Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleCreative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported Licence
Synthesis and applications of highly functionalized 1-halo-3-substituted bicyclo[1.1.1]pentanes†
Dimitri F. J.
Caputo
 a,
Carlos
Arroniz
a,
Carlos
Arroniz
 a,
Alexander B.
Dürr
a,
James J.
Mousseau
b,
Antonia F.
Stepan
c,
Steven J.
Mansfield
a and
Edward A.
Anderson
a,
Alexander B.
Dürr
a,
James J.
Mousseau
b,
Antonia F.
Stepan
c,
Steven J.
Mansfield
a and
Edward A.
Anderson
 *a
*a
aChemistry Research Laboratory, 12 Mansfield Road, Oxford, OX1 3TA, UK. E-mail: edward.anderson@chem.ox.ac.uk
bPfizer Worldwide Research and Development, Eastern Point Road, Groton, CT 06340, USA
cPfizer Worldwide Research and Development, 600 Main Street, Cambridge, MA 02139, USA
First published on 21st May 2018
Abstract
Bicyclo[1.1.1]pentanes (BCPs) are important bioisosteres of 1,4-disubstituted arenes, tert-butyl and acetylenic groups that can impart physicochemical benefits on drug candidates. Here we describe the synthesis of BCPs bearing carbon and halogen substituents under exceptionally mild reaction conditions, via triethylborane-initiated atom-transfer radical addition ring-opening of tricyclo[1.1.1.01,3]pentane (TCP) with alkyl halides. This chemistry displays broad substrate scope and functional group tolerance, enabling application to BCP analogues of biologically-relevant targets such as peptides, nucleosides, and pharmaceuticals. The BCP halide products can be converted to the parent phenyl/tert-butyl surrogates through triethylborane-promoted dehalogenation, or to other derivatives including carbonyls, alcohols, and heterocycles.
Introduction
Bioisosteres are important motifs in drug design,1 enabling the expansion of chemical and intellectual property space2 while also improving biological profiles relative to the parent functionality. Bicyclo[1.1.1]pentanes (BCPs) have shown particularly impressive results in this field as surrogates for 1,4-disubstituted arenes, tert-butyl, and alkyne groups, imparting desirable properties such as membrane permeability, solubility and metabolic stability.3,4 Examples include BCP analogues of the γ-secretase inhibitor BMS-708, 163 (1, Fig. 1a)5 and resveratrol (2),6 in which the BCP serves as a bioisostere for a p-substituted arene due to its comparable positioning of substituents; and of the pulmonary arterial hypertension agent bosentan (3, Fig. 1b), where a monosubstituted BCP replaces a tert-butyl group.7,8 Despite these favourable attributes, access to carbon-substituted BCPs remains a challenge. Their synthesis typically relies on multistep sequences from a small number of available precursors,9 or requires relatively harsh conditions,10 necessitating early-stage introduction of the BCP and limiting functional group tolerance.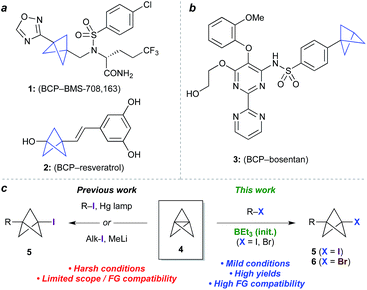 | ||
| Fig. 1 (a) Bicyclo[1.1.1]pentanes (BCPs) as 1,4-disubstituted arene bioisosteres. (b) BCP as a tert-butyl bioisostere. (c) Approaches to 1-halo-3-substituted BCPs in previous and current work. | ||
The BCP system is most commonly accessed through ‘strain release’11 reactions of tricyclo[1.1.1.01,3]pentane 4 (TCP),12 where in addition to classical approaches,3,13 recent work has seen the development of elegant methods for the synthesis of heteroatom-substituted BCPs.11,14 The insertion of TCP into C–X bonds would offer an appealing entry to carbon-substituted BCPs, as well as the opportunity for further functionalization of the halide product (5, Fig. 1c).15 To date however, this process has only been achieved using highly activated reagents (e.g. CF3I),13 or by mercury lamp irradiation of an alkyl or aryl halide,10d,e or methyllithium-promoted alkyl halide addition.10b Despite the importance of these contributions, all display limitations in substrate scope, functional group compatibility, or scalability, due to the constraints of the reaction conditions.
Atom transfer radical addition (ATRA) reactions using chemical initiators are an attractive alternative for TCP ring opening, but previously required a large excess of the radical precursor, or suffered from the formation of oligomeric ‘staffane’ byproducts due to multiple insertions into TCP.10d,13 Building on our studies of radical-mediated nucleoside alkynylation,16 we questioned whether triethylborane could serve as an effective initiator17 for the synthesis of 1-halo-3-substituted bicyclopentanes (Fig. 1c). Here we report the development of this method as an efficient and highly functional group tolerant route to halogenated BCPs, the utility of which are illustrated through various derivatizations. Importantly, the mild conditions of this chemistry allow the synthesis of bicyclopentanes that could not be accessed using other methods, and open up opportunities for the late-stage functionalization of more complex molecules.
Results and discussion
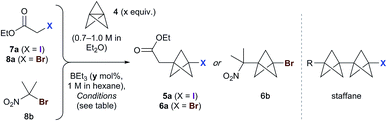
We began our studies using ethyl iodoacetate 7a, and were delighted to observe complete reaction in just 15 min at room temperature using 1.3 equivalents of TCP and 10 mol% triethylborane (1 M in hexane), with the product iodide 5a isolated in 83% yield (Table 1, entry 1). A mild exotherm was observed on addition of triethylborane to the reaction, which could be avoided by reducing the temperature (entry 2). The amount of initiator could be decreased to 1 mol% without detriment (entries 2–5), and the quantity of TCP could also be lowered (to 1.1 equiv.), affording 5a in 92% yield (entry 6). Successful reaction was similarly observed using TCP as a solution in dibutyl ether (0.19 M), which is significant for industrial applications (entry 7). The presence of triethylborane proved crucial, as reactions run in its absence failed to reach completion in the dark or light (entries 8 and 9).18 Importantly, no staffane byproducts were observed under the optimized conditions (entry 6).| Entry | Substrate | x (equiv.) | y (mol%) | T | t | Yielda (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
a Isolated yields. Figures in parentheses indicate incomplete reactions, and the ratio of starting material to product as judged by 1H NMR spectroscopic analysis of the crude reaction mixture.
b Reaction carried out in Bu2O (0.19 M).
c Reaction carried out in the dark.
d Isolated as a 6![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 mixture of 6a 1 mixture of 6a![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) staffane. staffane.
|
||||||
| 1 | 7a | 1.3 | 10 | rt | 15 min | 83 |
| 2 | 7a | 1.3 | 10 | 0 °C | 15 min | 87 |
| 3 | 7a | 1.3 | 5 | 0 °C | 15 min | 89 |
| 4 | 7a | 1.3 | 1 | 0 °C | 15 min | 95 |
| 5 | 7a | 1.3 | 0.5 | 0 °C | 15 min | (67![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 33) 33) |
| 6 | 7a | 1.1 | 1 | 0 °C | 15 min | 92 |
| 7 | 7a | 2.0 | 10 | rt | 16 h | 98b |
| 8 | 7a | 2.0 | 0 | rt | 20 h | (60![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 40)c 40)c |
| 9 | 7a | 2.0 | 0 | rt | 20 h | (33![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 67) 67) |
| 10 | 8a | 1.3 | 10 | rt | 20 h | 47d |
| 11 | 8b | 1.3 | 10 | rt | 15 min | 67 |
| 12 | 8b | 1.3 | 10 | 0 °C | 15 min | 73 |
| 13 | 8b | 1.3 | 1 | 0 °C | 15 min | (60![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 40) 40) |
Use of the equivalent bromoacetate 8a led to incomplete conversion, or significant staffane formation (entry 10).19 However, we were pleased to find that 2-bromo-2-nitropropane 8b underwent rapid reaction with 1.3 equivalents of TCP to afford 6b in 67% yield (entry 11).20 As with 7a, full conversion was maintained on cooling the reaction to 0 °C (73%, entry 12); however, lowering the quantity of triethylborane resulted in incomplete reaction (entry 13). The success of substrate 8b presumably reflects a more efficient bromine atom abstraction by the bicyclopentyl radical in the propagation step compared to ester 8a, due to the greater stability of the tertiary nitro-substituted radical.
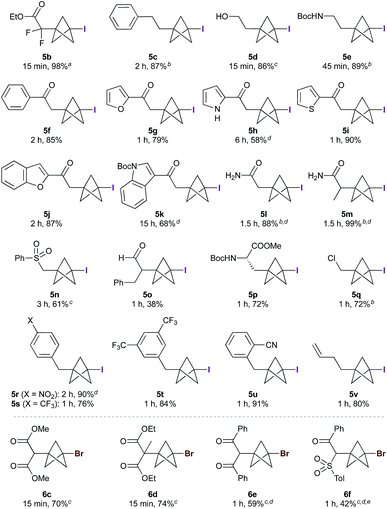
The scope of the triethylborane-initiated ATRA was next explored using organohalides featuring a variety of functional groups (Fig. 2).21 While the optimized conditions (Table 1, entry 6) translated smoothly to ethyl difluoroiodoacetate, giving bench-stable BCP 5b in 98% yield,22 incomplete reactions were observed in other cases. To ensure consistency, the substrate screen was therefore conducted using 10 mol% BEt3 and 1.3–2.0 equivalents of TCP at either 0 °C or room temperature, according to the requirements of the substrate. Alkyl iodides showed excellent reactivity, tolerating groups such as hydroxyls and carbamates (5c–e). α-Iodoketones gave high yields across a range of substrates, including heteroaromatics (5f–k). Other electron-withdrawing groups such as amides and sulfones also proved viable (5l–5n),20 including the sensitive but potentially valuable aldehyde 5o. The formation of 5p is particularly notable due to the potential utility of BCP analogues of amino acids;23 no racemization was observed in this reaction. Even chloroiodomethane was found to be a suitable substrate, delivering chloromethyl BCP 5q in good yield. Benzyl halides also underwent smooth reaction, providing electron-withdrawing substituents were present on the arene (which presumably accelerates the halide abstraction step from the intermediate BCP radical, 5r–5u).20 The involvement of radical intermediates was supported by the use of (iodomethyl)cyclopropane, which exclusively gave the ring-opened product 5v. Finally, other electron-deficient bromides proved suitable partners, affording products 6c–f in short reaction times; for these substrates, the presence of two electron-withdrawing groups proved essential for efficient bromine atom abstraction.
While the BCP iodide products are stable towards storage at −20 °C (particularly if crystalline), in some cases gradual coloration was observed at ambient temperature. Deiodination was expected to enhance BCP stability, and would simultaneously access the parent phenyl/tert-butyl bioisostere. We questioned whether triethylborane could again be used as initiator for this C–I bond reduction; pleasingly, the use of 1.3 equivalents of tris(trimethylsilyl)silane (TTMSS) as a non-toxic hydrogen atom source24 and 10 mol% BEt3 effected smooth deiodination of various BCP iodides (Scheme 1a), giving amide 9l, a BCP analogue of phenylalanine (9p), and trifluoroacetate salt 9e, the free base of the latter being a BCP equivalent of the monoaminergic neuromodulator phenethylamine. Given the use of the same initiator for both radical processes, a one-pot reaction sequence was also performed in which BCP 9a was prepared directly from 7a in a single operation (64%). Transformation of the iodide into substituents other than hydrogen was also explored (Scheme 1b): lithiation of 5s,10b followed by reaction of the resulting organolithium 10 with benzaldehyde or ethyl formate, gave alcohol 11 and aldehyde 12 respectively. Alternatively, transmetalation to the organozinc and cross-coupling with 2-bromopyridine afforded pyridyl BCP 13 (64%).10a,b Pleasingly, the synthesis of a phenol bioisostere6 (14) could also be accomplished by a borylation quench, followed by oxidation with sodium perborate.
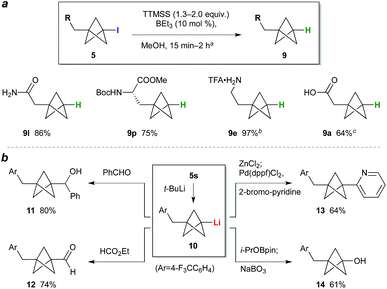 | ||
| Scheme 1 (a) BCP deiodination. aSee the ESI† for experimental conditions for each substrate. bDeiodination product from 5e treated with CF3CO2H (yield over two steps). cIodide 7a processed through TCP ring opening, deiodination, and hydrolysis (NaOH, MeOH) without purification. (b) BCP iodide functionalization. | ||
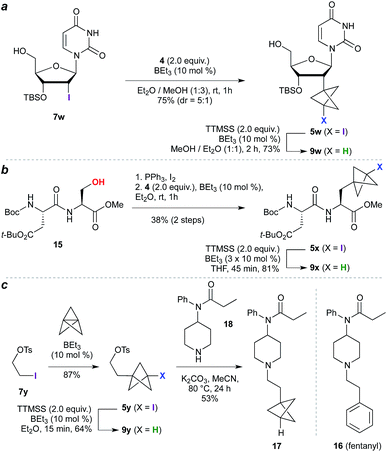
The high functional group tolerance and mild reaction conditions suggested that this methodology could be exploited in the functionalization of more complex organic molecules. For example, 2′-iodouridine derivative 7w (Scheme 2a) underwent successful ATRA reaction to generate 5w (75%, 5![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 dr), with deiodination delivering the 2′-deoxy-2′-BCP nucleoside 9w (73%). More generally, the availability of iodides from hydroxyl groups provides a multitude of opportunities for bioisostere installation: Appel reaction of the aspartate–serine dipeptide 15 (Scheme 2b) afforded iodide 5x, which on ATRA reaction and subsequent TTMSS reduction generated BCP-functionalized dipeptide 9x. This sequence corresponds to a three step conversion of a serine residue to a potential phenylalanine equivalent, and here delivers a BCP analogue of aspartame. Finally, we targeted application of the methodology to the opioid receptor agonist fentanyl (16, Scheme 2c). Synthesis of its BCP analogue 17 was accomplished from iodotosylate 7y where, pleasingly, the primary alkyl tosylate was tolerated in the initial high-yielding TCP ring-opening (87%). TTMSS-mediated reduction of the iodide product 5y afforded the useful BCP building block 9y, which underwent alkylation with norfentanyl 18 to afford fentanyl analogue 17 (53%).20
1 dr), with deiodination delivering the 2′-deoxy-2′-BCP nucleoside 9w (73%). More generally, the availability of iodides from hydroxyl groups provides a multitude of opportunities for bioisostere installation: Appel reaction of the aspartate–serine dipeptide 15 (Scheme 2b) afforded iodide 5x, which on ATRA reaction and subsequent TTMSS reduction generated BCP-functionalized dipeptide 9x. This sequence corresponds to a three step conversion of a serine residue to a potential phenylalanine equivalent, and here delivers a BCP analogue of aspartame. Finally, we targeted application of the methodology to the opioid receptor agonist fentanyl (16, Scheme 2c). Synthesis of its BCP analogue 17 was accomplished from iodotosylate 7y where, pleasingly, the primary alkyl tosylate was tolerated in the initial high-yielding TCP ring-opening (87%). TTMSS-mediated reduction of the iodide product 5y afforded the useful BCP building block 9y, which underwent alkylation with norfentanyl 18 to afford fentanyl analogue 17 (53%).20
While the mechanism of this C–X addition reaction likely involves a radical pathway, not least due to the cyclopropane ring fragmentation observed in the formation of 5v (Fig. 2), it is not immediately obvious why reaction propagation via halogen atom abstraction should proceed so efficiently, with avoidance of staffane formation. To explore this, we examined the reaction of α-iodo- and α-bromomethyl acetate with TCP from a theoretical perspective at the ROM062x/def2tzvp level25 (Fig. 3, in vacuo).26 Exergonic addition of the α-carbonyl radical to TCP (A) was found to proceed via transition state AB‡ (ΔG‡ = 12.5 kcal mol−1). Reaction of the resultant bicyclopentyl radical B with α-iodo- or α-bromomethyl acetate (iodine/bromine atom transfer, BI‡/BBr‡), or with TCP (leading to a staffane radical, BS‡), was computed. Predicted activation barriers of 7.3 and 13.3 kcal mol−1 for iodine atom abstraction and TCP capture respectively suggest that the former productive propagation step is significantly favoured over oligomerization (ΔΔG‡ = 6.1 kcal mol−1). In contrast, a barrier of 12.9 kcal mol−1 for bromine atom abstraction indeed suggests staffane formation to be competitive (ΔΔG‡ = 0.4 kcal mol−1), which is consistent with experimental observations (Table 1), and reflects the influence of C–X bond strength in the propagation phase of the reaction.
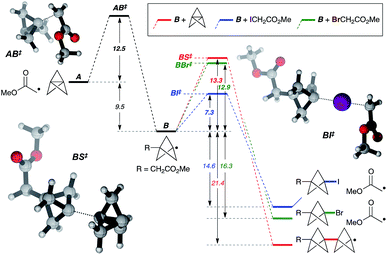 | ||
| Fig. 3 Theoretical analysis of the reaction pathway. Calculations carried out at the ROMO62x/def2tzvp level. Relative energies are in kcal mol−1. See the ESI for details.† | ||
Conclusions
In conclusion, we have developed an efficient triethylborane-promoted radical-based method to synthesize 1-halo-3-substituted bicyclo[1.1.1]pentanes from readily available iodide and bromide starting materials. The reaction displays broad substrate scope, and functional group compatibility that is not achievable using other methods, enabling application to the functionalization of complex substrates such as nucleosides, peptides and drug-like molecules. The carbon–halogen bond is easily reduced under similarly mild conditions to reveal the parent bioisostere, or functionalized via methods such as Negishi cross-coupling or oxidation. In addition to offering a new entry to highly-functionalized bicyclopentanes, the C–X bond offers much potential for subsequent transformations; investigations to this end are underway.Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.Acknowledgements
D. F. J. C. and S. J. M. are grateful to the EPSRC Centre for Doctoral Training in Synthesis for Biology and Medicine (EP/L015838/1) for studentships, generously supported by AstraZeneca, Diamond Light Source, Defence Science and Technology Laboratory, Evotec, GlaxoSmithKline, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, Syngenta, Takeda, UCB and Vertex. E. A. A. and C. A. thank the EPSRC for funding (EP/M019195/1). A. B. D. thanks the Heinrich Hertz Foundation for a Fellowship. We also thank the University of Oxford Advanced Research Computing (ARC) facility (DOI: 10.5281/zenodo.22558).Notes and references
- (a) N. A. Meanwell, Chem. Res. Toxicol., 2016, 29, 564–616 CrossRef PubMed; (b) N. A. Meanwell, J. Med. Chem., 2011, 54, 2529–2591 CrossRef PubMed; (c) G. A. Patani and E. J. LaVoie, Chem. Rev., 1996, 96, 3147–3176 CrossRef PubMed.
- F. Lovering, J. Bikker and C. Humblet, J. Med. Chem., 2009, 52, 6752–6756 CrossRef PubMed.
- (a) A. M. Dilmaç, E. Spuling, A. de Meijere and S. Bräse, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2017, 56, 5684–5718 CrossRef PubMed; (b) M. D. Levin, P. Kaszynski and J. Michl, Chem. Rev., 2000, 100, 169–234 CrossRef PubMed; (c) K. B. Wiberg, Chem. Rev., 1989, 89, 975–983 CrossRef.
- (a) For recent examples of other small ring compounds as bioisosteres, see: A. A. Kirichok, I. Shton, M. Kliachyna, I. Pishel and P. K. Mykhailiuk, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2017, 56, 8865–8869 CrossRef PubMed; (b) P. Lassalas, K. Oukoloff, V. Makani, M. James, V. Tran, Y. Yao, L. Huang, K. Vijayendran, L. Monti, J. Q. Trojanowski, V. M. Y. Lee, M. C. Kozlowski, A. B. Smith, K. R. Brunden and C. Ballatore, ACS Med. Chem. Lett., 2017, 8, 864–868 CrossRef PubMed; (c) P. Mukherjee, M. Pettersson, J. K. Dutra, L. Xie and C. W. am Ende, ChemMedChem, 2017, 12, 1574 CrossRef PubMed; (d) Y. P. Auberson, C. Brocklehurst, M. Furegati, T. C. Fessard, G. Koch, A. Decker, L. La Vecchia and E. Briard, ChemMedChem, 2017, 12, 590–598 CrossRef PubMed; (e) B. A. Chalmers, H. Xing, S. Houston, C. Clark, S. Ghassabian, A. Kuo, B. Cao, A. Reitsma, C.-E. P. Murray, J. E. Stok, G. M. Boyle, C. J. Pierce, S. W. Littler, D. A. Winkler, P. V. Bernhardt, C. Pasay, J. J. De Voss, J. McCarthy, P. G. Parsons, G. H. Walter, M. T. Smith, H. M. Cooper, S. K. Nilsson, J. Tsanaktsidis, G. P. Savage and C. M. Williams, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2016, 55, 3580–3585 CrossRef PubMed; (f) J. A. Bull, R. A. Croft, O. A. Davis, R. Doran and K. F. Morgan, Chem. Rev., 2016, 116, 12150–12233 CrossRef PubMed.
- A. F. Stepan, C. Subramanyam, I. V. Efremov, J. K. Dutra, T. J. O'Sullivan, K. J. DiRico, W. S. McDonald, A. Won, P. H. Dorff, C. E. Nolan, S. L. Becker, L. R. Pustilnik, D. R. Riddell, G. W. Kauffman, B. L. Kormos, L. Zhang, Y. Lu, S. H. Capetta, M. E. Green, K. Karki, E. Sibley, K. P. Atchison, A. J. Hallgren, C. E. Oborski, A. E. Robshaw, B. Sneed and C. J. O'Donnell, J. Med. Chem., 2012, 55, 3414–3424 CrossRef PubMed.
- Y. L. Goh, Y. T. Cui, V. Pendharkar and V. A. Adsool, ACS Med. Chem. Lett., 2017, 8, 516–520 CrossRef PubMed.
- M. V. Westphal, B. T. Wolfstädter, J.-M. Plancher, J. Gatfield and E. M. Carreira, ChemMedChem, 2015, 10, 461–469 CrossRef PubMed.
- (a) For other recent examples of BCPs in medicinal chemistry, see: N. D. Measom, K. D. Down, D. J. Hirst, C. Jamieson, E. S. Manas, V. K. Patel and D. O. Somers, ACS Med. Chem. Lett., 2017, 8, 43–48 CrossRef PubMed; (b) K. C. Nicolaou, J. Yin, D. Mandal, R. D. Erande, P. Klahn, M. Jin, M. Aujay, J. Sandoval, J. Gavrilyuk and D. Vourloumis, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2016, 138, 1698–1708 CrossRef PubMed; (c) R. Pellicciari, R. Filosa, M. C. Fulco, M. Marinozzi, A. Macchiarulo, C. Novak, B. Natalini, M. B. Hermit, S. Nielsen, T. N. Sager, T. B. Stensbøl and C. Thomsen, ChemMedChem, 2006, 1, 358–365 CrossRef PubMed.
- (a) P. Kaszynski and J. Michl, J. Org. Chem., 1988, 53, 4593–4594 CrossRef; (b) 1-azido-3-iodo BCP: K. B. Wiberg and N. McMurdie, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1994, 116, 11990–11998 CrossRef.
- (a) I. S. Makarov, C. E. Brocklehurst, K. Karaghiosoff, G. Koch and P. Knochel, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2017, 56, 12774–12777 CrossRef PubMed; (b) M. Messner, S. I. Kozhushkov and A. de Meijere, Eur. J. Org. Chem., 2000, 1137 CrossRef; (c) E. W. Della and D. K. Taylor, J. Org. Chem., 1994, 59, 2986–2996 CrossRef; (d) P. Kaszynski, A. C. Friedli and J. Michl, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1992, 114, 601–620 CrossRef; (e) P. Kaszynski, N. D. McMurdie and J. Michl, J. Org. Chem., 1991, 56, 307–316 CrossRef ; to our knowledge only esters and a ketone have been shown to be tolerated under mercury lamp irradiation, and only tetrahydropyranyl ethers under MeLi promoted TCP ring opening.
- (a) R. Gianatassio, J. M. Lopchuk, J. Wang, C.-M. Pan, L. R. Malins, L. Prieto, T. A. Brandt, M. R. Collins, G. M. Gallego, N. W. Sach, J. E. Spangler, H. Zhu, J. Zhu and P. S. Baran, Science, 2016, 351, 241 CrossRef PubMed; (b) J. M. Lopchuk, K. Fjelbye, Y. Kawamata, L. R. Malins, C.-M. Pan, R. Gianatassio, J. Wang, L. Prieto, J. Bradow, T. A. Brandt, M. R. Collins, J. Elleraas, J. Ewanicki, W. Farrell, O. O. Fadeyi, G. M. Gallego, J. J. Mousseau, R. Oliver, N. W. Sach, J. K. Smith, J. E. Spangler, H. Zhu, J. Zhu and P. S. Baran, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2017, 139, 3209–3226 CrossRef PubMed.
- K. R. Mondanaro and W. P. Dailey, Org. Synth., 1998, 75, 98 CrossRef . For a more recent preparation using PhLi see ref. 11a. Appropriate precautions should be taken in the preparation of 4 due to the need for relatively large volumes of organolithium solutions.
- K. B. Wiberg and S. T. Waddell, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1990, 112, 2194–2216 CrossRef.
- (a) R. M. Bär, S. Kirschner, M. Nieger and S. Bräse, Chem.–Eur. J., 2018, 24, 1373–1382 CrossRef PubMed; (b) J. Kanazawa, K. Maeda and M. Uchiyama, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2017, 139, 17791–17794 CrossRef PubMed; (c) K. Bunker, C. Guo, M. Grier, C. Hopkins, J. Pinchman, D. Slee, P. Q. Huang and M. Kahraman, WO Pat., 2016/044331, 2016; (d) Y. L. Goh and V. A. Adsool, Org. Biomol. Chem., 2015, 13, 11597–11601 RSC; (e) N. T. Thirumoorthi, C. J. Shen and V. A. Adsool, Chem. Commun., 2015, 51, 3139–3142 RSC; (f) Y. L. Goh, E. K. W. Tam, P. H. Bernardo, C. B. Cheong, C. W. Johannes, A. D. William and V. A. Adsool, Org. Lett., 2014, 16, 1884–1887 CrossRef PubMed; (g) K. D. Bunker, N. W. Sach, Q. Huang and P. F. Richardson, Org. Lett., 2011, 13, 4746–4748 CrossRef PubMed.
- (a) J. L. Adcock and A. A. Gakh, J. Org. Chem., 1992, 57, 6206–6210 CrossRef ; see also ref. 9a, 10b and 14c; (b) C. Mazal, A. J. Paraskos and J. Michl, J. Org. Chem., 1998, 63, 2116–2119 CrossRef.
- (a) M. M. Haugland, A. H. El-Sagheer, R. J. Porter, J. Peña, T. Brown, E. A. Anderson and J. E. Lovett, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2016, 138, 9069–9072 CrossRef PubMed; (b) M. Sukeda, S. Ichikawa, A. Matsuda and S. Shuto, J. Org. Chem., 2003, 68, 3465–3475 CrossRef PubMed; (c) M. Sukeda, S. Ichikawa, A. Matsuda and S. Shuto, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2002, 41, 4748–4750 CrossRef PubMed.
- (a) D. P. Curran and T. R. McFadden, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2016, 138, 7741–7752 CrossRef PubMed; (b) C. Ollivier and P. Renaud, Chem. Rev., 2001, 101, 3415–3434 CrossRef PubMed.
- While the reaction of 7a was not affected if conducted in degassed solvent under a nitrogen atmosphere (<15 min), the equivalent formation of 5s (Table 1) was significantly retarded, requiring 20 h reaction time to reach completion. We believe this supports a standard oxygen-mediated initiation mechanism. See ref. 17, and the ESI.†.
- For Et3B-promoted ATRA using 8a, see: H. Yorimitsu, H. Shinokubo, S. Matsubara, K. Oshima, K. Omoto and H. Fujimoto, J. Org. Chem., 2001, 66, 7776–7785 CrossRef PubMed.
- Low temperature single crystal X-ray diffraction data were 40 collected for 5m, 5r, 5s, 6b and 17 using a (Rigaku) Oxford Diffraction SuperNova A diffractometer. Raw frame data were collected and reduced using CrysAlisPro. The structures were solved using SuperFlip [ L. Palatinus and G. Chapuis, J. Appl. Crystallogr., 2007, 40, 786–790 CrossRef ] and refined using CRYSTALS [ P. W. Betteridge, J. R. Carruthers, R. I. Cooper, K. Prout and D. J. Watkin, J. Appl. Crystallogr., 2003, 36, 1487 CrossRef; R. I. Cooper, A. L. Thompson and D. J. Watkin, J. Appl. Crystallogr., 2010, 43, 1100–1107 CrossRef ]. See the ESI (CIF).† CCDC 1825056–1825060 contain the crystallographic data for this paper.†.
- See the ESI† for a discussion of substrates and functional groups that were not tolerated, or led to incomplete conversion, or significant staffane formation.
- This reaction was also conducted on a 5.00 mmol scale, which afforded 5b in 94% yield (1.50 g).
- (a) For examples of BCP amino acids, see ref. 4c, 8c, and: S. O. Kokhan, A. V. Tymtsunik, S. L. Grage, S. Afonin, O. Babii, M. Berditsch, A. V. Strizhak, D. Bandak, M. O. Platonov, I. V. Komarov, A. S. Ulrich and P. K. Mykhailiuk, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2016, 55, 14788–14792 CrossRef PubMed; (b) S. Pritz, M. Pätzel, G. Szeimies, M. Dathe and M. Bienert, Org. Biomol. Chem., 2007, 5, 1789–1794 RSC; (c) For additional examples, see: R. Pellicciari, M. Raimondo, M. Marinozzi, B. Natalini, G. Costantino and C. Thomsen, J. Med. Chem., 1996, 39, 2874–2876 CrossRef PubMed.
- (a) TTMSS has been employed in the reduction of BCP halides using AIBN as an initiator, see ref. 14c and e. Tributyltin hydride has also been used as the reducing agent, see ref. 10a; (b) N. T. Thirumoorthi and V. A. Adsool, Org. Biomol. Chem., 2016, 14, 9485–9489 RSC.
- (a) F. Weigend and R. Ahlrichs, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2005, 7, 3297–3305 RSC; (b) Y. Zhao and D. G. Truhlar, Theor. Chem. Acc., 2008, 120, 215–241 CrossRef.
- For appropriateness of the method chosen, see ref. 14b, and the ESI.†.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available. CCDC 1825056–1825060. For ESI and crystallographic data in CIF or other electronic format see DOI: 10.1039/c8sc01355a |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 |