 Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleCreative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported Licence
Correction: Rapid synthesis of internal peptidyl α-ketoamides by on resin oxidation for the construction of rhomboid protease inhibitors
Tim Van Kersavonda,
Raphael Konopatzkia,
Merel A. T. van der Plasscheb,
Jian Yangb and
Steven H. L. Verhelst*ab
aLeibniz Institute for Analytical Sciences ISAS, e.V., Otto-Hahn-Str. 6b, 44227 Dortmund, Germany
bKU Leuven, Department of Cellular and Molecular Medicine, Laboratory of Chemical Biology, Herestr. 49 box 802, 3000 Leuven, Belgium. E-mail: steven.verhelst@kuleuven.be
First published on 1st March 2021
Abstract
Correction for ‘Rapid synthesis of internal peptidyl α-ketoamides by on resin oxidation for the construction of rhomboid protease inhibitors’ by Tim Van Kersavond et al., RSC Adv., 2021, 11, 4196–4199, DOI: 10.1039/D0RA10614C.
The authors regret that an incorrect version of Fig. 1 was presented in the original manuscript. The R-group in compound 7 was incorrectly indicated as (CH2)5Ph. The corrected version of the figure with the R group as (CH2)4Ph is shown below.
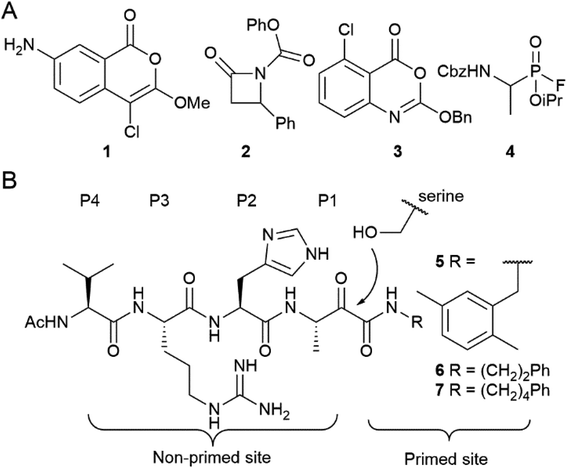 | ||
| Fig. 1 Examples of rhomboid inhibitors. (A) 4-Chloro-isocoumarins (1), β-lactams (2), benzoxazinones (3) and fluorophosphonates (4). (B) α-Ketoamide rhomboid inhibitors (5–7). The peptidic element in the non-primed site is indicated with the P1–P4 position according to the Schechter and Berger protease substrate nomenclature.1 | ||
The Royal Society of Chemistry apologises for these errors and any consequent inconvenience to authors and readers.
References
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2021 |
