Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleProduct distribution and mechanism of the OH− initiated tropospheric degradation of three CFC replacement candidates: CH3CF![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/h2_char_e001.gif) CH2, (CF3)2C
CH2, (CF3)2C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/h2_char_e001.gif) CH2 and (E/Z)-CF3CF
CH2 and (E/Z)-CF3CF![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/h2_char_e001.gif) CHF†
CHF†
Cynthia B. Rivelaa,
Carmen M. Tovarb,
Rodrigo Gibiliscob,
Mariano A. Teruel a,
Ian Barnesb,
Peter Wiesenb and
María B. Blanco
a,
Ian Barnesb,
Peter Wiesenb and
María B. Blanco *a
*a
aInstituto de Investigaciones en Fisicoquímica de Córdoba (I.N.F.I.Q.C.), CONICET, Dpto. de Fisicoquímica, Facultad de Ciencias Químicas, Universidad Nacional de Córdoba, Ciudad Universitaria, 5000 Córdoba, Argentina. E-mail: mblanco@fcq.unc.edu.ar
bPhysikalische Chemie/FBC, Bergische Universitaet Wuppertal, Wuppertal, Germany
First published on 14th February 2019
Abstract
The OH radical initiated photodegradation of 2-fluoropropene (CH3CF![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH2), 3,3,3-trifluoro-2-(tri-fluoromethyl)propene ((CF3)2C
CH2), 3,3,3-trifluoro-2-(tri-fluoromethyl)propene ((CF3)2C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH2) and (E/Z)-1,2,3,3,3-pentafluoropropene ((E/Z)-CF3CF
CH2) and (E/Z)-1,2,3,3,3-pentafluoropropene ((E/Z)-CF3CF![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CHF) has been investigated for the first time using a 1080 L quartz-glass environmental chamber at 298 ± 2 K and atmospheric pressure of synthetic air coupled with in situ FTIR spectroscopy to monitor reactants and products. The major products observed in the OH reaction were CH3C(O)F (98 ± 5)% together with HC(O)H (89 ± 7)% as a co-product, CF3C(O)F (103 ± 8)% together with HC(O)F (96 ± 7)% as a co-product and CF3C(O)CF3 (91 ± 8)% together with HC(O)H (98 ± 12)% as a co-product from the C1–C2 bond cleavage channel of the intermediate hydroxyalkoxy radical, formed by addition of OH to the terminal carbon of the double bond which is designated C1 of 2-fluoropropene, (E/Z)-1,2,3,3,3-pentafluoropropene and 3,3,3-trifluoro-2-(tri-fluoromethyl)propene, respectively. The present results are compared with previous studies for the reaction of OH with the separate isomers (E) and (Z) of 1,2,3,3,3-pentafluoropropene. In addition, atmospheric implications of the reactions studied are discussed.
CHF) has been investigated for the first time using a 1080 L quartz-glass environmental chamber at 298 ± 2 K and atmospheric pressure of synthetic air coupled with in situ FTIR spectroscopy to monitor reactants and products. The major products observed in the OH reaction were CH3C(O)F (98 ± 5)% together with HC(O)H (89 ± 7)% as a co-product, CF3C(O)F (103 ± 8)% together with HC(O)F (96 ± 7)% as a co-product and CF3C(O)CF3 (91 ± 8)% together with HC(O)H (98 ± 12)% as a co-product from the C1–C2 bond cleavage channel of the intermediate hydroxyalkoxy radical, formed by addition of OH to the terminal carbon of the double bond which is designated C1 of 2-fluoropropene, (E/Z)-1,2,3,3,3-pentafluoropropene and 3,3,3-trifluoro-2-(tri-fluoromethyl)propene, respectively. The present results are compared with previous studies for the reaction of OH with the separate isomers (E) and (Z) of 1,2,3,3,3-pentafluoropropene. In addition, atmospheric implications of the reactions studied are discussed.
1. Introduction
Fluorinated compounds are environmentally persistent and have been demonstrated to bioaccumulate and contribute to climate change.1,2As it is known, the Montreal and Kyoto Protocols represent global initiatives that have worked to decrease climate change.2,3 However, other actions have also led to a reduction in climate impact from halocarbons. Many halocarbons, such as hydrofluoroethers (HFEs), are used in refrigeration and air conditioning as replacements for ozone-depleting chemicals. One of the simplest means of decreasing atmospheric concentrations of these chemicals is through improved leakage rates that was implemented also by the United States Environmental Protection Agency.4 As a result, alternatives are being proposed that have lower Radiative Efficiency (REs) and Global Warming Potential (GWP), which include hydrofluorinated alkenes.5 Hydrofluorinated alkenes have IR absorption bands in the spectral regions where radiative forcing is most efficient, but they react relatively fast with OH radicals.6–9
Within hydrofluoroalkenes, 2-fluoropropene (2-FP), (E/Z)-isomeric mixture of 1,2,3,3,3-pentafluoropropene (PFP) and 3,3,3-trifluoro-2-(trifluoromethyl)propene (HXFP) are widely used as water repellents, inert fluids, coatings and as building blocks in the production of perfluorinated polymers.10,11
Emissions of these fluorinated alkenes to the atmosphere can occur during their production, processing and disposal and once in the atmosphere they will be subject to photodegradation mainly by OH radicals and to a lesser extent NO3 radicals and ozone and in certain environments also Cl atoms.6–9
In order to assess the contribution of the atmospheric photooxidation of hydrofluorinated alkenes to the oxidizing capacity of the atmosphere, to the global warming potential and to the possible formation of perfluoroacetic acids, detailed kinetic and mechanistic information on their tropospheric gas-phase degradation pathways are required. There have been reported in literature few kinetic studies of 1,2,3,3,3-pentafluoropropene with OH radical12–14 and the Cl-initiated oxidation of 3,3,3-trifluoro-2-(trifluoromethyl)propene.13,15
In contrast to the kinetic studies, only one product study concerning the OH- and Cl-initiated oxidation of (Z) and (E) individual isomers of 1,2,3,3,3-pentafluoropropene have been reported.12 This product distribution study12 was performed using a Pyrex reactor and FTIR technique as detection system. These authors have reported for both, Cl-atom and OH-radical-initiated atmospheric oxidations of CF3CF![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CHF, the presence of CF3C(O)F and HC(O)F in molar yields indistinguishable from 100% for both the (Z) and (E) isomer.
CHF, the presence of CF3C(O)F and HC(O)F in molar yields indistinguishable from 100% for both the (Z) and (E) isomer.
In addition, regarding to 3,3,3-trifluoro-2-(trifluoromethyl)propene, one product identification study of the OH and Cl initiated oxidation has been reported.15 This product distribution study was performed using an atmospheric simulation chamber and FTIR technique as detection system. HC(O)H and (CF3)2C(O) were identified as final oxidation products in both OH- and Cl-initiated oxidation of (CF3)2C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH2, while HC(O)Cl was additionally observed in the Cl-initiated oxidation.
CH2, while HC(O)Cl was additionally observed in the Cl-initiated oxidation.
No qualitative and quantitative products studies are currently available for OH-radical initiated degradation of 2-fluoropropene and 3,3,3-trifluoro-2-(trifluoromethyl)propene. In addition, there are not previous studies of the products distribution for the of OH with (E/Z)-isomeric mixture of 1,2,3,3,3-pentafluoropropene. Consequently, the present results are the first determination of the products distributions for the studied reactions.
Since, as stated above, fluorinated alkenes are widely used in the industry as chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) direct replacements and are released to the atmosphere in substantial amounts16 this motivated to us to investigate qualitatively and quantitatively the products formed in the OH-radical degradation of these fluoroalkenes according to:
OH + CH3CF![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH2 → products CH2 → products
| (1) |
OH + (CF3)2C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH2 → products CH2 → products
| (2) |
OH + (E/Z)-CF3CF![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CHF → products CHF → products
| (3) |
It is known that the main reaction pathway for OH radicals with unsaturated compounds is the addition to the double bond of the alkene unit. The major aim of the work was, to assess the relative importance of the different subsequent reaction pathways that are available to the hydroxyalkoxy radicals formed in the reactions studied. The results will contribute to an improved representation of the degradation of fluorinated alkenes in the atmospheric chemical models used to assess the environmental impact of chemicals and their contribution to the oxidizing capacity of the atmosphere.
2. Experimental
All the experiments were performed in a 1080 L quartz-glass reaction chamber at (298 ± 2) K and a total pressure of (760 ± 10) torr of synthetic air. A detailed description of the reactor can be found elsewhere17,18 and only a brief description is given here. The photolysis system consists of 32 superactinic lamps (Philips TL05 40W: 320–480 nm, λmax = 360 nm) and 32 low-pressure mercury vapor lamps (Philips TUV 40W; λmax = 254 nm). These lamps are wired in parallel and can be switched individually, which allows a variation of the light intensity, and thus also the photolysis frequency/radical production rate, within the chamber. The chamber is equipped with a White type multiple-reflection mirror system with a base length of (5.91 ± 0.01) m for sensitive in situ long path infrared absorption monitoring of reactants and products in the spectral range 4000–700 cm−1. The White system was operated at 82 traverses, giving a total optical path length of (484.7 ± 0.8) m. The IR spectra were recorded with a spectral resolution of 1 cm−1 using a Nicolet Nexus FT-IR spectrometer, equipped with a liquid nitrogen cooled mercury–cadmium–telluride (MCT) detector.A pumping system consisting of a turbo-molecular pump backed by a double stage rotary fore pump was used to evacuate the reactor to 10−3 torr. Three magnetically coupled Teflon mixing fans are mounted inside the chamber to ensure homogeneous mixing of the reactants.
Hydroxyl radicals were generated by the photolysis of H2O2 with the mercury lamps:
| H2O2 + hν → 2OH | (4) |
The initial concentrations used in the experiments for the hydrofluoroalkenes in ppm (1 ppm = 2.46 × 1013 molecule cm−3 at 298 K and 760 torr of total pressure) were: 0.7 for 2-fluoropropene, 0.1 for 3,3,3-trifluoro-2-(trifluoromethyl)propene and 0.7 for 1,2,3,3,3-pentafluoropropene, (E/Z) mixture. The initial concentration for the precursor of the oxidant was typically around 5 ppm for H2O2. The infrared absorption frequency at 1259.8, 1407.8 and 1197.1 cm−1 was used to monitor the concentration–time behavior of 2-fluoropropene, 3,3,3-trifluoro-2-(trifluoromethyl)propene and 1,2,3,3,3-pentafluoropropene, (E/Z) mixture, respectively. Readily identifiable products were monitored at the following absorption frequencies (in cm−1): HC(O)H at 2766; HC(O)F at 850; CF3C(O)F at 1897.8; CH3C(O)F at 1871.3 and CF3C(O)CF3 at 970.
The chemicals used in the experiments had the following purities as given by the manufacturer and were used as supplied: synthetic air (Air Liquide, 99.999%), 2-fluoropropene (Apollo Scientific) purity around 95%, 3,3,3-trifluoro-2-(tri-fluoromethyl)propene (Apollo Scientific) purity around 95%, 1,2,3,3,3-pentafluoropropene (Apollo Scientific, mixture (E/Z) isomers 97%; no manufacture details on isomer ratio) and H2O2 (Peroxide Chemie, 85%).
3. Results and discussion
To investigate the mechanisms of the OH-radical initiated oxidation of the title compounds, mixtures of H2O2/fluoroalkene/air were irradiated for periods of around 20 minutes during which infrared spectra where recorded with the FTIR spectrometer. Typically, 64 interferograms were co-added per spectrum over a period of approximately 1 min and 15–20 such spectra were collected during the course of the experiment.Dark reactions, photolysis of the fluoroalkenes studied in the absence of radical precursor reactions, and wall losses were negligible compared to the loss that occurred on OH radical photo-induced degradation.19
To facilitate the discussion of the results exemplary reaction schemes are shown for the reactions of OH with 2-fluoropropene, 3,3,3-trifluoro-2-(trifluoromethyl)propene and (E/Z)-isomeric mixture of 1,2,3,3,3-pentafluoropropene in Fig. 1, 2 and 3, respectively.
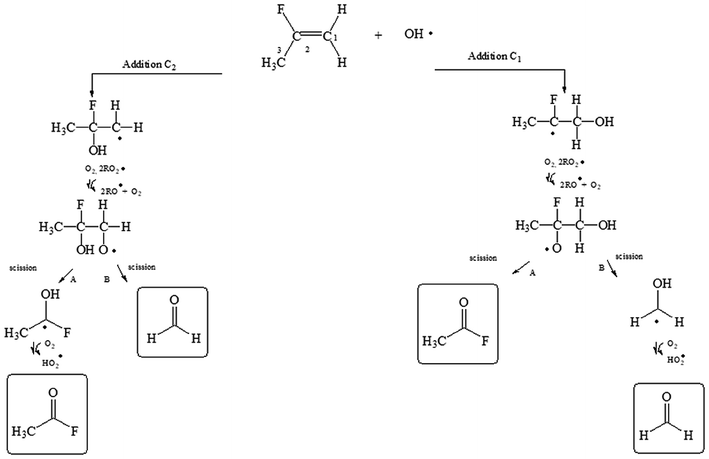 | ||
| Fig. 1 Mechanism for the reaction of 2-fluoropropene with OH radicals via addition of OH to the double bond. | ||
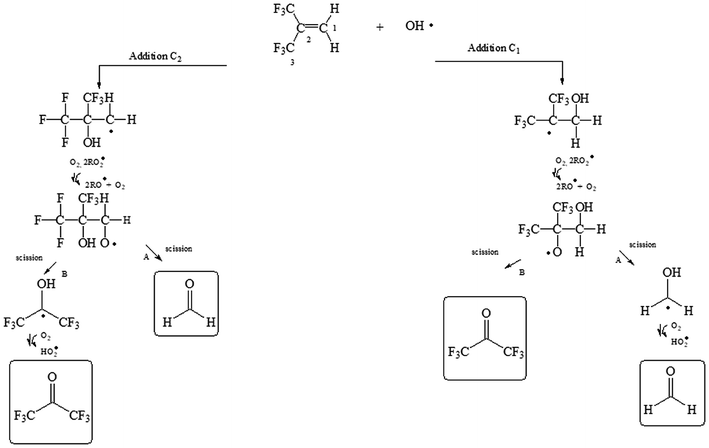 | ||
| Fig. 2 Mechanism for the reaction of 3,3,3-trifluoro-2-(trifluoromethyl)propene with OH radicals via addition of OH to the double bond. | ||
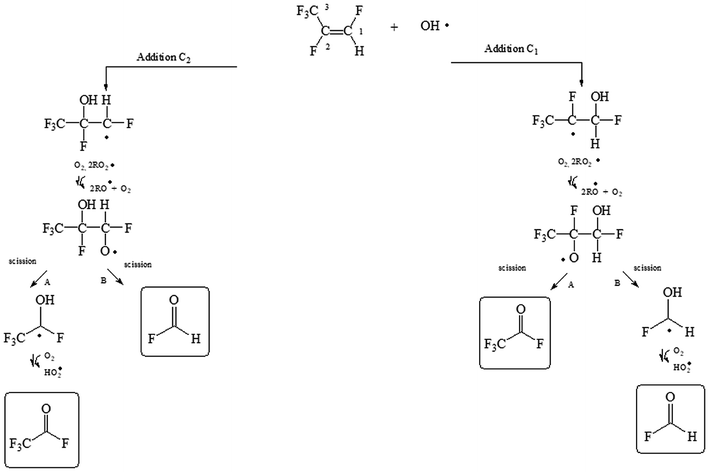 | ||
| Fig. 3 Mechanism for the reaction of 1,2,3,3,3-pentafluoropropene (mixture E/Z) with OH radicals via addition of OH to the double bond. | ||
For the OH radical reactions, the major reaction pathway involves initial addition of the OH to the carbon atom of the C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C bond, forming the hydroxyalkyl radicals.20,21
C bond, forming the hydroxyalkyl radicals.20,21
Under the conditions of the present study the hydroxyalkyl radicals will react with O2 to form the corresponding hydroxyalkyl peroxy radicals. In this work, under NOx-free experimental conditions peroxy self reactions will occur. These will result in the formation of the corresponding alkoxy radicals.
2-Fluoropropene + OH reaction
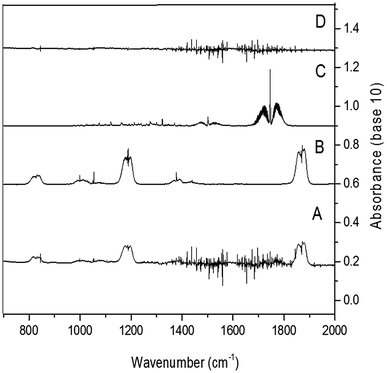
The OH radical could be added to the C1 or C2 of the double bond (see Fig. 1). And after the subsequent reactions with O2 and RO2 radicals, the hydroxyalkoxy radicals formed could decompose to give acetyl fluoride (CH3C(O)F) and formaldehyde (HC(O)H) if the addition of OH occur in C1 and/or C2.Fig. 4 shows IR spectra acquired after (panel A) UV irradiation of a mixture of 2-fluoropropene and H2O2 in air, in the absence of NOx where the 2-fluoropropene spectrum was subtracted. Panel B and C in Fig. 4 shows a reference spectra of CH3C(O)F, and HC(O)H, respectively. In Panel D is shown the residual product spectrum obtained after subtraction of reactants and identified products from the spectrum in panel A. CH3C(O)F and HC(O)H were readily identifiable as reaction products. The concentration–time profiles of CH3C(O)F and HC(O)H (Fig. S1 of ESI†) show that they are both primary products.
Least-squares analyses of plots of the concentrations of CH3C(O)F and HC(O)H, as a function of the amount of reacted 2-FP (Fig. S2†) give molar yields of (98 ± 5)% and (83 ± 6)%, respectively, for these compounds. Formaldehyde will be subject to secondary oxidation with OH whereas CH3C(O)F reacts only very slowly with OH and loss via secondary react with OH should be negligible. Correction of the HC(O)H yield for secondary reaction with OH using the method outlined in Tuazon et al. yields a final value of (89 ± 7)% for the formaldehyde yield corrected. The mechanism presented in Fig. 1 (addition to C1 and/or C2) predicts equal yields of HCHO and CH3C(O)F within the experimental error limits.
If the OH addition is produced in the less substituted carbon (C1) of 2-fluoropropene, the hydroxialcoxy radical (CH3CF(O˙)CH2OH) formed could also eliminate a –CH3 group according to:
| CH3CF(O˙)CH2OH → CH3˙ + FC(O)CH2OH | (5) |
Unfortunately, this compound (FC(O)CH2OH) is not commercially available for comparative and quantification purposes. However, an infrared spectrum has been simulated for FC(O)CH2OH using density functional methods (DFT) and composite quantum chemistry models of the Gaussian 09 chemistry package. In particular, the M06 hybrid meta exchange–correlation DFT method was used. The spectrum was calculated using the M06/6-31G(d,p) level of theory. The simulated spectrum is presented in Fig. S8 of the ESI.†
Absorptions bands corresponding to FC(O)CH2OH were not observed in the residual product spectra concluding that the pathway of –CH3 elimination (reaction (5)) was not observed under our experimental conditions.
3,3,3-Trifluoro-2-(trifluoromethyl)propene + OH reaction
Fig. S3, panel A† shows a spectrum of a HXFP/H2O2/air reaction mixture after irradiation and subtraction of spectral features due to HXFP, while panels B and C show the reference spectra of hexafluoroacetone and formaldehyde, respectively.In the residual product spectrum (Fig. S3, panel D†) absorption bands can be seen in the regions (1065–1143) cm−1.
Concentration–time profiles of 3,3,3-trifluoro-2-(trifluoromethyl)propene, hexafluoroacetone and formaldehyde are shown in Fig. S4.† The concentration–time profiles of HXFP, CF3C(O)CF3 and HC(O)H show that are all primary in origin. The amounts of hexafluoroacetone and formaldehyde formed, plotted as a function of the amount of reacted HXFP, are shown in Fig. S5.† The plots are linear and give molar yields for hexafluoroacetone and formaldehyde of (91 ± 8)% and (94 ± 12)%, respectively. The corrected yield of formaldehyde using Tuazon22 method was (98 ± 12)%.
The formation of hexafluoroacetone and formaldehyde with yields near to 100% indicates that OH could be added indistinctly to C1 and/or C2 (see Fig. 2). However, according to the chemical structure of 3,3,3-trifluoro-2-(trifluoromethyl)propene, it is expected that the OH addition to carbon 2 could be less probable than to the OH addition to Cl due to a possible steric hindrance on carbon 2 in the (CF3)2C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH2. Consequently, it can be proposed that the addition reaction with the OH radical, takes place on carbon 1, which has less nucleophilic character, due to the presence of the H atoms as substituent.
CH2. Consequently, it can be proposed that the addition reaction with the OH radical, takes place on carbon 1, which has less nucleophilic character, due to the presence of the H atoms as substituent.
(E/Z)-isomeric mixture of 1,2,3,3,3-pentafluoropropene + OH reaction
The OH radical could be added to the C1 or C2 of the double bond (see Fig. 3) followed by the subsequent reactions with O2 and RO2 radicals. The hydroxyalkoxy radicals formed could decompose to give acetyl fluoride (CF3C(O)F) and formyl fluoride (HC(O)F) if the addition of OH occurs to C1 and/or C2.Fig. S6† shows an IR spectrum acquired after UV irradiation of a mixture of (E/Z)-isomeric 1,2,3,3,3-pentafluoropropene and H2O2 in air in the absence of NOx where the bands of HFP were subtracted (panel A). Panel B and C in Fig. S6† show reference spectra of CF3C(O)F and HC(O)F, respectively. Panel D represents the residual product spectrum obtained after subtraction of reactants and identified products from the spectrum in panel A. CF3C(O)F and HC(O)F were readily identifiable as reaction products. The presence of unidentified absorption bands was negligible in the residual product spectrum. The concentration–time profiles of CF3C(O)F and HC(O)F shows that they are both primary products (Fig. S7†).
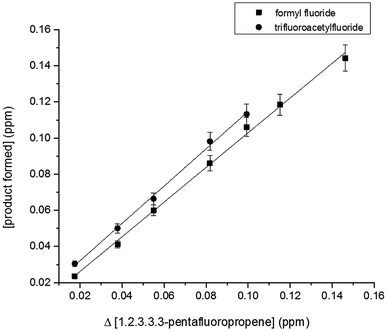
Least-squares analyses of plots of the concentrations of CF3C(O)F and HC(O)F as a function of the amount of reacted PFP (Fig. 5) give molar yields of (103 ± 8)% and (96 ± 7)%, respectively, for these compounds. The mechanism presented in Fig. 3 (addition to C1 and/or C2) predicts equal yields of HC(O)F and CF3C(O)F within the experimental error limits this is the case.
Hurley et al.,12 have studied the atmospheric chemistry of the Z and E isomers of CF3CF![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CHF initiated by OH radicals, Cl atoms and O3 molecules using a 140-L Pyrex reactor interfaced to a Mattson Sirius 100 FTIR spectrometer. They have reported yields of (94 ± 8)% for CF3C(O)F and (104 ± 9)% for HC(O)F in the OH initiated degradation of both isomers. Additionally, these authors determined molar yields of (98 ± 4)% for CF3C(O)F and (100 ± 5)% for HC(O)F for the Cl reactions with both CF3CF
CHF initiated by OH radicals, Cl atoms and O3 molecules using a 140-L Pyrex reactor interfaced to a Mattson Sirius 100 FTIR spectrometer. They have reported yields of (94 ± 8)% for CF3C(O)F and (104 ± 9)% for HC(O)F in the OH initiated degradation of both isomers. Additionally, these authors determined molar yields of (98 ± 4)% for CF3C(O)F and (100 ± 5)% for HC(O)F for the Cl reactions with both CF3CF![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CHF isomers. Our results are in excellent agreement with the values reported by Hurley et al.,12 indicating that the fate of CF3CF(OH)CO˙HF and CF3CO˙FCHF(OH) radicals formed is decomposition via C–C bond scission for both separate isomers and for the (E/Z) mixture of 1,2,3,3,3-pentafluoropropene.
CHF isomers. Our results are in excellent agreement with the values reported by Hurley et al.,12 indicating that the fate of CF3CF(OH)CO˙HF and CF3CO˙FCHF(OH) radicals formed is decomposition via C–C bond scission for both separate isomers and for the (E/Z) mixture of 1,2,3,3,3-pentafluoropropene.
To the best of our knowledge, this work represents the first product study of the reactions of OH radicals with 2-fluoropropene, (E/Z)-1,2,3,3,3-pentafluoropropene mixture and 3,3,3-trifluoro-2-(trifluoromethyl)propene. The reaction products obtained in this work, confirm that the reaction proceeds via an addition mechanism of the OH radical to the double bond similar to that proposed by Atkinson for the OH radical addition to alkenes.21,23
The hydroxyalkoxy radical formed in the OH addition step, decomposes in the presence of O2 and RO2 radicals, leading mainly to the corresponding halocarbonyl compound and HC(O)H or HC(O)F. Although the observed products do not indicate which is the main reaction pathway, we expected that the OH-addition to the less substituted carbon of the double bond (carbon 1) be the most likely.
The molar product yields obtained from linear least-squares analyses of the plots in Fig. 5, S2 and S5† are listed in Table 1. The errors given in Table 1 are the 2σ standard deviations from the analyses of the plots.
| Fluoroalkene | Product | Yielda (%) |
|---|---|---|
| a The errors quoted are 2σ statistical errors from the linear regression analysis.b Yield corrected for secondary reaction with OH radicals. | ||
CH3CF![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH2 CH2 |
HC(O)H | (89 ± 7)b |
| CH3C(O)F | (98 ± 5) | |
CF3(CF3)C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH2 CH2 |
HC(O)H | (98 ± 12)b |
| CF3C(O)CF3 | (91 ± 8) | |
(E/Z)-CF3CF![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CHF CHF |
CF3C(O)F | (103 ± 8) |
| HC(O)F | (96 ± 7) | |
Atmospheric implications
The persistence of fluoroalkenes in the atmosphere is relatively short, in the order of few days (dominated by OH radical chemistry).9 These short lifetimes indicate that the fluoro alkenes will be degraded near to their emission sources. Other processes, as photolysis, wet deposition and heterogeneous reactions are not expected to contribute significantly to the atmospheric removal of these compounds.7Among the products observed in the reactions studied, CF3C(O)F could be incorporate into rain-cloud-seawater, followed by hydrolysis to give trifluoroacetic acid (CF3C(O)OH, TFA) and acetic acid, respectively. TFA has been detected in surface of oceans, rivers and lakes and also in fog, snow and rainwater samples around the globe24,25 and it to be a ubiquitous persistent accumulating component of the hydrosphere.
Formyl fluoride (HC(O)F) and acetyl fluoride (CH3C(O)F) is believed to be removed of atmosphere by hydrolysis on contact with cloud-rain-seawater giving HF and HC(O)OH. Acetic and formic acid can contribute significantly to the acidity of precipitation and cloud water, especially in remote regions.26
On the other hand, hexafluoroacetone (CF3C(O)CF3) could photolyze or interact with water surfaces. Photolysis of hexafluoroacetone will generate CF3 radical and CO. The fate of CF3 radicals is the formation of CF2O, which is then hydrolyzed giving HF and CO2.27 Moreover, formaldehyde plays important roles in atmospheric photochemistry and air quality. It is a large component of the total Volatile Organic Compound (VOC) reactivity of the atmosphere, providing sources of new radicals that drive ozone formation.27 The major loss processes of HC(O)H are photolysis and reaction with the hydroxyl radical (OH). HC(O)H serves as an important primary source for the hydroperoxyl radical (HO2).
Since the degradation products can contribute to ozone and photooxidants formation in the troposphere to different degrees it is important to know the product branching in atmospheric conditions.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.Acknowledgements
María B. Blanco wishes to acknowledge the Alexander von Humboldt Foundation (AvH) and the authors wish to acknowledge Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG), DAAD-PROALAR (Germany), the EU project EUROCHAMP2 and EUROCHAMP 2020, SECYT (Argentina), CONICET (Argentina) for financial support of this research. C. B. R. wishes to acknowledge to CONICET for a doctoral fellowship and support.References
- A. R. Ravishankara, A. A. Turnipseed and N. R. Jensen, Hydrofluorocarbons Destroy Stratospheric Ozone?, Science, 1994, 263(5143), 71–75 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. J. Prather and J. Hsu, NF3, the greenhouse gas missing from Kyoto, Geophys. Res. Lett., 2008, 35(12), L12810 CrossRef.
- S. A. Montzka, M. McFarland, S. O. Andersen, B. R. Miller, D. W. Fahey, B. D. Hall, L. Hu, C. Siso and J. W. Elkins, Recent Trends in Global Emissions of Hydrochlorofluorocarbons and Hydrofluorocarbons: Reflecting on the 2007 Adjustments to the Montreal Protocol, J. Phys. Chem. A, 2015, 119(19), 4439–4449 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, U.S. EPA: Motor Vehicle Air Conditioners, http://opusinspection.com/documents/ Search PubMed.
- M. S. Reisch, New refrigerant takes heat, Chem. Eng. News, 2008, 86(46), 35–36 CrossRef.
- A. McIlroy and F. P. Tully, Kinetic study of hydroxyl reactions with perfluoropropene and perfluorobenzene, J. Phys. Chem., 1993, 97(3), 610–614 CrossRef CAS.
- V. L. Orkin, R. E. Huie and M. J. Kurylo, Rate constants for the reactions of OH with HFC-245cb (CH3CF2CF3) and some fluoroalkenes (CH2CHCF3, CH2CFCF3, CF2CFCF3, and CF2CF2), J. Phys. Chem. A, 1997, 101(48), 9118–9124 CrossRef CAS.
- G. Acerboni, J. A. Beukes, N. R. Jensen, J. Hjorth, G. Myhre, C. J. Nielsen and J. K. Sundet, Atmospheric degradation and global warming potentials of three perfluoroalkenes, Atmos. Environ., 2001, 35(24), 4113–4123 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Mashino, Y. Ninomiya, M. Kawasaki, T. J. Wallington and M. D. Hurley, Atmospheric chemistry of CF3CF=CF2: kinetics and mechanism of its reactions with OH radicals, Cl atoms, and ozone, J. Phys. Chem. A, 2000, 104(31), 7255–7260 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Steven and P. E. Brown, HFOs: new, low global warming potential refrigerants, ASHRAE J., 2009, 51(8), 22 Search PubMed.
- V. C. Papadimitriou, R. K. Talukdar, R. W. Portmann, R. Ravishankara and J. B. Burkholder, CF3CF=CH2 and (Z)-CF3CF=CHF: temperature dependent OH rate coefficients and global warming potentials, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2008, 10(6), 808–820 RSC.
- M. D. Hurley, J. C. Ball and T. J. Wallington, Atmospheric Chemistry of the Z and E Isomers of CF3CFCHF; Kinetics, Mechanisms, and Products of Gas-Phase Reactions with Cl Atoms, OH Radicals, and O3, J. Phys. Chem. A, 2007, 111(39), 9789–9795 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. M. Tovar, M. B. Blanco, I. Barnes, P. Wiesen and M. A. Teruel, Gas-phase reactivity study of a series of hydrofluoroolefins (HFOs) toward OH radicals and Cl atoms at atmospheric pressure and 298 K, Atmos. Environ., 2014, 88, 107–114 CrossRef CAS.
- V. C. Papadimitriou, Y. G. Lazarou, R. K. Talukdar and J. B. Burkholder, Atmospheric Chemistry of CF3CF=CH2 and (Z)-CF3CF=CHF: Cl and NO3 Rate Coefficients, Cl Reaction Product Yields, and Thermochemical Calculations, J. Phys. Chem. A, 2010, 115(2), 167–181 CrossRef PubMed.
- V. C. Papadimitriou, C. S. Spitieri and P. Papagiannakopoulos, Atmospheric chemistry of (CF3)2C=CH2: OH radicals, Cl atoms and O3 rate coefficients, oxidation end-products and IR spectra, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2015, 17(38), 25607–25620, 10.1039/c5cp03840e.
- J. B. Burkholder, R. A. Cox and A. R. Ravishankara, Atmospheric degradation of ozone depleting substances, their substitutes, and related species, Chem. Rev., 2015, 115(10), 3704–3759 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- I. Barnes, K. H. Becker and N. Mihalopoulos, An FTIR product study of the photooxidation of dimethyl disulfide, J. Atmos. Chem., 1994, 18(3), 267–289 CrossRef CAS.
- E. Gaona Colman, M. B. Blanco, I. Barnes, P. Wiesen and M. A. Teruel, Mechanism and Product Distribution of the O3-Initiated Degradation of (E)-2-Heptenal, (E)-2-Octenal, and (E)-2-Nonenal, J. Phys. Chem. A, 2017, 121, 5147–5155 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. B. Blanco, I. Bejan, I. Barnes, P. Wiesen and M. A. Teruel, OH-Initiated Degradation of Unsaturated Esters in the Atmosphere: Kinetics in the Temperature Range of 287 - 313 K, J. Phys. Chem. A, 2009, 113(20), 5958–5965 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. G. Calvert and G. Jack, The Mechanisms of Atmospheric Oxidation of the Alkenes, Oxford University Press, 2000 Search PubMed.
- R. Atkinson and J. Arey, Atmospheric degradation of volatile organic compounds, Chem. Rev., 200, 103(12), 4605–4638 CrossRef PubMed.
- E. C. Tuazon, H. MacLeod, R. Atkinson and W. P. L. Carter, Alpha-Dicarbonyl yields from the NOx-air photooxidations of a series of aromatic hydrocarbons in air, Environ. Sci. Technol., 1986, 20(4), 383–387 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. Atkinson, Gas-Phase Tropospheric Chemistry of Volatile Organic Compounds: 1. Alkanes and Alkenes, J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data, 2009, 26(2), 215–290 CrossRef.
- J. J. Orlando and G. S. Tyndall, The atmospheric oxidation of ethyl formate and ethyl acetate over a range of temperatures and oxygen partial pressures, Int. J. Chem. Kinet., 2010, 42(7), 397–413 CrossRef CAS.
- A. S. Pimentel, G. S. Tyndall and J. J. Orlando, Atmospheric chemistry of isopropyl formate and tert-butyl formate, Int. J. Chem. Kinet., 2010, 42(8), 479–498 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Wang, L. Du, J. Zhu, N. T. Tsona, S. Liu, Y. Wang, M. Ge and W. Wang, Gas-Phase Oxidation of Allyl Acetate by O3, OH, Cl and NO3: Reaction Kinetics and Mechanism, J. Phys. Chem. A, 2018, 122, 1600–1611 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. J. Wallington, W. F. Schneider, D. R. Worsnop, O. J. Nielsen, J. Sehested, W. J. Debruyn and J. A. Shorter, The Environmental Impact of CFC Replacements HFCs and HCFCs, Environ. Sci. Technol., 1994, 28(7), 320A–326A CAS.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available: IR spectra plots used in the identification of the products formed in the reaction of OH with: HXFP (Fig. S3) and PFP (Fig. S6). Concentration–time profiles for the reaction of OH with 2-FP, HXFP and PFP, Fig. S1, S4 and S7, respectively. Yield plots for the reaction of OH radicals with 2-FP (S2) and HXFP (S5) in the absence of NOx. See DOI: 10.1039/c8ra09627a |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2019 |