Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleCreative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported Licence
The role of hypervalent iodine(III) reagents in promoting alkoxylation of unactivated C(sp3)–H bonds catalyzed by palladium(II) complexes†
Payam
Abdolalian
 a,
Samaneh K.
Tizhoush
a,
Samaneh K.
Tizhoush
 a,
Kaveh
Farshadfar
a,
Kaveh
Farshadfar
 a and
Alireza
Ariafard
a and
Alireza
Ariafard
 *ab
*ab
aDepartment of Chemistry, Islamic Azad University, Central Tehran Branch, Poonak, Tehran, 1469669191, Iran
bSchool of Natural Sciences – Chemistry, University of Tasmania, Private Bag 75, Hobart, TAS 7001, Australia. E-mail: Alireza.Ariafard@utas.edu.au
First published on 14th April 2021
Abstract
Although Pd(OAc)2-catalysed alkoxylation of the C(sp3)–H bonds mediated by hypervalent iodine(III) reagents (ArIX2) has been developed by several prominent researchers, there is no clear mechanism yet for such crucial transformations. In this study, we shed light on this important issue with the aid of the density functional theory (DFT) calculations for alkoxylation of butyramide derivatives. We found that the previously proposed mechanism in the literature is not consistent with the experimental observations and thus cannot be operating. The calculations allowed us to discover an unprecedented mechanism composed of four main steps as follows: (i) activation of the C(sp3)–H bond, (ii) oxidative addition, (iii) reductive elimination and (iv) regeneration of the active catalyst. After completion of step (i) via the CMD mechanism, the oxidative addition commences with an X ligand transfer from the iodine(III) reagent (ArIX2) to Pd(II) to form a square pyramidal complex in which an iodonium occupies the apical position. Interestingly, a simple isomerization of the resultant five-coordinate complex triggers the Pd(II) oxidation. Accordingly, the movement of the ligand trans to the Pd–C(sp3) bond to the apical position promotes the electron transfer from Pd(II) to iodine(III), resulting in the reduction of iodine(III) concomitant with the ejection of the second X ligand as a free anion. The ensuing Pd(IV) complex then undergoes the C–O reductive elimination by nucleophilic attack of the solvent (alcohol) on the sp3 carbon via an outer-sphere SN2 mechanism assisted by the X− anion. Noteworthy, starting from the five coordinate complex, the oxidative addition and reductive elimination processes occur with a very low activation barrier (ΔG‡ 0–6 kcal mol−1). The strong coordination of the alkoxylated product to the Pd(II) centre causes the regeneration of the active catalyst, i.e. step (iv), to be considerably endergonic, leading to subsequent catalytic cycles to proceed with a much higher activation barrier than the first cycle. We also found that although, in most cases, the alkoxylation reactions proceed via a Pd(II)–Pd(IV)–Pd(II) catalytic cycle, the other alternative in which the oxidation state of the Pd(II) centre remains unchanged during the catalysis could be operative, depending on the nature of the organic substrate.
Introduction
Hypervalent iodine compounds have been widely used in organic synthesis as oxidants and reaction promoters over recent decades.1 Although these compounds themselves have the capacity to mediate many organic reactions, the addition of a catalyst is usually a prerequisite for certain transformations to occur.2 Among these catalysts, palladium complexes have been demonstrated to have great potential to promote numerous iodine(III)-mediated processes including the C–H functionalization and coupling reactions.3In this context, Rao et al. developed a method for alkoxylation of unactivated methylene and methyl C(sp3)–H bonds to prepare alkyl ethers using hypervalent iodine(III) reagents in the presence of a Pd(II) catalyst.4 According to the developed method, they showed that butyramide derivative 1 is alkoxylated in the presence of an alcohol as the solvent and the alkoxylation reagent, methoxybenziodoxole (BI–OMe, 2) as the oxidant, and Pd(OAc)2 as the catalyst (Scheme 1). This strategy for alkoxylation might receive specific attention due to its significance in modification of anti-inflammatory drugs such as ibuprofen and naproxen. It is worth mentioning that the importance of such a transformation has also prompted others to use similar methodologies for installing alkoxy groups onto other organic molecules using hypervalent iodine(III) reagents under Pd(II) catalysis even, in some cases, before that developed by Rao et al.5,6
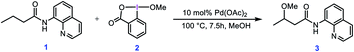 | ||
| Scheme 1 Palladium-catalyzed C(sp3)–H alkoxylation using the cyclic iodine(III) reagent 2 (BI–OMe) developed by Rao et al. | ||
In an attempt to explore the reaction mechanism, Rao et al. conducted an isotope labeling experiment in deuterated methanol (Scheme 2). On that basis, the only observed product was 4, implying that the methoxy group installed on the product must originate from the solvent and not from the oxidant. Interestingly, when different alcohols were used as the solvent, only product 5 was practically observed and when the reaction was run in 1,2-dichloroethane (DCE), the carboxylated product 6 was attained. All these findings suggest that the methoxy group of the oxidant must act as a spectator ligand and thus is never involved in the reductive elimination step in the catalytic cycle (vide infra).
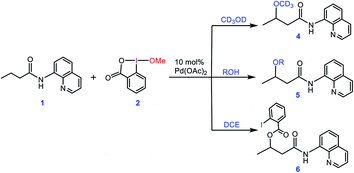 | ||
| Scheme 2 Different experiments performed by Rao et al. for confirming that the alkoxylation reagent is the alcohol solvent and the methoxy group of the oxidant 2 acts as a spectator. | ||
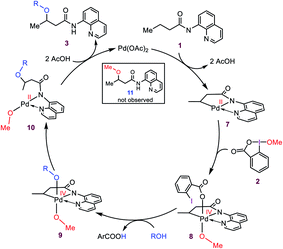
Based on the preliminary results briefly discussed above, Rao et al. proposed the catalytic cycle outlined in Scheme 3. Accordingly, the reaction was surmised to commence with the coordination of substrate 1 to Pd(OAc)2, followed by OAc ligands-assisted N–H and C(sp3)–H activation processes via the concerted metallation–deprotonation (CMD) mechanism7 to yield cyclopalladated intermediate 7. Subsequently, the oxidation of Pd(II) to Pd(IV) by the cyclic iodine(III) reagent 2 generates intermediate 8 from which a ligand exchange with the alcohol occurs to afford 9. The resultant intermediate finally forms product 3 by undergoing the C–OR reductive elimination followed by a substitution reaction. It is worth noting that this plausible mechanism has also been summarized in several recent reviews,3e,8 and proposed by several other researchers for interpreting alkoxylation reactions mediated by iodine(III) and catalyzed by palladium(II).4,5,6e,f,9a,b,f,h–j,m,n
The above-simplified description prompted us to investigate the detailed mechanism of the title reaction by applying density functional theory (DFT) with the aim of addressing the following questions: (i) how the Pd(II) is oxidized to the Pd(IV) by BI–OMe? (ii) Are 8 and 9 key intermediates on the catalytic cycle? If so, why does not the reductive elimination occur from 9 to give 11? If not, what are the key intermediates? Why is the carboxylate group, and not the methoxy, installed on the organic molecule when the solvent is not the alcohol (Scheme 2)? Is the formation of a Pd(IV) intermediate inevitable in the catalytic process? Does the C–O reductive elimination take place via an inner-sphere mechanism? Why does the reaction require a high temperature to occur? Through answering these questions, we hope to enhance understanding of the fundamental processes involved in numerous Pd(II)-catalyzed I(III)-mediated alkoxylation reactions.4,5,6e-g,9
Results and discussion
CMD mechanism
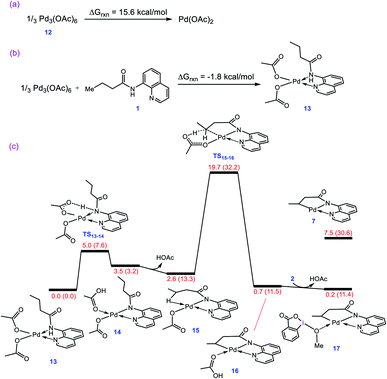
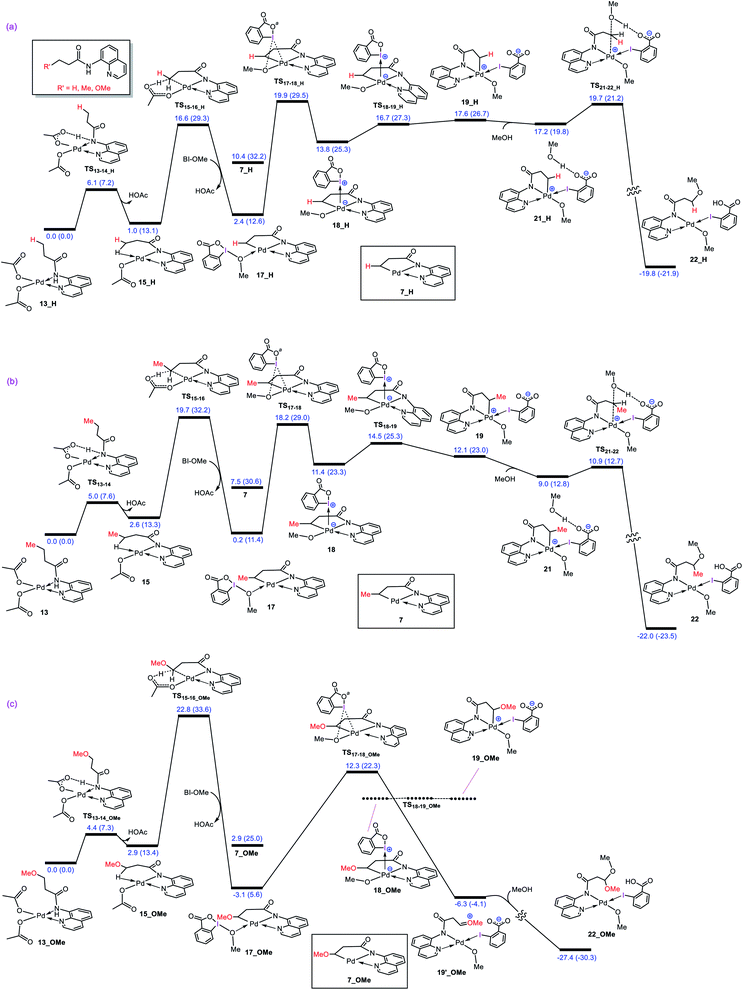
As described in the Introduction, the reaction is proposed to be initiated by activation of the N–H and C–H bonds of substrate 1 by Pd(OAc)2via the CMD mechanism. In analogy with the previous DFT studies,10 trimeric Pd3(OAc)6 is considered as the precatalyst for the palladium acetate; the trimeric form is computed to be 15.6 kcal mol−1 more stable than the monomeric Pd(OAc)2 (Fig. 1a). The breakdown of Pd3(OAc)6 into square planar complex 13 is computed to be exergonic by about −1.8 kcal mol−1 (Fig. 1b).The N–H deprotonation of the coordinated substrate by one of the acetate ligands gives complex 14 in which acetic acid occupies a vacant coordination site of Pd(II). This process is predicted to be extremely fast with ΔG‡ = 5.0 kcal mol−1. The acetic acid in this complex (14) binds weakly to the metal center and thus it can be easily replaced to give complex 15 with a Pd–H–C agostic interaction (Fig. 1c). The resultant complex then involves a second deprotonation process by the other acetate ligand to yield 16. We found that this key step is nearly thermoneutral and proceeds with an overall activation barrier of 19.7 kcal mol−1. The replacement of the weakly bonded acetic acid in 16 by BI–OMe gives 17 as an active species on the catalytic cycle (vide infra).
A preliminary evaluation of the mechanism proposed by Rao et al.
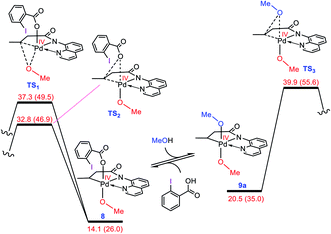
As discussed in the Introduction, Rao et al. proposed 8 and 9 as the key intermediates responsible for the catalytic alkoxylation process (Scheme 3). On that basis, the reductive elimination from 9 is expected to produce both products 3 and 11, which disagrees with the experimental findings. Similar key intermediates were also suggested by some other researchers for analogous alkoxylation reactions catalyzed by Pd(II) complexes.4,5,6e,f,9a,b,f,h–j,m,n To confirm the proposed mechanism is inoperative, we calculated the energy of intermediates 8 and 9a, and then evaluated the C–O reductive elimination from these two intermediates (Fig. 2). Several trends are apparent from this DFT investigation. First, based on the proposed mechanism (Scheme 3), the ligand exchange between 8 and the alcohol (solvent) is a prerequisite for the reductive elimination to produce the desired product. Our calculations show that the ligand exchange process is endergonic by 6.4 kcal mol−1 where the alcohol is MeOH, implying that the Pd center prefers to remain coordinated with the carboxylate ligand. Second, transition structures TS1 and TS2 are significantly lower in energy than TS3. It follows that the reductive elimination should preferentially occur from 8 and not 9a. Third, transition structure TS2 is by 4.5 kcal mol−1 lower in energy than TS1 indicating that 8 is more prone to be involved in the carbon–carboxylate coupling and not the carbon–alkoxy coupling.It is inferred from the above results that the mechanism proposed in the literature is not capable of accounting for the experimental data. This inconsistency spurred us to seek for some other alternatives. The following discloses a novel mechanism by which one can easily interpret the results of the Pd(II)-catalyzed I(III)-mediated alkoxylation reactions developed by Rao et al. and others.4,5,6e-g,9
Oxidative addition
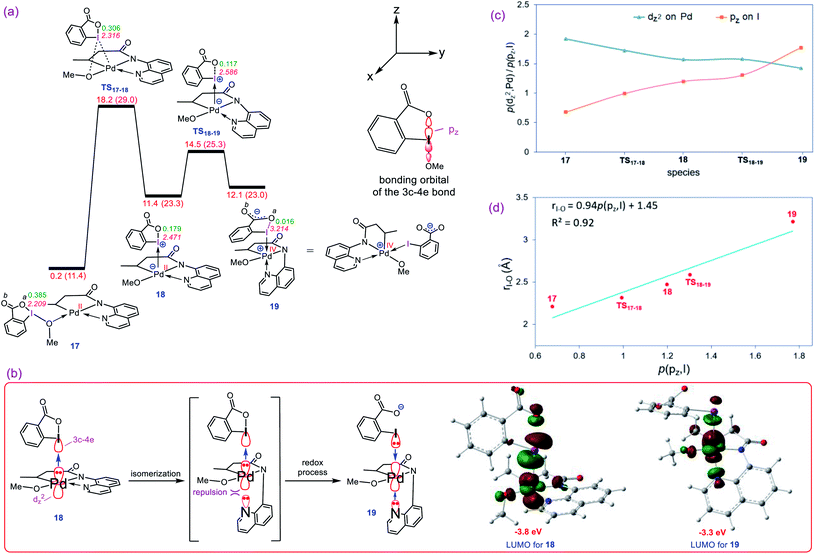
Our calculations show that the oxidative addition step starts with the formation of adduct 17 in which reagent BI–OMe binds to the palladium center through its methoxy group (Fig. 3a). Next, the OMe ligand is transferred from the iodine to the palladium via transition structure TS17-18 to give square pyramidal complex 18. The resultant five coordinate complex is formally an iodonium salt in which the Pd dz2 orbital interacts with an empty orbital on the iodine(III) having three-center-four-electron (3c-4e) character (Fig. 3b); the spatial distribution for the LUMO of 18 (Fig. 3b) indicates the antibonding orbital relating to such an interaction. Interestingly, we found that this complex is extremely reactive toward a redox process through undergoing a simple isomerization. The strong trans-influencing feature of the alkyl group causes the quinoline moiety of the tridentate ligand in 17 to coordinate relatively weakly to the Pd center and thus be highly susceptible to rearrangement. In this situation, the quinoline readily moves from the basal to the apical position via trigonal bipyramidal transition structure TS18-19 lying only 3.1 kcal mol−1 above 18 to give another square pyramidal structure (19) in that the alkyl group occupies the apical position. This ligand movement turns on a repulsive interaction between the nitrogen lone pair and the filled dz2 orbital, destabilizing the dz2 orbital, resulting in two electrons being transferred from the Pd(II) to the iodine(III) center, furnishing 19.11 As depicted in Fig. 3b, such an electron transfer turns off the Pd–N repulsive interaction and formally changes the oxidation state of the palladium center from +2 to +4. The spatial distribution for the LUMO of 19 (Fig. 3b) indicates the antibonding orbital relating to the simultaneous interaction of the lone pairs of the iodine and quinoline nitrogen atoms with the Pd(IV) dz2 orbital.The population changes of the palladium dz2 and iodine pz orbitals obtained by the NBO calculations for transformation 17 → 19 are shown in Fig. 3c. It follows from this figure that along the sequence, the Pd dz2 population decreases while the iodine pz population increases. The considerable changes in the pz population of the iodine atom supports the fact that the iodine(III) atom receives electrons from the Pd center and finally is reduced to the iodine(I) in 19. Due to an increase in population of the iodine pz orbital, the I–Oa bond distance becomes longer upon going from 17 to 19 (Fig. 3a) and finally is cleaved in 19 supported by Wiberg bond index (WBI) analysis showing an almost zero-bond order (0.016) between the I and Oa atoms. We found an excellent correlation between the I–Oa bond distance and the population of the iodine pz orbital with R2 = 0.92 (Fig. 3d).12 These computational results are clearly consistent with the oxidation of Pd(II) by the iodine(III) reagent through the unprecedented mechanism outlined in Fig. 3a.
Reductive elimination
Once the oxidative addition has taken place, the five-coordinate Pd(IV) complex 19 with a pendant carboxylate group is formed. The sixth coordination site of this Pd(IV) complex can be filled by this pendant carboxylate group to furnish complex 20 (Fig. 4). However, owing to the strong trans-influencing character of the alkyl moiety, the carboxylate binds weakly to the Pd(IV) center in 20, indicating a comparable stability for these two intermediates (19 and 20).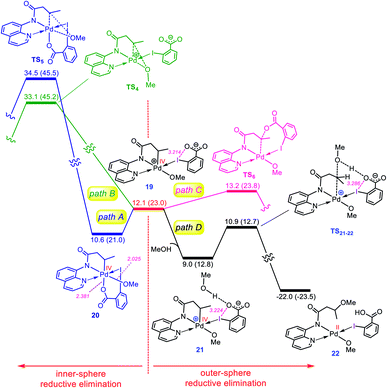 | ||
| Fig. 4 Calculated energy profile for C–O reductive elimination via pathways A–D. The selected distances (Å) are annotated in pink. Free energies (potential energies) are given in kcal mol−1. | ||
Now, we turn our attention to investigation of the C–O reductive elimination from these two Pd(IV) complexes. Based on our calculations, this step can proceed via at least four different variants, as shown in Fig. 4. Accordingly, pathways A and B involve the inner-sphere reductive elimination from complexes 19 and 20 by crossing concerted transition structures TS4 and TS5, respectively. These two pathways install the methoxy group of the oxidant on the final product. In pathway C, the C–O reductive elimination occurs through an outer-sphere SN2 mechanism involving the nucleophilic addition of the pendant carboxylate to the sp3 carbon bonded to the palladium by passing through transition structure TS6. This pathway leads to formation of the carboxylated product. In pathway D, a methanol pre-activated by the pendant carboxylate nucleophilically attacks the sp3 carbon to yield 22via transition structure TS21-22. In this pathway, the solvent serves as the alkoxylation reagent, and addition of the methanol to the sp3 carbon is accompanied by its deprotonation by the pendant carboxylate group. As can be seen from Fig. 4, TS21-22 is much lower in energy than other transition structures, implying that pathway D is kinetically favored over pathways A, B, and C. However, when the solvent is not the alcohol, pathway D is turned off and thus, in this case, the reaction should preferentially proceed via pathway C, confirmed by the fact that TS6 energetically lies considerably below TS4 and TS5.
The energy profile given in Fig. 4 can answer several questions asked in the Introduction. For example, on that basis, one can explain why the OMe group on the oxidant does not appear in the product, why the solvent (alcohol) serves as the alkoxylation reagent and why when the solvent is not an alcohol, the carboxylate group is installed on the product.
Regeneration of active catalyst 13
After completion of the C–O reductive elimination via pathway D, intermediate 22 is formed. The dissociation of the carboxylic acid from the resulting intermediate via trigonal bipyramidal transition structure TS22-23 yields 23 in which the methoxylated organic molecule acts as a tridentate ligand (Fig. 5). This complex subsequently participates in ligand exchange with one of the acetic acids produced from the CMD mechanism (Fig. 1) and generates the more stable intermediate 26 by passing through two transition structures TS24-25 and TS25-26. The higher stability of 26 than 23 implies that the Pd(II) center prefers to coordinate to the acetate rather than the methoxy ligand. The addition of the second acetic acid to 26via transition structure TS26-27 gives 27 from which 28 is formed by a proton transfer from the coordinated acetic acid to the nitrogen atom of the methoxylated molecule. The overall activation barrier for formation of 28 from 22 is computed to be less than 15 kcal mol−1. Finally, displacement of the coordinated product by substrate 1 leads to regeneration of active catalyst 13. From this point on, the second catalytic cycle begins. Since the active catalyst 13 lies 10.3 kcal mol−1 higher in energy than 26, the overall activation barrier to the C(sp3)–H activation in the second catalytic cycle increases to 30.0 kcal mol−1 (Fig. 5). Indeed, the ability of the N–H deprotonated product to form a tridentate complex causes this species to bind more strongly to the palladium(II) center than substrate 1. This feature retards the alkoxylation reaction by decreasing the activity of the catalyst, resulting in the process requiring a high temperature for completion.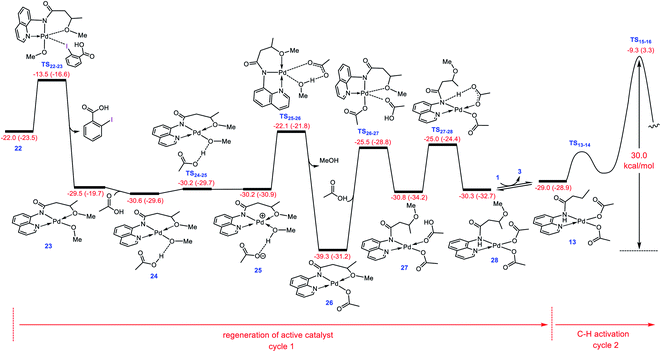 | ||
| Fig. 5 Calculated energy profile for regeneration of active catalyst 13 from 22. Free energies (potential energies) are given in kcal mol−1. | ||
Catalytic cycle proposed by the DFT calculations
The catalytic cycle shown in Scheme 4 summarizes our calculation results related to the mechanism of the title reaction. The reaction is initiated by coordination of substrate 1 to the Pd complex followed by deprotonation of the N–H and C(sp3)–H bonds by the OAc ligands to give cyclopalladated intermediate 16.13 Subsequently, the substitution of BI–OMe for HOAc affords 17. The OMe ligand in the resultant intermediate (17) is then transferred from iodine(III) to palladium(II) to give iodonium 18 stabilized by an anionic palladium(II) complex. Afterward, intermediate 18 undergoes isomerization by moving the quinoline moiety from the basal to the apical position, triggering a redox process by promoting two electrons from Pd(II) to iodine(III), leading to formation of Pd(IV) complex 19 with a pendant carboxylate group. This isomerization not only promotes the Pd(II) oxidation but also sets the stage ready for the reductive elimination by formation of a five-coordinate complex in which the reacting alkyl moiety occupies a position trans to the empty site.14 The addition of a methanol (solvent) to the ensuing complex then affords 21. In this intermediate, the methanol is stabilized by a hydrogen bonding interaction with the pendant carboxylate group. Next, the C–O reductive elimination takes place by nucleophilic attack of the methanol on the sp3 carbon via an outer-sphere SN2 mechanism to yield 22. Our calculations predict that starting from iodonium salt 18, the oxidative addition and the reductive elimination steps are extremely fast with ΔG‡ < 3.5 kcal mol−1 (Fig. 3 and 4). Later, the more stable complex 26 is furnished by following a series of chemical steps. The high stability of this species causes the regeneration of the active catalyst 13 to be considerably endergonic (∼10 kcal mol−1), resulting in the overall activation barrier to the subsequent catalytic cycle increasing to 30.0 kcal mol−1 (Fig. 5). This finding clearly explains why the alkoxylation reaction developed by Rao et al. requires a high temperature for completion (Scheme 1).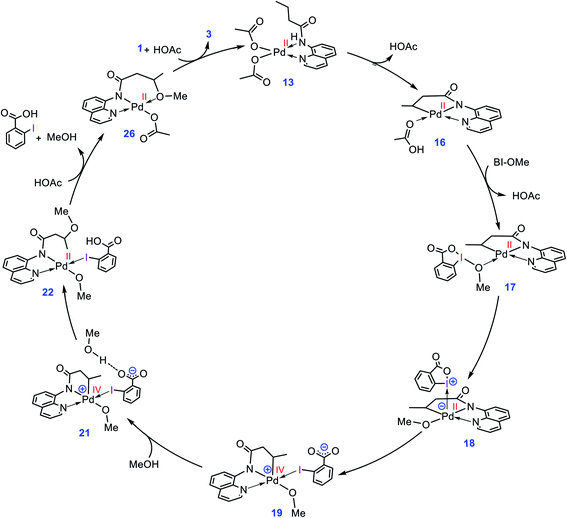 | ||
| Scheme 4 Catalytic cycle proposed by the DFT calculations for palladium-catalyzed C(sp3)–H alkoxylation using BI–OMe. | ||
Impact of the substituent on the reaction mechanism
In a separate study, Rao et al. used a similar method for preparation of acetals through double alkoxylation of the C(sp3)–H bonds of butyramide derivative 29 using BI–OMe as the oxidant and Pd(OAc)2 as the catalyst (Scheme 5).9b Based on the preliminary results, the authors proposed that the product of the first alkoxylation is the substrate for the second one.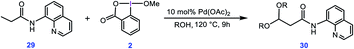 | ||
| Scheme 5 Palladium-catalyzed double alkoxylation of C(sp3)–H bonds using the cyclic iodine(III) reagent 2 (BI–OMe) developed by Rao et al. | ||
What interest us here is to explore how the electronic feature of the R′ substituent on a substrate affects the alkoxylation mechanism. Fig. 6 compares the energy profiles for alkoxylation of the substrates with R′ = H, Me, and OMe. Several points emerge from this comparison. First, the overall activation energy of the C–H activation step increases in the order R′ = H < Me < OMe. It is inferred from this result that the greater the electron donor property of the R group, the higher the activation barrier of the C–H activation. Indeed, a substituent with strong electron donating ability decreases the acidity of the hydrogen being abstracted, leading to the C–H activation to become more energy demanding. Second, the stability of three coordinate complex 7 (7_R′) is determined by the nature of the R′ group; an R′ group with strong electron donating ability increases the intrinsic stability of this coordinatively unsaturated species. It also finds that the relative energy of the transition structure TS17-18 (TS17-18_R′) depends on the intrinsic stability of this three coordinate species and decreases in the order R = H > Me > OMe. Third, although the formation of a Pd(IV) complex is unavoidable for the substrates with R′ = H and Me, this is not the case for the substrate with R′ = OMe. The IRC calculation shows that transition structure TS17-18_OMe directly connects 17-OMe to 19′_OMe. It follows that intermediates 18_OMe and 19_OMe are not local minimum and thus no Pd(IV) intermediate is formed in this case. Indeed, if we assume that 19_OMe is generated during the reaction, it is highly unstable and rapidly undergoes a redox process. This is because of the strong π-donor property of the OMe substituent, forcing the PdIV–C(sp3) σ-bond in 19_OMe to be completely polarized toward the palladium center, giving zwitterion complex 19′_OMe in which the Pd center bears an oxidation state of +2. In this case, the C–O coupling process from this zwitterion complex does not involve the reductive elimination step, and instead, it takes place via nucleophilic addition of the carboxylate-activated MeOH to the oxonium ion. The DFT calculations show that the addition of the methanol to the oxonium ion is extremely fast and proceeds without involvement of an intermediate. As a result, it is evident from our calculations that a change in the R substituent leads to an abrupt alteration in the reaction mechanism. Scheme 6 shows the modified catalytic cycle for alkoxylation of the substrate with R = OMe.
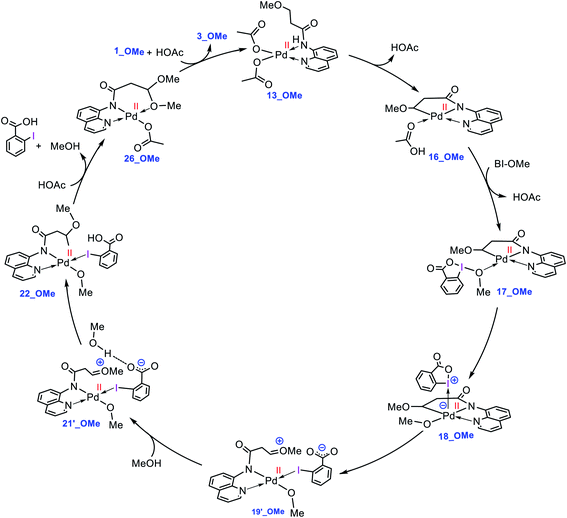 | ||
| Scheme 6 Catalytic cycle proposed by the DFT calculations for palladium-catalyzed C(sp3)−H alkoxylation of 1_OMe using BI–OMe. | ||
Assessing the generality of our proposed mechanism
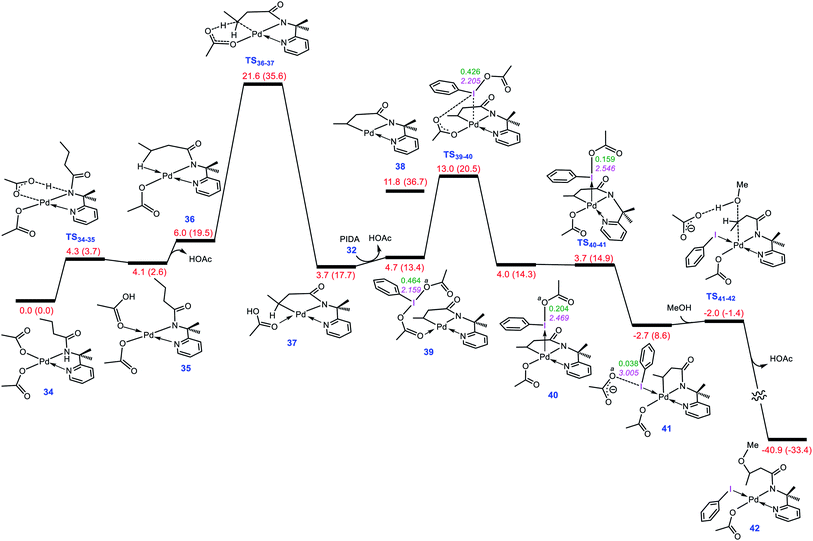
To evaluate whether the mechanism proposed in this study is applicable to interpret other alkoxylation reactions catalysed by Pd(II) complexes, we investigated the mechanism of the reaction shown in Scheme 7 developed by Shi.5 In this reaction, iodobenzenediacetate (PIDA) is used as the oxidant. The energy profile given in Fig. 7 indicates that the reaction is commenced by activation of the N–H and C–H bonds by the OAC ligands by surmounting an activation barrier of 21.6 kcal mol−1. The coordination of PIDA to the Pd(II) centre then sets the stage for the redox process. The transfer of the acetate ligand from the iodine to the Pd atom via transition structure TS39-40 gives iodonium ion 40. The overall activation barrier for this crucial step is calculated to be only 13.0 kcal mol−1, implying that similar to BI–OMe, PIDA is susceptible to forming the key iodonium intermediate. The ensuing species is extremely elusive and involves the required isomerization in a barrierless fashion to furnish 41 with a relative free energy of −2.7 kcal mol−1. The isomerization triggers the oxidation of Pd(II) to Pd(IV) through electron transfer to the iodine(III) atom. The redox process causes the I–Oa bond in 41 to be cleaved, supported by the negligible WBI value (0.038) between the I and Oa atoms. Starting from 41, addition of the methanol to the sp3 carbon atom takes place via transition structure TS41-42 with a free energy barrier as low as 0.7 kcal mol−1. According to our calculation results, once the OAc transfer from the iodine to the palladium has taken place via transition structure TS39-40, the oxidative addition and reductive elimination steps proceed in a barrierless fashion. These additional results lend support to the generality of our novel mechanism found by the DFT calculations for Pd(II)-catalyzed I(III)-mediated alkoxylation of C(sp3)–H bonds.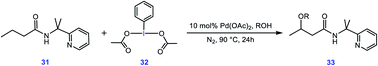 | ||
| Scheme 7 Palladium-catalyzed C(sp3)–H alkoxylation using the iodine(III) reagent 32 (PIDA) developed by Shi et al. | ||
Conclusion
In this work, we performed DFT calculations to elucidate the mechanism of the alkoxylation of the C(sp3)–H bonds using hypervalent iodine(III) reagents (ArIX2) catalysed by Pd(OAc)2. An unprecedented mechanism for this transformation is revealed by clarifying the oxidative addition step. The calculations indicate that this key step begins with the transfer of an X ligand from ArIX2 to a Pd–alkyl intermediate. The ligand transfer forms a square pyramidal Pd(II) complex in which iodonium [ArIX]+ occupies the apical position and is stabilized by interaction with the Pd dz2 orbital. The resultant complex then undergoes an isomerization by moving the ligand trans to the Pd–alkyl bond to the apical position. This isomerization considerably destabilizes the dz2 orbital, promoting the electron transfer from Pd(II) to I(III), resulting in the reduction of I(III) concomitant with the extrusion of the second X ligand as a free anion. The released anion then assists the alcohol (solvent) to nucleophilically attack the Pd(IV)–alkyl bond via an SN2 mechanism to form a new C–O bond. The information reported in this study is important in enhancing our understanding of the fundamental processes that underpin many catalytic reactions mediated by iodine(III) reagents and catalyzed by Pd(II) complexes and could assist scientists to design new catalytic reactions.Computational details
Gaussian 16 (ref. 15) was used to fully optimize all the structures reported in this paper at the M06 level of theory.16 For all the calculations, solvent effects were considered using the SMD solvation model17 with methanol as the solvent. The SDD basis set18 with effective core potential (ECP) was chosen to describe iodine and palladium. The 6-31G(d) basis set19 was used for other atoms. This basis set combination will be referred to as BS1. Frequency calculations were carried out at the same level of theory as those for the structural optimization. Transition structures were located using the Berny algorithm. Intrinsic reaction coordinate (IRC) calculations were used to confirm the connectivity between transition structures and minima.20 To further refine the energies obtained from the SMD/M06/BS1 calculations, we carried out single-point energy calculations in methanol using the M06 functional method for all of the structures with a larger basis set (BS2). BS2 utilizes the def2-TZVP basis set21 on all atoms with an effective core potential including scalar relativistic effect for palladium and iodine. Tight convergence criterion was also employed to increase the accuracy of the calculations. In this work, the free energy for each species in solution was calculated using the following formula:| G = E(BS2) + G(BS1) − E(BS1) + ΔG1 atm→1 M | (1) |
An additional correction to Gibbs free energies was made to consider methanol concentration where a MeOH is directly involved in transformations. In such a case, the free energy of MeOH is described as follows:
G(MeOH) = E(BS2) + G(BS1) − E(BS1) + ΔG1 atm→1 M + RT![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) ln(24.72) ln(24.72) | (2) |
The orbital population analysis and determination of the WBI bond orders were carried out by the NBO7 program.23
Author contributions
P. A., S. K. T. and K. F. performed the calculations. A. A. supervised the work and wrote the manuscript with contribution from the other authors.Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.Acknowledgements
We thank the Australian Research Council (ARC) for project funding (DP180100904) and the Australian National Computational Infrastructure and the University of Tasmania for the generous allocation of computing time. We would also like to thank Mrs Sheyda Hasanpour Aghdam for helping us in preparation of the graphical abstract. We also appreciate the financial support provided by Iran Science Elites Federation.Notes and references
- For selected reviews on hypervalent iodine chemistry, see: (a) P. J. Stang, J. Org. Chem., 2003, 68, 2997 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) V. V. Zhdankin and P. J. Stang, Chem. Rev., 2008, 108, 5299 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) T. Dohi and Y. Kita, Chem. Commun., 2009, 2073 RSC; (d) V. V. Zhdankin, J. Org. Chem., 2011, 76, 1185 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (e) J. Charpentier, N. Fruh and A. Togni, Chem. Rev., 2015, 115, 650 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (f) A. Yoshimura and V. V. Zhdankin, Chem. Rev., 2016, 116, 3328 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (g) S. V. Kohlhepp and T. Gulder, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2016, 45, 6270 RSC; (h) A. Parra, Chem. Rev., 2019, 119, 12033 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (i) B. Zhang, X. Li, B. Guo and Y. Du, Chem. Commun., 2020, 56, 14119 RSC.
- For selected reviews on metal-catalyzed iodine(III)-mediated organic reactions, see: (a) F. C. Sousa e Silva, A. F. Tierno and S. E. Wengryniuk, Molecules, 2017, 22, 780 CrossRef PubMed; (b) S. Banerjee, V. W. Bhoyare and N. T. Patil, Chem. Commun., 2020, 56, 2677 RSC.
- For selected reviews on palladium-catalyzed iodine(III)-mediated organic reactions, see: (a) A. J. Canty, Acc. Chem. Res., 1992, 25, 83 CrossRef CAS; (b) N. R. Deprez and M. S. Sanford, Inorg. Chem., 2007, 46, 1924 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) P. Sehnal, R. J. Taylor and I. J. Fairlamb, Chem. Rev., 2010, 110, 824 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (d) T. W. Lyons and M. S. Sanford, Chem. Rev., 2010, 110, 1147 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (e) S. E. Shetgaonkar and F. V. Singh, Front. Chem., 2020, 8, 705 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) G. Shan, X. Yang, Y. Zong and Y. Rao, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2014, 53, 2009 CrossRef; (b) G. Shan, X. Yang, Y. Zong and Y. Rao, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2013, 52, 13606 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- F.-J. Chen, S. Zhao, F. Hu, K. Chen, Q. Zhang, S.-Q. Zhang and B.-F. Shi, Chem. Sci., 2013, 4, 4187 RSC.
- (a) A. R. Dick, K. L. Hull and M. S. Sanford, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2004, 126, 2300 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) L. V. Desai, H. A. Malik and M. S. Sanford, Org. Lett., 2006, 8, 1141 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) G.-W. Wang and T.-T. Yuan, J. Org. Chem., 2010, 75, 476 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (d) Y. Wei, I. Deb and N. Yoshikai, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2012, 134, 9098 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (e) S.-Y. Zhang, G. He, Y. Zhao, K. Wright, W. A. Nack and G. Chen, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2012, 134, 7313 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (f) Z. Yin, X. Jiang and P. Sun, J. Org. Chem., 2013, 78, 10002 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (g) C. Zhang and P. Sun, J. Org. Chem., 2014, 79, 8457 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (h) S. J. Thompson, D. Q. Thach and G. Dong, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2015, 137, 11586 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (i) J. Kumar, A. Gupta and S. Bhadra, Org. Biomol. Chem., 2019, 17, 3314 RSC.
- (a) S. Winstein and T. Traylor, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1955, 77, 3747 CrossRef CAS; (b) B. Biswas, M. Sugimoto and S. Sakaki, Organometallics, 2000, 19, 3895 CrossRef CAS; (c) S. Nedd and A. N. Alexandrova, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2015, 17, 1347 RSC.
- (a) X. Yang, G. Shan, L. Wang and Y. Rao, Tetrahedron Lett., 2016, 57, 819 CrossRef CAS; (b) A. Banerjee, S. Sarkar and B. K. Patel, Org. Biomol. Chem., 2017, 15, 505 RSC; (c) J. Le Bras and J. Muzart, Eur. J. Org. Chem., 2017, 2017, 3528 CrossRef CAS; (d) J. He, M. Wasa, K. S. Chan, Q. Shao and J.-Q. Yu, Chem. Rev., 2017, 117, 8754 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (e) J. Kumar, A. Rahaman, A. K. Singh and S. Bhadra, Chem.–Asian J., 2020, 15, 673 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) T.-S. Jiang and G.-W. Wang, J. Org. Chem., 2012, 77, 9504 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) Y. Zong and Y. Rao, Org. Lett., 2014, 16, 5278 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) S. Shi and C. Kuang, J. Org. Chem., 2014, 79, 6105 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (d) T. Gao and P. Sun, J. Org. Chem., 2014, 79, 9888 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (e) F. Péron, C. Fossey, J. Sopkova-de Oliveira Santos, T. Cailly and F. Fabis, Chem.–Eur. J., 2014, 20, 7507 CrossRef PubMed; (f) M. Sun, L. Zhang, C.-W. Hua, Z. Wang, L.-K. Hou, S.-X. Cai and S. Li, Synlett, 2015, 26, 2843 CrossRef CAS; (g) S. Kolle and S. Batra, Org. Biomol. Chem., 2015, 13, 10376 RSC; (h) M. Yu, Z. Wang, M. Tian, C. Lu, S. Li and H. Du, J. Org. Chem., 2016, 81, 3435 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (i) L. Pan, L. Wang, Q. Chen and M. He, Synth. Commun., 2016, 46, 1981 CrossRef CAS; (j) S. Li, W. Zhu, F. Gao, C. Li, J. Wang and H. Liu, J. Org. Chem., 2017, 82, 126 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (k) F. C. Qiu, Q. Xie and B. T. Guan, Asian J. Org. Chem., 2018, 7, 107 CrossRef CAS; (l) B. Large, F. Bourdreux, A. Damond, A. Gaucher and D. Prim, Catalysts, 2018, 8, 139 CrossRef; (m) J. Kumar, A. Gupta and S. Bhadra, Org. Biomol. Chem., 2019, 17, 3314 RSC; (n) Y. Ren, Y. Liu, S. Gao, X. Dong, T. Xiao and Y. Jiang, Tetrahedron, 2020, 76, 130985 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) A. R. Dick, J. W. Kampf and M. S. Sanford, Organometallics, 2005, 24, 482 CrossRef CAS; (b) V. I. Bakhmutov, J. F. Berry, F. A. Cotton, S. Ibragimov and C. A. Murillo, Dalton Trans., 2005, 1989 RSC; (c) Y.-F. Yang, G.-J. Cheng, P. Liu, D. Leow, T.-Y. Sun, P. Chen, X. Zhang, J.-Q. Yu, Y.-D. Wu and K. Houk, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2014, 136, 344 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (d) M. R. Chapman, C. M. Pask, A. Ariafard and C. E. Willans, Chem. Commun., 2015, 51, 5513 RSC.
- There is an alternative mechanism for the oxidative addition from 18 in which the OMe ligand instead of the quinoline migrates to the apical position. We found that although this migration results in the oxidation of Pd(II), the redox process via this pathway involves a transition structure (TS18-19OMe) lying 10.7 kcal mol−1 higher in energy than TS18-19 (Fig. S1†). This result implies that this alternative mechanism is not favorable, supporting the importance of the isomerization through moving the ligand trans to the strong σ-donor alkyl group, as discussed in the oxidative addition section.
- The wave function analysis was also carried out along the IRC of TS17-18 and TS18-19 and the same conclusion was made (Fig. S2†).
- Recently, Yu, Shi and coworkers in a study on alkylation of aliphatic carboxamides catalyzed by Pd(II) complexes indicated that such a catalytic process involves a reversible C–H activation. For details see: Y. Li, P. Zhang, Y.-J. Liu, Z.-X. Yu and B.-F. Sh, ACS Catal., 2020, 10, 8212–8222 CrossRef CAS . Our calculations for the cyclopalladation step show that the activation barrier to the removal of the β-C–H proton by the OAc ligand viaTS15-16 (Fig. 1c) is much lower in energy than that of the α- and γ-positions (Fig. S3†). Since, the transition structures of other steps (TS17-18, TS18-19 and TS21-22, Fig. 3a and 4) lie below TS15-16, the C–H activation in this case is unlikely to be reversible and thus the regioselectivity of the alkoxylation reaction should be controlled by a kinetic preference for deprotonation of the β-C–H bond).
- Previous studies indicate that the C(sp3)–OR reductive elimination from Pd(IV) complexes should take place via an outer-sphere SN2 mechanism where RO– nucleophilically attacks a square pyramidal structure in which the reacting alkyl moiety occupies the apical position. For selected studies in this context, see: (a) N. M. Camasso, M. H. Pérez-Temprano and M. S. Sanford, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2014, 136, 12771 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) M. H. Pérez-Temprano, J. M. Racowski, J. W. Kampf and M. S. Sanford, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2014, 136, 4097 CrossRef PubMed; (c) I. M. Pendleton, M. H. Pérez-Temprano, M. S. Sanford and P. M. Zimmerman, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2016, 138, 6049 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (d) A. J. Canty, A. Ariafard, N. M. Camasso, A. T. Higgs, B. F. Yates and M. S. Sanford, Dalton Trans., 2017, 46, 3742 RSC; (e) N. M. Camasso, A. J. Canty, A. Ariafard and M. S. Sanford, Organometallics, 2017, 36, 4382 CrossRef CAS; (f) W. G. Whitehurst and M. J. Gaunt, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2020, 142, 14169 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. J. Frisch, G. W. Trucks, H. B. Schlegel, G. E. Scuseria, M. A. Robb, J. R. Cheeseman, G. Scalmani, V. Barone, G. A. Petersson, H. Nakatsuji, X. Li, M. Caricato, A. V. Marenich, J. Bloino, B. G. Janesko, R. Gomperts, B. Mennucci, H. P. Hratchian, J. V. Ortiz, A. F. Izmaylov, J. L. Sonnenberg, D. Williams-Young, F. Ding, F. Lipparini, F. Egidi, J. Goings, B. Peng, A. Petrone, T. Henderson, D. Ranasinghe, V. G. Zakrzewski, J. Gao, N. Rega, G. Zheng, W. Liang, M. Hada, M. Ehara, K. Toyota, R. Fukuda, J. Hasegawa, M. Ishida, T. Nakajima, Y. Honda, O. Kitao, H. Nakai, T. Vreven, K. Throssell, J. A. Montgomery, J. E. Peralta, F. Ogliaro, M. J. Bearpark, J. J. Heyd, E. N. Brothers, K. N. Kudin, V. N. Staroverov, T. A. Keith, R. Kobayashi, J. Normand, K. Raghavachari, A. P. Rendell, J. C. Burant, S. S. Iyengar, J. Tomasi, M. Cossi, J. M. Millam, M. Klene, C. Adamo, R. Cammi, J. W. Ochterski, R. L. Martin, K. Morokuma, O. Farkas, J. B. Foresman and D. J. Fox, Gaussian 16, Revision A.03, Gaussian, Inc., Wallingford CT, 2016 Search PubMed.
- Y. Zhao and D. G. Truhlar, Theor. Chem. Acc., 2008, 120, 215 Search PubMed.
- A. V. Marenich, C. T. Cramer and D. G. Truhlar, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2009, 113, 6378 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) M. Dolg, U. Wedig, H. Stoll and H. Preuss, J. Chem. Phys., 1987, 86, 866 CrossRef CAS; (b) A. Bergner, M. Dolg, W. Küchle, H. Stoll and H. Preuß, Mol. Phys., 1993, 80(6), 1431 CrossRef CAS.
- P. C. Hariharan and J. A. Pople, Theor. Chim. Acta, 1973, 28, 213 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) K. Fukui, J. Chem. Phys., 1970, 74, 4161 CrossRef CAS; (b) K. Fukui, Acc. Chem. Res., 1981, 14, 363 CrossRef CAS.
- F. Weigend, F. Furche and R. Ahlrichs, J. Chem. Phys., 2003, 119, 12753 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) V. S. Bryantsev, M. S. Diallo and W. A. Goddard III, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2008, 112, 9709 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) J. A. Keith and E. A. Carter, J. Chem. Theory Comput., 2012, 8, 3187 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) E. D. Glendening, J. K. Badenhoop, A. E. Reed, J. E. Carpenter, J. A. Bohmann, C. M. Morales, P. Karafiloglou, C. R. Landis and F. Weinhold, Natural Bond Order 7.0, Theoretical Chemistry Institute, University of Wisconsin, Madison, WI, 2018 Search PubMed; (b) E. D. Glendening, C. R. Landis and F. Weinhold, NBO 7.0: New Vistas in Localized and Delocalized Chemical Bonding Theory, J. Comput. Chem., 2019, 40, 2234 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available. See DOI: 10.1039/d1sc01230d |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2021 |