionaminic acid derivative 20 and the 7-epi-legionaminic acid derivative 19. | ||
With the nitrogen functionality in place at C-7, it was decided that the reduction and acylation should take place before the deprotection, as the acylation in the presence of free hydroxyl groups would acetylate them and consequently require a second deprotection. The first attempt at reduction of the azide in 13 involved treating 13 with zinc and ammonium chloride in aqueous methanol for half an hour,32 followed by filtration, evaporation of the solvent in vacuo, and acylation (Ac2O/Py) of the crude reaction mixture. This method was successful in giving the 7-acetamido derivative 15, however only in a disappointing 38% yield. Alternative conditions for the reduction of the azide are hydrogenation conditions, so 13 was exposed to a hydrogen atmosphere in the presence of palladium hydroxide on carbon. The crude product was acetylated (Ac2O/Py) to give a 68% yield of 7-epi-Leg derivative 15. These hydrogenation conditions were also applied to 14, which gave the protected Leg derivative 16 in a 67% yield. The presence of the second acetamide group in both 15 and 16 was confirmed using both 1H and 13C NMR spectroscopy. By 1H NMR, for compound 15 the presence of a second acetamido group could be seen by a second NH resonance at δ 5.75 ppm (the C-5 NH peak is at δ 6.53 ppm) and a second acetyl peak at δ 1.98 ppm (with the first at δ 1.99 ppm). By 13C NMR, two acetyl peaks could now be seen at δ 170 ppm and δ 23 ppm (carbonyl and methyl carbons, respectively), and the change in chemical shift of the C-7 peak from δ 70 ppm in 13 to δ 54 ppm in 15. Similar peaks for the additional acetamido group were also observed in the 1H & 13C spectra of compound 16. With the key modifications of the 7-acetamido and 9-deoxy functionality in place, the only remaining steps towards our target compounds was removal of the protecting groups: the two silyl ethers, the methyl ester and the methyl glycoside. We began with the silyl ethers and exposed 15 and 16 to 20% aqueous trifluoroacetic acid at room temperature for 2 hours, followed by removal of the solvent in vacuo. In this way the de-silylated derivatives 17 and 18 were obtained in high yield (Scheme 3). Compounds 17 and 18 had 1H & 13C NMR spectra consistent with their structures as shown, together with a parent ion in their mass spectra at m/z 385 [M + Na]+. The only remaining step was to remove the methyl ester and methyl glycoside; however, this was a step that proved challenging in our synthesis of pseudaminic acid,33 a very similar substrate. The method eventually successfully utilised in that approach involved the removal of the ester with 1 M NaOH, followed by the removal of the glycoside using acidic resin.33 Using this published strategy, 17 was stirred in 1 M NaOH overnight at room temperature, then acidified to pH 1 with Dowex-WX50(H+) resin and stirred overnight at 80 °C. Unfortunately, the major product of this reaction could no longer be identified as a nonulosonic acid. An alternative strategy was to remove just the methyl ester and leave the glycoside intact. To this end, 17 was stirred overnight at room temperature in 1 M NaOH, and after purification, the carboxylic acid 19 was isolated in quantitative yield. The same conditions were then used to quantitatively generate 20 from 18. This was confirmed by a mass spectrum m/z peak of 371.2 [M + Na]+, with the 1H and 13C NMR spectra of 19 and 20 being consistent with the structures shown. Significantly, this research marks the first reported chemical synthesis of 7-epi-legionaminic acid, also known as 8-epi-acinetaminic acid, a compound that has been reported as being found in Acinetobacter baumannii.34
Conclusions
Through our synthetic approach towards legionaminic acid analogues, we were able to synthesise the methyl glycosides of both 7-epi-legionaminic acid and legionaminic acid from a common precursor in 5 steps with an 18% yield and in 7 steps with an 8% yield, respectively. To date, this represents the first chemical synthesis of 7-epi-legionaminic acid, which can also be referred to as 8-epi-acinetaminic acid, a compound which has been isolated from Acinetobacter baumannii.34 We were also able to leave the functionalisation of the C-7 nitrogen to the very last step (excepting deprotection reactions), making this a very attractive approach for the synthesis of any other C-7 amide analogues of legionaminic acid.Experimental
General information
All the reactions were carried out under a nitrogen or an argon atmosphere and monitored by thin layer chromatography (TLC) using Merck precoated aluminium silica plates with detection by charring with 5% (v/v) H2SO4 in ethanol or by ultraviolet (UV) detection. All the chemicals were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich Chemicals Company. Solvents used in the reactions were either distilled prior to use, following protocols described in Armarego & Chai,35 or were purchased as anhydrous solvents of 99% purity or greater. ‘Flash’ chromatography using silica gel was performed routinely in order to purify all products. 1H and 13C NMR spectra were obtained using a Bruker 400 MHz spectrometer at 400 and 100 MHz, respectively. Signals are reported in terms of their chemical shift (δ in ppm) relative to CDCl3 (1H, δ 7.26 ppm and 13C, δ 77.0 ppm), CD3OD (1H, δ 3.30 ppm and 13C, δ 49.0 ppm), CD3CN (1H, δ 1.96 ppm and 13C, δ 1.39 ppm) and D2O (1H, δ 4.78 ppm and 13C external reference used). For 1H spectra, multiplicity, integration intensity, coupling constants and assignment values are reported, two-dimensional COSY, HSQC and HMBC spectra were used to aid assignment. 1H coupling constants are reported in their entirety for each peak seen within a spectrum. Mass spectral analysis was performed using a Bruker esquire 3000 electrospray ionisation mass spectrometer. IR spectral analysis was performed using a Bruker Alpha-P diamond ATR FT-IR spectrometer.Methyl(methyl 5-acetamido-3,5,9-trideoxy-9-iodo-D-glycero-D-galacto-non-2-ulopyranosid)onate (8)
To a solution of 7 (4.71 g, 14.0 mmol) in anhydrous tetrahydrofuran (140 mL), triphenylphosphine (5.49 g, 20.9 mmol), iodine chips (5.32 g, 20.9 mmol), and imidazole (1.90 g, 27.9 mmol) were added. After stirring for 2 h at reflux under a nitrogen atmosphere, Na2S2O5 (2.65 g, 14.0 mmol) in MeOH (140 mL) was added, the mixture absorbed onto non-flash silica, and evaporated in vacuo. The desired product (4.73 g, 10.8 mmol, 77%) was obtained using column chromatography on silica gel in CHCl3/MeOH (10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1), then EtOAc/MeOH (15
1), then EtOAc/MeOH (15![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1), and obtained as a yellow solid.
1), and obtained as a yellow solid.
1H NMR (400 MHz, CD3CN) δ 7.19 (1H, d, NH), 4.09 (1H, ddd, J4,3e = 5.0 Hz, J4,3a = 12 Hz, J4,5 = 8.5 Hz, H4), 3.76 (3H, s, CO2CH3), 3.70–3.75 (2H, m, H5, undetermined), 3.55–3.63 (2H, m, H9, undetermined), 3.43–3.48 (2H, m, H9′, undetermined), 3.20 (3H, s, COCH3), 2.28 (1H, dd, J3e,3a = 13.2 Hz, J3e,4 = 5.0 Hz, H3e), 1.98 (3H, s, AcN), 1.65 (1H, dd, J3a,3e = 13.2 Hz, J3a,4 = 12 Hz, H3a).
13C NMR (100 MHz CD3CN) δ 175.0 (C1), 169.1 (NCOCH3), 100.6 (C2), 72.7, 72.2, 70.4 (C6, C7, C8), 66.7 (C4), 53.9 (C5), 54.5 (CO2CH3), 52.2 (COCH3), 41.4 (C3), 23.7 (NCOCH3), 16.6 (C9).
m/z 470.1 [M + Na]+.
IR = 1737 cm−1 (CO2Me), 620 cm−1 (C–I).
Methyl(methyl 5-acetamido-3,5,9-trideoxy-D-glycero-D-galacto-non-2-ulopyranosid)onate (9)
To a solution of 8 (1.6 g, 3.7 mmol) in methanol (35 mL), Pd(OH)2/C (330 mg) and N,N-diisopropylethylamine (64 μL, 0.37 mmol) were added, and the reaction mixture fixed to a Parr hydrogenator under 300 kPa H2. After shaking for 18 h at room temperature additional DIPEA (64 μL, 0.37 mmol) was added, and the reaction allowed to continue. After a further 18 h, the reaction was filtered through a Celite pad and the solvent evaporated in vacuo. The desired product (492 mg, 1.53 mmol, 70%), as well as unreacted starting material (923 mg, 2.11 mmol) were obtained using column chromatography on silica gel in CHCl3/MeOH (7![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) and obtained as a white solid.
1) and obtained as a white solid.
1H NMR (400 MHz, CD3CN) δ 4.01 (1H, ddd, J4,3e = 5.0 Hz, J4,3a = 18.0 Hz, J4,5 = 13.3 Hz, H4), 3.87 (1H, dq, H8), 3.78 (3H, s, CO2CH3), 3.71 (1H, dd, J5,4 = 13.3 Hz, J5,6 = 6.6 Hz, H5), 3.28 (1H, dd, J6,5 = 6.6 Hz, J6,7 = 7.2 Hz, H6), 3.21 (3H, s, COCH3), 3.17 (1H, dd, H7), 2.28 (1H, dd, J3e,3a = 13.8 Hz, J3e,4 = 5.0 Hz, H3e), 1.95 (3H, s, AcN), 1.64 (1H, dd, J3a,3e = 13.8 Hz, J3a,4 = 18.0 Hz, H3a), 1.22 (3H, d, J9,8 = 6.28 Hz, H9).
13C NMR (100 MHz CD3OD) δ 174.8 (C1), 171.6 (NCOCH3), 100.6 (C2), 74.5 (C7), 72.1 (C8), 67.8 (C4), 53.7 (C5), 53.8 (CO2CH3), 51.9 (COCH3), 50.0 (C6), 41.6 (C3), 23.0 (NCOCH3), 21.5 (C9).
m/z 344.2 [M + Na]+.
IR = 1736 cm−1 (CO2Me).
Methyl(methyl 5-acetamido-4,8-O-bis-tert-butyldimethylsilyl-3,5,9-trideoxy-D-glycero-D-galacto-non-2-ulopyranosid)onate (5)
To a solution of 9 (662 mg, 2.06 mmol) in anhydrous dimethylformamide (10 mL), tert-butyldimethylsilyl chloride (869 mg, 5.77 mmol) and imidazole (825 mg, 12.1 mmol) were added. After stirring for 18 h at room temperature under a nitrogen atmosphere, the reaction was evaporated in vacuo. The desired product (847 mg, 1.54 mmol, 75%) was obtained using column chromatography on silica gel in EtOAc/Hex (2![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 3) and obtained as a white solid.
3) and obtained as a white solid.
1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 5.18 (1H, d, NH), 4.02–4.09 (2H, m, H4, H8), 3.78–3.82 (2H, m, H6, H7), 3.78 (3H, s, CO2CH3), 3.28 (1H, d, J5,6 = 14.9 Hz, J5,4 = 7.4 Hz, H5), 3.24 (3H, s, COCH3), 2.29 (1H, dd, J3e,3a = 13.1 Hz, J3e,4 = 5.0 Hz, H3e), 2.00 (3H, s, AcN), 1.73 (1H, dd, J3a,3e = 13.1 Hz, J3a,4 = 10.8 Hz, H3a), 1.30 (3H, s, H9), 0.87 (3×3H, s, (CH3)3CSi), 0.85 (3×3H, s, (CH3)3CSi), 0.07 (2×3H, s, CH3Si), 0.06 (3H, s, CH3Si), 0.05 (3H, s, CH3Si).
13C NMR (100 MHz CDCl3) δ 171.2 (C1), 168.6 (NCOCH3), 99.1 (C2), 73.6 (C7), 70.9 (C6), 69.1 (C8), 67.4 (C4), 53.8 (C5), 52.6 (CO2CH3), 51.3 (COCH3), 41.0 (C3), 26.0 ((CH3)CSi), 25.5 ((CH3)CSi), 23.4 (NCOCH3), 18.2 ((CH3)CSi), 17.8 ((CH3)CSi), −3.0 (CH3Si), −4.0 (CH3Si), −4.2 (CH3Si), −4.7 (CH3Si).
IR = 1749 cm−1 (CO2Me), 1047 cm−1 (Si–OC).
m/z 572.4 [M + Na]+.
Methyl(methyl 5-acetamido-4,8-O-bis-tert-butyldimethylsilyl-3,5,9-trideoxy-7-keto-D-glycero-L-altro-non-2-ulopyranosid)onate (10)
To a solution of 5 (254 mg, 0.46 mmol) in anhydrous dichloromethane (5 mL), Dess–Martin periodinane (294 mg, 0.69 mmol) was added. After stirring for 2 h at 0 °C under a nitrogen atmosphere, the reaction was diluted with diethyl ether, washed with 20% aq. Na2S2O3 and sat. aq. NaCl, dried (Na2SO4), and evaporated in vacuo. The desired product (209 mg, 0.38 mmol, 83%) was obtained using column chromatography on silica gel in Hex/EtOAc (3![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) and obtained as a white solid.
1) and obtained as a white solid.
1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 5.45 (1H, d, JNH,5 = 8.7 Hz, NH), 4.74 (1H, q, J8,9 = 6.8 Hz, H8), 4.37 (1H, d, J6,5 = 10.7 Hz, H6), 4.10 (1H, ddd, J4,3e = 5.0 Hz, J4,3a = 10.7 Hz, J4,5 = 9.4 Hz, H4), 3.87 (1H, q, J5,4 = 9.4 Hz, J5,6 = 10.7 Hz, J5,NH = 8.7 Hz, H5), 3.81 (3H, s, CO2CH3), 3.22 (3H, s, COCH3), 2.30 (1H, dd, J3e,3a = 13.2 Hz, J3e,4 = 5.0 Hz, H3e), 1.92 (3H, s, AcN), 1.80 (1H, dd, J3a,3e = 13.2 Hz, J3a,4 = 10.7 Hz, H3a), 1.42 (3H, d, J9,8 = 6.8 Hz, H9), 0.90 (3×3H, s, (CH3)3CSi), 0.84 (3×3H, s, (CH3)3CSi), 0.09 (3H, s, CH3Si), 0.06 (3H, s, CH3Si), 0.05 (3H, s, CH3Si), 0.03 (3H, s, CH3Si).
13C NMR (100 MHz CDCl3) δ 206.7 (C7), 169.7 (C1), 167.9 (NCOCH3), 99.5 (C2), 73.6 (C6), 72.3 (C8), 67.7 (C4), 54.3 (C5), 52.7 (CO2CH3), 51.1 (COCH3), 41.4 (C3), 25.8 ((CH3)CSi), 25.5 ((CH3)CSi), 23.5 (NCOCH3), 20.3 (C9), 18.3 ((CH3)CSi), 17.8 ((CH3)CSi), −4.5 (CH3Si), −4.9 (CH3Si), −4.9 (CH3Si), −4.9 (CH3Si).
IR = 1756 cm−1 (CO2Me), 1733 cm−1 (C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O), 1047 cm−1 (Si–OC).
O), 1047 cm−1 (Si–OC).
m/z 570.5 [M + Na]+.
Methyl(methyl 5-acetamido-4,8-O-bis-tert-butyldimethylsilyl-3,5,9-trideoxy-D-glycero-L-altro-non-2-ulopyranosid)onate (6)
To a solution of 10 (170 mg, 0.31 mmol) in anhydrous dichloromethane (3 mL) at −78 °C, a solution of cerium(III) chloride (347 mg, 0.93 mmol) in methanol (6 mL) was added. After stirring for 1 h under a nitrogen atmosphere, sodium borohydride (18 mg, 0.47 mmol) was added, and the reaction stirred for a further hour. After completion, the reaction was quenched with sat. aq. NH4Cl, evaporated in vacuo, dissolved in EtOAc, washed with H2O and sat. aq. NaCl, dried (Na2SO4), and evaporated in vacuo. The desired product (150 mg, 0.27 mmol, 88%) was obtained using column chromatography on silica gel in EtOAc/Hex (2![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 3) and obtained as a white solid.
3) and obtained as a white solid.
1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 5.45 (1H, d, JNH,5 = 9.0 Hz, NH), 4.07 (1H, q, J8,7 = 5.8 Hz, J8,9 = 6.2 Hz, H8), 3.99–4.06 (1H, m, H4), 3.74–3.82 (1H, m, H5), 3.77 (3H, s, CO2CH3), 3.67 (1H, dd, J6,7 = 3.3 Hz, J6,5 = 10.6 Hz, H6), 3.49 (1H, dd, J7,6 = 3.3 Hz, J7,8 = 5.8 Hz, H7), 3.24 (3H, s, COCH3), 2.23 (1H, dd, J3e,3a = 13.1 Hz, J3e,4 = 5.0 Hz, H3e), 1.96 (3H, s, AcN), 1.74 (1H, dd, J3a,3e = 13.1 Hz, J3a,4 = 10.6 Hz, H3a), 1.25 (3H, d, J9,8 = 6.2 Hz, H9), 0.88 (3×3H, s, (CH3)3CSi), 0.84 (3×3H, s, (CH3)3CSi), 0.10 (3H, s, CH3Si), 0.08 (3H, s, CH3Si), 0.04 (3H, s, CH3Si), 0.03 (3H, s, CH3Si).
13C NMR (100 MHz CDCl3) δ 170.1 (C1), 168.6 (NCOCH3), 98.9 (C2), 75.8 (C7), 73.6 (C6), 68.1 (C4), 68.0 (C8), 54.4 (C5), 52.5 (CO2CH3), 50.8 (COCH3), 41.1 (C3), 25.9 ((CH3)CSi), 25.6 ((CH3)CSi), 23.6 (NCOCH3), 18.1 ((CH3)CSi), 17.8 ((CH3)CSi), −4.0 (CH3Si), −4.4 (CH3Si), −4.8 (CH3Si), −4.8 (CH3Si).
IR = 1755 cm−1 (CO2Me), 1050 cm−1 (Si–OC).
m/z 572.5 [M + Na]+.
Methyl(methyl 5-acetamido-4,8-O-bis-tert-butyldimethylsilyl-3,5,9-trideoxy-7-trifluoromethanesulfonyl-D-glycero-D-galacto-non-2-ulopyranosid)onate (11)
To a solution of 5 (971 mg, 1.77 mmol) in anhydrous dichloromethane (20 mL) at −78 °C, trifluoromethane-sulphonic anhydride (415 μL, 2.47 mmol) and N,N-dimethylaminopyridine (634 mg, 5.19 mmol) were added. After stirring for 18 h at 4 °C under an argon atmosphere, the reaction was washed with cold 1 M HCl, followed by cold H2O, dried (Na2SO4), and evaporated in vacuo. The desired product (645 mg, 0.85 mmol, 74%), along with unreacted starting material (269 mg, 0.49 mmol) was obtained using column chromatography on silica gel in EtOAc/Hex (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 4) and obtained as a white solid.
4) and obtained as a white solid.
1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 5.60 (1H, d, JNH,5 = 7.0 Hz, NH), 5.09 (1H, dd, J7,6 = 2.6 Hz, J7,8 = 2.2, H7), 4.75 (1H, dd, J6,5 = 10.3 Hz, J6,7 = 2.6 Hz, H6), 4.56 (1H, ddd, J4,3e = 5.0 Hz, J4,3a = 10.7 Hz, J4,5 = 5.9 Hz, H4), 4.11 (1H, dq, J8,7 = 2.2 Hz, J8,9 = 6.3 Hz, H8), 3.78 (3H, s, CO2CH3), 3.23 (3H, s, COCH3), 3.02 (1H, ddd, J5,4 = 5.9 Hz, J5,NH = 7.0 Hz, J5,6 = 2.6 Hz, H5), 2.30 (1H, dd, J3e,3a = 13.2 Hz, J3e,4 = 5.0 Hz, H3e), 1.96 (3H, s, AcN), 1.64 (1H, dd, J3a,3e = 13.2 Hz, J3a,4 = 10.7 Hz, H3a), 1.35 (3H, d, J9,8 = 6.3 Hz, H9), 0.87 (3×3H, s, (CH3)3CSi), 0.85 (3×3H, s, (CH3)3CSi), 0.06 (3H, s, CH3Si), 0.06 (3H, s, CH3Si), 0.05 (3H, s, CH3Si), 0.03 (3H, s, CH3Si).
13C NMR (100 MHz CDl3) δ 170.6 (C1), 167.9 (NCOCH3), 120.1 (CF3SO2) 99.2 (C2), 90.9 (C7), 69.1 (C8), 68.8 (C6), 65.3 (C4), 57.0 (C5), 52.6 (CO2CH3), 51.2 (COCH3), 41.5 (C3), 25.6 ((CH3)CSi), 25.6 ((CH3)CSi), 23.7 (NCOCH3), 18.5 (C9), 18.0 ((CH3)CSi), 17.8 ((CH3)CSi), −4.6 (CH3Si), −4.9 (CH3Si), −4.9 (CH3Si), −5.2 (CH3Si).
Methyl(methyl 5-acetamido-4,8-O-bis-tert-butyldimethylsilyl-3,5,9-trideoxy-7-trifluoromethanesulfonyl-D-glycero-L-altro-non-2-ulopyranosid)onate (12)
To a solution of 6 (238 mg, 0.43 mmol) in anhydrous dichloromethane (5 mL) at −78 °C, trifluoromethane-sulphonic anhydride (102 μL, 0.61 mmol) and N,N-dimethylaminopyridine (265 mg, 2.17 mmol) were added. After stirring for 18 h at 4 °C under an argon atmosphere, the reaction was washed with cold 1 M HCl, followed by cold H2O, dried (Na2SO4), and evaporated in vacuo. The desired product (200 mg, 0.29 mmol, 68%), was obtained using column chromatography on silica gel in EtOAc/Hex (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 4) and obtained as a white solid.
4) and obtained as a white solid.
1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 5.60 (1H, d, JNH,5 = 7.5 Hz, NH), 5.10 (1H, dd, J7,6 = 1.1 Hz, J7,8 = 4.7, H7), 4.76 (1H, dd, J6,5 = 10.4 Hz, J6,7 = 1.1 Hz, H6), 4.56 (1H, ddd, J4,3e = 4.9 Hz, J4,3a = 11.0 Hz, J4,5 = 5.9 Hz, H4), 4.17 (1H, dq, J8,7 = 2.2 Hz, J8,9 = 6.3 Hz, H8), 3.78 (3H, s, CO2CH3), 3.23 (3H, s, COCH3), 2.99–3.07 (1H, m, H5), 2.31 (1H, dd, J3e,3a = 12.9 Hz, J3e,4 = 4.9 Hz, H3e), 2.19 (3H, s, AcN), 1.64 (1H, dd, J3a,3e = 12.9 Hz, J3a,4 = 11.0 Hz, H3a), 1.31 (3H, d, J9,8 = 6.3 Hz, H9), 0.88 (3×3H, s, (CH3)3CSi), 0.87 (3×3H, s, (CH3)3CSi), 0.14 (3H, s, CH3Si), 0.10 (3H, s, CH3Si), 0.09 (3H, s, CH3Si), 0.07 (3H, s, CH3Si).
13C NMR (100 MHz CDl3) δ 171.4 (C1), 168.2 (NCOCH3), 121.3 (CF3SO2) 99.1 (C2), 90.9 (C7), 69.2 (C8), 68.8 (C6), 65.0 (C4), 54.9 (C5), 52.5 (CO2CH3), 51.2 (COCH3), 40.2 (C3), 25.8 ((CH3)CSi), 25.7 ((CH3)CSi), 21.1 (NCOCH3), 19.7 (C9), 18.1 ((CH3)CSi), 17.9 ((CH3)CSi), −4.1 (2×CH3Si), −4.3 (CH3Si), −4.7 (CH3Si).
Methyl(methyl 5-acetamido-4,8-O-bis-tert-butyldimethylsilyl-3,5,7,9-tetradeoxy-7-azido-D-glycero-L-altro-non-2-ulopyranosid)onate (13)
To a solution of 11 (205 mg, 0.30 mmol) in anhydrous dimethylformamide (2.5 mL) at 0 °C, sodium azide (190 mg, 2.94 mmol) was added. After stirring for 18 h at 4 °C under an argon atmosphere, the reaction was evaporated in vacuo. The desired product (96 mg, 0.17 mmol, 57%) was obtained using column chromatography on silica gel in EtOAc/Hex (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 4) and obtained as a white solid.
4) and obtained as a white solid.
1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 5.33 (1H, d, JNH,5 = 8.6 Hz, NH), 4.22 (1H, ddd, J4,3e = 5.0 Hz, J4,3a = 10.4, J4,5 = 9.6 Hz, H4), 4.03 (1H, dq, J8,7 = 7.3 Hz, J8,9 = 6.2 Hz, H8), 3.97 (1H, dd, J6,5 = 10.4 Hz, J6,7 = 2.7 Hz, H6), 3.78 (3H, s, CO2CH3), 3.67 (1H, q, J5,4 = 9.6 Hz, J5,NH = 8.6 Hz, J5,6 = 10.4 Hz, H5), 3.31 (1H, dd, J7,6 = 2.7 Hz, J7,8 = 7.3 Hz, H7), 3.23 (3H, s, COCH3), 2.25 (1H, dd, J3e,3a = 13.1 Hz, J3e,4 = 5.0 Hz, H3e), 1.97 (3H, s, AcN), 1.69 (1H, dd, J3a,3e = 13.1 Hz, J3a,4 = 10.4 Hz, H3a), 1.29 (3H, d, J9,8 = 6.16 Hz, H9), 0.90 (3×3H, s, (CH3)3CSi), 0.84 (3×3H, s, (CH3)3CSi), 0.12 (3H, s, CH3Si), 0.09 (3H, s, CH3Si), 0.05 (3H, s, CH3Si), 0.04 (3H, s, CH3Si).
IR = 2106 cm−1 (N3), 1752 cm−1 (CO2Me), 1100 cm−1 (Si–OC).
m/z 597.5 [M + Na]+.
Methyl(methyl 5-acetamido-4,8-O-bis-tert-butyldimethylsilyl-3,5,7,9-tetradeoxy-7-azido-D-glycero-D-galacto-non-2-ulopyranosid)onate (14)
To a solution of 12 (163 mg, 0.24 mmol) in anhydrous dimethylformamide (2 mL) at 0 °C, sodium azide (155 mg, 2.39 mmol) was added. After stirring for 18 h at 4 °C under an argon atmosphere, the reaction was evaporated in vacuo. The desired product (81 mg, 11.9 mmol, 59%) was obtained using column chromatography on silica gel in EtOAc/Hex (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 4) and obtained as a white solid.
4) and obtained as a white solid.
IR = 2103 cm−1 (N3), 1753 cm−1 (CO2Me), 1098 cm−1 (Si–OC).
m/z 597.5 [M + Na]+.
Methyl(methyl 5,7-diacetamido-4,8-O-bis-tert-butyldimethylsilyl-3,5,7,9-tetradeoxy-D-glycero-L-altro-non-2-ulopyranosid)onate (15)
To a solution of 13 (91 mg, 0.16 mmol) in methanol (1.5 mL), Pd(OH)2/C (18 mg) was added. After stirring under a hydrogen atmosphere for 18 h at 25 °C, the reaction was filtered through a Celite pad, evaporated in vacuo, and redissolved in pyridine/acetic anhydride (2![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1, 3 mL). 4-Dimethylaminopyridine (10 mg, 0.08 mmol) was added, and the reaction stirred for 18 h at 25 °C under a nitrogen atmosphere. The reaction was then evaporated in vacuo, dissolved in ethyl acetate, washed with 1 M HCl followed by H2O, dried (Na2SO4), and evaporated in vacuo. The desired product (64 mg, 0.70 mmol, 68%) was obtained using column chromatography on silica gel in EtOAc/Hex (10
1, 3 mL). 4-Dimethylaminopyridine (10 mg, 0.08 mmol) was added, and the reaction stirred for 18 h at 25 °C under a nitrogen atmosphere. The reaction was then evaporated in vacuo, dissolved in ethyl acetate, washed with 1 M HCl followed by H2O, dried (Na2SO4), and evaporated in vacuo. The desired product (64 mg, 0.70 mmol, 68%) was obtained using column chromatography on silica gel in EtOAc/Hex (10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1).
1).
1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 6.53 (1H, d, JNH,5 = 8.4 Hz, C5NH), 5.75 (1H, d, JNH,5 = 7.9 Hz, C7NH), 4.38 (1H, dq, J8,7 = 2.2 Hz, J8,9 = 6.2, H8), 3.84–3.98 (3H, m, H4, H5, H7), 3.74 (3H, s, CO2CH3), 3.71–3.78 (1H, m, H6), 3.17 (3H, s, COCH3), 2.21 (1H, dd, J3e,3a = 13.2 Hz, J3e,4 = 4.4 Hz, H3e), 1.99 (3H, s, AcN), 1.98 (3H, s, AcN), 1.77 (1H, dd, J3a,3e = 13.2 Hz, J3a,4 = 10.4 Hz, H3a), 1.13 (3H, d, J9,8 = 6.2 Hz, H9), 0.88 (3×3H, s, (CH3)3CSi), 0.84 (3×3H, s, (CH3)3CSi), 0.10 (3H, s, CH3Si), 0.09 (3H, s, CH3Si), 0.03 (3H, s, CH3Si), 0.03 (3H, s, CH3Si).
13C NMR (100 MHz CDCl3) δ 169.9 (NCOCH3), 169.9 (NCOCH3), 168.0 (C1), 98.8 (C2), 73.2 (C6), 68.8 (C4), 64.7 (C8), 53.9 (C7), 53.3 (C5), 52.3 (CO2CH3), 50.3 (COCH3), 41.1 (C3), 25.9 ((CH3)CSi), 25.5 ((CH3)CSi), 23.6 (NCOCH3), 23.5 (C9), 23.3 (NCOCH3), 17.9 ((CH3)CSi), 17.8 ((CH3)CSi), −4.1 (CH3Si), −4.4 (CH3Si), −4.8 (CH3Si), −4.9 (CH3Si).
IR = 1756 cm−1 (CO2Me), 1042 cm−1 (Si–OC).
m/z 613.5 [M + Na]+.
Methyl(methyl 5,7-diacetamido-4,8-O-bis-tert-butyldimethylsilyl-3,5,7,9-tetradeoxy-D-glycero-D-galacto-non-2-ulopyranosid)onate (16)
To a solution of 14 (76 mg, 0.13 mmol) in methanol (1 mL), Pd(OH)2/C (15 mg) was added. After stirring under a hydrogen atmosphere for 18 h at 25 °C, the reaction was filtered through a Celite pad, evaporated in vacuo, and redissolved in pyridine/acetic anhydride (2![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1, 1.5 mL). 4-Dimethylaminopyridine (5 mg, 0.04 mmol) was added, and the reaction stirred for 18 h at 25 °C under a nitrogen atmosphere. The reaction was then evaporated in vacuo, dissolved in ethyl acetate, washed with 1 M HCl followed by H2O, dried (Na2SO4), and evaporated in vacuo. The desired product (52 mg, 0.09 mmol, 67%) was obtained using column chromatography on silica gel in EtOAc/Hex (7
1, 1.5 mL). 4-Dimethylaminopyridine (5 mg, 0.04 mmol) was added, and the reaction stirred for 18 h at 25 °C under a nitrogen atmosphere. The reaction was then evaporated in vacuo, dissolved in ethyl acetate, washed with 1 M HCl followed by H2O, dried (Na2SO4), and evaporated in vacuo. The desired product (52 mg, 0.09 mmol, 67%) was obtained using column chromatography on silica gel in EtOAc/Hex (7![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1).
1).
1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 6.53 (1H, d, JNH,7 = 6.8 Hz, C7NH), 5.94 (1H, d, C5NH), 4.36 (1H, ddd, J8,7 = 5.4 Hz, J8,9 = 6.0, H8), 3.85–3.89 (3H, m, H4, H5, H7), 3.72–3.78 (1H, m, H6), 3.72 (3H, s, CO2CH3), 3.14 (3H, s, COCH3), 2.19 (1H, dd, J3e,3a = 12.6 Hz, J3e,4 = 3.3 Hz, H3e), 1.97 (3H, s, AcN), 1.95 (3H, s, AcN), 1.75 (1H, dd, J3a,3e = 12.6 Hz, J3a,4 = 10.3 Hz, H3a), 1.10 (3H, d, J9,8 = 6.0 Hz, H9), 0.86 (3×3H, s, (CH3)3CSi), 0.81 (3×3H, s, (CH3)3CSi), 0.08 (3H, s, CH3Si), 0.06 (3H, s, CH3Si), 0.01 (3H, s, CH3Si), 0.01 (3H, s, CH3Si).
13C NMR (100 MHz CDCl3) δ 169.9 (NCOCH3), 169.9 (C1), 168.0 (NCOCH3), 98.7 (C2), 73.1 (C6), 68.8 (C4), 64.6 (C8), 53.9 (C7), 53.2 (C5), 52.3 (CO2CH3), 50.3 (COCH3), 41.1 (C3), 25.9 ((CH3)CSi), 25.5 ((CH3)CSi), 23.6 (NCOCH3), 23.5 (NCOCH3), 23.3 (C9), 17.9 ((CH3)CSi), 17.7 ((CH3)CSi), −4.2 (CH3Si), −4.4 (CH3Si), −4.8 (CH3Si), −4.9 (CH3Si).
IR = 1754 cm−1 (CO2Me), 1043 cm−1 (Si–OC).
m/z 613.5 [M + Na]+.
Methyl(methyl 5,7-diacetamido-3,5,7,9-tetradeoxy-D-glycero-L-altro-non-2-ulopyranosid)onate (17)
A solution of 15 (65 mg, 0.11 mmol) in trifluoroacetic acid/water (4![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1, 1 mL) was stirred for 2 h at 25 °C, then evaporated in vacuo. The desired product (39 mg, 0.11 mmol, 98%) was obtained using column chromatography on silica gel in EtOAc/MeOH (4
1, 1 mL) was stirred for 2 h at 25 °C, then evaporated in vacuo. The desired product (39 mg, 0.11 mmol, 98%) was obtained using column chromatography on silica gel in EtOAc/MeOH (4![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) and obtained as a white solid.
1) and obtained as a white solid.
1H NMR (400 MHz, CD3OD) δ 8.09 (1H, d, JNH,7 = 9.1 Hz, C7NH), 4.53 (1H, dq, J8,7 = 6.4 Hz, J8,9 = 6.4 Hz, H8), 3.83 (3H, s, CO2CH3), 3.82–3.97 (3H, m, H4, H5, H7), 3.62 (1H, dd, J6, 5 = 10.4 Hz, J6,7 = 1.6 Hz, H6), 3.21 (3H, s, COCH3), 2.35 (1H, dd, J3e,3a = 13.0 Hz, J3e,4 = 4.5 Hz, H3e), 2.35 (3H, s, AcN), 2.03 (3H, s, AcN), 1.69 (1H, dd, J3a,3e = 13.0 Hz, J3a,4 = 10.8 Hz, H3a), 1.11 (3H, d, J9,8 = 6.4 Hz, H9).
13C NMR (100 MHz CD3OD) δ 174.3 (NCOCH3), 173.5 (C1), 170.4 (NCOCH3), 100.3 (C2), 78.2 (C6), 67.3 (C4), 66.4 (C8), 54.4 (C5), 53.6 (CO2CH3), 53.3 (C7), 51.6 (COCH3), 41.4 (C3), 22.9 (NCOCH3), 22.6 (NCOCH3), 20.5 (C9).
IR = 1739 cm−1 (CO2Me).
m/z 385.3 [M + Na]+.
Methyl(methyl 5,7-diacetamido-3,5,7,9-tetradeoxy-D-glycero-D-galacto-non-2-ulopyranosid)onate (18)
A solution of 16 (43 mg, 0.07 mmol) in trifluoroacetic acid/water (4![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1, 1 mL) was stirred for 3 h at 25 °C, then evaporated in vacuo. The desired product (25 mg, 0.07 mmol, 94%) was obtained using column chromatography on silica gel in EtOAc/MeOH (4
1, 1 mL) was stirred for 3 h at 25 °C, then evaporated in vacuo. The desired product (25 mg, 0.07 mmol, 94%) was obtained using column chromatography on silica gel in EtOAc/MeOH (4![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) and obtained as a white solid.
1) and obtained as a white solid.
1H NMR (400 MHz, CD3OD) δ 4.52 (1H, ddd, J8,7 = 12.7 Hz, J8,9 = 6.4 Hz, H8), 3.93 (1H, dd, H7), 3.89 (1H, ddd, H4), 3.82 (3H, s, CO2CH3), 3.80–3.86 (1H, m, H5), 3.60 (1H, dd, H6), 3.19 (3H, s, COCH3), 2.34 (1H, dd, J3e,3a = 13.0 Hz, J3e,4 = 4.5 Hz, H3e), 2.34 (3H, s, AcN), 2.02 (3H, s, AcN), 1.68 (1H, dd, J3a,3e = 13.0 Hz, J3a,4 = 10.9 Hz, H3a), 1.10 (3H, d, J9,8 = 6.36 Hz, H9).
13C NMR (100 MHz CD3OD) δ 174.29 (NCOCH3), 173.47 (C1), 170.42 (NCOCH3), 100.27 (C2), 78.19 (C6), 67.28 (C4), 66.40 (C8), 54.37 (C5), 53.60 (CO2CH3), 53.31 (C7), 51.60 (COCH3), 41.40 (C3), 22.94 (NCOCH3), 22.56 (NCOCH3), 20.49 (C9).
IR = 1737 cm−1 (CO2Me).
m/z 385.3 [M + Na]+.
Methyl 5,7-diacetamido-3,5,7,9-tetradeoxy-D-glycero-L-altro-non-2-ulopyranosidonic acid (19)
A solution of 17 (39 mg, 0.11 mmol) in 1 M sodium hydroxide (1 mL) was stirred for 18 h at 25 °C and evaporated in vacuo. The desired product (37 mg, 0.11 mmol, 99%) was obtained using column chromatography on reversed phase silica gel in H2O and obtained as a white solid.1H NMR (400 MHz, D2O) δ 4.53 (1H, m, H8), 3.61–4.00 (3H, m, H4, H6, H7), 3.16–3.22 (1H, m, H5), 3.16 (3H, s, COCH3), 2.37 (1H, dd, J3e,3a = 13.2 Hz, J3e,4 = 4.7 Hz, H3e), 2.08 (3H, s, AcN), 2.07 (3H, s, AcN), 1.70 (1H, t, J3a,3e = 13.2 Hz, J3a,4 = 12.0 Hz, H3a), 1.10 (3H, d, J9,8 = 6.3 Hz, H9).
m/z 371.2 [M + Na]+.
Methyl 5,7-diacetamido-3,5,7,9-tetradeoxy-D-glycero-D-galacto-non-2-ulopyranosidonic acid (20)
A solution of 18 (26 mg, 0.07 mmol) in 1 M sodium hydroxide (1 mL) was stirred for 18 h at 25 °C and evaporated in vacuo. The desired product (25 mg, 0.07 mmol, 100%) was obtained using column chromatography on reversed phase silica gel in H2O and obtained as a white solid.1H NMR (400 MHz, D2O) δ 4.51 (1H, m, H8), 3.58–4.04 (4H, m, H4, H5, H6, H7), 3.17 (3H, s, COCH3), 2.32 (1H, dd, J3e,3a = 13.0 Hz, J3e,4 = 4.5 Hz, H3e), 2.32 (3H, s, AcN), 2.03 (3H, s, AcN), 1.69 (1H, t, J3a,3e = 13.0 Hz, J3a,4 = 10.9 Hz, H3a), 1.08 (3H, d, J9,8 = 6.4 Hz, H9).
m/z 371.2 [M + Na]+.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.Acknowledgements
The authors thank the Australian Postgraduate Award scheme for a PhD scholarship (to JRC) and Griffith University for additional support.Notes and references
- M. Zunk and M. J. Kiefel, RSC Adv., 2014, 4, 3413 RSC.
- Y. A. Knirel, E. T. Rietschel, R. Marre and U. Zähringer, Eur. J. Biochem., 1994, 221, 239 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Cazalet, S. Jarraud, Y. Ghavi-Helm, F. Kunst, P. Glaser, J. Etienne and C. Buchrieser, Genome Res., 2008, 18, 431 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. E. Tsvetkov, A. S. Shashkov, Y. A. Knirel and U. Zähringer, Carbohydr. Res., 2001, 331, 233 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. R. Haseley and S. G. Wilkinson, Eur. J. Biochem., 1997, 250, 617 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. J. Kenyon, A. Notaro, L. Y. Hsu, C. De Castro and R. M. Hall, Sci. Rep., 2017, 7, 1 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- E. Vinogradov, L. MacLean, H. H. Xu and W. Chen, Carbohydr. Res., 2014, 390, 42 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. A. Knirel, N. A. Kocharova, A. S. Shashkov, N. K. Kochetkov, E. V. Kholodkova and E. S. Stanislavsky, Eur. J. Biochem., 1987, 166, 189 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. A. Knirel, J. H. Helbig and U. Zähringer, Carbohydr. Res., 1996, 283, 129 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- E. V. Vinogradov, A. S. Shashkov, Y. A. Knirel, N. K. Kochetkov, J. Dabrowski, H. Grosskurth, E. S. Stanislavsky and E. V. Kholodkova, Carbohydr. Res., 1992, 231, 1 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. M. Logan, J. F. Kelly, P. Thibault, C. P. Ewing and P. Guerry, Mol. Microbiol., 2002, 46, 587 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. J. McNally, A. J. Aubry, J. P. M. Hui, N. H. Khieu, D. Whitfield, C. P. Ewing, P. Guerry, J. R. Brisson, S. M. Logan and E. C. Soo, J. Biol. Chem., 2007, 282, 14463 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Li, A. V. Perepelov, Q. Wang, S. N. Senchenkova, B. Liu, S. D. Shevelev, X. Guo, A. S. Shashkov, W. Chen, L. Wang and Y. A. Knirel, Carbohydr. Res., 2010, 345, 1581 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. A. Knirel, S. N. Senchenkova, A. S. Shashkov, S. D. Shevelev, A. V. Perepelov, L. Bin, L. Feng and L. Wang, Adv. Sci. Lett., 2009, 2, 384 CrossRef CAS.
- A. V. Perepelov, B. Liu, S. N. Senchenkova, A. S. Shashkov, S. D. Shevelev, L. Feng, L. Wang and Y. A. Knirel, Biochemistry, 2010, 75, 19 CAS.
- E. L. Nazarenko, A. S. Shashkov, Y. A. Knirel, E. P. Ivanova and I. S. Ovodov, Bioorg. Khim., 1990, 16, 1426 CAS.
- P. Edebrink, P.-E. Jansson, J. Bøgwald and J. Hoffman, Carbohydr. Res., 1996, 287, 225 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- N. Hashii, Y. Isshiki, T. Iguchi, K. Hisatsune and S. Kondo, Carbohydr. Res., 2003, 338, 1055 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- N. Hashii, Y. Isshiki, T. Iguchi and S. Kondo, Carbohydr. Res., 2003, 338, 1063 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. E. Tsvetkov, A. S. Shashkov, Y. A. Knirel and U. Zähringer, Carbohydr. Res., 2001, 335, 221 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Matthies, P. Stallforth and P. H. Seeberger, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2015, 137, 2848 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- O. Popik, B. Dhakal and D. Crich, J. Org. Chem., 2017, 82, 6142 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Santra, A. Xiao, H. Yu, W. Li, Y. Li, L. Ngo, J. B. McArthur and X. Chen, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2018, 57, 2929 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. J. Morrison and B. Imperiali, Biochemistry, 2014, 53, 624 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Zunk, J. Williams, J. Carter and M. J. Kiefel, Org. Biomol. Chem., 2014, 12, 2918 RSC.
- P. J. Garegg and B. Samuelsson, J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 1, 1979, 978 CAS.
- K. Furuhata, Trends Glycosci. Glycotechnol., 2004, 16, 143 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Dong, Z. Pei and O. Ramström, J. Org. Chem., 2006, 71, 3306 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Battistini, A. Giordani, A. Ermoli and G. Franceschi, Synthesis, 1990, 900 CrossRef CAS.
- D. B. Dess and J. C. Martin, J. Org. Chem., 1983, 48, 4155 CrossRef CAS.
- J.-L. Luche, L. Rodriguez-Hahn and P. Crabbé, J. Chem. Soc., Chem. Commun., 1978, 601 RSC.
- W. Lin, X. Zhang, Z. He, Y. Jin, L. Gong and A. Mi, Synth. Commun., 2002, 32, 3279 CrossRef CAS.
- J. T. Williams, L. Corcilius, M. J. Kiefel and R. T. Payne, J. Org. Chem., 2016, 81, 2607 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. J. Kenyon, A. Notaro, L. Y. Hsu, C. De Castro and R. M. Hall, Sci. Rep., 2017, 7, 1 CrossRef CAS.
- W. L. F. Armarego and C. L. L. Chai, Purification of Laboratory Chemicals, 7th edn, Elsevier, 2013 Search PubMed.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available. See DOI: 10.1039/c8ra07771a |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 |