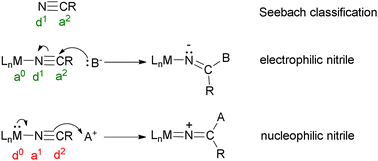
The success and power of homogeneous catalysis derives in large part from the wide choice of transition metal ions and their ligands. This tutorial review introduces examples where the reactivity of a ligand is completely reversed (umpolung) from Lewis basic/nucleophilic to acidic/electrophilic or vice versa on changing the metal and co-ligands. Understanding this phenomenon will assist in the rational design of catalysts and the understanding of metalloenzyme mechanisms. Labelling a metal and ligand with Seebach donor and acceptor labels helps to identify whether a reaction involving the intermolecular attack on the ligand is displaying native reactivity or reactivity umpolung. This has been done for complexes of nitriles, carbonyls, isonitriles, dinitrogen, Fischer carbenes, alkenes, alkynes, hydrides, methyls, methylidenes and alkylidenes, silylenes, oxides, imides/nitrenes, alkylidynes, methylidynes, and nitrides. The electronic influence of the metal and co-ligands is discussed in terms of the energy of (HOMO) d electrons. The energy can be related to the pKLACa (LAC is ligand acidity constant) of the theoretical hydride complexes [H–[M]–L]+ formed by the protonation of pair of valence d electrons on the metal in the [M–L] complex. Preliminary findings indicate that a negative pKLACa indicates that nucleophilic attack by a carbanion or amine on the ligand will likely occur while a positive pKLACa indicates that electrophilic attack by strong acids on the ligand will usually occur when the ligand is nitrile, carbonyl, isonitrile, alkene and η6-arene.