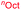
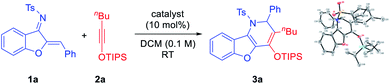Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleAn unusual formal migrative cycloaddition of aurone-derived azadienes: synthesis of benzofuran-fused nitrogen heterocycles†
Qiang
Feng‡
a,
An
Wu‡
 a,
Xinhao
Zhang
a,
Xinhao
Zhang
 b,
Lijuan
Song
*c and
Jianwei
Sun
b,
Lijuan
Song
*c and
Jianwei
Sun
 *ad
*ad
aDepartment of Chemistry, Shenzhen Research Institute, The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology, Clear Water Bay, Kowloon, Hong Kong SAR, China. E-mail: sunjw@ust.hk
bShenzhen Bay Laboratory, State Key Laboratory of Chemical Oncogenomics, Peking University Shenzhen Graduate School, Shenzhen, China
cSchool of Science, Harbin Institute of Technology (Shenzhen), Shenzhen, 518055, China. E-mail: songlijuan@hit.edu.cn
dThe Hong Kong Branch of Chinese National Engineering Research Centre for Tissue Restoration & Reconstruction, Clear, Water Bay, Kowloon, Hong Kong SAR, China
First published on 4th May 2021
Abstract
Aurone-derived azadienes are well-known four-atom synthons for direct [4 + n] cycloadditions owing to their s-cis conformation as well as the thermodynamically favored aromatization nature of these processes. However, distinct from this common reactivity, herein we report an unusual formal migrative annulation with siloxy alkynes initiated by [2 + 2] cycloaddition. Unexpectedly, this process generates benzofuran-fused nitrogen heterocyclic products with formal substituent migration. This observation is rationalized by less common [2 + 2] cycloaddition followed by 4π and 6π electrocyclic events. DFT calculations provided support to the proposed mechanism.
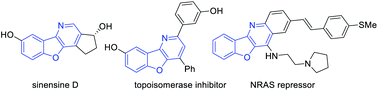
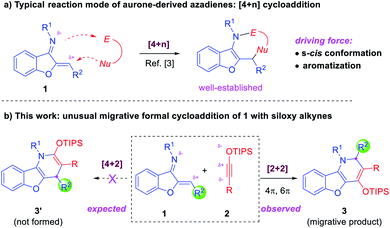
Benzofuran is an important scaffold in biologically important natural molecules and therapeutic agents.1 Among them, benzofuran-fused nitrogen heterocycles are particularly noteworthy owing to their broad spectrum of bioactivities for the treatment of various diseases (Fig. 1).2 Consequently, the development of efficient methods for their assembly has been a topic receiving enthusiastic attention from synthetic chemists.3 Notably, aurone-derived azadienes (e.g., 1) have been extensively employed as precursors toward these skeletons owing to their easy availability and versatile reactivity (Scheme 1a).3 The polarized conjugation system, combined with the preexisting s-cis conformation, has enabled them to serve as ideal annulation partners for the synthesis of nitrogen heterocycles of variable ring sizes. Moreover, the aromatization nature of these processes by forming a benzofuran ring provides additional driving force for them to behave as a perfect four-atom synthon for [4 + n] cycloaddition.3 In contrast, the use of such species as a two-atom partner for [2 + n] cycloaddition has been less developed.3c,k,4 Herein, we report a new migrative annulation leading to benzofuran-fused dihydropyridines of unexpected topology (Scheme 1b, with formal R2 migration), which is initiated by the less common [2 + 2] cycloaddition.
Siloxy alkynes are another important family of building blocks in organic synthesis.5–8 The presence of a highly polarized C–C triple bond enables such molecules to serve as versatile two-carbon cycloaddition partners in various annulation reactions.5–7 In the above context and in continuation of our interest in the study of such electron-rich alkynes,7 we envisioned that the reaction between aurone-derived azadienes 1 and siloxy alkynes 2 should lead to facile electron-inversed [4 + 2] cycloaddition to form benzofuran-fused dihydropyridine products (Scheme 1b). Interestingly, the expected product 3′ from direct [4 + 2] cycloaddition was not observed. Instead, a dihydropyridine product 3 with formal R2 migration was observed. Careful analysis of the mechanism suggested that a [2 + 2] cycloaddition followed by 4π and 6π electrocyclic steps might be responsible for this unexpected product topology (vide infra).
We began our investigation with the model substrates 1a and 2a, which were easily prepared in one step from aurone and 1-hexyne, respectively.8 Various Lewis acids were initially examined as potential catalysts for this cycloaddition (Table 1). Unfortunately, common Lewis acids (e.g., TiCl4, BF3·OEt2, Sc(OTf)3, In(OTf)3, and AgOTf) were all ineffective (entries 1–5). Substrate decomposition into an unidentifiable mixture was typically observed. However, further screening indicated that AgNTf2 served as an effective catalyst, leading to benzofuran-fused dihydropyridine 3a in 44% yield (entry 6). Careful analysis by X-ray crystallography confirmed that it was not formed by simple [4 + 2] cycloaddition, as the positions of the phenyl and the siloxy groups were switched (vs. the expected topology). The distinct catalytic performance of AgNTf2 (vs. AgOTf) suggested that the triflimide counter anion Tf2N− might be important. However, further screening of various metal triflimide salts did not improve the reaction efficiency (entry 7). Instead, we were delighted to find that the corresponding Brønsted acid HNTf2 served as a better catalyst (57% yield, entry 8). However, triflic acid (TfOH) led to no desired product in spite of complete conversion (entry 9). After considerable efforts in the optimization of other reaction parameters, an improved yield of 75% was obtained with 2.5 mol% of HNTf2 and 2.5 equivalents of 2a at 60 °C (entry 10). Solvent screening indicated that the reaction proceeded faster in DCE with comparable yield (entry 11). However, other solvents were all inferior (entries 12–15). Finally, with a reversed order of addition of the two reactants, the yield was slightly improved (entry 16). We believe that this might be related to the relative decomposition rates of the substrates.
| Entry | Catalyst | Solvent | Time (h) | Yield (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| a 2a (0.06 mmol) was added to the solution of 1a (0.05 mol) and the catalyst (10 mol%). Yield was determined by analysis of the 1H NMR spectrum of the crude mixture using CH2Br2 as an internal standard. b Run with 2.5 mol% catalyst and 2.5 equiv. of 2a at 60 °C. c 1a was added into the solution of 2a and the catalyst. d Yield in parentheses was isolated yield. | ||||
| 1 | TiCl4 | DCM | 9 | 0 |
| 2 | BF3·OEt2 | DCM | 9 | 0 |
| 3 | Sc(OTf)3 | DCM | 9 | 0 |
| 4 | In(OTf)3 | DCM | 9 | 0 |
| 5 | AgOTf | DCM | 9 | 0 |
| 6 | AgNTf2 | DCM | 9 | 44 |
| 7 | Sc(NTf2)3 | DCM | 9 | 0 |
| 8 | HNTf2 | DCM | 9 | 57 |
| 9 | HOTf | DCM | 9 | 0 |
| 10b | HNTf2 | DCM | 42 | 75 |
| 11b | HNTf2 | DCE | 18 | 72 |
| 12b | HNTf2 | CHCl3 | 18 | 20 |
| 13b | HNTf2 | THF | 18 | 0 |
| 14b | HNTf2 | MeCN | 18 | 0 |
| 15b | HNTf2 | EtOAc | 18 | 0 |
| 16b,c | HNTf2 | DCE | 18 | 81 (76)d |
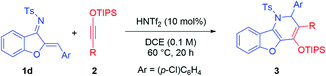
With the optimized conditions, we examined the reaction scope. A range of aurone-derived azadienes with different electron-donating and electron-withdrawing substituents at various positions smoothly participated in this formal migrative cycloaddition process with siloxy alkyne 2a (Scheme 2). The corresponding benzofuran-fused dihydropyridine products 3 were formed with excellent selectivity and moderate to good efficiency. A thiophene unit was also successfully incorporated into the product (3h). However, substitution with a pyridinyl group shut down the reactivity, even with 1.1 equivalents of HNTf2. Other siloxy alkynes bearing different alkyl substituents on the triple bond were also good reaction partners, except that these reactions were more efficient when the catalyst loading was increased to 10 mol% (Table 2). Unfortunately, direct aryl substitution on the alkyne triple bond resulted in essentially no reaction (entry 7). Notably, in spite of the strong acidic conditions, various functional groups, such as TIPS-protected alcohol (3p) and acetal (3c), were tolerated. Moreover, increasing steric hindrance in close proximity to the reaction centers (e.g., tBu group in 3i and 3r) did not obviously affect the reaction efficiency.
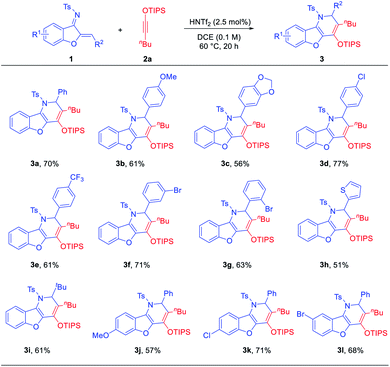 | ||
| Scheme 2 Scope of aurone-derived azadienes. Conditions: 1 (0.3 mmol), 2a (0.75 mmol), HNTf2 (2.5 mol%), DCE (3.0 mL), 60 °C. Isolated yield. | ||
Owing to the electron-rich silyl enol ether motif, the benzofuran-fused dihydropyridine products can be transformed into other related heterocycles upon treatment with electrophiles. For example, deprotection of the silyl group in 3d with TBAF in the presence of water produced ketone 4a (eqn (1)). In the presence of NBS or NCS, the corresponding bromoketone 4b and chloroketone 4c were obtained, respectively (eqn (2)). These reactions were both efficient and highly diastereoselective. The structures of 4b and 4c were also confirmed by X-ray crystallography. Moreover, deprotection of the N-tosyl group with Li/naphthalene followed by air oxidation led to the highly-substituted benzofuran-fused pyridine 5, the core structure of a family of bioactive molecules (eqn (3)).2
A possible mechanism is proposed to rationalize the unusual formal migrative process (Scheme 3). The reaction begins with LUMO-lowering protonation of the aurone-derived azadiene 1 by HNTf2.9 Then, the electron-rich alkyne attacks the resulting activated iminium intermediate I, leading to ketenium ion II after intermolecular C–C bond formation. Subsequent intramolecular cyclization from the electron-rich enamine motif to the electrophilic ketenium unit forms oxetene III. The formation of this oxetene can also be considered as a [2 + 2] cycloaddition of the two reactants.6a–d,11 Subsequent 4π-electrocyclic opening of oxetene III affords azatriene IV. Further 6π-electrocyclic closing leads to the observed product 3. This observed product topology is fully consistent with this pathway. It is worth noting that the excellent performance with HNTf2 might be attributed to the low nucleophilicity and good compatibility of its counter anion with the highly electrophilic cationic intermediates (e.g., ketenium II) in this process. We have also carried out DFT studies. The results indicated that the proposed pathway is energetically viable and consistent with the experimental data (Scheme 3 and Fig. S1†). Moreover, some other possible pathways that engage the nitrogen atom in intermediate II to directly attack the ketenium in a [4 + 2] mode were explored. However, no reasonable transition state could be located (Fig. S2†). Thus, the origin of preference toward [2 + 2] cycloaddition remains unclear.
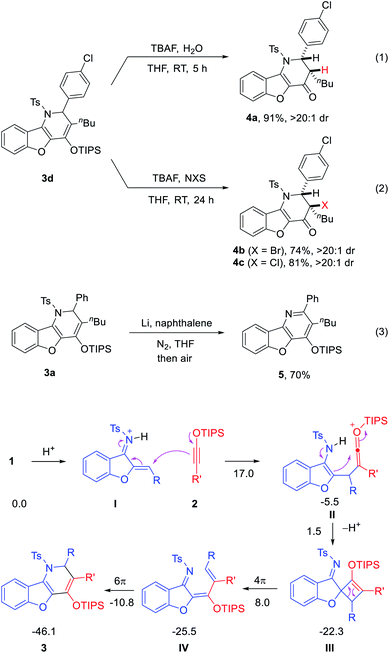 | ||
| Scheme 3 Proposed mechanism and free energies (in kcal mol−1) computed at the M06-2X(D3)/6-311G(d,p)-SMD//M06-2X/6-31G(d) level of theory. | ||
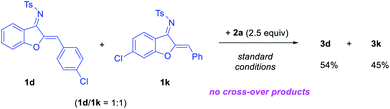
We also prepared TIPSNTf2 and examined its catalytic activity in this reaction since it is known that such a Lewis acid might be generated in situ.10 However, no reaction was observed when TIPSNTf2 was used in place of HNTf2, suggesting that it is unlikely the actual catalyst. Finally, in order to probe the nature of the substituent migration (intermolecular vs. intramolecular), we carried out a cross-over experiment (Scheme 4). Under the standard conditions, the reaction using a 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 mixture of 1d and 1k led to exclusive formation of 3d and 3k, without detection of any cross-over products. This result is consistent with the proposed intramolecular migration pathway.
1 mixture of 1d and 1k led to exclusive formation of 3d and 3k, without detection of any cross-over products. This result is consistent with the proposed intramolecular migration pathway.
In conclusion, we have discovered an unusual formal migrative cycloaddition of aurone-derived azadienes with siloxy alkynes. In the presence of a catalytic amount of HNTf2, this reaction provided expedient access to a range of useful benzofuran-fused dihydropyridine products with unexpected topology, distinct from normal [4 + 2] cycloaddition. Although aurone-derived azadienes are ideal four-atom synthons for direct [4 + n] cycloaddition, the present process is initiated by less common [2 + 2] cycloaddition, which is critical for the observed product formation. Subsequent electrocyclic opening and cyclization steps provide a reasonable rationale. The heterocyclic products generated from this process are precursors toward other useful structures, such as benzofuran-fused pyridines.
Author contributions
Q. F. and A. W. conceived and performed the experiments and wrote the paper. X. Z. and L. S. performed DFT calculations. J. S. conceived and directed the project and wrote the paper. All the authors discussed the results and commented on the manuscript.Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.Acknowledgements
Financial support was provided by the NSFC (22071210), Hong Kong RGC (16302719), and Innovation and Technology Commission (ITC-CNERC14SC01). We thank Dr Herman H. Y. Sung for help with structure elucidation by X-ray crystallography.References
- (a) K. M. Dawood, Expert Opin. Ther. Pat., 2013, 23, 1133–1156 CrossRef CAS; (b) H. Khanam and Shamsuzzaman, Eur. J. Med. Chem., 2015, 97, 483–504 CrossRef CAS; (c) A. Hiremathad, M. R. Patil, C. K. Rajappa, K. Chand, M. A. Santos and R. S. Keri, RSC Adv., 2015, 5, 96809–96828 RSC.
- (a) J.-Q. Liu, C.-F. Wang, X.-R. Peng and M.-H. Qiu, Nat. Prod. Bioprospect., 2011, 1, 93–96 CrossRef CAS; (b) H.-B. Kwon, C. Park, K.-H. Jeon, E. Lee, S.-E. Park, K.-Y. Jun, T. M. Kadayat, P. Thapa, R. Karki, Y. Na, M. S. Park, S. B. Rho, E.-S. Lee and Y. J. Kwon, Med. Chem., 2015, 58, 1100–1122 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) W. Peng, Z.-Y. Sun, Q. Zhang, S.-Q. Cheng, S.-K. Wang, X.-N. Wang, G.-T. Kuang, X.-X. Su, J.-H. Tan, Z.-S. Huan and T.-M. Ou, J. Med. Chem., 2018, 61, 6629–6646 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Selected recent cycloadditions of aurone-derived azadienes: (a) Z.-Q. Rong, M. Wang, C. H. E. Chow and Y. Zhao, Chem.–Eur. J., 2016, 22, 9483–9487 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) H. Ni, X. Tang, W. Zheng, W. Yao, N. Ullah and Y. Lu, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2017, 56, 14222–14226 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) L.-C. Yang, Z.-Q. Rong, Y.-N. Wang, Y. Z. Tan, M. Wang and Y. Zhao, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2017, 56, 2927–2931 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (d) Z.-Q. Rong, L.-C. Yang, S. Liu, Z. Yu, Y.-N. Wang, Z. Y. Tan, R.-Z. Huang, Y. Lan and Y. Zhao, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2017, 139, 15304–15307 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (e) J. Chen and Y. Huang, Org. Lett., 2017, 19, 5609–5612 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (f) Y.-N. Wang, L.-C. Yang, Z.-Q. Rong, T.-L. Liu, R. Liu and Y. Zhao, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2018, 57, 1596–1600 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (g) J. Chen, P. Jia and Y. Huang, Org. Lett., 2018, 20, 6715–6718 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (h) H.-P. Xie, L. Sun, B. Wu and Y.-G. Zhou, J. Org. Chem., 2019, 84, 15498–15507 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (i) R. Zeng, C. Shan, M. Liu, K. Jiang, Y. Ye, T.-Y. Liu and Y.-C. Chen, Org. Lett., 2019, 21, 2312–2316 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (j) T. Fan, Z.-J. Zhang, Y.-C. Zhang and J. Song, Org. Lett., 2019, 21, 7897–7901 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (k) A.-S. Marques, T. Duhail, J. Marrot, I. Chataigner, V. Coeffard, G. Vincent and X. Moreau, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2019, 58, 9969–9973 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (l) Y.-Z. Liu, Z. Wang, Z. Huang, X. Zheng, W.-L. Yang and W.-P. Deng, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2020, 59, 1238–1242 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) B. M. Trost and Z. Zuo, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2020, 59, 1243–1247 CrossRef PubMed; (b) Q.-Y. Fang, M.-H. Yi, X.-X. Wu and L.-M. Zhao, Org. Lett., 2020, 22, 5266–5270 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) Y.-X. Wang, Y.-N. Lua, L.-L. Xu, F.-T. Sheng, J. P. Zhang, W. Tan and F. Shi, Synthesis, 2020, 52, 2979–2986 CAS; (d) K. Liu, J. Yang and X. Li, Org. Lett., 2021, 23, 826–831 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Reviews of siloxy alkynes: (a) M. Shindo, Tetrahedron, 2007, 63, 10–36 CrossRef CAS; (b) H. Qian, W. Zhao and J. Sun, Chem. Rec., 2014, 14, 1070–1085 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Representative examples of cycloaddition of siloxy alkynes: [2 + 2] cycloaddition: (a) C. J. Kowalski and G. S. Lal, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1988, 110, 3693–3695 CrossRef CAS; (b) C. J. Kowalski and S. Sakdarat, J. Org. Chem., 1990, 55, 1977–1979 CrossRef CAS; (c) M. Shindo, S. Oya, Y. Sato and K. Shishido, Heterocycles, 2000, 52, 545–548 CrossRef CAS; (d) R. F. Sweis, M. P. Schramm and S. A. Kozmin, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2004, 126, 7442–7443 CrossRef CAS PubMed ; [3 + 2] cycloaddition: ; (e) X. Qi and J. M. Ready, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2008, 47, 7068–7070 CrossRef CAS PubMed ; [4 + 2] cycloaddition: ; (f) R. L. Danheiser, A. Nishida, S. Savariar and M. P. Trova, Tetrahedron Lett., 1988, 29, 4917–4920 CrossRef CAS; (g) R. L. Danheiser, R. G. Brisbois, J. L. Kowalczyk and R. F. Miller, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1990, 112, 3093–3100 CrossRef CAS; (h) W. F. Austin, Y. Zhang and R. L. Danheiser, Org. Lett., 2005, 7, 3905–3908 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (i) M. Movassaghi, M. D. Hill and O. K. Ahmad, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2007, 129, 10096–10097 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (j) Y. E. Türkmen, T. J. Montavon, S. A. Kozmin and V. H. Rawal, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2012, 134, 9062–9065 CrossRef PubMed; (k) J. R. Cabrera-Pardo, D. I. Chai, S. Liu, M. Mrksich and S. A. Kozmin, Nat. Chem., 2013, 5, 423–427 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (l) T. J. Montavon, Y. E. Türkmen, N. A. Shamsi, C. Miller, C. S. Sumaria, V. H. Rawal and S. A. Kozmin, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2013, 52, 13576–13579 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (m) C. S. Sumaria, Y. E. Türkmen and V. H. Rawal, Org. Lett., 2014, 16, 3236–3239 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Our efforts in the study of siloxy alkynes: (a) W. Zhao, Z. Wang and J. Sun, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2012, 51, 6209–6213 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) W. Zhao, Z. Li and J. Sun, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2013, 135, 4680–4683 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) W. Zhao, H. Qian, Z. Li and J. Sun, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2015, 54, 10005–10008 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (d) A. Wu, Q. Feng, H. H. Y. Sung, I. D. Williams and J. Sun, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2019, 58, 6776–6780 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (e) A. Wu, H. Qiang, W. Zhao and J. Sun, Chem. Sci., 2020, 11, 7957–7962 RSC.
- M. P. Schramm, V. Shubinets and S. A. Kozmin, Org. Synth., 2010, 87, 253–262 CrossRef.
- Review on HNTf2: W. Zhao and J. Sun, Chem. Rev., 2018, 118, 10349–10392 CrossRef CAS.
- M. B. Boxer and H. Yamamoto, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2006, 128, 48–49 CrossRef CAS.
- H.-Z. Bu, H.-H. Li, W.-F. Luo, C. Luo, P.-C. Qian and L.-W. Ye, Org. Lett., 2020, 22, 648–652 CrossRef CAS.
Footnotes |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available. CCDC 2045484, 2079164 and 2079165. For ESI and crystallographic data in CIF or other electronic format see DOI: 10.1039/d1sc00941a |
| ‡ These authors contributed equally to this work. |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2021 |