Alternative materials for interfacial polymerization: recent approaches for greener membranes
Adi
Ben-Zvi†
ab,
Usman
Taqui Syed†
cd,
Guy Z.
Ramon
 *abe and
Suzana
Nunes
*abe and
Suzana
Nunes
 cdf
cdf
aDepartment of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Technion—Israel Institute of Technology, Haifa, 320000, Israel. E-mail: ramong@technion.ac.il; Tel: +972-4-8292580
bNanoscience and Nanotechnology Program, Technion-Israel Institute of Technology, Haifa 32000, Israel
cEnvironmental Science and Engineering Program, Biological and Environmental Science and Engineering Division (BESE), King Abdullah University of Science and Technology (KAUST), 23955-6900, Thuwal, Saudi Arabia
dAdvanced Membranes and Porous Materials (AMPM) Center, King Abdullah University of Science and Technology (KAUST), Saudi Arabia
eWolfson Department of Chemical Engineering, Technion—Israel Institute of Technology, Haifa, 320000, Israel
fChemistry Program and Chemical Engineering Program, Physical Science and Engineering Division (BESE), King Abdullah University of Science and Technology (KAUST), 23955-6900, Thuwal, Saudi Arabia
First published on 23rd April 2024
Abstract
Thin-film selective layers fabricated via interfacial polymerization (IP) form the core of membrane-based water purification and desalination, as well as other molecular separations. The monomers and organic solvents used in the reaction are for the most part toxic chemicals, likely to be banned in the near future, for environmental protection. There is, therefore, a growing need to find alternative, sustainable, materials that can produce adequate membranes for industrial applications, fabricated via IP. The present work summarizes recent studies on fabricating RO/NF/OSN membranes via IP using sustainable solvents and/or monomers, in comparison to the toxic chemicals used to fabricate polyamide, the chosen polymeric material for the commercial selective membrane layer. The properties of these ‘green’ materials are described, as well as the properties of the resultant membranes, discussing possible limitations in the fabrication techniques and the benefits of the process. Furthermore, an eco-scale score is calculated for representative membranes, demonstrating the utility of this tool for assessing the ‘greenness’ of the fabricated membranes. Overall, the presented literature shows that there is a great potential for fabricating more sustainable and scalable membranes. However, studies exhibit various limitations, for example, no standardization for performance tests and performance criteria for every membrane type, which prevents accurate and true comparisons among different membranes. Suggestions are made, where applicable, for future work to add aspects that assess the potential of fabricated membranes to future industrial applications. Finally, and most importantly, there is still a need for improved fundamental understanding of IP, with which to facilitate the search of alternative sustainable materials for membrane fabrication with desired properties.
1. Introduction
Thin films fabricated via interfacial polymerization (IP) are widely used in industrial applications, such as micro-encapsulation and the separation layer for water purification membranes.1–3 IP comprises various condensation chemistries, most commonly polyamides, polyesters, polyureas, etc. The selected IP chemistry for the state-of-the-art water separation membranes is polyamide (PA),1 which was first synthesized in the late 1970s by Cadotte and co-workers, and turned out to be the most significant breakthrough in desalination technology, achieving >99% salt rejection in seawater.4,5 With their exceptional performance, along with facile and readily up-scalable manufacturing, PA membranes have become the industry standard for Nanofiltration (NF) and Reverse Osmosis (RO) applications.6–8 Furthermore, they are integrated in various other industrial processes, such as wastewater treatment, water purification, microencapsulation, and industrial substances separation.9–11 Nonetheless, since their first fabrication, TFC membranes have not undergone significant improvements.12–14TFC PA membranes comprise a thin, dense, and cross-linked PA selective layer synthesized via a rapid, exothermic Scotten–Baumann (acylation) polycondensation reaction of two polyfunctional monomers. The commonly-used monomers for RO membranes are Trimesoyl-Chloride (TMC), dissolved in hexane, and m-Phenylene Diamine (MPD) or Piperazine (PIP, for NF) in water (Fig. 1).15
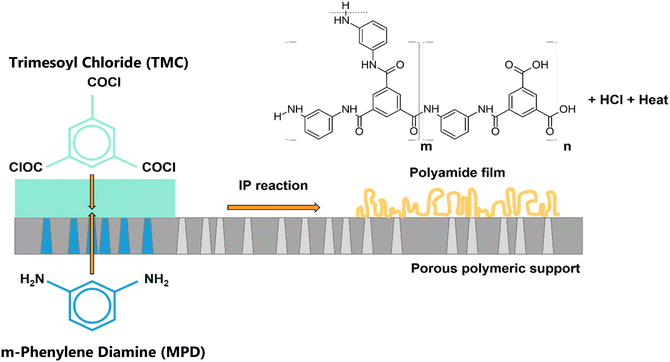 | ||
| Fig. 1 IP reaction between MPD in the aqueous phase and TMC in the organic phase producing cross-linked polyamide, HCl and heat are by-products.15 | ||
The acyl group in TMC is added to the amine monomer forming an amide bond, releasing HCl and heat as by-products of the reaction.15–18 The amine monomers are better soluble in hexane than TMC in water; therefore, the reaction occurs at the organic side of the interface and is diffusion limited.15 Besides the mentioned monomers, IP can be performed using other monomers with a variety of chemical structures. However, the success of the IP process for continuous scale-up production not only mandates a complete reaction leading to a defect-free selective layer, but potentially benefits from being very rapid, which may limit the industrial implementation of many reported approaches.
IP has been optimized by the industry for decades, making it a highly competitive process, but only recently has its sustainability begun to be questioned. The reaction involves the use of hazardous organic solvents, such as hexane, heptane, benzene, and cyclohexane, as well as petroleum-based and toxic monomers.19–22 Among the common chemicals for the fabrication of RO membrane by IP (MPD, TMC, and hexane), MPD is the most hazardous and toxic, while hexane is used in much larger quantities but is less hazardous.23 These chemicals have serious health and environmental adverse effects, to the point that recent European legislation has classified some of them as carcinogenic, designated to be banned from industrial use in the near future.20,21 The search for green alternatives for organic solvents would assist the global solvent market, which is estimated to produce 37.4 million metric tons by 2030,24 to align with the United Nations’ sustainable development goals (SDGs) for 2030.25,26 The global membrane manufacturing has a great share in the production of toxic wastewater, as well as to pollute the environment through the evaporation of organic solvents.20 It was estimated in the last decade that 10 billion liters of wastewater (containing mostly organic solvents and polymers) were produced annually by desalination membrane production processes solely.27 Therefore, there is a growing need to fabricate membranes using sustainable materials, eliminating the adverse effects the membrane industry has on the environment. Thus, our focus in this work will be on the alternative greener approaches within the framework of IP related membrane production.
To design greener industrial processes and achieve the international target of sustainability that arose since the concept of green chemistry was first formulated in 1990s,28 chemists use the Twelve Principles of Green Chemistry that were introduced in 1998 by Paul Anastas and John Warner.29 In the light of these principles, Szekely et al. (2014) outlined the main principles needed for producing more sustainable organic solvent nanofiltration (OSN) membranes, which are relevant for NF and RO membranes as well because they encompass similar processes.30 The principles are as the following (a) utilization of green solvents, (b) the use of low-toxicity chemicals, (c) the use of renewable and sustainable raw materials, (d) fabrication of membranes at room temperature, and (e) design of degradable membranes.30
The present work focuses on recent published attempts made to substitute the hazardous organic solvents and the toxic amine monomers by bio-based or otherwise more sustainable materials in an IP process solely, to derive TFC membrane for NF/OSN/RO processes, and to replace the existing polyamide chemistry. Finding ‘green materials’ that perform IP, following the five principles of Szekely et al.30 and using them to fabricate a greener membrane without compromising its performance, is challenging. We summarize the resultant ‘greener’ membrane performance, while considering these principles. We also demonstrate the calculation of an Eco-Scale score, that provides a quantitive value of the membrane greenness (Fig. 2). Lastly, the underlying motivation of this work is to understand where the process of moving towards sustainable RO/NF membranes stands and to address the gaps and limitations it experiences.
2. Sustainable materials for IP-based membrane fabrication
In recent years, several studies have successfully incorporated bio-based polymers and either less toxic solvents or without the use of solvents for membrane fabrication via IP. Herein, we review studies that use ‘green solvents’ and/or ‘green monomers’, mentioning their origin, properties, the resultant membrane performance, their advantages, and disadvantages. The fabricated membrane properties are summarized in Tables 2 and 3, and a demonstration of how to calculate the ‘greenness’ of the membrane is presented later in section 3.2.1 ‘Green’ solvents
The properties of organic solvents have a major influence on the IP reaction as it involves many aspects that affect the resultant membrane morphology and performance. The main properties affecting the reaction and resultant morphology are its vapor pressure (high vapor pressure solvent may cause vaporization of the organic phase during IP and crumpling of the formed film),31 interfacial tension with the aqueous phase (low interfacial tension increases the partitioning of the aqueous monomer to the organic phase and hence the reaction rate; furthermore, the interface will be more easily deformed resulting in film crumpling), the aqueous monomer solubility in the organic solvent, and viscosity (the latter two will increase the aqueous monomer's diffusion rate and hence the polymerization rate), for a more detailed mechanistic description of the organic solvent effects on IP reaction, see ref. 15. The main characteristic required for an organic solvent in IP is its water-immiscibility to create a biphasic system that contains an interface, and the ability of the organic monomer to dissolve in it. The physical properties of representative ‘greener’ solvents from different categories, used for NF/OSN/RO membrane fabrication via IP, are summarized in Table 1.| Solvent | Water-solvent interfacial tension [mN m−1] | Viscosity [mPa s] | Vapor pressure [Pa] |
|---|---|---|---|
| n-Hexane | 50.8 | 0.31 | 20![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 398.3 398.3 |
| [C4mim][Tf2N] | 13.69 | 63.05 | — |
| Hexyl acetate | 18.8 | 0.86–1.17 | 176 |
| Decanoic acid | — | 4.3@50 °C | 0.048@25 °C |
| α-Pinene | — | 1.3@25 °C | 630@25 °C |
| p-Cymene | 36.41 | 0.8333 | 200 |
Hartanto et al.20 used a mixture of 50![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 50 [C4mim][Tf2N] (IL) and hexyl acetate, to reduce the costs and make IL-based processes more feasible for the industry. Hexyl acetate is an environmentally friendly solvent and cheaper than IL. The mixture has higher interfacial tension and lower viscosity than the pure IL41 (Table 1), resulting in a higher MPD concentration required (0.5 wt%) and lower TMC concentration (0.3 wt%).20 Considering large-scale usage, the membrane performance achieved using IL and IL + hexyl acetate has lower NaCl rejection (94–97%) than membranes used for RO applications (>99%), but it is still considered a good performance, that can be used for various industrial applications. In this case, ILs are still expensive compared to hexane, but the use of a mixture with hexyl acetate reduces the costs and makes it feasible for industrial use.
50 [C4mim][Tf2N] (IL) and hexyl acetate, to reduce the costs and make IL-based processes more feasible for the industry. Hexyl acetate is an environmentally friendly solvent and cheaper than IL. The mixture has higher interfacial tension and lower viscosity than the pure IL41 (Table 1), resulting in a higher MPD concentration required (0.5 wt%) and lower TMC concentration (0.3 wt%).20 Considering large-scale usage, the membrane performance achieved using IL and IL + hexyl acetate has lower NaCl rejection (94–97%) than membranes used for RO applications (>99%), but it is still considered a good performance, that can be used for various industrial applications. In this case, ILs are still expensive compared to hexane, but the use of a mixture with hexyl acetate reduces the costs and makes it feasible for industrial use.
Zheng et al.43 fabricated polyamide/poly(m-phenylene isophthalamide) (PMIA) TFC membranes for OSN, using a novel IL-assisted method. Dope solutions formulated by an environmentally benign IL [EMIm][OAc] were used to cast the porous PMIA membrane substrates. The IP reaction between amine monomers (i.e., piperazine and polyethyleneimine) in the aqueous phase and aromatic acyl chlorides (i.e., phthaloyl chloride and 1,3,5-benzenetricarboxylic chloride) in the IL [BMIm][Tf2N] phase led to the synthesis of the selective layer on the PMIA surface. When a fabricated TFC membrane with a favourable selection of monomers with the IL as the organic solvent was compared to a membrane with the same monomer composition but with n-hexane as the organic phase solvent, the newly synthesized membrane had up to three times enhanced permeance and maintained high rejections for Congo Red and vitamin B12; however, this is not an adequate comparison, because the monomer selection was optimized for this IL system. The enhancement in the membrane permeance was attributed to the high viscosity of the ILs, which reduced the rate of monomer diffusion in the organic phase; further reducing the mass transfer at the interface, causing the selective layer formed to be much thinner and less cross-linked. Furthermore, the residual IL phase containing the organic monomers can be reused to fabricate more membranes. In subsequent work, Yao et al.44 retained ILs as a replacement for organic phase and ventured into developing TFC OSN membranes with sandwich-like structures via IP on metalorganic framework (MOF) nanosheet-modified microporous polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) substrate surface. The IP monomers are mixed amine (polyethyleneimine and PIP) in the aqueous phase and TMC in the hydrophobic IL phase. The IL was 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium bis[(trifluoromethyl)sulfonyl]imide ([BMIm][Tf2N]), which was similar to the earlier reported study.43 MOF nanosheets of micrometer lateral dimensions and nanometer thickness (1.5 ± 0.6 nm) could be deposited on the PVDF substrate as an interlayer to facilitate the IP reaction.
The low volatility of ILs comparing to hexane has advantages relating to the IP reaction in addition to lower toxicity. One example is the preparation of covalent organic frameworks (COFs) by IP, which is affected by a disturbance in the liquid–liquid interface as the volatile solvents evaporate. To overcome this limitation, Gao et al.,45 proposed the synthesis of several imine-linked freestanding COF membranes having varying thickness and morphology at tuneable IL–H2O interfaces. In both, the water and ILs, the monomer diffusion was controlled due to the hydrogen bonding between the amine monomers and the catalyst (p-toluenesulfonic acid), and the high viscosity of ILs. The crystallinity of the COF membranes could further be improved by varying the alkyl chain length of cations in the ILs (enabling regulation of the interfacial tension and interfacial region size). However, a main disadvantage of COF approaches is the long time required for an adequate selective layer formation, which is usually much larger than a fabrication process in a continuous mode allowed by the instrumental set-up.
While the examples focus on IL in the organic phase, there are reasons to use hydrophilic IL as the polar phase when working with monomers of limited solubility in water.46,47 Although the performance seems to increase, these studies cannot be classified as a greener approach when ILs replace water as aqueous phase. Lastly, in most cases, the IL is used as an additive.48,49
In subsequent work, Falca et al.,50 used oleic acid as a replacement for hexane in the organic phase. The resulting high-performing composite membrane was selective for small molecules with a molecular weight cut-off (MWCO) of 650 g mol−1 and a high permeance of ∼57 L per m2 per h per bar. Oleic acid, a green solvent derived from coconut, has a low vapor pressure and high boiling point. These properties may be favorable in synthesizing TFC membranes, but like decanoic acid, the high viscosity would require higher temperatures for an effective membrane formation.
Abdellah et al.51 used alpha-pinene, an organic compound extracted from plants (e.g. rosemary, basil, pine), as the organic solvent for IP reaction between terephthaloyl chloride (TPC) and catechin or quercetin in two different studies. Catechin or quercetin are both considered ‘green’ monomers and will be described in the next section. Alpha-pinene has a lower vapor pressure than hexane and this reduces the amounts of solvent used and eliminates the possibility of explosion. However, its vapor pressure is not negligible (Table 1) and higher than other solvents mentioned here. The resultant membrane showed high stability in harsh aprotic solvents, and its performance is competitive with other membranes in literature (see Table 2 and previous reports51,52) with relatively high DMF permeance of 2.6 L per m2 per h per bar and MWCO of 300 g mol−1. The effect of solely changing the solvent to alpha-pinene cannot be deduced because these membranes had other variations from the commonly used membrane. Alpha-pinene has a slightly higher viscosity than hexane, which would slightly decrease the MPD and TMC diffusion rate to the reaction zone. This membrane followed almost all of the ‘green’ principles30 except that the organic monomer used was not considered ‘green’.
Welch et al.55 used molecular layer deposition to produce polyamide by gas phase deposition. Within 48 cycles, a 15 nm film was fabricated by the reaction between vaporized MPD and TMC, without solvents, and thus, RO membrane performance was achieved. The process requires high temperatures (115 °C) and low pressure, and the reaction time is higher than conventional IP. Fabrication in a large scale of robust films is a challenge.
Promoting the IP reaction from the vapor phase might be an alternative to the classical organic solvent liquid system, but optimization and further investigation are still needed.
Table 2 compiles a list of studies using IP to prepare membranes by using green solvents. The key components and results of the studies, along with the advantages and disadvantages, are mentioned. The comparison must be carefully analyzed since the membranes were not tested under the same conditions. An agreement on testing protocols in the nanofiltration and reverse osmosis field would be highly advantageous to guide the development of new membranes. Recently OSN and RO database of membrane performance were released.57,58 These databases serve as an essential tool of comparison among different membranes; however, the comparison should be carefully assessed because the testing procedure was not uniform.
| Ref. | Organic solvent | Origin | Membrane type | Aqueous monomer | Organic monomer | Support | Product | MWCO [g mol−1] | Rejection [%] | Permeance [L per m2 h per bar] | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PIPA: poly(m-phenylene isophthalamide), DHTA: 2,5-dihydroxyterephthalaldehyde, TMGC: triaminoguanidinium chloride, BTTH: 1,3,5-benzenetriamine trihydrochloride, DETA: diethylenetriamine. | ||||||||||||
| 41 | [C4mim] [Tf2N] | IL | RO | MPD | TMC | PI | PA | N/A | 96.8% NaCl | Water: 1.09 | • Reduced surfactants | • Increased TMC conc. |
| • Reduced amine conc. | • High costs | |||||||||||
| • Reduced fouling | • Moderately toxic | |||||||||||
| • Increased permeance | ||||||||||||
| • Recycled organic phase | ||||||||||||
| • Non-volatile | ||||||||||||
| 42 | Aliquat | IL | SRNF/STNF | MPD/HDA | TMC/BADGE | PSF/PI | PA/Epoxy | N/A | ∼45% of ethyl acetate | Water/ethanol mixture: < 0.05 | • Relatively inexpensive IL | • Additional need of co-solvents |
| • No satisfactory performance | ||||||||||||
| • Long reaction time of 72h | ||||||||||||
| 20 | 50![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 50 [C4mim][Tf2N] 50 [C4mim][Tf2N]![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) hexyl acetate hexyl acetate |
IL, hexyl acetate from plants | FO, RO | MPD | TMC | PI | PA | N/A | 94.5% NaCl | Water: 0.41 | • Better performance than pure IL | • Increased TMC conc. |
| • Lower costs than pure IL | ||||||||||||
| • Hexyl acetate is derived from plants | ||||||||||||
| 43 | [BMIm][Tf2N] | IL | OSN | PIP + PEI | TMC/PDC | PMIA | PA/PIPA | 320–479 | >99% for both congo red and vitamin B12 | Water: 2.15, (with Congo red), Water: 3.6, (with, vitamin B12) | • Strong tolerance to various organic solvents with good stability | • Requires heating to 60 °C for crosslinking |
| • Enhanced separation performance | • Expensive IL | |||||||||||
| • Recycle of IL for greenness | ||||||||||||
| 44 | [BMIm][Tf2N] | IL | OSN | PIP + PEI | TMC | Modified Cu-TCPP nano-sheets on PVDF | PVDF/t-Cu-TCPP/PA | N/A | 98.9% brilliant blue; 95% congo red | Water: 2.7 | • Steady performance throughout the 36 h NF of the Rose Bengal/ethanol mixture | • Cu-TCPP nanosheets and ILs are expensive |
| • Good performance in the concentration of lecithin in methanol | ||||||||||||
| 45 | [CnMim][Tf2N] | IL | OSN | BD | TFB | Nylon | COF | N/A | 98% Alcacian blue | Acetonitrile using C12M IL: ∼523 | • High permeance for acetonitrile, acetone, water, methanol, and ethanol | • Extremely long reaction time |
| • Excellent selective rejection of dyes | • Difficulty in scale-up | |||||||||||
| 59 | Hexane in first step and then [αN111][Gly] amino acid IL | Crude oil and IL | NF | PIP | TMC | PES | Amino acid based IL-TFC | 267 | MgSO4: 91.4% | Water: 12.6 | • Amino acid IL acts as humectant to preserve wettability and prevents permeability reduction after heating for storing membrane at dry-state | • Longer reaction time |
| • Higher selectivity for sodium than the commercial membranes mentioned | • TFC membrane is submerged in the amino acid IL for up to 12 h. | |||||||||||
| • Selectivity towards MgSO4 is lower than pristine TFC standard membrane | ||||||||||||
| 60 | Toluene and then[MimAP][Tf2N]/dichloromethane | Crude oil and IL | NF | PIP | TMC | PAN | PA | 500–600 | Mg2+: 81.9; Li+: 45.2 | Water: 37.8 | • Stable performance for Mg2+/Li+ separation | • Requires annealing temperature of 80 °C |
| • Possibility of using Li from brine with high Mg2+/Li + ratio. | ||||||||||||
| 21 | Decanoic acid | plants | OSN | PEI | TMC | PAN | PA | 650 | 99% congo red | Methanol with congo red: 60 | • High stability | • High energy costs |
| • Excellent separation performance | ||||||||||||
| • Non-volatile | ||||||||||||
| • Solvent derived from plants | ||||||||||||
| 50 | Oleic acid | Bio based | OSN | MPD | TMC | PAN | PA | 650 | 99.9% direct red 80 | Water: 57 | • Non-volatile | • Requirement of post-heat treatment |
| 52 | Alpha-pinene | Plants | OSN | Catechin | TPC | CA | Polyester | 500 | 92% amido black; 87% Sudan Blue | DMF: 1.4 | • Good performance | |
| 51 | Alpha-pinene | Plants | OSN | Quercetin in NaOH | TPC | Cellulose | Polyester | 300 | 90% methyl orange; 96% amido black | DMF: 2.6 | • Solvent derived from plants | • Flammable |
| 61 | p-Cymene | plants | OSN | Tannic acid | Priamine | PET | TA/Priamine free-standing film | 395 | 90%styrene dimer | Acetone: 13.7 | • Excellent performance | • Relatively high vapor pressure |
| • Solvent derived from plants | ||||||||||||
| 53 | Vapour | — | OSN | MPD | TMC (vapour) | PI | PA | 260 | 98.5% Rose Bengal | Water with Rose Bengal: 2.4 | • Decreased liquid waste. | • Increased energy costs |
| • Increased permeance | • Designing a new process | |||||||||||
| 54 | Vapour | — | NF | DETA + COOH-TiO2 | TMC (vapour) | PSf | PA | N/A | Na+:87% Cu2+: 87% Hg2+: 77% Pb2+: 83% | Water: 37.8 | • Enhanced performance obtained against heavy metal ions | • Requires additional step of introducing nanoparticles to form nanocomposite (TFN) membrane. |
| • Incorporated TiO2-NPs enhanced the antifouling tendency. | • Large amount of TMC required | |||||||||||
| • Reduces liquid waste | ||||||||||||
| 62 | No solvent | — | NF | APPD | β CD | P84 PI | Polyester | N/A | Congo red/NaCl: 99.1/7.87 | Water: 209 at 2 bar | • Single step crosslinking and IP simultaneously | • Initial tendency of fouling of membranes |
| • Excellent antifouling characteristics | ||||||||||||
| • High dye rejection and salt permeation for dye/salt mixtures | ||||||||||||
| 56 | No solvent | — | RO | DHTA in phase 1 TMGC or BTTH in phase 2 | — | PAN | COF | N/A | NaCl: 93–93.6% | Water: 1.7–3.7 | • Eliminates organic phase completely. | • Requires NaOH |
| • No use of heat during IP and thus, is a green manufacturing method | • More efforts to realistically scale-up | |||||||||||
| 55 | No solvent | — | RO | MPD | TMC | NF270 | PA | N/A | NaCl:97–99% | Water: 1.4–1.6 | • A controlled process to fabricate consistent films | • High temp. (115 °C) |
| • Scalable | • Vacuum | |||||||||||
| • Long and challenging fabrication process | ||||||||||||
2.2 Green aqueous monomers
Replacing the toxic amine monomer in an IP reaction is challenging. The monomer should be sufficiently reactive to create a highly crosslinked thin film and must be soluble in appropriate, immiscible liquids (ideally green solvents).61 Green monomers are a sort of natural reagents, the building blocks of polymers, which are abundant, nontoxic, cheap, environmentally friendly, renewable, and sustainable as they are usually sourced from biorefineries, bioplastics, plants, bio wastes or renewable oil.63,64Table 3 summarizes the ‘green’ aqueous monomers used for IP in recent studies and the fabricated membrane properties, and a calculation tool to assess the ‘greenness’ of the membrane is demonstrated in section 3.| Ref. | Aqueous phase | Origin | Membrane type | Organic monomer | Organic solvent | Support | Product | MWCO [g mol−1] | Rejection [%] | Permeance [L per m2 per h per bar] | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 65 | Polyphenol: morin hydrate in methanol | Guava | OSN | TPC | Cyclohexane | PAN | Polyester | 800 | 96% Brilliant blue | Brilliant blue in NMP: 0.3 | • Simple fabrication method. | • Morin isn't soluble in water. |
| • Easy to upscale. | • Usage of methanol | |||||||||||
| • Stable in harsh organic solvents. | ||||||||||||
| • Excellent performance. | ||||||||||||
| • Low-cost | ||||||||||||
| 52 | Polyphenol: catechin | Apples and other fruits | OSN | TPC | Alpha-pinene | Cellulose | Polyester | 500 | 92% amido black; 87% sudan blue | 1.4: DMF | • Easy fabrication. | A prior reaction of the polyphenol in base conditions to better react in IP. |
| • High stability | ||||||||||||
| 51 | Polyphenol: quercetin | Caper black-tea etc. | OSN | TPC | Alpha-pinene | Cellulose | Polyester | 300 | 90% methylorange; 96% amido black | 2.6: DMF | • Easy fabrication. | |
| • High stability | ||||||||||||
| 66 | Polyphenol: tannic acid | Tea, berries, wood, etc. | NF | TMC | Hexane | PES | Polyester | N/A | 42% Na2SO4; 99% congo red | 20 | Good antifouling properties | Salt rejection is not high |
| 22 | Polyphenol: tannic acid | Date fruit | OSN | TPC | Cyclohexane | PAN | Polyester | 800 | 95% Brilliant blue, 88% congo red | Brilliant blue in NMP: 0.08 | • Stable. | Fair performance |
| • Cost-effective. | ||||||||||||
| • Optional scale-up process | ||||||||||||
| 67 | Polyphenol: EGCG – PEI | Green tea | NF/OSN | TMC | Hexane | PTFE | EGCG-PEI-TMC/PTFE membrane | 380 | 99.9% methyl orange, 95.5% Na2SO4 | Water: 9.15 | Robust and stable membrane | PEI was used which is a toxic amine monomer. |
| 68 | Polyphenol: Allylated Gallic acid in phosphate buffer solution | Gall nut, oak bark & other plants | NF | TMC | Isopar G | PAN | Polyester | 327 with the use of co-monomer MPD | >99% congo red, 81% methyl orange, 59% Na2SO4 | Water: 47.6 | • High water flux | For increasing the rejection of dyes, MPD was used as a co-monomer |
| • Synergistic use of polyphenol based monomer | ||||||||||||
| 69 | Cyclodextrin (CD): cyclic oligosaccharide, in 1 M NaOH | Starch | NF/OSN | TC | Hexane | PAN | Polyester | — | 91–95% Methyl orange | Water: 20 | • Low-cost materials. | • Relatively high concentration of cyclodextrin (6.5%w/v). |
| • Commercially available reagents. | • Reaction in high pH | |||||||||||
| • Repeatable fabrication process. | ||||||||||||
| 70 | Cyclodextrin (CD): α-CD, β-CD and <γ-CD in NaOH solution | wheat/maize/potato starch | OSN | TMC | Hexane | Matrimid | Polyester | α-CD (320 Da) <β-CD (400 Da) <γ-CD (550 Da) | 99.4% rose Bengal, 98.6 brilliant blue, 86.3% methyl orange | Water: 5.5, Methanol: 4.9, Ethanol: 3.8, DMF: 0.9, NMP: 0.8, Cyclohexane: 4.5, Hexane: 6.0 | • Only work on Janus membrane using cyclodextrin as a monomer | • NaOH was used as a catalyst in the aqueous phase. |
| • Molecularly engineered IP reaction allows permeance for organic & non-organic solvents | • Fair performance permeance of solvents | |||||||||||
| 71 | Cyclodextrin (CD): β-CD | Starch | NF | TMC | Heptane | PES | Polyester | N/A | 95.6% congo red, 94.4% methyl blue | Water: 104.6 (0.1% β-CD), Water: 197.6 (1.8% β-CD) | • High water flux | • Requires post heat treatment of 60 °C. |
| • Highly chlorine resistant | • Requires 1.8 wt% β-CD | |||||||||||
| 72 | Cyclodextrin (CD): β-CD with graphene quantum dots as additives | Starch | NF | TMC | Heptane | PES | Polyester | 860 (1.8% β-CD and 0.3% graphene quantum dots) | >93.0% Eriochrome black T and congo red | Water: 122 (1.8% β-CD), Water: 474.7 (1.8% β-CD and 0.3% graphene quantum dots as additives) | • Extremely high water flux | • Requires post heat treatment of 60 °C. |
| • Highly chlorine resistant | • Use of expensive and low toxic graphene quantum dots | |||||||||||
| 73 | Cyclodextrin (CD): β-CD with triethylamine | Starch | NF | TMC | Hexane | Multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) on PVDF membrane | Polyester | 590 (2% β-CD on MWCNTs substrates) | 96.4% congo red, 97.4% brilliant green | Water: 179.93 (2% β-CD on MWCNTs substrates) | • Extremely high water flux | • Use of MWCNTs |
| • Highly chlorine resistant | • Use of NaOH and triethylamine | |||||||||||
| • Good separation performance for dye/salts mixture | ||||||||||||
| 74 | Polysaccharide chitosan | Crustaceans | NF | TMC | Hexane | PSF | Polyamide | 800 | 91.9% Na2SO4 | 5.22 | Chitosan reduces the amount of the amine monomer needed. | Chitosan has to be dissolved in acidic solution (pH∼2) and heated. |
| 75 | Glucose - mono, maltose - di, and raffinose – trisaccharides with 1 M NaOH | Tissues of most plants, honey and fruits | NF | TMC | Hexane | PES | Polyester | 464 (glucose), 495 (maltose) 485 (raffinose) | ∼95% Na2SO4 | Water: 33.7 with glucose | Completes circular economy as sugar-based membranes were used to separate sugar from aqueous solution | • NaOH was used as a catalyst in the aqueous phase. |
| • High concentration (5 wt%) of aqueous monomer | ||||||||||||
| 76 | Glucose - mono, sucrose - di, and raffinose – trisaccharides with 1 M NaOH | Tissues of most plants, honey and fruits | Loose NF | TMC | Hexane | PES | Polyester | 783 with optimized 0.6 wt% sucrose | Congo red/Na2SO4: 99.4/11.2, direct blue 23/NaCl: 98.8/3.3 | Water: 52.4 with sucrose | • Reasonable dye/salt rejection | NaOH was used as a catalyst in the aqueous phase |
| 77 | Sugar alcohol: meso-erythritol | Corn | Loose NF | TMC | Hexane | PES | Polyester | N/A | Congo red/Na2SO4: 99.6/11, direct red 23/NaCl: 95.2/5.6 | Water: 53.2 | • Good antifouling ability | |
| 78 | Glucose - mono, sucrose - di, and raffinose – trisaccharides, Cyclodextrin (CD): β-CD | Tissues of most plants, honey and fruits, and starch | NF | TMC | Heptane | PAN | Polyester | 440 with glucose as optimized monomer | 99.5% Na2SO4 | Water: 16.1 | • Highly chlorine resistant | • NaOH was used as a catalyst in the aqueous phase. |
| • Very high rejection of Na2SO4 salt | • Use of heat at the cost of money | |||||||||||
| 79 | Dopamine (DA) | Mussels | NF | TMC | Heptane | PES | DA/TMC | 64% Na2SO4, 97% congo red | Water: 7.5 | • Stable | Its performance is not good enough for NF. | |
| • Simple preparation | ||||||||||||
| 80 | Sulfonated dopamine (SDA) | Mussels | NF + OSN | TMC | Cyclohexane | HPAN | SDA-TMC | 2000 | 90% Na2SO4, 99.9% congo red, methyl blue. | Water: 10.4 | • Stable | • Preparation of SDA requires heating. |
| • High permeance | • High MWCO | |||||||||||
| 81 | Dopamine hydrochloride (PDA), norepinephrine (PNE) and tannic acid (TA) | PDA: Mussels | NF | TMC | Isol-C | PSF | Polyester | 650 (PDA) 715 (PNE), 832 Tannic acid | ∼93% Na2SO4 for 2 wt% PDA | Water: 8.4 | • Chemically stable | NaOH was used as a catalyst with PDA/PNE in the aqueous phase. |
| PNE: neurotransmitter | • Reaction chemistry is well-known | |||||||||||
| TA: Trees, fruits | ||||||||||||
| 82 | Dopamine hydrochloride (PDA) and glucose with MOFs additive | Mussels and tissues of most of plants | NF + OSN | TMC | Hexane | PI | PA | N/A | 99.9% Na2SO4, 98.9%, MgSO4 97% MgCl2 92.3% NaCl | Water: 39.3, IPA: 18.5 Acetone: 30.1 EA:18.3 DMF: 5.5 | • Excellent chemical and mechanical stability | Use of low-toxic MOFs as additives |
| • Multifunctional TFN membranes | ||||||||||||
| 83 | Amino acid: L-lysine | Diet of poultry, fish, beans etc. | NF | TMC | Hexane | PSF | PA | 1150 | Naphthol green B/NaCl: 99.2/2.75 | Water: 36.15 | • High salt concentration sensitivity | High MWCO |
| • Good dye/salt separation | ||||||||||||
| • No additives or catalysts | ||||||||||||
| 84 | Lignin alkali (LA) | Plants’ cell walls | NF + OSN | TMC | Hexane | PSF | Polyester | 630 | 97.3% Brilliant blue; 97.8% Congo red. 51.4% MgSO4 | Water: 1.7 | • Stable | Moderately low salt rejection for NF application. |
| • Low cost | ||||||||||||
| • Easy reaction | ||||||||||||
| 85 | Tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane (THAM) in 0.1 M NaOH solution | Condensation of nitromethane with formaldehyde | NF + OSN | TMC | Hexane | PES | Poly(ester amide) | N/A | 99.9% Na2SO4 (7.5% THAM), CR/NaCl: 98.8/7.5 (0.5% THAM) | Water: 11.1 (7.5% THAM), water: >45 (0.5% THAM) | • Multifunctional TFC membranes | • Use of NaOH solution as a catalyst |
| • Easy membrane fabrication with alternating ester and amide linkages | • Requires post heat treatment |
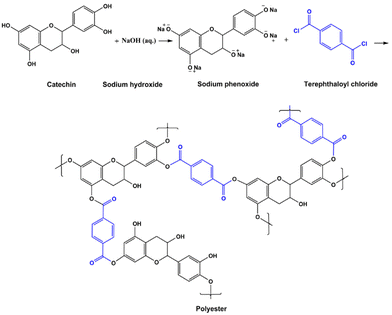 | ||
| Fig. 3 The IP reaction between catechin and TPC, yielding polyester.52 | ||
Zhang et al.,66 Pérez-Manríquez et al.,22 and Park et al.61 used tannic acid, a type of polyphenol found in plants, as the aqueous monomer. They used different organic monomers, organic solvents, and supports (Tables 3 and Table 4). The resultant membranes varied in their performance, while the best performing membrane was that of Park et al.61 Zhang et al.66 fabricated membranes with excellent antifouling properties probably due to the enrichment of hydroxyl groups in the polyester thin film. Pérez-Manríquez et al.22 produced a stable membrane that could in principle be scaled up.
| Ref. | Aqueous phase | Origin | Membrane type | Organic monomer | Organic solvent | Support | Product | MWCO [g mol−1] | Rejection [%] | Permeance [L per m2 per h per bar] | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 61 | Polyphenol: tannic acid | Trees, plants nuts and fruits | OSN | Priamine | p-Cymene | Recycled PET | Priamine-TA | 395 | 90% styrene dimer | 13.7 (acetone) | • Excellent performance888 • All membrane's components are ‘green’ | • Extensive OSN studies need to be performed |
| 23 | 2% acetic acid in chitosan | Shrimp shells | OSN | plant-based 2,5-furandicarboxaldehyde (FDA) | 3% TamiSolve in eucalyptol solution | Recycled PET | Chitosan | 317 | 100% Rose Bengal in acetone, 96% methyl orange in acetone | 12 (acetone) | • Need of organic catalysts: TMG/DMAP/TEA | |
| 86 | Genipin in 0.1% citric acid solution | hydrolysis of geniposide extracted from the fruits | OSN | Priamine | Eucalyptol solution | PLA fibers support with TBAB | Polyamide | 281 | 90% styrene dimer 99.6% oil separation from water mixture | 10 (acetone), 5.6 (water) in oil/water separation | • Multifunctional to permeate organic solvents and to separation oil from water | • Expensive technique to obtain electrospun fibers |
| • All membrane's components are ‘green’ |
Zhang et al.67 used polyphenol from green tea, epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), to fabricate NF membrane. They first performed a Michael addition/Schiff base reaction between the pyrogallol groups in EGCG and amine groups in polyethyleneimine (PEI), later amidation reaction with TMC onto poly(tetrafluoro ethylene) (PTFE) resulted in a crossed-linked EGCG-PEI-TMC/PTFE product (see Fig. 4). The use of PEI, which is considered a toxic amine monomer, reduces the sustainability of the membrane; however, its optimized concentration is 1 w/v%, half the MPD concentration commonly used. The use of EGCG for the production of NF membranes compared to those produced solely by the reaction between PEI and TMC increased the stability of the membrane due to the stronger adhesion to the support.67 The resultant membrane had very good performance and stability.
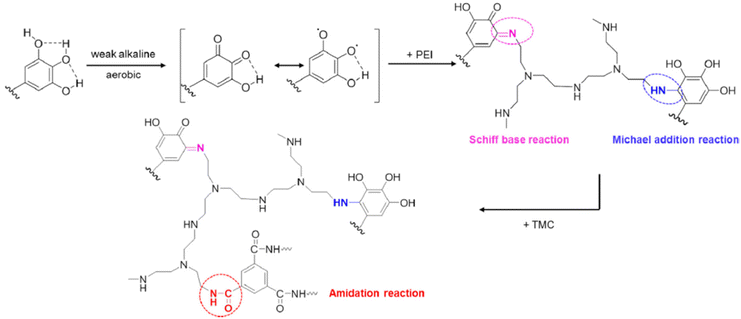 | ||
| Fig. 4 Reaction mechanism between pyrogallol groups of EGCG, amine groups of PEI, and acyl-chloride.67 | ||
Alhazmi et al.68 used allylated gallic acid as IP monomer to react with TMC. The MWCO was tuned between 700 and 327 g mol−1 by changing the chemical composition and reaction time. The allyl functionality integrated into the membrane network offers the chance for post-functionalization.
To conclude, membranes fabricated using bio-polyphenols showed overall competitive performance, as seen in Table 3, were easily fabricated, and have good potential to replace or to come in addition to the aqueous monomer commonly used for OSN/NF membranes.
In continuation, Jin et al.77 reported the use of a sugar alcohol, meso-erythritol, followed by sugar bio-monomers such as sucrose76 replacing the amine monomer. These membranes were evaluated for the wastewater treatment of textile industries, as they offered adequate dye/salt separation, wherein 99.6% of Congo Red dye was rejected and 89% of Na2SO4 salt was permeated (at a water flux of 53.2 L per m2 per h per bar)77 and 99.4% of Congo Red dye was rejected and 88.8% of Na2SO4 salt was permeated (at a water flux of 52.4 L per m2 per h per bar).76
Cyclodextrins (CDs) constitute a family of cyclic oligosaccharides, which are plant-based produced derived from starch. They have abundant active –OH groups for crosslinking as well as a cavity in the middle of their structure, named alpha, beta, or gamma macrocycles. The cavity enables selective transport of molecules with a sizes range of 0.47–0.95 nm. When they are used as IP monomers in a fully crosslinked network, the cavities can act as “preformed” pores. However, to have full advantage of CD cavities as selective pathways, the space between the CD unities must be minimized. CDs also have disadvantages compared to MPD: their hydroxyl groups are less reactive towards acyl-chloride than amines, and they tend to agglomerate in aqueous solutions. A pioneering approach to effectively produce CD membranes was proposed by Villalobos et al.,69 they used CD as the aqueous monomer and succeeded in optimizing the preparation conditions (high concentration of the aqueous monomer, hydrophilic and highly porous support, high pH). CD reacted with terephtaloyl chloride (TC) to produce polyester. The fabricated membrane had high performance: its permeance was an order of magnitude higher than commercially available OSN membranes, and its rejection of methyl orange is slightly lower than polyamide TFC membranes.
In a practically identical approach, Liu et al.70 further explored the fabrication of membranes by molecularly engineering the IP of CD and TMC to construct precise molecular sieving architectures (Fig. 5). Preferential transport for polar solvents is claimed to occur outside the cavities, while the methylene (–CH2–) groups located at the interior of CD's cavities generate inner hydrophobic cavities for the transportation of non-polar solvents, giving a double character to the membrane recognized as a “Janus” system, as depicted in Fig. 5. The study employed positron annihilation spectroscopy (PAS) to confirm that larger free volume and higher microporosity are generated with a larger inner cavity of the type of CD. Based on the rejection ratio of various dyes, the estimated MWCOs of various CDs and TMC based nanofilms are 320 g mol−1, 400 g mol−1 and 550 g mol−1 for α, β and γ-CDs respectively. These are in accordance with the free volumes and inner cavity sizes of α-CD < β-CD < γ-CD. Lastly, the chosen β-CD and TMC based freestanding nanofilms exhibited shape-selective functions for 3D molecules and reasonable permeances for both polar (methanol, 4.9 L per m2 per h per bar) and nonpolar solvents (n-hexane, 6.3 L per m2 per h per bar).
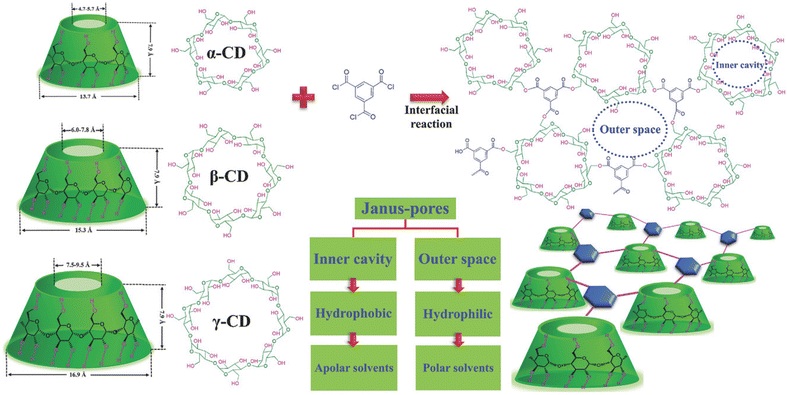 | ||
| Fig. 5 Chemical structures and architectures of the crosslinked cyclodextrins and TMC, to produce molecular sieving nanofilms by IP.70 | ||
Polyester, the selective layer network when using unmodified CD or polyphenol as monomers can have advantages over polyamide chemistry, which has been highly successful for TFC membranes, in term of chlorine resistance.71,87 Polyamide is not resistant towards chlorine which is a drawback for large-scale desalination plants that cannot clean the RO system with sodium hypochlorite.71,88,89 Xue et al.71 therefore explored the potential advantages of CD polyester membranes, prepared by a procedure similar to that described above, in terms of their chlorine resistance. High fluxes ranging from 104.6 L per m2 per h per bar to 197.6 L per m2 per h per bar were reported by altering the concentration of β-CDs in between 0.1 to 1.8 wt% and the rejection of Congo red and methyl blue dyes was 95.6% and 94.4%, respectively. The desirably high flux was attributed to the synergistic effect of the intrinsic cavity and inactive –OH groups of β-CD which resulted in the formation of water channels and a loose selective layer. The most striking result of this work was indeed the confirmation of a remarkable chlorine resistance even when exposing to 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 ppm of sodium hydrochloride solution for 96 h. Besides the low reactivity and need for high pH during synthesis, a drawback of this work was that heat treatment is needed to promote crosslinking of the selective layer and to remove the n-heptane organic solution.
000 ppm of sodium hydrochloride solution for 96 h. Besides the low reactivity and need for high pH during synthesis, a drawback of this work was that heat treatment is needed to promote crosslinking of the selective layer and to remove the n-heptane organic solution.
With the objective of achieving even higher permeability, while maintaining solute selectivity, more sophisticated approaches were investigated, such as introducing graphene quantum dots or carbon nanotubes as an additive to the β-CD monomer in the aqueous solution.72,73 However, the cost of graphene quantum dots and the complex pre-steps of obtaining not-so-economical MWCNTs poses a disadvantage. Nevertheless, the increase of the complexity for the membrane preparation is not an advantage for the industrial fabrication and application.
Regarding the high-performance properties of CD membranes, the availability and low cost of the reactants make the process feasible for large-scale usage; however, the requirement of high pH reduces their attractivity. A much more effective approach was later proposed and demonstrated by Huang et al.,90 they functionalized CDs with amino groups and then used them as monomers for IP. Amines are more reactive; hence a thin, defect-free selective layer was formed, which was able to separate molecules efficiently with MWCO around 350 g mol−1. By using this procedure, the selective layer is highly crosslinked and constituted by 61.5% of β-CD, each unit covalently connected with four others. The membranes rejected more than 99% brilliant blue. The rigid CD cavities rejected molecules with kinetic size larger than 0.61 nm. They distinguish molecules by shape as well, the rejections of Safranine O and methylene blue were 72% and 38%, respectively, even though their size is similar (351 and 320 g mol−1). With the fast reactivity of the amino functionalization, the IP reaction can be easily translated to machines analogous to those used in the industry. The scalability should be therefore straight forward. The amino functionalization preferentially occurs in the narrow rim of the β-CD molecule and the reaction with the acid chloride is regiospecific.90 The resulting layer is therefore asymmetric, having different degrees of hydrophilicity on each side, reflected by water contact angles of 29° (high density of unreacted hydroxyl groups) and 72°. This fact has been further explored by Jiang et al.91 with the perspective of obtaining aligned macrocycle pores for nanofiltration practically with the approach again applied to CD and extended to 4-sulfocalix[4]arene.
Tang et al.74 used chitosan, a polysaccharide abundant in crustaceans, to fabricate a NF membrane. First, chitosan was used as the only aqueous phase monomer (0.8% w/v) reacting with TMC in hexane (0.8% w/v); next, together with PIP (0.55% w/v chitosan, 0.25% w/v PIP) in the aqueous phase, the IP reaction with TMC was performed to produce polyamide (Fig. 6). Chitosan is a polymer with long chain molecules that reduce its penetration ability to the organic phase, as opposed to PIP which diffuses more easily to the organic phase and reacts with TMC. Therefore, the addition of PIP increases the polymerization rate and a significant increase in pure water flux (∼5 L per m2 per h per bar) was reported, and a slight decrease in salt rejection (∼3%) in comparison to the performance of the pure chitosan NF membrane which has salt rejection of 91.9% for Na2SO4 and water permeance of 5.22 L per m2 per h per bar, moreover the addition of chitosan could reduce the usage of the amine monomer concentration (0.8% vs. 2%).74 However, to dissolve chitosan in the aqueous phase it must be heated and under acidic conditions, which reduces process sustainability and upscaling potential.
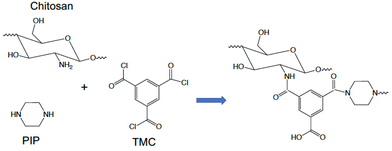 | ||
| Fig. 6 The IP reaction between chitosan and PIP with TMC to produce polyamide.74 | ||
In a recent study, Abdi et al.62 explored the separation of mixtures of dye/salt wherein P84 co-polyimide was modified with β-CD by a green method. In this research work IP between N,N-bis(3-aminopropyl)-1,3-propanediamine (APPD) and β-CD in a green solvent formulated novel β-CD incorporated P84 co-polyimide nanofiltration (NF) membranes. The difference in this method was that the chemical crosslinking between the P84 co-polyimide membranes and APPD, and the IP with β-CD would take place in one step. Initially, APPD would be dissolved in water at different β-CD concentrations and since all the mixed solutions would have a pH higher than 12.33, this would favor the reactivity of the β-CD leading to a strengthening of the electrostatic attraction of β-CD with APPD. When the P84 membrane is immersed in this solution, chemical crosslinking and IP would simultaneously occur. The unreacted hydroxide groups on the outer surface of β-CD would help increase water permeability and form a negatively charged surface, while the interior cavity of the 3D bowl-like structure would enhance the size-sieving capability of the membrane. As a result, the dye/salt separation efficiency of the β-CD incorporated NF membranes increases and turns it to a favorable system for the treatment of salt-containing dye wastewater treatment.
Ding et al.80 added sulfonic acid groups to dopamine, resulting in sulfonated dopamine (SDA) as the aqueous monomer reacting with TMC via IP (Fig. 7). They reported that the sulfonic acid groups contribute to the restraining of IP and to the hydrophilicity of the fabricated membranes. The salt rejection of the SDA-NF membrane was lower than of the DA-NF membrane they fabricated, whereas the SDA-NF membrane water flux was higher. The SDA-NF membrane performed an excellent dye rejection (∼99.9%) even for dyes with MW of 320 g mol−1; however, the MWCO is very high (2000 g mol−1), which does not go along with the dye rejection performance reported. The preparation of SDA included the addition of propanesulfonate and ammonia to DA, following heating of the solution to 50 °C for 18 h. This may reduce the sustainability and the feasibility of industrial usage.
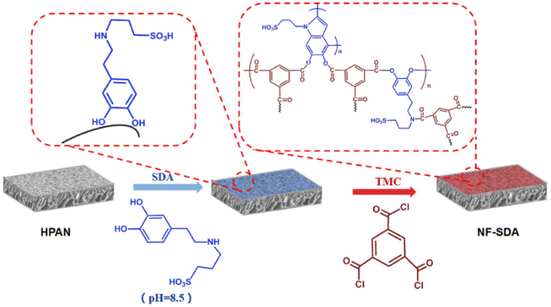 | ||
| Fig. 7 Preparation of NF membranes by IP, using sulfonated dopamine (SDA) and TMC as monomers.80 | ||
Along a similar line of research, Shah et al.81 employed bio-monomers, namely dopamine hydrochloride (PDA) and DL-norepinephrine hydrochloride (PNE), which are derivatives of amino acids, for replacing toxic monomers in the aqueous phase. The amine, phenol and catechol functional groups of PDA and PNE aid in forming a dense thin-film selective layer with enhanced chemical and structural stability even in harsh environments compared to the previously mentioned amino acid derivatives based monomers. TMC was used in the organic phase, constituted by a light alkylate Isol-C solution. The permeation was tested with poly(propylene glycol) oligomers with varied molecular weights, revealing that PDA, PNE and tannic led to membranes exhibiting approximate MWCOs of 650 g mol−1, 715 g mol−1, and 832 g mol−1, respectively. Comparing all three NF membranes, the PDA based-membrane exhibited a relatively higher flux and rejection rate for bivalent ions. The water permeability was 8.14 L per m2 per h per bar and with a Na2SO4 rejection of ∼93%. Thus, in comparison to the two earlier works of DA and SDA-based monomers, the dopamine hydrochloride-based TFC membranes had better permeability and salt rejection. Lastly, as concluded by the authors in this work, these TFC-NF membranes require further fine-tuning of the properties for their implementation in various industrial applications.
Another work by Zhang et al.82 extended the protocol of using DA hydrochloride as an aqueous monomer by combining it with glucose and MOFs to prepare nanocomposite membranes for precise and ultrafast molecular separations. The IP reaction of polydopamine and glucose in the presence of compatible MOF additives enabled the formation of ultrathin selective layers on the surface of porous substrates. These ultrathin nanocomposite membranes derived from natural compounds offered enhanced chemical stability and water flux permeability of 39.3 L per m2 per h per bar. Due to the synergistic effects of each of the components, the reported solvent permeances of these ultrathin nanocomposite membranes were two orders of magnitude higher than that of commercially available OSN membrane.92 However, the incorporation of MOFs compromises the green advantage of DA and glucose and makes the scaling-up processes more difficult.
Another amino acid-based monomer, L-lysine, was explored as an aqueous monomer in IP with TMC. Xu et al.83 used readily available, non-toxic, and cheaper amino acids like L-lysine with two amino groups that can rapidly react with TMC. The membrane is presented as charge-mosaic. By using L-lysine, a loose inner structure was obtained for fast transport of salts and water and efficient rejection of dyes. Extensive discussions related to the plausible mechanisms of the salt concentration sensitivity (the water flux of the L-lysine based membrane had a linear increase with the salt concentration in the feed solution) of the charge-mosaic NF membranes were presented in this work. The optimized membrane exhibited desirably high separation efficiency to salts/dyes mixtures (retention of over 99.2% for Naphthol green B dye and NaCl rejection of 2.75%) coupled with an unusual salt concentration sensitivity. The measured water flux of 36.15 L per m2 per h per bar was 13 times higher than the pure water flux reported in the literature and these findings were confirmed after rigorous cycles of repetition. This study could open doors for potential industrial applications such as in textile industry where separation of salts and dyes are inevitable or during pre-treatment in salination.
This interesting study shows THAM as a potentially suitable monomer for controlled IP, which was difficult to achieve with the traditional polyamide or polyester membranes. The controlled tunability provides a wide range of structures, as higher THAM concentration was tested for desalination application wherein a water permeance of 11 L per m2 per h per bar and Na2SO4 salt rejection of 97.1% was recorded. Contrarily, lower THAM concentration, a loosely crosslinked structure showed dye removable rate of 95% and a lowered NaCl rejection of <7.5% with high water permeance of >45 L per m2 per h per bar. Therefore, tunable crosslinked membranes can be further exploited for task-specific separation processes. Lastly, as THAM contains three hydroxyl groups, lower reactivity with TMC was addressed, by adding NaOH to the aqueous phase the OH groups are deprotonated69 and aid in forming alkoxide ions with improved reactivity. However, during IP, extended time was required to promote the reaction as well as thermal post-treatment, which needs to be considered for further scale-up.
2.3 Pursuit for greener membranes combining green solvents and green monomers
Recent studies reported pioneering work in preparing green membranes wherein both the toxic organic solvents and toxic monomers have been replaced by green alternatives.23,61,86 Furthermore, these membranes were fabricated at room temperature, thereby fulfilling all sustainable principles by Szekely et al. (2014).30 Park et al.61 fabricated a totally green membrane for the first time. p-Cymene was used as the organic sustainable solvent in the IP reaction, it is derived from plants, such as origanum, eucalyptus, etc. It has low viscosity and moderate to high vapor pressure, is considered flammable and its interfacial tension with water is lower than hexane (Table 1). The product was not polyester because they did not use acyl chloride as the organic monomer, but priamine. The polymerization reaction was Schiff-base and Michael-addition between the pyrogallol groups of tannic acid (they were first converted to quinone) and the amine groups of priamine resulting in the formation of imine and amine groups (see Fig. 8). Its performance show high permeance of different solvents (e.g. 13.7 L per m2 per h per bar for acetone) and a low MWCO (395 g mol−1). The fabrication process is easy and can be scaled up; however, the costs of the green solvent and the green monomers may be much higher than the commonly used ones.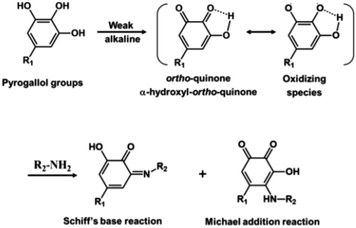 | ||
| Fig. 8 Reaction mechanism between pyrogallol groups of TA and amine groups of priamine.61 | ||
Following the above work, Park et al.23 designed thin-film composite (TFC) membranes via IP of chitosan, a shrimp farming waste material, in the aqueous phase and plant-based 2,5-furandicarboxaldehyde in the organic phase, on an upcycled polyethylene terephthalate porous support. TamiSolve was employed as a green solvent for the first time, to activate the selective layer of the chitosan-based TFC membrane. This resulted in significant enhancement in the permeance of various pure solvents including ethanol, methyl ethyl ketone, acetone, and acetonitrile, with no remarkable defects and high solute rejections. This work successfully targeted the replacement of toxic and fossil-based solvents and reagents in developing high-performance and solvent-resistant nanofiltration membranes.
Yang et al. fabricated a biodegradable electrospun nanofibrous support, made of polylactic acid (PLA) and gelatin as an interlayer.86 PLA and gelatin were dissolved using dimethyl carbonate (a green solvent) and water. The hydrophilicity of the support was enhanced due to the presence of the interlayer, gelatin. IP of natural monomers was employed to fabricate green polyamide TFC membranes on the porous support. The natural monomers (plant-based) used were genipin in the aqueous phase and priamine in organic solvent eucalyptol. The fabricated final membranes showed excellent acetone permeance up to 10 L per m2 per h per bar and a 99.6% of oil removal rate in water treatment at a water permeance of 5.6 L per m2 per h per bar. These membranes have excellent solvent stability and OSN performance which potentiates its use in sustainable membrane manufacturing. Considering the underlying motivation of this review, more efforts from the scientific community can be directed towards producing greener membranes by IP which include both green solvents and green monomers, exhibiting enhanced process performance.
3. Eco-Scale greenness assessment tool towards IP
Green chemistry encourages reducing the use of toxic chemicals/reagents, employing energy-efficient equipment, and generating minimal waste.28 Recent trends in chemical processes focus on the miniaturization of the sample preparation devices, the development of solventless or solvent-minimized extraction techniques, and the utilization of less toxic solvents.94 The twelve principles of green chemistry serve as a basic guideline for inducing greenness in the design of chemical procedures.29 Several metrics have been developed for the evaluation of the greenness of chemical processes, of which Analytical Eco-Scale, Green Analytical Procedure Index, and Analytical Greenness Metric are among the important tools for assessing the greenness of chemical processes.95,96 All these metrics take different aspects of the analytical/chemical procedure into account to provide the green index of the procedure. However, Eco-Scale is the most widely employed greenness assessment tool due to its simplicity in calculation and as it provides a quantitative assessment of the method's greenness in the form of a number that can be compared with an ideal score of 100.94–96Although the membrane community has been continually seeking to harness the sustainability metrics offered by membrane technologies, there is a sporadic distribution of works reported on utilizing ‘greenness assessment tools’ in this field of research. Here, we attempt to uphold the principles of green chemistry by exploring the analytical Eco-Scale tool to compare the greenness of the IP reaction for the fabrication of representative membranes, each one from the three categories described in the previous sections, namely, green solvents, green monomers, and total green membranes. For comparison, the Eco-Scale of the standard membrane fabricated via IP using MPD/TMC as monomers and hexane as organic solvent, is calculated as well. Briefly, the underlying motivation of this section is to evaluate the effective greenness of the materials/procedure for performing IP to obtain TFC membranes. It also distinguishes between the overlapping perception of green and sustainable chemistry, wherein the former concerns the environment, and the latter deals more broadly towards economics, ecology and society.97
The Eco-Scale assessment tool was proposed by Gałuszka et al.98 based on the calculation of a numerical total score classifying the greenness level of the investigated analytical method. An ideal green procedure has a total score of 100 with no penalty points. Penalty points representing the harmful impacts of the method on the environment are subtracted from the total score. Negative effects on the environment include hazardous solvents consumed, high energy consumption, and the amount of waste generated. According to this assessment tool, there are three classifications: a green method, which has a final total score of more than 75 points; a non-green method, which has a final total score between 50 and 75 points; and inadequate green analysis and extremely harmful to the health/environment if the final score is below 50 points. The penalty points of hazards are calculated based on the following criteria: non-hazard, which has no pictogram and 0 penalty points; less severe hazard chemical, which has only one penalty point and a more severe hazard, which has two penalty points. The penalty points are also extended towards energy consumption and purification steps of the materials involved, if any, during the process.
The Eco-Scale assessment in this review was carried out using the freely available Eco-Scale calculator (https://ecoscale.cheminfo.org/calculator) and the software is based on the paper by Aken et al.99 There were following assumptions while carrying out the analysis: (i) The materials and process employed only for the IP section were considered, (ii) The type of membrane support and its procedure to obtain them was not considered, (iii) The technical set-up for IP was assumed to be a common set-up without the need for any special glassware/glove box/unconventional set-up, (iv) the pre- and post-treatment steps like heating were considered.
As seen in Table 5, it is clearly evident that the classical example of IP has an undesirable Eco-Scale score of 73 as it uses toxic monomers like TMC and MPD along with hexane as an organic solvent and requires post-heat treatment for crosslinking.100 Merely by replacing hexane with greener organic solvent alternative like oleic acid increased the Eco-Scale score of the IP process to 88.50 Furthermore, the same group chose an alternative greener monomer allylated gallic acid and instead of n-hexane, isopar-G was used as a solvent and the crosslinking was performed at room temperature conditions.68 This resulted in the Eco-Scale score of 90. Avoiding toxic substances like MPD monomer and n-hexane organic solvent saved 10 penalty points each. However, 5 penalty points each were attributed to the usage of TMC and a non-green solvent like Isopar-G. Lastly, sub-section 2.4 dealt with green membranes produced by combining both greener monomers and green organic solvents, and no post-heat treatment at elevated temperatures was involved. The Eco-Scale score of the first work by Park et al.,61 was 90 as p-cymene was used as the organic solvent and priamines were used as the organic monomers.61 The penalty points were applied for these two as p-cymenes, a bio-derived green solvent imparts irritation to the eyes and skin, and priamines are a bit expensive and not so readily available. The other two works on green membranes by Park et al., and Yang et al., from the same research group23,86 obtained the highest Eco-Scale scores of 95 each. In the former work, chitosan from shrimp shells was used and the latter work used priamines as the green monomer. Although both are bio-derived greener options, their cost and availability are a concern. Anyhow, a clear distinction can be witnessed from Table 5 as alternatives uphold the spirit of green chemistry by increasing the Eco-Scale score and substantially contributing to more sustainable processes, which was the essence of the contribution of the present review.
| Aqueous monomer | Organic monomer | Organic solvent | Category of IP work | Eco-Scale score | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MPD | TMC | n-Hexane | Classical IP | 73 | 100 |
| MPD | TMC | Oleic acid | Green solvent | 88 | 50 |
| Allyl gallic acid | TMC | Isopar G | Green monomer | 90 | 68 |
| Tannic acid | Priamine | p-Cymene | Green membrane | 90 | 61 |
| Chitosan | FDA | Eucalyptol | Green membrane | 95 | 23 |
| Genepin | Priamine | Eucalyptol | Green membrane | 95 | 86 |
4. Conclusions
This work summarizes the recent advances reported on sustainable variations of organic solvents and monomers used for NF/OSN/RO membrane fabrication via the IP reaction. Clearly, there is a wide variety of sustainable solvents and monomers that can be used, and there is a need for more specific criteria of what makes a better solvent or monomer. To this end, better understanding of IP fundamentals provides insight on the desired properties of materials involved in the reaction. Another noteworthy outcome of this review is the apparent lack of agreed-upon criteria for performance tests of a specific membrane type. For example, in the case of OSN membranes, different dyes were used in different studies to measure rejection, the permeance was measured using different liquids, and the MWCO was not consistently reported. These variations make it very difficult to compare between membranes and scrutinize the impact of variations in materials and fabrication conditions. Ideally, every membrane type should have specific criteria and an experimental protocol for evaluating its performance. Moreover, when studying an effect of a specific parameter on the fabricated membrane performance, this parameter should be the only one changed, if possible, otherwise it is not possible to clearly gauge its impact on the reaction and on the resultant membrane.Furthermore, the objective of these studies is to find alternate, sustainable materials to replace the commonly used toxic materials; therefore, it would be very useful to include an industrial perspective, e.g., estimated costs, reaction times, upscaling potential, and possibly other aspects of industrial relevance. In lieu of this, many ‘green’ membranes will remain in the academic literature without their application in industry.
The last aspect of this review is the evaluation of the greenness of the membrane materials used in the IP process by employing an Eco-Scale greenness assessment tool. The results clearly distinguished the importance of using greener solvents and greener monomers as they had less environmental penalty points when compared with the classical monomers (TMP and MPD) and organic solvent (n-hexane) used in IP for producing membranes.
Author contributions
Adi Ben-Zvi: conceptualization, investigation, visualization, writing – original draft, writing – review & editing. Usman Taqui Syed: conceptualization, investigation, visualization, writing – original draft, writing – review & editing. Guy Z. Ramon: conceptualization, supervision, writing – review & editing, funding acquisition. Suzana Nunes: supervision, writing – review & editing, funding acquisition.Conflicts of interest
The authors confirm that they are not affiliated with or involved in any organization or entity that has a financial or non-financial interest in the subject matter or materials covered in this article.Acknowledgements
AB was supported, in part, by the Jewish National Fund (JNF)'s ‘climate’ fellowship. UTS was supported, in part, by the the King Abdullah University of Science and Technology. The research was partially supported by the Israel Science Foundation, grant #3041/21.References
- V. Freger and G. Z. Ramon, Polyamide desalination membranes: Formation, structure, and properties, Prog. Polym. Sci., 2021, 122, 101451 CrossRef CAS.
- G. Ozkan, et al., A review of microencapsulation methods for food antioxidants: Principles, advantages, drawbacks and applications, Food Chem., 2019, 272, 494–506 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. J. Raaijmakers and N. E. Benes, Current trends in interfacial polymerization chemistry, Prog. Polym. Sci., 2016, 63, 86–142 CrossRef CAS.
- J. E. Cadotte, Evolution of composite reverse osmosis membranes, in Materials science of synthetic membranes, 1985, pp. 273–294 Search PubMed.
- J. E. Cadotte, et al., A new thin-film composite seawater reverse osmosis membrane, Desalination, 1980, 32, 25–31 CrossRef.
- M. Kurihara and T. Sasaki, The pursuits of ultimate membrane technology including low pressure seawater reverse osmosis membrane developed by “mega-ton water system” project, J. Membr. Sci. Res., 2017, 3(3), 157–173 Search PubMed.
- R. J. Petersen, Composite reverse osmosis and nanofiltration membranes, J. Membr. Sci., 1993, 83(1), 81–150 CrossRef CAS.
- K. P. Lee, T. C. Arnot and D. Mattia, A review of reverse osmosis membrane materials for desalination—Development to date and future potential, J. Membr. Sci., 2011, 370(1–2), 1–22 CrossRef CAS.
- Z. Zhang, et al., From reverse osmosis to nanofiltration: Precise control of the pore size and charge of polyamide membranes via interfacial polymerization, Desalination, 2019, 466, 16–23 CrossRef CAS.
- S. P. Nunes, et al., Thinking the future of membranes: Perspectives for advanced and new membrane materials and manufacturing processes, J. Membr. Sci., 2020, 598, 117761 CrossRef CAS.
- V. Freger, Kinetics of film formation by interfacial polycondensation, Langmuir, 2005, 21(5), 1884–1894 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- I. Sadeghi, P. Kaner and A. Asatekin, Controlling and expanding the selectivity of filtration membranes, Chem. Mater., 2018, 30(21), 7328–7354 CrossRef CAS.
- J. R. Werber, C. O. Osuji and M. Elimelech, Materials for next-generation desalination and water purification membranes, Nat. Rev. Mater., 2016, 1(5), 1–15 Search PubMed.
- B.-H. Jeong, et al., Interfacial polymerization of thin film nanocomposites: a new concept for reverse osmosis membranes, J. Membr. Sci., 2007, 294(1–2), 1–7 CrossRef CAS.
- I. Nulens, et al., Re-thinking polyamide thin film formation: How does interfacial destabilization dictate film morphology?, J. Membr. Sci., 2022, 656, 120593 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Behera and A. K. Suresh, Kinetics of interfacial polycondensation reactions–development of a new method and its validation, Polymer, 2017, 127, 28–44 CrossRef CAS.
- B. Ukrainsky and G. Z. Ramon, Temperature measurement of the reaction zone during polyamide film formation by interfacial polymerization, J. Membr. Sci., 2018, 566, 329–335 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Wang, et al., Controlled growth of polyamide films atop homogenous and heterogeneous hydrogels using gel–liquid interfacial polymerization, Macromol. Chem. Phys., 2019, 220(13), 1900100 CrossRef PubMed.
- W. Xie, et al., Toward the next generation of sustainable membranes from green chemistry principles, ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng., 2020, 9(1), 50–75 CrossRef.
- Y. Hartanto, et al., Interfacial polymerization of thin-film composite forward osmosis membranes using ionic liquids as organic reagent phase, J. Membr. Sci., 2020, 601, 117869 CrossRef.
- C. Ong, et al., Green synthesis of thin-film composite membranes for organic solvent nanofiltration, ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng., 2020, 8(31), 11541–11548 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Pérez-Manríquez, P. Neelakanda and K.-V. Peinemann, Tannin-based thin-film composite membranes for solvent nanofiltration, J. Membr. Sci., 2017, 541, 137–142 CrossRef.
- S.-H. Park, et al., Solvent-resistant thin-film composite membranes from biomass-derived building blocks: chitosan and 2, 5-furandicarboxaldehyde, ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng., 2021, 10(2), 998–1007 CrossRef.
- Worldwide Solvents Market Analysis, Global Solvents Industry, in https://www.reportlinker.com/p05561789/Global-Solvents-Industry.html?utm_source=GNW. November 2023, Global Industry Analysts.
- United Nations Sustainable Developmental Goals, #Envision 2030, https://social.desa.un.org/issues/disability/envision-2030/17goals-pwds. 2023 29/11/2023.
- X. Dong, et al., Polymers and solvents used in membrane fabrication: a review focusing on sustainable membrane development, Membranes, 2021, 11(5), 309 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Razali, et al., Sustainable wastewater treatment and recycling in membrane manufacturing, Green Chem., 2015, 17(12), 5196–5205 RSC.
- P. Anastas and N. Eghbali, Green chemistry: principles and practice, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2010, 39(1), 301–312 RSC.
- P. T. Anastas and J. C. Warner, Green chemistry, Frontiers, 1998, 640(1998), 850 Search PubMed.
- G. Szekely, et al., Sustainability assessment of organic solvent nanofiltration: from fabrication to application, Green Chem., 2014, 16(10), 4440–4473 RSC.
- L. E. Peng, et al., Does interfacial vaporization of organic solvent affect the structure and separation properties of polyamide RO membranes?, J. Membr. Sci., 2021, 625, 119173 CrossRef CAS.
- N. Indraswati, et al., Density and viscosity for a binary mixture of ethyl valerate and hexyl acetate with 1-pentanol and 1-hexanol at 293.15 K, 303.15 K, and 313.15 K, J. Chem. Eng. Data, 2001, 46(1), 134–137 CrossRef CAS.
- PUBCHEM, National Library of Medicine, USA, https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/. [cited 2023 21/11/2023].
- P-Cymene, https://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/chris/CMP.pdf. 1999, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, Government Agency, USA.
- M. Tariq, et al., Viscosity of (C2–C14) 1-alkyl-3-methylimidazolium bis (trifluoromethylsulfonyl) amide ionic liquids in an extended temperature range, Fluid Phase Equilib., 2011, 301(1), 22–32 CrossRef CAS.
- R. L. Gardas, et al., Interfacial tensions of imidazolium-based ionic liquids with water and n-alkanes, Fluid Phase Equilib., 2010, 294(1–2), 139–147 CrossRef CAS.
- I. Nulens, et al., MPD and TMC supply as parameters to describe synthesis-morphology-performance relationships of polyamide thin film composite membranes, J. Membr. Sci., 2023, 667, 121155 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Mariën, et al., Sustainable process for the preparation of high–performance thin–film composite membranes using ionic liquids as the reaction medium, ChemSusChem, 2016, 9(10), 1101–1111 CrossRef PubMed.
- Y. Deng, et al., Influence of oxygen functionalities on the environmental impact of imidazolium based ionic liquids, J. Hazard. Mater., 2011, 198, 165–174 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. D. Rogers and K. R. Seddon, Ionic liquids–solvents of the future?, Science, 2003, 302(5646), 792–793 CrossRef PubMed.
- H. Marien and I. F. Vankelecom, Optimization of the ionic liquid-based interfacial polymerization system for the preparation of high-performance, low-fouling RO membranes, J. Membr. Sci., 2018, 556, 342–351 CrossRef CAS.
- P.-R. Van den Mooter, L. Dedvukaj and I. F. Vankelecom, Use of Ionic Liquids and Co-Solvents for Synthesis of Thin-Film Composite Membranes, Membranes, 2021, 11(4), 297 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. Zheng, et al., Fabrication of thin-film composite membranes for organic solvent nanofiltration by mixed monomeric polymerization on ionic liquid/water interfaces, J. Membr. Sci., 2021, 636, 119551 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Yao, et al., Using Cu-TCPP Nanosheets as Interlayers for High-Performance Organic Solvent Nanofiltration Membranes, ACS Appl. Nano Mater., 2022, 5(12), 18718–18729 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Gao, et al., The Ionic Liquid–H2O Interface: A New Platform for the Synthesis of Highly Crystalline and Molecular Sieving Covalent Organic Framework Membranes, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2021, 13(30), 36507–36516 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Bai, et al., Ionic liquid regulated interfacial polymerization process to improve acid-resistant nanofiltration membrane permeance, J. Membr. Sci., 2022, 641, 119882 CrossRef CAS.
- N. Verma, et al., Ionic Liquid-Mediated Interfacial Polymerization for Fabrication of Reverse Osmosis Membranes, Membranes, 2022, 12(11), 1081 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Ni, H. Peng and Q. Zhao, Ultrathin Poly (Ionic Liquid) Nanomembranes for High Performance Mg2+/Li+ Separation, Adv. Mater. Interfaces, 2022, 9(32), 2201797 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Qiu, et al., β-Cyclodextrin-ionic liquid functionalized chiral composite membrane for enantioseparation of drugs and molecular simulation, J. Membr. Sci., 2022, 660, 120870 CrossRef CAS.
- G. Falca, et al., Naturally extracted hydrophobic solvent and self-assembly in interfacial polymerization, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2021, 13(37), 44824–44832 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. H. Abdellah, et al., Effective interfacially polymerized polyester solvent resistant nanofiltration membrane from bioderived materials, Adv. Sustainable Syst., 2018, 2(7), 1800043 CrossRef.
- M. H. Abdellah, et al., A catechin/cellulose composite membrane for organic solvent nanofiltration, J. Membr. Sci., 2018, 567, 139–145 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Paseta, et al., Vapor phase interfacial polymerization: A method to synthesize thin film composite membranes without using organic solvents, Green Chem., 2021, 23(6), 2449–2456 RSC.
- S. Karki and P. G. Ingole, Development of polymer-based new high performance thin-film nanocomposite nanofiltration membranes by vapor phase interfacial polymerization for the removal of heavy metal ions, Chem. Eng. J., 2022, 446, 137303 CrossRef CAS.
- B. C. Welch, et al., Molecular layer deposition for the fabrication of desalination membranes with tunable metrics, Desalination, 2021, 520, 115334 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Wang, et al., Aqueous Two-Phase Interfacial Assembly of COF Membranes for Water Desalination, Nano-Micro Lett., 2022, 14(1), 216 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. L. Ritt, et al., The open membrane database: Synthesis–structure–performance relationships of reverse osmosis membranes, J. Membr. Sci., 2022, 641, 119927 CrossRef CAS.
- OSN Database at KAUST. https://osndb.kaust.edu.sa/en-US/#/diagram2024 17/03/2024.
- H.-F. Xiao, et al., Amphibian-inspired amino acid ionic liquid functionalized nanofiltration membranes with high water permeability and ion selectivity for pigment wastewater treatment, J. Membr. Sci., 2019, 586, 44–52 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Wu, et al., A novel nanofiltration membrane with [MimAP][Tf2N] ionic liquid for utilization of lithium from brines with high Mg2+/Li+ ratio, J. Membr. Sci., 2020, 603, 117997 CrossRef CAS.
- S.-H. Park, et al., Hydrophobic thin film composite nanofiltration membranes derived solely from sustainable sources, Green Chem., 2021, 23(3), 1175–1184 RSC.
- Z. G. Abdi, J.-Y. Lai and T.-S. Chung, Green modification of P84 co-polyimide with β-cyclodextrin for separation of dye/salt mixtures, Desalination, 2023, 549, 116365 CrossRef CAS.
- R. Mülhaupt, Green polymer chemistry and bio–based plastics: dreams and reality, Macromol. Chem. Phys., 2013, 214(2), 159–174 CrossRef.
- J. Wang, A. Qin and B. Z. Tang, Multicomponent polymerizations involving green monomers, Macromol. Rapid Commun., 2021, 42(6), 2000547 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Pérez-Manríquez, P. Neelakanda and K.-V. Peinemann, Morin-based nanofiltration membranes for organic solvent separation processes, J. Membr. Sci., 2018, 554, 1–5 CrossRef.
- Y. Zhang, et al., Composite nanofiltration membranes prepared by interfacial polymerization with natural material tannic acid and trimesoyl chloride, J. Membr. Sci., 2013, 429, 235–242 CrossRef CAS.
- N. Zhang, et al., Nanofiltration membrane via EGCG-PEI co-deposition followed by cross-linking on microporous PTFE substrates for desalination, Sep. Purif. Technol., 2020, 232, 115964 CrossRef.
- B. Alhazmi, et al., Naturally Derived Allylated Gallic Acid for Interfacially Polymerized Membranes, ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng., 2022, 10(41), 13585–13594 CrossRef CAS.
- L. F. Villalobos, T. Huang and K. V. Peinemann, Cyclodextrin films with fast solvent transport and shape–selective permeability, Adv. Mater., 2017, 29(26), 1606641 CrossRef PubMed.
- J. Liu, et al., Precise molecular sieving architectures with Janus pathways for both polar and nonpolar molecules, Adv. Mater., 2018, 30(11), 1705933 CrossRef PubMed.
- J. Xue, et al., Chlorine-resistant polyester thin film composite nanofiltration membranes prepared with β-cyclodextrin, J. Membr. Sci., 2019, 584, 282–289 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Xue, et al., High-flux nanofiltration membranes prepared with β-cyclodextrin and graphene quantum dots, J. Membr. Sci., 2020, 612, 118465 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Li, et al., Thin-film composite polyester nanofiltration membrane with high flux and efficient dye/salts separation fabricated from precise molecular sieving structure of β-cyclodextrin, Sep. Purif. Technol., 2021, 276, 119352 CrossRef CAS.
- Y.-J. Tang, et al., Novel chitosan-piperazine composite nanofiltration membranes for the desalination of brackish water and seawater, J. Polym. Res., 2018, 25, 1–12 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Zheng, et al., Sugar-based membranes for nanofiltration, J. Membr. Sci., 2021, 619, 118786 CrossRef CAS.
- P. Jin, et al., Low-pressure highly permeable polyester loose nanofiltration membranes tailored by natural carbohydrates for effective dye/salt fractionation, J. Hazard. Mater., 2022, 421, 126716 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. Jin, et al., Erythritol-based polyester loose nanofiltration membrane with fast water transport for efficient dye/salt separation, Chem. Eng. J., 2021, 406, 126796 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Shen, et al., Thermal-facilitated interfacial polymerization toward high-performance polyester desalination membrane, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2021, 9(13), 8470–8479 RSC.
- J. Zhao, et al., Dopamine composite nanofiltration membranes prepared by self-polymerization and interfacial polymerization, J. Membr. Sci., 2014, 465, 41–48 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Ding, H. Wu and P. Wu, Development of nanofiltration membranes using mussel-inspired sulfonated dopamine for interfacial polymerization, J. Membr. Sci., 2020, 598, 117658 CrossRef CAS.
- A. A. Shah, et al., Preparation of highly permeable nanofiltration membranes with interfacially polymerized biomonomers, J. Membr. Sci., 2021, 627, 119209 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Zhang, et al., Robust natural nanocomposites realizing unprecedented ultrafast precise molecular separations, Mater. Today, 2020, 36, 40–47 CrossRef CAS.
- R. Xu, et al., Preparation and performance of a charge-mosaic nanofiltration membrane with novel salt concentration sensitivity for the separation of salts and dyes, J. Membr. Sci., 2020, 595, 117472 CrossRef.
- S. Zhan, et al., Green lignin–based polyester nanofiltration membranes with ethanol and chlorine resistance, J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 2022, 139(1), 51427 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Zhang, et al., Novel poly (ester amide) membranes with tunable crosslinked structures for nanofiltration, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2022, 14(8), 10782–10792 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Yang, et al., Biobased thin-film composite membranes comprising priamine–genipin selective layer on nanofibrous biodegradable polylactic acid support for oil and solvent-resistant nanofiltration, Green Chem., 2022, 24(13), 5291–5303 RSC.
- W. Tang, et al., Highly selective and permeable β-cyclodextrin based polyester nanofiltration membranes maintaining good chlorine resistance, J. Membr. Sci., 2023, 685, 121976 CrossRef CAS.
- K. L. Cho, et al., Chlorine resistant glutaraldehyde crosslinked polyelectrolyte multilayer membranes for desalination, Adv. Mater., 2015, 27(17), 2791–2796 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Yao, et al., High performance polyester reverse osmosis desalination membrane with chlorine resistance, Nat. Sustainability, 2021, 4(2), 138–146 CrossRef.
- T. Huang, et al., Ultrathin 2D–layered cyclodextrin membranes for high–performance organic solvent nanofiltration, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2020, 30(4), 1906797 CrossRef CAS.
- Z. Jiang, et al., Aligned macrocycle pores in ultrathin films for accurate molecular sieving, Nature, 2022, 609(7925), 58–64 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Li, et al., Nanofibrous hydrogel composite membranes with ultrafast transport performance for molecular separation in organic solvents, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2019, 7(33), 19269–19279 RSC.
- R. A. Durst and B. R. Staples, Tris/Tris· HCl: a standard buffer for use in the physiologic pH range, Clin. Chem., 1972, 18(3), 206–208 CrossRef CAS.
- S. S. Soliman, et al., Greenness assessment profile of a QbD screen-printed sensor for real-time monitoring of sodium valproate, Microchem. J., 2022, 182, 107859 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Gamal, et al., Comparative study of four greenness assessment tools for selection of greenest analytical method for assay of hyoscine N-butyl bromide, Anal. Methods, 2021, 13(3), 369–380 RSC.
- M. Sajid and J. Płotka-Wasylka, Green analytical chemistry metrics: A review, Talanta, 2022, 238, 123046 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Mutlu and L. Barner, Getting the terms right: green, sustainable, or circular chemistry?, Macromol. Chem. Phys., 2022, 223(13), 2200111 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Gałuszka, et al., Analytical Eco-Scale for assessing the greenness of analytical procedures, TrAC, Trends Anal. Chem., 2012, 37, 61–72 CrossRef.
- K. Van Aken, L. Strekowski and L. Patiny, EcoScale, a semi-quantitative tool to select an organic preparation based on economical and ecological parameters, Beilstein J. Org. Chem., 2006, 2(1), 3 Search PubMed.
- G.-Y. Chai and W. B. Krantz, Formation and characterization of polyamide membranes via interfacial polymerization, J. Membr. Sci., 1994, 93(2), 175–192 CrossRef CAS.
Footnote |
| † These authors contributed equally to this work. |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2024 |