Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleRepresentative 2D-material-based nanocomposites and their emerging applications: a review
Akeel Qadir†
 ab,
Top Khac Le†
ab,
Top Khac Le† c,
Muhammad Malik†d,
Kossi Aniya Amedome Min-Dianeye,
Imran Saeedf,
Yiting Yu
c,
Muhammad Malik†d,
Kossi Aniya Amedome Min-Dianeye,
Imran Saeedf,
Yiting Yu ab,
Jeong Ryeol Choi*g and
Phuong V. Pham
ab,
Jeong Ryeol Choi*g and
Phuong V. Pham *h
*h
aResearch Center of Smart Sensing Chips, Ningbo Institute of Northwestern Polytechnical University, Ningbo 315103, China
bKey Laboratory of Micro/Nano Systems for Aerospace (Ministry of Education), Shaanxi Province Key Laboratory of Micro and Nano Electro-Mechanical Systems, Department of Microsystems Engineering, Northwestern Polytechnical University, Xi'an 710072, China
cDepartment of Physics and Energy Harvest Storage Research Center, University of Ulsan, Ulsan 44610, South Korea
dDepartment of Electrical Engineering and Technology, Government College University, Faisalabad 38000, Pakistan
eDépartement de Physique, Faculté Des Sciences (FDS), Université de Lomé, Lomé 01BP1515, Togo
fInstitute of Aviation Studies, University of Management and Technology, Lahore 54000, Pakistan
gDepartment of Nanoengineering, Kyonggi University, Suwon 16227, South Korea. E-mail: choiardor@hanmail.net
hZJU-Hangzhou Global Scientific and Technological Innovation Center (HIC), School of Micro-Nano Electronics, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310027, China. E-mail: phuongpham@zju.edu.cn
First published on 7th July 2021
Abstract
Composites (or complex materials) are formed from two or many constituent materials with novel physical or chemical characteristics when integrated. The individual components can be combined to create a unique composite material through mechanical transfer, physical stacking, exfoliation, derivative chemical mixtures, mixtures of solid solutions, or complex synthesis processes. The development of new composites based on emerging 2D nanomaterials has allowed for outstanding achievements with novel applications that were previously unknown. These new composite materials show massive potential in emerging applications due to their exceptional properties, such as being strong, light, cheap, and highly photodegradable, and their ability to be used for water splitting and energy storage compared to traditional materials. The blend of existing polymers and 2D materials with their nanocomposites has proven to be immediate solutions to energy and food scarcity in the world. Although much literature has been reported in the said context, we tried to provide an understanding about the relationship of their mechanisms and scope for future application in a comprehensive way. In this review, we briefly summarize the basic characteristics, novel physical and chemical behaviors, and new applications in the industry of the emerging 2D-material-based composites.
1. Introduction
A composite material is formed by mixing at least two materials, often with different properties, resulting in unique output characteristics compared to the single material, i.e., a high strength-to-weight ratio, low density, high modulus, excellent fatigue resistance, improved creep rupture strength, superior corrosion prevention, and low coefficient of thermal expansion.1 The development and advancement of next-generation composite materials have been widely observed in the aerospace industry and the mechanical industry, construction industry, biomedical industry, automobile industry, optoelectronic industry, and electrical and electronic packaging industry.2 An additional benefit of composite materials is customization because they can transform into complex shapes.Two-dimensional (2D) materials are composed of multiple thin layers. These layers are weekly coupled through van der Waals interactions. A single-atom-thick layer usually has a thickness of few nanometres. Electrons in these layers are free to move in the 2D plane, but quantum mechanics governs their restricted motion in the third direction. These materials can be further classified as the zero-dimensional (0D), e.g., quantum dots; one-dimensional (1D), e.g., nanoribbons, nanotubes, and nanowires; two-dimensional (2D) monolayer materials, e.g., single-atom graphene sheets; and three-dimensional (3D), e.g., nanoballs and nanocones. Materials such as graphene, transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDs), quantum dots, transition metal oxides (TMOs), graphitic C3N4, 2D clay materials, hexagonal boron nitride (hBN), black phosphorus (BP), silicene, and germanene are made up entirely of their surface and are often only a single atom thick, falling in the 2D material category. A composite made of these 2D materials is called a 2D material composite. The typical traditional materials and composites, i.e., metals, wood, reinforced plastics, fiber-reinforced, fiberglass, Kevlar, carbon fiber, and polymers, have been overcome by these new 2D materials. These new 2D materials have been emerged as potential candidates for next-generation devices due to their exceptional mechanical strength, flexibility, and rigidity, as well as their enhanced electrical and optical properties.3–23 Notably, recent advances in growth techniques enable high-uniformity and large-area 2D materials, which lower the production cost and enhance the quality of 2D-based devices.24,25 The engineering of 2D composited materials needs systematic and interactive strategies to achieve the optimum material properties. This process demands the application of several methods and technologies for the (i) investigation of the specific mechanical, electrical, optical, chemical, and physical properties of composited materials; (ii) analysis of the design, manufacturing, and composition influences on the material characteristics; (iii) optimization of the material characteristics according to the appropriate working condition and application, e.g., prediction of material efficiency/reliability; and (iv) development of quantitative characterization approaches and analysis in the sense of various working conditions.26
Composites are gaining a considerable amount of attention due to their outstanding properties. As seen in Fig. 1, since the last decade of the 21st century, the interest of the 2D material research community in composite materials, illustrated in annual publications, has remarkably increased. In relation to semiconductors, group transition metal dichalcogenides, e.g., MX2, have been intensively studied, most likely due to their quantum confinement effect-induced variation in electric, optical, and chemical properties.3,4,24,25 For example, the chemical reactivity of MX2 is site-dependent; i.e., the edge of TMDs with abundant active sites is more chemically reactive than the basal plane, thus effectively producing more hydrogen.25 Moreover, the high surface-to-volume ratio of 2D material is also a primary advantage when it is composited. For instance, the application of carbon-encapsulated Fe3O4 nanoparticles (NPs) as a high-rate lithium-ion battery anode material is known to be beneficial for next-generation batteries.27
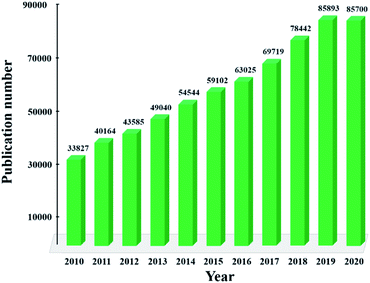 | ||
| Fig. 1 Publications on 2D-material-based composites from 2010 to 2020. Source: ISI Web of Science (search: “2D Composites”). | ||
The 2D-material-based composites exhibited various boosted properties, such as improved mechanical strength and flexibility, enhanced electrical conductivity, high optical transparency, high resistance to chemicals and fire, high strength-to-weight ratios, wear resistance, and corrosion resistance.4,27–31 Herein, we present a short review of 2D-material-based composites and their characterizations, classifications, and advantages regarding physics and mechanics related to recent studies. While the novelty of nanocomposites in previous reports has lied on only several proper aspects, either 2D materials or single applications that forming 2D composites such as biocomposites, fiber-reinforced composites and hybrid composites, gas sensing,28 battery,32,33 only graphene,34–37 carbon nanotubes (CNTs) and MXenes for energy storage,38 strain sensor,39,40 mechanics,41 metal,42 protein,43 dentistry,44 orthopaedic and bone,45 polymer,46,47 humid sensor,48 or biology;49 in this review article, we would like to emphasize in other aspects that formed new nanocomposites based on polymers and metals as well as the latest achievements of new synthesized-2D materials enabling to fabricate new nanocomposite species. In addition, the representative applications on strain engineering, thermal characters, photocatalyst and water splitting, optoelectronics, solar energy, and other promising applications (e.g., degradation of organic pollutants, enhanced strength and stiffness) are pointed out. In particular, the representative fabrication techniques and applications on the latest achievements of new 2D materials are addressed. Science and modern technology have been always looking for possible solutions for the ever-growing need for energy and fuel resources. The industrial revolution has brought a big challenge for technologists to provide new opportunities for energy production, harvesting, and conservation. As we discussed previously, there is a significant role of novel materials-based composites for solving major challenges faced by humanity. We will present a brief overview of the contribution of nanocomposites specifically for energy-related applications, for example, photocatalysis, water splitting, and solar energy. Today, it is necessary to discover new nanocomposite assemblies that could integrate artificial and natural materials by implementing modern manufacturing processes. The classification of 2D composites, including carbon; graphene; polymers; and ceramic, metal, and bio-based materials, is shown in Fig. 2.
2. Composite classifications
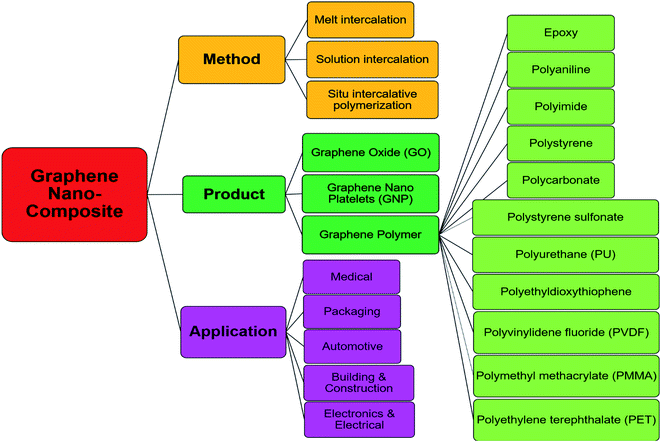
2.1 Polymer-based composites
Polymer composite is composed of more than two phases, such as polymer/polymer or filler (metal or fiber)-based polymer composite. Compared to traditional materials such as ceramic and clay, polymer composites were developed later. They have been widely used in the electronics, food packaging industry, and medical industry due to their low cost, low density, corrosion resistance, easy design, and processing. Traditional polymer fillers such as metals and minerals are in macroscale, which have been widely used in various applications. However, these additives cannot remarkably improve the properties due to the limited interfacial structure between them and the matrix. To further enhance the performance of the composites, reducing the size of fillers into microscale and nanoscale the primary strategy. Carbon being a nano-sized material, have the novel ability to form a covalent bond with other atoms, and due to this ability, various carbon species usually include polymer composite. Graphene is a 2D material that also belongs to the carbon family, dominates the entire 2D family, and has been studied a lot for various aspects since its discovery in 2004. Thin-film graphene can be synthesized by multiple means, e.g., chemical vapor deposition (CVD), chemical or plasma exfoliation from natural graphite, and mechanical cleavage using scotch tape.16,50 However, for graphitic oxide, Hummers et al. developed a rapid, relatively safe method by treating graphite with essentially a water-free mixture of concentrated sulfuric acid, sodium nitrate, and potassium permanganate graphite.51 Fig. 3 summarizes some methods, products, and applications of graphene composites.Liu et al. synthesized a series of 0D, 1D, and 2D WS2 mixed with graphene oxide (GO) and reduced graphene oxide (RGO) nanosheets and then employed vacuum filtration to form WS2/GO and WS2/RGO composites,32 as shown in Fig. 4A and B. The WS2/RGO composite exhibits excellent cyclic stability (100 cycles) and a high-rate capability 697.7 mA h g−1. This composite structure not only revealed higher ability than pure WS2 but also showed high reversible capacity. On the other hand, Chen et al. prepared a composite by integrating WS2 (few-layer sheets) and nitrogen-doped graphene (WS2/NG) via facile surfactant-assisted synthesis under hydrothermal conditions high transportation of electrons. The performance as a high energy density lithium-ion battery anode was evaluated (from 100 to 5000 mA g−1). They found that the performance of the composite was dependent on the number of WS2 layers. The best cyclability (average of only 0.08% capacity fade per cycle for 100 cycles) was achieved when the composite formed with a surfactant![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) tungsten precursor ratio of 1
tungsten precursor ratio of 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1.33 A schematic illustration is shown in Fig. 4C. Multifunctional graphene nanocomposites exhibit more substantial enhancement at considerably low loading than conventional composites.34 This leads to potential multifunctional applications.
1.33 A schematic illustration is shown in Fig. 4C. Multifunctional graphene nanocomposites exhibit more substantial enhancement at considerably low loading than conventional composites.34 This leads to potential multifunctional applications.
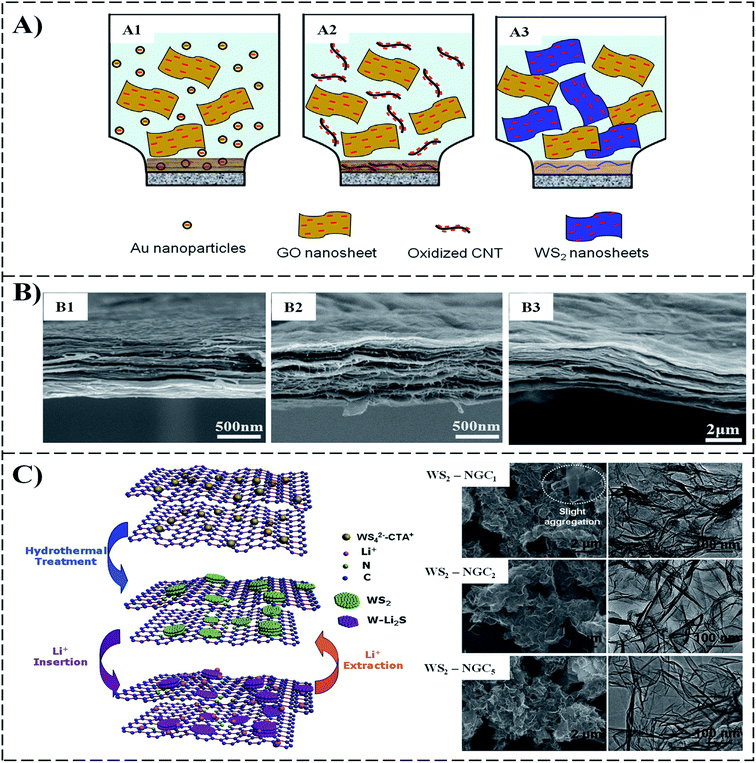 | ||
| Fig. 4 (A) Schematic illustration formation negatively like-charged, (A1) Au/GO, (A2) CNT/GO, (A3) WS2/GO lamellar composite films by direct filtration. (B) Cross-section SEM images of, (B1) Au/GO, (B2) CNT/GO and (B3) WS2/rGO WG-2-1 films,32 (C) schematic illustration, SEM and TEM of the preparation of WS2–NG composites.33 | ||
Nanocomposites are used to combine different nanoscale materials to achieve optimal material properties. Nanocarbon-based composite materials showed enhanced electrochemical, bacterial detection, gas sensing, chemical sensing, strain/pressure sensing, energy storage, and organic electrolyte properties, which are advantageous for various applications.28,38,39,52–57 Conductive graphene composites are made by adding graphene to matrix materials, such as polymers and metal, using a specific method to produce a conductive composite. Their dependence on the conductive filler characterizes the electrical conductivity of composites. The high content ratio of conductive fillers enhances the transport of free electrons inside the material, which leads to an increase in electrical conductivity. This also improves the physicochemical qualities of the host matrix/material. Some experimental results show that the host matrix can enhance its electrical and mechanical properties better than other composites, e.g., carbon nanotubes (CNTs) or clay.58 Consequently, graphene-based composites reveal various advantageous properties, such as high electrical and thermal conductivity, enhanced mechanical properties, and improved flame retardant and gas barrier properties.35,36,59,60
One possible way to bond these novel properties for applications is to integrate graphene sheets into a composite material. The production of such composites requires graphene sheets to be unified and equally scattered over a sufficient scale into various matrices. Stankovich et al. reported a bottom-up chemical method to tune graphene sheet properties via a solution mixture of exfoliated (chemical reduction) phenyl isocyanate-treated graphite oxide sheets with polystyrene (PS)37 (see Fig. 5). This PS–graphene composite showed a percolation threshold of ∼0.1 vol% and conductivity of ∼0.1 S m−1 at room temperature, which was sufficient for various electrical applications. Xie et al. prepared a graphene-based conductive polymer composite via the mixture of a solution containing GO and a PVA precursor. The RGO was fabricated by employing the γ-ray irradiation of GO through the water/ethanol mixture. The composite films revealed good electrical conductivity and visible transmittance.
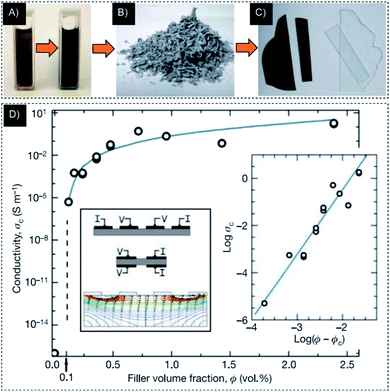 | ||
Fig. 5 (A) Suspension of phenylisocyanate-treated GO and dissolved polystyrene in DMF before/after a reduction through N,N-dimethylhydrazine. (B) The fabricated composite powder via coagulation in methanol. (C) Hot-pressed graphene-based composite and pure polystyrene processed in the same way. (D) The conductivity of composite as a function of filler volume fraction. Right inset, log![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) σc plotted against log(Φ − Φc).37 σc plotted against log(Φ − Φc).37 | ||
Xuejiao et al.61 obtained novel flexible and conductive polylactic acid–cellulose nanofibril–graphene/polypyrrole (PLA–CNF–GR/PPy) composite films by adding cellulose nanofibril (CNF) and graphene powder into polylactic acid (PLA)/polypyrrole (PPy) composite through inexpensive, eco-friendly, low-temperature, and polymerization synthesis. The proposed conductive film exhibited many unique properties, e.g., high enhanced tensile strength (5.6%), thermal stability, and high conductivity. In addition, the electrical conductivity of the proposed composite film was improved from 0.12 to 1.06 S cm−1 and demonstrated high flexible stability, with only 7.5% deviation after ∼100 bendable cycles. The novel conductive composite represents a new field of potential applications of biodegradable materials and could be considered for use in sensors, flexible electrodes, and flexible displays in future electronics.
Graphene-based devices and composites are subjected to the doping of graphene to enhance the material's electrical conductivity. In this regard, Fan et al.62 proposed highly conductive few-layer graphene (FLG)-based composites, exhibiting vastly enhanced electrical conductivity from 1.4 × 103 to 2.1 × 103 S m−1 by adding 4.42–5.1 vol% FLG. The dopant type and level could be manipulated by incorporating FLG as matrixes. Here, three metal oxides with various oxygen vacancies (α-Al2O3, 3% mol yttria-stabilized zirconia, and 8% mol yttria-stabilized zirconia) were employed as matrix materials to form this nanocomposite.
For electrochemical energy storage devices, enlightening the availability of ions in the electrodes is important for rate performance and charge storage. Gao et al.38 synthesized Mxene@CNTs by using knotted CNTs to break 2D layers of Mxene Ti3C2, as shown in Fig. 6A. This structure can improve the capacitance (reaching 130 F g−1 (276 F cm−3)) in organic electrolytes. Zhao et al.53 successfully prepared the LiMn2O4-based composite microspheres using a spray-drying technique with nanosized LiMn2O4 particles as host materials and VXC-72R NPs as a dispersing agent embedded with nanocarbon black (VXC-72R) particles and exhibiting a high initial discharge capacity of 127.4 mA h g−1 with good cycling stability at 0.5 °C. Recently, nanocarbons, including nanosheets (CNShs), carbon nanotubes (CNTs), and nanoboxes (CNBxs), have attracted the attention of composite researchers. Xu et al. synthesized carbon-coated troilite FeS (C@FeS) of different morphologies (NPs, nanosheets, and nanoplates) with the surfactant-assisted solution-based method,64 as shown in Fig. 6B. The concentration of 1-dodecanethiol and temperate treatment are used to control the morphologies that form NPs, nanosheets, and nanoplates with a low concentration at 180 °C, a high concentration at 220 °C, and a higher concentration at 280 °C, respectively. The C2FeS nanosheet exhibited exceptional Li storage properties with good stability (charge/discharge cyclability) and a high specific capacity that reaches 233 mA h g−1 during one hundred cycles at fast charge/discharge rates. General polymers usually synthesize thermo- or thermosetting-plastics with metal fiber, carbon, glass, and so on.30,31,65,66 Thermoset composites are manufactured by mixing hard resin to achieve higher strength and higher temperature resistance than thermoplastics.41,67,68 Zhi et al.69 fabricated polymethyl methacrylate/boron nitride nanosheet (PMMA/BNNS) transparent composites. As a result, the elastic modulus and strength of PMMA were improved to 22% and 11% with 0.3 wt% BNNS fractions, respectively.
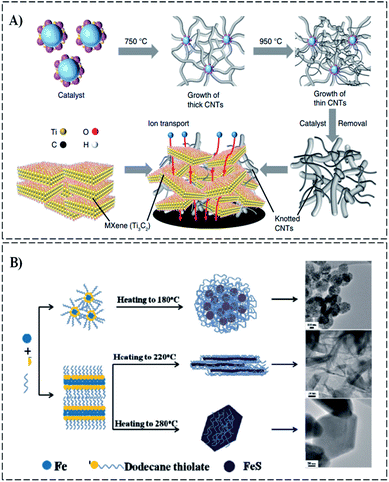 | ||
| Fig. 6 (A) Schematical growth of CNTs and the formation of MXene-knotted CNT composite electrode.38 (B) Schematical growth mechanism of C@FeS composites with the carbon layer and FeS nanoparticles (NPs), nanosheets, and nanoplates.63 | ||
Recently, some conductive polymers, such as poly(3-hexylthiophene-2,5-diyl) (P3HT), phenyl-C61-butyric-acid-methyl ester (PCBM), polythiophene (PTH), and polyaniline (PANI), have been studied for application in heterojunction devices. Cho et al.70 successfully synthesized edge-selectively functionalized graphene/polyamide 6 (EFG/PA6) composites. The electrical conductivity of EFG/PA6 was strongly improved compared with initial graphite, ball-milled graphene, and nanoplatelet graphene. Liu et al.71 synthesized mesoporous conductive polymer using mixture block copolymer micelles and 2D electrochemically exfoliated graphene, GO, MoS2, and titania nanosheets. Fig. 7 illustrates the schematic of the polymer-based composite using a single GO layer. These conductive polymers exhibit improved electrochemical capacitance and rate performance.
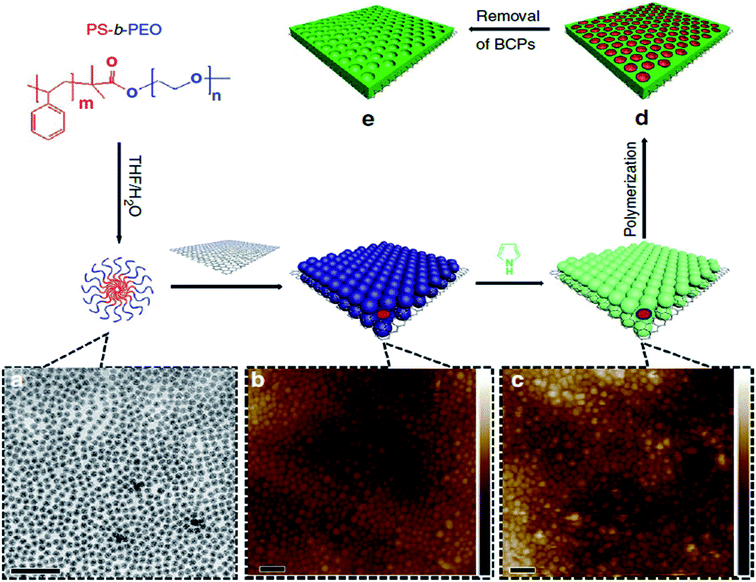 | ||
| Fig. 7 Schematic of fabricating of 2D mesoporous conductive polymers. (a) TEM image and formation process of spherical BCP. (b) AFM image and the self-assembled BCP micelles on GO surface. (c) AFM image and co-assembly of BCP micelles and pyrrole monomers on GO surface. (d) Polymerization of pyrrole monomers on the addition of ammonium persulfate initiator. (e) Mesoporous polypyrrole (PPy) nanosheets.71 | ||
2.2 Metal-based composites
The matrix material uses metallic nanomaterials such as Mg, Cu, Ag, Al, Ni, and Ti to form a 2D metal composite.72 Al-based composites are popularly applied in the automobile and aerospace industries due to their outstanding properties, such as low density and thermal expansion, superior stiffness strength, and improved wear resistance.42,73,74 In addition, Ag-based composites are the most widely used in electric devices due to their high electric conductivity.72 Deng et al.75 obtained a sandwich-stacked SnO2/Cu hybrid nanosheet by rolling and compressing a SnO2/Cu layer with carbon black. The stacked SnO2/Cu nanosheet (Fig. 8) reveals the tight clamp between the layers. Pan et al.76 prepared a composite of Ag particles and MoS2 using the sonication method and a multifunction organic ligand. The MoS2 sheets were obtained by exfoliating MoS2 powder under sonication. SEM and TEM image results show that the Ag particles were anchored and uniformly distributed on the surface of MoS2 nanosheets.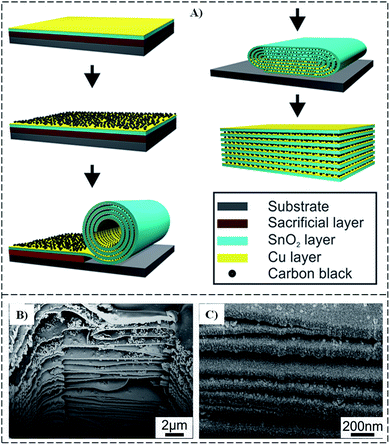 | ||
| Fig. 8 (A) Schematic illustration and (B and C) cross-sectional SEM images of SnO2/Cu hybrid nanosheets.75 | ||
3. Bio-composites
Novel composites from the equivalent combination of 2D materials and biomaterials in biotechnology have attracted considerable interest because they can possess the desired properties and optimized performance.43 In particular, biomedical nanocomposites have a potential application in medicine, e.g., dental treatment,44,77 bone tissue engineering,45 drug delivery,46 and wound dressings.45,46 The precise drug delivery to sites of tumors can improve treatment and reduce injury by minimizing adverse effects.78 Moreover, recent studies demonstrate that biocomposite materials exhibit thermal stability and enhanced tensile, tearing strength, and durability.49,79–82 Fig. 9A shows some 2D materials for biocomposite applications.83 In addition, the demand for biodegradable, environmentally friendly materials in areas such as bio-packaging has driven researchers to develop biocomposites.84–88 Cheng et al.89 investigated the interaction between graphene and several peptide structures of silk fibroin. The results reveal that graphene can affect the structure of all four types of silks, namely, pure amorphous, pure crystalline, a segment from the N-terminal, a combined amorphous and crystalline segment (Fig. 9B).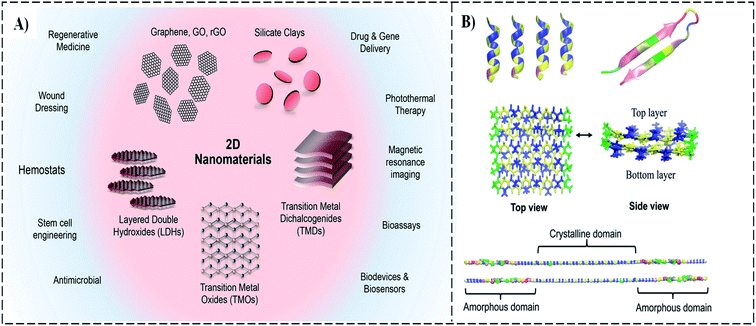 | ||
| Fig. 9 (A) The 2D nanomaterials for biological applications.83 (B) Simulations of peptide structure without graphene in water, including pure amorphous, pure crystalline, a segment from N-terminal, integrated amorphous, and crystal segment.89 | ||
The advancements in materials composition always come with some merits and demerits. Firstly, discussing the merits of the composites. The nanocomposites outperformed excellent strength-weight and stiffness-weight ratios, usually called specific strength and specific modulus characteristics. We come up with a reduced production cost as compared to conventional materials with tunable mechanical characteristics. Composite materials exhibit excellent resistance to chemicals attack, corrosion, and outdoor weathering when used for aviation and paint industries. Some general advantages of composites include their light weightiness, improved fatigue life, reduced assembly designs, and repeatable features for the high-tech industry. There are some inherited demerits for the composite materials includes susceptibility to impact damage, difficulty in reconfiguring constituents, poor strength in the out-of-plane direction, and provision of an extra safe environment to ensure extended life span.
4. Applications of 2D materials and their composites
Composite products are appropriate for applications where high-performance is essential, such as race cars, aerospace, sporting goods, boats, and industrial applications. For example, because of its durability, lightweight, heat resistance, and supreme strength, carbon fiber has been used for decades for world-changing machines like high-speed sports cars, formula 1 race cars, aircraft engines, and aerospace equipment. Another example of the most widely used composite material is fiberglass. This composite has applications in utility poles, recreational and industrial equipment. Last but not least, fiberglass strut also has applications is in external environments where a structure is subject to chemical exposure. These include water treatment plants, outdoor walkways, decks, and utility poles. Some other ideal applications of the composite are constructions, infrastructure, large complex-shaped structures such as retaining walls and floating roofs.On the other hand, low-dimensional (2D) materials and their composites have shown exceptional chemical, optical, electrical, and physical properties since their emergence. For example, conventional fuel sources are non-renewable and environmentally unfriendly. Therefore, the demand for the storage of these new conversed renewable energies, such as wind energy and solar energy, into electrical power, is high nowadays. One promising solution is to store these energies into an electrochemical device. The low-dimensional (2D) materials either used as heterostructures or composites have been widely used in electrochemical devices and significantly extended the performance limits for two main reasons: first, more opportunities for ion binding to active sites due to large specific surface area; secondly, 2D materials restacking enhance interlayer spacing, allowing more room for insertion and extraction of ions.90 Materials used in conventional electronic devices are mainly categorized as semiconductors, insulators, and conductors. As a counterpart, 2D materials also demonstrated exemplary performance in the classification mentioned above for the device-level operation. However, competing with the silicon (Si) industry for scalability, uniformity, and repeatability is still challenging, but, notably, stacking structures of different 2D materials leads to outstanding performance enhancement of electronic devices. In this section, we briefly review the representative properties of 2D materials and their nanocomposites for potential applications and challenges in various fields of science.
4.1 Strain engineering for 2D composites
Strain in 2D composites is applied to modify electronic properties such as the bandgap and charge transport mechanism. Strain-modulated sensors fabricated by the nanoinclusion of CNTs in cement show great potential for futuristic smart city sensors in the construction industry. The stated sensor's resolution is significantly improved compared to that of the conventional strain gauge or accelerometers.40 Graphene, having zero bandgap, when strained by about 15–30%, opens up a bandgap of few hundreds of meV as per theoretical calculations.91 A novel nanocomposite graphene nanoplatelets (GNP) modifies the behavior of epoxy under different tensile stresses, which may contribute to the development of more durable epoxies.92 Various studies related to bandgap tuning by the application of strain suggest that more exploration is warranted. Table 1 illustrates physical properties of common 2D materials.| Material | Number of layers | Young's modulus (GPa) | Pretension (mN m−1) | Breaking stress (GPa) | Breaking strain (%) | Characterization method | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Graphene (mechanical exfoliated) | 1 | 1000 ± 100 | 70–740 | 130 ± 10 | ∼12 | Indentation on circular membrane | 93 |
| 23–43 | ∼1000 | N/A | N/A | N/A | Electrostatic force | 94 | |
| 4 | 930 ± 48 | N/A | N/A | N/A | Pressurizing membranes | 95 | |
| 1–5 | 1000 ± 31 | N/A | N/A | N/A | Pressurizing membranes | 96 | |
| 1, 2 | 2400 ± 400 (1 L), 2000 ± 500 (2 L) | N/A | N/A | N/A | Pressurizing membranes | 97 | |
| 3–14 | ∼800 | N/A | N/A | N/A | Indentation on beam | 98 | |
| Graphene (mechanical exfoliated + Ar plasma irradiation) | 1 | ∼1550 | 200–800 | 80–94 | N/A | Indentation on circular membrane | 99 |
| Graphene (GO reduced) | 1 | 250 ± 150 | N/A | N/A | N/A | Spring constant of beam | 100 |
| Raphene (CVD growth) | 1 | ∼157 | ∼85 | ∼35 | N/A | Indentation on circular membrane | 101 |
| 1 | ∼1000 | N/A | ∼121 (small grains), ∼140 (large grains) | N/A | Indentation on circular membrane | 102 | |
| 1 | ∼800 | ∼100 | ∼55 | N/A | Indentation on circular membrane | 103 | |
| MoS2 (mechanical exfoliated) | 1, 2 | 270 ± 100 (1 L), 200 ± 60 (2 L) | 20–100 | 22 ± 4 (1 L), 21 ± 6 (2 L) | 6–11 | Indentation on circular membrane | 104 |
| 5–25 | 300 ± 10 | 0.15 ± 0.15 | N/A | N/A | Spring constant of circular membrane | 105 | |
| 5–25 | 330 ± 70 | 50 ± 20 | N/A | N/A | Indentation on circular membrane | 106 | |
| MoS2 (CVD growth) | 1, 2 | 260 ± 18 (1 L), 231 ± 10 (2 L) | 110 ± 40 (1 L) | N/A | N/A | Indentation on circular membrane | 107 |
| WS2 (CVD growth) | 1 | 272 ± 18 | 150 ± 30 | N/A | N/A | Indentation on circular membrane | 107 |
| WSe2 (mechanical exfoliated) | 5, 6, 12, 14 | 170 ± 7 (5 L), 166 ± 6 (6 L), 168 ± 7 (12 L), 165 ± 6 (14 L) | 638 ± 22 (5 L), 691 ± 37 (6 L), 499 ± 34 (12 L), 137 ± 26 (14 L) | >12 | >7.3 | Indentation on circular membrane | 108 |
| BP (mechanical exfoliated) | 17–35 | 27 ± 4 (armchair direction), 59 ± 12 (zigzag direction) | N/A | 2.2 (armchair direction), 4.2 (zigzag direction) | 7.2 (armchair direction), 6.5 (zigzag direction) | Spring constant of beam | 109 |
| 17, 37 | 276 ± 32 (17 L), 90 ± 6.4 (37 L) | 180–1200 | >25 | >8 | Indentation on circular membrane | 110 | |
| GO (solution-based deposition) | 1–3 | 208 ± 23 (1 L), 224 ± 18 (2 L), 230 ± 27 (3 L) | 54 ± 14 (1 L), 32 ± 6 (2 L), 28 ± 4 (3 L) | N/A | N/A | Indentation on circular membrane | 111 |
| Mica (mechanical exfoliated) | 2–14 | 202 ± 22 | 140 ± 80 | 4–9 | 2–4.5 | Indentation on circular membrane | 112 |
| h-BN (CVD growth) | 2, 4, 5 | 279 ± 20 (2 L), 269 ± 13 (4 L), 252 ± 15 (5 L) | 8.8 ± 1.2 (2 L), 12.8 ± 1.3 (4 L), 15.7 ± 1.5 (5 L) | ∼9 | 2.2 | Indentation on circular membrane | 113 |
Along with graphene, TMD-based nanocomposites have attracted a considerable amount of attention for strain-modulated applications. Theoretical calculations suggest that the direct quasi-particle (QP) energy gap of MoS2 reduces to ∼0.8 eV with the application of 9% biaxial strain. The indirect QP can also be decreased by applying the strain on MoS2, and the same result can be anticipated for other TMDCs. On the other hand, in single-layer black phosphorous, an increase of 0.65 eV was observed at an optical gap of 4.5% under the uniaxial strain applied in the ZZ direction.114 This significant correlation between bandgap and strain allows for other 2D materials and their composites to perform well in emerging multidisciplinary technology.
Usually, uniaxial strain is applied through stretching or bending the substrate or producing ripples at the surface of the substrate and then transferring any 2D material. In Fig. 10, strain engineering for MoS2 can be seen with uniaxial and biaxial strain. The photo luminance (PL) test shows a reduction in intensity with the application of uniaxial strain in monolayer MoS2. The A exciton PL peak in the bottom panel of Fig. 10A, related to the direct bandgap of MoS2, shifted to relatively lower energies with the application of tensile uniaxial strain, pointing towards the closing of the bandgap. The uniaxial strain has been reported in other 2D semiconductors such as in WSe2 and MoSe2, which shows a very close phonon–excitation correlation. In Fig. 10A, a different approach is used to introduce strain in the material. The expansion and contraction are caused by a polypropylene substrate that carries 2D material flakes. Via the thermal development of piezoelectric substrate, biaxial strain can also be induced in MoS2 flakes on such substrates or by creating a difference in pressure across the suspended MoS2 membrane.
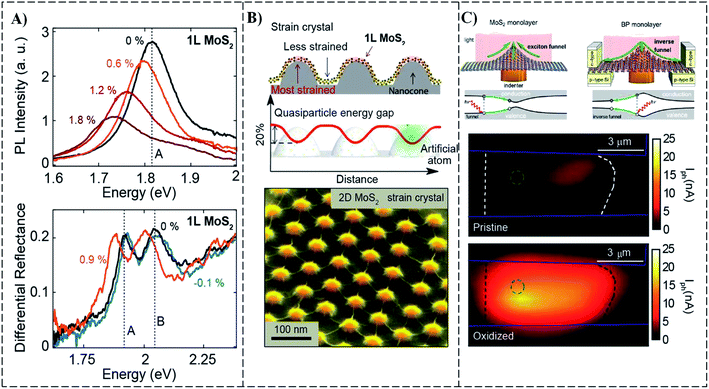 | ||
| Fig. 10 (A) Bandgap tuning of uniaxial and biaxial of monolayer MoS2 under different strain conditions. (B) Nanocones in substrate introduce periodic and local strain on top MoS2. (C) Excitonic funneling and inverse funneling effects in 2D semiconductors. The bottom part shows inverse funneling from a strained HfS2-based photodetector.119 | ||
An exciton peak in the differential reflectance spectra shifts to lower energies under a biaxial tensile strain (∼0.9%) and to higher energies under a compressive strain (∼0.1%) not only in monolayers; strain engineering also influences interlayer coupling when applied to multilayered 2D stacking, as reported for a few layers of BP and tuning of the energy of interlayer excitons in bilayer MoS2 straintronic devices can be fabricated based on the strain manipulation of 2D semiconducting materials and their composites.115–117 By controlling the biaxial strain level induced by thermal expansion, a single-layer MoS2-based photodetector can be tuned. The photoresponsivity can be enhanced up to three orders of magnitude, with a response time of from 1.5 s to 80 ms.118 In-plane anisotropy of the MoS2-based photodetector fabricated on PDMS (polydimethylsiloxane) also exhibited a uniaxial strain dependency. It showed a linear polarization anisotropic ratio, which could reach a value higher than two under 4.5% stretching of the polymer substrate. This anisotropic behaviour has the potential to mimic neuromorphic-based sensors that utilize weight updating upon polarization stimulus.
It has been reported that inhomogeneous local strain distributions in a single structured device provoked significant performance enhancements by the creation of wrinkles or pseudomagnetics and single-photon emissions by exciton-funneling effects119 as shown in Fig. 10B, in which a tilted SEM image of nanocores is presented. Localization of exciton within a structure is called exciton funneling, and this controls the motion of exciton as a result of the inhomogeneous distribution of strain, as seen in Fig. 10C (top panel). The left side of the top panel shows the exciton funneling of monolayer MoS2, and the inverse funneling effect for monolayer black phosphorous is shown on the right.
Due to the sub-10 nanometer vertical profile of composites, the characterization, control, and monitoring of strain is gaining attention due to the suitability of macroscopic homogeneity and low density of composites.47,120 Traditionally, Raman spectroscopy is considered to be an efficient tool for 3D–2D material characterization.
The recently reported photoluminescence (PL) spectroscopy and Raman spectroscopy are applied to observe the non-uniform distributions of the band gap in single-layer WS2 upon application of strain, and the analysis is extended to WS2 thin-film nanocomposites to validate the method.122 The other characterization techniques involve field emission scanning electron microscopy and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, which are used to observe the bonding profile of nanocomposites based on multi-walled CNTs.123 Vertically stacking results in interlayer coupling, which is strongly influenced by the application of strain. Interestingly, applying strain “laterally” to heterojunctions of 2D materials and their composites results in a unique class of phenomenon. The lateral heterostructure for single-layer electronics has been well studied and reported.124 Spatial modulation was observed for a lateral PN junction fabricated with MoS2 and WSe2; the energy distributions of both 2D materials affect the band structure due to lattice mismatch and cause local strain distributions. Further predictions state that band structure modification results in carrier confinement, leading to high mobility and low-power electronic devices.114,125,126
The tensile strength is a reaction of the materials to resist when forces are applied in tension. It is often defined as stress needed to break the sample. It is usually expressed in Pascals or psi (pounds per sq. inch). The tensile strength is a very crucial property of polymers which are supposed to undergo a stretch or elongations for example fiber should have better tensile strength for its common applications. When compared with the conventional polymers, functional nanocomposites exhibit greater tensile strength. For example, cellophane films and nitrile rubber sheet have tensile strengths of 50–120 MPa and 20–30 MPa, respectively whereas carbon fiber reinforced polymer composites range from 1200 to 2410 MPa, depending on fiber orientation and other design factors.
4.2 Thermal properties of 2D composites
Some 2D nanocomposites with efficient transport properties were proven to be suitable candidate materials for applications involved in thermal management. Well-known 2D materials, when fabricated with other composites or polymers, exhibit crossing-band features. For example, when graphene is rolled.Around vertically aligned with graphene films and penetrated in liquid PDMS, it shows thermal conductivity of about 614.85 W m−1 K−1, which is an enhancement of ∼3329% compared with pristine PDMS.127
Engineering the fabrication process of 2D materials and their composites can also lead to the modulation of thermal profiles; for example, by controlling the isotope concentration of hBN, one can modulate its thermal conductivity up to 585 W m−1 K−1 at room temperature, which is 80% higher than that previously reported in experimental observations. Moreover, various enhancements in the thermal conductivity of graphene are reported using impurity deposition,134 dimensionality cross-over, the effect of isotope manipulation,125 chemical functionalization, and length-dependent characteristics.114,135
By utilizing the van der Waals (vdWs) interaction of layered materials, thermal conductivity can be tuned according to the ingredients of the specific composite. For the case, including only a small amount of an excellent thermal conductor, for example, graphene, in the target composite, one can significantly improve its thermal conductivity with engineered loading. The interesting aspect of h-BN is its electrically insulating ability in parallel with thermal conduction, which suggests its potential use in graphene-based heterostructures.48 The thermal conductivity of other layered two-dimensional materials such as hBN is significantly dependent on temperature, thickness (number of layers), and type of polymers used during the fabrication process. Previously Table 2 reported results had discrepancies between theoretical estimations and experimental outcomes. This is attributed to the difference in crystal quality and/or lattice mismatches, polymer (PDMS/PMMA-assisted manufacturing) residuals, and any other contaminations that resulted in additional phonon scattering, thus decreasing thermal conductivity.136
| Sample | Thickness | Method | κ (W m−1 K−1) | Comments | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MoS2 | Monolayer | Raman | 62.2 | Supported | 128 |
| MoS2 | 11 layers | Raman | 52 | CVD, transferred, suspended | 129 |
| TaSe2 film | 45 nm film | Raman | 9 | Exfoliated, suspended | 130 |
| WSe2 | 62 nm film | TDTR | 0.05 | Cross plane, disordered | 131 |
| TiS2 | Bulk | Parallel thermal conductance method | 0.69 | Organic intercalation | 132 |
| WS2 | Monolayer/bilayer | Raman | 32/53 | CVD, suspended | 133 |
In the domain of layered 2D materials, TMDs play a very important role in applications where thermal management is involved. MoS2, which is widely used in optoelectronics devices, exhibits strong layer-dependent behaviour in terms of bandgap engineering, i.e., from an indirect bandgap (1.3 eV) in bulk MoS2 to a direct bandgap (1.8 eV) in the monolayer,137 in addition to the creation of different phonon-scattering modes.135 An experimental study showed few layer-dependent thermal transport characteristics of CVD-grown MoS2. The thermal conductivity of MoS2 (11 layers) is measured to be about 52 W m−1 K−1 at room temperature. From bulk to the monolayer, thermal conductivity has a decreasing trend, as shown in Fig. 11.121 This is attributed to the higher phonon scattering induced by the change in the inharmonic force constant and the smaller group velocity of various phonon modes.
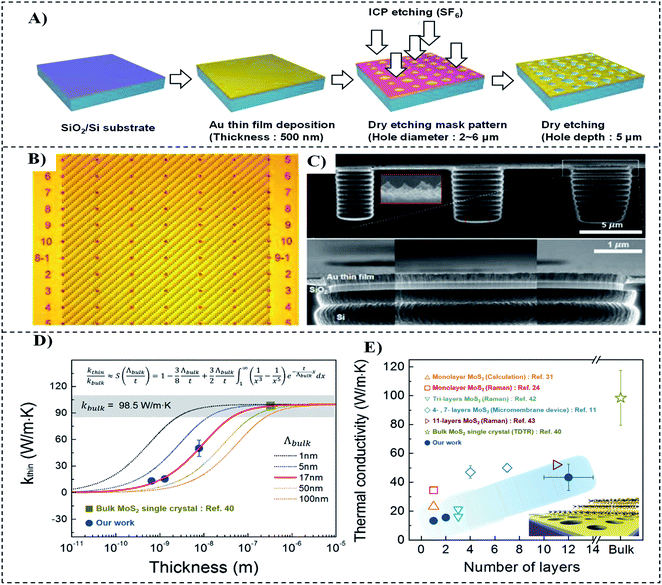 | ||
| Fig. 11 (A) Fabrication steps of the Au/SiO2/Si substrate with microcavity arrays (B) top view, (C) side view, (D) thickness-dependent thermal conductivity of MoS2, (E) summary of thermal conductivity for MoS2 films.121 | ||
One recent study shows an anomalous behaviour of thermal conductivity in a 2D composite known as tungsten ditelluride (Td-WTe2).114 The study shows that thermal conductivity directly correlates with the number of layers of the stated 2D composite, which is attributed to the change in the phonon dispersion relations. With the addition of the layer numbers, optical phonon branches move downward, providing more channels for the Umklapp scattering and decreasing thermal conductivity.
A continuous increase in the layer number causes the low-frequency optical phonon branches to have high group velocity and leads to the increase in lattice thermal conductivity. Table 2 shows the thermal conductivity of different two-dimensional materials and composites.
BP is a well-known layered material used for many electronic and optoelectronic applications.114 Due to its stability issue of BP at ambient temperature, passivation and anti-oxidation must be used during the measurement of its thermal profile.126 Initial studies on the thermal conductivity of BP identified nearly 10 W m−1 K−1 in bulk polycrystalline samples of BP. One interesting property of BP is anisotropy for thermal conductivity. A predictive study presented by Jain and McGaughey127 showed a strong in-plane anisotropic ratio of thermal conductivity of 3.5 along zigzag (ZZ = 36 W m−1 K−1) to armchair (AM = 110 W m−1 K−1) orientation at a room temperature of 300 K. Zhu et al. exposed the 3D anisotropic thermal conductivity of BP and demonstrated results with different crystalline orientations induced by changing group velocity.137 The contribution of ZA mode for thermal conductivity is relatively low compared with the surface scattering for 2D-BP-like materials.127
Various types of 2D layered composites belonging to group V–VI materials are drawing significant attention towards their thermoelectric applications, such as the bismuth tellurides Bi2Te3 and Bi2Se3 and Sb2Te3. They consist of vdW-connected quintuple layers that are in-plane covalently bonded. There are several attractive features of these composites. For example, materials like bismuth telluride Bi2Te3 and others are known for their good thermoelectric properties and show potential for use as topological insulators due to their reduced electric conductivity. However, one challenging research domain for these layered composites is the isolation or decoupling of their thermal and electrical properties. Numerous attempts have been made, but no significant results have been shown. For example, the thickness-dependent thermoelectric properties of antimony telluride, Sb2Te3, show that with proper tuning and controlling the grain size, its electric and thermal decoupling can be achieved.
4.3 2D-materials-based composites in photocatalysts and water splitting
Recently, many efforts have been made in designing semiconductor-mediated photocatalysts. The photocatalyst is used in a process in which acceleration of a photoreaction happens in the presence of a catalyst when solar energy (or a light source) separates the electron–hole pair within a host substrate, and these separated components contribute to oxidation and reduction simultaneously, thus producing chemical energy (hydrogen fuel). Although several studies on 2D semiconductor photocatalysts have been conducted to date, degradation, low cost, charge transfer kinetics, and recycling remain issues that obstruct the broad application of thin semiconductor-based photocatalysts. Here, the role of the 2D materials and their heterostructures are examined to address the above-mentioned shortcomings of the existing materials. The 2D-material-based photocatalyst has gained tremendous attention because of its thickness-dependent physical, mechanical, chemical, and optical properties. The mainstream domains encompass water splitting, oxidation/reduction, CO2 reduction, N2 fixation, and NO2 removal. Zhu et al.138 fabricated a two-dimensional/two-dimensional (2D/2D) Bi2O2CO3/Bi4O5Br2 (BOC/BOB) heterostructure as a photocatalyst by stacking the ultrathin nanosheets of Bi2O2CO3 and Bi4O5Br2 by one-step hydrothermal synthesis (Fig. 12). They concluded that, by optimizing the content of BOC, the 30% BOC/BOB composite can display superior photocatalytic activity (53.2%) for NOx removal under simulated solar light illumination, as shown in Fig. 12, which is much sophisticated than that of single-phase BOB (37.9%) or BOC (20.4%).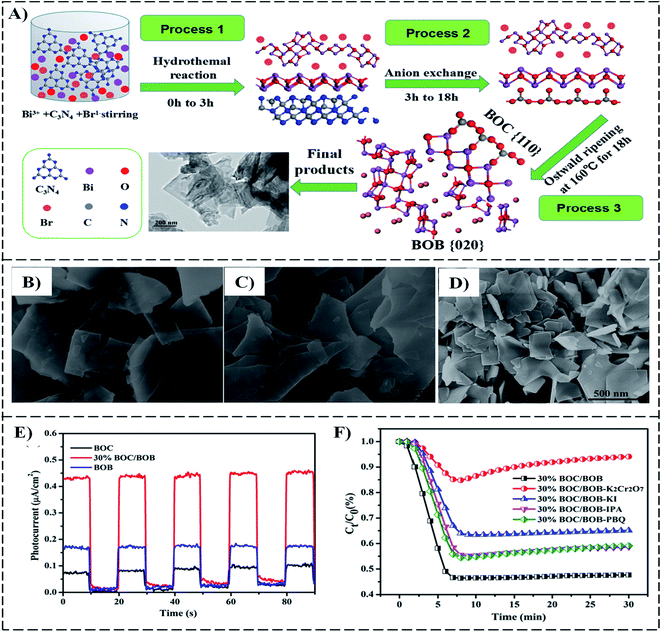 | ||
| Fig. 12 (A) Schematic of the formation mechanism for 2D/2D Bi2O2CO3/Bi4O5Br2 (BOC/BOB) heterojunction; SEM images of, (B) BOB, (C) BOC, and (D) 30% BOC/BOB, respectively, (E) photocurrent densities, (F) photocatalytic activity of 30% BOC/BOB composite photocatalyst under various scavengers.138 | ||
With large surface-to-volume ratios, 2D materials have attracted the attention of researchers due to their large surface availability allowing co-catalysts to survive and the abundancy for charge carriers.114 In addition, the reduced thickness of 2D layered materials, even down to a single atom, ensures less traveling from the bulk to the surface by a photo-induced charge carrier, which contributes to high yield. Although 2D materials have tremendous characteristics, there are still some challenges to be addressed. One big challenge is the scarcity of surface-active sites in 2D materials for photoactivity, even if there is an abundance of charge carriers, because these consist of relatively unsaturated atoms, which are often found on the edges of the 2D surface without surface defects or absorption states. Besides this, a wide bandgap is required for the strong reductive/oxidative ability for photocatalysis. This requires shorter wavelengths in the ultraviolet (UV) band, which is only 4% of solar energy.
Researchers conduct material engineering, such as vacancy engineering, with the 2D layered materials and composites; elemental doping; integration with other semiconductors, metal, or metal oxides;135 and morphology and structure control. After analyzing bandgap and structural orientation/arrangements, many 2D materials and composites have shown excellent photocatalysts. Graphitic carbon nitride (g-C3N4) is a layered material with a special allotrope of covalent carbon nitride. It possesses a condensed and conjugated structure, exhibits great tolerance to neutral and acidic and alkaline surroundings, and possesses a bandgap of 2.7 eV, which is enough for photocatalytic hydrogen generation. Due to the weak vdW interlayer interaction can be easily transformed from bulk to nanosheets, which have shown excellent performance in photocatalytic water splitting.135 Due to the abundance of its defect states, it is also observed that it provides additional sites for the activity of photocatalysts. Similarly, BP is also considered a good candidate for such a process as its bandgap is tunable by the number of layers. Zhu et al. reported that with ball milling with LiOH, 2D BP achieved a hydrogen evolution rate of 512 μmol g−1 h−1 under visible light, which was deemed a good value by the investigators, and they believe that it should be further examined in future research.125
Two-dimensional-material-based composites, their derivatives, and metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) have also been widely used in photocatalysis-based water splitting research due to their tunable and unique architectures, distinctive features, and desirable structural details.91 It is believed that, amongst others, graphitic carbon nitride (g-C3N4) and graphene are two important factors in achieving the coveted properties of low charge recombination, efficient electron conductivity, fast kinetics, high photoabsorbance activity, and a large surface area for water splitting to produce hydrogen. It has been conceived that various techniques can raise the production of hydrogen, including synthesis-controlled morphology, surface functionalization, nano-heterostructures, doping with noble metal particles, and surface decoration of nanoparticles in 2D cages. By cleverly engineering the electronic structure and utilizing hybridization, composites such as electrochemically reduced thin films (e.g., α-Fe2O3),135 layered oxyhalides (FeOBr, Bi4VO8Cl, etc.), metal chalcogenides, thiophosphates (CoPS3), 2D MOFs, and metal-free semiconducting materials, can be produced.114
Particularly, 2D-based composites exhibit multiple advantages such as larger specific surface areas, good conductivity, superior electron mobility, catalyst support, prolonging cyclability, and good optical properties. Therefore, 2D-based composites may provide a new generation of materials for excellent photocatalytic activity compared with one- and three-dimensional materials. The large specific surface areas lead to a great number of active sites on the surface. The good conductivity and high electron mobility lead to an ultrafast electron transfer platform to facilitate the transfer, enhanced separation of photogenerated charges, and reduced recombination of electron–hole pairs. Consequently, 2D layered composites are opening up a new stream of enhanced photocatalysis for future energy harvesting applications.
4.4 2D-materials-based composites in optoelectronics
Two-dimensional-material-based composites have been widely used in optoelectronics since their emergence. Layer-dependent bandgap tunability and broadband detection make the 2D composites a suitable candidate to be used in optoelectronics devices. The electron–photon interaction is more exciting at the nanoscale, which also evolves plasmonic properties of 2D materials. By analyzing the physics behind 2D materials and their composites, researchers identified and quantified nearly different two-dimensional materials and composites trigonal and hexagonal for the maximum optical TAR (transmittance, absorption, and reflection) at different wavelengths ranging between near-infrared (NIR) to deep UV. Layer-dependent bandgap alignment and work functions give freedom of choice for desired optical response.91 Band gaps of 2D materials can be engineered through some reported ways of intercalation, control of the number of layers, heterostructure, strain engineering, and the dominant electric field effects. Recently discovered 2D materials exhibit highly tunable bandgaps ranging from infrared (0.3–1.6 eV) for bilayer graphene and black phosphorous (BP), visible (1.7–3.1 eV) for TMDs, and UV (3.2–6 eV) for hBN, thus enabling the scientific community to develop a wide range of optoelectronic devices.139–141 The localized hot excitonic effect in thinner 2D heterostructures gives rise to an ultrafast charge transfer rate and higher photocurrent generation.125 The superposition (heterostructure) of monolayers of MoSe2 and WSe2 resulted in the localization of excitons, irrespective of negligible interlayer coupling.Expansion in the material library for optical and optoelectronic devices is an ongoing process. Design rules using effective medium theory are being formulated for newly emerged nanocomposites to be effectively utilized in the industry.142,143 A meaningful effort towards the previous expansion was recently reported. Selectively mixing tunable, transparent As–S (Se) NPs and an acrylate monomer as initiators was carried out to observe the enhanced amplitude-phase modulation relax parameter the composite. This combines the chalcogenide glass composite with polymer.144
4.5 Other applications
It is always advantageous to extract the maximum benefits from natural resources, such as water flow, solar energy, and coal/natural gases. Photovoltaics is a well-known process for the extraction of electricity using solar energy. The 2D nanocomposite is also used to modify filtration materials, which are further utilized in point-of-use (POU) water treatment systems. With restricted access to sanitarily safe water resources, the POU water treatment system and device are of considerable importance. The filtering materials employed in POU systems can thoroughly remove the contaminant.Jakubczak et al.145 have reported a ground-breaking 2D Ti3C2/Al2O3/Ag/Cu nanocomposite-modified filtration material with the potential in POU water treatment, which collected 99.6% of bacteria in the filter. Sher et al.146 synthesized Cd-doped ZnO nanocomposites based on g-C3N4 (Cd–ZnO/g-C3N4 NCs) through the co-precipitation method. The products were utilized against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacterial strains to estimate their antibacterial activities. Qamar et al.147 also synthesized an efficient photocatalytic composite Ni/ZnO/g-C3N4 (NiZG), using Ni-doped ZnO NPs with graphitic carbon nitride (g-C3N4) and a cost-effective chemical co-precipitation approach. The catalytic proficiency of NiZG composites was evaluated by determining the UV-vis absorption spectra for methylene blue, and the bactericidal ability was tested against Gram-positive and Gram-negative microbes.147
The aerospace, automotive, and electronics industries require new 2D-material-reinforced epoxy composites with excellent mechanical properties and high thermal conductivity. In this regard, Han et al. studied and investigated the effect of adding hBN sheets and graphene platelets (GnPs), achieving improved thermal conductivity and enhanced mechanics of the epoxy resin. As a result, GnPs improved the energy release rate of epoxy by 338%, whereas BN increased it by 260%, and both at 2 wt%. Thermal conductivity of the epoxy/GnP and epoxy/BN composites was enhanced by 135% and 64% respectively, both at 4 wt%.148 Moreover, Sanchez et al. obtained a thermal conductivity of 0.22 W m−1 K−1 for pristine epoxy (EP) and further investigated the effect of a hybrid filler composed of zero-dimensional (0D) spherical micro-sized aluminum oxide (Al2O3) and 2D flake-like hBN.149 Ren et al. placed Sb2S3 NPs on highly crumpled Ti3C2Tx nanosheets using the wet chemical reaction. The evenly distributed Sb2S3 NPs resolved the restack issue of the Ti3C2Tx nanosheets upon repetitive charging/discharging cycles, producing rich voids for rapid electron/Na+ transport and reducing the volume expansion effect from Sb2S3. The composite showed a high capacity (329 mA h g−1 at 100 mA g−1 after 100 cycles), high rate capability, and high cycling performance (215 mA h g−1 at 2 A g−1 when utilized as a sodium-ion battery (SIB) anode and also maintaining 118 mA h g−1 after 500 cycles).150 Furthermore, Syamsai et al. prepared a bi-metallic titanium–tantalum carbide MXene, TixTa(4−x)C3, by etching Al atoms from the parent TixTa(4−x)AlC3 MAX phase, which showed an outstanding electrochemical redox performance attributed to the creation of a promising, stable bi-metallic MXene material, enabling the storage of Li-ions on the layer surface. Additionally, the TixTa(4−x)C3 MXene anode displayed a high aptitude rate due to its good electron and Li-ion transport, indicating that it is a promising candidate as a Li-ion anode material.151 García et al. obtained MoTe2/MoSe2 flake composite films using an isothermal closed-space vapor transformation, with successful applications in those that demand high interfaces, favoring gas or ion exchange reactions with TMDs. The oxide precursor films were prepared from a Mo isopropoxide solution in isopropanol (IPA), and acid catalysis induced by HCl and thermal annealing at 200 °C, 400 °C, and 600 °C improved the condensation after xerogel formation.152 On the other hand, MXene/polymer nanocomposites have been investigated, and it has been found that MXene could significantly enhance the mechanical, electrical, and thermal behaviors of polymers. MXene/polymer nanocomposite structures have been observed to provide considerably good results in sensing, biomedical, environmental monitoring, energy, and other fields.153
Finally, we would like to emphasize the characteristics of several representative 2D-layered materials, e.g., graphene, g-C3N4, and MoS2, and the recent progress in 2D-layered composites for photocatalysts, including photocatalytic hydrogen production, bacterial disinfection, and the degradation of organic pollutants, as illustrated in Fig. 13.
5. Conclusion and perspectives
In summary, we briefly presented representative 2D-material-based composites and their characterizations, classifications, and advantages regarding physics and mechanics related to recent studies as well as emphasize other aspects that formed new nanocomposites based on polymers and metals and the latest achievements of new synthesized-2D materials enabling to fabricate of new nanocomposite species. The 2D material family and their composites widened the performance band of conventional devices supported by the synergy of modern fabrication techniques and measurement/characterization tools. Two-dimensional materials, e.g., graphene, BP, h-BN, TMDs, or MXenes, contributed to a tremendous advancement in multidisciplinary science and engineering. These materials are either exploited in the form of homo- and hetero-structures or polymer-reinforced nanocomposites depending on how many performance parameters can be improved by structural engineering or through functionalization. However, interesting chemistry exists when the above-stated materials combine with other layered materials of similar groups, such as tellurium, selenium, sulphur, antimony, bismuth, and more with crystalline structures. These 2D-material-based composites have the potential to expand the application areas of conventional 2D-based materials and devices.Although the enormous potential of the 2D materials-based polymer composites have been demonstrated in various fields, there are still many challenges in their practical applications. First, the mass production of layered composite materials for advanced applications is a significant challenge. Secondly, the synchronization of technological advancements for both mass production and corresponding applications is one of the key factors in pursuing novel composites. The integration of polymers and a metal framework with 2D materials has broadened the scope of composites. It is believed that the composite material-oriented approach could be used to resolve some technical challenges, such as energy storage for future applications, water purification, low-energy consumption electronics, bio-inspired computing,91 biomedical applications,114 and efficient catalysis.137 Many efforts have been reported for the mass production of these composites for commercialization154 so that these material-based devices can be marketed as early as possible. However, the balance between quality and quantity is still a major issue, as state-of-art fabrication is needed for aliasing functionalities of similar devices in a batch of products, adding financial loading.
Nanosheet-based composites and the utilization of an MOF have made considerable contributions to broadening the sensitivity of existing devices, as sensors are one of the fundamental elements in industrial automation. During detection and sensing, two major challenges still need to be addressed. The first considers the sample matrix effect, which contains ionic contaminations, macromolecules, and particles are added in unwanted signal processing.137 Further exploration in terms of characterization of such composites is needed to develop specific fabrication techniques that may lower these anomalies/artefacts and produce consistent detection results while working in a human-friendly environment and optimal lab conditions. The second consideration is scalable fabrication methods in parallel with controlling the quality and quantity for future technological industry.
From the in-depth exploration of nanocomposites based on 2D materials, polymers, ceramics, and many more, we have high expectations regarding the development of the future industry via a synergistic approach. Various scientific fields can be benefitted by expanding the nanocomposite materials library e.g., (a) for the detection of specific pathogens and intelligent drug delivery systems (SDDs) in the medical field; (b) nanocomposites for the packaging and plastic industry to enhance processability, modify product properties, and provide protection against thermal or UV light influences; (c) the enhancement of mechanical properties, tensile strength, and weight reduction and improvement to flame retardants for the automotive industry, transportation, sporting goods, aviation, and he space industry. Moreover, self-lubricating composites are a kind of advanced material where solid lubricant materials, such as graphite, hBN, MoS2, CNT, and graphene, are used as a primary or secondary reinforcement to achieve better mechanical and tribological properties. Moreover, metal-based nanocomposite (e.g., gold, silver, and copper nanoparticles; graphene; CNTs, graphene oxide; and other 2D-material-based nanocomposites) are being utilized to enhance electrically conductive properties in the domain of flexible/wearable electronics, organic electronics, textiles, and solar cells. In addition, nanocomposites-based thin films are also used as coatings and flexible displays. Nanocomposites also have applications in the field of photocatalysts, gas sensors, supercapacitors, and broadband sensors for optical and THz band construction. It is strongly believed that the development of 2D-derived nanocomposites carries the optimized solutions of humanity's ever-existed problems of energy, food scarcity, security, and communication at an accelerated pace. Strong research collaboration and the provision of more channels for technology exchange may boost this pace.
Two-dimensional material-based composites are expected to play an essential role in future technologies. Although many significant research efforts have been made, applications using 2D material composites remain limited. Considerable challenges still exist, such as the possibility of large-scale production, enhanced cycling stability, and reduced costs for commercialization. Furthermore, the intrinsic properties of 2D materials are susceptible and dependent on many factors, including surface chemistry, neighboring materials, underlying substrate, and interfaces. Moreover, production methods also have a significant influence on heterostructure applications, e.g., the composited material's performance, reproducibility, and reliability. Studies tend to focus on several properties but skip other relations. This leads to the inefficiency of using composites. For example, some investigators are interested in improving the optical–electrical properties, while other properties are not discussed. Similarly, some reports show the enhanced photocatalytic performance of 2D material composites while ignoring the possibility of cycling stability. Therefore, to enhance the performance of micro-nano devices using 2D material composites, the synchronous properties require further investigation. The combined investigation methods can help to accurately choose the components and accurately control the concentration. These conjunctions will optimize the synchronous conditions that improve the performance and present the opportunity of commercialization.
Two-dimensional composites based on multiple materials require more attention. For example, many studies have reported the production of a polymer composite by adding a single 2D material, and, as result, they observed enhancement in one or two properties; on other hand, there are only a few reports that explored the production of polymer composites by adding more than one (two or three) 2D materials together. It is apparent that each individual 2D material has its unique properties and advantages over other materials but also some downsides. For example, it is well known that graphene has high electrical conductivity, which favours being used in the energy storage device as a conductive filler. However, it has been stated that many graphene-based polymer composites exhibit very low energy density. To solve this issue, the idea of mixing graphene with other 2D materials was proposed.155 In this regard, MoS2 sheets were mixed with reduced graphene oxide (rGO) to obtain a hybrid aerogel that could be used as electrode material for supercapacitors, possessing properties of both 2D materials. We believe more effort should be made in fundamentally researching the various aspects of 2D-material-based composites produced by mixing more than one 2D material for practical applications.
Author contributions
All authors contributed to writing the manuscript, overall draft preparation, review, and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MSIT) (no: NRF-2021R1F1A1062849), and Ningbo Research Institute, post-doctoral research funding, project code 14001-5140210003 (grant no: NB-YS-2021005060118), and Ningbo Natural Science Foundation (grant no: 202003N4033), and National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) (61950410607), and the Priority Research Center Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF), which is funded by the Ministry of Education (NRF-2019R1A6A1A11053838).References
- S. M. M. Amir et al., Nondestructive testing method for Kevlar and natural fiber and their hybrid composites, in Durability and Life Prediction in Biocomposites, Fibre-Reinforced Composites and Hybrid Composites, Woodhead Publishing, 2019, pp. 367–388 Search PubMed.
- D. K. Rajak, D. D. Pagar, R. Kumar and C. I. Pruncu, Recent progress of reinforcement materials: a comprehensive overview of composite materials, J. Mater. Res. Technol., 2019, 8(6), 6354–6374 CrossRef CAS.
- C. T. Le, et al., Impact of selenium doping on resonant second-harmonic generation in monolayer MoS2, ACS Photonics, 2017, 4(1), 38–44 CrossRef CAS.
- R. Akashi, et al., Two-Dimensional Valley Electrons and Excitons in Noncentrosymmetric 3R-MoS2, Phys. Rev. Appl., 2015, 4(1), 014002 CrossRef.
- V. P. Pham, Hexagon flower quantum dot-like Cu pattern formation during low-pressure chemical vapor deposited graphene growth on a liquid Cu/W substrate, ACS Omega, 2018, 3(7), 8036–8041 CrossRef.
- V. P. Pham, et al., Chlorine-trapped CVD bilayer graphene for resistive pressure sensor with high detection limit and high sensitivity, 2D Mater., 2017, 4(2), 025049 CrossRef.
- V. P. Pham, A. Mishra and G. Y. Yeom, The enhancement of Hall mobility and conductivity of CVD graphene through radical doping and vacuum annealing, RSC Adv., 2017, 7(26), 16104–16108 RSC.
- V. P. Pham, K. H. Kim, M. H. Jeon, S. H. Lee, K. N. Kim and G. Y. Yeom, Low damage pre-doping on CVD graphene/Cu using a chlorine inductively coupled plasma, Carbon, 2015, 95, 664–671 CrossRef CAS.
- K. N. Kim, V. P. Pham and G. Y. Yeom, Chlorine radical doping of a few layer graphene with low damage, ECS J. Solid State Sci. Technol., 2015, 4(6), 5095–5097 CrossRef.
- V. P. Pham, K. N. Kim, M. H. Jeon, K. S. Kim and G. Y. Yeom, Cyclic chlorine trap-doping for transparent, conductive, thermally stable and damage-free graphene, Nanoscale, 2014, 6(24), 15301–15308 RSC.
- V. P. Pham, et al., Low energy BCl3 plasma doping of few-layer graphene, Sci. Adv. Mater., 2016, 8(4), 884–890 CrossRef CAS.
- V. P. Pham, Cleaning of graphene surfaces by low-pressure air plasma, R. Soc. Open Sci., 2018, 5(5), 172395 CrossRef.
- V. P. Pham, A library of doped-graphene images via transmission electron microscopy, Journal of Carbon Research, 2018, 4(2), 34 CrossRef.
- V. P. Pham, Graphene etching: how could it be etched, Current Graphene Science, 2018, 2(1), 15–20 CrossRef.
- V. P. Pham and G. Y. J. A. M. Yeom, Recent advances in doping of molybdenum disulfide: industrial applications and future prospects, Adv. Mater., 2016, 28(41), 9024–9059 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- V. P. Pham, H.-S. Jang, D. Whang and J.-Y. Choi, Direct growth of graphene on rigid and flexible substrates: progress, applications, and challenges, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2017, 46(20), 6276–6300 RSC.
- K. A. A. Min-Dianey, T. K. Le, J. R. Choi and P. V. Pham, Advanced Optical Detection through the Use of a Deformably Transferred Nanofilm, Nanomaterials, 2021, 11(3), 816 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Rajendran, A. N. Reshetilov and A. K. Sundramoorthy, Preparation of hybrid paper electrode based on hexagonal boron nitride integrated graphene nanocomposite for free-standing flexible supercapacitors, RSC Adv., 2021, 11(6), 3445–3451, 10.1039/D0RA10735B.
- G. Jeevanandham, R. Jerome, N. Murugan, M. Preethika, K. Vediappan and A. K. Sundramoorthy, Nickel oxide decorated MoS2 nanosheet-based non-enzymatic sensor for the selective detection of glucose, RSC Adv., 2020, 10(2), 643–654, 10.1039/C9RA09318D.
- N. Murugan, R. Jerome, M. Preethika, A. Sundaramurthy and A. K. Sundramoorthy, 2D-titanium carbide (MXene) based selective electrochemical sensor for simultaneous detection of ascorbic acid, dopamine and uric acid, J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2021, 72, 122–131 CrossRef.
- J. Rajendran, A. N. Reshetilov and A. K. Sundramoorthy, An electrochemically exfoliated graphene/poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) nanocomposite-based electrochemical sensor for the detection of nicotine, Mater. Adv., 2021, 2(10), 3336–3345 RSC.
- R. Jerome and A. K. Sundramoorthy, Preparation of hexagonal boron nitride doped graphene film modified sensor for selective electrochemical detection of nicotine in tobacco sample, Anal. Chim. Acta, 2020, 1132, 110–120 CrossRef CAS.
- R. Jerome, P. V. Keerthivasan, N. Murugan, N. R. Devi and A. K. Sundramoorthy, Preparation of Stable CuO/Boron Nitride Nanocomposite Modified Electrode for Selective Electrochemical Detection of L–Cysteine, ChemistrySelect, 2020, 5(29), 9111–9118 CrossRef CAS.
- V. Senthilkumar, L. C. Tam, Y. S. Kim, Y. Sim, M. J. Seong and J. I. Jang, Direct vapor phase growth process and robust photoluminescence properties of large area MoS2 layers, Nano Res., 2014, 7(12), 1759–1768 CrossRef CAS.
- A. D. Nguyen, et al., Nitrogen-Plasma-Treated Continuous Monolayer MoS2 for Improving Hydrogen Evolution Reaction, ACS Omega, 2019, 4(25), 21509–21515 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- E. Vera-Cárdenas, et al., Microanalysis of carbon and glass fiber obtained by resin transfer molding process to manufacture blades for wind turbines, Microsc. Microanal., 2018, 24(S1), 1082–1083 CrossRef.
- C. He, S. Wu, N. Zhao, C. Shi, E. Liu and J. Li, Carbon-Encapsulated Fe3O4 Nanoparticles as a High-Rate Lithium Ion Battery Anode Material, ACS Nano, 2013, 7(5), 4459–4469 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. Wan, et al., Flexible transparent films based on nanocomposite networks of polyaniline and carbon nanotubes for high-performance gas sensing, Small, 2015, 11(40), 5409–5415 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Z. Huang, et al., Photoelectrochemical-type sunlight photodetector based on MoS2/graphene heterostructure, 2D Materials, 2015, 2(3), 035011 CrossRef.
- B. C. Ray, Temperature effect during humid ageing on interfaces of glass and carbon fibers reinforced epoxy composites, J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2006, 298(1), 111–117 CrossRef CAS.
- J. P. Davim and P. Reis, Study of delamination in drilling carbon fiber reinforced plastics (CFRP) using design experiments, Compos. Struct., 2003, 59(4), 481–487 CrossRef.
- Y. Liu, W. Wang, Y. Wang and X. Peng, Homogeneously assembling like-charged WS2 and GO nanosheets lamellar composite films by filtration for highly efficient lithium ion batteries, Nano Energy, 2014, 7, 25–32 CrossRef CAS.
- D. Chen, et al., In situ nitrogenated graphene–few-layer WS2 composites for fast and reversible Li+ storage, Nanoscale, 2013, 5(17), 7890–7896 RSC.
- V. Dhand, K. Y. Rhee, H. Ju Kim and D. Ho Jung, A comprehensive review of graphene nanocomposites: research status and trends, J. Nanomater., 2013, 2013, 14 Search PubMed.
- K. Chu, C. C. Jia and W. S. Li, Effective thermal conductivity of graphene-based composites, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2012, 101(12), 121916 CrossRef.
- X. Huang, X. Qi, F. Boey and H. Zhang, Graphene-based composites, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2012, 41(2), 666–686 RSC.
- S. Stankovich, et al., Graphene-based composite materials, Nature, 2006, 442(7100), 282–286 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Gao, et al., Maximizing ion accessibility in MXene-knotted carbon nanotube composite electrodes for high-rate electrochemical energy storage, Nat. Commun., 2020, 11(1), 6160 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Wu, et al., Strain Sensors with Adjustable Sensitivity by Tailoring the Microstructure of Graphene Aerogel/PDMS Nanocomposites, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2016, 8(37), 24853–24861 CrossRef CAS.
- A. D’alessandro, F. Ubertini, S. Laflamme and A. L. Materazzi, Towards smart concrete for smart cities: Recent results and future application of strain-sensing nanocomposites, Journal of Smart Cities, 2015, 1(1), 3 Search PubMed.
- S. D. Thoppul, J. Finegan and R. F. Gibson, Mechanics of mechanically fastened joints in polymer–matrix composite structures–a review, Compos. Sci., 2009, 69(3–4), 301–329 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Haghshenas, Metal–matrix composites, Reference Module in Materials Science and Materials Engineering, pp. 03950-3, 2016 Search PubMed.
- M. C. Demirel, M. Vural and M. Terrones, Composites of proteins and 2D nanomaterials, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2018, 28(27), 1704990 CrossRef.
- A. K. Nayak, S. Mazumder, T. J. Ara, M. T. Ansari, and M. S. Hasnain, Calcium fluoride-based dental nanocomposites, in Applications of Nanocomposite Materials in Dentistry, Elsevier, 2019, pp. 27–45 Search PubMed.
- M. S. Hasnain and A. K. Nayak, Nanocomposites for improved orthopedic and bone tissue engineering applications, in Applications of Nanocomposite Materials in Orthopedics, Elsevier, 2019, pp. 145–177 Search PubMed.
- F. Guo, S. Aryana, Y. Han and Y. Jiao, A review of the synthesis and applications of polymer–nanoclay composites, Appl. Sci., 2018, 8(9), 1696 CrossRef.
- V. Mittal, Characterization of nanocomposite materials: an overview, Characterization Techniques for Polymer Nanocomposites, 2012 Search PubMed.
- W. D. Lin, C. T. Liao, T. C. Chang, S. H. Chen and R. J. Wu, Humidity sensing properties of novel graphene/TiO2 composites by sol–gel process, Sens. Actuators, B, 2015, 209, 555–561 CrossRef CAS.
- R. A. Ilyas, S. M. Sapuan, M. R. Ishak and E. S. Zainudin, Water transport properties of bio-nanocomposites reinforced by sugar palm (Arenga Pinnata) nanofibrillated cellulose, J. Adv. Res. Fluid Mech. Therm. Sci., 2018, 51(2), 234–246 Search PubMed.
- X. J. Lee, et al., Review on graphene and its derivatives: Synthesis methods and potential industrial implementation, J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng., 2019, 98, 163–180 CrossRef CAS.
- S. William, J. Hummers and R. E. Offeman, Preparation of graphitic oxide, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1958, 80(6), 1339 CrossRef.
- A. Sharma, N. Sharma, A. Kumari, H. J. Lee, T. Kim and K. M. Tripathi, Nano-carbon based sensors for bacterial detection and discrimination in clinical diagnosis: A junction between material science and biology, Appl. Mater. Today, 2020, 18, 100467 CrossRef.
- H. Zhao, Y. Li, D. Shen, Q. Yin and Q. Ran, Significantly enhanced electrochemical properties of LiMn2O4-based composite microspheres embedded with nano-carbon black particles, J. Mater. Res. Technol., 2020, 9(4), 7027–7033 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Wu, S. Peng, Z. J. Han, H. Zhu and C. H. Wang, Ultrasensitive and Stretchable Strain Sensors Based on Mazelike Vertical Graphene Network, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2018, 10(42), 36312–36322 CrossRef CAS.
- F. Zhang, et al., Multi-modal strain and temperature sensor by hybridizing reduced graphene oxide and PEDOT:PSS, Compos. Sci. Technol., 2020, 187, 107959 CrossRef CAS.
- W. Xu, Y. Huang, X. Zhao, X. Jiang, T. Yang and H. Zhu, Patterning of graphene for highly sensitive strain sensing on various curved surfaces, Nano Select, 2021, 2(1), 121–128 CrossRef.
- T. Yang, X. Zhao, Y. He, and H. Zhu, 6 - Graphene-Based Sensors, in Graphene, ed. H. Zhu, Z. Xu, D. Xie, and Y. Fang, Academic Press, 2018, pp. 157–174 Search PubMed.
- B. Alemour, M. H. Yaacob, H. N. Lim and M. R. Hassan, Review of Electrical Properties of Graphene Conductive Composites, Int. J. Nanoelectron. Mater., 2018, 11(4), 371–398 Search PubMed.
- B. Sang, Z. W. Li, X. H. Li, L. G. Yu and Z. J. Zhang, Graphene-based flame retardants: a review, J. Mater. Sci., 2016, 51(18), 8271–8295 CrossRef CAS.
- D. Pierleoni, et al., Graphene-based coatings on polymer films for gas barrier applications, Carbon, 2016, 96, 503–512 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Xuejiao, Z. Qinfeng, W. Tianhao and Z. Liping, Electrically Conductive Graphene-Based Biodegradable Polymer Composite Films with High Thermal Stability and Flexibility, Nano, 2018, 13(3), 1850033 CrossRef.
- Y. Fan, L. Kang, W. Zhou, W. Jiang, L. Wang and A. Kawasaki, Control of doping by matrix in few-layer graphene/metal oxide composites with highly enhanced electrical conductivity, Carbon, 2015, 81, 83–90 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Xu, et al., Controlled soft-template synthesis of ultrathin C@ FeS nanosheets with high-Li-storage performance, ACS Nano, 2012, 6(6), 4713–4721 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Xu, et al., Controlled soft-template synthesis of ultrathin C@FeS nanosheets with high-Li-storage performance, ACS Nano, 2012, 6(6), 4713–4721 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Xu, D. D. L. Chung and C. Mroz, Thermally conducting aluminum nitride polymer-matrix composites, Composites, Part A, 2001, 32(12), 1749–1757 CrossRef.
- M. Mukherjee, C. K. Das and A. Kharitonov, Fluorinated and oxyfluorinated short Kevlar fiber-reinforced ethylene propylene polymer, Polym. Compos., 2006, 27(2), 205–212 CrossRef CAS.
- Z. M. Dang, J. K. Yuan, J. W. Zha, T. Zhou, S. T. Li and G. H. Hu, Fundamentals, processes and applications of high-permittivity polymer–matrix composites, Prog. Mater. Sci., 2012, 57(4), 660–723 CrossRef CAS.
- M. R. Wisnom, M. Gigliotti, N. Ersoy, M. Campbell and K. D. Potter, Mechanisms generating residual stresses and distortion during manufacture of polymer–matrix composite structures, Composites, Part A, 2006, 37(4), 522–529 CrossRef.
- C. Zhi, Y. Bando, C. Tang, H. Kuwahara and D. Golberg, Large-scale fabrication of boron nitride nanosheets and their utilization in polymeric composites with improved thermal and mechanical properties, Adv. Mater., 2009, 21(28), 2889–2893 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Cho, et al., Enhanced electrical conductivity of polymer nanocomposite based on edge-selectively functionalized graphene nanoplatelets, Compos. Sci., 2020, 189, 108001 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Liu, et al., Patterning two-dimensional free-standing surfaces with mesoporous conducting polymers, Nat. Commun., 2015, 6(1), 1–9 Search PubMed.
- J. Mei, Y. Zhang, T. Liao, Z. Sun and S. X. Dou, Strategies for improving the lithium-storage performance of 2D nanomaterials, Natl. Sci. Rev., 2018, 5(3), 389–416 CrossRef CAS.
- P. K. Mallick, Materials, design and manufacturing for lightweight vehicles, Woodhead publishing Elsevier, 2020 Search PubMed.
- M. Y. Lyu and T. G. Choi, Research trends in polymer materials for use in lightweight vehicles, Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf., 2015, 16(1), 213–220 CrossRef.
- J. Deng, et al., Sandwich-stacked SnO2/Cu hybrid nanosheets as multichannel anodes for lithium ion batteries, ACS Nano, 2013, 7(8), 6948–6954 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Pan, Y.-T. Liu, X.-M. Xie and X.-D. Zhu, Coordination-Driven Hierarchical Assembly of Silver Nanoparticles on MoS2 Nanosheets for Improved Lithium Storage, Chem.–Asian J., 2014, 9(6), 1519–1524 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Xing, et al., Graphene oxide/black phosphorus nanoflake aerogels with robust thermo-stability and significantly enhanced photothermal properties in air, Nanoscale, 2017, 9(24), 8096–8101 RSC.
- M. Qiu, et al., Novel concept of the smart NIR-light–controlled drug release of black phosphorus nanostructure for cancer therapy, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., 2018, 115(3), 501–506 CrossRef CAS.
- R. A. Ilyas, et al., Sugar palm (Arenga pinnata (Wurmb.) Merr) cellulosic fibre hierarchy: a comprehensive approach from macro to nano scale, J. Mater. Res. Technol., 2019, 8(3), 2753–2766 CrossRef CAS.
- M. J. Halimatul, S. M. Sapuan, M. Jawaid, M. R. Ishak and R. A. Ilyas, Effect of sago starch and plasticizer content on the properties of thermoplastic films: mechanical testing and cyclic soaking-drying, Polimery, 2019, 64, 422–431 CrossRef CAS.
- M. J. Halimatul, S. M. Sapuan, M. Jawaid, M. R. Ishak and R. A. Ilyas, Water absorption and water solubility properties of sago starch biopolymer composite films filled with sugar palm particles, Polimery, 2019, 64, 595–603 CAS.
- H. Abral, et al., A simple method for improving the properties of the sago starch films prepared by using ultrasonication treatment, Food Hydrocolloids, 2019, 93, 276–283 CrossRef CAS.
- D. Chimene, D. L. Alge and A. K. Gaharwar, Two-Dimensional Nanomaterials for Biomedical Applications: Emerging Trends and Future Prospects, Adv. Mater., 2015, 27(45), 7261–7284 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. L. Sanyang, R. A. Ilyas, S. M. Sapuan, and R. Jumaidin, Sugar palm starch-based composites for packaging applications, in Bionanocomposites for packaging applications, Springer, 2018, pp. 125–147 Search PubMed.
- R. A. Ilyas, S. M. Sapuan, M. R. Ishak and E. S. Zainudin, Sugar palm nanofibrillated cellulose (Arenga pinnata (Wurmb.) Merr): effect of cycles on their yield, physic-chemical, morphological and thermal behavior, Int. J. Biol. Macromol., 2019, 123, 379–388 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. A. Ilyas, S. M. Sapuan, M. R. Ishak and E. S. Zainudin, Effect of delignification on the physical, thermal, chemical, and structural properties of sugar palm fibre, BioResources, 2017, 12(4), 8734–8754 CAS.
- R. A. Ilyas, S. M. Sapuan, M. L. Sanyang, M. R. Ishak and E. S. Zainudin, Nanocrystalline cellulose as reinforcement for polymeric matrix nanocomposites and its potential applications: a review, Curr. Anal. Chem., 2018, 14(3), 203–225 CrossRef CAS.
- R. A. Ilyas, S. M. Sapuan, M. R. Ishak, and E. S. Zainudin, Sugar palm nanocrystalline cellulose reinforced sugar palm starch composite: Degradation and water-barrier properties, in IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, IOP Publishing, 2018, vol. 368, no. 1, p. 012006 Search PubMed.
- Y. Cheng, et al., Peptide–graphene interactions enhance the mechanical properties of silk fibroin, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2015, 7(39), 21787–21796 CrossRef CAS.
- W. Liu, B. Ullah, C.-C. Kuo and X. Cai, Two-Dimensional Nanomaterials-Based Polymer Composites: Fabrication and Energy Storage Applications, Adv. Polym. Technol., 2019, 2019, 4294306 Search PubMed.
- H. Aoki and S. D. Mildred, Physics of Graphene, Springer Science & Business Media, 2013 Search PubMed.
- S. Shadlou, B. Ahmadi Moghadam and F. Taheri, The effect of strain-rate on the tensile and compressive behavior of graphene reinforced epoxy/nanocomposites, Mater. Des., 2014, 59, 439–447 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Lee, X. Wei, J. W. Kysar and J. J. S. Hone, Measurement of the elastic properties and intrinsic strength of monolayer graphene, Science, 2008, 321(5887), 385–388 CrossRef CAS.
- C. L. Wong, M. Annamalai, Z. Q. Wang and M. Palaniapan, Characterization of nanomechanical graphene drum structures, J. Micromech. Microeng., 2010, 20(11), 115029 CrossRef.
- J. S. Bunch, et al., Impermeable Atomic Membranes from Graphene Sheets, Nano Lett., 2008, 8(8), 2458–2462 CrossRef CAS.
- S. P. Koenig, N. G. Boddeti, M. L. Dunn and J. S. Bunch, Ultrastrong adhesion of graphene membranes, Nat. Nanotechnol., 2011, 6(9), 543–546 CrossRef CAS.
- J.-U. Lee, D. Yoon and H. Cheong, Estimation of Young's Modulus of Graphene by Raman Spectroscopy, Nano Lett., 2012, 12(9), 4444–4448 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. Li, Z. You, G. Haugstad and T. Cui, Graphene fixed-end beam arrays based on mechanical exfoliation, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2011, 98(25), 253105 CrossRef.
- G. López-Polín, et al., Increasing the elastic modulus of graphene by controlled defect creation, Nat. Phys., 2015, 11(1), 26–31 Search PubMed.
- C. Gómez-Navarro, M. Burghard and K. Kern, Elastic Properties of Chemically Derived Single Graphene Sheets, Nano Lett., 2008, 8(7), 2045–2049 CrossRef.
- C. Vargas, et al., Softened Elastic Response and Unzipping in Chemical Vapor Deposition graphene, Nano Lett., 2011, 11, 2259–2263 CrossRef PubMed.
- G.-H. Lee, et al., High-Strength Chemical-Vapor–Deposited Graphene and Grain Boundaries, Science, 2013, 340(6136), 1073–1076 CrossRef CAS.
- Q.-Y. Lin, et al., Stretch-Induced Stiffness Enhancement of Graphene Grown by Chemical Vapor Deposition, ACS Nano, 2013, 7(2), 1171–1177 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Bertolazzi, J. Brivio and A. Kis, Stretching and Breaking of Ultrathin MoS2, ACS Nano, 2011, 5(12), 9703–9709 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Castellanos-Gomez, M. Poot, G. A. Steele, H. S. J. van der Zant, N. Agraït and G. Rubio-Bollinger, Mechanical properties of freely suspended semiconducting graphene-like layers based on MoS2, Nanoscale Res. Lett., 2012, 7(1), 233 CrossRef PubMed.
- A. Castellanos-Gomez, M. Poot, G. A. Steele, H. S. J. van der Zant, N. Agraït and G. Rubio-Bollinger, Elastic Properties of Freely Suspended MoS2 Nanosheets, Adv. Mater., 2012, 24(6), 772–775 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. Liu, et al., Elastic Properties of Chemical-Vapor-Deposited Monolayer MoS2, WS2, and Their Bilayer Heterostructures, Nano Lett., 2014, 14(9), 5097–5103 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. Zhang, V. Koutsos and R. Cheung, Elastic properties of suspended multilayer WSe2, ACS Nano, 2016, 108(4), 042104 Search PubMed.
- J. Tao, et al., Mechanical and Electrical Anisotropy of Few-Layer Black Phosphorus, ACS Nano, 2015, 9(11), 11362–11370 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J.-Y. Wang, Y. Li, Z.-Y. Zhan, T. Li, L. Zhen and C.-Y. Xu, Elastic properties of suspended black phosphorus nanosheets, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2016, 108(1), 013104 CrossRef.
- J. W. Suk, R. D. Piner, J. An and R. S. Ruoff, Mechanical Properties of Monolayer Graphene Oxide, ACS Nano, 2010, 4(11), 6557–6564 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Castellanos-Gomez, et al., Mechanical properties of freely suspended atomically thin dielectric layers of mica, Nano Res., 2012, 5(8), 550–557 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Song, et al., Large Scale Growth and Characterization of Atomic Hexagonal Boron Nitride Layers, Nano Lett., 2010, 10(8), 3209–3215 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Velický and P. S. Toth, From two-dimensional materials to their heterostructures: An electrochemist's perspective, Appl. Mater. Today, 2017, 8, 68–103 CrossRef.
- S. Bandyopadhyay, Straintronics: Digital and Analog Electronics With Strain-Switched Nanomagnets, IEEE Open J. Nanotechnol., 2020, 1, 57–64 Search PubMed.
- A. A. Bukharaev, A. K. Zvezdin, A. P. Pyatakov and Y. K. Fetisov, Straintronics: a new trend in micro- and nanoelectronics and materials science, Phys.-Usp., 2018, 61(12), 1175–1212 CrossRef CAS.
- I. Y. Sahalianov, T. M. Radchenko, V. A. Tatarenko, G. Cuniberti and Y. I. Prylutskyy, Straintronics in graphene: Extra large electronic band gap induced by tensile and shear strains, J. Appl. Phys., 2019, 126(5), 054302 CrossRef.
- P. Gant, P. Huang, D. Pérez de Lara, D. Guo, R. Frisenda and A. Castellanos-Gomez, A strain tunable single-layer MoS2 photodetector, Mater. Today, 2019, 27, 8–13 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Chaves, et al., Bandgap engineering of two-dimensional semiconductor materials, npj 2D Mater. Appl., 2020, 4(1), 29 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Chen, X. Gao and D. Xu, Recent Advances in Characterization Techniques for the Interface in Carbon Nanotube-Reinforced Polymer Nanocomposites, Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng., 2019 DOI:10.1155/2019/5268267.
- J. J. Bae, et al., Thickness-dependent in-plane thermal conductivity of suspended MoS2 grown by chemical vapor deposition, Nanoscale, 2017, 9(7), 2541–2547, 10.1039/C6NR09484H.
- F. Wang, S. Li, M. A. Bissett, I. A. Kinloch, Z. Li and R. J. Young, Strain engineering in monolayer WS2 and WS2 nanocomposites, 2D Materials, 2020, 7(4), 045022 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Singla, A. Pal Singh, S. Kumar, G. Singh and N. Kumar, Characterization of MWCNTs-polystyrene nanocomposite based strain sensor, Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng., Part E, 2020, 0954408920966301 Search PubMed.
- A. H. Loo, B. Alessandra, S. Zdenek and P. Martin, Exfoliated transition metal dichalcogenides (MoS2, MoSe2, WS2, WSe2): An electrochemical impedance spectroscopic investigation, Electrochem. Commun., 2015, 50, 39–42 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Zhu, T. Zhang, Z. Sun, H. Chen, J. Guan, X. Chen, H. Ji, P. Du and S. Yang, Adv. Mater., 2017, 29, 1605776 CrossRef PubMed.
- Y. W. Song, Carbon nanotube and graphene photonic devices, in Photodetectors Materials, Devices and Applications, Woodhead Publishing, 2016, pp. 47–85 Search PubMed.
- A. Jain and A. J. McGaughey, Strongly anisotropic in-plane thermal transport in single-layer black phosphorene, Sci. Rep., 2015, 5, 8501 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Taube, J. Judek, A. Łapińska and M. Zdrojek, Temperature-dependent thermal properties of supported MoS2 monolayers, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2015, 7(9), 5061–5065 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Sahoo, A. P. S. Gaur, M. Ahmadi, M. J. F. Guinel and R. S. Katiyar, Temperature-dependent Raman studies and thermal conductivity of few-layer MoS2, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2013, 117(17), 9042–9047 CrossRef CAS.
- Z. Yan, et al., Phonon and thermal properties of exfoliated TaSe2 thin films, J. Appl. Phys., 2013, 114(20), 204301 CrossRef.
- C. Chiritescu, et al., Ultralow thermal conductivity in disordered, layered WSe2 crystals, Science, 2007, 315(5810), 351–353 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Wan, et al., Flexible n-type thermoelectric materials by organic intercalation of layered transition metal dichalcogenide TiS2, Nat. Mater., 2015, 14(6), 622–627 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- N. Peimyoo, J. Shang, W. Yang, Y. Wang, C. Cong and T. Yu, Thermal conductivity determination of suspended mono-and bilayer WS2 by Raman spectroscopy, Nano Res., 2015, 8(4), 1210–1221 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Dominik and K. Andras, Breakdown of High-Performance Monolayer MoS2 Transistors, ACS Nano, 2012, 6(11), 10070–10075 CrossRef.
- S. Riazimehr, A. Bablich, D. Schneider, S. Kataria, V. Passi, C. Yim, G. S. Duesberg and M. C. Lemme, Spectral sensitivity of graphene/silicon heterojunction photodetectors, Solid-State Electron., 2016, 115, 207–212 CrossRef CAS.
- M. A. Kinch, Fundamentals of Infrared Detector Materials, Society of Photo Optical, 2007 Search PubMed.
- J. Zhu, H. Park, J.-Y. Chen, X. Gu, H. Zhang, S. Karthikeyan, N. Wendel, S. A. Campbell, M. Dawber, X. Du, M. Li, J.-P. Wang, R. Yang and X. Wang, Revealing the origins of 3D anisotropic thermal conductivities of black phosphorus, Adv. Electron. Mater., 2016, 2, 1600040 CrossRef.
- G. Zhu, et al., Constructing a 2D/2D Bi2O2CO3/Bi4O5Br2 heterostructure as a direct Z-scheme photocatalyst with enhanced photocatalytic activity for NOx removal, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2019, 493, 913–925 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Kittel and P. McEuen, Introduction to Solid State Physics, Wiley, New York, 1996 Search PubMed.
- X. Bao, Q. Ou, Z. Q. Xu, Y. Zhang, Q. Bao and H. Zhang, Band structure engineering in 2D materials for optoelectronic applications, Adv. Mater. Technol., 2018, 3(11), 1800072 CrossRef.
- W. Zhang, Q. Wang, Y. Chen, Z. Wang and A. T. S. Wee, van der Waals stacked 2D layered materials for optoelectronics, 2D Materials, 2016, 3(2), 022001 CrossRef.
- D. Werdehausen, et al., Design rules for customizable optical materials based on nanocomposites, Opt. Mater. Express, 2018, 8(11), 3456–3469 CrossRef CAS.
- D. Werdehausen et al., Using effective medium theories to design tailored nanocomposite materials for optical systems, in Current Developments in Lens Design and Optical Engineering XIX, International Society for Optics and Photonics, 2018, vol. 10745, p. 107450H Search PubMed.
- J. Burunkova, et al., Polymer–chalcogenide glass nanocomposites for amplitude–phase modulated optical relief recording, J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron., 2019, 30(10), 9742–9750 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Jakubczak, et al., Filtration Materials Modified with 2D Nanocomposites—A New Perspective for Point-of-Use Water Treatment, Materials, 2021, 14(1), 182 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Sher, et al., The controlled synthesis of g-C3N4/Cd-doped ZnO nanocomposites as potential photocatalysts for the disinfection and degradation of organic pollutants under visible light irradiation, RSC Adv., 2021, 11(4), 2025–2039 RSC.
- M. A. Qamar, et al., Designing of highly active g-C3N4/Ni-ZnO photocatalyst nanocomposite for the disinfection and degradation of the organic dye under sunlight radiations, Colloids Surf., A, 2021, 614, 126176 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Han, et al., Mechanical, toughness and thermal properties of 2D material- reinforced epoxy composites, Polymer, 2019, 184, 121884 CrossRef CAS.
- W. A. Lee Sanchez, et al., Enhanced Thermal Conductivity of Epoxy Composites Filled with Al2O3/Boron Nitride Hybrids for Underfill Encapsulation Materials, Polymers, 2021, 13(1), 147 CrossRef.
- M. Ren, et al., Hierarchical Composite of Sb2S3 Decorated on Highly Crumpled Ti3C2Tx nanosheets for Enhanced Sodium Storage Properties, Electrochim. Acta, 2021, 137835 CrossRef CAS.
- R. Syamsai, et al., Double transition metal MXene (TiXTa4−XC3) 2D materials as anodes for Li-ion batteries, Sci. Rep., 2021, 11(1), 688 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Fernández García, V. Torres Costa, O. de Melo, F. Agulló Rueda, G. R. Castro and M. Manso Silvan, Growth of out-of-plane standing MoTe2(1-X)Se2X/MoSe2 composite flake films by sol–gel nucleation of MoOy and isothermal closed space telluro-selenization, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2021, 546, 149076 CrossRef.
- X. Chen, et al., MXene/Polymer Nanocomposites: Preparation, Properties, and Applications, Polym. Rev., 2021, 61(1), 80–115 CrossRef CAS.
- C. J. Angammana, R. J. Gerakopulos and S. H. Jayaram, Mass Production of Nanocomposites Using Electrospinning, IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl., 2019, 55(1), 817–824 CAS.
- A. Gigot, et al., Mixed 1T–2H Phase MoS2/Reduced Graphene Oxide as Active Electrode for Enhanced Supercapacitive Performance, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2016, 8(48), 32842–32852 CrossRef CAS.
Footnote |
| † These authors contributed equally to this work. |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2021 |