Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleOrganic deliquescence: organic vapor-induced dissolution of molecular salts†
Kazuyuki Ishii *,
Kei Yokomori,
Kei Murata
*,
Kei Yokomori,
Kei Murata ,
Seiji Nakamura and
Kyoko Enomoto
,
Seiji Nakamura and
Kyoko Enomoto
Institute of Industrial Science, The University of Tokyo, 4-6-1 Komaba, Meguro-ku, Tokyo, 153-8505, Japan. E-mail: k-ishii@iis.u-tokyo.ac.jp
First published on 28th June 2022
Abstract
This report demonstrates organic vapor-induced dissolution of several molecular salts (i.e., organic deliquescence), like water vapor-induced deliquescence. Systematic experiments indicate that appropriate organic deliquescent responses to volatile organic compounds can be designed according to the principle, “like dissolves like”. The phenomena will be useful for developing agents to collect various volatile organic compounds.
The importance of interactions between solid materials and gaseous molecules has recently been highlighted in the context of (i) CO(g) adsorption or H2 storage using metals,1–8 (ii) vapor molecule detection in the environment,9–17 and (iii) uptake and catalysis involving gaseous molecules, e.g., CO2 reduction,18–22 despite the limited interactions allowed by the extremely low density of gaseous molecules (∼10−3 times the density of liquids).
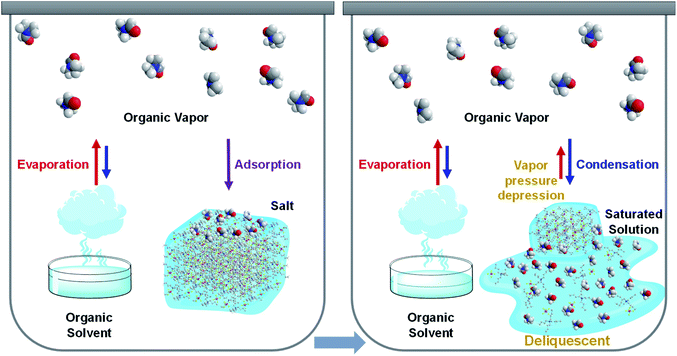
Deliquescence is an essential phenomenon that relies on interactions between solid chemicals and water vapor;23–25 specifically, solid chemicals absorb enough water vapor to become dissolved in an aqueous solution. This behavior has been observed as far back as ancient times when table salt containing nigari (magnesium chloride) hardened under high humidity. To date, deliquescence has been reported for various chemicals (e.g., citric acid, sodium hydroxide, potassium carbonate, magnesium chloride, calcium chloride), which capture water vapor from the atmosphere and spontaneously create aqueous solutions in humid conditions. For some water-soluble chemicals, simply increasing the environmental humidity can promote deliquescence (observed as the solid → liquid change) without heating or adding liquid. This phenomenon can be exploited to capture atmospheric water vapor, and calcium chloride (CaCl2) has been employed as a chemical desiccant. However, to our knowledge, deliquescence involving organic vapor has not yet been reported, despite increased efforts to remove environmental volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in recent decades.26–30 This may be because there are significantly lesser amounts of organic vapors in human living environments than there are water vapors in humid conditions. This report describes organic vapor-induced deliquescent phenomena involving several solid molecular salts that undergo solid → liquid changes in response to organic vapors. These changes were systematically investigated by varying the solid molecular salts and organic vapors in a closed system and confirmed to result from deliquescent phenomena, rather than melting (by heating) or dissolution (by adding liquid). Moreover, the organic vapor-induced deliquescence could be designed by considering the molecular structural relationship between the salt and the target organic vapor, thereby highlighting the generalizability of this behavior. Thus, deliquescent phenomena (previously believed to occur only with water vapor) were observed and designed with various organic vapors; these findings will be useful for treating environmental VOCs.
Fig. 1a shows the setup for organic vapor exposure experiments (further details in the ESI†). Briefly, ∼0.5 mg of powdered salt on a thin glass plate was placed onto blue cobalt glass, and 1.0 mL of organic solvent was divided among two small reservoirs in a 9 cm Petri dish. After isolating the system by adding a top glass cover sealed with grease, changes to the physical state of various salt powders were monitored under exposure to various organic vapors at room temperature. In a typical control experiment (i.e., water vapor-induced deliquescence of CaCl2; Fig. S1 and Movie S1†), the CaCl2 powder clearly changed to an aqueous solution via deliquescence.
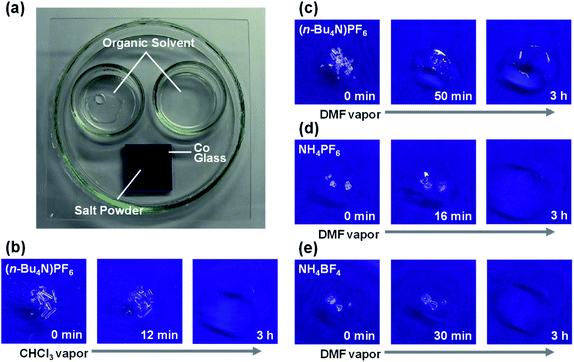 | ||
| Fig. 1 Organic deliquescence. (a) Experimental setup for organic vapor exposure in a sealed system. Organic deliquescent behaviors of (n-Bu4N)PF6 (b and c), NH4PF6 (d), and NH4BF4 (e) exposed to CHCl3 (b) or DMF (c–e) (Movies S2–S5,† respectively). | ||
First, we evaluated the deliquescence of tetrabutylammonium hexafluorophosphate ((n-Bu4N)PF6), which is a common organic salt that is soluble in organic solvents and widely used as an electrolyte in electrochemical experiments. When chloroform (CHCl3) widely used as a solvent in chemical industry was employed as the organic solvent, the (n-Bu4N)PF6 powder gradually changed to liquid, while the amount of CHCl3 in the Petri dish reservoirs decreased (Fig. 1b and Movie S2†). This solid → liquid change was similar to the water vapor-induced CaCl2 deliquescence under analogous conditions. After three hours of CHCl3 vapor exposure, the entire area around (n-Bu4N)PF6 became liquid, and its weight increased by 1.8 times, thus confirming that the solid → liquid change was not caused by melting. These results were highly reproducible (p < 0.05), although the phase-change initiation depended on the experimental conditions (e.g., crystal size, organic solvent surface area). Thus, CHCl3 was transferred from the reservoirs to the (n-Bu4N)PF6 powder, allowing (n-Bu4N)PF6 to dissolve in CHCl3 owing to its high solubility (0.64 g (n-Bu4N)PF6 can be dissolved in 1.0 g CHCl3 at 20 °C). These results confirmed that deliquescent phenomena could be induced by an organic solvent (organic deliquescence). However, such organic deliquescence was not observed for inorganic salts that were insoluble in CHCl3 (e.g., ammonium hexafluorophosphate (NH4PF6), ammonium tetrafluoroborate (NH4BF4), sodium chloride (NaCl)).
Next, analogous experiments were performed using N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF), which is used in large quantity for wet spinning and is a common polar organic solvent that can dissolve various types of salts. With DMF (Fig. 1c–e and Movies S3–S5†), solid → liquid changes were observed for organic ((n-Bu4N)PF6) and some inorganic salts (NH4PF6 and NH4BF4), but not for NaCl and not for any salts without DMF (example control experiments with NH4PF6 shown in Fig. S2†). After three hours of DMF vapor exposure, the weights of the salt components increased by 3.1, 6.9, and 7.2 times for (n-Bu4N)PF6, NH4PF6, and NH4BF4, respectively. Repeated experiments showed that p < 0.05 for the solid → liquid change of (n-Bu4N)PF6, and the sample weight of (n-Bu4N)PF6 under DMF vapor exposure was monitored over time by constructing a closed system in an analytical balance. The DMF vapor concentration was also monitored with a VOC monitor connected to the closed system. When the DMF vapor concentration exceeded ∼4 × 103 ppm (∼0.4 kPa), the solid → liquid change was initiated (Movie S6†). Then, the sample weight clearly increased after the DMF vapor concentration reached ∼5 × 103 ppm (∼0.5 kPa) corresponding to the saturation vapor pressure.31–33 Therefore, the observed phenomena were also attributed to organic deliquescence. To clarify the differences between the tested molecular salts, their solubilities in DMF were determined: 1.27 g (n-Bu4N)PF6, 1.07 g NH4PF6, or 0.29 g NH4BF4 could be dissolved in 1.0 g DMF at 20 °C, whereas NaCl was insoluble in DMF. In general, organic deliquescent phenomena were observed with organic and inorganic ammonium salts that were soluble in the target organic solvent. When using a polar organic solvent (DMF), the amount of transferred (i.e., collected) solvent was much greater than the amount of salt. This is an important feature of organic deliquescence, compared with conventional adsorption phenomena. To evaluate organic deliquescence by non-ammonium salts, similar experiments were performed using tetraphenylphosphonium bromide ((Ph4P)Br) with CHCl3 (solubility = 0.29 g g−1) or DMF (solubility = 0.25 g g−1) at 20 °C; solid → liquid changes were observed in both cases (Fig. 2a, b and Movies S7, S8†). After three hours of vapor exposure, the weight of the (Ph4P)Br component increased by 2.0 or 1.7 times in the presence of CHCl3 or DMF, respectively. Thus, organic deliquescent phenomena can occur with non-ammonium salts (e.g., (Ph4P)Br) that are soluble in organic solvents.
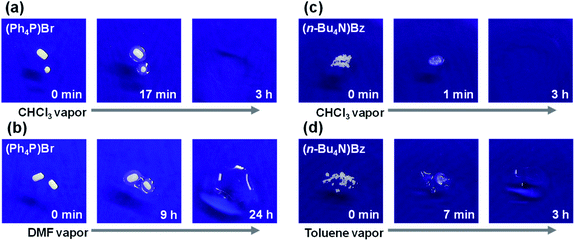 | ||
| Fig. 2 Organic deliquescent behaviors of (Ph4P)Br (a and b) and (n-Bu4N)Bz (c and d) exposed to CHCl3 (a and c), DMF (b), or toluene (d) (Movies S7–S9†). | ||
The observed organic deliquescence involved three processes (Fig. 3): (i) the evaporation of pure organic solvent generates organic vapor, which adsorbs onto the surface of the salt powder; (ii) some salt dissolves, thereby creating a small amount of saturated organic solution on the powder surface; (iii) because the vapor pressure is depressed in the saturated organic solution, the continuous supply of organic vapor (from evaporation) is condensed into the organic solution, thus allowing further dissolution of the salt. This condensation cycle continues until the vapor pressure of the highly-concentrated organic solution becomes comparable to that of the atmosphere. Meanwhile, evaporation reduces the amount of organic solvent in the reservoirs, and the organic vapor is transferred and condensed, thus increasing the amount of liquid around the salt component. The choice of molecular salt and its solubility in organic solvents are crucial factors for promoting organic deliquescence because the vapor pressure depression of the highly-concentrated solution is proportional to the molar concentration (i.e., each salt molecule splits into a cation and an anion in solution, which increases ion molar concentrations and facilitates vapor pressure depression). Thus, organic deliquescence can occur with salts exhibiting high solubility in organic solvents.
Toluene used as a paint solvent is an important VOC whose emissions should be reduced; however, none of the aforementioned salts (i.e., (n-Bu4N)PF6, NH4PF6, NH4BF4, (Ph4P)Br, NaCl) exhibited organic deliquescence or solubility in non-polar toluene. Instead, based on the general rule that “like dissolves like”, tetrabutylammonium benzoic acid ((n-Bu4N)Bz) was used, owing to its superior solubility in toluene (2.42 g (n-Bu4N)Bz in 1.0 g toluene at 20 °C). A solid → liquid change was observed when using (n-Bu4N)Bz and toluene as the salt and organic solvent, respectively (Fig. 2d and Movie S9†), and no change was noted in the absence of toluene (Fig. S3†). After three hours of toluene vapor exposure, the weight of the (n-Bu4N)Bz component increased by 1.1 times, which indicated organic deliquescence. These results confirm that (n-Bu4N)Bz is suitable for organic deliquescence of toluene. The (n-Bu4N)Bz salt also exhibited high solubility in CHCl3 (2.06 g g−1) and DMF (1.64 g g−1), which enabled organic deliquescence in the presence of CHCl3 (Fig. 2c and Movie S10†) and DMF vapors (Fig. S3†). After three hours of vapor exposure, the weight of the (n-Bu4N)Bz component increased by 1.1 or 3.9 times when using CHCl3 or DMF solvents, respectively.
In summary, this report elucidates the solid → liquid changes of molecular salts in response to organic vapors and provides the first experimental demonstration of organic vapor-induced deliquescence by systematically investigating various salts and organic solvents. In contrast to water vapor-induced deliquescence by common chemicals under humid conditions, organic deliquescence had not been observed because of the low concentrations of atmospheric VOCs in human living environments. The results presented herein indicate that organic deliquescence is not unusual, but rather, organic deliquescent systems can be designed to target specific solvents based on the general rule that “like dissolves like”. Considering the success of CaCl2 as a chemical desiccant to capture atmospheric water vapor and the urgent need to remove large volumes of VOCs from facilities using organic solvents,26–30 organic deliquescence represents a promising approach for developing agents to collect VOCs.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (KAKENHI) grant number JP17H06375.Notes and references
- I. Langmuir, Trans. Faraday Soc., 1922, 17, 621–654 RSC.
- L. F. Razon and R. A. Schmitz, Catal. Rev.: Sci. Eng., 1986, 28, 89–164 CrossRef CAS.
- A. D. Allian, K. Takanabe, K. L. Fujdala, X. Hao, T. J. Truex, J. Cai, C. Buda, M. Neurock and E. Iglesia, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2011, 133, 4498–4517 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. A. van Santen, M. Neurock and S. G. Shetty, Chem. Rev., 2010, 110, 2005–2048 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Föhlisch, M. Nyberg, J. Hasselström, O. Karis, L. G. M. Pettersson and A. Nilsson, Phys. Rev. Lett., 2000, 85, 3309–3312 CrossRef PubMed.
- J. Graetz, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2009, 38, 73–82 RSC.
- A. Schneemann, J. L. White, S. Kang, S. Jeong, L. F. Wan, E. S. Cho, T. W. Heo, D. Prendergast, J. J. Urban, B. C. Wood, M. D. Allendorf and V. Stavila, Chem. Rev., 2018, 118, 10775–10839 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. P. Suh, H. J. Park, T. K. Prasad and D.-W. Lim, Chem. Rev., 2012, 112, 782–835 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. R. Stetter and J. Li, Chem. Rev., 2008, 108, 352–366 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. R. Askim, M. Mahmoudi and K. S. Suslick, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2013, 42, 8649–8682 RSC.
- L. You, D. Zha and E. V. Anslyn, Chem. Rev., 2015, 115, 7840–7892 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- O. S. Wenger, Chem. Rev., 2013, 113, 3686–3733 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Kato, A. Omura, A. Toshikawa, S. Kishi and Y. Sugimoto, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2002, 41, 3183–3185 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- V. W.-W. Yam, V. K.-M. Au and S. Y.-L. Leung, Chem. Rev., 2015, 115, 7589–7728 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Zhang, B. Lin, Z.-H. Chen and Z.-N. Chen, J. Mater. Chem., 2012, 22, 11427–11441 RSC.
- M. Kato, H. Ito, M. Hasegawa and K. Ishii, Chem.–Eur. J., 2019, 25, 5105–5112 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- E. Li, K. Jie, M. Liu, X. Sheng, W. Zhu and F. Huang, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2020, 49, 1517–1544 RSC.
- E. Fujita, Coord. Chem. Rev., 1999, 185, 373–384 CrossRef.
- E. Boutin, L. Merakeb, B. Ma, B. Boudy, M. Wang, J. Bonin, E. Anxolabéhère-Mallart and M. Robert, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2020, 49, 5772–5809 RSC.
- E. E. Benson, C. P. Kubiak, A. J. Sathrum and J. M. Smieja, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2009, 38, 89–99 RSC.
- R. Francke, B. Schille and M. Roemelt, Chem. Rev., 2008, 118, 4631–4701 CrossRef PubMed.
- W.-H. Wang, Y. Himeda, J. T. Muckerman, G. F. Manbeck and E. Fujita, Chem. Rev., 2015, 115, 12936–12973 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. T. Martin, Chem. Rev., 2000, 100, 3403–3454 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. J. Mauer and L. S. Taylor, Pharm. Dev. Technol., 2010, 15, 582–594 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. J. Mauer and L. S. Taylor, Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol., 2010, 1, 41–63 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Volatile Organic Compounds in the Atmosphere, ed. R. E. Hester and R. M. Harrison, RSC, Cambridge, UK, 1995 Search PubMed.
- C. Lai, Z. Wang, L. Qin, Y. Fu, B. Li, M. Zhang, S. Liu, L. Li, H. Yi, X. Liu, X. Zhou, N. An, Z. An, X. Shi and C. Feng, Coord. Chem. Rev., 2021, 427, 213565 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Li, L. Zhang, Z. Yang, P. Wang, Y. Yan and J. Ran, Sep. Purif. Technol., 2020, 235, 116213 CrossRef CAS.
- B. Predel, M. Hoch and M. Pool, Phase Diagrams and Heterogeneous Equilibria A Practical Introduction, Springer-Verlag, New York, 2004 Search PubMed.
- M. S. Rahbar and T. Kaghazchi, Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol., 2005, 2, 207–215 CrossRef CAS.
- The saturation vapor pressure of DMF is 0.49 kPa at 25 °C based on International Chemical Safety Cards.
- Time dependence of powder X-ray diffraction was measured during the powder of (n-Bu4N)PF6 was exposed to DMF (Fig. S4†). After the organic deliquescence was initiated, the intensity in the small angle region (2θ ∼ 8–11 degree) decreased in contrast to the unchanged intensity in the wide angle region. This suggests that in organic deliquescence, the disorder in nm–μm order initially occurs before the dissolution.
- Even when using unsaturated DMF vapor (∼80%), the organic deliquescence of (n-Bu4N)PF6 was confirmed to occur within 30 min. In this experiment, N2 gas containing unsaturated DMF vapor was flowed to the powder of (n-Bu4N)PF6 in a box.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available: Experimental procedures and observation in control experiments. See https://doi.org/10.1039/d2ra03390a |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2022 |