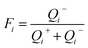Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleDynamic security assessment and the countermeasures analysis of land ecology in Henan province from 2007 to 2017
Yongbo
Su
 *
*
School of Civil Engineering and Architecture, Anyang Normal University, Anyang, Henan 455000, China. E-mail: suyongbo@haut.edu.cn
First published on 10th October 2019
Abstract
The accurate control of the degree of land development and the objective assessment of current land ecology are important issues that human beings must consider. Taking Henan province as the research area, this paper uses the Driver–Pressure–State–Impacts–Response (DPSIR) conceptual model to establish an assessment index system of land ecological security, and employs the Technique for Order Preference by Similarity to Ideal Solution (TOPSIS) assessment model to evaluate the land ecological security of Henan province from 2007 to 2017. The assessment results show that the land ecological security value of Henan province is generally continuously improving in 2007–2017 (from 0.5640 in 2007 to 0.6512 in 2017), but there were minor fluctuations in 2009, 2013 and 2016. In 2012, the land ecological security level starts to improve from a critically secure state to a secure state. Finally, according to the evaluation results and the actual situation of Henan province, specific countermeasures are put forward from the three main factors that cause the low value of land ecological security: state, response and pressure.
1 Introduction
As a scarce resource, land is the material basis for the sustainable development of economy and society. Land plays an important role in the process of human survival and development. However, the problem of unreasonable development of land resources occurs when people are pursuing economic development, further leading to increasingly prominent human-land conflicts, as well as serious ecological problems such as soil erosion and pollution in some areas. Once these problems get more serious to exceed the bearing capacity of land ecosystem, they will have an irreversible negative impact on the land ecology, and the maintenance of land ecology will become very difficult. This will further cause tremendous pressure on the sustainable development of society and ecological environment.1 The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) of the United Nations released the special report on climate change and land in Geneva on August 8, 2019, and it points out that climate change is threatening food security and aggravating desertification and land degradation. It is widely acknowledged that land is confronted with great pressure due to population growth and changing patterns of land use, which will exacerbate climate change, and thus the report appeals countries to use land in a sustainable way. As a matter of fact, accurate assessment of land ecology can help humans to take targeted measures to prevent and reduce land degradation, maintain the productivity of land, and sometimes even reverse the adverse impacts brought by climate change on land.Ecological security is a complex issue that involves many aspects. It can be understood in both a broad and narrow sense. The former is represented by the definition put forward by the international institute of applied systems analysis:2–4 Ecological security refers to a state in which necessary resources for human survival and development, social order and human adaptability to environmental changes are not threatened.4 It includes natural, economic and social aspects. In a narrow sense, ecological security refers to the security of natural and semi-natural ecosystems, i.e., the overall integrity and health of ecosystems.5,6 To maintain regional ecological security, the key is to strengthen the management of regional ecological environment. Ecological security assessment enables to determine the integrity and sustainability of ecosystems under various risks,7,8 and provide a basis for ecological regulation, management and decision-making,9,10 thus it is an important part of ecological security research. Based on the general land assessment, the land ecological security assessment selects several representative ecological characteristics for special assessment, and judges the state of land ecosystem and the ecological risk of land use, to make the lands meet the needs of national or regional sustainable survival and development,11 which is an important aspect of the research on land ecological security.
In recent years, with the increasing attention of the ecological environment, the regional land ecological security assessment has received extensive attention from both scholars and governments.12–14 Ecological security research started relatively late in China. In the late 1990s, some Chinese scholars began to pay attention to the issue of ecological security. Following the research abroad, the related research in China gradually developed from conceptual discussion and theoretical study in an early stage to the use of GIS models, mathematical statistics15,16 and evaluation models developed by international researchers17 to comprehensively evaluate the ecological security pattern,18 status,19 quality20 and ecological carrying capacity21 of multiple evaluation objects and typical regions. At the first meeting of the National Security Council of China, the issues of homeland security and ecological security have been included in the strategic scope of national security, and the issues have been defined in a new way. D. Makowski et al. used the European Community as the research object to construct an optimization model for agricultural land resource utilization.22 M. Hodson et al. discussed the issue of “ecological security” from the national perspective.23 Some researchers paid special attention to the selection of assessment models and the construction of assessment index systems.19,24,25 In terms of assessment models, quantitative mathematical models have been widely used in ecological security assessment, such as gray target model,26 entropy method,27 comprehensive assessment method,28 gray correlation analysis method,20 and matter element model,15etc. Some scholars also consider the relationship between ecosystem and socio-economic system through systematic decomposition, construct an appropriate evaluation index system and empower it. After evaluating the evaluation unit one by one, the evaluation unit is realized through spatial superposition, model calculation and other steps.29–34 In terms of the construction of assessment index system, the researchers mainly construct the models from the perspectives of natural–socio–economic–environment system and the Pressure–State–Response (PSR) model.1,14,25 On this basis, in order to more accurately describe the relationship between the various elements of the system, the European Environment Agency proposed the Driver–Pressure–State–Impacts–Response (DPSIR) model in 1998. The DPSIR model has shown great advantages in assessing the environment and sustainable development. For example, many scholars have employed the DPSIR model to assess the sustainable use of land resources in China, as well as the assessment of planning environmental impact,17,35–40etc. The DPSIR model covers a wide range of fields, including environmental protection, resource utilization and social development. Inspired by the DPSIR model, we can integrate land use, social development, environmental issues and government policies to build an ecological security assessment index system. The indexes have certain independence with each other and can also reflect the regional land ecological security in a more comprehensive way. The TOPSIS method is a simple and effective method to solve multi-attribute decision problems. Its goal is to select an optimal solution that is closest to the positive ideal solution and farthest from the negative ideal solution.41 Also, the model calculates the distance between the data in each evaluation unit and the positive ideal solution and the negative ideal solution as well as the proximity to the “positive ideal solution”, and then assesses and ranks each unit.
Based on expert evaluation and the relevant literatures42–45 and the basic situation of Henan province, this paper constructs the assessment index system of land ecological security in Henan province by DPSIR model. This paper then conducts a dynamic evaluation on the land ecological security in Henan province from 2007 to 2017 through statistical bulletins and related materials using the TOPSIS method. Henan is a large agricultural province with underdeveloped economy. It has ecological and environmental problems like many other Chinese provinces.46,47 The research results are expected to provide evidence for relevant decision makers.
2. Overview of the research area
Henan province is located in the central and eastern part of China, the middle and lower reaches of the Yellow River, with north latitude of 31°23′–36°22′, and east longitude of 110°21′–116°39'. Henan is located in the West of Anhui and Shandong, and in the South of Hebei and Shanxi. Henan has 17 provincially-administered municipalities, and 1 county-level city, Jiyuan, directly under the administration of the provincial government. According to the statistics, the GDP of Henan province achieved a continuous 10 year increase in 2007–2017, from 15![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 012 billion RMB in 2007 to 444.553 billion RMB in 2017, but the province's GDP growth rate has slowed down from 14.6% in 2007 to 9.2% in 2017. Henan is a province not only produces great amount of grain but also has a large population. With the progress of society and the rapid development of the economy, the contradiction between people and land has become increasingly prominent, and the per capita cultivated land is gradually decreasing. Also, due to predatory agricultural production represented by excessive fertilization and pesticide abuse, the land environmental quality has been declining for years, soil erosion is getting more serious, and the land reserve is poor, which brings great challenges to the sustainable development and utilization of land in the later stage. However, people's demand for land is increasing, which further highlights the contradiction between land supply and demand. Therefore, accurately assessing the state and dynamic changes of land ecological security in Henan province and adopting effective measures for intervention and governance have far-reaching significance for ensuring the sustainable use of land resources and the overall development of economy and society.
012 billion RMB in 2007 to 444.553 billion RMB in 2017, but the province's GDP growth rate has slowed down from 14.6% in 2007 to 9.2% in 2017. Henan is a province not only produces great amount of grain but also has a large population. With the progress of society and the rapid development of the economy, the contradiction between people and land has become increasingly prominent, and the per capita cultivated land is gradually decreasing. Also, due to predatory agricultural production represented by excessive fertilization and pesticide abuse, the land environmental quality has been declining for years, soil erosion is getting more serious, and the land reserve is poor, which brings great challenges to the sustainable development and utilization of land in the later stage. However, people's demand for land is increasing, which further highlights the contradiction between land supply and demand. Therefore, accurately assessing the state and dynamic changes of land ecological security in Henan province and adopting effective measures for intervention and governance have far-reaching significance for ensuring the sustainable use of land resources and the overall development of economy and society.
3. Assessment methods
3.1 Establishment of land ecological security assessment index system
When carrying out economic activities, human beings exert “pressure” on natural resources and environment, which forces natural resources and environment to change the original “state”. Therefore, the overall ecological balance has been destroyed to a certain extent, causing some impacts on the eco-system. As a result, human society must launch corresponding economic and environmental policies to intervene the activities, that is, “response”, in order to alleviate environmental pressure, maintain the sustainability of the entire system, and achieve the harmonious development of economy, society and environment. For land ecological security assessment, it involves various fields. Due to the natural and socio-economic driving forces, fierce competition occurs between the use of land resources and the protection of the ecological environment. Especially in the less developed regions of China, some cities extremely pursue economic development, and ignore environmental pressures, which have caused serious environmental problems, some of which are even irreversible. Under this circumstance, the land ecosystem shows a state which is the result of the combination of driving force and pressure. Such state can be characterized by representative indexes, such as the proportion of cultivated land area and forest coverage. In order to make the land ecosystem more complete and secure for human use, people must take corresponding interventions, that is, the “response” of human society. Based on the basic idea of DPSIR model and the existing research results, this paper follows the principle of comparability, comprehensiveness and non-compliance,48 and takes into account the basic situation of Henan province, the operability of the method and the availability of data. Based on the statistical analysis of the existing indexes, this paper uses the frequency analysis method to screen out the indexes with higher frequency of use, and then uses the Delphi method to consult experts in related fields. After three rounds of repeated consultation and indexes modification, this paper obtains the final land ecological security assessment index system (Table 1).| Objective layer | Index layer | Criterion layer | Index property | Weight factors W1 | Weight factors W2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Land ecological security assessment (A) | Driving force (B1) | Natural population growth rate (B11) | − | 0.0462 | 0.0381 |
| GDP increase rate (B12) | + | 0.0481 | 0.0471 | ||
| Effective irrigation area (B13) | + | 0.0589 | 0.0532 | ||
| Unemployment rate (B14) | − | 0.0625 | 0.0655 | ||
| Pressure (B2) | Population density (B21) | − | 0.054 | 0.0610 | |
| Energy consumption per 10 thousand GDP (B22) | − | 0.0319 | 0.0311 | ||
| Sulfur dioxide emission (B23) | − | 0.0425 | 0.0435 | ||
| Industrial waste water discharge (B24) | − | 0.0243 | 0.0243 | ||
| State (B3) | Proportion of cultivated land area (B31) | − | 0.1467 | 0.1467 | |
| Agricultural mechanization level (B32) | + | 0.0522 | 0.0522 | ||
| Forest coverage rate (B33) | + | 0.0765 | 0.0765 | ||
| Per capita GDP (B34) | + | 0.0371 | 0.0289 | ||
| Impact (B4) | Grain yield (B41) | + | 0.0388 | 0.0375 | |
| Economic density (B42) | + | 0.0359 | 0.0359 | ||
| Proportion of tertiary industry (B43) | + | 0.0436 | 0.0415 | ||
| Per capita net income in rural area (B44) | + | 0.0331 | 0.0331 | ||
| Response (B5) | Fixed investment growth rate (B51) | + | 0.0427 | 0.0509 | |
| Park green area (B52) | + | 0.0420 | 0.0419 | ||
| Comprehensive utilization amount of industrial solid waste (B53) | + | 0.0198 | 0.0198 | ||
| Yearly afforestation area (B54) | + | 0.0632 | 0.0713 |
3.2 Determination of the weight of indexes
The indexes of land ecological security assessment are classified and the weights are determined by analytic hierarchy process to make the assessment results more scientific and reasonable. In order to ensure the objectivity of the experts, the Delphi method is used for assessment, and ten relevant experts with rich knowledge and experience from universities, government agencies and industries are invited to score the indexes, where judgment matrix is constructed to judge and modify the indexes. Finally, the weight of each index is obtained (weight factors W1 in Table 1). Considering that the land ecological security involves a wide range of fields and there is no comparability between the indexes, it is necessary to eliminate the dimensional influence through mathematical transformation. This paper uses the following methods49 for standardization:For positive indexes:
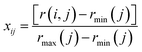 | (1) |
For negative indexes:
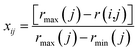 | (2) |
3.3 Assessment method
The TOPSIS method is used to establish a comprehensive assessment model. The specific steps are as follows:(1) Consider the weights of the assessment indexes and establish a weighted normalized matrix U:U = |uij|mn = WjXij where Wi is the index weight; Xij is the standardized matrix.
(2) Find positive ideal solutions and negative ideal solutions. Positive ideal solution: U+j = {maxuij}, (i = 1, 2, …, m), negative ideal solution: U−j = {minuij}, (i = 1, 2, …, m).
(3) Calculate the distance Q+ between the assessment object and the positive ideal solution, and the distance Q− between the assessment object and the negative ideal solution, in 2007–2017 of Henan province, where: 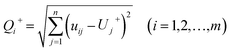 ,
, 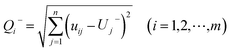
(4) Find the proximity Fi of each assessment object and the ideal solution:
| Assessed value | Level | Assessment results | Features | Countermeasures |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| a Remark: compared with other land ecological security evaluation method, such as gray target model,26 entropy method,27 comprehensive assessment method,28 gray correlation analysis method,20 and matter element model,15etc., the TOPSIS method can make full use of the original data. However, it should be pointed out that, this method can only reflect the proximity within the evaluation objects instead of that to the ideal optimal scheme. Especially, when the value of each index of the evaluation object is relatively close, which is scare for large sample, overestimate or underestimate may happen. | ||||
| <0.2 | I | Very unsafe | The ecological environment of the land is seriously damaged, the ecological process is difficult to reverse, the ecological problems are very serious and often evolve into ecological environmental disasters. | Extreme need to be strengthened |
| 0.2–0.4 | II | Unsafe | The ecological environment of the land is greatly damaged, the ecological environment is relatively more serious, and it is prone to ecological and environmental disasters; once the ecological environment is disturbed, it will be difficult to recover. | Special need to be strengthened |
| 0.4–0.6 | III | Critical safety | The structure of the land ecosystem has been damaged to a certain extent, but its basic functions can still exist; ecological problems are relatively more prominent, ecological and environmental disasters occur occasionally, and it is easy to deteriorate after being disturbed. | To be strengthened |
| 0.6–0.8 | IV | Safer | The structure of the land ecosystem is slightly damaged and can operate normally; the land ecosystem can usually recover itself after being disturbed by the outside world; the ecological environment disaster is not prominent. | Appropriate need to be strengthened |
| >0.8 | V | Ideal security | Generally, the structure of the land ecosystem has not been destroyed, the overall operation is good, and its self-recovery ability is strong. | Maintained |
4 Assessment results and analysis
4.1 Data source and assessment results
Land ecosystem is a natural–economic–social complex ecosystem, involving natural, economic and social aspects. Therefore, according to the characteristics, economic conditions and development goals of land ecological security in Henan province, this paper consults relevant industry experts to determine the more important evaluation factors and the types of indicators they belong to.The economic and social statistics of Henan in 2007–2017 are obtained from Henan Statistical Yearbook, Environmental State Bulletin of Henan province, and Statistical Bulletin on National Economic and Social Development, etc., as shown in Table 3. The standardized data are shown in Table 4. The method mentioned in the previous section is used to construct the TOPSIS model, and the positive ideal solution Q+, negative ideal solution Q− and comprehensive proximity Fi of Henan province from 2007 to 2017 are obtained (Table 5).
| Index | Year | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | |
| Natural population growth rate (%) | 4.9 | 4.97 | 4.99 | 4.95 | 4.94 | 5.16 | 5.51 | 5.78 | 5.65 | 6.15 | 5.98 |
| GDP increase rate (%) | 14.6 | 12.1 | 10.9 | 12.5 | 11.9 | 10.1 | 9 | 8.9 | 8.3 | 8.1 | 7.8 |
| Effective irrigation area (103 hm2) | 4955.84 | 4989.2 | 5033.03 | 5080.96 | 5150.44 | 5205.63 | 4969.11 | 5101.74 | 5333.9 | 5360.28 | 5389.79 |
| Unemployment rate (%) | 3.41 | 3.4 | 3.5 | 3.38 | 3.35 | 3.08 | 3.09 | 2.97 | 2.96 | 3 | 2.76 |
| Population density (persons per km2) | 560.48 | 564.61 | 568.08 | 563.2 | 562.2 | 563.2 | 563.7 | 565 | 567.7 | 570.8 | 572.4 |
| Energy consumption per 10 thousand GDP (tons of standard coal/10 thousand GDP) | 1.285 | 1.219 | 1.156 | 0.81 | 0.79 | 0.73 | 0.71 | 0.68 | 0.63 | 0.6 | 0.55 |
| Sulfur dioxide emission (t) | 156.39 | 145.2 | 135.5 | 133.87 | 137.05 | 127.59 | 125.4 | 119.82 | 114.43 | 41.36 | 28.63 |
| Industrial waste water discharge (10 thousand t) | 29.64 | 30.91 | 33.4 | 35.87 | 37.9 | 40.37 | 41.26 | 42.28 | 43.35 | 40.21 | 40.91 |
| Proportion of cultivated land area (%) | 43.13 | 49.05 | 48.97 | 48.97 | 48.87 | 48.84 | 48.75 | 48.66 | 48.54 | 48.57 | 48.58 |
| Agricultural mechanization level (kW hm−2) | 8718.7 | 9429.3 | 9817.9 | 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 195.94 195.94 |
10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 515.8 515.8 |
10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 872.7 872.7 |
11![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 150 150 |
11![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 476.8 476.8 |
11![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 710.08 710.08 |
9858.82 | 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 038.3 038.3 |
| Forest coverage rate (%) | 22.64 | 22.64 | 20.16 | 22.19 | 22.68 | 22.98 | 23.3 | 23.3 | 23.62 | 24.12 | 24.53 |
| Per capita GDP (RMB) | 16![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 012 012 |
19![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 181 181 |
20![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 597 597 |
24![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 446 446 |
28![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 661 661 |
31![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 499 499 |
34![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 211.5 211.5 |
37![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 071.7 071.7 |
39![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 222.39 222.39 |
42![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 575 575 |
47![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 130 130 |
| Grain yield (10 thousand tons) | 5245.22 | 5365.48 | 5389 | 5437.1 | 5542.5 | 5638.6 | 5713.69 | 5772.3 | 6067.1 | 5946.6 | 5973.4 |
| Economic density (10 thousand RMB per km) | 898.92 | 1078.98 | 1166.47 | 1382.75 | 1612.63 | 1772.40 | 1927.60 | 2092.10 | 2215.69 | 2423.47 | 2693.89 |
| Proportion of tertiary industry (%) | 29.3 | 28.6 | 29.1 | 28.1 | 28.8 | 33.7 | 35.5 | 36.9 | 39.5 | 41.8 | 42.7 |
| Per capita net income in rural area (RMB) | 3851.6 | 4454.24 | 4806.95 | 5523.73 | 6604.03 | 7524.94 | 8475.34 | 9416.1 | 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 852.86 852.86 |
11![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 696.74 696.74 |
12![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 719.18 719.18 |
| Fixed investment growth rate (%) | 35.6 | 30.7 | 30.6 | 22.2 | 27 | 21.4 | 22.5 | 19.2 | 16.5 | 13.7 | 10.4 |
| Park green area (hm2) | 8.93 | 8.96 | 8.98 | 9 | 9.2 | 9.2 | 9.3 | 9.93 | 9.2 | 10.4 | 12 |
| Comprehensive utilization amount of industrial solid waste (10 thousand tons) | 6048.43 | 7123.8 | 8064.29 | 8380.44 | 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 901.95 901.95 |
11![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 597.47 597.47 |
12![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 465.81 465.81 |
12![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 300 300 |
11![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 456.11 456.11 |
10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 485.55 485.55 |
11![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 537.22 537.22 |
| Yearly afforestation area (hm2) | 41.39 | 40.09 | 41.99 | 27.71 | 27.87 | 22.83 | 26 | 26 | 20 | 14.9 | 18.09 |
| Index | Year | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | |
| Natural population growth rate (%) | 1.0000 | 0.9440 | 0.9280 | 0.9600 | 0.9680 | 0.7920 | 0.5120 | 0.2960 | 0.4000 | 0.0000 | 0.1360 |
| GDP increase rate (%) | 1.0000 | 0.6324 | 0.4559 | 0.6912 | 0.6029 | 0.3382 | 0.1765 | 0.1618 | 0.0735 | 0.0441 | 0.0000 |
| Effective irrigation area (103 hm2) | 0.0000 | 0.0769 | 0.1779 | 0.2883 | 0.4484 | 0.5756 | 0.0306 | 0.3362 | 0.8712 | 0.9320 | 1.0000 |
| Unemployment rate (%) | 0.1216 | 0.1351 | 0.0000 | 0.1622 | 0.2027 | 0.5676 | 0.5541 | 0.7162 | 0.7297 | 0.6757 | 1.0000 |
| Population density (persons per km2) | 1.0000 | 0.3465 | 0.6376 | 0.2282 | 0.1443 | 0.2282 | 0.2701 | 0.3792 | 0.6057 | 0.8658 | 1.0000 |
| Energy consumption per 10 thousand GDP (tons of standard coal/10 thousand GDP) | 0.0000 | 0.9102 | 0.8245 | 0.3537 | 0.3265 | 0.2449 | 0.2177 | 0.1769 | 0.1088 | 0.0680 | 0.0000 |
| Sulfur dioxide emission (t) | 0.0000 | 0.9124 | 0.8365 | 0.8237 | 0.8486 | 0.7746 | 0.7574 | 0.7138 | 0.6716 | 0.0996 | 0.0000 |
| Industrial waste water discharge (10 thousand t) | 1.0000 | 0.0926 | 0.2743 | 0.4544 | 0.6025 | 0.7826 | 0.8476 | 0.9220 | 1.0000 | 0.7710 | 0.8220 |
| Proportion of cultivated land area (%) | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 0.9854 | 0.9854 | 0.9696 | 0.9644 | 0.9482 | 0.9334 | 0.9130 | 0.9182 | 0.9195 |
| Agricultural mechanization level (kW hm−2) | 0.0000 | 0.2375 | 0.3675 | 0.4938 | 0.6008 | 0.7201 | 0.8128 | 0.9220 | 1.0000 | 0.3811 | 0.4411 |
| Forest coverage rate (%) | 0.5675 | 0.5675 | 0.0000 | 0.4645 | 0.5767 | 0.6453 | 0.7185 | 0.7185 | 0.7918 | 0.9062 | 1.0000 |
| Per capita GDP (RMB) | 0.0000 | 0.1018 | 0.1473 | 0.2710 | 0.4065 | 0.4977 | 0.5849 | 0.6768 | 0.7459 | 0.8536 | 1.0000 |
| Grain yield (10 thousand tons) | 0.0000 | 0.1463 | 0.1749 | 0.2335 | 0.3617 | 0.4786 | 0.5700 | 0.6413 | 1.0000 | 0.8534 | 0.8860 |
| Economic density (10 thousand RMB per km) | 0.0000 | 0.1003 | 0.1491 | 0.2695 | 0.3976 | 0.4866 | 0.5731 | 0.6647 | 0.7336 | 0.8493 | 1.0000 |
| Proportion of tertiary industry (%) | 0.0822 | 0.0342 | 0.0685 | 0.0000 | 0.0479 | 0.3836 | 0.5068 | 0.6027 | 0.7808 | 0.9384 | 1.0000 |
| Per capita net income in rural area (RMB) | 0.0000 | 0.0680 | 0.1077 | 0.1886 | 0.3104 | 0.4142 | 0.5214 | 0.6275 | 0.7895 | 0.8847 | 1.0000 |
| Fixed investment growth rate (%) | 1.0000 | 0.8056 | 0.8016 | 0.4683 | 0.6587 | 0.4365 | 0.4802 | 0.3492 | 0.2421 | 0.1310 | 0.0000 |
| Park green area (hm2) | 0.0000 | 0.0098 | 0.0163 | 0.0228 | 0.0879 | 0.0879 | 0.1205 | 0.3257 | 0.0879 | 0.4788 | 1.0000 |
| Comprehensive utilization amount of industrial solid waste (10 thousand tons) | 0.0000 | 0.1676 | 0.3141 | 0.3634 | 0.7563 | 0.8647 | 1.0000 | 0.9742 | 0.8427 | 0.6914 | 0.8553 |
| Yearly afforestation area (hm2) | 0.9779 | 0.9299 | 1.0000 | 0.4729 | 0.4788 | 0.2927 | 0.4097 | 0.4097 | 0.1883 | 0.0000 | 0.1178 |
| Item | Year | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | |
| Q − | 0.1925 | 0.1841 | 0.1795 | 0.1720 | 0.1767 | 0.1789 | 0.1772 | 0.1817 | 0.1930 | 0.1921 | 0.2104 |
| Q + | 0.1488 | 0.1367 | 0.1487 | 0.1338 | 0.1214 | 0.1101 | 0.1172 | 0.1047 | 0.1022 | 0.1198 | 0.1127 |
| F 1 | 0.5640 | 0.5738 | 0.5469 | 0.5625 | 0.5928 | 0.6190 | 0.6019 | 0.6343 | 0.6537 | 0.6159 | 0.6512 |
| F 2 | 0.5762 | 0.5809 | 0.5550 | 0.5588 | 0.5871 | 0.6092 | 0.6017 | 0.6324 | 0.6429 | 0.6069 | 0.6415 |
| Security level | III | III | III | III | III | IV | IV | IV | IV | IV | IV |
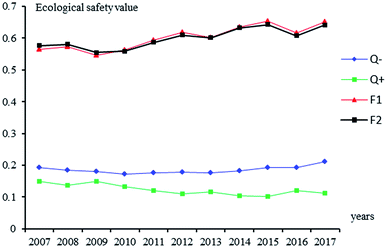
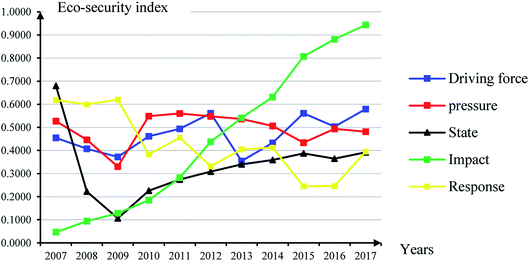
It can be seen from Table 5 and Fig. 1 that the land ecological security state of Henan province in 2007–2017 is generally continuously improving, and the value of land ecological security has increased from 0.5640 to 0.6512, but there are minor fluctuations in the year of 2009, 2013, and 2016. Since 2007, Q+ has shown a gradual decline trend, and it is close to the positive ideal solution. There are small repeated fluctuations in 2009, 2013 and 2016. Q− has been increasing year by year since 2010, deviating from the negative ideal solution. In the past eleven years, the value of land ecological security in Henan province (proximity) has generally increased after experiencing a small trough in 2009, reaching 0.6537 in 2015. Although there is a small fluctuation in 2016, the value still can reach 0.6159 in this year. In 2007, the risk level of the land ecological security state begins to increase steadily along with small fluctuations. Since 2012, the risk level has been improved to level IV, which is a relatively secure state. Overall, in the past eleven years, the unsecure state of land ecology of Henan province can be divided into two stages, i.e. the critically secure state in 2007–2011 and the secure state in 2012–2017. The land ecological security situation in Henan province is closely related to the excessive pursuit of social and economic development benefits while neglecting the ecological benefits (Fig. 2 shows that “impact” shows a steady growth trend, while “pressure” and “state” are at a low level.). In many areas of the province, the functions of land ecosystem gradually degenerate, especially in undeveloped areas where the land ecological environment is seriously damaged and the resulting ecological and environmental disasters have also increased significantly. Since 2009, with the increasing awareness of the public and the special attention from the governments at all levels, the land security situation in Henan Province has improved year by year, especially since 2012, when the land ecological security situation has been improved from level III to level IV and land ecological problems have been greatly alleviated. However, on the whole, the land ecological security situation is still very serious. Although the land ecological security situation has been continuously improved, the annual improvement is small, and the security level is still at the lower limit of the secure state. It is still possible to encounter the threats such as water and soil loss, land resource degradation, and industrial pollution, etc. in the future. Therefore, it is necessary to continue to pay much attention to the protection of land resources, increase the corresponding capital investment, and take the protection of land resources as one of the important tasks of economic development. From the assessment results of various subsystems in Henan province from 2007 to 2017 (Fig. 2), the “impact” has shown a steady growth trend, which is reflected in the continuous improvement of grain yield, economic density, the proportion of tertiary industry and the per capita net income in rural areas; the “driver” and “pressure” are fluctuating, mainly reflected in the continuous reduction of sulfur dioxide emissions, but the industrial wastewater discharge is still growing at a certain speed, and other indexes are controlled to varying degrees; although the “response” and “state” also present the fluctuations, their overall security values are low. Especially since 2014, both of them have fallen below 0.4, indicating that Henan province is still at a lower level in terms of agricultural mechanization level, afforestation, and industrial solid waste utilization, which requires more investment and control in these areas.
In order to further validate the assessment results, the weighting factors in W1 are replaced by W2 (Table 1). Correspondingly, the evaluation values of each index are given by Table 5. Comparing these two cases, i.e., the weighting factors in W1 and W2, the evaluation values are slightly altered, but can still reflect the land ecological security in Henan province.
4.2 Regional assessment of land ecological security in Henan Province
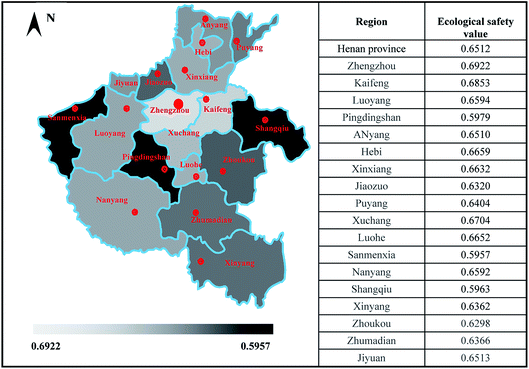
From the topography, the terrain in Henan is generally high in the West and low in the East. The North, West and South of Henan are surrounded by mountains. The middle, East and North are the North China Plain, the West is the mountains, the Southwest is the Nanyang Basin, and the Southeast is the Dabie Mountains. Therefore, the land resources in each region vary greatly. When people use land resources, they exert different degrees of disturbance to their ecological environment. From the perspective of space, the land ecological security state in Henan province also has varies greatly. In this paper, the 18 cities in Henan province are used as assessment units. By the above-mentioned assessment methods, this paper analyzes the data of each index in each assessment unit in 2017, and quantitative calculation and assessment are carried out to obtain the proximity of the land ecological security of each assessment unit in 2017 (Fig. 3). It can be seen from the Fig. 3 that in 2017, except that the ecological securities of Sanmenxia, Shangqiu and Pingdingshan are in a critically secure state, other regions are all in a relatively secure state. Specifically, the proximity of the land ecological security of Zhengzhou, Kaifeng and Xuchang is higher than 0.67, which is close to the middle area of the secure state. The proximity of other cities is basically between 0.6 and 0.65, which is in the lower limit area of the secure state. This is mainly because since Zhengzhou has been recognized as a national regional central city, it pays special attention to high-quality development, promotes green and healthy economic growth, and shifts to the mode of low input, low consumption, low emission and high efficiency. So, the land ecological security level of Zhengzhou city is increased year by year to 0.6922, far above the provincial average. By contrast, affected by the factors such as location and topography, Sanmenxia is in a relatively low state of economic and social development, which directly affects the intensity of ecological governance and the investment of infrastructures, resulting in poor urban land ecological security (the assessed value of land ecological security is only 0.5957). As a traditional agricultural area located in the eastern part of Henan province, Shangqiu is in a relatively slow state of urbanization and industrialization. The per capita GDP and per capita disposable income of Shangqiu are lower than those of other cities in Henan province, which directly affects the results of land ecological security assessment and lowers the level of land ecological security (the assessed value of land ecological security is only 0.5963).4.3 Regional measures for land ecological security in Henan province
Tilting slightly from the Northwest to the Southeast, Shangqiu city is located on the alluvial plain of Yellow River, with a flat terrain. In 2017, security of land ecology in this area was still in a critical state (Table 2 and Fig. 3). The main reason is that the economic development of this region is relatively slow, and the land use is extensive in addition to the prominent contradiction between the protection of resources and the guarantee of development. So the requirements of the comprehensive, coordinated and sustainable development should be based on so as to reasonably arrange land for non-agricultural construction and protection of ecological environment, mainly guarantee the infrastructure such as energy, traffic, and water conservancy in city centre, area of industrial concentration, and key towns, as well as land for the development of strategic support industry, safeguard the land of people's livelihood for low-rent housing, and promote the harmony between economic development and population, resources and environment.
As an important coal and chemical base in China, Pingdingshan, as the transitional area which spans two climatic regions of subtropical zone and warm temperate zone, is located in the compact layer of city group in the central plain. With the exploitation of mineral resources, a large number of toxic or harmful pollutants would result in the change of surface structure, and pollution of the surrounding soil, water and atmosphere, through the surface water runoff and atmospheric dust, which would consequently destroy the original environmental system. Therefore, the government should introduce corresponding policies to strengthen the management of land, such as formulating scientific standards for land use, standardizing the examination and approval system of land, carrying out necessary ecological restoration, etc. At the same time, it should also attach importance to the management of agricultural land, optimizing the use of land, and improving the utilization rate of land.
5 Countermeasures analysis of land ecological security in Henan province
5.1 The relationship between environment and human beings
We human beings have already utilized most of the land resources on the earth, directly affecting more than 70 percent of the ice-free surface in the world. Ever since industrialization, the land surface temperature on the earth has risen by almost twice as much as that of the global average, and the ability of soil to sequester carbon is decreasing along with the increase of temperature. According to the special report issued by IPCC on land use, greenhouse gas emissions from agriculture, forestry and other land use methods account for 23 percent of the total amount, and the natural absorption of carbon dioxide by land is about one third of the amount of carbon dioxide emitted by the burning of fossil fuels and industry. Due to the reduction of vegetation and organic matter in soil, the land that suffers from desertification and degradation would decrease in the capacity to store carbon. Along with the increasing trend of carbon emissions, the carbon budget would be affected, which would exacerbate climate change. In terms of the world, each country and area, the area of the land is relatively fixed, and if large areas of land are unable to be used for farming and grazing due to desertification and land degradation, then it would inevitably result in the consequence that the rest of the available farmland and pasture would be under more pressure, which would affect food security and lead to the consequence that food production is difficult to meet the needs of the ever-increasing population. Therefore, it is necessary for us to strengthen land management, take the road of sustainable land management, prevent and decrease land degradation, maintain land productivity and improve ecological environment of land.5.2 Countermeasures
Ecological civilization is actually regarded as the symbol of the harmonious relationship between human and nature,51–53 and the construction of ecological civilization refers to the reflection and regulation over the disharmony between human and nature. While seeking for rapid economic development, different cities in Henan province should attach importance to protecting the ecological environment of land, deal with the relationship between economic and social development and land ecological protection, strengthen the degree of supervision over ecological security of land, and construct ecological civilization of land. According to the results obtained from analysis (Fig. 2), the main influencing factors for the low value shown in ecological security of land are “state”, “response” and “pressure” in recent years. Therefore, relevant measures should be taken to improve the value of ecological security in these three aspects on the basis of the actual situation in Henan province.(1) Improving the value of “status” should start from increasing the proportion of cultivated land area and improving the coverage rate of forest (Table 1). Specifically speaking, it is necessary to further strengthen the protection of cultivated land, improve the requisition-compensation balance, and maintain appropriate usage of ecological land. The protection of cultivated land has close relationship with the food security, ecological security and social stability of a country. Henan province has a large population and thus the demand for grain and other agricultural products, as well as the improvement of people's living standards, will be greater and greater with the increase of population year by year. However, the potential for the production of land is limited, and it is necessary to maintain a steady and slight increase in the area of cultivated land for the purpose of ensuring the steady supply of grain and agricultural products. Therefore, we are required to strengthen the protection of cultivated land, especially basic farmland, and at the same time, it is quite necessary for us to protect the existing forest land and grassland. According to the planning of soil and water conservation, the measures adopted for close cultivation of rangeland and natural restoration should be applied in accordance with the actual situation in different areas, so as to enlarge the coverage of grassland area, conserve water, prevent and reduce water loss and soil erosion, and strictly protect plants, condensation structure of sand lichen, etc. In addition, tree cutting shall be conducted in a reasonable way, and clear cutting should be strictly controlled. At the same time, government departments should strengthen the efforts paid for research and development, so as to improve the level of agricultural mechanization, and promote farmers to increase economic returns, thus increasing per capita GDP.
(2) Improving the value of “response” should start mainly from the aspects of increasing the green area of parks, improving the comprehensive utilization amount of industrial solid waste, and accelerating the area of afforestation (Table 1). Firstly, go on to promote the greening construction in county and town, expand the scale of green space in urban area, and improve the quality of greening as well. Each city should treat the green space in park as the focus, the green space in the street as the ornament, the greening on road, the green belt and the green landscape belt along the river as the network, and the square as the highlight, so as to create the greening system in city, and increase the green area in park. Secondly, industrial development funds at provincial level should be used as a whole so as to encourage enterprises to carry out the cycling production, guide the industrial enterprises to conduct the work of comprehensive resource utilization, implement tax preferential policies for the comprehensive utilization of resources, promote to form a cross-area alliance of industrial solid waste industry for the whole industry chain, explore the PPP mode for the comprehensive utilization of industrial solid waste recycling, explore to build the extended system of producer responsibility, strengthen supervision and management, and strictly perform standards for admittance into the industry. Thirdly, protect and nurture the forest ecosystem, stop commercial logging of natural forests, continue to implement the project of natural forest protection, consolidate achievements attained in converting farmland into forests, and carry out large-scale actions of afforestation. Accelerate afforestation in areas unsuitable for cultivation, close off mountains to foster forests, and restore vegetation in ecologically fragile areas, so as to expand the area of forests. Moreover, artificially foster forests at the initial stage, transform forests with low yield and low efficiency, and cultivate multi-layer, mixed and different-age forests to improve the quality of forest.
(3) Increase the value of “pressure”. It should mainly start from three aspects: decreasing energy consumption per ten thousand Yuan of GDP, reducing emissions of sulfur dioxide and the emissions industrial wastewater. Firstly, carry out the work related to energy conservation, consumption decreasing, emission reduction and efficiency enhancement for enterprises through technological innovation, project driving, construction of scientific research institutions and other measures. Secondly, in terms of reducing sulfur dioxide emissions, use the technology of desulfurization from raw coal, remove about 40–60% of inorganic sulfur in coal, and give priority to the use of low sulfur fuels, such as low sulfur coal and natural gas; improve the technology of coal burning so as to reduce the emissions of sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxide from coal burning. For example, the technology of liquid coal burning should be adopted so that limestone and dolomite added can react with sulfur dioxide, and generate calcium sulfate which can be discharged with ash residue. Thus, the flue gas formed after coal combustion is desulfurized before being discharged into the atmosphere. The lime-base process can be used to remove 85–90% of sulfur dioxide gas in the flue gas. When it comes to the development of new energy sources, such as solar energy, wind energy, nuclear energy, and combustible ice, etc., it will cause new pollution, and the consumption cost is very high if it is used because the technology is not mature enough currently. Thirdly, reduce and eliminate the amount of waste water discharged from the sources of pollution, reform production process to reduce waste water discharge, and adopt reused water and water recycling systems as far as possible. Control the concentration of pollutants in wastewater and recycle useful products. Dispose garbage in urban area and industrial waste. Make comprehensive planning and rational layout, carry out regional comprehensive treatment, and take preventive measures for the water body where water pollution may occur. Make comprehensive planning and treatment for sources of water pollution, put an end to the arbitrary discharge of industrial wastewater and municipal sewage, and set discharge standards. Treat the waste water of the same industry together so as to reduce the number of pollution sources and facilitate management. Fifthly, manage polluted water bodies in a planned way, strengthen monitoring and management, formulate laws and standards for control, set up the agencies responsible for environmental protection management, coordinate and supervise various departments and factories to protect water sources, promulgate relevant laws and regulations, and formulate specific regulations on protecting water bodies, controlling and managing water pollution.
(4) With regard to the “driving force” and “Impact”, the actual situation in Henan province should be taken into account. In an effort to develop economy, the people-oriented concept should be adhered, and satisfying the demands of people and promoting people's all-round development should be treated as the basic starting point for promoting economic and social development. At the same time, with improving the quality of people the quality of life as the basis, speed up the all-round development of social economy. Allocate production factors rationally, optimize industrial structure, save the use of natural resources, and achieve the coordinated and sustainable development of population, resources and environment.
6 Conclusion and discussion
(1) Based on the DPSIR model and the TOPSIS method, the land ecological security of Henan province in China has been evaluated in this study. It has shown that the overall land ecological security situation, reflected by five factors including “driving force”, “pressure”, “state”, “impact”, “response”, in Henan province has been gradually improved from 2007 to 2017. However, it should be pointed out that among these five factors, the security values of the “state”, “response” and “pressure” are still relatively lower, which are mainly manifested in the arable land surface, increasing proportion of area, lower forest coverage, less green area in parks, more sulfur dioxide and more industrial wastewater discharge, etc. Besides, according to the evaluation results in this work, the land ecological security level of three cities, including Shanmenxia, Shangqiu and Pingdingshan, is in the critical security state. Generally, the results of this study are accordance with the actual situation, which illustrate the feasibility and reliability of this method. This paper provides a new evaluation method for the sustainable land utilization, which can provide reference for other countries and regions as well as help relevant departments to improve land quality via pointed measures.(2) As an effective tool for solving problems concerning environment and social development, DPSIR model can analyze the interaction between human and environmental system from a systematic point of view, and can reflect the utilization of the land. Nevertheless, the evaluation results may be subjective to some extent, since the evaluation index system might vary depending on different decision makers. Therefore, it is suggested that one should consult experts in relevant fields before determining the evaluation index system.
(3) Generally, the TOPSIS method can truly, intuitively and reliably reflect the actual situation. This is essentially because the original data are firstly normalized before utilization, thus the effect of different indicators can be eliminated and the information of the original data can be in full use. However, the weight information of the evaluation index may be subjective in this work, although the Delphi method has been employed to reduce subjectivity. Future work will focus on how to obtain more objective weight information.
(4) At present, foreign studies mainly focus on identifying the external conflicts and pressures of the ecosystem, and analyzing the interaction between the external pressures and the ecosystem. Most of the research scales are at the global or national level. The research objects are mainly aimed at developing countries and countries in poverty and marginalization. Most of the studies of Chinese scholars focus on the exploration of basic theories and empirical testing of research, and their research scales focus on the regional level. The follow-up research should further strengthen the extension of research field and focus on the development of research branches on the basis of strengthening the empirical test and practical application of basic theory.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.Acknowledgements
This work was funded by Science and Technology Research Project (No. 192102310263, No. 192102310523) from Henan Province, China.References
- H. Huang, J. J. Tan, C. Chen and C. C. Liu, Res. Soil Water Conserv., 2016, 23(3), 220–224 Search PubMed.
- H. Y. Wang, F. Qin, X. C. Zhang, C. C. Zhang and P. J. Li, Sci. Geogr. Sin., 2017, 50, 51–61 Search PubMed.
- C. X. Liu, X. L. Wu and L. Wang, Appl. Geogr., 2019, 105, 1–14 CrossRef.
- L. B. Ma, W. J. Cheng, J. Bo, X. Y. Li and Y. Gu, Sustainability, 2018, 10, 771 CrossRef.
- Y. S. Shi, J. Q. Li and M. Q. Xie, Ecol. Indic., 2018, 85, 729–741 CrossRef.
- D. Yu, D. Y. Wang, W. B. Li, S. H. Liu, Y. L. Zhu and W. J. Wu, et al. , Sustainability, 2018, 10(2), 394 CrossRef.
- X. B. Xu, G. S. Yang, Y. Tan, Q. L. Li, H. P. Zhuang, R. R. Wan, W. Z. Su and J. Zhang, Sci. Total Environ., 2016, 554–555, 7–16 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Q. Zhang, J. Peng, Y. X. Liu and J. S. Wu, Urban Ecosyst., 2016, 20(3), 1–14 CrossRef.
- X. Liu, H. T. Liu, J. C. Chen, T. W. Liu and Z. L. Deng, J. Cleaner Prod., 2018, 188, 158–170 CrossRef.
- W. Jogo and R. Hassan, Ecol. Econ., 2010, 69, 1569–1579 CrossRef.
- H. Li, L. Nan and S. P. Li, Areal Research and Development, 2017, 36(6), 136–141 Search PubMed.
- S. K. Sahu, J. Anim. Plant Sci., 2011, 21(2), 388–395 Search PubMed.
- D. F. Wu, Y. Y. Liu and Y. H. Liu, et al. , Chin. J. Eco-Agric., 2015, 23(3), 257–267 Search PubMed.
- Y. X. Zhou, Y. X. LI and Y. Y. Sun, et al. , J. Agric. Resour. Environ., 2016, 33(4), 320–326 Search PubMed.
- Y. D. Chen, Q. Y. Yang, R. H. Yang and L. Zeng, Arid. Land Geogr., 2018, 41(1), 185–194 Search PubMed.
- J. Peng, H. L. Li, Y. X. Liu, Y. N. Hu and Y. Yang, Acta Geograph. Sin., 2018, 73, 701–710 Search PubMed.
- H. L. Liu, Y. L. Xie, W. Y. Jia and P. J. Shi, Econ. Geogr., 2018, 38, 161–169 Search PubMed.
- K. J. Yu, S. S. Wang and D. H. Li, Acta Ecol. Sin., 2009, 29, 1189–1204 Search PubMed.
- X. H. Zhang, H. P. Niu and Z. Z. Guo, J. Nat. Disasters, 2014, 23(2), 21–30 Search PubMed.
- Z. S. Wang, S. L. Zhang and F. Chen, et al. , Areal Research and Development, 2017, 36(4), 121–124 Search PubMed.
- Y. L. Zhu, M. J. Li and R. H. Gu, Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin, 2017, 26, 2057–2064 Search PubMed.
- D. Makowski, E. M. T. Hendrix and M. K. V. Ittersum, et al. , Ecol. Model., 2000, 131, 65–77 CrossRef.
- M. Hodson and S. Marvin, Int. J. Urban Reg. Res., 2009, 33(1), 193–215 CrossRef.
- H. Zhang, A. Q. Wang and B. Y. Song, Sci. Geogr. Sin., 2017, 37(11), 1778–1784 Search PubMed.
- L. Li, S. T. Hou, Y. Zhao and X. L. Zheng, Res. Soil Water Conserv., 2014, 21(1), 188–192 Search PubMed.
- Y. L. Hou, G. Li, J. F. Qu, K. Wang, S. Liu and M. Y. Ge, Res. Soil Water Conserv., 2017, 24(1), 285–290 Search PubMed.
- P. Huang, M. Guo and S. R. Lan, J. Shenyang Agric. Univ., 2015, 17(3), 337–341 Search PubMed.
- J. Li, R. F. Zhao and D. Liang, Areal Research and Development, 2018, 37(2), 151–157 Search PubMed.
- Y. F. Li, X. Sun, X. D. Zhu and H. H. Cao, Ecol. Model., 2010, 221(19), 2251–2260 CrossRef.
- L. Pei, L. M. Du and G. J. Yue, Procedia Environ. Sci., 2010, 2, 832–841 CrossRef.
- B. L. Han, H. X. Liu and R. S. Wang, Ecol. Model., 2015, 318(1), 217–225 CrossRef.
- J. Y. Tian and G. S. Gang, Energy Procedia, 2012, 16, 1180–1186 CrossRef.
- D. Liu and Q. Chang, Acta Ecol. Sin., 2015, 35(5), 111–121 CrossRef.
- J. Y. Lin, T. Lin and S. H. Cui, Ecol. Indic., 2012, 13(1), 294–302 CrossRef.
- M. Borji, A. Moghaddam Nia, A. Malekian, A. Salajegheh and S. Khalighi, Arabian J. Geosci., 2018, 11(8), 158 CrossRef.
- B. J. Goble, T. R. Hill and M. R. Phillips, Coast. Manag., 2017, 45(93), 1–18 Search PubMed.
- M. Spano, F. Gentile, C. Davies and R. Lafortezza, Land Use Policy, 2017, 61, 242–250 CrossRef.
- M. Elliott, D. Burdon, J. P. Atkins and A. Borja, et al. , Mar. Pollut. Bull., 2017, 118(1–2), 27–40 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Ehara, K. Hyakumura, R. Sato, K. Kurosawa, K. Araya and H. Sokh, et al. , Ecol. Econ., 2018, 149, 226–238 CrossRef.
- H. Y. Yu, F. Zhang, L. Cao, J. Wang and S. T. Yang, Acta Ecol. Sin., 2017, 37(19), 6355–6369 Search PubMed.
- C. L. Hwang and K. Yoon, Multiple attributes decision making methods and applications, Springer, 1981 Search PubMed.
- H. Gupta and M. K. Barua, Sci. Total Environ., 2018, 633, 122–139 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Wang, W. Zhou and S. T. A. Pickett, et al. , Sci. Total Environ., 2019, 662, 824–833 CrossRef CAS.
- O. Mehdi, M. H. S. Seied and R. Abbas, et al. , Sci. Total Environ., 2018, 627, 1363–1376 CrossRef.
- L. B. Ma, J. Bo and X. Y. Li, et al. , Sci. Total Environ., 2019, 674, 424–438 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. J. Feng, Q. Q. Yang, Z. H. Hong and L. Cui, Geocarto Int., 2018, 33(15), 470–488 CrossRef.
- Y. J. Feng, Q. Q. Yang, X. H. Tong and L. Chen, Sci. Total Environ., 2018, 633, 1469–1479 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. L. Gong and S. Sun, Qinghai Soc. Sci., 2017,(6), 96–102 Search PubMed.
- Z. S. Xu, Uncertain Multiple Attribute Decision Making: Methods and Applications, Tsinghua University Press, 2004, pp. 7–10 Search PubMed.
- P. Wang, W. D. Xu and Y. W. Deng, et al. , Journal of Hengyang Normal University, 2016, 37(3), 81–86 Search PubMed.
- Y. Jin, Clean Technol. Environ. Policy, 2008, 10(2), 111–112 CrossRef.
- Y. Wen, T. S. Wang and Z. S. Deng, Meteorol. Environ. Res., 2014, 20(7), 45–50 Search PubMed.
- M. M. Chelan, A. Alijanpour, H. Barani, J. Motamedi, H. Azadi and S. V. Passel, Sci. Total Environ., 2018, 112, 637–638 Search PubMed.
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2019 |