Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleDunaliella Salinas based Sn–carbon anode for high-performance Li-ion batteries†
Yuhua Yang ab,
Yecheng Dongc,
Ziwei Zhangd,
Zhichao Xic,
Junhuai Xiang
ab,
Yecheng Dongc,
Ziwei Zhangd,
Zhichao Xic,
Junhuai Xiang *ab,
Xiaohua Ouyanga,
Tingting Wanga,
Li Qiua and
Jun Zhou*d
*ab,
Xiaohua Ouyanga,
Tingting Wanga,
Li Qiua and
Jun Zhou*d
aSchool of Materials and Mechanical & Electrical Engineering, Jiangxi Science and Technology Normal University, Nanchang 330038, P. R. China. E-mail: Xiangjunhuai@163.com
bJiangxi Key Laboratory of Surface Engineering, Jiangxi Science and Technology Normal University, Nanchang 330038, P. R. China
cInformation Engineering School, Nanchang University, Nanchang 330038, P. R. China
dSchool of Communications and Electronics, Jiangxi Science and Technology Normal University, Nanchang 330013, P. R. China. E-mail: B12070015@hnu.edu.cn; Tel: +8613767508792
First published on 3rd December 2021
Abstract
Long life, high capacity, environmental friendliness and good rate performance are the most important elements in the research of lithium ion batteries (LIBs). In this paper, Sn–carbon composite electrode materials are prepared using Dunaliella Salinas based carbon (amorphous carbon) as an amorphous carbon precursor combined with tin. Hence, an amorphous carbon template enwrapped by Sn particles forms a core–shell structure (Sn–carbon composite), the annealed Dunaliella Salinas based carbon makes up the carbon core, and Sn particles form the shell of the material. The components of the materials, microstructure and electrochemical properties of LIBs were characterized and tested. The results show that the prepared Sn–carbon composite electrode materials have high purity and combine with amorphous carbon uniformly. The Sn–carbon composite exhibits excellent performance as a LIB anode, its discharge capacities of the 1st, 2nd, and 4th cycles are 1777.39, 944.15 and 722.46 mA h g−1 at a current density of 100 mA g−1, and the capacity is 619.09 mA h g−1 after stable cycling at a current density of 200 mA g−1. The capacity continues to rise at a high current density of 1000 mA g−1 and is 574.97 mA h g−1 at its maximum, demonstrating the excellent performance of the electrode.
Introduction
Traditional fossil energy, hydraulic electrogenerating and new types of energy harnessing, such as wind energy, tidal energy, solar energy, etc., cannot fulfill the growing demands for energy use.1,2 Therefore, lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) have become increasingly more important.3–11 These cells can not only store electrical energy, but also act as portable energy sources for our daily lives. LIBs have the advantages of high energy density, environmental friendliness, low weight, high capacity and so on, and are widely used in mobile phones, laptops, electric vehicles and other devices.12–16 However, the high capacity, long life and excellent rate performances of LIBs still need to be further improved, and their costs needs to be reduced continuously to meet the expanding application market.16–23There are a large number of tin resources in the earth, and smelting costs are low.24,25 At the same time, the theoretical capacity of tin is high for LIBs, at up to 981 mA h g−1.26–28 LIBs have been prepared using metal tin compounded with carbon in the previous literature, and the performance of the associated LIBs is good, but the carbon almost acts as a template.29,30 Dunaliella Salinas, a type of micro-algae, is widely found in the oceans and salt lakes. It is non-toxic and harmless to human beings, and at the same time, it has high salt tolerance, therefore making Dunaliella Salinas a perfect choice to use as a carbon source to absorb and compound metal tin ions.18,31,32 Therefore, based on the idea of absorbing and compounding metal tin ions using Dunaliella Salinas, in this work, Dunaliella Salinas based carbon was selected as a carbon source, and tin tetrachloride was absorbed and compounded after cultivation in a 200‰ salinity environment, then the Sn–amorphous carbon composite (Sn–carbon composite) electrode material was obtained after being annealed under argon protection. In the electrochemical testing of LIBs, as an anode, the experimental results of the Sn–carbon composite show that it has high capacity, stability and good rate performance.
Materials and methods
Experimental raw materials
The experimental reagents were purchased directly, anhydrous ethanol (CH3CH2OH) was acquired from Tianjin Fuyu Fine Chemical Co., Ltd, and tin tetrachloride (SnCl4) was obtained from Tianjin Guanfu Fine Chemical Co., Ltd, which were supplied as analytical reagents and not further purified prior to their use. The culture concentration of sodium chloride was 200‰, according to a normal f/2 culture medium. The chemicals and artificial seawater for Dunaliella Salinas culture were purchased directly, and were all analytical reagents and used without further purification.Preparation of Sn–carbon composite LIB materials
Firstly, the prepared f/2 culture solution and the Dunaliella Salinas solution were mixed in a 3![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 ratio and shaken under an illumination intensity of 6000 Lux, where illumination under light and dark conditions were alternated according to 14
1 ratio and shaken under an illumination intensity of 6000 Lux, where illumination under light and dark conditions were alternated according to 14![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10 h, and the mixture was shaken well three times at regular intervals. After 14 days of culture, the process was continued for 10 days according to the 3
10 h, and the mixture was shaken well three times at regular intervals. After 14 days of culture, the process was continued for 10 days according to the 3![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 ratio used above. The resultant product was used as a precursor for amorphous carbon.
1 ratio used above. The resultant product was used as a precursor for amorphous carbon.
Secondly, 4 L of amorphous carbon precursor was taken up, to which 15 g of tin tetrachloride particles were added and the mixture was shaken gently until it melted slowly over 48 h. Then, the solution was centrifuged for 2 min at 1100 rpm in order to get rid of the bottom slag. The liquid supernatant was then centrifuged at 5000 rpm for 10 min to obtain a precipitate. The precipitate was washed with concentrated hydrochloric acid and deionized water (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 m m−1) twice, and subsequently washed with anhydrous ethanol and deionized water twice, before being treated by cryodesiccation.
1 m m−1) twice, and subsequently washed with anhydrous ethanol and deionized water twice, before being treated by cryodesiccation.
Finally, the dried material was annealed in a tubular furnace under an argon atmosphere. The heating rate was 6.7 °C min−1, and the time of temperature preservation was 1 minute after 800 °C. After annealing, the material was cooled naturally. The prepared sample was Sn–carbon composite, which was used as an electrode material.
Characterization of Sn–carbon composite LIB materials
The phase composition and crystallization of the samples were investigated using an X-ray powder diffractometer (XRD, Rigaku D/max-2500, Cu Kα, λ = 0.154056 nm). The diffraction angle (2θ) was in the range of 5–80°. The microstructures of the samples were measured by field emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM, FEI Nova NanoSEM 230, 15 kV). Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and high-resolution TEM (HRTEM) images were recorded using a Jeol 2100f microscope. Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA, PerkinElmer, Diamond TG/DTA) was carried out from room temperature to 1000 °C at a heating rate of 10 °C min−1 in air.Electrochemical measurements of Sn–carbon composite LIBs
0.1 g of Sn–carbon composite powder was blended with 0.0215 g of acetylene black, which was then added into a 0.5 g solution of N-methylpyrrolidone containing 0.0215 g of polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF), then the slurry was spread onto copper foil to use as a working anode and a lithium sheet was used as the counter electrode. The Sn–carbon composite active material represented 70% of the whole anode (w/w, the whole anode does not include the weight of the copper foil). The loading of the Sn–carbon composite active material was up to 0.5 mg cm−2. The electrolyte was 1 M L−1 LiPF6 in ethylene carbonate (EC)–diethyl carbonate (DEC), where the volumetric ratio of EC to DEC was 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1, and microporous polypropylene was used as the separator between the working anode and metallic lithium sheet. Coin batteries were assembled under an argon atmosphere in a glove box. The battery capacity and rate performance test equipment used was a Xinwei battery testing system (Neware BTS-CT-3008-TC 5.X, Shenzhen, China), which was operated over a test voltage range of 0.01–3 V. The capacity was measured based on the whole content of the Sn–carbon composite material. Cyclic voltammetry (CV) curves and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (Chenhua CHI 660E, Shanghai, China) measurements were recorded on an electrochemical workstation. The CV scan rate was 0.5 mV s−1. The frequency range of the impedance tests was 0.01 Hz to 100 kHz.
1, and microporous polypropylene was used as the separator between the working anode and metallic lithium sheet. Coin batteries were assembled under an argon atmosphere in a glove box. The battery capacity and rate performance test equipment used was a Xinwei battery testing system (Neware BTS-CT-3008-TC 5.X, Shenzhen, China), which was operated over a test voltage range of 0.01–3 V. The capacity was measured based on the whole content of the Sn–carbon composite material. Cyclic voltammetry (CV) curves and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (Chenhua CHI 660E, Shanghai, China) measurements were recorded on an electrochemical workstation. The CV scan rate was 0.5 mV s−1. The frequency range of the impedance tests was 0.01 Hz to 100 kHz.
Results and discussion
The synthesis of the Sn–carbon composite sample is shown in Fig. 1a. After 14 days' culture, SnCl4 particles were added into Dunaliella Salinas solution, then they were soaked for 48 h. Then, the mixed solution was centrifuged, dried and annealed to obtain a Sn–carbon composite sample. Overall, the preparation process is very simple.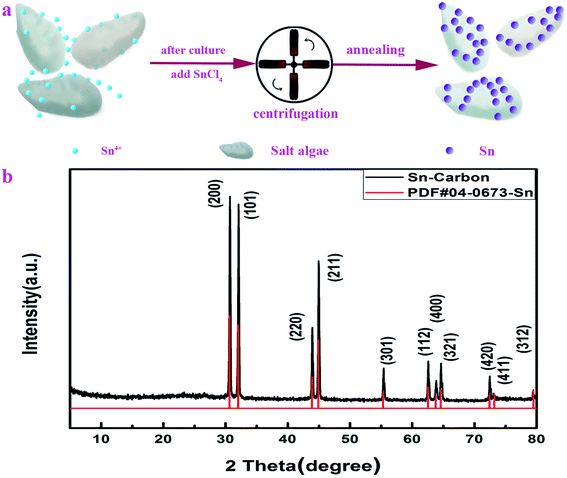 | ||
| Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of the materials synthesis process and XRD pattern of the Sn–carbon composite sample. (a) Schematic diagram. (b) XRD pattern. | ||
Fig. 1b shows the XRD diffraction pattern of the prepared Sn–carbon composite sample. It can be seen from the figure that each diffraction peak of the Sn–carbon composite sample is almost sharp and straight, showing that its crystallinity is very high. Its four highest characteristic peaks located at (200), (101), (220) and (211) coincide well with the corresponding standard diffraction peaks of PDF#04-0673-Sn. It is worth noting that the other diffraction peaks also correspond well, indicating that the tin tetrachloride added in the preparation process is completely transformed into simple Sn after annealing. Because argon gas is used in the annealing process, it is the reduction of carbon in the annealing process that leads to the formation of metallic Sn. At high temperature, the Dunaliella Salinas based carbon becomes a carbon phase. There is no obvious carbon diffraction peak in Fig. 1b, but there is a weak diffraction peak near to 26.6° corresponding to a carbon peak, which indicates that the diffraction peak intensity of Sn is much stronger than that of the carbon diffraction peak, so the diffraction peak of carbon appears as being very weak in intensity. From Fig. 1b, because there is only Sn material, this proves that the sample has no other metal impurities. From the XRD data and using the Debye–Scherrer equation, the Sn particles have average size of about 162.75 nm.
In order to understand the microstructure of the prepared Sn–carbon composite, the morphology was investigated using field emission scanning electron microscopy (SEM), as shown in Fig. 2. Fig. 2a shows an SEM image, in which it can be seen that the Sn–carbon composite is composed of lots of elliptical-shaped matter and a large number of small particles, which is the result of a large number of metal Sn particles attaching to the surface of the amorphous carbon. At the same time, this shows that the metal Sn particles widely exist and are distributed uniformly in the sample, but that the Sn particles are of different sizes. Because plenty of Sn particles attach to the surfaces of amorphous carbon, we only observe Sn particles on the elliptic amorphous carbon, where the amorphous carbon acts as a firm template.33 In fact, Dunaliella Salinas exhibits different shapes, oval or pear-shaped, and the size generally becomes smaller with an increase in the salinity. In order to determine its particular shape, Fig. 2b shows another shape of Dunaliella Salinas, similar to a pear shape, of around 2.3 μm in length and 1.3 μm in width. Fig. 2b also shows a larger metal Sn particle of about 2.2 μm in size without the influence of an electron beam, and it has defects on its surface.34
The elemental maps shown in Fig. 2c–e further confirm the distribution of the Sn particles and amorphous carbon. Fig. 2c shows a selected-location SEM image, whereas Fig. 2d and e just show that the elements Sn and C are distributed with no repeat, implying that the Sn particles are mainly spherical and that the amorphous carbon is pear-shaped. In order to further investigate the shape of the amorphous carbon thoroughly, the elemental map of C in the sample was recorded using energy dispersive spectroscopy mapping. As can be seen from the original SEM image in ESI Fig. 1a,† the sample has four types of irregular amorphous carbon, the EDS mapping in ESI Fig. 1b† also shows concentrated C dots, which constitute the corresponding amorphous carbon. ESI Fig. 1† shows that the Dunaliella Salinas has no regular shape.
TEM and HRTEM images were recorded to discover the microstructure of the material. As shown in Fig. 3a, the side view TEM image displays that the surface of the Sn–carbon composite sample has plenty of grainy black plots that vary in size and most of which are not more than 10 nm in size. The magnified TEM image of the side view further displays the size of the particles, as shown in Fig. 3b, wherein most of the particles are around 5 nm. In the meantime, we can also see that there are a lot of Sn particles distributed in the sample. Fig. 3a and b reflects that Sn particles have reached nanoscale size, because the TEM sample was prepared via ultrasonic treatment, and the outer Sn particles on the amorphous carbon were washed. From Fig. 1b and 2a, b, it is easy to conclude that the inner Sn particles are far smaller than the Sn particles far from the surface, which further implies that the Sn particles form small particles first, but then as time passes, the Sn particles grow increasingly larger. The HRTEM image (see Fig. 3c) implies that the crystallinity of the Sn–carbon composite is good, and that the interplanar spacing is about 0.273 nm, coinciding with the (101) lattice plane shown in Fig. 1b. Fig. 3d shows two kinds of shapes of the amorphous carbon. One is a long strip of amorphous carbon, which is 1.5 μm in width and 4 μm in length and has the same dimensions at both ends. The other shape is a pear-shaped Dunaliella Salina, which coincides with Fig. 2, which is around 1 μm in width on its biggest side and 2.5 μm in length. We can see there are a few black block-like materials in or outside the amorphous carbon, as found in our early research,31,32,35 which consider to be a core–shell structure.
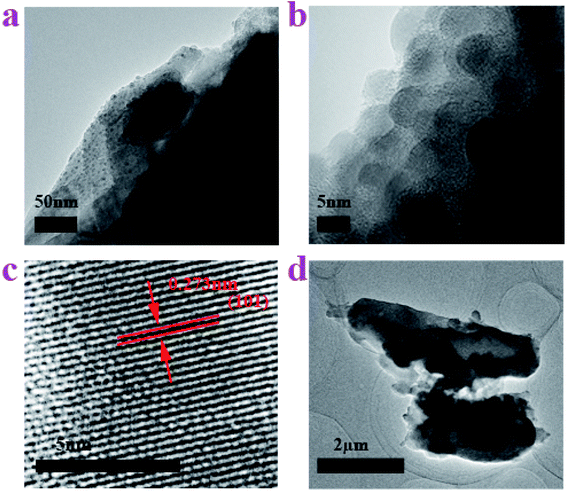 | ||
| Fig. 3 TEM images of the Sn–carbon composite sample. (a) TEM image of side view. (b) Enlarged TEM image of side view. (c) HRTEM image. (d) Shape of the amorphous carbon. | ||
ESI Fig. 2a† shows the partial section of amorphous carbon after being washed with hydrochloric acid, from which we can see that its surface is smooth except for some adhered particles. The HRTEM image of this amorphous carbon (see ESI Fig. 2b†) implies that the Dunaliella Salinas based carbon is mainly composed of amorphous carbon.
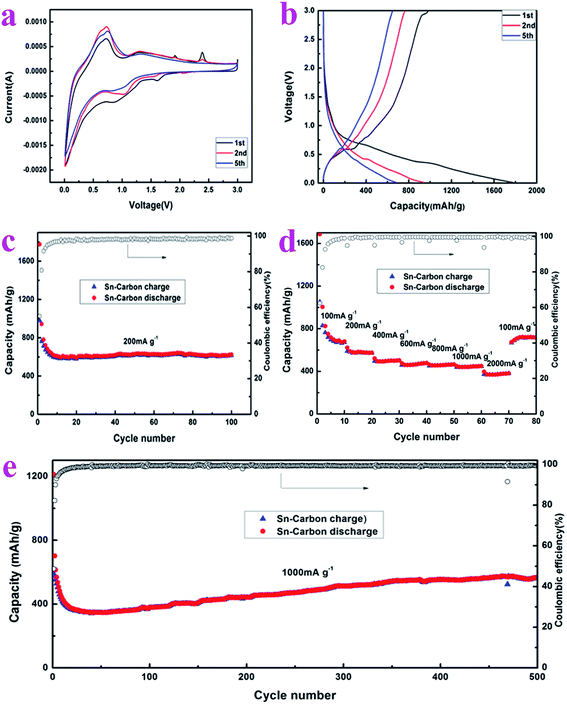
In order to understand the electrochemical properties of the prepared Sn–carbon composite samples, as shown in Fig. 4, the cyclic voltammetry (CV) curves, charge/discharge cycle curves, capacity at a current density of 200 mA g−1, cycling stability and coulombic efficiency, rate performance and capacity, and cycling stability and coulombic efficiency at a current density of 1000 mA g−1 were measured using an electrochemical workstation and battery testing system. Fig. 4a shows the CV curves recorded at a scan rate 0.5 mV s−1 over a voltage range of 0.01–3.0 V. The curves feature two oxidation peaks at 1.6 V and 0.9 V, which means that the Sn–carbon composite electrode exhibits a discharge plateau at these two places. This stage will form a solid electrolyte interphase (SEI) layer, and the Li ions will shuttle back and forth between the anode and cathode.36 The peak at 1.6 V is small and sharp, meaning that the plateau is very small. In the second and fifth cycles, the peak at 1.6 V decreases slowly until it disappears, while the peak at 0.9 V shifts to 1.0 V (the second cycle) and then widens. In the first charge process, there are four charge reduction peaks at 0.6, 1.3, 1.9, 2.4 V, respectively, in which the first two voltages are flat and large, which indicates that the two plateaus have a great influence on the batteries, while the latter two voltage plateaus are very sharp, implying that the influence on the electrode is small. It is worth noting that in the second and fifth cycles, the peaks at 1.9 and 2.4 V disappear, which means that these reactions are irreversible, while the peaks at 0.7 and 1.3 V are still present, indicating that these reactions are influential, especially that at 0.7 V during charge/discharge.
The charge/discharge curves can be seen in Fig. 4b, recorded at a current density of 200 mA g−1 across a voltage range of 0.01–3 V, wherein it can be seen that there are two discharge plateaus at 0.9 V and 0.4 V for the first discharge course, and that the discharge plateaus disappear gradually during the second and fifth cycles of discharge, respectively. The specific discharge capacity for the first time reaches 1777.39 mA h g−1. The reason why the discharge plateaus disappear and the specific capacity of the first discharge decreases greatly in the second cycle is due to the formation of the first solid electrolyte interface and irreversible partial capacity loss. The CV curves in Fig. 4a also show its gradual disappearance. On the other hand, it may be that as the current density is higher at 200 mA g−1 during discharge, the small plateau at 1.6 V is invisible. During the first charge, there are two obvious charge plateaus at 0.6 V and 2.9 V, and the first charge specific capacity is 979.17 mA h g−1. During the second and fifth cycles of charging, the charge plateau gradually disappears. The charge plateaus at 1.3, 1.9, 2.4 V in the CV curves are invisible in the charge curves due to the high current density of 200 mA g−1 during charging. It can be observed from the charge/discharge process that the coulombic efficiency of the first charge/discharge is 55.10%. The reactions that occur during charge/discharge may be as follows:
| Sn + xLi+ + xe− ↔ LixSn (0 ≤ x ≤ 4.4) | (1) |
| C + xLi+ + xe− ↔ LixC | (2) |
The capacity, stability and corresponding coulombic efficiency of the electrode are important parameters of an electrode material. As shown in Fig. 4c, the cycling performance of the Sn–carbon composite electrode was measured at a current density of 200 mA g−1, the charge/discharge range was 0.01–3.0 V and the number of cycles was 100. Over the first few cycles, due to the formation of the solid electrolyte interface membrane and the loss in the partial irreversible capacity, and the marginal electrode reaction at the surface of the electrolyte, there is a fast reduction in the charge/discharge specific capacities of the electrode. However, the coulombic efficiency increases rapidly from 55.10% for the first cycle, to 80.79% in the second cycle, and reaches more than 98% soon after a few cycles. At the same time, the discharge specific capacities of the Sn–carbon composite electrode at the 10th, 20th, 40th, 60th, 80th, and 100th cycles are 608.42, 589.13, 618.52, 629.14, 627.04, 623.50 mA h g−1, respectively, and the average discharge specific capacity for each cycle is 619.09 mA h g−1, and at the same time, it can be seen from Fig. 4c that the Sn–carbon composite electrode maintains very good cycling stability. This shows that our prepared Sn–carbon composite electrode is a good electrode material, but ordinary Sn anodes often exhibit poor cyclability.37
In order to study the adaptability to frequency variation of the Sn–carbon composite electrode, we measured its rate performance upon increasing the current density. Fig. 4d shows that the average discharge specific capacities of the Sn–carbon composite electrode at current densities of 100, 200, 400, 600, 800, 1000 and 2000 mA g−1 are 821.23, 583.10, 499.94, 467.80, 459.79, 444.93 and 376.18 mA h g−1, respectively. When the current density returns to 100 mA g−1, the discharge specific capacity of the electrode increases to 711.94 mA h g−1. If the discharge specific capacities of the first three cycles are excluded, the discharge specific capacities not only rise, but also exceed the capacities noted during the previous measurement at 100 mA g−1. It is worth noting that when the current densities rise through 400, 600, 800, 1000 mA g−1 (current density increases of 33.33%, 25%, 20%, respectively), the discharge specific capacities only slightly decrease (6.43%, 1.71%, 3.23%, respectively), and the capacities are very stable. This means that the rate performance of the Sn–carbon composite electrode is excellent, making it particularly suitable for applications that require a high current charge and discharge. In terms of coulombic efficiency, the first coulombic efficiency of the Sn–carbon composite electrode reaches 62.38% when the current density is 100 mA g−1, and the coulombic efficiency reaches more than 98% at the seventh cycle, and more than 99% during the subsequent tests when the current density is increased. The first coulombic efficiency changes from 55.10% at a current density of 200 mA g−1 to 62.38% at a current density of 100 mA g−1, which implies that a higher current has an important influence on the coulombic efficiency for the first charge/discharge cycle.
As shown in ESI Fig. 4† (TGA data of the Sn–carbon composite), according to the retained weight of 86.52% at 800 °C, and the detailed TGA analysis of the Sn–C composite in ref. 34, after our calculations, the Sn (wt%) was found to be 68.18% and that of the amorphous carbon (wt%) was 31.82%. Using the theoretical capacity of Sn 981 mA h g−1, and that of carbon 372 mA h g−1, the theoretical capacity of the Sn–carbon composite can be calculated as 787.21 mA h g−1.
In view of the capacity change of the Sn–carbon composite electrode, we also tested it at high current density (see Fig. 4e). At a current density of 1000 mA g−1, the discharge specific capacities of the Sn–carbon composite electrode at the 1st, 2nd, 10th, 100th, 200th, 400th, and 500th cycles are 1212.05, 701.44, 432.63, 379.61, 442.44, 554.42 and 564.36 mA h g−1, respectively. The results of 500 cycles show that in the previous cycles, due to the formation of the SEI membrane and the influence of ion mobility, the capacity of the electrode decreases rapidly, and the capacity begins to rise slowly and continuously when the discharge specific capacity decreases to 350 mA h g−1. The maximum discharge specific capacity reaches 574.97 mA h g−1, which means that the efficiency of ion conductivity is accelerated in the process of continuous high current charge and discharge, and that lithium ions can be embedded and removed increasingly efficiently from lithium tin alloy. The continuous increase in capacity is due to the thick coating of active material and the difficulty of electrolyte infiltration over a short period, which makes the active material close to the current collector unable to contribute towards the battery capacity. With further charge and discharge, the active material is further activated, and the active material and electrolyte near to the current collector are fully infiltrated, thus further improving the capacity of the batteries.
Conclusion
In this paper, a Sn–carbon composite electrode was prepared using Dunaliella Salinas to absorb and compound metal tin, and its composition (XRD), morphology (SEM, TEM, HRTEM) and various electrochemical properties (CV curves, charge/discharge curves, cycling stability, rate performance) were investigated. Through these characterization methods and tests, it can be seen that the pure phase metal tin with amorphous carbon exhibits excellent properties. At a current density of 200 mA g−1, the discharge specific capacity after 100 cycles is as high as 619.09 mA h g−1. The capacity increases continuously at a high current density of 1000 mA g−1, even reaching as high as 574.97 mA h g−1, which shows its high current density tolerance. It can also be seen that its rate performance is very good, with a capacity of as high as 376.18 mA h g−1 at a current density of 2000 mA g−1, and after a continuous increase in high current during charge and discharge, the recovery performance of the capacity is good. At a current density of 100 mA g−1, the discharge capacity of the battery is as high as 716.01 mA h g−1. This shows that the electrode materials prepared using Dunaliella Salinas to absorb and compound metal tin exhibit high capacity and excellent rate performance, and in addition, they are low in cost. This preparation method can thus be used to prepare materials for use in high-performance lithium-ion batteries.Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no competing financial interest.Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the Jiangxi Provincial Natural Science Foundation (No. 20202BABL204049), the Education Department of Jiangxi Province (No. GJJ170898) and the Doctoral Scientific Research Foundation of Jiangxi Science and Technology Normal University (No. 2019BSQD014, No. 2020BSQD017).References
- W. Xie, S. Li, S. Wang, S. Xue, Z. Liu and X. Jiang, et al., N-doped amorphous carbon coated Fe3O4/SnO2 coaxial nanofibers as a binder-free self-supported electrode for lithium ion batteries, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2014, 6, 20334–20339 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Boota, K. B. Hatzell, M. Alhabeb, E. C. Kumbur and Y. Gogotsi, Graphene-containing flowable electrodes for capacitive energy storage, Carbon, 2015, 92, 142–149 CrossRef CAS.
- Z. Deng, H. Jiang, Y. Hu, Y. Liu, L. Zhang and H. Liu, et al., 3D Ordered Macroporous MoS2@C Nanostructure for Flexible Li-Ion Batteries, Adv. Mater., 2017, 29, 1603020 CrossRef PubMed.
- Y. Li, B. Xu, H. Xu, H. Duan, X. Lu and S. Xin, et al., Hybrid Polymer/Garnet Electrolyte with a Small Interfacial Resistance for Lithium-Ion Batteries, Angew. Chem., 2017, 56, 753–756 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Liu, X. Li, J. Huang, J. Li, P. Zhou and J. Liu, et al., Three-dimensional graphene-based nanocomposites for high energy density Li-ion batteries, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2017, 5, 5977–5994 RSC.
- S. Ni, P. Huang, D. Chao, G. Yuan, L. Zhang and F. Zhao, et al., Amorphous GaN@Cu Freestanding Electrode for High-Performance Li-Ion Batteries, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2017, 27, 1701808 CrossRef.
- T. Xu, Q. Meng, M. Yang, W. Zhi and B. Cao, Electrophoretic Deposition of SnFe2O4–Graphene Hybrid Films as Anodes for Lithium Ion Batteries, Aust. J. Chem., 2017, 70, 1073 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Li, J. Lu, Z. Chen and K. Amine, 30 Years of Lithium-Ion Batteries, Adv. Mater., 2018, 30, 1800561 CrossRef.
- G. Qian, X. Liao, Y. Zhu, F. Pan, X. Chen and Y. Yang, Designing Flexible Lithium-Ion Batteries by Structural Engineering, ACS Energy Lett., 2019, 4, 690–701 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Liu, L. Lin, X. Bi, L. Tian, K. Yang and J. Liu, et al., In situ quantification of interphasial chemistry in Li-ion battery, Nat. Nanotechnol., 2019, 14, 50–56 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Inceoglu, A. A. Rojas, D. Devaux, X. C. Chen, G. M. Stone and N. P. Balsara, Morphology–Conductivity Relationship of Single-Ion-Conducting Block Copolymer Electrolytes for Lithium Batteries, ACS Macro Lett., 2014, 3, 510–514 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Huang, S. Gao, A. Wu, K. Cheng, X. Li and X. Gao, et al., Fe3N constrained inside C nanocages as an anode for Li-ion batteries through post-synthesis nitridation, Nano Energy, 2017, 31, 74–83 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Xie, M. Saubanère and M. L. Doublet, Requirements for reversible extra-capacity in Li-rich layered oxides for Li-ion batteries, Energy Environ. Sci., 2017, 10, 266–274 RSC.
- B. Li, N. Jiang, W. Huang, H. Yan, Y. Zuo and D. Xia, Thermodynamic Activation of Charge Transfer in Anionic Redox Process for Li-Ion Batteries, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2018, 28, 1704864 CrossRef.
- S. H. Ha, K. H. Shin, H. W. Park and Y. J. Lee, Flexible Lithium-Ion Batteries with High Areal Capacity Enabled by Smart Conductive Textiles, Small, 2018, 14, 1703418 CrossRef PubMed.
- X. Gao, X. Sun, Z. Jiang, Q. Wang, N. Gao and H. Li, et al., Introducing nanodiamond into TiO2-based anode for improving the performance of lithium-ion batteries, New J. Chem., 2019, 43, 3907–3912 RSC.
- M. Xu, L. Fei, W. Zhang, T. Li, W. Lu and N. Zhang, et al., Tailoring Anisotropic Li-Ion Transport Tunnels on Orthogonally Arranged Li-Rich Layered Oxide Nanoplates Toward High-Performance Li-Ion Batteries, Nano Lett., 2017, 17, 1670–1677 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Niu, R. Shao, J. Liang, M. Dou, Z. Li and Y. Huang, et al., Biomass-derived mesopore-dominant porous carbons with large specific surface area and high defect density as high performance electrode materials for Li-ion batteries and supercapacitors, Nano Energy, 2017, 36, 322–330 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Wang, Q. Pan, Q. Wu, X. Zhang, Y. Huang and A. Lushington, et al., Ultrasmall MoS2 embedded in carbon nanosheets-coated Sn/SnOx as anode material for high-rate and long life Li-ion batteries, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2017, 5, 4576–4582 RSC.
- J. Zhu, G. Zhang, X. Yu, Q. Li, B. Lu and Z. Xu, Graphene double protection strategy to improve the SnO2 electrode performance anodes for lithium-ion batteries, Nano Energy, 2014, 3, 80–87 CrossRef CAS.
- B. Li, N. Jiang, W. Huang, H. Yan, Y. Zuo and D. Xia, Thermodynamic Activation of Charge Transfer in Anionic Redox Process for Li-Ion Batteries, Studies on Anionic Redox in Li-Rich Cathode Materials of Li-Ion Batteries, Springer, Singapore, 2019, pp. 99–121 Search PubMed.
- J. Guo, S. Zhao, H. Yang, F. Zhang and J. Liu, Electron regulation enabled selective lithium deposition for stable anodes of lithium-metal batteries, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2019, 7, 2184–2191 RSC.
- Q. Xie, W. Li and A. Manthiram, A Mg-Doped High-Nickel Layered Oxide Cathode Enabling Safer, High-Energy-Density Li-Ion Batteries, Chem. Mater., 2019, 31, 938–946 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Kravchyk, L. Protesescu, M. I. Bodnarchuk, F. Krumeich, M. Yarema and M. Walter, et al., Monodisperse and inorganically capped Sn and Sn/SnO2 nanocrystals for high-performance Li-ion battery anodes, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2013, 135, 4199–4202 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. Liang, L. Ju, S. Koul, A. Kushima and Y. Yang, Self-Supported Tin Sulfide Porous Films for Flexible Aluminum-Ion Batteries, Adv. Energy Mater., 2019, 9, 1802543 CrossRef.
- H. Zhang, C. Feng, Y. Zhai, K. Jiang, Q. Li and S. Fan, Cross-Stacked Carbon Nanotube Sheets Uniformly Loaded with SnO2 Nanoparticles: A Novel Binder-Free and High-Capacity Anode Material for Lithium-Ion Batteries, Adv. Mater., 2009, 21, 2299–2304 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Yu, L. Gu, C. Wang, A. Dhanabalan, P. A. van Aken and J. Maier, Encapsulation of Sn@carbon nanoparticles in bamboo-like hollow carbon nanofibers as an anode material in lithium-based batteries, Angew. Chem., 2009, 48, 6485–6489 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. Li, J.-Y. Hwang and Y.-K. Sun, Nano/Microstructured Silicon–Graphite Composite Anode for High-Energy-Density Li-Ion Battery, ACS Nano, 2019, 13, 2624–2633 CAS.
- G. Derrien, J. Hassoun, S. Panero and B. Scrosati, Nanostructured Sn–C Composite as an Advanced Anode Material in High-Performance Lithium-Ion Batteries, Adv. Mater., 2007, 19, 2336–2340 CrossRef CAS.
- K.-H. Nam, G.-K. Sung, J.-H. Choi, J.-S. Youn, K.-J. Jeon and C.-M. Park, New high-energy-density GeTe-based anodes for Li-ion batteries, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2019, 7, 3278–3288 RSC.
- Y. Yang, B. Wang, J. Zhu, J. Zhou, Z. Xu and L. Fan, et al., Bacteria Absorption-Based Mn2P2O7-Carbon@Reduced Graphene Oxides for High-Performance Lithium-Ion Battery Anodes, ACS Nano, 2016, 10, 5516–5524 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Yang, J. Zhou, Z. Xu, L. Fan and B. Lu, Freestanding flexible Ni12P5 in bacteria based carbon@reduced graphene oxides paper for lithium-ion anode, Mater. Lett., 2017, 207, 153–156 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Zhou, Y. Zhao, T. Bian, L. Shang, H. Yu and L. Z. Wu, et al., Bubble template synthesis of Sn2Nb2O7 hollow spheres for enhanced visible-light-driven photocatalytic hydrogen production, Chem. Commun., 2013, 49, 9872–9874 RSC.
- I. Sultana, T. Ramireddy, M. M. Rahman, Y. Chen and A. M. Glushenkov, Tin-based composite anodes for potassium-ion batteries, Chem. Commun., 2016, 52, 9279–9282 RSC.
- Y. Yang, K. Xu, B. Zhao, N. Liu and J. Zhou, The Bacteria Absorption-based Yolk-Shell Ni3P-Carbon@Reduced Graphene Oxides for Lithium-Ion Batteries, J. Renewable Mater., 2021, 9, 855–865 CAS.
- D. Diddens and A. Heuer, Lithium Ion Transport Mechanism in Ternary Polymer Electrolyte-Ionic Liquid Mixtures: A Molecular Dynamics Simulation Study, ACS Macro Lett., 2013, 2, 322–326 CrossRef CAS.
- R. Hu, H. Liu, M. Zeng, J. Liu and M. Zhu, Progress on Sn-based thin-film anode materials for lithium-ion batteries, Chin. Sci. Bull., 2012, 57, 4119–4130 CrossRef CAS.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available. See DOI: 10.1039/d1ra06443f |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2021 |