Heat, pH, and salt: synthesis strategies to favor formation of near-infrared emissive DNA-stabilized silver nanoclusters†
Rweetuparna
Guha
 a,
Malak
Rafik
a,
Anna
Gonzàlez-Rosell
a,
Malak
Rafik
a,
Anna
Gonzàlez-Rosell
 a and
Stacy M.
Copp
a and
Stacy M.
Copp
 *abc
*abc
aDepartment of Materials Science and Engineering, University of California, Irvine, CA 92697, USA. E-mail: stacy.copp@uci.edu
bDepartment of Physics and Astronomy, University of California, Irvine, CA 92697, USA
cDepartment of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, University of California, Irvine, CA 92697, USA
First published on 27th July 2023
Abstract
We present chemical synthesis strategies for DNA-stabilized silver nanoclusters (AgN-DNAs) with near-infrared (NIR) emission in the biological tissue transparency windows. Elevated temperatures can significantly increase chemical yield of near-infrared nanoclusters. In most cases, basic pH favors near-infrared nanoclusters while micromolar amounts of NaCl inhibit their formation.
AgN-DNAs are promising emitters for biosensing and bioimaging applications.1,2 These ultrasmall nanoparticles consist of only 10 to 30 silver atoms encapsulated by one to three single-stranded DNA oligomer templates.3,4 AgN-DNAs are reported to exhibit DNA sequence-encoded excitation and emission wavelengths5,6 as well as high Stokes shifts,7 quantum yields,8 and photostabilities.9–11 The large combinatorial space of DNA sequence has enabled researchers to design a diverse set of AgN-DNAs with emission wavelengths ranging from 400 nm to 1200 nm, far into the NIR.12–17 The sequence-encoded, tunable properties of AgN-DNAs and their spectral sensitivity to analytes have led to chemical sensing, biosensing, and imaging applications.1,2
We used high-throughput experiments and machine learning to discover thousands of new AgN-DNAs.12–16 This approach enabled successful design of DNA ligand sequences that stabilize AgN-DNAs with specific visible and NIR emission colors. NIR-emissive AgN-DNAs are of particular interest as novel biocompatible emitters because biological tissues and fluids scatter, absorb, and emit far less light in the tissue transparency windows.18 Photophysical properties and atomic structures of NIR AgN-DNAs discovered in high-throughput experiments have since been reported.7,19–26 Mastracco, et al. dramatically expanded the space of known NIR-emissive AgN-DNAs with over 100 10-base DNA sequences that stabilize AgN-DNAs with peak emission > 800 nm.12 This large data set holds promise for rapid development of NIR AgN-DNAs for bioimaging applications in the tissue transparency windows.
This study is motivated by two challenges we identified regarding chemical synthesis of NIR-emissive AgN-DNAs. First, we and others have observed that NIR AgN-DNAs often take several days to a week after chemical reduction to form in appreciable quantities; in contrast, visibly emissive AgN-DNAs typically form within hours and up to one day.8,19,24 Second, we observe discrepancies between emission spectra of NIR AgN-DNAs prepared in microwell plates during high throughput experiments versus individually synthesized in single microcentrifuge tubes. Many brightly emissive NIR-emissive AgN-DNAs identified in high-throughput experiments form with exceptionally low chemical yield or are even undetectable when prepared in single microcentrifuge tubes. In some cases, formation of visibly emissive AgN-DNAs by the same DNA template sequence appears to compete with the NIR-emissive AgN-DNA of interest. To advance NIR AgN-DNAs for bioimaging applications, this study identifies the causes of discrepancies between microplate synthesis and microcentrifuge tube synthesis, thereby establishing procedures to scale up NIR-emissive AgN-DNAs.
We first investigate how synthesis of AgN-DNAs differs between microplate and microcentrifuge tube. Robotic liquid handling routines for high-throughput AgN-DNA synthesis were designed for good agreement with “by-hand” synthesis of visibly emissive AgN-DNAs12–16 (ESI,† Section 1.2) We observe one key difference between these two methods: AgN-DNA samples synthesized in single microcentrifuge tubes are stored at 4 °C immediately after NaBH4 reduction, except during periodic and brief fluorimetry to assess product formation. Microwell plates are exposed to room temperature for much longer periods after NaBH4 reduction because fluorimetry of an entire 384-microwell plates takes ∼4 hours, and plates are scanned one day and one week after reduction. Moreover, the microwell plate can rise above room temperature in the unrefrigerated plate reader. Thus, we hypothesized that heating above 4 °C favors formation of NIR-emissive AgN-DNAs.
To test this hypothesis, we investigated how storage temperature after reduction affects AgN-DNA formation. Six different DNA templates were selected as listed in Table 1, with optimized concentrations of DNA and AgNO3, and the peak emission wavelength(s), λp, of emitters produced by these templates. Sequences were chosen from a library of 10-base DNA oligomers designed using machine learning. Selection for this study is based on formation of far-red to NIR products in high-throughput experiments.12–16
| Name | DNA sequence (5′ to 3′) | λ p/nm | [DNA]/μM | [AgNO3]/μM |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DNA-1 | ACCGCCGGGA | 680/820 | 25 | 125 |
| DNA-2 | CGAACCGGGC | 644/820 | 25 | 187.5 |
| DNA-3 | AGGCGATCAT | 580/844 | 25 | 187.5 |
| DNA-4 | GCCCCCCCGC | 670 | 25 | 125 |
| DNA-5 | CACCCCGAGC | 714 | 20 | 300 |
| DNA-6 | TAGCCCCTGT | 562 | 25 | 125 |
AgN-DNAs were synthesized as detailed in ESI.† First, AgNO3 is mixed with an aqueous solution of DNA template in 10 mM NH4OAc at pH 7, room temperature (21 °C); studies show that this forms Ag+–DNA complexes.27–29 Second, the sample is incubated at 21 °C for 15 minutes. Third, Ag+–DNA complexes are reduced by freshly prepared NaBH4 solution at 0.5 molar ratio to AgNO3 at 21 °C. Finally, solutions are stored in the dark at four distinct conditions until measurement two days later: (1) 4 °C, the “standard” method used for single tube synthesis, (2) 37 °C for 4 hours followed by storage at 4 °C, (3) 21 °C, and (4) 37 °C for 4 hours followed by storage at 21 °C. 37 °C was chosen because well plates are warm to the touch after a 4 hour scan and because thermal stability of AgN-DNAs at 37 °C is relevant for in vivo applications. Heating above 40 °C was avoided due to past evidence of irreversible conversion to larger silver nanoparticles above 40 °C.8
Fig. 1 compares AgN-DNA emission spectra for the four storage conditions above. When stored only at 4 °C, DNA-1 forms a single dominant product with emission peak λp = 680 nm, but when stored at 21 °C and 37 °C for various times, a new AgN-DNA species with λp = 820 nm forms (Fig. 1a). Similarly, DNA-2 displays a single λp = 644 nm peak when stored at 4 °C, but a new NIR-emissive AgN-DNA (λp = 820 nm) forms at higher temperatures (Fig. 1b). For both DNA-1 and DNA-2, NIR peak intensity is greatest when temperature is highest: 37 °C for 4 hours followed by storage at 21 °C for 44 hours. For both DNA-3 (λp = 844 nm) and DNA-4 (λp = 670 nm), emission intensity of the far-red and NIR peaks exhibit ca. two- and three-fold increases, respectively, with increased temperature (Fig. 1c and d). For DNA-3, this increase accompanies a decrease in a minor λp = 580 nm peak, suggesting that a smaller AgN-DNA product preferentially forms at lower temperatures. These results support that increased post-reduction storage temperature enhances chemical yield of far-red to NIR-emissive AgN-DNAs, even forming new NIR AgN-DNA species that are not detectable at 4 °C. Increased temperature also significantly shortens the days- to week-long incubation times for NIR AgN-DNA formation.8,19,24
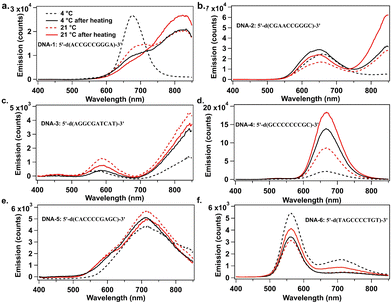 | ||
| Fig. 1 UV-excited emission spectra of AgN-DNAs prepared at various temperatures and recorded two days after AgN-DNA synthesis. (a) DNA-1, (b) DNA-2, (c) DNA-3, (d) DNA-4, (e) DNA-5, and (f) DNA-6. Samples were stored at 4 °C (dashed black), 21 °C (dashed red), 4 °C after heating at 37 °C for 4 h (solid black) and at 21 °C after heating at 37 °C for 4 h (solid red). (Fluorimetry was performed on a well plate reader with 850 nm upper spectral range; Fig. S1 (ESI†) shows emission spectra up to 950 nm on a different detector.) | ||
Elevated temperature does not increase chemical yield of all far-red or NIR AgN-DNAs. Increased temperature causes negligible increase in brightness for DNA-5 (Fig. 1e). For DNA-6, both emissive species decreased in brightness with increased temperature (Fig. 1f). Thus, the optimum storage temperature varies among AgN-DNA species and should be tuned to optimize yield of a specific AgN-DNA, just as DNA and AgNO3 concentrations are optimized.
Others have reported temperature effects on AgN-DNA synthesis. Swasey, et al. reported heating a red-emissive AgN-DNA at 40 °C to improve chemical yield,30 and Petty, et al. reported that temperature influenced absorption, excitation, and emission spectra of a NIR-emissive AgN-DNA by ∼20 nm.25 We note that Vosch, et al. have measured temperature-dependent emission spectra of compositionally pure AgN-DNAs,8,31 while here all spectra are collected at room temperature after heating.
The NIR-emissive AgN-DNA formed by DNA-3 has molecular formula (DNA)2[Ag20]12+.4 We used high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (ESI-MS) (Table S3, ESI†) to show that the λp = 670 nm species stabilized by DNA-4 is (DNA)2[Ag14]8+ (Fig. S13, ESI†). ESI-MS supports that DNA-6 stabilizes a λp = 562 nm (DNA)2[Ag12]8+ and a NIR-emissive (DNA)2[Ag15]9+ (Fig. S14, ESI†). These findings agree with reports of how AgN-DNA electron count correlates with fluorescence spectra.32 Detailed analysis of all emitters is beyond the scope of this study.
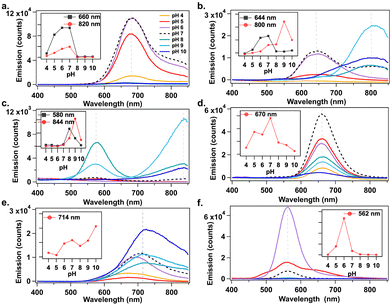
Studies show that pKa values of deprotonable nucleobases vary over a range of 2 ΔpKa from 15 to 55 °C.33 Lee, et al., reported sensing of adenosine 5′-triphosphate (ATP) using pH-dependent change in emission spectra of AgN-DNAs.34 The temperature dependence of nucleobase pKa motivated us to investigate how solution pH affects AgN-DNA formation. AgN-DNAs were synthesized in 10 mM NH4OAc solutions from pH 4 to 10. UV-excited emission spectra were recorded after 2 days of storage at 4 °C (ESI†). Fig. 2 shows that AgN-DNAs with visible emission peaks are brighter at acidic to neutral pH, whereas basic pH favors NIR AgN-DNAs in most cases. For example, products formed by DNA-6 (λp = 562 nm) are 6-fold brighter at pH 6 compared to pH 7 (Fig. 2f). Similarly, visibly emissive products associated with DNA-1 (λp = 680 nm), DNA-2 (λp = 644 nm), and DNA-4 (λp = 670 nm) are brightest at pH 7 (Fig. 2a, b and d). Preparation at basic pH can significantly increase the brightness of NIR-emissive AgN-DNAs. For DNA-2 (λp = 644 nm at pH 7), the NIR emissive species (λp = 800 nm) increases gradually for pH > 7 (Fig. 2b). DNA-4 strongly favors formation of the λp = 820 nm species at pH 9 (Fig. 2c). DNA-5 red-shifts and increases in emission intensity at basic pH (Fig. 2e). (Note that peak wavelengths of the NIR species for DNA-2 differ in Fig. 1b and 2b; purification and mass spectral analysis are needed to confirm if the same NIR species forms at basic pH versus elevated temperature.) Thus, solution pH could be used to dramatically increase synthesis yield of far-red and NIR-emissive AgN-DNAs. Earlier studies by Vosch, et al. showed that photophysical properties of AgN-DNAs stabilized by a cytosine-rich DNA oligomer are unaffected by changes in pH and ionic strength,35 suggesting that pH does not always affect AgN-DNA formation. Further studies are required to fully understand how higher pH favors NIR AgN-DNAs.
Finally, we investigated effects of NaCl on AgN-DNA emission spectra because residual reagents from commercial nucleic acid synthesis can cause variability in batch-to-batch AgN-DNA synthesis. Chlorido ligands were recently reported on AgN-DNAs, a (DNA)2[Ag16Cl2]8+ and (DNA)2[Ag15Cl]8+, even though no chloride source was added during AgN-DNA synthesis.24 This finding supports that residual reagents from solid-phase synthesis can significantly affect AgN-DNA product formation and may cause discrepancy between high-throughput and single-tube AgN-DNA synthesis. To investigate how residual chloride influences AgN-DNA formation, the six species in Table 1 were synthesized at their optimal storage temperature at pH 7 (Table S2, ESI†). Two days later, NaCl was added at final concentrations of 250 μM to 1000 μM (∼10 to ∼100-fold excess of chloride per nanocluster). Emission spectra were measured 1 to 6 h (1 h interval), 24 h, and 72 h after NaCl addition. To interpret the results, we first consider DNA-6. Fig. 3a–e show that DNA-6 emission spectrum evolves over time for specific concentrations of NaCl.
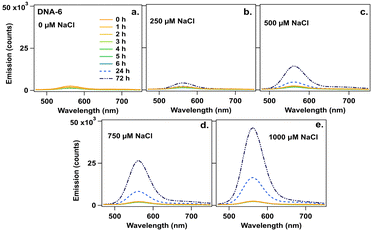 | ||
| Fig. 3 Emission spectra for DNA-6 at 0 to 6, 24, and 72 h (legend) (a) without NaCl (0 μM) and after addition of NaCl at (b) 250 μM, (c) 500 μM, (d) 720 μM, and (e) 1000 μM. | ||
Fig. 4 summarizes percent intensity change of the peak that increased most significantly with NaCl addition for each DNA strand. DNA-6 exhibits the most dramatic intensity increase with NaCl, up to 30-fold for 1000 μM NaCl at 72 h (Fig. 4f). For DNA-1, 2, and 3, which form both visible and NIR species, only visible species increase in intensity with NaCl addition (Fig. 4a–c), while associated NIR-emissive species either undergo smaller intensity increases or are unstable in NaCl (Fig. S7, ESI†). Specific emission spectral changes in the presence of NaCl vary widely among emitters and may depend sensitively on specific nanocluster structure. For example, DNA-4 and 5 form emitters that brighten at 250 μM NaCl, whereas visible species from DNA-1, 2 and 3 require 750 or 1000 μM NaCl concentrations for significant increase. These results support that variations in residual chloride in commercial oligomers could contribute to discrepancies between AgN-DNA batches, possibly favoring formation of visible AgN-DNAs over NIR AgN-DNAs. Ongoing research is focused on the chemical synthesis process for AgN-DNAs with chlorido ligands, which is beyond the scope of this study.
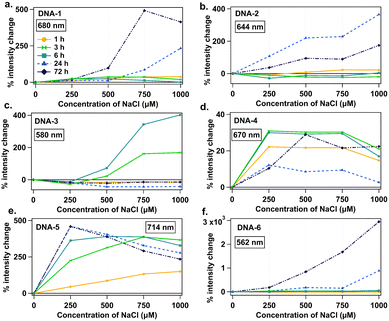 | ||
| Fig. 4 Percent intensity change as a function of NaCl concentration for (a) DNA-1, (b) DNA-2, (c) DNA-3, (d) DNA-4, and (e) DNA-5, and (f) DNA-6, specifically for the emission peak that increases the most with NaCl addition. Legend represents time points of 1 (yellow circles), 3 (green double triangles), 6 (teal squares), 24 (light blue triangles), and 72 hours (navy diamonds). Fig. S8 (ESI†) also shows data for 2, 4, and 5 hours. | ||
We hypothesize that changes in nucleobase pKa with temperature and pH are partly responsible for observed changes in formation of NIR AgN-DNAs between microwell plate and single tube synthesis, with additional effects from variations in residual salts. Since changes in nucleobase pKa with temperature and pH depend on oligomer length and neighboring nucleobases,33 these effects will be sequence specific and may be complex. Sensitivity of AgN-DNAs to pH and halide ions could be exploited for novel biocompatible sensors. Future studies may determine why NIR-emissive products tend to favor basic pH and elevated temperature.
In summary, we showed how storage temperature, solution pH, and small amounts of NaCl influence chemical yield of visible and NIR-emissive AgN-DNAs. Increased storage temperature of AgN-DNAs post-reduction can significantly increase emission intensity of far red and NIR AgN-DNAs, and in some cases is crucial to form measurable amounts of NIR AgN-DNAs. Basic pH promotes formation of NIR DNAs, whereas near-neutral pH favors red and far-red AgN-DNAs. Lastly, NaCl can significantly increase brightness of red and far-red AgN-DNA species. The synthesis strategies presented here are critical for the study of NIR-emissive AgN-DNAs and may expedite development of these fluorophores for NIR fluorescence bioimaging. Researchers using recently reported libraries of DNA template sequences for NIR AgN-DNAs12,16 should employ these synthesis methods, rather than conventional AgN-DNA synthesis methods that often favor smaller, visibly emissive AgN-DNAs.
This work was supported by NSF Biophotonics CBET-2025790. M. R. acknowledges a UC Irvine Office of Access and Inclusion Pathways to PhD Fellowship.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.Notes and references
- Y. Chen, M. L. Phipps, J. H. Werner, S. Chakraborty and J. S. Martinez, Acc. Chem. Res., 2018, 51, 2756–2763 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. Guha and S. M. Copp, in Modern Avenues in Metal-Nucleic Acid Chemistry, ed. J. Müller and B. Lippert, CRC Press, 2023, ch. 12, pp. 291–342 Search PubMed.
- A. Gonzàlez-Rosell, C. Cerretani, P. Mastracco, T. Vosch and S. M. Copp, Nanoscale Adv., 2021, 3, 1230–1260 RSC.
- R. Guha, A. Gonzàlez-Rosell, M. Rafik, N. Arevalos, B. Katz and S. Copp, ChemRxiv, 2023 DOI:10.26434/chemrxiv-2023-hftx9.
- S. M. Copp, D. Schultz, S. Swasey, J. Pavlovich, M. Debord, A. Chiu, K. Olsson and E. Gwinn, J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2014, 5, 959–963 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- E. G. Gwinn, P. O'Neill, A. J. Guerrero, D. Bouwmeester and D. K. Fygenson, Adv. Mater., 2008, 20, 279–283 CrossRef CAS.
- S. A. Bogh, M. R. Carro-Temboury, C. Cerretani, S. M. Swasey, S. M. Copp, E. G. Gwinn and T. Vosch, Methods Appl. Fluoresc., 2018, 6, 024004 CrossRef PubMed.
- V. A. Neacşu, C. Cerretani, M. B. Liisberg, S. M. Swasey, E. G. Gwinn, S. M. Copp and T. Vosch, Chem. Commun., 2020, 56, 6384–6387 RSC.
- J. Yu, S. Choi, C. I. Richards, Y. Antoku and R. M. Dickson, Photochem. Photobiol., 2008, 84, 1435–1439 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Yu, S. Choi and R. M. Dickson, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2009, 48, 318–320 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Y. New, S. T. Lee and X. D. Su, Nanoscale, 2016, 8, 17729–17746 RSC.
- P. Mastracco, A. Gonzàlez-Rosell, J. Evans, P. Bogdanov and S. M. Copp, ACS Nano, 2022, 16, 16322–16331 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. M. Copp, P. Bogdanov, M. Debord, A. Singh and E. Gwinn, Adv. Mater., 2016, 28, 3043 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. M. Copp, A. Gorovits, S. M. Swasey, S. Gudibandi, P. Bogdanov and E. G. Gwinn, ACS Nano, 2018, 12, 8240–8247 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. M. Copp, S. M. Swasey, A. Gorovits, P. Bogdanov and E. G. Gwinn, Chem. Mater., 2020, 32, 430–437 CrossRef CAS.
- S. M. Swasey, S. M. Copp, H. C. Nicholson, A. Gorovits, P. Bogdanov and E. G. Gwinn, Nanoscale, 2018, 10, 19701–19705 RSC.
- B. Sengupta, C. M. Ritchie, J. G. Buckman, K. R. Johnsen, P. M. Goodwin and J. T. Petty, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2008, 112, 18776–18782 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- G. Hong, A. L. Antaris and H. Dai, Nat. Biomed. Eng., 2017, 1, 0010 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Gonzàlez-Rosell, R. Guha, C. Cerretani, V. Rück, M. B. Liisberg, B. B. Katz, T. Vosch and S. M. Copp, J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2022, 13, 8305–8311 CrossRef PubMed.
- C. Cerretani, J. Kondo and T. Vosch, RSC Adv., 2020, 10, 23854–23860 RSC.
- C. Cerretani, J. Kondo and T. Vosch, CrystEngComm, 2020, 22, 8136–8141 RSC.
- M. B. Liisberg, Z. Shakeri Kardar, S. M. Copp, C. Cerretani and T. Vosch, J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2021, 12, 1150–1154 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Cerretani, H. Kanazawa, T. Vosch and J. Kondo, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2019, 58, 17153–17157 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Gonzàlez-Rosell, S. Malola, R. Guha, N. R. Arevalos, M. F. Matus, M. E. Goulet, E. Haapaniemi, B. B. Katz, T. Vosch, J. Kondo, H. Häkkinen and S. M. Copp, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2023, 145, 10721–10729 CrossRef PubMed.
- J. T. Petty, C. Fan, S. P. Story, B. Sengupta, A. S. Iyer, Z. Prudowsky and R. M. Dickson, J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2010, 1, 2524–2529 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. T. Petty, C. Fan, S. P. Story, B. Sengupta, M. Sartin, J. C. Hsiang, J. W. Perry and R. M. Dickson, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2011, 115, 7996–8003 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Müller, Coord. Chem. Rev., 2019, 393, 37–47 CrossRef.
- S. Naskar, R. Guha and J. Müller, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2020, 59, 1397–1406 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Kondo, Y. Tada, T. Dairaku, Y. Hattori, H. Saneyoshi, A. Ono and Y. Tanaka, Nat. Chem., 2017, 9, 956–960 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. M. Swasey, N. Karimova, C. M. Aikens, D. E. Schultz, A. J. Simon and E. G. Gwinn, ACS Nano, 2014, 8, 6883–6892 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Cerretani, M. R. Carro-Temboury, S. Krause, S. A. Bogh and T. Vosch, Chem. Commun., 2017, 53, 12556–12559 RSC.
- S. M. Copp and A. Gonzàlez-Rosell, Nanoscale, 2021, 13, 4602–4613 RSC.
- J. C. González-Olvera, J. Martínez-Reyes, E. González-Jasso and R. C. Pless, Biophys. Chem., 2015, 206, 58–65 CrossRef PubMed.
- J. D. Lee, J. Cang, Y.-C. Chen, W.-Y. Chen, C.-M. Ou and H.-T. Chang, Biosens. Bioelectron., 2014, 58, 266–271 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Gambucci, C. Cerretani, L. Latterini and T. Vosch, Methods Appl. Fluoresc., 2019, 8, 014005 CrossRef PubMed.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available: Experimental details, full absorbance and emission spectra. See DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/d3cc02896h |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2023 |