Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleRapid characterization of the chemical constituents of Sanhua decoction by UHPLC coupled with Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry†
Yanhui Zhao a,
Miao Wangb,
Lin Suna,
Xue Jianga,
Min Zhao
a,
Miao Wangb,
Lin Suna,
Xue Jianga,
Min Zhao *a and
Chunjie Zhao
*a and
Chunjie Zhao *a
*a
aSchool of Pharmacy, Shenyang Pharmaceutical University, Wenhua Road 103, Shenhe District, Shenyang 110016, Liaoning Province, China. E-mail: lab433@163.com
bSchool of Life Science and Biopharmaceutics, Shenyang Pharmaceutical University, Wenhua Road 103, Shenyang, Liaoning Province, China
First published on 10th July 2020
Abstract
Sanhua decoction, a famous Chinese herbal formula has been widely used for the treatment of stroke. In our study, a rapid, swift and straightforward analytical method with the help of UHPLC-FT-ICR-MS/MS was successfully developed for the first time to separate and identify the chemical constituents of Sanhua decoction. Chromatography was performed on a Universal XB C18 column (150 mm × 2.1 mm, 1.8 μm) using a mobile phase containing 0.1% formic acid–water (A) and acetonitrile (B). A total of 137 compounds in Sanhua decoction were identified or tentatively characterized. The findings revealed the fact that Sanhua decoction mainly contains flavonoids (in Aurantii fructus immaturus and Rheum palmatum L.), anthraquinones (in Rheum palmatum L.), coumarins (in Notopterygii Rhizoma Et Radix), phenylpropanoid glycosides, alkaloids and lignans (in Magnoliae Officmalis Cortex), which made up the key ingredients existing in Sanhua decoction. This study is hoped to be meaningful for the characterization of components in other traditional Chinese medicines, and lay the foundation for research on the pharmacology of Sanhua decoction.
1. Introduction
Traditional Chinese medicines (TCMs) play an important role in Chinese medicine due to their wide application and efficacy, particularly in the management of chronic diseases.1 TCMs are composed of complex chemical constituents for multi-target treatment, and produce synergistic effects and reduce side effects. Although there has been a lot of research on TCMs, the active ingredients of most traditional Chinese medicine prescriptions remain unknown. Therefore, developing a fast and efficient analysis method to separate and identify complex constituents in TCMs is necessary for illustrating the pharmacological material basis of TCMs.Sanhua decoction (SHD), a famous Chinese herbal formula, is recorded in the classic traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) book Suwen Bingji Qiyi Baomingji (Plain Questions: Discourse on Mechanism for Preserving Life). It consists of four crude herbs: Zhishi (Aurantii fructus immaturus), Dahuang (Rheum palmatum L.), Houpu (Magnoliae Officmalis Cortex) and Qianghuo (Notopterygii Rhizoma Et Radix). SHD is used widely for the treatment of stroke. It can improve ischemic cerebral edema and brain blood barrier (BBB) permeability.2 It has been documented that Zhishi has neuroprotective, antioxidant, anti inflammatory and anti-apoptotic effects.3 Dahuang can protect neurons from hypoxic-ischemic brain damage.4 Houpu can protect neural damage from cerebral ischemia and reperfusion by suppressing cerebral inflammation and improving BBB function.5 Qianghuo has a function of anti-thrombosis, increasing cerebral blood flow and improving cerebral blood circulation.6 However, the chemical material basis of SHD has not been studied in detail until now.
As the complexity of traditional Chinese medicine, it is very important to establish a sensitive and reliable detection method. Chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) is widely used for its high sensitivity and specificity. Ultra high performance liquid chromatography (UHPLC) coupled with Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry (FT-ICR-MS) as the most powerful instrument with high resolution, accuracy and sensitivity play a role in analyzing different kinds of complex samples.7–10 It provides an unambiguous elemental composition and information about the isotopic abundance of ions to help determine the compositions and structures of chemical constituents. By usage of this technology, Li et al. characterized 179 constituents in Rhodiola crenulata as well as 37 prototypes and 142 metabolites in rats.11 Guan et al. characterized 120 constituents in Sijunzi decoction12 and Liu et al. characterized 174 constituents in Gegenqinlian decoction as well as 107 prototypes and 67 metabolites in rats.13 The results show that this method is useful in detecting and indenting chemical constituents and metabolites by information about accurate molecular weight and MS2.
In this study, a rapid and simple approach by UHPLC-FT-ICR-MS was established for the systematical characterization of the constituents of SHD. This constituent characterization and structural elucidation provided significant information for a pharmacological study of SHD.
2. Material and methods
2.1 Chemicals and materials
The purchase of key ingredients including, Aurantii fructus immaturus (batch number: 170![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 901; source: Sichuan China), Rheum palmatum L. (batch number: 20
901; source: Sichuan China), Rheum palmatum L. (batch number: 20![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 181
181![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 101; source: Gansu China), Magnoliae Officmalis Cortex (batch number: 181
101; source: Gansu China), Magnoliae Officmalis Cortex (batch number: 181![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 001; source: Sichuan China) and Notopterygii Rhizoma Et Radix (batch number: 13
001; source: Sichuan China) and Notopterygii Rhizoma Et Radix (batch number: 13![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 112
112![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 501; source: Sichuan China) was made from Guoda pharmacy (Shenyang, China), which followed identification by Professor Jingming Jia (Department of TCM, Shenyang Pharmaceutical University, Shenyang, China). The key source of the reference compounds (purity > 98%), including sennoside B, nodakenin, narirutin, sennoside A, neohesperidin, naringenin, hesperetin, nobiletin was Shanghai Yuanye Bio-Technology Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China); naringin, hesperidin and honokiol was attained from the National Institute for the Control of Pharmaceutical and Biological Products (Beijing, China). In addition, acetonitrile of HPLC grade, together with formic acid of LC-MS grade was attained from Fisher Scientific (Fair Lawn, NJ, USA), followed by attaining the purified water from Wahaha (Hangzhou, China).
501; source: Sichuan China) was made from Guoda pharmacy (Shenyang, China), which followed identification by Professor Jingming Jia (Department of TCM, Shenyang Pharmaceutical University, Shenyang, China). The key source of the reference compounds (purity > 98%), including sennoside B, nodakenin, narirutin, sennoside A, neohesperidin, naringenin, hesperetin, nobiletin was Shanghai Yuanye Bio-Technology Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China); naringin, hesperidin and honokiol was attained from the National Institute for the Control of Pharmaceutical and Biological Products (Beijing, China). In addition, acetonitrile of HPLC grade, together with formic acid of LC-MS grade was attained from Fisher Scientific (Fair Lawn, NJ, USA), followed by attaining the purified water from Wahaha (Hangzhou, China).
2.2 Preparation of SHD for analysis
Following the documentary records of SHD, four constituting herbs that included Aurantii fructus immaturus (40 g), Rheum palmatum L. (40 g), Magnoliae Officmalis Cortex (40 g) and Notopterygii Rhizoma Et Radix (40 g) were soaked in water for 60 min, then decocted two times in 80 mL water for a period of 1 h each time in a glass flask and the ensuing solution was mixed and dried with the help of lyophilization. Prior to the analysis, dissolution the 0.5 g of dried powder was dissoluted by 5 mL methanol-aqueous (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) solution, soaking for 15 min with 80 °C water.
1) solution, soaking for 15 min with 80 °C water.
2.3 Instrument and analytical conditions
The sample was analyzed by the UHPLC-DAD-FT-ICR-MS system contains an Agilent 1260 UHPLC system combined with a Bruker Solarix7.0T FT-ICR-MS system (Germany) and Bruker Compass-Hystar workstation (Bruker, Germany). Chromatography was carried out on a Universal XB C18 column (150 mm × 2.1 mm, 1.8 μm; Kromat, USA) at the temperature of 35 °C. The mobile phase contained 0.1% formic acid–water (A) and acetonitrile (B). The gradient conditions were as follows: 8–12% (B) in 0 to 10 min, 12–13% (B) in 10 to 12 min, 13–18% (B) in 13 to 18 min, 18–24% (B) in 17 to 28 min, 24–30% (B) in 28 to 31 min, 30–36% (B) in 31 to 35 min, 36–55% (B) in 35 to 37 min, 55–90% (B) in 37 to 47 min, which was delivered at a flow rate of 0.2 mL min−1 and injection volume was 2 μL.The mass spectra were performed with positive as well as negative electrospray ionization (ESI) modes, followed by setting the optimized conditions are as follows: capillary voltage, 4.5 kV; plate offset, 500 v; nebulizer gas pressure, 4.0 bar; dry gas flow rate, 8 L min−1; dry gas temperature, 200 °C; ion accumulation time, 0.15 s, and flight time, 0.6 ms. Full scan mass spectrometry data were recorded between m/z 100 and 1200 amu and the collision energy was ranged from 10 eV to 30 eV for MS/MS experiments.
3. Results and discussion
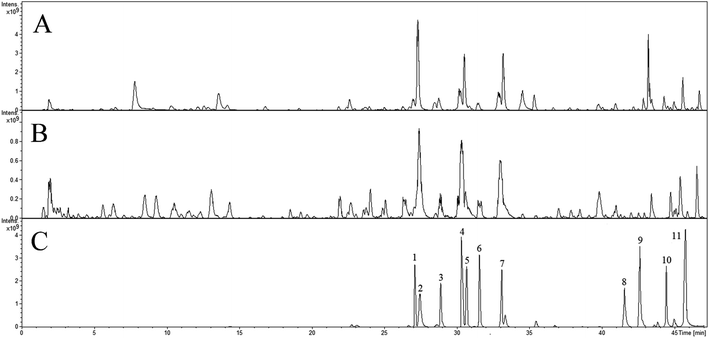
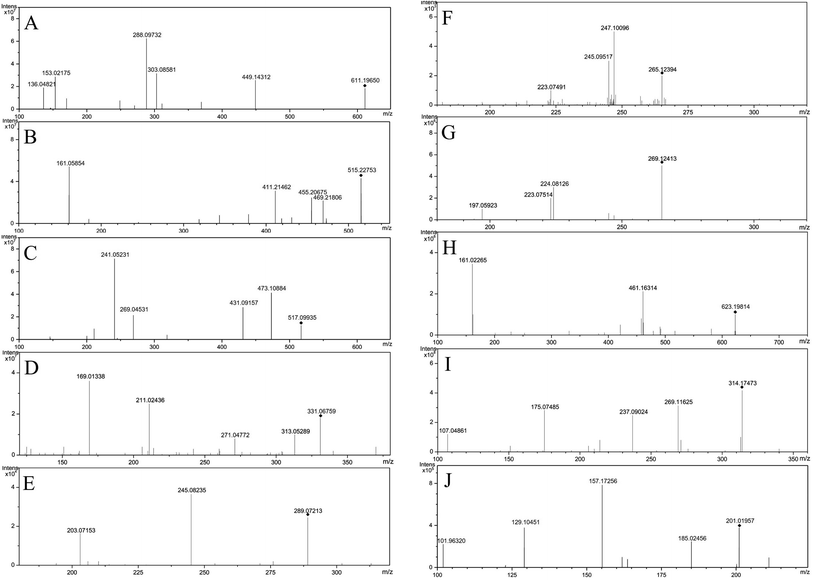
The Fig. 1 reveals the base peak ion chromatograms (BPC) of SHD in positive as well as negative ion modes, together with the respective compounds. The extract ion chromatograms (EIC) of each molecule weight were correspondingly attained for detecting the associated compound followed by presenting in support information Fig. S1.† Comparing with reference compounds, eleven peaks from SHD were accurately identified by the retention times and MS fragments in positive ion mode. The peak of 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 in Fig. 1C were sennoside B, nodakenin, narirutin, naringin, sennoside A, hesperidin, neohesperidin, naringenin, hesperetin, honokiol, nobiletin, respectively. The others were predicted by Bruker workstation, whether or not the mass error values between the identified molecular weights with the measured molecular weights were below 3.0 ppm. If yes, it can infer the chemical structure of each component by the retention time and MS/MS data with published literature.14–28 In the end, a total of 137 compounds were identified and characterized, whereas their layouts were presented in support information Fig. S2.†The MS/MS spectra of representative compounds are shown in Fig. 2, and displaying deduced fragmentation pathways are shown in Fig. 3. Except that, the formula, retention time, MS data, calculated m/z, error, ion mode and MS/MS data of other detected components were listed in Table 1.
| No. | tR (min) | Identification | Formula | Monoisotopic mass (m/z) | Detected mass (m/z) | Ion mode | ppm | MS/MS (m/z) | Main source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a Ps: C represented Aurantii fructus immaturus; R represented Rheum palmatum L.; M represented Magnoliae Officmalis Cortex; N represented Notopterygii Rhizoma Et Radix. | |||||||||
| 1 | 2.07 | Quinic acid | C7H12O6 | 193.07066 | 193.07024 | [M + H]+ | 2.21 | 147.04051, 129.05446 | C |
| 2 | 2.64 | Galloyl-glucoside | C13H16O10 | 331.06707 | 331.06759 | [M − H]− | −1.57 | 313.05289, 271.04772, 211.02436, 169.01338, 125.00325 | R |
| 3 | 2.91 | 1-Galloyl-di-glucoside | C19H26O15 | 493.11989 | 493.12035 | [M − H]− | −0.93 | 373.07705, 331.06771, 313.05667, 271.04642 | R |
| 4 | 3.21 | Gallic acid | C7H6O5 | 169.01425 | 169.01447 | [M − H]− | −1.30 | 151.00284, 125.02324 | R |
| 5 | 4.85 | Catechin-3-O-glucoside | C21H24O11 | 451.12459 | 451.12518 | [M − H]− | −1.31 | 289.07014, 245.08287 | R |
| 6 | 5.59 | Rebouoside C | C20H30O12 | 461.16645 | 461.16674 | [M − H]− | −0.64 | 299.11268, 137.05927 | M |
| 7 | 6.04 | Chlorogenic acid | C16H18O9 | 353.08781 | 353.08824 | [M − H]− | −1.23 | 191.09726, 179.76826, 173.10064 | N |
| 8 | 7.02 | Catechin-5-O-glucoside | C21H24O11 | 451.12459 | 451.12504 | [M − H]− | −1.01 | 289.07156, 245.08176, 203.07109 | R |
| 9 | 7.79 | Magnocurarine | C19H24NO3+ | 314.17507 | 314.17473 | [M + H]+ | 1.07 | 269.11618, 237.08974, 175.07514, 107.04887 | M |
| 10 | 10.40 | Catechin | C15H14O6 | 289.07176 | 289.07211 | [M − H]− | −1.22 | 245.08146, 205.04962, 203.06974 | R |
| 11 | 10.63 | Cryptochlorogenic acid | C16H18O9 | 353.08781 | 353.08825 | [M − H]− | −1.25 | 191.10029, 179.14054, 173.10065 | N |
| 12 | 10.64 | Syringin | C17H24O9 | 395.13125 | 395.13094 | [M + Na]+ | 0.80 | 372.08647, 343.94804, 208.09042, 137.03937 | M |
| 13 | 13.55 | Magnoflorine | C20H24NO4+ | 342.16998 | 342.16967 | [M + H]+ | 0.91 | 297.10956, 282.08696, 265.08507, 237.08972 | M |
| 14 | 16.29 | (R)-Oblongine | C19H24NO3+ | 314.17507 | 314.17475 | [M + H]+ | 1.02 | 269.11625, 237.09024, 175.07485, 107.04861 | M |
| 15 | 16.62 | Epicatechin | C15H14O6 | 289.07176 | 289.07213 | [M − H]− | −1.26 | 245.08235, 203.07153 | R |
| 16 | 18.49 | Teupolioside | C35H46O20 | 785.25097 | 785.24931 | [M − H]− | 2.11 | 649.28262, 623.38565, 477.34832 | M |
| 17 | 19.22 | Aloe-emodin-O-di-glucoside | C27H30O15 | 593.15119 | 593.15142 | [M − H]− | −0.38 | 431.09851, 269.04559, 239.03448 | R |
| 18 | 19.31 | Apigenin-6,8-di-C-glucoside | C27H30O15 | 595.16575 | 595.16502 | [M + H]+ | 1.23 | 577.15636, 505.13492, 475.12405 | C |
| 19 | 20.32 | Xanthoplanine | C21H25O4N+ | 356.18563 | 356.18528 | [M + H]+ | 1.01 | 311.12628, 296.10825, 280.10864 | M |
| 20 | 20.74 | Asimilobine | C17H17O2N | 268.13321 | 268.13294 | [M + H]+ | 0.99 | 251.10647, 236.08474, 219.08076, 191.08617 | M |
| 21 | 21.26 | Echinacoside | C35H46O20 | 785.25097 | 785.24959 | [M − H]− | 1.76 | 649.28357, 623.38647, 477.34187 | M |
| 22 | 21.76 | Chysoeriol-6,8-di-C-glucoside | C28H32O16 | 625.17631 | 625.17579 | [M + H]+ | 0.84 | 607.16748, 535.14662, 505.13284 | C |
| 23 | 21.95 | 1-Cinnamoyl-6-O-(glucosyl)-galloyl-glucoside | C28H32O16 | 623.16176 | 623.16247 | [M − H]− | −1.15 | 461.10814, 331.06702, 313.05827, 211.02305 | R |
| 24 | 22.31 | Scopoletin | C10H8O4 | 193.04954 | 193.04935 | [M + H]+ | 0.95 | 178.02482, 165.05373, 122.03784 | C |
| 25 | 22.45 | 2-O-Cinnamyl-β-D-glucoside | C15H18O7 | 309.09798 | 309.09841 | [M − H]− | −1.39 | 237.07692, 201.01967, 146.96590 | R |
| 26 | 22.55 | Emodin-O-glucuronic acid methyl ester | C22H20O11 | 459.09329 | 459.09358 | [M − H]− | −0.65 | 269.04543, 241.05106, 225.05490, 213.05525 | R |
| 27 | 23.60 | Decuroside V | C20H20O10 | 447.12617 | 447.12576 | [M + Na]+ | 0.91 | 263.08937, 245.08472 | N |
| 28 | 23.73 | Xanthotoxol | C11H6O4 | 203.03389 | 203.03379 | [M + H]+ | 0.45 | 173.07564, 145.04536, 117.05273 | C |
| 29 | 23.73 | Bergaptol | C11H6O4 | 201.01933 | 201.01957 | [M − H]− | −1.17 | 185.02456, 157.17256, 129.10451, 101.96320 | N |
| 30 | 23.76 | 1-O-Cinnamyl-β-D-glucoside | C15H18O7 | 309.09798 | 309.09843 | [M − H]− | −1.47 | 248.95978, 161.04574, 146.96419 | R |
| 31 | 23.77 | Bergaptol-O-β-D-glucopyranoside | C17H16O9 | 365.08671 | 365.08641 | [M + H]+ | 0.81 | 201.03287, 159.17264, 131.10514 | N |
| 32 | 24.94 | Natsudaidain-3-O-glucoside | C27H32O14 | 581.18648 | 581.18599 | [M + H]+ | 0.85 | 419.13174, 273.07487, 153.01846 | C |
| 33 | 24.97 | Narirutin-4′-O-glucoside | C33H42O19 | 743.23931 | 743.23875 | [M + H]+ | 0.75 | 581.18682, 435.12794, 273.07526 | C |
| 34 | 25.16 | Eriocitrin | C27H32O15 | 597.18140 | 597.18096 | [M + H]+ | 0.73 | 435.12791, 289.06947, 153.01849 | C |
| 35 | 25.35 | Resveratrol-4′-O-glucoside | C20H22O8 | 389.12419 | 389.12479 | [M − H]− | −0.83 | 245.08196, 227.07138, 199.07567, 135.04384 | R |
| 36 | 25.47 | Isolindleyin | C23H26O11 | 477.14024 | 477.14067 | [M − H]− | −0.90 | 313.05691, 211.02328, 169.01307, 125.02387 | R |
| 37 | 25.79 | Lindleyin | C23H26O11 | 477.14024 | 477.14071 | [M − H]− | −1.12 | 313.05659, 211.02454, 169.01340, 125.02321 | R |
| 38 | 26.19 | Limonin | C26H30O8 | 471.20134 | 471.20060 | [M + H]+ | 0.83 | 425.19343, 339.19426, 161.05897 | C |
| 39 | 26.19 | Rhein-8-O-β-D-glucoside | C21H18O11 | 445.07763 | 445.07816 | [M − H]− | −1.21 | 285.07559, 267.03326, 257.07879, 241.07041 | R |
| 40 | 26.28 | Nicotiflorin | C27H30O15 | 595.16575 | 595.16515 | [M + H]+ | 1.00 | 419.13403, 390.09214, 287.07785 | C |
| 41 | 26.28 | Naringenin-7-O-glucoside | C21H22O10 | 435.12857 | 435.12833 | [M + H]+ | 0.56 | 272.07462, 227.18968, 177.22102, 165.13608 | C |
| 42 | 26.29 | Eriodictyol | C15H12O6 | 289.07066 | 289.07051 | [M + H]+ | 0.53 | 153.01692, 135.06538, 107.04796 | C |
| 43 | 26.42 | Limonin-17-β-D-glucoside | C32H42O14 | 649.25018 | 649.25108 | [M − H]− | −1.39 | 487.19725, 425.18954, 339.18671 | C |
| 44 | 26.49 | Neoeriocitrin | C27H32O15 | 597.18140 | 597.18134 | [M + H]+ | 0.52 | 435.12786, 289.06814, 153.01794 | C |
| 45 | 26.55 | Isosakuranetin | C16H14O5 | 287.09140 | 287.09138 | [M + H]+ | 0.38 | 153.01718, 133.065095 | C |
| 46 | 27.07 | Alhagidin | C34H44O20 | 771.23532 | 771.23656 | [M − H]− | −1.61 | 635.18786, 609.19823, 161.02394 | M |
| 47 | 27.17 | Cinnamoyl-6-O-galloyl-diglucoside | C28H32O16 | 623.16176 | 623.16185 | [M − H]− | −1.50 | 475.10891, 331.06765, 313.05664 | R |
| 48 | 27.25 | Nodakenin | C20H24O9 | 407.13476 | 407.13536 | [M − H]− | −1.48 | 247.04625, 229.14536, 175.41575 | N |
| 49 | 27.29 | Marmesin | C14H14O4 | 247.09649 | 247.09655 | [M + H]+ | −0.28 | 153.01714 | C |
| 50 | 27.38 | Veronicastroside | C27H30O15 | 595.16575 | 595.16502 | [M + H]+ | 0.84 | 577.15147, 457.10763, 295.05903 | C |
| 51 | 27.40 | Sennoside B | C42H38O20 | 861.18837 | 861.18831 | [M − H]− | −1.71 | 699.13514, 655.14385, 389.08791 | R |
| 52 | 27.44 | Emodin-O-di-glucoside | C27H30O15 | 593.15119 | 593.15112 | [M − H]− | −1.24 | 269.04549, 240.04318, 225.05493 | R |
| 53 | 28.01 | Cassiachromone | C13H12O4 | 231.06628 | 231.06653 | [M − H]− | −1.09 | 269.04549, 240.04321 | R |
| 54 | 28.96 | Narirutin | C27H32O14 | 581.18648 | 581.18594 | [M + H]+ | 0.94 | 435.12779, 419.13317, 273.07528 | C |
| 55 | 29.56 | Isorhoifolin | C27H30O14 | 579.17083 | 579.17056 | [M + H]+ | 0.47 | 449.14346, 303.08368, 153.01728 | C |
| 56 | 29.64 | Chrysophanol-1,8-O-di-glucoside | C27H30O14 | 577.15628 | 577.15658 | [M − H]− | −0.52 | 415.10387, 253.04962, 225.05395 | R |
| 57 | 30.04 | Acteoside | C29H36O15 | 623.19814 | 623.19902 | [M − H]− | −0.36 | 461.16314, 161.02265 | M |
| 58 | 30.15 | 1-Dihydro-p-coumaroyl-6-O-galloyl-glucoside | C22H24O12 | 479.11950 | 479.12006 | [M − H]− | −1.16 | 461.10874, 313.05591, 169.01294, 125.02296 | R |
| 59 | 30.21 | Prunin | C21H22O10 | 435.12857 | 435.12887 | [M + H]+ | −0.68 | 273.07329, 153.01674 | C |
| 60 | 30.22 | Natsudaidai | C21H22O9 | 419.13366 | 419.13349 | [M + H]+ | 0.39 | 390.09212, 389.09134, 371.08154 | C |
| 61 | 30.36 | Naringin | C27H32O14 | 581.18648 | 581.18605 | [M + H]+ | 0.75 | 435.12862, 419.13274, 273.07564 | C |
| 62 | 30.80 | Sennoside A | C42H38O20 | 885.18486 | 885.18538 | [M + Na]+ | −0.59 | 701.13594, 657.14538, 391.08807, 270.03807 | R |
| 63 | 30.94 | Isoacteoside | C29H36O15 | 623.19814 | 623.19925 | [M − H]− | −1.77 | 461.16741, 161.02568 | M |
| 64 | 30.98 | Laccaic acid-D-O-glucoside | C22H20O12 | 475.08740 | 475.08820 | [M − H]− | −0.91 | 431.09851, 269.03452, 253.05063, 240.04252 | R |
| 65 | 31.45 | Rhoifolin | C27H30O14 | 579.17083 | 579.17057 | [M + H]+ | 0.57 | 433.10764, 271.05967, 153.02389 | C |
| 66 | 31.45 | Neodiosmin | C28H32O15 | 609.18140 | 609.18107 | [M + H]+ | 0.77 | 301.07091, 286.04659 | C |
| 67 | 31.48 | Isosakuranin | C22H24O10 | 449.14422 | 449.14408 | [M + H]+ | 0.96 | 301.06877, 287.09012, 286.04485 | C |
| 68 | 31.59 | Hesperidin | C28H34O15 | 611.19705 | 611.19650 | [M + H]+ | 0.10 | 449.14312, 303.08581, 288.09732, 153.02175, | C |
| 69 | 32.03 | Nodakenetin | C14H14O4 | 245.08193 | 245.08221 | [M − H]− | −1.14 | 229.10047, 211.64807, 175.42487 | N |
| 70 | 32.36 | Physcion-1-O-glucuronic acid | C22H20O11 | 459.09329 | 459.09368 | [M − H]− | −0.86 | 283.06124, 268.03815, 212.04737, 184.05123 | R |
| 71 | 32.78 | Diosmin | C28H32O15 | 607.16684 | 607.16710 | [M − H]− | −0.42 | 299.10025, 284.29568 | C |
| 609.18140 | 609.18081 | [M + H]+ | 0.96 | 301.06863![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 286.04525 286.04525 |
|||||
| 72 | 32.89 | Neohesperidin | C28H34O15 | 611.19705 | 611.19637 | [M + H]+ | 0.53 | 449.14228, 303.08417, 153.01734 | C |
| 73 | 32.89 | Hesperetin-7-O-glucoside | C22H24O11 | 465.13914 | 465.13958 | [M + H]+ | −0.92 | 303.08652, 288.03284, 153.01532 | C |
| 74 | 32.90 | Sakuranetin | C22H24O10 | 449.14422 | 449.14477 | [M + H]+ | −1.22 | 301.06945, 287.08765, 286.045473 | C |
| 75 | 32.97 | Magnoloside E | C28H34O15 | 609.18249 | 609.18261 | [M − H]− | 0.19 | 447.15213, 315.11019, 161.02613 | M |
| 76 | 33.05 | Homoeriodictyol | C16H14O6 | 303.08631 | 303.08630 | [M + H]+ | 0.06 | 288.04856, 153.01712, 117.03375 | C |
| 77 | 33.18 | Limocitrin-3-O-(3-hydroxy-3-methylglutarate)-glucoside | C29H32O17 | 653.17123 | 653.17394 | [M + H]+ | −0.73 | 539.13891, 347.07494 | C |
| 78 | 33.40 | 1-Dihydrocinnamoyl-6-O-galloyl-glucoside | C22H24O11 | 463.12459 | 463.12503 | [M − H]− | −0.97 | 331.06693, 313.05656, 211.02564, 169.01332 | R |
| 79 | 34.30 | Magnolignan B | C18H20O5 | 315.12380 | 315.12417 | [M − H]− | −0.95 | 267.10167, 249.09178, 221.09658, 133.06619 | M |
| 80 | 34.51 | Meranzin | C15H16O4 | 261.11214 | 261.11203 | [M + H]+ | 0.42 | 243.10142, 159.04375, 103.05456 | C |
| 81 | 34.59 | Hesperidone hydrate | C15H18O5 | 296.14925 | 296.14925 | [M + HH4]+ | 0.00 | 403.12656, 418.12351, 165.05352 | C |
| 82 | 35.89 | Diosmetin-7-O-(6′′-O-acetyl) neohesperidoside | C30H34O17 | 667.18688 | 667.18653 | [M + H]+ | −0.26 | 301.07182, 286.05412 | C |
| 83 | 36.14 | Natsudaidain-3-O-(3-hydroxy-3-methylglutarate)-glucoside | C33H40O18 | 725.22874 | 725.22824 | [M + H]+ | 0.47 | 581.18621, 419.13224 | C |
| 84 | 36.29 | Magnolignan A | C18H20O4 | 299.12888 | 299.12924 | [M − H]− | −1.18 | 239.10865, 221.10746 | M |
| 85 | 37.01 | Physcion-8-O-glucuronic acid | C22H20O11 | 459.09329 | 459.09369 | [M − H]− | −0.89 | 283.06138, 268.03804, 239.03501, 224.04837 | R |
| 86 | 38.08 | Cinnamoyl-6-O-galloyl-glucoside | C22H22O11 | 461.10894 | 461.10948 | [M − H]− | −1.18 | 401.08794, 313.05874, 285.03987, 271.04612 | R |
| 87 | 39.00 | Didymin | C28H34O14 | 595.20213 | 595.20196 | [M + H]+ | 0.70 | 433.14783, 287.09001, 153.01794 | C |
| 88 | 39.08 | Beta-hydroxyacteoside | C29H36O16 | 639.19306 | 639.19315 | [M − H]− | −0.14 | 503.14287, 477.16173, 161.02408, 133.03174 | M |
| 89 | 39.39 | 6-Methoxy-8-O-β-D-glucoside | C20H24O9 | 407.13476 | 407.13521 | [M − H]− | −1.12 | 253.04989, 201.09011, 146.96598 | R |
| 90 | 39.47 | Magnoloside A | C29H36O15 | 623.19705 | 623.19645 | [M + H]+ | 0.95 | 461.16607, 161.02574 | M |
| 91 | 39.51 | Chrysophanol isomer | C15H10O4 | 253.05063 | 253.05093 | [M − H]− | −1.23 | 225.05517, 210.03072, 197.06054 | R |
| 92 | 39.52 | Chrysophanol-1-O-glucoside | C21H20O9 | 415.10346 | 415.10402 | [M − H]− | −1.35 | 253.04884, 225.05627, 209.05942 | R |
| 93 | 39.70 | Emodin-O-glucoside | C21H20O10 | 431.09837 | 431.09867 | [M − H]− | −0.7 | 269.04562, 241.04997, 225.05524 | R |
| 94 | 39.74 | 3,5,6,7,8,3′,4′-Heptamethoxy flavone | C22H24O9 | 433.14931 | 433.14910 | [M + H]+ | 0.49 | 418.12356, 403.12656, 165.05354 | C |
| 95 | 39.79 | 1-P-Coumaroyl-6-O-galloyl-di-glucoside | C29H36O16 | 639.19306 | 639.19367 | [M − H]− | −0.96 | 477.13972, 313.05688, 211.02412, 141.03624 | R |
| 96 | 39.87 | Sakuranin | C16H14O5 | 287.09142 | 287.09127 | [M + H]+ | 0.46 | 153.01721, 133.06492 | C |
| 97 | 39.88 | Poncirin | C28H34O9 | 595.20213 | 595.20168 | [M + H]+ | 0.73 | 433.14812, 287.09110, 153.16712 | C |
| 98 | 39.93 | Magnoloside M | C29H36O15 | 623.19705 | 623.19643 | [M + H]+ | 0.99 | 461.16597, 161.02576 | M |
| 99 | 39.98 | 6′-O-trans-Feruloylnodakenin | C30H32O12 | 583.18213 | 583.18148 | [M − H]− | 1.07 | 247.10278, 229.44072, 175.28676 | N |
| 607.17865 | 607.17861 | [M + Na]+ | −0.02 | 249.11947, 177.29759 | |||||
| 100 | 40.24 | Chrysophanol | C15H10O4 | 253.05063 | 253.05094 | [M − H]− | −1.21 | 225.05537, 210.03104, 202.88598 | R |
| 101 | 40.93 | Marmin | C19H24O5 | 333.16965 | 333.16942 | [M + H]+ | 0.70 | 163.03837, 107.08582 | C |
| 102 | 41.15 | 2-(2′-hydroxypropyl)-5-methyl-7-hydroxychromone | C13H14O4 | 233.08193 | 233.08217 | [M − H]− | −1.01 | 189.05568, 146.96597, 129.97617 | R |
| 103 | 41.29 | Magnolignan C | C18H20O4 | 299.12888 | 299.12928 | [M − H]− | −1.33 | 258.09247, 239.10852, 197.06244 | M |
| 104 | 41.55 | Naringenin | C15H12O5 | 273.07575 | 273.07562 | [M + H]+ | 0.48 | 153.17823, 133.06712 | C |
| 105 | 42.12 | Procyanidin B | C30H26O12 | 577.13515 | 577.13535 | [M − H]− | −0.49 | 425.08747, 407.07637, 289.07107 | R |
| 106 | 42.26 | Physcion-8-O-glucuronic acid methyl ester | C23H22O11 | 473.10894 | 473.10946 | [M − H]− | −1.11 | 283.06094, 268.03811, 240.04325 | R |
| 107 | 42.27 | Emodin-O-malonyl-glucose | C24H22O13 | 517.09876 | 517.09935 | [M − H]− | −1.15 | 473.10884, 431.09157, 269.04531, 241.05131 | R |
| 108 | 42.51 | Chrysophanol-8-O-glucoside | C21H20O9 | 415.10346 | 415.10400 | [M − H]− | −1.30 | 253.04984, 225.05618, 209.05959 | R |
| 109 | 42.51 | Emodin | C15H10O5 | 269.04555 | 269.04588 | [M − H]− | −1.22 | 241.05016, 225.05524, 197.06027 | R |
| 110 | 42.53 | Aloe-emodin-O-glucoside | C21H20O10 | 431.09885 | 431.09886 | [M − H]− | −1.14 | 269.04462, 239.03647, 211.02524 | R |
| 111 | 42.61 | Physcion-1-O-glucoside | C22H22O10 | 445.11402 | 445.11460 | [M − H]− | −1.30 | 427.03257, 283.06205, 269.04607 | R |
| 112 | 42.61 | Physcion | C16H12O5 | 283.06120 | 283.06162 | [M − H]− | −1.49 | 283.07696, 268.04557, 240.04266 | R |
| 113 | 42.62 | Hesperetin | C16H14O6 | 303.08631 | 303.08608 | [M + H]+ | 0.77 | 153.01741, 110.04783 | C |
| 114 | 42.85 | Magnatriol | C15H14O3 | 241.08702 | 241.08730 | [M − H]− | −1.17 | 223.07597, 197.09716, 133.06719 | M |
| 115 | 42.97 | Magnolignan E | C18H18O4 | 297.11323 | 297.11365 | [M − H]− | −1.39 | 225.09132, 184.05786, 183.04759 | M |
| 116 | 43.29 | 5-Hydroxy-6,7,3′,4′,5′-pentamethoxyflavone | C20H20O8 | 389.12309 | 389.12283 | [M + H]+ | 0.67 | 374.09631, 359.08221, 356.08174, 328.07931 | C |
| 117 | 43.54 | 5-o-Demethylnobiletin | C20H20O7 | 373.12818 | 373.12781 | [M + H]+ | 0.73 | 358.10001, 343.07224, 325.06554, 297.06973 | C |
| 118 | 43.78 | Demethylnobiletin | C20H20O8 | 389.12309 | 389.12282 | [M + H]+ | 0.79 | 359.08112, 360.07831, 341.06984 | C |
| 119 | 44.32 | Obovatol | C18H18O3 | 281.11832 | 281.11866 | [M − H]− | −1.20 | 267.10174, 249.08513 | M |
| 120 | 44.54 | Sinensetin | C20H20O7 | 373.12818 | 373.12790 | [M + H]+ | 0.74 | 175.01549, 147.03194, 119.01593 | C |
| 121 | 44.59 | Honokiol | C18H18O2 | 265.12340 | 265.12413 | [M − H]− | −0.42 | 224.08126, 223.07514, 197.05923 | M |
| 122 | 44.59 | O-Prenyl-umbelliferone | C14H14O3 | 229.08072 | 229.08726 | [M − H]− | −1.04 | 160.01707, 142.17814 | N |
| 123 | 44.74 | Aloe-emodin | C15H10O5 | 269.04555 | 269.04598 | [M − H]− | −1.60 | 253.05121, 240.04247, 211.03968 | R |
| 124 | 44.94 | Magnaldehyde D | C16H14O3 | 253.08702 | 253.08735 | [M − H]− | −1.32 | 235.07963, 207.08634, 194.04012 | M |
| 125 | 45.13 | Phelloptein | C17H16O5 | 323.08899 | 323.08875 | [M + Na]+ | 0.76 | 269.07627, 231.01796 | N |
| 126 | 45.25 | Notopterol | C21H22O5 | 353.13945 | 353.13988 | [M − H]− | −1.21 | 203.17578, 159.09786, 147.63478 | N |
| 377.13594 | 377.13559 | [M + Na]+ | 0.95 | 205.20652, 161.11072 | |||||
| 127 | 45.38 | Rhein | C15H8O6 | 283.02481 | 283.02504 | [M − H]− | −0.82 | 257.04507, 239.03461, 211.03958 | R |
| 128 | 45.38 | Danthron | C14H8O4 | 239.03498 | 239.03530 | [M − H]− | −1.33 | 186.73096, 141.51394, 130.71196 | R |
| 129 | 45.58 | Nobiletin | C21H22O8 | 403.13874 | 403.13819 | [M + H]+ | 1.41 | 373.09359, 355.08584, 327.08476 | C |
| 130 | 45.69 | Nomilin | C28H34O9 | 515.22756 | 515.22753 | [M + H]+ | 0.05 | 469.21806, 455.20675, 411.21462, 161.05854 | C |
| 131 | 45.88 | Notoptol | C21H22O5 | 353.13945 | 353.13987 | [M − H]− | −1.19 | 225.17472, 207.13978, 189.14075 | N |
| 377.13594 | 377.13563 | [M + Na]+ | 0.97 | 227.19076, 209.14289 | |||||
| 132 | 46.17 | Magnaldehyde E | C16H14O3 | 253.08702 | 253.08735 | [M + H]+ | −1.32 | 225.09424, 184.05624, 183.05074 | M |
| 133 | 46.17 | Magnolol | C18H18O2 | 265.12340 | 265.12394 | [M − H]− | −0.39 | 247.10096, 245.09517, 223.07491 | M |
| 134 | 46.19 | p-Hydroxyphenethyl anisate | C16H16O4 | 295.09408 | 295.09386 | [M + Na]+ | 0.73 | 153.07368, 138.08654 | N |
| 135 | 46.54 | Obovaaldehyde | C16H14O4 | 269.08193 | 269.08215 | [M − H]− | −0.80 | 152.01478, 124.02018 | M |
| 136 | 46.70 | Isosinensetin | C20H20O7 | 373.12818 | 373.12783 | [M + H]+ | 0.94 | 358.10398, 343.08158, 315.08276 | C |
| 137 | 46.70 | Tangeretin | C20H20O7 | 395.11012 | 395.10998 | [M + Na]+ | 0.35 | 278.54947, 276.55982, 243.12708 | C |
3.1 Characterization of flavonoids in SHD
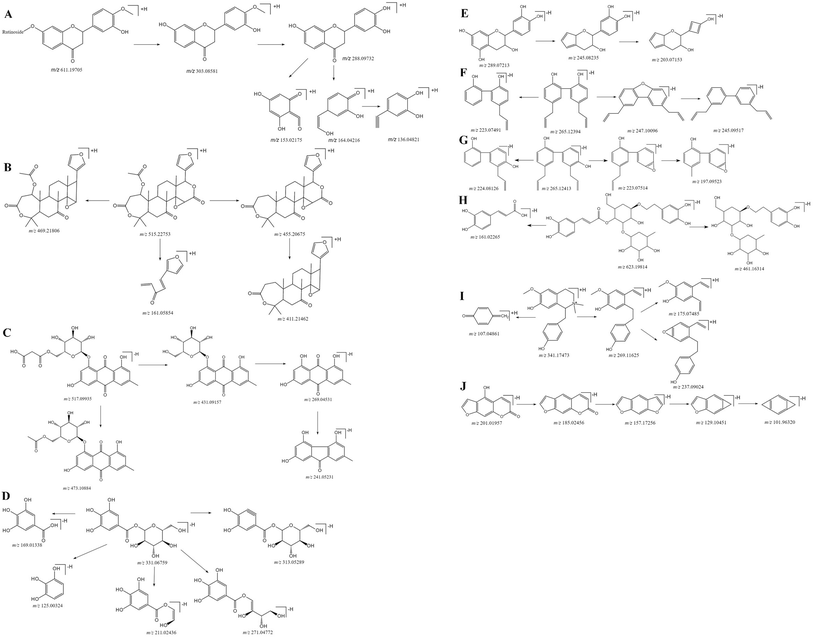
Flavonoids have a typical cyclohexene structure in the C ring, which is unstable and easy to break it for Diels–Alder reaction (RDA), and get the characteristic fragment ions 1,3A and 1,3B. Flavonoid glycosides have methoxy group, firstly losing the glycosyl groups, followed by losing the methyl groups, at last cleavage of the C ring. The mass spectral fragmentation of flavonoids by hesperidin as an example was described. In positive ion mode, adduct ion at m/z 611.19650 ([M + H]+) indicating an elemental composition of C28H34O15. The MS/MS spectrum (Fig. 3A) is presented that the main fragment ions are m/z 449.14312, 303.08581, 288.09732, 153.02175 as well as 136.04821. Among them, m/z 449.14312 and 303.08581 are inferred by cleaving of the glycosidic linkage and losing C6H10O5 (162 Da) or C12H20O9 (308 Da) from the ion of [M − H]+, m/z 288.09732 is the result of losing CH3 (15 Da) from m/z 303.08581, and m/z 153.02175 and m/z 136.04821 was due to the Diels–Alder reaction from m/z 288.09732. The characterization of other flavonoids in SHD was performed based on the fragmentation patterns and related literatures.14–183.2 Characterization of triterpenoids in SHD
Triterpenoids are prone to lose H2O (18 Da), CO (28 Da) and CO2 (44 Da), due to the presence of lactone rings. Nomilin was selected to illustrate the fragmentation pathways. In positive ion mode, adduct ion at m/z 515.22753 ([M + H]+) indicating an elemental composition of C28H34O9. The MS/MS spectrum (Fig. 3B) is presented that the main fragment ions are m/z 469.21806, 455.20675, 411.21462, 161.05854. Among them, m/z 469.21806 is inferred by losing CO and H2O (46 Da) from [M + H]+, m/z 455.20675 is presumed by losing C2H4O2 (60 Da) from [M + H]+, m/z 411.21462 is the result of losing CO2 (44 Da) from m/z 455.20675, and m/z 161.05854 is estimated by losing C18H26O7 (354 Da) from [M + H]+. The characterization of other triterpenoids in SHD was performed based on the fragmentation patterns and related literatures.15,193.3 Characterization of anthraquinones in SHD
The common characteristic of MS2 in anthraquinones is the continuous loss of CO (28 Da). Anthraquinone glycosides can lose glycosyl and CO, continually. Aglycones can be judged by [aglycone − H]−. Anthraquinone glycosides can lose methyl-glucuronide (190 Da), cinnamoyl (148 Da), malonyl (86 Da), acetyl-glucose (204 Da), and glucose (162 Da). Emodin-O-malonylglucose was selected to illustrate the fragmentation pathways. In negative ion mode, adduct ion at m/z 517.09935 ([M − H]−) indicating an elemental composition of C24H22O13. The mass spectrum (Fig. 3C) shows that the main fragment ions are m/z 473.10884, 431.09157, 269.04531 and 241.05131. Among them, m/z 473.10884 is presumed by losing of CO2 (44 Da) from [M − H]−, m/z 431.09157 is inferred by losing of the C3H2O3 (86 Da) from [M − H]−, and m/z 269.04531 is speculated by cleaving of the glycosidic linkage and losing C6H10O5 (162 Da) from m/z 431.09157, m/z 241.05131 is the result of losing CO (28 Da) at m/z 269.04531. The characterization of anthraquinone compounds in SHD is inferred from this cleavage rule and related literatures.20,213.4 Characterization of glucosides in SHD
Glucosides are formed by the esterification of acid with glucose. According to the type of acid, it can be divided into cinnamoyl-glucose, dihydrocinnamoyl-glucose, p-cinnamoyl-glucose, dihydro-p-cinnamoyl glucose, galloyl-glucose, and resveratrol-galloyl-glucose in rhubarb. They are vulnerable to loss of neutral fragments 148 Da, 150 Da, 164 Da, 166 Da, 170 Da, and 228 Da, respectively. Galloyl-glucose was selected to illustrate the fragmentation pathways. In negative ion mode, adduct ion at m/z 331.06759 ([M − H]−) indicating an elemental composition of C13H16O10. The mass spectrum (Fig. 3D) shows that the main fragment ions are m/z 313.05289, 271.04772, 211.02436, 169.01338, and 125.00325. Among them, m/z 313.05289 is presumed by losing H2O (18 Da) from [M − H]−, m/z 271.04772 is inferred by losing C2H4O2 (60 Da) from [M − H]−, m/z 211.02436 is the result of losing C4H8O4 (120 Da) from [M − H]−, m/z 169.01338 is speculated by cleaving of the glycosidic linkage and losing glucose C6H10O5 (162 Da) from [M − H]−, and m/z 125.00325 is deduced by losing CO2 (44 Da) from m/z 169.01338. The characterization of glucosides in SHD is concluded by referring to the cleavage rule and related literature.213.5 Characterization of epicatechin in SHD
Epicatechin was selected to illustrate the fragmentation pathways for catechins. The adduct ion at 289.07213 ([M − H]−) indicating an elemental composition of C15H14O6, and the MS/MS spectrum (Fig. 3E) is presented that the main fragment ions are m/z 245.08235, 203.07153. Among them, m/z 245.08235 is presumed by losing CO2 (44 Da) from [M − H]−, and m/z 203.07153 is inferred by losing of C2H2O (42 Da) from m/z 245.08235. The characterization of catechins in SHD is concluded by referring to the cleavage rule and related literatures.21–233.6 Characterization of lignans in SHD
Most of the lignans have the presence of allyl and hydroxyl groups, which relative positions are different, their cleavage methods will be different. Honokiol and magnolol were selected to illustrate the fragmentation pathways. Magnolol showed m/z 265.12394 ([M − H]−) in the negative ion mode, which indicated the elemental composition of C18H18O2. The mass spectrum (Fig. 3F) shows that the main fragment ions are m/z 247.10096, 245.09517, 223.07491. Among them, m/z 247.10096 is presumed by losing H2O (18 Da) from [M − H]−, m/z 245.09517 is inferred by losing H2 (2 Da) from m/z 247.10096, and m/z 223.07491 is obtained by losing C3H6 (42 Da) from [M − H]−. Honokiol showed m/z 265.12413 ([M − H]−) in the negative ion mode, which indicated the elemental composition of C18H18O2. The mass spectrum (Fig. 3G) shows that the main fragment ions are m/z 224.08126, 223.07514, 197.05923. Among them, m/z 224.08126 is presumed by losing C3H5 (41 Da) from [M − H]−, m/z 223.07514 is inferred by losing C3H6 (42 Da) from [M − H]−, and m/z 197.05923 is obtained by losing of C2H2 (26 Da) by m/z 223.07514. The characterization of lignans in SHD is concluded by referring to the cleavage rule and related literatures.24,253.7 Characterization of phenylpropanoid glycosides in SHD
The phenylpropanoid glycosides are composed of glucose and phenethyl alcohol, which mainly based on the loss of coffee groups (162 Da). Verbascoside is chosen as an example to explain the cleavage pathway. It showed m/z 623.19814 ([M − H]−) in the negative ion, which indicated an elemental composition of C29H36O15. The mass spectrum (Fig. 3H) shows that its main fragment ion is m/z 461.16314, 161.02265. Among them, m/z 461.16314 is presumed by losing C9H6O3 (162 Da) from [M − H]−, and m/z 161.02265 is inferred by losing C20H30O12 (462 Da) from [M − H]−. The characterization of phenylpropanoid glycosides in SHD is concluded by referring to the cleavage rule and related literatures.24,253.8 Characterization of alkaloids in SHD
The main rupture method of alkaloids is the loss of N. (R)-Oblongine is chosen as an example to explain the cleavage pathway. It showed an m/z 314.17473 ([M + H]+) in the positive ion mode, which indicated the elemental composition of C19H24NO3+. The mass spectrum (Fig. 3I) shows that the main fragment ions are m/z 269.11625, 237.09024, 175.07485, 107.04861. Among them, m/z 269.11625 is presumed by losing C2H6NH (45 Da) from [M + H]+, m/z 237.09024 is inferred by losing CH4O (32 Da) at m/z 269.11625, m/z 175.07485 is obtained by losing C6H6O (94 Da) from m/z 269.11625, and m/z 107.04861 is speculated by losing C12H18NO2 (207 Da) from [M + H]+. The characterization of alkaloids in SHD is concluded by referring to the cleavage rule and related literature.253.9 Characterization of coumarins in SHD
The main cleavage mode of coumarins is loss of CO and CO2, while coumarin glycosides lose glucose firstly, and then break by the above-mentioned cleavage law. Bergaptol is chosen as an example to explain the cleavage pathway. It showed an m/z 201.01957 ([M − H]−) in the negative ion mode, which indicated an elemental composition of C11H6O4. The mass spectrum (Fig. 3J) shows that the main fragment ions are m/z 185.02456, 157.17256, 129.10451, 101.96320. Among them, m/z 185.02456 is presumed by losing OH (17 Da) from [M − H]−, m/z 157.17256 is presumed by losing CO (28 Da) from m/z 185.02456, m/z 129.10451 is inferred by losing CO (28 Da) from m/z 157.17256, and m/z 101.96320 is obtained by losing CO (28 Da) from m/z 129.10451. The characterization of coumarins in SHD is concluded by referring to the cleavage rule and related literatures.26–284. Conclusions
In our study, a rapid, swift and straightforward analytical method with the help of UHPLC-FT-ICR-MS/MS was successfully developed for the first time to separate and identify the chemical constituents of SHD. A total of 137 compounds in SHD were identified or tentatively characterized, and 11 compounds were accurately identified by reference. The research indicated that SHD mainly contains 42 flavonoids (in Aurantii fructus immaturus and Rheum palmatum L.), 3 triterpenoids (in Aurantii fructus immaturus), 23 anthraquinones (in Rheum palmatum L.), 14 glucosides, 5 catechins and 2 anthranone (in Rheum palmatum L.), 11 phenylpropanoid glycosides, 5 alkaloids and 11 lignans (in Magnoliae Officmalis Cortex), 16 coumarins (in Notopterygii Rhizoma Et Radix and in Aurantii fructus immaturus),which has laid the foundation for prospective research associated with SHD. And it is hoped to be useful to identify and characterize the components in other TCMs. And it provided a basis for finding the prototype components and metabolites in the serum of containing SHD.In this study, the structure of the compound, except for the comparison of the reference, was obtained through the combination of retention time, accurate primary and secondary mass spectrometry information, cracking rules of the same compound and literature comparison. The identification of compound structure by this method is limited to known compounds, because this method only mass spectrometry for identification.
Abbreviations
| TCMs | Traditional Chinese medicines |
| SHD | Sanhua decoction |
| Zhishi | Aurantii fructus immaturus |
| Dahuang | Rheum palmatum L |
| Houpu | Magnoliae Officmalis Cortex |
| Qianghuo | Notopterygii Rhizoma Et Radix |
| BBB | Brain blood barrier |
| UHPLC-FT-ICR-MS/MS | Ultra high performance liquid chromatography coupled with Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry |
| BPC | Base peak ion chromatograms |
| EIC | Extract ion chromatograms |
| RDA | Diels–Alder reaction |
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the facilities and assistance provided by Dr Fei Han of the Bruker Corporation.References
- L. Zhang, J. B. Yan, X. M. Liu, Z. G. Ye, X. H. Yang, R. Meyboom, K. Chan, D. Shaw and P. Duez, J. Ethnopharmacol., 2012, 140, 519–525, DOI:10.1016/j.jep.2012.01.058.
- C. Zhang, G. Q. Zheng and H. J. Huang, Chin. J. Integr. Tradit. West. Med. Intensive Crit. Care, 2007, 6, 352–356, DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1008-9691.2007.06.009.
- J. Bi, H. Zhang, J. Lu and W. Lei, Mol. Med. Rep., 2016, 14, 5408–5414, DOI:10.3892/mmr.2016.5919.
- Y. Ma, X. Xia, J. M. Cheng and Y. Q. Kuang, Neurochem. Res., 2014, 39, 1809–1816, DOI:10.1007/s11064-014-1395-y.
- X. Liu, X. Chen, Y. Zhu, K. Wang and Y. Wang, Metab. Brain Dis., 2017, 32, 1109–1118, DOI:10.1007/s11011-017-0004-6.
- X. Wu, Y. B. Zhang, L. Zhang and X. W. Yang, J. Chromatogr. B: Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci., 2018, 1092, 244–251, DOI:10.1016/j.jchromb.2018.06.006.
- S. Forcisi, F. Moritz, B. Kanawati, D. Tziotis, R. Lehmann and P. Schmitt-Kopplin, J. Chromatogr. A, 2013, 1292, 51–56, DOI:10.1016/j.chroma.2013.04.017.
- D. F. Smith, A. Kiss, F. E. Leach, E. W. Robinson, L. PasaTolic and R. M. Heeren, Anal. Bioanal. Chem., 2013, 405, 6069–6076, DOI:10.1007/s00216-013-7048-1.
- Y. N. Wang, M. Zhao, Y. B. Yu, M. Wang and C. J. Zhao, RSC Adv., 2016, 6, 39642–39651, 10.1039/c6ra01428c.
- Y. N. Wang, M. Zhao, Y. F. Ou, B. W. Zeng, X. Y. Lou, M. Wang and C. J. Zhao, J. Chromatogr. B: Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci., 2016, 1020, 120–128, 10.1039/c6ra01428c.
- Y. Li, Y. Y. Zhao, X. Li, T. F. Liu, X. W. Jiang and F. Han, J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal., 2017, 149, 318–328, DOI:10.1016/j.jpba.2017.10.032.
- Z. Guan, M. Wang, Y. Cai, H. M. Yang, M. Zhao and C. J. Zhao, J. Chromatogr. B: Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci., 2018, 1086, 11–22, DOI:10.1016/j.jchromb.2018.04.009.
- T. Liu, X. M. Tian, Z. Q. Li, F. Han, B. Ji, Y. L. Zhao and Z. G. Yu, J. Chromatogr. B: Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci., 2018, 1079, 69–84, DOI:10.1016/j.jchromb.2018.02.001.
- H. F. Chen, W. G. Zhang, J. B. Yuan, Y. G. Li, S. L. Yang and W. L. Yang, J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal., 2012, 59, 90–95, DOI:10.1016/j.jpba.2011.10.013.
- Y. He, Z. Li, W. Wang, S. Sooranna, Y. Shi, Y. Chen, Y. Chen, C. Q. Wu, J. G. Zeng, Q. Tang and H. Q. Xie, Molecules, 2018, 23, 2189, DOI:10.3390/molecules23092189.
- R. Tong, M. Peng, C. Tong, K. K. Guo and S. Y. Shi, J. Chromatogr. B: Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci., 2018, 1077–1078, 1–6, DOI:10.1016/j.jchromb.2018.01.031.
- W. Y. Liu, C. Zhou and C. M. Yan, Chin. J. Nat. Med., 2012, 10, 456–463, DOI:10.1016/S1875-5364(12)60087-9.
- X. J. Zhao, Q. Q. Liu and T. Xing, J. Southwest Jiaot. Univ., 2018, 40, 20–29, DOI:10.13718/j.cnki.xdzk.2018.11.003.
- Y. Jiang, R. Liu, J. Chen, M. Liu, B. Liu, L. Z. Yi and S. Liu, J. Chromatogr. A, 2019, 1600, 197–208, DOI:10.1016/j.chroma.2019.04.051.
- Y. Liu, L. Li, Y. Q. Xiao, J. Q. Yao, P. Y. Li, D. R. Yu and Y. L. Ma, Food Chem., 2016, 192, 531–540, DOI:10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.07.013.
- L. Zhang, H. Y. Liu, L. L. Qin, Z. X. Zhang, Q. Wang, Q. Q. Zhang, Z. W. Lu, S. L. Wei, X. Y. Gao and P. F. Tu, J. Sep. Sci., 2015, 38, 511–522, DOI:10.1002/jssc.201400971.
- J. Han, M. Ye, M. Xu, X. Qiao, H. B. Chen, B. R. Wang, J. H. Zheng and D. A. Guo, Planta Med., 2008, 74, 873–879, DOI:10.1097/BCR.0b013e31818480b8.
- Y. Li, M. Wang, Q. Zhang, Y. Tian, F. G. Xu and Z. J. Zhang, Anal. Methods, 2014, 6, 1720–1727, 10.1039/c3ay41986j.
- K. Guo, C. Tong, Q. Fu, J. Xu, S. Shi and Y. Xiao, J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal., 2019, 170, 153–160, DOI:10.1016/j.jpba.2019.03.044.
- K. P. Sun, K. M. Qin, W. D. Li, S. Y. Peng, J. Jin, B. Yang and B. C. Cai, World Chin. Med., 2019, 14, 287–291, DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1673-7202.2019.02.007.
- Y. H. Li, S. Y. Jiang, Y. L. Guan, X. Liu, L. M. Zhou, S. X. Huang, H. D. Sun, S. L. Peng, Y. Zhou, 2006, 64, 405–411. DOI:10.1365/s10337-006-0052-2.
- K. Xu, S. Jiang, Y. Zhou, B. Xia, X. Xu, Y. Zhou, Y. Li, M. Wang and L. Ding, J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal., 2011, 56, 1089–1093, DOI:10.1016/j.jpba.2011.07.034.
- X. Liu, S. Jiang, K. Xu, H. Sun, Y. Zhou, X. Xu, J. Yi, Y. Gu and L. S. Ding, J. Ethnopharmacol., 2009, 126, 474–479, DOI:10.1016/j.jep.2009.09.011.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available. See DOI: 10.1039/d0ra02264k |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2020 |