Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleCreative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported Licence
Correction: 5-Heptadecylresorcinol attenuates oxidative damage and mitochondria-mediated apoptosis through activation of the SIRT3/FOXO3a signaling pathway in neurocytes
Jie
Liu
a,
Yu
Wang
a,
Yiming
Hao
a,
Zongwei
Wang
a,
Zihui
Yang
a,
Ziyuan
Wang
a and
Jing
Wang
*ab
aChina-Canada Joint Lab of Food Nutrition and Health (Beijing), Beijing Technology & Business University (BTBU), Beijing 100048, China. E-mail: wangjing@th.btbu.edu.cn
bBeijing Advanced Innovation Center for Food Nutrition and Human Health, Beijing Technology & Business University, Beijing 100048, China
First published on 26th March 2020
Abstract
Correction for ‘5-Heptadecylresorcinol attenuates oxidative damage and mitochondria-mediated apoptosis through activation of the SIRT3/FOXO3a signaling pathway in neurocytes’ by Jie Liu et al., Food Funct., 2020, DOI: 10.1039/c9fo03028j.
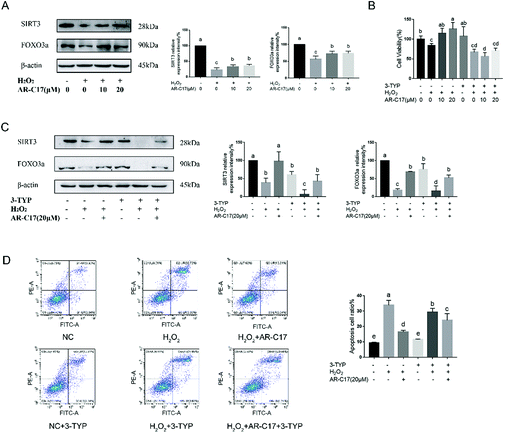
The authors regret the incorrect version of Fig. 4 was included in the original article. The correct version of Fig. 4 is presented below.
The Royal Society of Chemistry apologises for these errors and any consequent inconvenience to authors and readers.
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2020 |