Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleUranium(IV) alkyl cations: synthesis, structures, comparison with thorium(IV) analogues, and the influence of arene-coordination on thermal stability and ethylene polymerization activity†‡
Nicholas R.
Andreychuk
a,
Balamurugan
Vidjayacoumar
a,
Jeffrey S.
Price
a,
Sophie
Kervazo
b,
Craig A.
Peeples
c,
David J. H.
Emslie
 *a,
Valérie
Vallet
*a,
Valérie
Vallet
 *b,
André S. P.
Gomes
*b,
André S. P.
Gomes
 b,
Florent
Réal
b,
Florent
Réal
 b,
Georg
Schreckenbach
b,
Georg
Schreckenbach
 *c,
Paul W.
Ayers
*c,
Paul W.
Ayers
 *a,
Ignacio
Vargas-Baca
*a,
Ignacio
Vargas-Baca
 a,
Hilary A.
Jenkins
a and
James F.
Britten
a
a,
Hilary A.
Jenkins
a and
James F.
Britten
a
aDepartment of Chemistry, McMaster University, 1280 Main St. West, Hamilton, L8S 4M1, Ontario, Canada. E-mail: emslied@mcmaster.ca
bUniversité Lille, UMR 8523 – Physique des Lasers Atoms et Molecules, F-59000 Lille, France. E-mail: valerie.vallet@univ-lille.fr
cDepartment of Chemistry, University of Manitoba, Winnipeg, R3T 2N2, Manitoba, Canada. E-mail: schrecke@cc.umanitoba.ca
First published on 10th November 2022
Abstract
Reaction of [(XA2)U(CH2SiMe3)2] (1; XA2 = 4,5-bis(2,6-diisopropylanilido)-2,7-di-tert-butyl-9,9-dimethylxanthene) with 1 equivalent of [Ph3C][B(C6F5)4] in arene solvents afforded the arene-coordinated uranium alkyl cations, [(XA2)U(CH2SiMe3)(ηn-arene)][B(C6F5)4] {arene = benzene (2), toluene (3), bromobenzene (4) and fluorobenzene (5)}. Compounds 2, 3, and 5 were crystallographically characterized, and in all cases the arene is π-coordinated. Solution NMR studies of 2–5 suggest that the binding preferences of the [(XA2)U(CH2SiMe3)]+ cation follow the order: toluene ≈ benzene > bromobenzene > fluorobenzene. Compounds 2–4 generated in C6H5R (R = H, Me or Br, respectively) showed no polymerization activity under 1 atm of ethylene. By contrast, 5 and 5-Th (the thorium analogue of 5) in fluorobenzene at 20 and 70 °C achieved ethylene polymerization activities between 16![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 800 and 139
800 and 139![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 200 g mol−1 h−1 atm−1, highlighting the extent to which common arene solvents such as toluene can suppress ethylene polymerization activity in sterically open f-element complexes. However, activation of [(XA2)An(CH2SiMe3)2] {M = U (1) or Th (1-Th)} with [Ph3C][B(C6F5)4] in n-alkane solvents did not afford an active polymerization catalyst due to catalyst decomposition, illustrating the critical role of PhX (X = H, Me, Br or F) coordination for alkyl cation stabilization. Gas phase DFT calculations, including fragment interaction calculations with energy decomposition and ETS-NOCV analysis, were carried out on the cationic portion of 2′-Th, 2′, 3′ and 5′ (analogues of 2-Th, 2, 3 and 5 with hydrogen atoms in place of ligand backbone methyl and tert-butyl groups), providing insight into the nature of actinide–arene bonding, which decreases in strength in the order 2′-Th > 2′ ≈ 3′ > 5′.
200 g mol−1 h−1 atm−1, highlighting the extent to which common arene solvents such as toluene can suppress ethylene polymerization activity in sterically open f-element complexes. However, activation of [(XA2)An(CH2SiMe3)2] {M = U (1) or Th (1-Th)} with [Ph3C][B(C6F5)4] in n-alkane solvents did not afford an active polymerization catalyst due to catalyst decomposition, illustrating the critical role of PhX (X = H, Me, Br or F) coordination for alkyl cation stabilization. Gas phase DFT calculations, including fragment interaction calculations with energy decomposition and ETS-NOCV analysis, were carried out on the cationic portion of 2′-Th, 2′, 3′ and 5′ (analogues of 2-Th, 2, 3 and 5 with hydrogen atoms in place of ligand backbone methyl and tert-butyl groups), providing insight into the nature of actinide–arene bonding, which decreases in strength in the order 2′-Th > 2′ ≈ 3′ > 5′.
Introduction
Cationic early transition metal and f-element alkyl complexes for solution ethylene polymerization are typically generated by reaction of a neutral dialkyl complex (isolated, or generated in situ) with a strong electrophile such as [CPh3][B(C6F5)4], [HNMe2Ph][B(C6F5)4], B(C6F5)3 or methylaluminoxane (MAO), with subsequent polymerization achieved by repeated ethylene coordination and 1,2-insertion steps.1,2 These activation and polymerization reactions are commonly conducted in arene or alkane solvents; the former is standard in academic laboratories,3 while the latter is often favored in industry.4–7 However, olefin polymerization catalysts are frequently generated in situ without isolation and characterization. Therefore, the nature and impact of arene solvent coordination is not well explored, and only a handful of early transition metal or f-element alkyl cations which exist as arene-solvent-separated ion pairs have been isolated; crystallographically-characterized examples are shown in Fig. 1.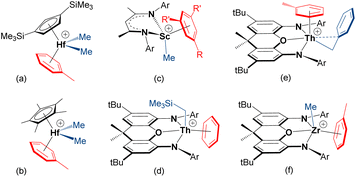 | ||
| Fig. 1 Crystallographically-characterized early transition metal and f-element alkyl cations which exist as arene-solvent-separated ion pairs (R = Me or Br and R′ = H, or R = R′ = Me; Ar = C6H3iPr2-2,6 or C6H2iPr3-2,4,6).8,10,13,14,18–20 | ||
The arene in [(CpTMS2)HfMe2(η6-toluene)][MeB(C6F5)3] {CpTMS2 = 1,3-C5H3(SiMe3)2} (a in Fig. 1), and the zirconium analogue, is tightly coordinated, as evidenced by a lack of exchange between free and bound toluene on the NMR timescale.8 Similar metal–arene binding was observed in [Cp*MMe2(η6-toluene)][MeB(C6F5)3] {M = Hf (b in Fig. 1) and Zr}, whereas coordinated toluene is more labile in the titanium analogue.9,10 Nevertheless, both the titanium [Cp*TiR3] (R = Me or Bn) compounds and their heavier congeners [Cp*MR3] (M = Zr, R = Me or Bn; M = Hf, R = Me) were reported to exhibit appreciable ethylene polymerization activity when combined with B(C6F5)3 in toluene.11,12
The mesitylene-coordinated scandium cation (c in Fig. 1), was shown to be an active ethylene polymerization catalyst in bromobenzene, but achieved negligible activity in more-donating toluene, highlighting the impact of arene coordination on polymerization activity.13,14 McConville et al. also proposed arene-coordinated [{CH2(CH2NAr)2}TiR(η6-toluene)]+ {Ar = o-xylyl or C6H3iPr2-2,6} cations to explain greatly reduced α-olefin polymerization activities in the presence of toluene.15,16 By contrast, toluene in [{tBuNSiMe2(η5,η1-C5Me3CH2)}Ti(toluene)]-[B(C6F5)4] is only weakly bound in solution, and this compound is highly active for ethylene (1 atm) polymerization in toluene.17
The thorium19,21 and zirconium18 4,5-bis(anilido)xanthene complexes (d–f in Fig. 1) were reported by one of us (Emslie et al.). In the toluene-coordinated trimethylsilylmethyl thorium complex, toluene is not displaced to any significant extent in bromobenzene (in the presence of 5 equiv. of free toluene), and free and coordinated toluene only undergo slow exchange on the NMR timescale at room temperature. In the solid state, the Th–arenecentroid distances in [(XA2)Th(CH2SiMe3)(η6-benzene)][B(C6F5)4] and [(XA2)Th(CH2Ph)(η6-toluene)][B(C6F5)4] {XA2 = 4,5-bis(2,6-diisopropylanilido)-2,7-di-tert-butyl-9,9-dimethylxanthene} are 2.95 and 2.94 Å, respectively, and the thorium cations are inactive for ethylene (1 atm) polymerization in benzene and toluene. By contrast, toluene in [(XN2)ZrMe(η6-toluene)][B(C6F5)4] {XN2 = 4,5-bis(2,4,6-triisopropylanilido)-2,7-di-tert-butyl-9,9-dimethylxanthene} is substantially displaced in bromobenzene, even in the presence of 10 equiv. of toluene, and free and coordinated toluene undergo rapid exchange at room temperature. Consistent with more facile toluene displacement, the zirconium complexes are highly active ethylene (1 atm) polymerization catalysts in both toluene and bromobenzene (max. 883![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 g mol−1 atm−1 h−1). The potential for tetraarylborate counteranions, especially BPh4−, to π-coordinate to early transition metal or f-element alkyl species, and the impact of this coordination on olefin polymerization, has also been discussed.22–28
000 g mol−1 atm−1 h−1). The potential for tetraarylborate counteranions, especially BPh4−, to π-coordinate to early transition metal or f-element alkyl species, and the impact of this coordination on olefin polymerization, has also been discussed.22–28
Herein we describe the synthesis of a series of uranium cations, [(XA2)U(CH2SiMe3)(ηn-arene)][B(C6F5)4] {arene = benzene, toluene, bromobenzene and fluorobenzene}, and crystallographic characterization of the benzene, toluene and fluorobenzene complexes; the latter is the first example of an f-element π-coordinated to a fluoroarene. We also evaluate the ethylene (1 atm) polymerization activity of the uranium(IV) alkyl cations, and their thorium(IV) analogues, generated in a range of solvents including toluene, bromobenzene, n-alkanes and fluorobenzene. Furthermore, we describe computational studies on several of the arene-coordinated uranium and thorium alkyl cations, providing insight into the nature and relative strength of actinide-arene π-coordination.
To date, the majority of molecular actinide ethylene polymerization catalysts29 are metallocene and ansa-metallocene complexes, such as  (WCA = weakly-coordinating anion, often a tetra(aryl)borate), largely developed by Marks and co-workers.30–37 For example,
(WCA = weakly-coordinating anion, often a tetra(aryl)borate), largely developed by Marks and co-workers.30–37 For example, 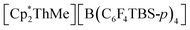 (TBS = tert-butyldimethylsilyl) achieved a high activity of 920
(TBS = tert-butyldimethylsilyl) achieved a high activity of 920![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 g mol−1 h−1 atm−1 in toluene.30 However, actinide ethylene polymerization catalysts supported by non-carbocyclic ancillary ligands have also recently emerged.38 For example, Eisen and co-workers reported the bis(amidinate) actinide(IV) chloro complexes [(2-pyridylamidinate)2AnCl(μ-Cl)2Li(TMEDA)] (2-pyridylamidinate = {(Me3SiN)2C(2-py)}; An = Th, U) which upon activation with MAO, [CPh3][B(C6F5)4] and/or Al(iBu)3, produced polyethylene with activities ranging from 100 to 10
000 g mol−1 h−1 atm−1 in toluene.30 However, actinide ethylene polymerization catalysts supported by non-carbocyclic ancillary ligands have also recently emerged.38 For example, Eisen and co-workers reported the bis(amidinate) actinide(IV) chloro complexes [(2-pyridylamidinate)2AnCl(μ-Cl)2Li(TMEDA)] (2-pyridylamidinate = {(Me3SiN)2C(2-py)}; An = Th, U) which upon activation with MAO, [CPh3][B(C6F5)4] and/or Al(iBu)3, produced polyethylene with activities ranging from 100 to 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 g mol−1 h−1 atm−1.39 However, the active species were not isolated or spectroscopically investigated. Additionally, Leznoff and co-workers reported a variety of neutral uranium(IV) dialkyl complexes,40 [{κ3-(ArNCH2CH2)2O}U(CH2R)2] (Ar = 2,6-iPr2C6H3; R = SiMe3, Ph), [(tBuNON)U(CH2SiMe3)2], and dimeric [(tBuNON)U{CH(SiMe3)(SiMe2CH2)}]2 (tBuNON = {(tBuNSiMe2)2O}), supported by flexible pincer ligands that achieved ethylene polymerization activities of 20–600 g mol−1 h−1 atm−1 in hexane.
000 g mol−1 h−1 atm−1.39 However, the active species were not isolated or spectroscopically investigated. Additionally, Leznoff and co-workers reported a variety of neutral uranium(IV) dialkyl complexes,40 [{κ3-(ArNCH2CH2)2O}U(CH2R)2] (Ar = 2,6-iPr2C6H3; R = SiMe3, Ph), [(tBuNON)U(CH2SiMe3)2], and dimeric [(tBuNON)U{CH(SiMe3)(SiMe2CH2)}]2 (tBuNON = {(tBuNSiMe2)2O}), supported by flexible pincer ligands that achieved ethylene polymerization activities of 20–600 g mol−1 h−1 atm−1 in hexane.
Results and discussion
Experimental studies
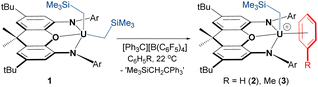
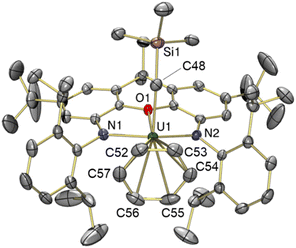
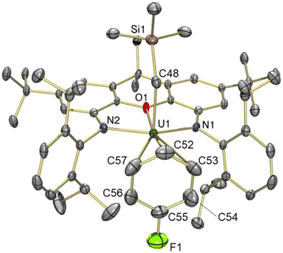
Reaction of orange-red [(XA2)U(CH2SiMe3)2] (1)41 with 1 equiv. of [Ph3C][B(C6F5)4] in benzene or toluene afforded the uranium alkyl cations, [(XA2)U(CH2SiMe3)(ηn-arene)][B(C6F5)4]·2(arene) {ηn-arene = η6-benzene (2) and η3-toluene (3)} (Scheme 1), which were obtained as deep brown crystals in over 70% yield after crystallization from benzene or toluene layered with hexanes at −30 °C.In the solid state, 2 exists as a solvent-separated ion pair in which the uranium(IV) monoalkyl cation is stabilized by η6-coordination to benzene (Fig. 2). Cation 2 has approximate Cs symmetry (with the plane of symmetry bisecting opposing C–C bonds in coordinated benzene) and structurally resembles the neutral dialkyl precursor [(XA2)U(CH2SiMe3)2] (1), but with the trimethylsilylmethyl anion in the plane of the XA2 ligand replaced by benzene. If the arene in 2 is viewed as the occupant of a single coordination site, uranium adopts a pseudo square-pyramidal geometry with the trimethylsilylmethyl ligand in the apical position. This structure is similar to that of [(XA2)Th(CH2SiMe3)(η6-C6H6)][B(C6F5)4] (2-Th),19 but: (a) the benzene ligand in 2 is rotated by 30° (the plane of symmetry in 2-Th runs through two of the benzene carbon atoms), and (b) the An–N, An–O, and An–Calkyl distances in 2 are shorter due to the smaller ionic radius of uranium(IV) versus thorium(IV) (0.89 vs. 0.94 Å for a coordination number of 6).42 Additionally, the ligand backbone is less planar in 2 in order to accommodate a shorter N(1)⋯N(2) distance, and the O–An–Calkyl angle is slightly more acute {87.22(9) in 2vs. 91.3(1)° in 2-Th}, reflecting increased steric hindrance around the smaller actinide metal.
The bonds between uranium and the XA2 ligand in cationic 2 are 0.03–0.06 Å shorter than those in neutral 1. By contrast, the U–Calkyl distance in 2 is 2.365(3) Å, which is similar to the U–C distances for the alkyl group in an apical position in neutral 1 (2.368(7) and 2.380(7) Å), suggesting that the influence of increased uranium electrophilicity on the U–Calkyl distance in 2 is partially offset by tighter XA2 coordination combined with increased steric hindrance arising from η6-arene coordination. The latter steric effect is supported by a more acute O–U–Capical angle of 87.22(9)° in 2 (cf. 94.8(2) and 95.0(2)° in 1). Compound 2 also exhibits an expanded U–C–Si angle of 133.8(2)° (cf. 128.2(3)-130.8(3)° in 1), likely resulting from increased steric hindrance (or strengthened α-agostic interactions, although this seems less likely given that the U–Calkyl–H angles in 2 {100(2)-102(2)°} are not especially acute43).
To the best of our knowledge, other structurally-characterized uranium alkyl cations are limited to compounds a,44b![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 45 and c
45 and c![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 45 in Fig. 3, all of which feature anion or donor-solvent coordination.47 The terminal U–Calkyl bond length in 2 is very similar to those in methyl complexes a and b {2.39(1) and 2.395(6) Å, respectively}. By contrast, the U–Calkyl distance in c is significantly longer than that in 2 as a result of polyhapto benzyl ligand coordination.
45 in Fig. 3, all of which feature anion or donor-solvent coordination.47 The terminal U–Calkyl bond length in 2 is very similar to those in methyl complexes a and b {2.39(1) and 2.395(6) Å, respectively}. By contrast, the U–Calkyl distance in c is significantly longer than that in 2 as a result of polyhapto benzyl ligand coordination.
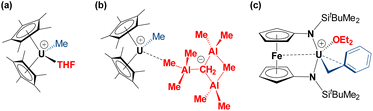 | ||
| Fig. 3 Literature examples of crystallographically characterized uranium alkyl cations.44–46 | ||
The U–Carene distances in 2 range from 3.097(3) to 3.249(3) Å, resulting in a U–centroid distance of 2.86 Å and an average U–Carene distance of 3.17 Å. Other structurally characterized uranium(IV) complexes featuring intermolecular coordination of a neutral arene are limited to Cotton's hexamethylbenzene species; dimetallic [{(η6-C6Me6)UCl2}2(μ-Cl)3][AlCl4], and trimetallic [{(η6-C6Me6)UCl2(μ-Cl)3}2(UCl2)], with average U–Carene distances of 2.92–2.94 Å, and average U–centroid distances of 2.55–2.58 Å.48,49 The U–Carene distances in Cotton's complexes are significantly shorter than those in 2, presumably as a consequence of the increased donor ability of mesitylene versus benzene, decreased steric hindrance, and perhaps also increased electrophilicity at uranium.
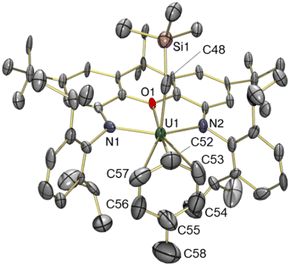
The solid-state structure of toluene-coordinated 3 (Fig. 4) is similar to that of 2, except that coordinated toluene is rotated approximately 30° relative to coordinated benzene in 2, so that the Cipso–Cmethyl bond of toluene lies approximately in the plane of symmetry for the molecule, minimizing unfavourable steric interactions with the flanking 2,6-diisopropylphenyl groups. Furthermore, toluene in 3 is much less symmetrically bound than benzene in 2, as demonstrated by the relatively shorter U–Cpara (3.05(2) Å) and U–Cmeta (3.13(2) and 3.36(2) Å) bonds, and relatively longer U–Cortho (3.47(2) and 3.70(2) Å) and U–Cipso (3.78(2) Å) distances, leading to an expanded U–centroid distance of 3.14 Å, and an average U–Carene distance of 3.42 Å. All of these U–Carene distances are above the sum of the covalent radii for U and Csp2 (2.69 Å),50 but are well within the sum of the van der Waals radii (4.48 Å).51 However, an η3-coordination mode is tentatively assigned, given that the O–U vector passes through toluene in much closer proximity to the meta and para carbon atoms; by comparison, the O–U vector in 2 approximately intersects with the centroid of benzene.
The U–N {2.21(1) and 2.22(1) Å}, U–O {2.417(9) Å} and U–Calkyl {2.36(2) Å} bond lengths, and the U–Calkyl–Si {136.8(7)°} and O–U–Calkyl {88.8(4)°} angles in 3 are very similar to those in 2, suggesting that although toluene is an intrinsically superior donor, the steric inability of the bulkier arene to achieve an η6-coordination mode limits the electron density it can provide to the metal centre, resulting in a similarly electrophilic cation. However, in contrast to the bent xanthene backbone (18.9°) of cation 2, the ligand backbone in 3 is close to planar, with only a 5.9° angle between the xanthene aryl rings. This increase in backbone planarity is likely required to reposition the flanking isopropyl groups to sterically accommodate the methyl substituent of the toluene ligand; the shortest Me2HC⋯CHMe2 distance (between the flanking 2,6-diisopropylphenyl groups) in 3 is 5.25 Å versus 4.54 Å in 2.
Other toluene-coordinated uranium(IV) complexes have not been reported. However, we previously reported the toluene-coordinated thorium(IV) complex, [(XA2)Th(CH2Ph)(η6-C6H5Me)][B(C6F5)4] (e in Fig. 1), which features a benzyl group in place of a (trimethylsilyl)methyl group. In this thorium benzyl cation, the arene occupies an axial rather than an equatorial position, and the Th–Ctoluene distances {3.063(5) to 3.435(6) Å} span a narrower range than those in 3, leading to a substantially shorter An–centroid distance of 2.94 Å.19
In crystalline form, 2·2 benzene and 3·x toluene (x = 1 or 2) suffer from poor solubility in benzene or toluene,§ and as such, 1H NMR spectra were recorded in bromobenzene-d5, in which both cations dissolve readily. Upon dissolution of 2·2 benzene and 3·2 toluene in C6D5Br, the major signals in the room-temperature 1H NMR spectra are identical, consisting of sixteen paramagnetically shifted and broadened signals ranging from +80 to −41 ppm. These resonances are consistent with an XA2 uranium(IV) monoalkyl fragment with the expected Cs symmetry in solution. However, the presence of approximately three equivalents of free protio-benzene (from 2·2 benzene) or protio-toluene (from 3·2 toluene) indicates that the uranium-bound arenes of cations 2 and 3 are largely liberated upon dissolution in C6D5Br, generating [(XA2)U(CH2SiMe3)(C6D5Br)][B(C6F5)4] (4-d5; Scheme 2) in situ as the major product, in which bromobenzene may be π- or κ1Br-coordinated. Cation 4-d5 is also formed directly via the reaction of 1 with [Ph3C][B(C6F5)4] in C6D5Br, with 2H NMR resonances between −29 and −30 ppm for coordinated bromobenzene-d5 (Fig. 5).
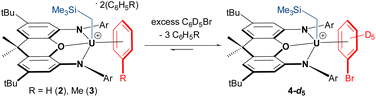 | ||
| Scheme 2 In situ generation of C6D5Br-coordinated cation 4-d5 (Ar = 2,6-diisopropylphenyl); although bromobenzene is depicted as π-coordinated, κ1-coordination via bromine cannot be ruled out. | ||
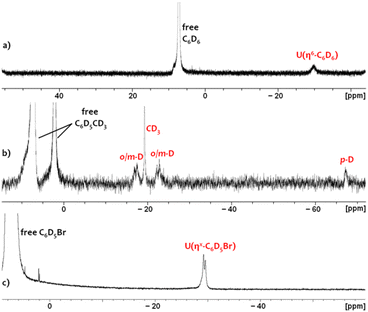 | ||
| Fig. 5 2H NMR spectra of (a) 2-d6 in C6H5Br containing 5 equiv. of C6D6, (b) 3-d8 in C6H5Br containing 5 equiv. of toluene-d8, and (c) 4-d5 in neat C6D5Br. | ||
In order to observe the 1H NMR signals for the XA2 ligand and the alkyl group in 2 and 3, samples of 2·2 benzene and 3·2 toluene were dissolved in C6D5Br spiked with 100 equivalents of C6D6 or C6D5CD3, respectively. In each case, this yielded 16 resonances (these resonances were already present in low concentration when 2·2 benzene or 3·2 toluene was dissolved in neat C6D5Br) that are slightly shifted relative to those for 4-d5, indicating that the equilibrium has been driven almost entirely towards [(XA2)U(CH2SiMe3)(ηn-C6D5R)][B(C6F5)4] (R = D (2-d6) or CD3 (3-d8). As such, the binding preferences of the [(XA2)U(CH2SiMe3)]+ cation can be deduced to follow the order: toluene ≈ benzene > bromobenzene.
Upon dissolution of 2·2 benzene in C6D5Br, the 1H NMR signal for coordinated benzene in 2 (present in an approximate 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 5 ratio with 4-d5) was located at −29.4 ppm. This assignment was validated by independently synthesizing and isolating the deuterobenzene-coordinated cation, 2-d6·2 C6D6, which gave rise to a lone 2H NMR resonance at −29.8 ppm in a C6H5Br solution spiked with 5 additional equivalents of C6D6 (Fig. 5). Furthermore, this 2H NMR signal was completely eliminated upon subsequent addition of 100 equiv. of protio-benzene. Analogously, the 2H NMR spectrum of 3-d8·2 C7D8 (in C6H5Br spiked with 5 equiv. of toluene-d8) afforded four deuterium resonances at −17.5, −19.3, −22.8, and −67.3 ppm with relative integrations of 2
5 ratio with 4-d5) was located at −29.4 ppm. This assignment was validated by independently synthesizing and isolating the deuterobenzene-coordinated cation, 2-d6·2 C6D6, which gave rise to a lone 2H NMR resonance at −29.8 ppm in a C6H5Br solution spiked with 5 additional equivalents of C6D6 (Fig. 5). Furthermore, this 2H NMR signal was completely eliminated upon subsequent addition of 100 equiv. of protio-benzene. Analogously, the 2H NMR spectrum of 3-d8·2 C7D8 (in C6H5Br spiked with 5 equiv. of toluene-d8) afforded four deuterium resonances at −17.5, −19.3, −22.8, and −67.3 ppm with relative integrations of 2![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 3
3![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 2
2![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1, respectively (Fig. 5). These signals correlate to four low-intensity resonances in the 1H NMR spectrum of 3·2 C7H8 in pure C6D5Br, and were eliminated upon addition of 100 equivalents of protio-toluene.
1, respectively (Fig. 5). These signals correlate to four low-intensity resonances in the 1H NMR spectrum of 3·2 C7H8 in pure C6D5Br, and were eliminated upon addition of 100 equivalents of protio-toluene.
Observation of signals for both free and coordinated benzene or toluene in the 1H NMR spectra of 2·2 benzene and 3·2 toluene (in C6D5Br, with or without added benzene or toluene) demonstrates that degenerate exchange between free and coordinated arenes is slow on the NMR timescale at room temperature. This behaviour mirrors that previously reported for [(XA2)Th(CH2SiMe3)(η6-C6H5Me)][B(C6F5)4] (3-Th), for which well-separated 1H and 13C NMR resonances were observed for free and coordinated toluene at room temperature, with corresponding exchange cross peaks in the 2D-EXSY NMR spectrum. However, for 3-Th in C6D5Br at the same concentration, no signals due to a bromobenzene-coordinated cation were observed, indicating that the equilibrium between a toluene- and a bromobenzene-coordinated cation lies substantially further towards the former in the case of thorium versus uranium.
In bromobenzene-d5 solutions of 2·2 benzene and 3·2 toluene, the dominant cationic species, C6D5Br-bound 4-d5, is thermally stable for months at room temperature, and can tolerate heating at 60 °C for at least one hour with minimal decomposition. However, at 80 °C, 4-d5 decomposed over the course of 8 hours, yielding a mixture of unidentified paramagnetic products and SiMe4 as a major by-product. The thermal stability profile of cation 4-d5 is very similar to that of its neutral dialkyl precursor 1, which decomposes at 80 °C over the course of 24 hours. The stability of 4-d5 is remarkable, given that cationic monoalkyl derivatives typically suffer from deteriorated thermal stability relative to their neutral dialkyl precursors. The high thermal stability of 4-d5 in solution likely stems from the inflexibly positioned steric bulk of the XA2 ligand combined with increased coordinative saturation afforded by bromobenzene coordination (most likely π-coordination given the similarity of the 1H NMR spectra for 2-d6, 3-d8 and 4-d5, and the observation of fluorobenzene π-coordination in 5; vide infra). The effect of arene-coordination on thermal stability is also illustrated by the enhanced thermal stability of 3-d8 generated in toluene-d8;§ this cation is stable for at least 72 hours at 80 °C, only decomposing over 4 hours at 125 °C.
Neutral 1 and the thorium analogue 1-Th are inactive for ethylene (1 atm) polymerization at 20, 70 and 100 °C in n-alkane solvents. Additionally, cationic 2–4 (in benzene, toluene, and bromobenzene, respectively), and the in situ generated thorium analogues of 2 and 3, failed to yield polymer under 1 atm of ethylene at 20 and 70 °C. This suggests that, in these cations, ethylene is unable to compete with arene solvent for actinide coordination.
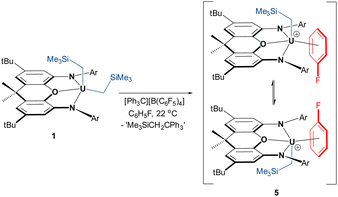
In an effort to implant the cationic [(XA2)U(CH2SiMe3)]+ fragment into a less coordinatively supportive environment, the reaction of 1 with [Ph3C][B(C6F5)4] was conducted in fluorobenzene, resulting in a change in the solution colour from bright-red to deep-brown. Crystals of [(XA2)U(CH2SiMe3)(η3-C6H5F)][B(C6F5)4]·C6H5F (5·C6H5F; vide infra) were isolated after crystallization from C6H5F/n-pentane at −30 °C, and 5 (free from non-coordinated fluorobenzene) was obtained in 91% yield after exposure to vacuum (Scheme 3).
In C6D5Br, cation 5 is converted entirely to bromobenzene-bound 4-d5, with release of one equivalent of free fluorobenzene. Therefore, fluorobenzene-coordinated 5 was generated directly in C6H5F spiked with approximately 10% cyclohexane-d12. At room temperature, the 1H NMR spectrum of 5 in C6H5F/C6D12 revealed only six resonances; those for the tert-butyl groups, the para-positions of the 2,6-diisopropylphenyl rings, the CH1,8 and CH3,6 positions of the xanthene backbone, and the UCH2 and SiMe3 protons. All XA2 protons located above/below the plane of the xanthene backbone of the XA2 ligand were broadened to the extent that they were not observed. These data are indicative of rapid migration of the CH2SiMe3 group from one side of the ligand backbone to the other, which requires dissociation and re-association of coordinated fluorobenzene (or degenerate associative substitution); Scheme 3. However, at −36 °C, 16 signals ranging from +107 to −91 ppm were observed, consistent with a Cs-symmetric cation, as observed for 2–4 at 25 °C (1H or 19F NMR signals for coordinated C6H5F could not be located).
The solid state structure of 5 revealed a familiar arene solvent-separated ion pair with approximate Cs-symmetry, comprised of a uranium(IV) cation with an axially-positioned trimethylsilyl-methyl ligand, and fluorobenzene π-coordinated in the plane of the ligand (Fig. 6). The Cipso–F bond length in 5 {1.362(7) Å} is significantly shorter than the Cipso–Cmethyl distance in 3 {1.47(3) Å}, and is equal within error to that for free fluorobenzene {1.355(2) Å from gas phase electron diffraction}.52
Structurally, 5 bears resemblance to 3, with very similar U–N and U–Calkyl bond distances, a relatively planar xanthene backbone (the angle between the xanthene aryl rings is 7.1°), and an arene ligand that is asymmetrically coordinated as a consequence of monosubstitution. The C–F bond of the fluorobenzene ligand lies approximately in the plane of symmetry of the molecule. However, the fluorine substituent of fluorobenzene is significantly smaller53,54 than the methyl group of toluene, resulting in shorter U–Cipso and longer U–Cpara distances in 5, and a shorter U–centroid distance (3.08 Å in 5vs. 3.14 Å in 3).
Compound 5 is the first crystallographically-characterized example of an f-element bound to a neutral fluoroarene. The majority of complexes bearing π-coordinated fluoroarene ligands contain electron-rich transition metals with d6, d8 and d10 electronic configurations.55 By contrast, fluoroarenes coordinated to electrophilic early transition metal centres tend to be κ1-F coordinated (Fig. 7).56–58
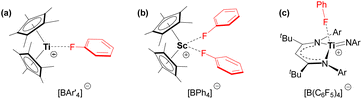 | ||
Fig. 7 Fluoroarene complexes of electrophilic transition metals. (a) [(Cp*)2Ti(κ1-FC6H5)][BAr′4] (Ar′ = Ph or C6F5), (b) [(Cp*)2Sc(κ1-FC6H5)2][BPh4], and (c) [(nacnac)Ti![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) NAr(κ1-FC6H5)][B(C6F5)4] (nacnac = {CH(C(tBu)NAr)2}−; Ar = 2,6-diisopropylphenyl).56–58 NAr(κ1-FC6H5)][B(C6F5)4] (nacnac = {CH(C(tBu)NAr)2}−; Ar = 2,6-diisopropylphenyl).56–58 | ||
A 1 mM solution of [(XA2)U(CH2SiMe3)(η3-C6H5F)][B(C6F5)4] (5) in fluorobenzene under ethylene (1 atm; 20 °C; 30 min) achieved a polymerization activity of 52![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 400 g mol−1 h−1 atm−1; a stark contrast to the lack of polymerization observed for cations generated in benzene, toluene and bromobenzene. This confirms that XA2 uranium(IV) alkyl complexes can in fact serve as ethylene polymerization catalysts in the absence of competitively binding arene solvents, and the activity of 5 increased slightly to 60
400 g mol−1 h−1 atm−1; a stark contrast to the lack of polymerization observed for cations generated in benzene, toluene and bromobenzene. This confirms that XA2 uranium(IV) alkyl complexes can in fact serve as ethylene polymerization catalysts in the absence of competitively binding arene solvents, and the activity of 5 increased slightly to 60![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 g mol−1 h−1 atm−1 at 70 °C (Table 1). The relatively small increase in activity from 20 to 70 °C suggests that catalyst deactivation becomes significant at higher temperature, and indeed, reducing the polymerization time (at 70 °C) to 5 minutes afforded an activity of 139
000 g mol−1 h−1 atm−1 at 70 °C (Table 1). The relatively small increase in activity from 20 to 70 °C suggests that catalyst deactivation becomes significant at higher temperature, and indeed, reducing the polymerization time (at 70 °C) to 5 minutes afforded an activity of 139![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 200 g mol−1 h−1 atm−1.
200 g mol−1 h−1 atm−1.
| M | Solvent | Temp (°C) | PE (g) | Activityc | T m (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a Polymerization conditions: 0.005 mmol of catalyst (<10 mg), 5 mL of solvent, 30 min (arene solvents; unless otherwise specified) or 24 hours (alkane solvents). b Catalysts were generated in situ by reaction of [(XA2)An(CH2SiMe3)2] with [CPh3][B(C6F5)4]; these reactions were allowed to proceed for 30 minutes (in C6H6, C6H5Me, C6H5Br, or o-C6H4F2), 3.5 hours (in C6H5F), or 24 hours {in alkane solvents under ethylene (1 atm)}. c Activities are measured in (g of PE)·(mol of An)−1·h−1·(atm of C2H4)−1. d Peak melting temperature, Tm, from DSC (re-melt). e Reactions were carried out in alkane with (i) 0 equiv. of added arene solvent (Th and U), (ii) 3 equiv. of added toluene (U only), and (iii) 3 equiv. of added C6H5F (U only). For polymerization reactions at 20 °C, alkane = hexanes. For polymerization reactions at 70 °C, alkane = n-heptane. f A shorter polymerization time of 5 minutes was used. | |||||
| U, Th | C6H6 | 20, 70 | 0 | 0 | n/a |
| U, Th | C6H5Me | 20 | 0 | 0 | n/a |
| U, Th | alkanee | 20, 70 | 0 | 0 | n/a |
| U | C6H5Br | 20, 70 | 0 | 0 | n/a |
| U | C6H5F | 20 | 0.131 | 52![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 400 400 |
130.6 |
| U | C6H5F | 70 | 0.150 | 60![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 000 |
127.0 |
| U | C6H5Ff | 70 | 0.058 | 139![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 200 200 |
126.5 |
| Th | C6H5F | 20 | 0.042 | 16![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 800 800 |
136.7 |
| Th | C6H5F | 70 | 0.144 | 57![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 600 600 |
131.6 |
| U | o-C6H4F2 | 20 | 0.028 | 11![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 200 200 |
125.9 |
| U | o-C6H4F2 | 70 | 0 | 0 | n/a |
Based on the success of 5 as a polymerization catalyst in fluorobenzene, the reaction of colourless 1-Th with one equiv. of [Ph3C][B(C6F5)4] was also carried out in fluorobenzene, forming a vibrant orange solution over the course of 3.5 hours, which polymerized ethylene (1 atm) with an activity of 16![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 800 g mol−1 h−1 atm−1 at 20 °C (the same activity was obtained after activation for 24 hours), and 57
800 g mol−1 h−1 atm−1 at 20 °C (the same activity was obtained after activation for 24 hours), and 57![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 600 g mol−1 h−1 atm−1 at 70 °C, illustrative of appreciable thorium catalyst thermal stability. To the best of our knowledge, cationic 5 and 5-Th are the most active non-cyclopentadienyl actinide catalysts for homogeneous ethylene polymerization reported to date.
600 g mol−1 h−1 atm−1 at 70 °C, illustrative of appreciable thorium catalyst thermal stability. To the best of our knowledge, cationic 5 and 5-Th are the most active non-cyclopentadienyl actinide catalysts for homogeneous ethylene polymerization reported to date.
Reaction of 1 with [Ph3C][B(C6F5)4] in 1,2-difluorobenzene also yielded a deep brown solution, providing ethylene polymerization activities of 11![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 200 and 0 g mol−1 h−1 atm−1 at 20 and 70 °C, respectively (Table 1), indicating that the catalytic species formed in 1,2-difluorobenzene is less thermally stable than that formed in fluorobenzene; the 1H NMR spectrum of the cation generated in 9
200 and 0 g mol−1 h−1 atm−1 at 20 and 70 °C, respectively (Table 1), indicating that the catalytic species formed in 1,2-difluorobenzene is less thermally stable than that formed in fluorobenzene; the 1H NMR spectrum of the cation generated in 9![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 o-C6H4F2/C6D12 at 20 °C was not clean and was accompanied by significant SiMe4 evolution, suggestive of competitive cation formation and decomposition. Furthermore, reactions between 1 or 1-Th and [Ph3C][B(C6F5)4] in alkane solvents (generated over 24 hours under 1 atm of ethylene at 20 °C; for uranium, with or without 3 equiv. of added toluene or fluorobenzene) did not yield an active polymerization catalyst; with 1, cation decomposition afforded a grey precipitate and considerable amounts of H2(XA2). A similar lack of polymerization activity was observed for cations generated from 1 in 1,3-difluorobenzene, mesitylene, C6F6, and α,α,α-trifluorotoluene,¶ indicating that C6H5F achieves a delicate balance between being sufficiently coordinating to stabilize the required alkyl cation, and sufficiently labile to allow ethylene to access the metal centre. The choice of alkyl group also plays an important role in determining catalytic activity, given that the reaction of the dibenzyl complex, [(XA2)U(CH2Ph)2] (6; prepared from the reaction of [(XA2)UCl3K(dme)3] with 2 equiv. of KCH2Ph; an X-ray crystal structure is provided in Fig. S20‡), with [Ph3C][B(C6F5)4] in fluorobenzene¶ failed to yield an active polymerization catalyst under ethylene (1 atm) at 20 or 70 °C.
1 o-C6H4F2/C6D12 at 20 °C was not clean and was accompanied by significant SiMe4 evolution, suggestive of competitive cation formation and decomposition. Furthermore, reactions between 1 or 1-Th and [Ph3C][B(C6F5)4] in alkane solvents (generated over 24 hours under 1 atm of ethylene at 20 °C; for uranium, with or without 3 equiv. of added toluene or fluorobenzene) did not yield an active polymerization catalyst; with 1, cation decomposition afforded a grey precipitate and considerable amounts of H2(XA2). A similar lack of polymerization activity was observed for cations generated from 1 in 1,3-difluorobenzene, mesitylene, C6F6, and α,α,α-trifluorotoluene,¶ indicating that C6H5F achieves a delicate balance between being sufficiently coordinating to stabilize the required alkyl cation, and sufficiently labile to allow ethylene to access the metal centre. The choice of alkyl group also plays an important role in determining catalytic activity, given that the reaction of the dibenzyl complex, [(XA2)U(CH2Ph)2] (6; prepared from the reaction of [(XA2)UCl3K(dme)3] with 2 equiv. of KCH2Ph; an X-ray crystal structure is provided in Fig. S20‡), with [Ph3C][B(C6F5)4] in fluorobenzene¶ failed to yield an active polymerization catalyst under ethylene (1 atm) at 20 or 70 °C.
Polyethylene produced using fluorobenzene-bound 5 and the thorium analogue, 5-Th, was insufficiently soluble in 1,2,4-trichlorobenzene at 140 °C for analysis by Gel Permeation Chromatography (GPC). The limited solubility of these polymers suggests that they are of high molecular weight, which is supported by the high peak melting temperatures (Tm; from Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) re-melt) which range from 125.9 to 136.7 °C.59 However, polyethylene formed using the unstable catalyst generated in 1,2-difluorobenzene could be solubilised, and GPC analysis indicates a polymer of moderate molecular weight, with an Mw of 2.9 × 104 and Mn of 1.1 × 104 g mol−1, and a polydispersity index (PDI) of 2.61, which is sufficiently low, considering the low thermal stability of the catalyst, to suggest a single-site polymerization mechanism.39
Computational studies
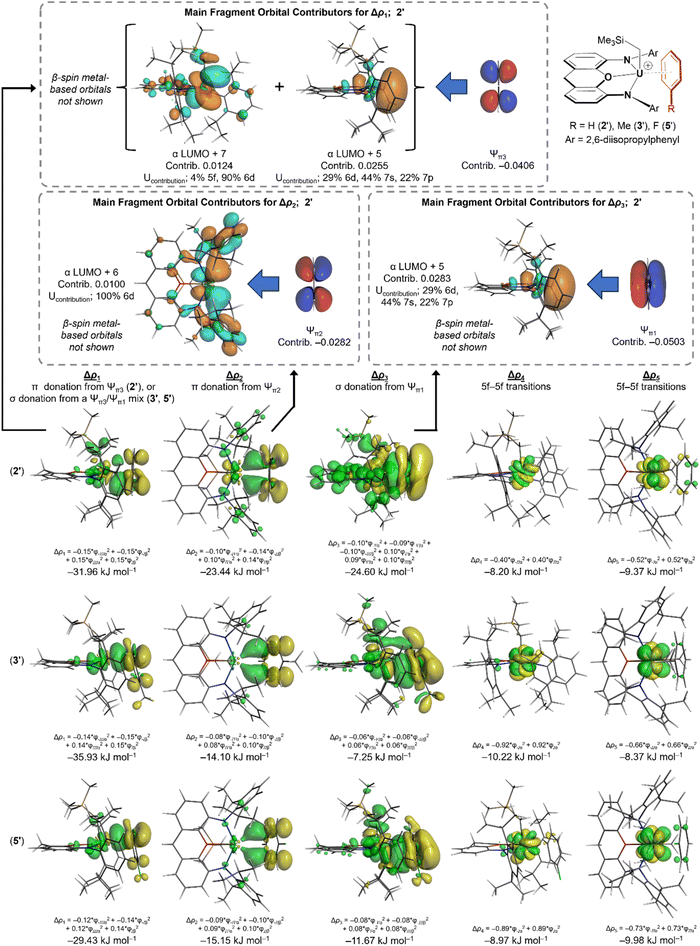
To gain insight into the nature and relative strength of actinide–arene bonding in 2, 2-Th, 3, and 5, we turned to DFT calculations (ADF/AMS, gas-phase, all-electron (without frozen cores), PBE, D3-BJ, TZ2P, scalar ZORA, charge +1, CS symmetry; for uranium complexes, spin-unrestricted with a spin polarization of 2). Calculations were carried out on the cationic portion of analogues of 2, 3, and 5 in which the two methyl groups and two tert-butyl groups on the xanthene backbone were replaced by hydrogen atoms: [(XA2′)U(CH2SiMe3)(arene)]+ {arene = benzene (2′), toluene (3′) and fluorobenzene (5′)}. The geometry optimized structures of 2′, 3′, and 5′ match well with the X-ray crystal structures of 2, 3 and 5; the U–N, U–O, and U–Calkyl, bonds are within 0.03–0.06 Å of the crystallographic values, which is within the expected accuracy of the method, and the U–C–Si and O–U–arenecentroid angles are reproduced to within 4°. The U–arenecentroid distances in 2′, 3′ and 5′ are slightly overestimated, with calculated values that are 0.04, 0.19 and 0.10 Å longer than the experimental values for 2, 3 and 5. For 3′ and 5′, this is concomitant with an overestimation of the U–arenecentroid–Cipso angles, although the greater deviation in the case of 3′ may be due to the lower quality X-ray structure of 3.For [(XA2′)U(CH2SiMe3)(C6H5F)]+, a slightly higher energy minimum (5a′) in which fluorobenzene is η4-coordinated via the ipso and ortho carbon atoms as well as fluorine was also located. Attempted geometry optimization starting from a structure in which one molecule of fluorobenzene is κ1F-coordinated lead only to 5′ or 5a′, although a minimum with two κ1F-coordinated fluorobenzene ligands (5b′) was located (without symmetry constraints). Values of ΔG (298 K) for conversion of 5′ to 5a′ or 5b′ were 3.3 and 15.0 kJ mol−1, respectively, suggesting that 5a and 5b may play a role in fluorobenzene solutions of 5. Computational analysis of the bonding in 5a′ and 5b′ is provided in the ESI.‡
Spin-restricted calculations were also carried out on [(XA2′)Th(CH2SiMe3)(η6-benzene)]+ (2′-Th), and Cs symmetric structures which differ from one another by a 30° rotation in the benzene ligand (around the Th–benzenecentroid axis) were found to lie within 1 kJ mol−1 of one another: the structure in which the plane of symmetry runs through two of the benzene carbon atoms was used for further discussion since this orientation matches that in the solid state structure. The Th–N, Th–O, Th–Calkyl, and Th–arenecentroid distances are within 0.01–0.06 Å of the crystallographic values for 2-Th,19 and the Th–C–Si and O–Th–arenecentroid angles are reproduced to within 0.2° and 10° respectively (this structure is only 3.5 kJ mol−1 lower in energy than the structure constrained to have the same O–Th–arenecentroid angle as the X-ray crystal structure).
Significant An–C Mayer bond orders60 were observed to all six benzene carbon atoms in 2′ (0.12–0.14) and 2′-Th (0.08–0.09), reflective of η6-arene coordination; for comparison, the An–Calkyl bonds in 2′ and 2′-Th have Mayer bond orders of 0.72 and 0.66, respectively. By contrast, approximate η3-toluene and η3-fluorobenzene coordination in 3′ and 5′ results in significant (>0.10) Mayer bond orders between uranium and the meta and para arene carbon atoms (0.17 and 0.14 to the para carbon, and 0.10 and 0.11 to the meta carbon atoms, respectively), whereas the U–C Mayer bond orders to the ipso and ortho arene carbon atoms are 0.05 or less.
Actinide–arene bonding was further investigated by considering the interactions between the (XA2′)An(CH2SiMe3)+ and arene fragments in 2′-Th, 2′, 3′ and 5′ using the energy decomposition analysis61 of Ziegler and Rauk.62,63 This approach affords an overall interaction energy, ΔEint, which is divided into five components:
| ΔEint = ΔEelec + ΔEorb + ΔEdisp + ΔEPauli + ΔEprep | (1) |
The ΔEelec component represents the electrostatic interaction energy (calculated using frozen charge distributions for both fragments), ΔEorb is the orbital interaction energy (this term includes all contributions resulting from intrafragment polarization), ΔEdisp is the dispersion interaction energy, ΔEPauli corresponds to Pauli repulsion, and ΔEprep is the energy needed to bring the fragments from their optimum geometries to their geometries in the unfragmented complex.
Energy decomposition analysis of 2′-Th, 2′, 3′ and 5′ afforded interaction energies (ΔEint; BSSE-corrected) of −104, −91, −90 and −79 kJ mol−1, respectively (Table 2), indicating that (a) benzene is more tightly coordinated in the thorium cation than the uranium cation, likely due to reduced steric hindrance around the larger metal (vide infra), and (b) the strength of uranium–arene bonding decreases in the order 2′ ≈ 3′ > 5′. Weaker fluorobenzene binding is consistent with the results of solution NMR studies on 2, 3 and 5, and the high ethylene polymerization activity of 5 compared to 2 and 3, which were catalytically inactive (vide supra).
| Arene | 2′-Th | 2′ | 3′ | 5′ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C6H6 | C6H6 | C6H5Me | C6H5F | ||
| EDA | ΔEelec | −112.2 | −139.9 | −119.4 | −109.7 |
| ΔEorb | −123.8 | −141.6 | −111.5 | −110.0 | |
| ΔEPauli | 160.1 | 213.7 | 165.9 | 164.5 | |
| ΔEDisp | −63.2 | −63.2 | −60.7 | −59.9 | |
| ΔEprep | 28.4 | 32.6 | 28.3 | 28.6 | |
| BSSE | −6.8 | −7.5 | −7.0 | −7.5 | |
| ΔEint | −104.0 | −90.9 | −90.4 | −79.0 | |
| ETS-NOCV | ΔE1 | −30.7 (25%) | −32.0 (23%) | −35.9 (32%) | −29.4 (27%) |
| ΔE2 | −24.7 (20%) | −23.4 (17%) | −14.1 (13%) | −15.2 (14%) | |
| ΔE3 | −25.2 (20%) | −24.6 (17%) | −7.3 (6%) | −11.7 (11%) | |
| ΔE4 | — | −8.2 (6%) | −10.2 (9%) | −9.0 (8%) | |
| ΔE5 | — | −9.4 (7%) | −8.4 (7%) | −10.0 (9%) | |
| Other | −44.0 (35%) | −44.4 (31%) | −36.2 (32%) | −35.3 (32%) |
In benzene-coordinated 2′, the ΔEorb (−142 kJ mol−1) and ΔEelec (−140 kJ mol−1) contributions to bonding are nearly identical, indicative of substantial covalent character in the U–benzene interaction. Bonding between benzene and the (XA2′)An(CH2SiMe3)+ fragment in 2′-Th involves weaker orbital and electrostatic interactions than in the 2′ (by 18 and 28 kJ mol−1, respectively), but a more negative ΔEint is obtained due to significantly reduced Pauli repulsion around the larger actinide element (ΔEPauli is 54 kJ mol−1 lower in 2′-Th than in 2′).
While ΔEint is very similar for U–toluene bonding in 3′ and U–benzene bonding in 2′, significant differences are observed in the individual contributors: ΔEelec and ΔEorb in 3′ are less negative by 21 and 31 kJ mol−1 as a consequence of η3-coordination, but this coordination mode also reduces ΔEPauli by 48 kJ mol−1. Bonding between U(IV) and fluorobenzene in 5′ involves very similar ΔEorb and ΔEPauli contributions to those in 3′ (within 1.5 kJ mol−1), likely because the reduced donor ability of fluorobenzene is offset by closer approach of this less-hindered arene (the U–arenecentroid distance is 3.18 Å in 5′versus 3.33 Å in 3′). However, U–C6H5F bonding is weaker overall due to a 9 kJ mol−1 reduction in ΔEelec resulting from the electron withdrawing character of the fluorine substituent. Notably, the dispersion interactions between the metal fragment and each of the three arenes are nearly identical in energy (between −60 and −63 kJ mol−1), as are the preparation energies for these structures (between 28 and 33 kJ mol−1).
The deformation density (Δρ) associated with the orbital interaction component (ΔEorb) of the arene–metal interactions in 2′, 2′-Th, 3′, and 5′ was further divided using the Extended Transition State and Natural Orbitals for Chemical Valence (ETS-NOCV) method64–67 (Table 2; deformation density isosurfaces are shown in Fig. 8; the NOCVs and fragment orbitals associated with each of the ETS-NOCV contributions are shown in Fig. S29–S43‡). For 2′, five distinct contributions were elucidated, labelled Δρ1–Δρ5 (with energies ΔE1–ΔE5).|| These five interactions sum to 69% of ΔEorb, with many smaller contributions accounting for the remaining 31%. Δρ1 and Δρ2 involve π-donation to uranium from the two highest-energy occupied π-molecular orbitals of benzene (Ψπ2 and Ψπ3), whereas Δρ3 involves σ-donation to uranium from the lowest energy benzene π-molecular orbital (Ψπ1); the most significant fragment orbitals contributing to Δρ1, Δρ2 and Δρ3 (for 2′) are depicted in Fig. 8. By contrast, Δρ4 and Δρ5 involve transfer of an unpaired electron between f-orbitals, due to changes in f-orbital energy upon arene coordination. The relative energies of these components are ΔE1 > ΔE2 ≈ ΔE3 > ΔE4 ≈ ΔE5. The metal acceptor orbitals associated with Δρ1, Δρ2 and Δρ3 have significant uranium 5f, 6d, 7s and/or 7p character; details are provided in Fig. S29–S43.‡ ETS-NOCV calculations on the thorium analogue, 2′-Th, afforded very similar results, but without the Δρ4 and Δρ5 contributions due to an absence of f-electrons (Table 2).
ETS-NOCV calculations on toluene- and fluorobenzene-coordinated 3′ and 5′ afforded a similar set of five major contributions (Δρ1–Δρ5; Table 2 and Fig. 8), but with the following differences arising from approximate η3-arene coordination: (a) whereas Δρ1 for 2′ involves π-donation from the benzene HOMO (Ψπ3) to uranium, Δρ1 for 3′ and 5′ involves σ-donation; mixing of the Ψπ1 and Ψπ3 orbitals cancels the wavefunction on part of the aromatic ring and enhances it on the other, leading to bonding involving primarily the meta and para carbon atoms. The resulting ΔE1 (−36 kJ mol−1 for 3′ and −29 kJ mol−1 for 5′) is comparable to that for 2′ (−32 kJ mol−1). (b) The π-donor interaction associated with Δρ2 in 3′ and 5′ is less effective than that in 2′, resulting in ΔE2 values of −14 and −15 kJ mol−1 respectively (cf. −23 kJ mol−1 for 2′). (c) The Δρ3 interaction (involving σ-donation from Ψπ1 to uranium) is significantly weaker in 3′ and 5′, giving rise to ΔE3 values of −7 and −12 kJ mol−1 respectively (cf. −25 kJ mol−1 for 2′).
Summary and conclusions
A series of uranium cations, [(XA2)U(CH2SiMe3)(ηn-arene)][B(C6F5)4] {arene = benzene (2), toluene (3), bromobenzene (4) and fluorobenzene (5)} have been isolated (2, 3 and 5) or generated in situ (4). 2H NMR signals were observed for the coordinated arene in 2-d6 in C6H5Br containing 2 or more equiv. of C6D6, 3-d8 in C6H5Br containing 2 or more equiv. of toluene-d8, and 4-d5 in neat C6D5Br. By contrast, signals for coordinated C6H5F in 5 (in a 9![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 mixture of C6H5F/cyclohexane-d12) could not be located, and fluxional room temperature behaviour (involving rapid migration of the uranium alkyl group from one side of the xanthene backbone to the other) is consistent with rapid fluorobenzene dissociation and re-association from 5 (or degenerate associative substitution). These data suggest that the binding preferences of the [(XA2)U(CH2SiMe3)]+ cation follow the order: toluene ≈ benzene > bromobenzene > fluorobenzene.
1 mixture of C6H5F/cyclohexane-d12) could not be located, and fluxional room temperature behaviour (involving rapid migration of the uranium alkyl group from one side of the xanthene backbone to the other) is consistent with rapid fluorobenzene dissociation and re-association from 5 (or degenerate associative substitution). These data suggest that the binding preferences of the [(XA2)U(CH2SiMe3)]+ cation follow the order: toluene ≈ benzene > bromobenzene > fluorobenzene.
Compounds 2·2 benzene, 3·toluene, and 5·fluorobenzene were crystallographically characterized, and are rare examples of arene-coordinated alkyl cations. Compound 5 is the first structurally-characterized example of an f-element complex bearing a neutral fluoroarene ligand, and π-coordination of fluorobenzene in 5 is unusual, given that fluorobenzene is κ1F-coordinated in all crystallographically characterized group 3 and 4 fluorobenzene complexes.
Cations 2–4, and the thorium analogues (2-Th and 3-Th)19 are inactive for ethylene (1 atm) polymerization. By contrast, cations generated in fluorobenzene (5 and the thorium analogue 5-Th) achieved moderate to high activities,68 highlighting the extent to which common arene solvents such as toluene can reduce or quench polymerization activity, especially for sterically-open post-metallocene f-element alkyl cations. Uranium alkyl cation generation in less-donating o-C6H4F2 also afforded an active polymerization catalyst, but with diminished thermal stability. Furthermore, actinide cation generation in hexanes led to extensive decomposition, and did not give rise to an active catalyst system, and similar results were obtained for cations generated from 1 in arene solvents which are less-able to coordinate as a consequence of increased steric hindrance and/or reduced donor ability (m-C6H4F2, C6F6, C6H5CF3 and mesitylene). These results highlight the extent to which C6H5F achieves the right balance between being sufficiently coordinating to stabilize the uranium and thorium alkyl cations, and sufficiently labile to provide ethylene with access to the metal centre.
DFT calculations were carried out to gain insight into the nature of actinide–arene bonding in the cationic portion of 2, 2-Th, 3, and 5. Key findings were: (a) actinide–arene bonding in 2′, 2′-Th, 3′ and 5′ (analogues of 2, 2-Th, 3 and 5 with hydrogen atoms in place of ligand backbone methyl and tert-butyl groups) is appreciably covalent, with similar values of the orbital interaction and electrostatic contributions. (b) Benzene is more tightly coordinated in the thorium cation (2′-Th) than the uranium cation (2′). This is due to reduced steric hindrance around the larger metal, and occurs even though the orbital interaction and electrostatic contributions to bonding are diminished for 2′-Thversus2′. (c) η3-arene coordination reduces the orbital interaction and electrostatic contributions to bonding in toluene-coordinated 3′, relative to 2′, but a concomitant decrease in Pauli repulsion leads to a nearly identical overall interaction energy. (d) Bonding between U(IV) and fluorobenzene (in 5′) affords orbital interaction and Pauli repulsion contributions that are similar to those in toluene-coordinated 3′, likely because the reduced donor ability of fluorobenzene is offset by closer approach of the less sterically hindered arene. However, the overall interaction energy is ∼10 kJ mol−1 less negative due to a reduction in the electrostatic contribution to bonding (resulting from the electron withdrawing character of the fluorine substituent). (e) ETS-NOCV calculations indicate that bonding in 2′ involves σ- and π-donation (×2) from the three filled π-molecular orbitals of benzene, as well as transfer of the two unpaired electrons between f-orbitals (due to changes in f-orbital energy upon arene coordination). (f) ETS-NOCV calculations on 2′-Th were very similar to those for 2′, but without the intra-fragment f-electron transfer, due to an absence of f-electrons. (g) ETS-NOCV calculations on 3′ and 5′ afforded a related bonding picture, but with differences due to the η3-arene coordination mode, resulting in weakening of two of the orbital interaction contributions. Overall, the strength of actinide–arene bonding decreased in the order 2′-Th > 2′ ≈ 3′ > 5′. Weaker fluorobenzene binding (in 5) is consistent with the results of solution NMR studies on 2, 3 and 5, and the high ethylene polymerization activity of 5 compared to that of 2, 2-Th, and 3, which were catalytically inactive.
Experimental section
General details
An argon-filled MBraun UNIlab glove box equipped with a −30 °C freezer was employed for the manipulation and storage of air-sensitive ligands and complexes. Preparative reactions were performed on a double manifold high vacuum line equipped with an Edwards RV12 vacuum pump (ultimate pressure 1.5 × 10−3 torr) using standard techniques,69 and vacuum was measured periodically using a Varian Model 531 Thermocouple Gauge Tube with a Model 801 Controller. Residual oxygen and moisture was removed from the argon or ethylene stream by passage through an Oxisorb-W scrubber from Matheson gas products. Commonly utilized specialty glassware includes the swivel frit assembly, thick-walled Straus flasks equipped with Teflon stopcocks, and J-Young or Wilmad-LabGlass LPV NMR tubes. A VWR Clinical 200 Large capacity centriguge (with 28° fixed-angle rotors that hold 12 × 15 mL or 6 × 50 mL tubes, and in combination with VWR high-performance polypropylene conical centrifuge tubes) located within a glove box was used where indicated.Anhydrous 1,3,5-trimethylbenzene (mesitylene) (98%), α,α,α-trifluorotoluene (≥99%), fluorobenzene (99%), hexafluorobenzene (99%), 1,2-difluorobenzene (98%), 1,3-difluorobenzene (≥99%), and bromobenzene (99%) were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich. Hexanes, n-pentane, benzene, toluene and THF were purchased from Caledon, and deuterated solvents (C6D6, toluene-d8, C6D5Br) were purchased from ACP Chemicals.
Hexanes, n-pentane, benzene and THF were initially dried and distilled at atmospheric pressure from sodium/benzophenone, while toluene was dried and distilled at atmospheric pressure from sodium. These solvents were then stored over an appropriate drying agent (toluene, benzene, THF = Na/Ph2CO; hexanes, n-pentane = Na/Ph2CO/tetraglyme) and introduced to reactions or solvent storage flasks via vacuum transfer with condensation at −78 °C. Mesitylene was dried and distilled under reduced pressure (<10 mTorr) from sodium/benzophenone, whereas α,α,α-trifluorotoluene, fluorobenzene, hexafluorobenzene, 1,2-difluorobenzene, and 1,3-difluorobenzene were dried and distilled at reduced pressure (<10 mTorr) from 4 Å molecular sieves. Bromobenzene was dried and distilled under reduced pressure (<10 mTorr) at elevated temperature (60 °C) from 4 Å molecular sieves. Deuterated solvents were dried over sodium/benzophenone (C6D6, toluene-d8) or 4 Å molecular sieves (C6D5Br), and degassed via three freeze–pump–thaw cycles prior to distillation into a storage flask under a static vacuum.
[Th(NO3)4(H2O)4], UO3, and [Ph3C][B(C6F5)4] (97%; used as received) were purchased from Strem Chemicals. Na, NaH, and LiCH2SiMe3 (1.0 M in n-pentane) were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich. Argon and ethylene of 99.999% purity were purchased from Praxair. Prior to use, solid LiCH2SiMe3 was obtained by removal of solvent in vacuo. Before use, all traces of moisture and ethanol were eliminated from H2(XA2) by stirring with NaH (4 equiv.) in toluene for 16 hours at room temperature, followed by filtration and evaporation to dryness in vacuo. All dried/purified reagents were stored under vacuum or argon. H2(XA2),70 UCl4,71 [(XA2)ThCl2(dme)],70 [(XA2)Th(CH2SiMe3)2] (1-Th),70 [(XA2)UCl3{K(dme)3}], [(XA2)U(CH2SiMe3)2]41 and KCH2Ph72 were prepared using literature procedures. [ThCl4(dme)2] was prepared using two different methods: a modified version of the procedure reported by Gambarotta et al.,73 and the procedure of Kiplinger et al. (at 50 °C).74
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (1H, 2H, 19F) experiments were performed on Bruker AV-200, DRX-500 and AV-600 spectrometers. Spectra were obtained at 298 K unless otherwise specified. 1H NMR spectra are referenced relative to SiMe4 through a resonance of the protio impurity of the solvent; C6D6 (δ 7.16 ppm), toluene-d8 (δ 7.09, 7.01, 6.97, 2.08 ppm), C6D5Br (δ 7.30, 7.02, 6.94 ppm), cyclohexane-d12 (10%) in C6H5F or o-C6H4F2 (δ 1.34 ppm). 19F NMR spectra were referenced using an external standard of CFCl3 (0.0 ppm). Herein, for XA2, Aryl = 2,6-diisopropylphenyl. Peaks in the 1H NMR spectra of paramagnetic uranium(IV) complexes were assigned primarily based on integration. Occasionally, the para-aryl, CH,1,8 CH3,6 and tert-butyl signals could be readily identified as they are often unaffected by the presence/absence of top-bottom symmetry on the NMR timescale. Furthermore, the para-Ar signal often appeared as a triplet at room temperature, allowing definite assignment. For uranium alkyl complexes, significantly broadened 1H NMR signals (typically integrating to approximately 2H) shifted to particularly low- or high- frequencies were speculatively assigned as the UCH2 alpha-protons given their close proximity to the paramagnetic U(IV) centre.
X-ray crystallographic analyses were performed on suitable crystals coated in Paratone oil and mounted on a SMART APEX II diffractometer with a 3 kW Sealed tube Mo generator in the McMaster Analytical X-ray (MAX) Diffraction Facility. Crystal mounting, X-ray data collection at 100 K (5 and 6), 150 K (2), or 173 K (3), and structure solution and refinement were carried out by Dr Hilary Jenkins and Dr Jim Britten of the McMaster Analytical X-ray (MAX) Diffraction Facility. A semi-empirical absorption correction was applied using redundant data. Raw data was processed using XPREP (as part of the APEX2.2.0 software), and solved by direct (SHELX-97 or SHELXTL)75 methods. The structures were completed by difference Fourier synthesis and refined with full-matrix least-squares procedures based on F2. In all cases, non-hydrogen atoms were refined anisotropically (with the exception of carbon and oxygen atoms composing lattice solvent in 5 and 6) and hydrogen atoms were generated in ideal positions and then updated with each cycle of refinement (with the exception of hydrogen atoms on C48 in 2 and 5, which were located from the difference map and refined isotropically). Refinement was performed with SHELXL76 using WinGX or Olex2.77
Combustion elemental analyses were performed on a Thermo EA1112 CHNS/O analyzer by Ms. Meghan Fair or Dr Steve Kornic at McMaster University, and on a Carlo Erba EA 1110 CHN elemental analyzer at Simon Fraser University by Mr Farzad Haftbaradaran, with sample preparation conducted by Dr Wen Zhou in the Leznoff group at Simon Fraser University.
Polyethylene samples were investigated by Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) using a TA Instruments DSC Q20. Samples were measured between 40 and 180 °C using a heating and cooling rate of 10 °C min−1; peak melting temperatures were obtained from the second of two heating runs.
Gel permeation chromatograms (GPCs) were recorded on an Agilent PL220 high temperature instrument equipped with differential refractive index (DRI) and viscometry (VS) detectors at the University of Warwick, Coventry, UK by Dr Daniel W. Lester and Dr Ian Hancox. The system was equipped with 2 × PLgel Mixed D columns (300 × 7.5 mm) and a PLgel 5 μm guard column. Samples were dissolved in 1,2,4-trichlorobenzene and left to solubilize for 12 h on an Agilent PL SP260VS at 140 °C, and all data was calibrated against polystyrene. The mobile phase was trichlorobenzene stabilized with 250 ppm BHT and run at a flow rate of 1 mL min−1 at 160 °C.
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) C, 58.49; H, 4.80; N, 1.47%. Found: C, 58.62; H, 4.73; N, 1.22%. Conducting the alkyl abstraction reaction in benzene-d6 followed by an identical work-up yielded the deuterobenzene isotopologue 2-d6 in comparable yield. 2H NMR (bromobenzene + 5 equivalents benzene-d6, 92.1 MHz, 298 K): δ −29.84 (v broad s, 6D, η6-C6D6).
C, 58.49; H, 4.80; N, 1.47%. Found: C, 58.62; H, 4.73; N, 1.22%. Conducting the alkyl abstraction reaction in benzene-d6 followed by an identical work-up yielded the deuterobenzene isotopologue 2-d6 in comparable yield. 2H NMR (bromobenzene + 5 equivalents benzene-d6, 92.1 MHz, 298 K): δ −29.84 (v broad s, 6D, η6-C6D6).
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) cation 5 is readily converted to C6D5Br-bound cation 4-d5 in bromobenzene-d5, therefore the 1H NMR spectrum in this solvent is identical to that of 4-d5, but containing one equivalent of free fluorobenzene. 1H NMR (fluorobenzene + 10% cyclohexane-d12, 600.1 MHz, 298 K): 37.14, 20.65, −13.09 (s, 3 × 2H, CH,1,8 CH,3,6 aryl-para CH), 4.95 (s, 18H, CMe3), −14.13 (s, 9H, SiMe3), −59.34 (broad s, 2H, UCH2). 1H NMR (fluorobenzene + 10% cyclohexane-d12, 600.1 MHz, 237 K): 106.24 (broad s, 2H), 46.26, 24.70, −17.95 (s, 3 × 2H, CH,1,8 CH,3,6 aryl-para CH), 44.48, 28.26, 5.34 (s, 3 × 2H, CHMe2, aryl-meta CH), 31.61, 21.42, 9.85, −20.06 (s, 4 × 6H, CHMe2), 6.08 (s, 18H, CMe3), −15.46, −22.88 (s, 2 × 3H, CMe2), −18.47 (s, 9H, SiMe3), −90.98 (broad s, 2H, UCH2). 19F{1H} NMR (fluorobenzene + 10% cyclohexane-d12, 188.2 MHz, 298 K): δ −113.38 (s, free C6H5F), −134.18 (broad s, 8F, o-C6F5), −165.19 (t, 3J19F–19F = 21 Hz, 4F, p-C6F5), −169.01 (broad t, 3J19F–19F = 19 Hz, 8F, m-C6F5); signals for coordinated fluorobenzene were not observed between +1200 and −1200 ppm at 25 or –35 °C. Anal. Calcd for C81H78N2OSiUBF21
cation 5 is readily converted to C6D5Br-bound cation 4-d5 in bromobenzene-d5, therefore the 1H NMR spectrum in this solvent is identical to that of 4-d5, but containing one equivalent of free fluorobenzene. 1H NMR (fluorobenzene + 10% cyclohexane-d12, 600.1 MHz, 298 K): 37.14, 20.65, −13.09 (s, 3 × 2H, CH,1,8 CH,3,6 aryl-para CH), 4.95 (s, 18H, CMe3), −14.13 (s, 9H, SiMe3), −59.34 (broad s, 2H, UCH2). 1H NMR (fluorobenzene + 10% cyclohexane-d12, 600.1 MHz, 237 K): 106.24 (broad s, 2H), 46.26, 24.70, −17.95 (s, 3 × 2H, CH,1,8 CH,3,6 aryl-para CH), 44.48, 28.26, 5.34 (s, 3 × 2H, CHMe2, aryl-meta CH), 31.61, 21.42, 9.85, −20.06 (s, 4 × 6H, CHMe2), 6.08 (s, 18H, CMe3), −15.46, −22.88 (s, 2 × 3H, CMe2), −18.47 (s, 9H, SiMe3), −90.98 (broad s, 2H, UCH2). 19F{1H} NMR (fluorobenzene + 10% cyclohexane-d12, 188.2 MHz, 298 K): δ −113.38 (s, free C6H5F), −134.18 (broad s, 8F, o-C6F5), −165.19 (t, 3J19F–19F = 21 Hz, 4F, p-C6F5), −169.01 (broad t, 3J19F–19F = 19 Hz, 8F, m-C6F5); signals for coordinated fluorobenzene were not observed between +1200 and −1200 ppm at 25 or –35 °C. Anal. Calcd for C81H78N2OSiUBF21![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) C, 54.92; H, 4.44; N, 1.58%. Found: C, 54.96; H, 4.61; N, 1.55%.
C, 54.92; H, 4.44; N, 1.58%. Found: C, 54.96; H, 4.61; N, 1.55%.
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) C, 67.14; H, 7.02; N, 2.57%. Found: C, 67.22; H, 7.23; N, 2.67%.
C, 67.14; H, 7.02; N, 2.57%. Found: C, 67.22; H, 7.23; N, 2.67%.
Visualization of the computational results was performed using the ADF/AMS-GUI (SCM) or Biovia Discovery Studio Visualizer. Orbitals and deformation densities were generated with a fine grid using the densf auxiliary program.
Analytical frequency calculations90–92 were conducted on all geometry optimized structures (including geometry optimized fragments) to ensure that the geometry optimization led to an energy minimum or (when using Cs symmetry) a situation where any imaginary frequency corresponds to a breaking of the symmetry; for 2′, 2′-Th, 3′, and 5′, imaginary frequencies were obtained (ranging from −52 to −8 cm−1, with intensities ≤ 0.4 km−mol) corresponding to rotations which also would break the Cs symmetry. Analytical frequency calculations were also used to obtain thermodynamic parameters for 5′, 5a′, and 5b′.
Bonding was analyzed in more detail using a fragment approach (with energy decomposition analysis62,63 and ETS-NOCV analysis64–67) that considered the interaction of cationic (XA2′)An(CH2SiMe3)+ fragments with neutral arene ligands (fragments were generated from the TZ2P geometry optimized structures of each complex, and geometries were frozen). The thresholds for (a) population analysis of each deformation density contribution in terms of individual SFO's, (b) orbital interaction energy contributions corresponding to deformation density components originating from each NOCV-pair, and (c) NOCV eigenvalues were lowered to 0.001, 1, and 0.03, respectively. Fragment interaction calculations involving uranium were conducted using the unrestricted fragments method. Preparation energies (ΔEprep) were obtained by allowing the fragments to adopt equilibrium geometries (i.e. geometry optimized, without imposed symmetry). Basis set superposition errors (BSSEs) were calculated through the use of ghost atoms with no nuclear charge and no electrons to contribute to the molecule (using the molecular fragments method).
Data availability
All relevant experimental data is included as ESI.‡Author contributions
Nicholas R. Andreychuk: investigation, visualization, writing – original draft, review & editing. Balamurugan Vidjayacoumar: investigation. Jeffrey S. Price: formal analysis, investigation, visualization, writing – original draft, review & editing. Sophie Kervazo: formal analysis, investigation, visualization. Craig A. Peeples: formal analysis, investigation. David J. H. Emslie: conceptualization, funding acquisition, project administration, supervision, writing – original draft, review & editing. Valérie Vallet: formal analysis, investigation, funding acquisition, project administration, resources, supervision, visualization. André S. P. Gomes & Florent Réal: funding acquisition, resources, supervision. Georg Schreckenbach: funding acquisition, supervision, writing – review & editing. Paul W. Ayers: funding acquisition, supervision, writing – review & editing. Ignacio Vargas-Baca: supervision, writing – review & editing. Hilary A. Jenkins & James F. Britten: formal analysis.Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.Acknowledgements
D. J. H. E. and G. S. thank NSERC of Canada for a Discovery Grant, and D. J. H. E. thanks the Digital Research Alliance of Canada (previously Compute Canada) for a 2020 Resources for Research Groups (RRG) grant. P. W. A. thanks NSERC, Digital Research Alliance of Canada, and the Canada Research Chairs for funding and computational resources. S. K., V. V., A. S. P. G. and F. R. acknowledge funding Labex CaPPA (Grant No ANR-11-LABX-0005-01). N. R. A. thanks the Government of Ontario for an Ontario Graduate Scholarship (OGS), and McMaster University for a Richard Fuller Memorial Scholarship. We are very grateful to Dr Wen Zhou in the Leznoff group at Simon Fraser University for preparing and submitting Elemental Analysis samples on our behalf.Notes and references
- A. A. Trifonov and D. M. Lyubov, Coord. Chem. Rev., 2017, 340, 10 CrossRef CAS.
- D. Peng, X. Yan, C. Yu, S. Zhang and X. Li, Polymer Chemistry, 2016, 7, 2601 RSC.
- A. A. Altaf, A. Badshah, N. Khan, S. Marwat and S. Ali, J. Coord. Chem., 2011, 64, 1815 CrossRef CAS.
- I. D. Burdett and R. S. Eisinger, in Handbook of Industrial Polyethylene and Technology: Definitive Guide to Manufacturing, Properties, Processing, Applications and Markets, ed. M. A. Spalding and A. M. Chatterjee, Scrivener Publishing, Beverly, MA, 2018, ch. 3, p. 61 Search PubMed.
- J. M. Asua, Polymer Reaction Engineering, Blackwell Publishing, Ames, Iowa, 2007 Search PubMed.
- A. Peacock and A. Calhoun, Polymer Chemistry: Properties and Applications, Carl Hanser Verlag, Munich, 2006 Search PubMed.
- D. Malpass, Introduction to Industrial Polyethylene: Properties, Catalysts and Processes, Wiley-Scrivener, Hoboken, 2010 Search PubMed.
- S. J. Lancaster, O. B. Robinson, M. Bochmann, S. J. Coles and M. B. Hursthouse, Organometallics, 1995, 14, 2456 CrossRef CAS.
- D. J. Gillis, M.-J. Tudoret and M. C. Baird, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1993, 115, 2543 CrossRef CAS.
- D. J. Gillis, R. Quyoum, M.-J. Tudoret, Q. Wang, D. Jeremic, A. W. Roszak and M. C. Baird, Organometallics, 1996, 15, 3600 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Pellecchia, A. Proto, P. Longo and A. Zambelli, Makromolekulare Chemie-Rapid Communications, 1992, 13, 277 CrossRef CAS.
- Q. Wang, R. Quyoum, D. J. Gillis, M.-J. Tudoret, D. Jeremic, B. K. Hunter and M. C. Baird, Organometallics, 1996, 15, 693 CrossRef CAS.
- P. G. Hayes, W. E. Piers and M. Parvez, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2003, 125, 5622 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. G. Hayes, W. E. Piers and M. Parvez, Chem. Eur. J., 2007, 13, 2632 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. D. Scollard, D. H. McConville, N. C. Payne and J. J. Vittal, Macromolecules, 1996, 29, 5241 CrossRef CAS.
- J. D. Scollard and D. H. McConville, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1996, 118, 10008 CrossRef CAS.
- Y.-X. Chen and T. J. Marks, Organometallics, 1997, 16, 3649 CrossRef CAS.
- K. S. A. Motolko, J. S. Price, D. J. H. Emslie, H. A. Jenkins and J. F. Britten, Organometallics, 2017, 36, 3084 CrossRef CAS.
- C. A. Cruz, D. J. H. Emslie, C. M. Robertson, L. E. Harrington, H. A. Jenkins and J. F. Britten, Organometallics, 2009, 28, 1891 CrossRef CAS.
- Sadow et al. also recently reported toluene-coordinated [Nd{C(SiHMe2)3}(η6-toluene){HB(C6F5)3}2] which can be viewed as an neodymium alkyl dication with tight coordination of two HB(C6F5)3– anions: B. M. Schmidt, A. Pindwal, A. Venkatesh, A. Ellern, A. J. Rossini and A. D. Sadow, ACS Catal., 2019, 9, 827 CrossRef CAS.
- C. A. Cruz, D. J. H. Emslie, L. E. Harrington and J. F. Britten, Organometallics, 2008, 27, 15 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Bochmann, G. Karger and A. J. Jaggar, J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun., 1990, 1038 RSC.
- A. D. Horton and J. H. G. Frijns, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. Engl., 1991, 30, 1152 CrossRef.
- M. Bochmann and A. J. Jaggar, J. Organomet. Chem., 1992, 424, C5 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Bochmann, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. Engl., 1992, 31, 1181 CrossRef.
- G. G. Hlatky, H. W. Turner and R. R. Eckman, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1989, 111, 2728 CrossRef CAS.
- B.-T. Guan, B. L. Wang, M. Nishiura and Z. M. Hou, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2013, 52, 4418 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. Li, M. Nishiura, J. Cheng, W. Zhang, Y. Li and Z. Hou, Organometallics, 2013, 32, 4142 CrossRef CAS.
- D. J. H. Emslie, N. R. Andreychuk and C. A. Cruz, in The Lanthanides and Actinides: Synthesis, Reactivity, Properties and Applications, ed. S. T. Liddle, D. P. Mills and L. S. Natrajan, World Scientific Publishing Co., 2022, ch. 7, p. 311 Search PubMed.
- L. Jia, X. Yang, C. L. Stern and T. J. Marks, Organometallics, 1997, 16, 842 CrossRef CAS.
- Y.-X. Chen, C. L. Stern, S. Yang and T. J. Marks, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1996, 118, 12451 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Jia, X. Yang, C. Stern and T. J. Marks, Organometallics, 1994, 13, 3755 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Yang, W. A. King, M. Sabat and T. J. Marks, Organometallics, 1993, 12, 4254 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Yang, C. L. Stern and T. J. Marks, Organometallics, 1991, 10, 840 CrossRef CAS.
- Z. Lin, J.-F. Le Marechal, M. Sabat and T. J. Marks, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1987, 109, 4127 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. X. Chen, M. V. Metz, L. T. Li, C. L. Stern and T. J. Marks, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1998, 120, 6287 CrossRef CAS.
- See for example: (a) T. J. Marks, L. Ja and X. Yang, U.S. Pat., 5477895, 1995 Search PubMed; (b) T. J. Marks and Y.-X. Chen, U.S. Pat., 6229034B1, 2001 Search PubMed; (c) T. J. Marks and Y.-X. Chen, U.S. Pat., 6274752B1, 2001 Search PubMed; (d) T. J. Marks and Y.-X. Chen, U.S. Pat., 6403732B2, 2002 Search PubMed; (e) T. J. Marks and Y.-X. Chen, U.S. Pat., 6388114B1, 2002 Search PubMed; (f) R. E. Campbell Jr., U.S. Pat., 4665046, 1987 Search PubMed.
- Isoprene polymerization catalysts generated in situ by reaction of non-carbocyclic thorium trialkyl complexes with 2 equiv. of [CPh3][B(C6F5)4] (in the presence of AliBu3) have also been reported: G. R. Qin and J. H. Cheng, Dalton Trans., 2019, 48, 11706 RSC.
- E. Domeshek, R. J. Batrice, S. Aharonovich, B. Tumanskii, M. Botoshansky and M. S. Eisen, Dalton Trans., 2013, 42, 9069 RSC.
- C. E. Hayes and D. B. Leznoff, Organometallics, 2010, 29, 767 CrossRef CAS.
- N. R. Andreychuk, S. Ilango, B. Vidjayacoumar, D. J. H. Emslie and H. A. Jenkins, Organometallics, 2013, 32, 1466 CrossRef CAS.
- R. D. Shannon, Acta Cryst, 1976, A32, 751 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Turculet and T. D. Tilley, Organometallics, 2002, 21, 3961 CrossRef CAS.
- W. J. Evans, S. A. Kozimor and J. W. Ziller, Organometallics, 2005, 24, 3407 CrossRef CAS.
- H. M. Dietrich, J. W. Ziller, R. Anwander and W. J. Evans, Organometallics, 2009, 28, 1173 CrossRef CAS.
- M. J. Monreal and P. L. Diaconescu, Organometallics, 2008, 27, 1702 CrossRef CAS.
- A cationic thorium aryl complex, [Cp*2ThPh(THF)][BPh4], has also been reported: R. R. Langeslay, C. J. Windorff, M. T. Dumas, J. W. Ziller and W. J. Evans, Organometallics, 2018, 37, 454 CrossRef CAS.
- G. C. Campbell, F. A. Cotton, J. F. Haw and W. Schwotzer, Organometallics, 1986, 5, 274 CrossRef CAS.
- F. A. Cotton and W. Schwotzer, Organometallics, 1985, 4, 942 CrossRef CAS.
- B. Cordero, V. Gómez, A. E. Platero-Prats, M. Revés, J. Echeverría, E. Cremades, F. Barragán and S. Alvarez, Dalton Trans., 2008, 2832 RSC.
- S. Alvarez, Dalton Trans., 2013, 42, 8617 RSC.
- G. Portalone, G. Schultz, A. Domenicano and I. Hargittai, J. Mol. Struct., 1984, 118, 53 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Pauling, The Nature of the Chemical Bond, Cornell University Press, New York, 3rd edn, 1960 Search PubMed.
- M. Mantina, A. C. Chamberlin, R. Valero, C. J. Cramer and D. G. Truhlar, J. Phys. Chem. A, 2009, 113, 5806 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- See for example: (a) A. Prades, M. Fernandez, S. D. Pike, M. C. Willis and A. S. Weller, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2015, 54, 8520 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) S. D. Pike, I. Pernik, R. Theron, J. S. McIndoe and A. S. Weller, J. Organomet. Chem., 2015, 784, 75 CrossRef CAS; (c) H. Lei, J. C. Fettinger and P. P. Power, Inorg. Chem., 2012, 51, 1821 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (d) A. K. Renfrew, A. D. Phillips, E. Tapavicza, R. Scopelliti, U. Rothlisberger and P. J. Dyson, Organometallics, 2009, 28, 5061 CrossRef CAS; (e) A. B. Chaplin and A. S. Weller, Organometallics, 2010, 29, 2332 CrossRef CAS; (f) T. B. Ditri, A. E. Carpenter, D. S. Ripatti, C. E. Moore, A. L. Rheingold and J. S. Figueroa, Inorg. Chem., 2013, 52, 13216 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (g) M. M. D. Roy, M. J. Ferguson, R. McDonald and E. Rivard, Chem. Commun., 2018, 54, 483 RSC; (h) A. Friedrich, J. Eyselein, J. Langer and S. Harder, Organometallics, 2021, 40, 448 CrossRef CAS.
- M. W. Bouwkamp, J. de Wolf, I. D. Morales, J. Gercama, A. Meetsma, S. I. Troyanov, B. Hessen and J. H. Teuben, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2002, 124, 12956 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. W. Bouwkamp, P. H. M. Budzelaar, J. Gercama, I. Del Hierro Morales, J. M. de Wolf, A. S. I. Troyanov, J. H. Teuben and B. Hessen, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2005, 127, 14310 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- F. Basuli, H. Aneetha, J. C. Huffman and D. J. Mindiola, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2005, 127, 17992 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. H. Lee, Y. H. La and J. W. Park, Organometallics, 2000, 19, 344 CrossRef CAS.
- A. J. Bridgeman, G. Cavigliasso, L. R. Ireland and J. Rothery, J. Chem. Soc., Dalton Trans., 2001, 2095 RSC.
- F. M. Bickelhaupt and E. J. Baerends, in Reviews in Computational Chemistry, ed. K. B. Lipkowitz and D. B. Boyd, Wiley-VCH, New York, 2000, vol. 15, pp. 1 Search PubMed.
- T. Ziegler and A. Rauk, Inorg. Chem., 1979, 18, 1755 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Ziegler and A. Rauk, Inorg. Chem., 1979, 18, 1558 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Mitoraj and A. Michalak, Organometallics, 2007, 26, 6576 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Michalak, M. Mitoraj and T. Ziegler, J. Phys. Chem. A, 2008, 112, 1933 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. P. Mitoraj, A. Michalak and T. Ziegler, Organometallics, 2009, 28, 3727 CrossRef CAS.
- M. P. Mitoraj, A. Michalak and T. Ziegler, J. Chem. Theory Comput., 2009, 5, 962 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- V. C. Gibson and S. K. Spitzmesser, Chem. Rev., 2003, 103, 283 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- B. J. Burger and J. E. Bercaw, Experimental Organometallic Chemistry – A Practicum in Synthesis and Characterization, American Chemical Society, Washington D.C., 1987, vol. 357, p. 79 Search PubMed.
- C. A. Cruz, D. J. H. Emslie, L. E. Harrington, J. F. Britten and C. M. Robertson, Organometallics, 2007, 26, 692 CrossRef CAS.
- J. L. Kiplinger, D. E. Morris, B. L. Scott and C. J. Burns, Organometallics, 2002, 21, 5978 CrossRef CAS.
- P. L. Bailey, R. A. Coxall, C. M. Dick, S. Fabre, L. C. Henderson, C. Herber, S. T. Liddle, D. Lorono-Gonzalez, A. Parkin and S. Parsons, Chem. Eur. J., 2003, 9, 4820 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Athimoolam, S. Gambarotta and I. Korobkov, Organometallics, 2005, 24, 1996 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Cantat, B. L. Scott and J. L. Kiplinger, Chem. Commun., 2010, 46, 919 RSC.
- G. M. Sheldrick, Acta Crystallogr., Sect. A: Found. Crystallogr., 2008, 64, 112 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- G. M. Sheldrick, Acta Crystallogr., Sect. C: Struct. Chem., 2015, 71, 3 Search PubMed.
- O. V. Dolomanov, L. J. Bourhis, R. J. Gildea, J. A. K. Howard and H. Puschmann, J. Appl. Crystallogr., 2009, 42, 339 CrossRef CAS.
- ADF 2020.102, SCM, Theoretical Chemistry, Vrije Universiteit, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, https://www.scm.com Search PubMed.
- G. Te Velde, F. M. Bickelhaupt, E. J. Baerends, C. Fonseca Guerra, S. J. A. Van Gisbergen, J. G. Snijders and T. Ziegler, J. Comput. Chem., 2001, 22, 931 CrossRef CAS.
- J. P. Perdew, K. Burke and M. Ernzerhof, Phys. Rev. Lett., 1996, 77, 3865 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- E. van Lenthe, E. J. Baerends and J. G. Snijders, J. Chem. Phys., 1993, 99, 4597 CrossRef CAS.
- E. van Lenthe, E. J. Baerends and J. G. Snijders, J. Chem. Phys., 1994, 101, 9783 CrossRef CAS.
- E. van Lenthe, A. Ehlers and E.-J. Baerends, J. Chem. Phys., 1999, 110, 8943 CrossRef CAS.
- E. van Lenthe, J. G. Snijders and E. J. Baerends, J. Chem. Phys., 1996, 105, 6505 CrossRef CAS.
- E. van Lenthe, R. van Leeuwen, E. J. Baerends and J. G. Snijders, Int. J. Quantum Chem., 1996, 57, 281 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Grimme, J. Anthony, S. Ehrlich and H. Krieg, J. Chem. Phys., 2010, 132, 154104 CrossRef PubMed.
- S. Grimme, S. Ehrlich and L. Goerigk, J. Comput. Chem., 2011, 32, 1456 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. D. Becke, J. Chem. Phys., 1988, 88, 2547 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Franchini, P. H. T. Philipsen and L. Visscher, J. Comput. Chem., 2013, 34, 1819 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Bérces, R. M. Dickson, L. Y. Fan, H. Jacobsen, D. Swerhone and T. Ziegler, Comput. Phys. Commun., 1997, 100, 247 CrossRef.
- H. Jacobsen, A. Bérces, D. P. Swerhone and T. Ziegler, Comput. Phys. Commun., 1997, 100, 263 CrossRef CAS.
- S. K. Wolff, Int. J. Quantum Chem., 2005, 104, 645 CrossRef CAS.
Footnotes |
| † Dedicated to Prof. Gary J. Schrobilgen for 50 years of outstanding contributions to fundamental Inorganic Chemistry. |
| ‡ Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available: NMR spectra, X-ray crystal structure of [(XA2)U(CH2Ph)2]·THF (6·THF), GPC data, representative DSC data, and computational data. CCDC 1848272–1848275 contain the supplementary crystallographic data for 2, 3, 5 and 6, respectively. For ESI and crystallographic data in CIF or other electronic format see DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/d2sc04302e |
| § When generated in situ in benzene or toluene, compounds 2 and 3 remained in solution, at least on a timescale of hours. However, solid samples of 2·2 benzene and 3·x toluene (x = 1 or 2) were very poorly soluble in benzene or toluene (i.e. they could not readily be re-dissolved). |
| ¶ The reaction of 1 with [Ph3C][B(C6F5)4] in 1,3-difluorobenzene yielded a yellow-brown solution; the analogous reactions in mesitylene, C6F6, and α,α,α-trifluorotoluene yielded oily black-brown, brown, or black-green precipitates, respectively. In contrast, reaction of a dark green-brown solution of [(XA2)U(CH2Ph)2] (7) with [Ph3C][B(C6F5)4] in C6H5F afforded a yellow-brown solution. |
| || The deformation density contributions (Δρn) obtained from ETS-NOCV calculations are numbered (n) based on qualitative analysis of the deformation density isosurfaces. |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2022 |