Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleCreative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported Licence
DOI: 10.1039/D0RA90112A
(Correction)
RSC Adv., 2020, 10, 41249-41249
Correction: Exploring the antifouling effect of elastic deformation by DEM–CFD coupling simulation
Limei Tiana,
E. Jina,
Jianfu Wanga,
Xiaoming Wanga,
Wei Bing*ab,
Huichao Jina,
Jie Zhaoa and
Luquan Rena
aKey Laboratory of Bionic Engineering (Ministry of Education), Jilin University, No. 5988 Renmin Street, Changchun 130022, China. E-mail: lmtian@jlu.edu.cn
bAdvanced Institute of Materials Science, Changchun University of Technology, Changchun 130012, P. R. China. E-mail: bingwei@ccut.edu.cn
Received
20th October 2020
, Accepted 20th October 2020
First published on 11th November 2020
Abstract
Correction for ‘Exploring the antifouling effect of elastic deformation by DEM–CFD coupling simulation’ by Limei Tian et al., RSC Adv., 2019, 9, 40855–40862, DOI: 10.1039/C9RA06761B.
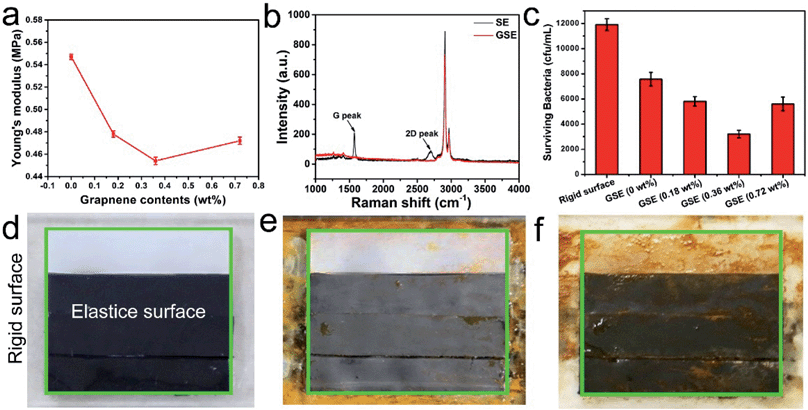
The authors regret that Fig. 2e and f in the original article displayed incorrect images. The correct version of Fig. 2 is given below. These changes do not affect the overall conclusions of the article.
The Royal Society of Chemistry apologises for these errors and any consequent inconvenience to authors and readers.
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2020 |