 Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleCreative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported Licence
Periodontal disease and emerging point-of-care technologies for its diagnosis
Jayesh
Korgaonkar†
ab,
Azra Yaprak
Tarman†
ab,
Hatice
Ceylan Koydemir
 *ab and
Sasanka S.
Chukkapalli
*a
*ab and
Sasanka S.
Chukkapalli
*a
aDepartment of Biomedical Engineering, Texas A&M University, College Station, TX 77843, USA. E-mail: hckoydemir@tamu.edu; schukkapalli@tamu.edu
bCenter for Remote Health Technologies and Systems, Texas A&M Engineering and Experiment Station, College Station, TX 77843, USA
First published on 7th June 2024
Abstract
Periodontal disease (PD), a chronic inflammatory disorder that damages the tooth and its supporting components, is a common global oral health problem. Understanding the intricacies of these disorders, from gingivitis to severe PD, is critical for efficient treatment, diagnosis, and prevention in dental care. Periodontal biosensors and biomarkers are critical in improving oral health diagnostic skills. Clinicians may accomplish early identification, tailored therapy, and efficient tracking of periodontal diseases by using these technologies, ushering in a new age of accurate oral healthcare. Traditional periodontitis diagnostic methods frequently rely on physical probing and visual examinations, necessitating the development of point-of-care (POC) devices. As periodontal disorders necessitate more precise and rapid diagnosis, incorporating novel innovations in biosensors and biomarkers becomes increasingly crucial. These innovations improve our capacity to diagnose, monitor, and adapt periodontal therapies, bringing in the next phase of customized and effective dental healthcare. The review discusses the characteristics and stages of PD, clinical treatment techniques, prominent biomarkers and infection-associated factors that may be employed to determine PD, biomedical sensing, and POC appliances that have been created so far to diagnose stages of PD and its progression profile, as well as predicting future developments in this field.
1. Introduction
Periodontal disease (PD) stands out as a leading chronic inflammatory condition that impacts the tissues surrounding and providing support to the teeth. PD is roughly estimated to impact approximately 19% of the adult population worldwide, which accounts for over 1 billion cases globally. In the United States, nearly half, specifically 47.2%, of adults aged 30 years and older are reported to have some degree of PD.1,2Since it is a chronic inflammatory disease, developing better tools to diagnose it early, monitor the disease progression, and recovery during PD therapy is essential. The current clinical practices of frequent health visits, inspection, and probing followed by radio imaging are laborious and expensive, preventing patients from seeking medical help. Hence, there is an urgent need to identify and develop highly sensitive, specific, rapid, and patient-friendly tools.
Recent advancements in micro and nanofabrication have transformed the telecommunications field and sensor creation by shrinking components, increasing efficiency, and adding complex functionality into smaller, more adaptable systems. Smartphones, for example, use microelectromechanical system (MEMS) sensors such as accelerometers and gyroscopes, which improve user experiences through features such as motion detection and screen orientation adjustment.3 Furthermore, tiny sensors are used in wearable fitness trackers to track physical activity and health factors.4–6 Personal electronics have been altered by incorporating micro and nanotechnology sensors, increasing convenience and functionality.
Sensors based on micro and nanotechnology have ushered in an age of innovation in bioanalyte sensing, providing an adaptable platform for detecting a broad spectrum of chemicals, from ions to cells.7–10 This technical advancement utilizes three main sensory modalities: optical, electrical, and mechanical sensing, each with certain advantages. For example, optical sensing uses concepts of light interactions with target molecules to provide label-free detection and real-time monitoring.11 Electrical sensing uses variations in conductivity generated by bioanalyte binding, with implications ranging from tracking glucose to DNA detection.12,13 Mechanical sensors detect relationships among mechanical forces and bioanalytes, allowing for precise and sensitive detection.14
The transformational potential for both micro and nanotechnology sensors extends beyond general bioanalyte detection to the area of oral health, with the ability to redefine how we handle periodontal illnesses. These cutting-edge technologies promise precise and early identification of PD, allowing for prompt interventions and individualized treatment plans for better oral health and an improved smile.
This review article provides information about several aspects of PD identification and therapy using sensors and biomarker analysis. This article begins with an introduction to PD, discussing the important role played by the sensors for effective PD detection, highlighting their importance in enabling accurate clinical classification and treatment strategies across all phases of the disease. The paper systematically reviews the existing methods, ranging from conventional probing techniques to modern scanning systems and collection of sample methods, while discussing their shortcomings. Additionally, we provide information on several biomarkers for PD detection, focusing on the possibility of saliva-based biomarker analysis. Subsequently, we review biomedical technologies ranging from mobile sensors to in vitro point-of-care (POC) devices, elucidating their application in PD diagnosis and their limitations and benefits. The review concludes with a discussion on future trends in periodontal diagnosis and therapy, emphasizing the possible role of sensing and biomarkers in transforming the field of periodontal healthcare.
2. PD and its clinical importance
A. Pathophysiology of PD
PD is a chronic inflammatory condition that influences the supportive structures of teeth, encompassing the gums, periodontal ligament, and alveolar bone. The progression of PD is typically characterized by increased levels of oral pathobiont-associated host-mediated inflammation, tissue damage, and, ultimately, bone loss around the teeth. The pathophysiology of the disease is characterized by the distinct apical migration of the junctional epithelium and the loss of marginal periodontal ligament fibers. This process facilitates the apical spread of bacterial biofilm along the root surface.15 Gingival inflammation is initiated by the formation of bacterial biofilm. However, the onset and advancement of PD hinge on the dysbiosis, or imbalance, within the oral microbiome16 (Fig. 1). As the disease progresses, the periodontal pockets (the space between the tooth and gum) may become deeper, and the gum tissue may recede, exposing the tooth root.17,18 These events could potentially lead to increased sensitivity, pain, and mobility of the affected teeth.19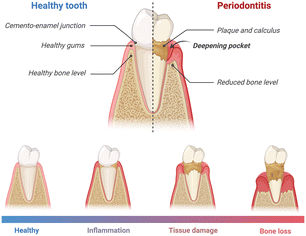 | ||
| Fig. 1 Schematic illustration of PD stages. As the disease progresses, the inflammation, tissue damage, and bone loss become more severe. Created with https://www.BioRender.com. | ||
B. Diagnosis criteria
The progression of PD is typically classified according to the severity of the symptoms and the extent of tissue damage. PD is clinically diagnosed as visible clinical attachment loss (CAL) by circumferential assessment of the erupted dentition with a standardized periodontal probe with reference to the cemento-enamel junction (CEJ). As it is a visible measurement, there is always room for error while predicting clinical attachment level using a standard periodontal probe. Multiple case definitions have recently been proposed for PD diagnosis to reduce the error range. According to a classification that utilizes the American Academy of Periodontology (AAP)/Centers for Disease Control (CDC) case definition for epidemiologic surveillance and the European Federation of Periodontology (EFP) case definition, a patient has a PD case in the context of clinical care if.201. Interdental CAL is detectable at ≥2 non-adjacent teeth or.
2. Buccal or oral CAL ≥3 mm with pocketing >3 mm is detectable at ≥2 teeth.
Another alternative classification was proposed based on clinical attachment through periodontal probing and radiographic examination of alveolar bone loss. This approach gauzes the aftermath of previous episodes of deterioration and it requires a 2 to 3 mm threshold change before a site can be defined as having experienced a significant anatomic event.21 Advancements in research regarding oral and PD diagnosis are moving toward methods whereby PD risk can be identified and quantified by objective measures, i.e. biomarkers. In the past, efforts have been put to classify staging based on the severity and extent of an individual's measurable extent of destroyed and damaged tissue attributable to PD and grading to estimate the future risk of PD progression and responsiveness to standard therapeutic principles. Based on this, PD is graded into four simpler stages:22 stage 1 (initial PD): which is characterized as the borderline between gingivitis and periodontitis, representing the early stages of attachment loss. Stage 2 (moderate PD): it is characterized by established periodontitis and shows the characteristic damages caused to tooth support on clinical examination. Stage 3 (severe PD): this stage is characterized by significant damage to the attachment apparatus, and tooth loss may result in the absence of advanced treatment. Stage 4 (advanced PD): in this more advanced stage, PD can cause considerable damage to the periodontal support and cause significant tooth loss, which could translate into loss of masticatory function.
The next clinical classification based on diagnostic factors like interdental CAL, radiographic bone loss, probing, and tooth loss classifies PD into four stages. According to this classification, stage 1 will include interdental CAL to be 1 to 2 mm, radiographic bone loss to be <15%, probing depth to be <4 mm, stage II will encompass interdental CAL to be 3 to 4 mm, radiographic bone loss to be 15% to 35%, probing depth to be <5 mm, stage 3 will encompass interdental CAL to be >5 mm, radiographic bone loss extending to the middle or apical root of the teeth 15% to 35%, probing depth to be >6 mm, stage IV will encompass interdental CAL to be >5 mm, radiographic bone loss extending to the middle or apical third of the root, masticatory dysfunction, severe ridge defect.23
3. Current clinical methods for PD diagnosis and treatment
A. PD diagnosis methods
B. Clinically established treatments for PD
Chronic PD is often treated using nonsurgical therapy, which involves mechanical debridement of supragingival and subgingival dental plaque and calculus by scaling and root canal treatment. If there is an observed residual inflammation, patients are often given adjunctive therapy, which involves diverse options like local delivery of drugs, systemic antibiotics, or systemic host modulation agents.31• Local delivery of drugs includes the provision of adjunctive drugs/antibiotics, such as doxycycline, or antimicrobials, such as chlorhexidine, or anti-inflammatory agents, which are usually delivered directly to the periodontal pocket using a delivery system for localized treatment.32
• Systemic antibiotics include broad-spectrum antibiotics either alone or in combination with antibiotics targeting Gram-negative bacteria. They are employed in the usual adult dose range for 1–3 weeks.33–35
• Systemic host modulation agents include using compounds that act through the inhibition of matrix metalloproteinases. However, despite the availability of these treatment options, it is significant to note that nonsurgical periodontal treatment has limitations in terms of the long-term maintenance of deep periodontal pockets, the risk for disease recurrence, and the need for the skill of the clinical operator. With regard to systemic antibiotic therapy, increased antibiotic resistance has been observed among patients with PD in recent years.36 Also, the unique periodontal environment and biofilm formation abilities make these bacteria less susceptible to antibiotics.37,38
Hence, there is a discrete need for new therapeutic strategies to treat PD. As the clinical attachment and bone loss are more evident, treatment goals should focus on controlling inflammation, preventing disease progression, and ultimately creating conditions enabling patients to maintain a healthy, functional dentition.
4. Biomarkers used for the diagnosis of PD
A biomarker is defined as a substance that can be measured and evaluated as an indicator of normal physiological processes, pathogenic processes, or pharmacologic responses to therapy.39 Biomarkers are vital tools in medical studies and diagnostics, as they provide a window into the human body's physiological and pathological events.40 These biomarkers could be diverse analytes ranging from specific nucleic acids and proteins to metabolites and could provide essential information on diseases' existence, progression, and seriousness. Potential biomarkers of disease that could provide usefulness for assessing PD activity would either play a role in the pathogenesis of the disease or be released as a consequence of tissue damage during the progression of PD. Various biological media are vividly used as a source in the diagnosis of PD. These include saliva, gingival crevicular fluid (GCF),41 subgingival plaque, serum, and tissue biopsies.42 The following parts of this review paper will dive into the complex world of biomarkers used to diagnose PD. In addition, we will look at the most recent advances in biomarker development and validation approaches, as well as the revolutionary impact they have on healthcare and medicine.A. Saliva as diagnostic biofluid for PD
Saliva, by itself, serves as a valuable biofluid containing various analytes, including cytokines and matrix metalloproteinases, which can be used to detect PD and bone remodeling. Traditional clinical examinations might not offer early illness detection or an accurate assessment of disease. On the other hand, new technologies capable of identifying particular cytokines and proteinases in saliva enable rapid chair-side testing and individualized medication methods. The use of new technologies can improve the power of clinical dental examinations, medical history evaluations, and evidence-based, tailored risk care for PD by identifying customized phenotypes and host-derived mediators. The study of Korte and Kinney et al.,43 thoroughly evaluated saliva biomarkers and combination markers, such as PD pathogens, that can considerably improve medical decision-making in PD development, risk evaluation, and diagnosis. Research by Buzalaf et al.,44 emphasized the importance of biomarkers in avoiding illness, evaluation, and prognosis, and their presence in diverse biological fluids, specifically in saliva, which is regarded as a powerful diagnostic tool because of its capacity to reflect pathophysiological states in the body as well as enable non-invasive and quick identification of biomarkers associated with dental and systemic disorders. Another study by Frodge et al.,31 investigated saliva as a diagnostic medium for measuring bone remodeling in the setting of PD. It explored the usage and quantification of specific biomarkers such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), C-telopeptide pyridinoline cross-links of type I collagen (ICTP), and receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappa B ligand (RANKL) found in saliva that can shed light on the bone erosion and formation processes linked with PD to create non-invasive and accessible diagnostic techniques for monitoring the development and extent of PD. The following section focuses on the biomarkers that can be found in saliva. While significant efforts are being made to develop effective indicators for early detection of PD, more validation is required before the broad deployment of chairside POC sensors in clinical settings.30Several salivary biomarkers have been identified that can be used to identify the PD stage and provide a general sense of disease progression. PD is generally divided into four stages with varying degrees of inflammation, degradation of connective tissue, and bone resorption. Interleukin-1beta (IL-1β), interleukin-6 (IL-6), macrophage inflammatory protein-1 alpha (MIP-1α), and TNF-α are factors released from various types of cells that play a role in the inflammatory phase.43,45–49
As the disease advances, the connective tissue around the affected area degrades, ultimately leading to bone loss. Matrix metalloproteinase-8 (MMP-8)49 and matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9),43,48 are the two biomarkers for the next stages of the disease, and their increased levels are associated with collagen degradation. Inhibition of MMP-8 and other collagenolytic enzymes is done by tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinase-1 (TIMP-1).49 The levels of this enzyme decrease with the progression of the disease, while alkaline phosphatase levels are found to be increased due to calcification.50,51 As for bone resorption markers, ICTP is observed to be a biomarker as its levels were found to be associated with the later stages of periodontitis and its confirmed contribution to further collagen degradation.48 Osteoprotegerin (OPG) is another crucial factor that normally functions in bone development and maintenance.52 It competitively inhibits osteoclast activity by binding with the RANKL. A recent study has shown a correlation between OPG levels and the PD stage. After treatment, the OPG levels decreased, while the stable group already had low OPG levels. Along with the other degradation markers, OPG could be a potential marker for the disease. While OPG inhibits RANKL activity, interactions with RANKL cause bone resorption by stimulating the proliferation and activity of osteoclasts.53 Hence, levels of both OPG–RANKL and RANK–RANKL can be used to assess the progression.54 In another study, it has been reported that inhibiting actomyosin contractility through the inhibition of myosin light chain kinase, rho kinase, or myosin ATPase activity in cultured periodontal ligament fibroblasts (PdLFs) consistently led to a reduction in messenger RNA levels of the bone regulatory protein OPG. Consequently, the study concluded that OPG is responsive to actomyosin tension in human periodontal ligament fibroblasts.55
The saliva of chronic PD patients was found to exhibit upregulated levels of IL-18,57 and following nonsurgical PD therapy, IL-18 levels showed a decrease. Additionally, active P. gingivalis and its lipopolysaccharide (LPS) were identified as agents that upregulate IL-18 expression. IL-18, in turn, was demonstrated to stimulate the expression of matrix metalloproteinase, and its overexpression was linked to inflammatory bone loss following oral bacterial infection.
In a study conducted on 33 Korean adults using multiplexed bead immunoassay by Kim et al., they observed that IL-1β levels were increased in the patients with significant bleeding status while IL-1a levels were high for the periodontal disease. Among the two, IL-1β was verified as significant after ROC curve analysis. The sensitivity of the cytokine was 88.24%, and the specificity was 62.5%.58
IL-6 is a pleiotropic cytokine, which produces more than one effect that similar to IL-1β is produced by an array of different cell types, including monocytes and macrophages. It can be induced to be produced and secreted by PAMPs such as LPS or IL-1β.59 IL-6 can bind the membrane-bound receptor (IL-6R) or soluble IL-6 receptor (sIL-6R). Binding with the membrane-bound receptor leads to acute phase response, infection defense, metabolism, and tissue regeneration, while binding with the soluble form leads to inflammation, also referred to as trans-signaling. Additionally, IL-6 leads to T helper cells' differentiation and immunoglobulin secretion by B-lymphocytes, further contributing to the immunity and inflammatory response seen in the periodontal site. Like IL-1β, IL-6 increases the production of MMPs, specifically MMP-1, which leads to collagen degradation around the inflamed tissue.60 GCF gathered from PD sites has been reported as having increased levels of IL-6 that can be used to determine the stage of the disease.61,62
Macrophages secrete MIP-1α, a chemotactic chemokine responsible for the recruitment of various inflammatory cells and functions in various aspects of the immune response. In addition, it can also activate bone resorption.63 MIP-1α is an excellent biomarker for the disease, as it has shown remarkable levels of being present at the site of inflammation in various studies regarding PD.64,65
Nisha et al.,'s study has shown the potential clinical benefit of using MIP-1α and MCP-1 as diagnostic tools to differentiate between the disease states. MIP-1α particularly has shown significant sensitivity and specificity in differentiating between healthy and gingivitis states. ROC curve analysis has shown that MIP-1α exhibited 100% sensitivity and 88% specificity in distinguishing, while MCP-1 showed 84.1% sensitivity and 88% specificity. Overall, the study highlighted the positive statistical correlation between the clinical parameters and the cytokine levels. However, in the future, longitudinal studies should be conducted to determine the predictive nature of the cytokines.65
TNF-α is an inflammatory cytokine that can be found in either a membrane-bound form or a soluble form. The soluble form is synthesized through the processing of membrane-bound by TNF-α-converting enzymes. The TNF-α inflammatory activities are directed by either type 1 receptors or type 2 receptors. While type 1 can bind to membrane-bound and soluble forms, type 2 can only bind to soluble forms.66 TNF-α is one of the most prominent cytokines seen in the infection sites, and it also plays an important role in bone remodeling. Type 1 acts as a promoter for osteoclastogenesis, while type 2 acts as an inhibitor for apoptosis even during the inflammatory response.67
Romero-Castro et al., have shown that even in small quantities, TNF-α is a valuable biomarker as the levels of it correlate with pathogens associated with PD. The study investigated the oral microbiota and the production of proinflammatory molecules such as TNF-α, which causes the release of collagen degradation enzymes. The analysis was conducted on 80 subjects, where 35 were diagnosed with chronic PD. Checkerboard hybridization was used to analyze the site's composition, and ELISA was used to measure TNF-α, MMP-8, and MMP-9 levels. In conclusion, the study highlighted that PD-related pathogens increase the levels of TNF-α, which makes the cytokines a valuable biomarker for diagnosis.68
To measure the real-time episodic progression of the PD course, neutrophil collagenase (MMP8), which has been identified as a major collagenolytic enzyme that can cause periodontal tissue destruction in PD, has been proposed as a biomarker by Denis F. Kinane and colleagues. It was observed that MMP8 levels were present in GCF, peri-implant sulcular fluid, mouth rinse, and saliva.71 Authors emphasize using this test to detect subclinical PD before clinical or X-radiographic manifestations, as the test is positive with increased levels of MMP8 in oral fluids ahead of active PD.
Aspartate aminotransferase (AST) is an enzyme that functions in the reversible transfer reaction of the amino group between aspartate and glutamate. AST is found in different types of tissues, such as hepatocytes, skeletal muscles, and the periodontal site.72 AST is retained in the cytoplasm of cells and is released by dead or injured cells. Thus, at the periodontal site, elevated levels of AST can be observed, and the levels can be used to determine the progression of the disease.73,74
Lastly, alkaline phosphatase (ALP) is a membrane-bound metalloenzyme that removes the phosphate group from proteins and nucleotides. There are various isoforms of ALP; thus, the enzyme can be observed in other parts of the body, too, apart from the periodontal site.72 The enzyme is not specific to PD; however, elevated levels have been observed in various studies.75 The enzyme is released during inflammation by cells associated with PD, such as osteoblasts and fibroblasts, and it is noted as a marker for bone formation.76
Osteocalcin (OC) is among the most abundant proteins found in human bone, and it is synthesized by osteoblasts. Notably, OC is associated with the inhibition of bone mineralization. In a study by Bullon et al.,77 they observed that the low serum osteocalcin concentration was associated with a remarkably higher percentage of decrease in PD and CAL after therapy. Also, low saliva osteocalcin concentrations were highly related with higher percentages of decrease in PD. In another study by Kunimatsu et al.,78 they observed that in gingivitis patients, no significant amounts of osteocalcin were detected, while in the case of PD patients, on the other hand, osteocalcin levels were detected, ranging between 0 and 540 pg per tube and positively correlated with these clinical parameters (P < 0.01) of PD.
Osteopontin (OPN) is a single-chain polypeptide that is highly concentrated at sites where osteoclasts are attached to the underlying mineral surface. Studies by Kido et al.79 revealed a significant increase in OPN levels, which coincided with increased probing depth measures in PD. Another study by Sharma et al.80 observed that GCF OPN concentrations increased proportionally with the progression of PD, and when nonsurgical periodontal treatment was provided, GCF OPN levels were significantly reduced.
Vernal et al.,32 studied the degree of RANKL expression in people with chronic PD. They observed that in chronic PD, large levels of RANKL, a substance implicated in the breakdown of bones, is predominantly released by CD4+ T cells. This shows that CD4+ T cells may have a role in PD-associated bone loss. Another study by Belibasakis et al.,36 focuses on the involvement of the RANKL and OPG systems in clinical PD. This system regulates bone remodeling and plays a role in the evolution of PD. They observed an intricate association between the ratio of RANKL to OPG levels and alveolar bone resorption in PD.
Chen et al.,37 investigated the generation of RANKL within the setting of PD to determine the cellular sources of RANKL production. They tried to assess how cellular types contribute to its expression, as understanding the cellular origins of RANKL could provide light on the mechanisms behind the loss of bone in periodontal conditions.84
Hirai et al.,86 using modified antigens, demonstrated that the patient serum IgG levels against RgpA were observed to be the highest among all the antigens expressed in P. gingivalis of PD patients. They proposed that the N-terminus of recombinant RgpA was excellent in differentiating between diseased and non-diseased states (with a sensitivity of 0.85, specificity of 0.9, and area under the curve of 0.915) and could be a potential biomarker for detection of PD.
Damgaard et al.,87 noted that seven bacterial species, including P. gingivalis, exhibited a significantly higher relative abundance in the saliva of individuals with aggressive PD compared to orally healthy controls. They reported that the salivary abundance of P. gingivalis could effectively distinguish between individuals with aggressive PD (AUC: 0.80, p = 0.0001) and chronic PD (AUC: 0.72, p = 0.006) from healthy controls.
In a study conducted by Na et al.,88 four distinct sets of oral microbiomes from buccal and supragingival mucosa were utilized to develop a prediction model for PD. Through the assessment of prediction model performance, they demonstrated that the abundance of the oral microbiome could serve as an effective metric for predicting PD. The study concluded by underscoring the potential of oral microbiome abundance in buccal mucosa and supragingival plaque as microbial markers for diagnosing PD.
B. GCF as diagnostic biofluid for PD detection
GCF is a biofluid that develops naturally in the crevices surrounding teeth and has been shown to include useful indicators concerning oral health. GCF in PD patients contains inflammatory cells, enzymes, antibodies, and various other inflammatory agents. Markers that promote inflammation, such as IL-1, IL-6, and IL-8, and also TNF-α, which play a vital part in the etiology of periodontal conditions, can be used to assess the degrees of inflammation.89Chaudhari et al.,45 using the GCF as a sample for diagnosis, assessed the correlation of levels of IL-1β in GCF to the clinical parameters of chronic periodontitis. They observed a strong correlation between periodontal tissue destruction and IL-1β.
In a study conducted by Becerik et al.,90 based on 80 individuals and four groups, which included 20 with chronic periodontitis, 20 with generalized aggressive periodontitis, 20 with gingivitis patients, and 20 healthy subjects, they observed that chronic patients and generalized aggressive periodontal patients had significantly higher IL-1β, IL-6, and IL-11 levels when compared with healthy subjects in GCF. Furthermore, GCF LIF levels of the chronic and generalized aggressive patients were lower than those of the healthy group. In another study by Afacan et al.91 using GCF from both chronic and aggressive periodontitis, it was observed that there was increased GCF hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha, vascular endothelial growth factor, and TNF-α levels in chronic and aggressive PD.
In a study conducted by Khalaf et al.,92 involving 60 participants, including 30 individuals with chronic PD and 30 healthy subjects, it was observed that levels of TGF-β1 were notably increased in the serum, saliva, and GCF of PD patients when compared to the control group. Bostanci et al.,93 in a quantitative proteomic analysis study of GCF samples with five healthy subjects and five aggressive periodontitis patients. Utilizing LC/MS, they noted that GCF proteins cystatin-B and defensins were exclusively detected in the samples from healthy controls. Additionally, annexin-1 was observed in samples from healthy individuals at levels five times higher than in other samples.
Silva et al.,94 evaluated the level of GCF biomarkers, inflammatory cells, and periodontal pathogens associated with attachment loss. Their study evaluated 56 patients with moderate or severe chronic periodontitis, and they observed higher RANK-L, IL-1β, and MMP-13 levels at sites exhibiting active PD. Palcanis et al.,95 explored the possible use of elastase as a marker of PD development. Elastase is a metabolic enzyme involved in tissue breakdown and inflammation found in GCF. They observed levels of elastase in the setting of PD to use it to predict the severity and progression. Elastase levels in the periodontium have the potential to represent the amount of tissue injury and inflammation. Understanding its function in the progression of PD can lead to more accurate disease stage evaluations and the creation of tailored medicines for PD. Kinney et al., evaluated the sensitivity and specificity of GCF biomarkers to detect sites with disease activity.96 Their study was based on a cohort that examined 100 patients over a 12-month period. They concluded that GCF alone provided low sensitivity and high specificity values, 23% and 95%, respectively. Baliban et al., tried to predict health or disease from GCF samples using a biomarker combination with high throughput proteomic analysis. They observed that glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase, thymidine phosphorylase, and Ig kappa chain V-I region AG were associated with healthy conditions.97
5. Biomedical sensing and monitoring technologies for detection of PD
A variety of novel technologies and equipment have emerged with the goal of improving PD identification and management. In the subsequent sections, we will describe these cutting-edge technologies that have the potential to change the scene of oral health tracking, especially PD diagnosis. We will start by examining ‘in-mouth wireless sensors’, that offer real-time information about oral problems, and then shift our focus to ‘Wearable gadgets’ that integrate smoothly into daily life and that have the potential to provide continuous information on gum health status. In the subsequent sections, we will shed some light on ‘In vitro POC devices’, with a focus on ‘Paper-based assays’, ‘Immunoassays’, and ‘Probing’ procedures, each giving distinct benefits in the diagnosis and assessment of periodontal disorders.A. In vitro POC devices
Lee et al.,101 developed biosensors for early PD detection and disease stage predictions. Human odontogenic ameloblast-associated protein (ODAM) has been discovered as a possible biomarker due to their association with the severity of periodontitis. Aptamers were created via a rigorous procedure known as GO-SELEX, which includes a pair binding to separate ODAM sites. Aptamer characterization methods included GO-FRET, SPR, CD, and magnetic beads. The resulting aptamer pair, OD64 and OD35, had dissociation constants (Kd) of 47.71 and 51.36 nM, respectively. The sandwich-type SPR biosensor detected minimal concentrations of 0.24 nM and 1.63 nM in buffered and saliva samples. This aptamer pair is used in a successful lateral flow strip biosensor, which has the potential to revolutionize POC detection for periodontal disorders using non-invasive saliva-based approaches, hence improving healthcare systems.
The research work of Bae et al.,102 proposed an innovative method for developing self-perceived periodontal illness sensors for early detection. The sensors are made of ZnO nanofilms with selectively laminated Au nanoparticles (NPs) using the atomic layer deposition and thermal evaporation processes. The improved ZnO laminated with Au NPs displayed exceptional gas sensing capabilities, particularly for detecting ppb-level quantities of methyl mercaptan (CH3SH), a volatile sulfur molecule linked to PD. The sensors demonstrated remarkable selectivity with a gas reaction of 4.99% for 50 ppb of CH3SH and a detection limit of 50 ppb. This work emphasized the possibility of these mixed sensors for consistent and repeatable detection of CH3SH in a variety of gas atmospheres, making them a promising tool to aid in early PD treatment.
Herr et al.,104 explored the development of a POC diagnosis for quantifying salivary biomarkers related to PD, specifically MMP8. A monolithic disposable cartridge was designed to be used as a compact analytical tool. The microfluidic method made it possible to analyze saliva hands-free by combining salivary pre-treatment with electrophoretic immunoassays for rapid results. When the performance of this device was compared to a conventional colorimetric sandwich ELISA, a high correlation between them was observed after linear regression analysis. The device was able to successfully for measuring MMP8 levels in both healthy and diseased subjects, and it was observed that increased MMP8 levels were found be to present in PD patients, which also correlated with the bone and tissue loss observed in and around the disease site. The device eliminates the time-consuming steps used in ELISA and uses a single antibody, making it less time-consuming and more cost-efficient. This study concluded by proposing longitudinal studies to observe the MMP8 levels as PD progresses and mentioned other potential applications in which the device may be used.
B. In-mouth wireless sensors
In-mouth wireless sensors are one of the revolutionary advances in diagnosing and tracking oral health. These compact and distinct gadgets are created to be more comfortably placed within the mouth cavity and give immediate data on various parameters related to periodontal conditions. Table 1 summarizes crucial characteristics linked to in-mouth wireless sensors, such as practical use, advantages and focus on individual oral healthcare.| Major properties of the sensor | Materials used in the design | Sensing scheme | Biomarker | Sensitivity | Cross-reactivity tested | Total duration | Sample type | Target location in the mouth | Ref. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tooth patch | Bioresorbable, wireless | Water-soluble silk fibroin films (base), graphene (electrodes), gold | Capacitance change | Bacteria (H. pylori) | 1 bacteria | Commercial mouthwash | Real-time, 15–20 min | DI water or human saliva | Tooth | 106 |
| Mouth guard biosensor | Wireless | Polyethylene terephthalate glycol (PETG) s, Pt and Ag/AgCl electrodes, | Enzymatic | Glucose | A range of 5–1000 μmol L−1 of glucose | Galactose, fructose, mannitol, sorbitol and xylitol | Long-term real-time monitoring (exceeding 5 h) | Artificial saliva | The patient's dentition | 107 |
| Pacifier biosensor | Wireless | Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) Ag/AgCl ink silicone nipples acrylonitrile butadiene styrene | Electrochemical detection – enzymatic | Glucose | Limit of detection of 0.04 mM | Uric acid and ascorbic acid | ∼30 min after a meal | Artificial saliva | Mouth | 108 |
| Mouthguard biosensor | Wireless | PPD Ag/AgCl conductive ink | Electrochemical detection – enzymatic | Uric acid | 2.45 μA mM−1 (correlation coefficient R2 = 0.998) | Ascorbic acid | Hourly for 5 hours | Artificial saliva, human saliva | The patient's dentition | 109 |
| Portable electrochemical biosensors | Wireless | Vaspin, thrombin, and ODAM | Electrochemical aptamers | Vaspin & thrombin | 0.02 nM and 1 nM of the limit of detection in buffer and saliva, respectively | PBS, α-amylase, HSA, human saliva | Short time analysis | Saliva or GCF | Ex vivo | 110 |
Mannoor et al.,106 presented a new technology that permits the simple attachment of graphene nanosensors on biomaterials, like tooth enamel. The nanosensors may be effortlessly transferred onto other biomaterials by printing graphene onto a water-soluble silk, resulting in an entirely biointerfaced sensing platform (Fig. 2Aa and Ab). The graphene nanosensors may be fine-tuned to detect specific analytes, and the use of a resonating coil removes the requirement for power or connections from outside. Incorporating peptide–graphene nanosensors onto a tooth enables remote tracking of respiration and bacterium detection in saliva, providing a versatile and widely applicable application to detect biochemical targets (Fig. 2Ac).
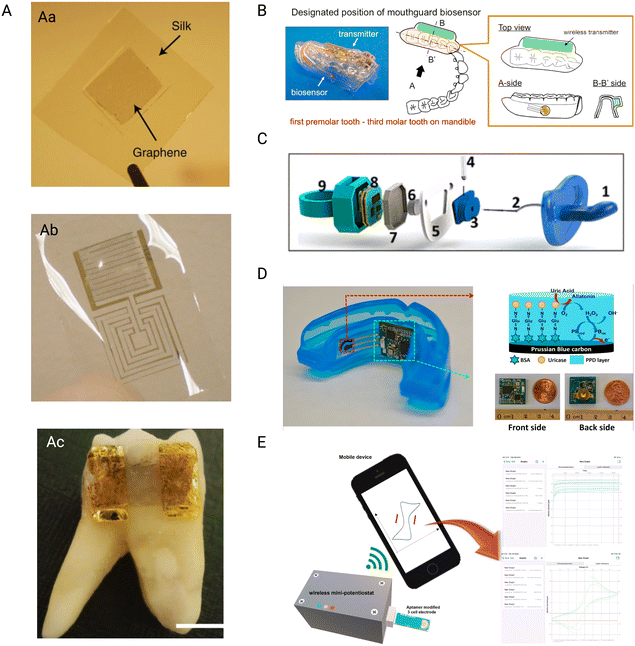 | ||
| Fig. 2 Wireless sensors. A) Graphene-based tooth sensor (Aa) graphene monolayers are printed onto the water-soluble silk layer using a simple transfer printing method (Ab) the biosensor is fabricated using shadow mask-assisted electron beam evaporation to generate the electrode pattern on the graphene-silk hybrid. (Ac) the complete dissolution of the silk in water has led to a strong attachment of the biosensor to the human molar. Reproduced with permission (Mannoor et al.106) 2012, Springer Nature. B) Schematic figure of the proposed custom-made mouthguard with the glucose sensor and wireless transmitter, allowing for constant measurements. Reproduced with permission (Arakawa et al.107) 2016, Elsevier. C) Schematic figure showing the assembly of the pacifier; (1) commercially available pacifier nipple, (2) saliva collection inlet, (3) electrochemical chamber, (4) PB–GOx electrode, (5) pacifier centerpiece, (6) pacifier outlet, (7) pacifier cap for insulation, (8) wireless potentiostat, (9) pacifier back piece. Reproduced with permission (García-Carmona et al.108) 2019, American Chemical Society. D) Photograph of the biosensor with amperometric circuit board, red arrow shows the schematic representation of the reagent layer of the working electrode while the green arrow shows the close up photographs of the amperometric circuit board. Reproduced with permission (J. Kim et al.109) 2015, Elsevier. E) Schematic representation of the aptamer duo-based portable electrochemical biosensors used for the early detection of PD. Reproduced with permission (Joe et al.110) 2022, Elsevier. | ||
The research of Arakawa et al.,107 developed detachable “Cavitas sensors” for non-invasive saliva glucose monitoring in the human oral cavity. (Fig. 2B) A salivary biosensor with Pt and Ag/AgCl electrodes was created and tested on mouthguard support having an enzyme membrane. Electrodes were generated on the mouthguard's polyethylene terephthalate glycol (PETG) surface. A glucose oxidase (GOD) film was deposited on the Pt working electrode. The biosensor was integrated smoothly between a glucose sensor and a wireless measuring system. When tested in vitro, the biosensor demonstrated a strong link between the output current and the glucose levels. The glucose sensor can detect glucose highly accurately throughout a range of 5–1000 mol L−1 of glucose in artificial saliva made of salts and proteins, which spans the entire range of levels of glucose present in human saliva. Researchers demonstrated how the sensor and wireless connection module could track saliva sugar in a phantom jaw that mimics the anatomy of the human mouth cavity. The telemetry system achieved reliable, long-term, real-time monitoring (over 5 hours). The mouthguard biosensor can be beneficial as a unique approach for non-invasive salivary glucose monitoring in real-time for better dental patient management.
Wearable sensors in non-invasive monitoring of physiological indicators are emerging clinical technologies. Since newborns cannot provide input concerning discomfort or health problems, compact and non-harmful monitoring devices are desperately needed. The first chemical wearable sensor for neonatal monitoring is described in the research by García-Carmona et al.,108 described pacifier functions as a mobile wireless device for non-invasive chemical tracking in the infant's saliva. The infant's teething on the pacifier results in effective saliva collection and facilitates a unidirectional flow through the mouth toward the electrochemical chamber, which houses the enzymatic biosensor and is positioned outside the mouth cavity (Fig. 2C). The platform's capabilities for detecting glucose in diabetic adults were tested and compared with their blood levels with a favorable correlation, proving the sensor's good performance. The baby-friendly device combines saliva sampling, electrochemical sensors, and tiny wireless electronics on a single pacifier base. This integration simplifies real-time and selective infant health monitoring, making it a pioneering wearable sensor specializing in infant chemical saliva detection. The preliminary demonstration of tracking glucose opens up new avenues for monitoring metabolites in newborns and neonates utilizing saliva as a non-invasive sample.
Kim et al.,109 developed a unique mouthguard device to measure salivary uric acid (SUA) levels non-invasively. The mouthguard includes an enzyme-modified screen-printed electrode system as well as tiny electronics such as a potentiostat, microcontroller, and Bluetooth connection. Unlike radio-frequency identification (RFID)-based systems, this wireless mouthguard allows for real-time data transmission to cell phones and various other consumer devices for instant processing and storage. The biosensor device detects uric acid in human saliva with good sensitivity, selectivity, and stability, making it suitable for healthy people and patients with hyperuricemia. This wearable monitoring system, which can expand to other sensors, has promise for various wellness and fitness applications.
Joe et al.,110 describe the creation of a mobile mini-potentiostat for electrochemical aptasensors to enable convenient and quick POC testing. (Fig. 2E). The performance of the mini-potentiostat was compared to that of a benchtop potentiostat, and two model biomarkers of protein (i.e., vaspin and thrombin) were effectively detected using matched aptamer pairs. The portable mini-potentiostat was used to create a sandwich-type binding couple of aptamers-based electrochemical biosensors for detecting PD by monitoring the ODAM biomarker. The biosensor outperformed prior approaches like surface plasmon resonance or lateral flow tests regarding linear range and sensitivity. This innovative portable biosensor has the potential to detect early-stage periodontal disorders utilizing genuine samples such as salivary or GCF in a short period of time at the POC.
C. Other non-wireless sensors
Besides in-mouth wireless sensors, many other non-wireless sensor technologies have major advancements in periodontal diagnostic and analysis. These sensors also have some distinct advantages, which enable them to make early detections and monitor periodontal conditions. To better understand these sensors and their qualities, Table 2 provides a succinct description of the necessary features and future applications of these non-wireless in oral healthcare.| Major properties of the sensor | Materials used in the design | Sensing scheme | Biomarker | Sensitivity | Cross-reactivity tested | Total duration | Sample type | Target location in the mouth | Ref. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Microcontact imprinted SPR sensors | Microcontact-imprinted optical | Protein-modified glass surface and a gold electrode | Electrochemical aptamers | Rgp and Kgp | 125–500 nM | Trypsin, chymotrypsin, HSA | Real-time | Arg and Lys specific gingipains Rgp and Kgp | In vitro diagnostics | 111 |
| Sodium selective sensors | Polyimide membrane with magnetic nano-inclusions | PVC, 2-nitrophenyl octyl ether, o-NPOE, p-tert-butyl calix[4]arene | Sodium level | GCF | Linear rang 3.1 × 10−5–10−1 mol dm−3 | Chloride | 45 s | GCF | In vitro and ex vivo | 112 |
| ODAM | GO-SELEX | Aptamers modified gold chips | Sandwich-type binding configuration of aptamers | Buffer and saliva samples | Minimum detectable concentration of 0.24 nM in buffered and 1.63 nM in saliva | α-Amylase | Not mentioned | Human saliva | In vitro diagnostics | 113 |
Hix-Janssens et al.111 focused on creating a monitoring strategy for the early detection of periodontitis, a prevalent gum disease linked to tooth loss and possible linkages to cardiovascular and Alzheimer's disorders. The method combines surface plasmon resonance (SPR)-based biosensor technology with high-affinity microcontact imprinted polymer-based receptors. (Fig. 3A) The gingipain proteases released by the periodontitis-associated bacteria P. gingivalis are specifically targeted as possible biomarkers in this investigation. The imprinted surfaces exhibited excellent selectivity and affinities toward gingipains, with lower detection limits than clinically relevant concentrations. This monitoring method shows potential for reliable and precise measurement of gingipain concentrations in biofluids and patient samples, allowing for early-stage periodontitis diagnosis. The work by Totu et al.112 presents the creation of sodium-selective sensors employing sodium-selective membranes incorporating magnetic nano-inclusions. The membranes are made of p-tert-butylcalix(4), an ionophore, and a polymeric matrix (polyvinyl chloride). The sensors have a constant range for sodium levels and a near-Nernstian electrochemical output. With a response duration of forty-five seconds, these tiny sensors can detect ions from GCF inside the periodontal pockets, overcoming the difficulties of collecting enough fluid for analysis. The sensors can detect changes in inorganic ion levels, assisting in the early detection and avoidance of PD. (Fig. 3B) The study of Hong et al.114 underlines the significance of oral cavity and diet monitoring for proper individualized healthcare management. It emphasizes the requirement for a wearable sensory system capable of continuous real-time analysis. The paper examines the classification of biosensing technologies and offers an overview of recent breakthroughs in wearable sensor creation for oral cavity and food monitoring. It also investigates the possibility of wearable sensors in tackling difficulties linked to food-intake tracking and saliva analysis in a variety of societal situations, such as elderly individuals, non-face-to-face interactions, and worldwide pandemics. Through the use of wearable sensors and the evaluation of large amounts of healthcare data, the review intends to accelerate a paradigm change toward customized healthcare and digital medicine. The study by Lee et al.113 addresses the creation of biosensors for the early detection of PD. It makes use of a pair of highly specific aptamers to identify ODAM, a possible biomarker for PD. These sandwich-type biosensors provide sensitive and precise ODAM detection, which can be critical for early illness diagnosis. (Fig. 3C) This study helps improve diagnostic tools for early detection and PD treatment.
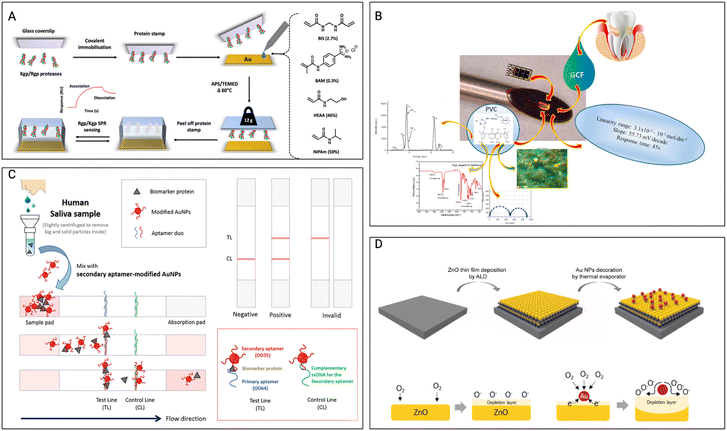 | ||
| Fig. 3 Other non-wireless sensors A) the preparation of μ-contact imprinted polymer film on an SPR sensor-chip involves, Lys-specific and Arg-specific gingipain proteases, Kgp, and Rgp, which are covalently linked to glass microscope coverslips. The SPR sensor-chip is then coated with a solution containing the designated monomers, followed by the protein stamp positioned onto the chip, and polymerization taking place during an overnight thermal curing process. Once cured, the glass coverslip is detached, yielding the MIP sensor chip. Reproduced with permission (Hix-Janssens et al.111) 2023, American Chemical Society. B) Schematic illustration of ODAM detection on the lateral flow biostrip. The assembled paper strips were employed in the creation of a sandwich-type lateral flow strip biosensor, utilizing a matched pair of aptamers. The potential for detecting ODAM through sandwich-type LFS biosensors were tested. Reproduced with permission (Totu et al.112) 2018, Elsevier. C) The aim was to create an innovative device designed for localized sensing within the periodontal pocket, focusing on specific inorganic ions in GCF. The approach involves the integration of membranes containing magnetic nanoparticles and ionophores, embedded within diverse polymeric matrices. Reproduced with permission (B. H. Lee et al.,113 “The Sensitive Detection of ODAM by Using Sandwich-Type Biosensors with a Cognate Pair of Aptamers for the Early Diagnosis of Periodontal Disease”) 2019, Elsevier. D) Schematic representation of the surface for the ZNO nanofilm with incorporation of Au nanoparticles, the ZnO-based gas sensor and Au NPs-decorated ZnO-based gas sensor. Reproduced with permission (Bae et al.102) 2022, Elsevier. | ||
The research by Bae et al.102 describes the creation of self-perceived periodontal illness sensors at the nanometric scale by mixing zinc oxide nanofilms and gold nanoparticles. (Fig. 3D) These sensors are designed to make it easy for individuals to keep track of their personal periodontal (gum) health. Zinc oxide nanofilms and gold nanoparticles are important components that are used to identify particular biomarkers linked with PD. The sensors are made to be extremely sensitive and selective, allowing them to detect early signs of gum disease. This technology has the potential to provide non-invasive and easy-to-use oral health monitoring.
6. Future trends
A. Transferring diagnostic insights: lessons from diabetes for PD diagnosis
PD and diabetes both share a two-way street relationship. Just as your oral health can influence your blood glucose levels, your blood glucose levels can also impact the condition of your gums. Because of this intricate interplay, we present some fascinating evolutions of diagnostic technologies in diabetes and explore how the lessons learned in diabetes diagnosis can potentially enhance our approach to diagnosing PD. The diagnosis of diabetes has evolved with time as technological advancements have completely changed the field. The original diabetes diagnostic technologies focused mostly on detecting glucose in urine in the early twentieth century.115 Basic chemical tests that entailed mixing urine with reactive chemicals to detect the presence of excess glucose, a sign of diabetes, were utilized by clinicians.116 In the 1970s, the development of blood glucose monitoring technologies constituted a watershed moment in the discipline. This groundbreaking technique enabled the direct detection of levels of glucose in the bloodstream, providing doctors with real-time data to monitor swings in glucose levels more accurately.117 Another key accomplishment was the incorporation of non-invasive and constant glucose monitoring devices. Miniaturized wearable gadgets that can continually monitor glucose levels without the need for repeated finger pricks are becoming more common. These devices use cutting-edge detecting innovations, such as optical detectors and enzyme-based electrochemical detectors, to provide diabetics and their medical professionals with an in-depth knowledge of their blood glucose profiles, allowing for more informed and proactive diabetes management.118 Further, recent advances in AI and data analysis dramatically impacted diabetes diagnosis.119 Algorithms based on machine learning and prediction120 models have been used to evaluate vast amounts of patient data, allowing for early detection of those at risk for developing diabetes and the implementation of individualized treatment plans suited to each patient's specific needs. Therefore, Identifying reliable biomarkers and risk factors can facilitate early screening for periodontal disease. Technological innovations such as AI algorithms and continuous monitoring devices used in diabetes management can be adapted to track oral health and predict periodontal disease risk. Additionally, leveraging multidisciplinary care teams and initiating studies with an emphasis on translational science can improve periodontal disease diagnosis and management. Adopting these strategies for diabetes care can lead to better diagnostic technologies in the case of PD.B. Challenges in PD diagnosis
With regard to PD, traditional techniques of diagnosing have mostly relied on clinical examination, which includes visual inspection, probing of periodontal pockets,121 and dental radiographs.122 While these approaches are still used to identify and classify PD,123 their dependence on subjective assessment and limits in capturing the entire degree of disease development have posed considerable obstacles. Although significant breakthroughs have been made, such as incorporating digital radiography124 and applying computer-aided measures for measuring the bone resorption and periodontal pocket depth, these innovations have not fundamentally revolutionized the diagnostic paradigm. The absence of significant advances in non-invasive, preliminary identification technologies has hampered the capacity to diagnose periodontitis in its early stages, limiting the possibility of prompt intervention and preventative treatments. Periodontitis diagnosis has not yet benefited from the same level of technical advancement. While research into periodontal biomarkers125 and genetic vulnerability has revealed promising possibilities for early detection and risk evaluation, translating these results into clinical procedures has been fairly restricted, resulting in a continuing disconnect between technological research and patient care.126 Recently, U.S. Food and Drug Administration has approved two AI-based medical devices, Videa Perio Assist127 and Adravision Perio,128 for better diagnosis of PD. In addition, using sophisticated imaging modalities such as cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT)129 and 3D imaging130 has demonstrated some promise in giving a more thorough examination of periodontal structures.131 However, the accessibility and expense of these technologies have created substantial hurdles to general adoption, limiting their value in ordinary clinical practice and their influence on enhancing early detection and therapeutic planning for periodontitis.C. Role of engineering innovation in periodontal diagnosis
Engineering innovation, interdisciplinary collaboration, and low-cost development are the major building blocks in POC development for PD diagnosis. Establishing a synergy between basic biology and engineering is the need of the hour. This collaboration should focus more on i) developing tools that enable accuracy and sensitivity, ii) identifying specific biomarkers, iii) working on miniaturization of devices as per the patient needs, low-cost manufacturing, longitudinal monitoring, machine learning, and real-time data analysis, regulatory approval, and standardization. (Fig. 4).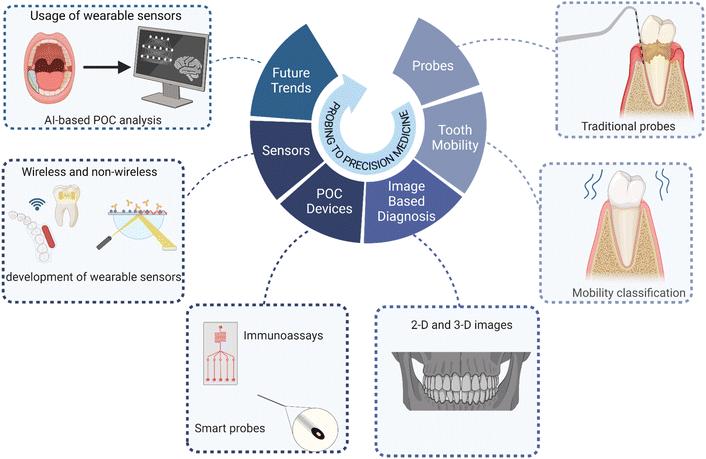 | ||
| Fig. 4 Evolution of diagnostic technology in PD: from clinical probing to precision medicine. Created with https://www.BioRender.com. | ||
In addition, recent advances in bioengineering, like nanoparticles, can revolutionize the area of diagnosis as they will enable the development of sensors that can detect biomarkers associated with PD and provide real-time data for diagnosis and monitoring.
7. Conclusion
In conclusion, this review highlights the characteristics and progression of PD, clinical treatment methods, specific biomarkers and pathogens that can be used to diagnose PD, biomedical sensors, and POC devices that have been developed to diagnose PD stage and progression profile while predicting the future works related to this field. Combining engineering with disease diagnosis and progression has many benefits since many people worldwide experience some form of PD; thus, identifying the stage of PD is essential for proper analysis and choosing the correct treatment pathway. Sensors have the potential to be the next step in clinical applications for PD diagnosis as they provide fast, real-time, cost-efficient, high-accuracy, and highly sensitive results using biomarkers established by previous research. Examining different types of biomarkers in one sensor accurately establishes the stage of the disease, which physicians can use to treat the patients with more targeted treatments and POCs. Furthermore, the next advancements for diagnosing and treating PD would be providing patients with wearable wireless sensors that provide immediate results about their disease progression. Another aspect of these sensors is that they are not bound to be only used with PD; their working principle can also be used in many other diseases.Author contributions
Jayesh Korgaonkar: conceptualization, resources, writing – original draft; Azra Yaprak Tarman: conceptualization, writing – original draft, visualization; Hatice Koydemir: conceptualization, resources, writing – review & editing, supervision; Sasanka Chukkapalli: conceptualization, resources, writing – original draft, review & editing, supervision.Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.Acknowledgements
Hatice Ceylan Koydemir acknowledges the support of the Department of Biomedical Engineering of Texas A&M University, the Texas A&M Engineering Experiment Station, and NSF-funded ERC PATHS-UP (Award No. 1648451).Notes and references
- Global oral health status report: towards universal health coverage for oral health by 2030 [Internet] [cited 2023 Dec 15], Available from: https://www.who.int/publications-detail-redirect/9789240061484.
- P. I. Eke, B. A. Dye, L. Wei, G. O. Thornton-Evans, R. J. Genco, J. Beck, G. Douglass and R. Page, Prevalence of periodontitis in adults in the United States: 2009 and 2010, J. Dent. Res., 2012, 91(10), 914–920 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Beeby, MEMS Mechanical Sensors, Artech House, 2004, p. 282 Search PubMed.
- S. Patel, H. Park, P. Bonato, L. Chan and M. Rodgers, A review of wearable sensors and systems with application in rehabilitation, J. Neuroeng. Rehabil., 2012, 9(1), 21 CrossRef PubMed.
- H. C. Koydemir and A. Ozcan, Wearable and Implantable Sensors for Biomedical Applications, Annu. Rev. Anal. Chem., 2018, 11(1), 127–146 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- W. Xu and H. C. Koydemir, Non-invasive biomedical sensors for early detection and monitoring of bacterial biofilm growth at the point of care, Lab Chip, 2022, 22(24), 4758–4773 RSC.
- I. I. Bogoch, H. C. Koydemir, D. Tseng, R. K. D. Ephraim, E. Duah and J. Tee, et al., Evaluation of a Mobile Phone-Based Microscope for Screening of Schistosoma haematobium Infection in Rural Ghana, Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg., 2017, 96(6), 1468 CrossRef PubMed.
- H. Wang, H. Ceylan Koydemir, Y. Qiu, B. Bai, Y. Zhang and Y. Jin, et al., Early detection and classification of live bacteria using time-lapse coherent imaging and deep learning, Light: Sci. Appl., 2020, 9(1), 118 CrossRef PubMed.
- T. Liu, Y. Li, H. C. Koydemir, Y. Zhang, E. Yang and M. Eryilmaz, et al., Rapid and stain-free quantification of viral plaque via lens-free holography and deep learning, Nat. Biomed. Eng., 2023, 7(8), 1040–1052 CrossRef PubMed.
- E. Istif, H. Mirzajani, Ç. Dağ, F. Mirlou, E. Y. Ozuaciksoz and C. Cakır, et al., Miniaturized wireless sensor enables real-time monitoring of food spoilage, Nat. Food, 2023, 4(5), 427–436 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Li, S. K. Cushing and N. Wu, Plasmon-enhanced optical sensors: a review, Analyst, 2015, 140(2), 386–406 RSC.
- M. Labib, E. H. Sargent and S. O. Kelley, Electrochemical Methods for the Analysis of Clinically Relevant Biomolecules, Chem. Rev., 2016, 116(16), 9001–9090 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Wang, Electrochemical Glucose Biosensors, Chem. Rev., 2008, 108(2), 814–825 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- N. Pamme, Magnetism and microfluidics, Lab Chip, 2006, 6(1), 24–38 RSC.
- R. J. Lamont, H. Koo and G. Hajishengallis, The oral microbiota: dynamic communities and host interactions, Nat. Rev. Microbiol., 2018, 16(12), 745–759 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Cekici, A. Kantarci, H. Hasturk and T. E. Van Dyke, Inflammatory and immune pathways in the pathogenesis of periodontal disease, Periodontol. 2000, 2014, 64(1), 57–80 CrossRef PubMed.
- G. Hajishengallis and R. J. Lamont, Polymicrobial communities in periodontal disease: Their quasi-organismal nature and dialogue with the host, Periodontol. 2000, 2021, 86(1), 210–230 CrossRef PubMed.
- G. Hajishengallis and R. J. Lamont, Beyond the red complex and into more complexity: the polymicrobial synergy and dysbiosis (PSD) model of periodontal disease etiology, Mol. Oral Microbiol., 2012, 27(6), 409–419 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- E. Könönen, M. Gursoy and U. K. Gursoy, Periodontitis: A Multifaceted Disease of Tooth-Supporting Tissues, J. Clin. Med., 2019, 8(8), 1135 CrossRef PubMed.
- M. S. Tonetti, H. Greenwell and K. S. Kornman, Staging and grading of periodontitis: Framework and proposal of a new classification and case definition, J. Periodontol., 2018, 89(S1), S159–S172 CrossRef PubMed.
- M. Taba, J. Kinney, A. S. Kim and W. V. Giannobile, Diagnostic Biomarkers for Oral and Periodontal Diseases, Dent. Clin. North Am., 2005, 49(3), 551–571 CrossRef PubMed.
- W. V. Giannobile, T. M. Braun, A. K. Caplis, L. Doucette-Stamm, G. W. Duff and K. S. Kornman, Patient stratification for preventive care in dentistry, J. Dent. Res., 2013, 92(8), 694–701 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. S. Tonetti, H. Greenwell and K. S. Kornman, Staging and grading of periodontitis: Framework and proposal of a new classification and case definition, J. Periodontol., 2018, 89(Suppl 1), S159–S172 Search PubMed.
- G. Greenstein, Contemporary interpretation of probing depth assessments: diagnostic and therapeutic implications, A literature review, J. Periodontol., 1997, 68(12), 1194–1205 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. S. Lee, Y. S. Jeon, F. J. Strauss, H. I. Jung and R. Gruber, Digital scanning is more accurate than using a periodontal probe to measure the keratinized tissue width, Sci. Rep., 2020, 10(1), 3665 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. H. Gibbs, J. W. Hirschfeld, J. G. Lee, S. B. Low, I. Magnusson and R. R. Thousand, et al., Description and clinical evaluation of a new computerized periodontal probe-the Florida Probe, J. Clin. Periodontol., 1988, 15(2), 137–144 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- N. P. Lang, A. Joss, T. Orsanic, F. A. Gusberti and B. E. Siegrist, Bleeding on probing., A predictor for the progression of periodontal disease?, J. Clin. Periodontol., 1986, 13, 590–596 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Giargia and J. Lindhe, Tooth mobility and periodontal disease, J. Clin. Periodontol., 1997, 24(11), 785–795 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- V. Machado, L. Proença, M. Morgado, J. J. Mendes and J. Botelho, Accuracy of Panoramic Radiograph for Diagnosing Periodontitis Comparing to Clinical Examination, J. Clin. Med., 2020, 9(7), 2313 CrossRef PubMed.
- T. J. Ko, K. M. Byrd and S. A. Kim, The Chairside Periodontal Diagnostic Toolkit: Past, Present, and Future, Diagnostics, 2021, 11(6), 932 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- B. D. Frodge, J. L. Ebersole, R. J. Kryscio, M. V. Thomas and C. S. Miller, Bone Remodeling Biomarkers of Periodontal Disease in Saliva, J. Periodontol., 2008, 79(10), 1913–1919 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. Vernal, N. Dutzan, M. Hernández, S. Chandía, J. Puente and R. León, et al., High Expression Levels of Receptor Activator of Nuclear Factor-Kappa B Ligand Associated With Human Chronic Periodontitis Are Mainly Secreted by CD4+ T Lymphocytes, J. Periodontol., 2006, 77(10), 1772–1780 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Delatola, B. G. Loos and M. L. Laine, Three periodontitis phenotypes: Bone loss patterns, antibiotic-surgical treatment and the new classification, J. Clin. Periodontol., 2020, 47(11), 1371–1378 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Sanz, D. Herrera, M. Kebschull, I. Chapple, S. Jepsen and T. Beglundh, et al., Treatment of stage I-III periodontitis-The EFP S3 level clinical practice guideline, J. Clin. Periodontol., 2020, 47(Suppl 22), 4–60 CrossRef PubMed.
- A. J. van Winkelhoff, T. E. Rams and J. Slots, Systemic antibiotic therapy in periodontics, Periodontol. 2000, 1996, 10, 45–78 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- G. N. Belibasakis and N. Bostanci, The RANKL-OPG system in clinical periodontology, J. Clin. Periodontol., 2012, 39(3), 239–248 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- B. Chen, W. Wu, W. Sun, Q. Zhang, F. Yan and Y. Xiao, RANKL Expression in Periodontal Disease: Where Does RANKL Come from?, BioMed Res. Int., 2014, 2014, e731039 Search PubMed.
- L. M. Golub and H. M. Lee, Periodontal therapeutics: Current host-modulation agents and future directions, Periodontol. 2000, 2020, 82(1), 186–204 CrossRef PubMed.
- Biomarkers Definitions Working Group, Biomarkers and surrogate endpoints: preferred definitions and conceptual framework, Clin. Pharmacol. Ther., 2001, 69(3), 89–95 CrossRef PubMed.
- S. Tsuchida, M. Satoh, H. Umemura, K. Sogawa, Y. Kawashima and S. Kado, et al., Proteomic analysis of gingival crevicular fluid for discovery of novel periodontal disease markers, Proteomics, 2012, 12(13), 2190–2202 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Gingivitis – an overview|ScienceDirect Topics [Internet] [cited 2023 Nov 5], Available from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/medicine-and-dentistry/gingivitis.
- Biopsy – an overview|ScienceDirect Topics [Internet] [cited 2023 Nov 5], Available from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/medicine-and-dentistry/biopsy.
- D. L. Korte and J. Kinney, Personalized medicine: an update of salivary biomarkers for periodontal diseases, Periodontol. 2000, 2016, 70(1), 26–37 CrossRef PubMed.
- M. A. R. Buzalaf, A. d. C. Ortiz, T. S. Carvalho, S. O. M. Fideles, T. T. Araújo and S. M. Moraes, et al., Saliva as a diagnostic tool for dental caries, periodontal disease and cancer: is there a need for more biomarkers?, Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn., 2020, 20(5), 543–555 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. U. Chaudhari, G. N. Byakod, P. F. Waghmare and V. M. Karhadkar, Correlation of levels of interleukin-1β in gingival crevicular fluid to the clinical parameters of chronic periodontitis, J. Contemp. Dent. Pract., 2011, 12(1), 52–59 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. P. Engebretson, J. T. Grbic, R. Singer and I. B. Lamster, GCF IL-1beta profiles in periodontal disease, J. Clin. Periodontol., 2002, 29(1), 48–53 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. P. Costa, G. L. Trevisan, G. O. Macedo, D. B. Palioto, S. L. S. Souza and M. F. M. Grisi, et al., Salivary interleukin-6, matrix metalloproteinase-8, and osteoprotegerin in patients with periodontitis and diabetes, J. Periodontol., 2010, 81(3), 384–391 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Al-Sabbagh, A. Alladah, Y. Lin, R. J. Kryscio, M. V. Thomas and J. L. Ebersole, et al., Bone remodeling-associated salivary biomarker MIP-1α distinguishes periodontal disease from health, J. Periodontal Res., 2012, 47(3), 389–395 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- U. K. Gursoy, E. Könönen, P. Pradhan-Palikhe, T. Tervahartiala, P. J. Pussinen and L. Suominen-Taipale, et al., Salivary MMP-8, TIMP-1, and ICTP as markers of advanced periodontitis, J. Clin. Periodontol., 2010, 37(6), 487–493 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. A. Chambers, J. M. Crawford, S. Mukherjee and R. L. Cohen, Aspartate aminotransferase increases in crevicular fluid during experimental periodontitis in beagle dogs, J. Periodontol., 1984, 55(9), 526–530 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. S. Miller, J. D. Foley, A. L. Bailey, C. L. Campell, R. L. Humphries and N. Christodoulides, et al., Current developments in salivary diagnostics, Biomarkers Med., 2010, 4(1), 171–189 CrossRef PubMed.
- C. S. Miller, C. P. King, M. C. Langub, R. J. Kryscio and M. V. Thomas, Salivary biomarkers of existing periodontal disease: A cross-sectional study, J. Am. Dent. Assoc., JADA, 2006, 137(3), 322–329 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- W. M. Sexton, Y. Lin, R. J. Kryscio, D. R. Dawson, J. L. Ebersole and C. S. Miller, Salivary Biomarkers of Periodontal Disease in Response to Treatment, J. Clin. Periodontol., 2011, 38(5), 434–441 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. S. Kohli and V. S. Kohli, Role of RANKL-RANK/osteoprotegerin molecular complex in bone remodeling and its immunopathologic implications, Indian J. Endocrinol. Metab., 2011, 15(3), 175–181 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. C. Tamashunas, A. Katiyar, Q. Zhang, P. Purkayastha, P. K. Singh and S. S. Chukkapalli, et al., Osteoprotegerin is sensitive to actomyosin tension in human periodontal ligament fibroblasts, J. Cell. Physiol., 2021, 236(8), 5715–5724 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. Cheng, Z. Wu, M. Li, M. Shao and T. Hu, Interleukin-1β is a potential therapeutic target for periodontitis: a narrative review, Int. J. Oral Sci., 2020, 12(1), 2 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. Trieu-Cuot, C. Poyart-Salmeron, C. Carlier and P. Courvalin, Nucleotide sequence of the erythromycin resistance gene of the conjugative transposon Tn1545, Nucleic Acids Res., 1990, 18(12), 3660 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Y. Kim, K. R. Kim and H. N. Kim, The Potential Impact of Salivary IL-1 on the Diagnosis of Periodontal Disease: A Pilot Study, Healthcare, 2021, 9(6), 729 CrossRef PubMed.
- The role of IL-6 in the pathogenesis of periodontal disease – Irwin – 1998 – Oral Diseases – Wiley Online Library [Internet] [cited 2023 Nov 5], Available from: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/j.1601-0825.1998.tb00255.x.
- K. Naruishi and T. Nagata, Biological effects of interleukin-6 on Gingival Fibroblasts: Cytokine regulation in periodontitis, J. Cell. Physiol., 2018, 233(9), 6393–6400 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Rose-John, K. Winthrop and L. Calabrese, The role of IL-6 in host defence against infections: immunobiology and clinical implications, Nat. Rev. Rheumatol., 2017, 13(7), 399–409 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Geivelis, D. W. Turner, E. D. Pederson and B. L. Lamberts, Measurements of Interleukin-6 in Gingival Crevicular Fluid From Adults With Destructive Periodontal Disease, J. Periodontol., 1993, 64(10), 980–983 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Macrophage Inflammatory Protein-1 Alpha (MIP-1 alpha)/CCL3: As a Biomarker|SpringerLink [Internet] [cited 2023 Nov 5], Available from: https://link.springer.com/referenceworkentry/10.1007/978-94-007-7696-8_27.
- C. L. de Lima, A. C. Acevedo, D. C. Grisi, M. Taba Jr, E. Guerra and G. De Luca Canto, Host-derived salivary biomarkers in diagnosing periodontal disease: systematic review and meta-analysis, J. Clin. Periodontol., 2016, 43(6), 492–502 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. J. Nisha, A. Suresh, A. Anilkumar and S. Padmanabhan, MIP-1α and MCP-1 as salivary biomarkers in periodontal disease, Saudi Dent. J., 2018, 30(4), 292–298 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. I. Jang, A. H. Lee, H. Y. Shin, H. R. Song, J. H. Park and T. B. Kang, et al., The Role of Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha (TNF-α) in Autoimmune Disease and Current TNF-α Inhibitors in Therapeutics, Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2021, 22(5), 2719 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. T. Steeve, P. Marc, T. Sandrine, H. Dominique and F. Yannick, IL-6, RANKL, TNF-alpha/IL-1: interrelations in bone resorption pathophysiology, Cytokine Growth Factor Rev., 2004, 15(1), 49–60 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- N. S. Romero-Castro, M. Vázquez-Villamar, J. F. Muñoz-Valle, S. Reyes-Fernández, V. O. Serna-Radilla and S. García-Arellano, et al., Relationship between TNF-α, MMP-8, and MMP-9 levels in gingival crevicular fluid and the subgingival microbiota in periodontal disease, Odontology, 2020, 108(1), 25–33 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- I. Luchian, A. Goriuc, D. Sandu and M. Covasa, The Role of Matrix Metalloproteinases (MMP-8, MMP-9, MMP-13) in Periodontal and Peri-Implant Pathological Processes, Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2022, 23(3), 1806 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- G. Sapna, S. Gokul and K. Bagri-Manjrekar, Matrix metalloproteinases and periodontal diseases, Oral Dis., 2014, 20(6), 538–550 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. F. Kinane, P. G. Stathopoulou and P. N. Papapanou, Periodontal diseases, Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers, 2017, 3(1), 1–14 Search PubMed.
- A. D. Aulbach and C. J. Amuzie, Biomarkers in Nonclinical Drug Development, in A Comprehensive Guide to Toxicology in Nonclinical Drug Development [Internet], ed. A. S. Faqi, Academic Press, Boston, 2nd edn, 2017, ch. 17, pp. 447–471, Available from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780128036204000177 Search PubMed.
- T. S. Sheth and S. J. Verma, Analysis of aspartate aminotransferase in gingival crevicular fluid: A study with initial therapy, J. Indian Soc. Periodontol., 2011, 15(3), 235–239 CrossRef PubMed.
- G. R. Persson, T. A. DeRouen and R. C. Page, Relationship between levels of aspartate aminotransferase in gingival crevicular fluid and gingival inflammation, J. Periodontal Res., 1990, 25(1), 17–24 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- N. Rasaei, A. Ghadiri, M. Peighan, A. Rekabi and N. Atashkar, Evaluation of alkaline phosphatase in gingival crevicular fluid and saliva of patients with periodontitis and healthy individuals, J. Family Med. Prim. Care, 2022, 11(11), 6983–6987 CrossRef PubMed.
- P. Koppolu, S. Sirisha, A. Mishra, K. Deshpande, A. S. Lingam and D. H. Alotaibi, et al., Alkaline phosphatase and acid phosphatase levels in saliva and serum of patients with healthy periodontium, gingivitis, and periodontitis before and after scaling with root planing: A clinico-biochemical study, Saudi J. Biol. Sci., 2021, 28(1), 380–385 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. Bullon, L. Chandler, J. J. Segura Egea, R. Perez Cano and A. Martinez Sahuquillo, Osteocalcin in serum, saliva and gingival crevicular fluid: their relation with periodontal treatment outcome in postmenopausal women, Med. Oral Patol. Oral Cir. Bucal., 2007, 12(3), E193–E197 Search PubMed.
- K. Kunimatsu, S. Mataki, H. Tanaka, N. Mine, M. Kiyoki and K. Hosoda, et al., A cross-sectional study on osteocalcin levels in gingival crevicular fluid from periodontal patients, J. Periodontol., 1993, 64(9), 865–869 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Kido, T. Nakamura, Y. Asahara, T. Sawa, K. Kohri and T. Nagata, Osteopontin in gingival crevicular fluid, J. Periodontal Res., 2001, 36(5), 328–333 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. G. D. Sharma and A. R. Pradeep, Gingival crevicular fluid osteopontin levels in periodontal health and disease, J. Periodontol., 2006, 77(10), 1674–1680 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. D. Palys, A. D. Haffajee, S. S. Socransky and W. V. Giannobile, Relationship between C-telopeptide pyridinoline cross-links (ICTP) and putative periodontal pathogens in periodontitis, J. Clin. Periodontol., 1998, 25(11 Pt 1), 865–871 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. M. Golub, H. M. Lee, R. A. Greenwald, M. E. Ryan, T. Sorsa and T. Salo, et al., A matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor reduces bone-type collagen degradation fragments and specific collagenases in gingival crevicular fluid during adult periodontitis, Inflamm. Res. Off. J. Eur. Histamine Res. Soc. Al., 1997, 46(8), 310–319 CAS.
- W. V. Giannobile, K. F. Al-Shammari and D. P. Sarment, Matrix molecules and growth factors as indicators of periodontal disease activity, Periodontol. 2000, 2003, 31, 125–134 CrossRef PubMed.
- B. D. Frodge, J. L. Ebersole, R. J. Kryscio, M. V. Thomas and C. S. Miller, Bone Remodeling Biomarkers of Periodontal Disease in Saliva, J. Periodontol., 2008, 79(10), 1913–1919 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. Han, P. M. Bartold, C. Salomon and S. Ivanovski, Salivary Outer Membrane Vesicles and DNA Methylation of Small Extracellular Vesicles as Biomarkers for Periodontal Status: A Pilot Study, Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2021, 22(5), 2423 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. Hirai, T. Yamaguchi-Tomikawa, T. Eguchi, H. Maeda and S. Takashiba, Identification and Modification of Porphyromonas gingivalis Cysteine Protease, Gingipain, Ideal for Screening Periodontitis, Front. Immunol., 2020, 11, 1017 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Damgaard, A. K. Danielsen, C. Enevold, L. Massarenti, C. H. Nielsen and P. Holmstrup, et al., Porphyromonas gingivalis in saliva associates with chronic and aggressive periodontitis, J. Oral Microbiol., 2019, 11(1), 1653123 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. S. Na, S. Y. Kim, H. Han, H. J. Kim, J. Y. Lee and J. H. Lee, et al., Identification of Potential Oral Microbial Biomarkers for the Diagnosis of Periodontitis, J. Clin. Med., 2020, 9(5), 1549 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Z. Nazar Majeed, K. Philip, A. M. Alabsi, S. Pushparajan and D. Swaminathan, Identification of Gingival Crevicular Fluid Sampling, Analytical Methods, and Oral Biomarkers for the Diagnosis and Monitoring of Periodontal Diseases: A Systematic Review, Dis. Markers, 2016, 2016, e1804727 Search PubMed.
- S. Becerik, V. Ö. Öztürk, H. Atmaca, G. Atilla and G. Emingil, Gingival Crevicular Fluid and Plasma Acute-Phase Cytokine Levels in Different Periodontal Diseases, J. Periodontol., 2012, 83(10), 1304–1313 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- B. Afacan, V. Ö. Öztürk, Ç. Paşalı, E. Bozkurt, T. Köse and G. Emingil, Gingival crevicular fluid and salivary HIF-1α, VEGF, and TNF-α levels in periodontal health and disease, J. Periodontol., 2019, 90(7), 788–797 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Khalaf, J. Lönn and T. Bengtsson, Cytokines and chemokines are differentially expressed in patients with periodontitis: possible role for TGF-β1 as a marker for disease progression, Cytokine+, 2014, 67(1), 29–35 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- N. Bostanci, W. Heywood, K. Mills, M. Parkar, L. Nibali and N. Donos, Application of label-free absolute quantitative proteomics in human gingival crevicular fluid by LC/MS E (gingival exudatome), J. Proteome Res., 2010, 9(5), 2191–2199 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- N. Silva, N. Dutzan, M. Hernandez, A. Dezerega, O. Rivera and J. C. Aguillon, et al., Characterization of progressive periodontal lesions in chronic periodontitis patients: levels of chemokines, cytokines, matrix metalloproteinase-13, periodontal pathogens and inflammatory cells, J. Clin. Periodontol., 2008, 35(3), 206–214 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. G. Palcanis, I. K. Lariava, B. R. Wells, K. A. Suggs, J. R. Landis and D. E. Chadwick, et al., Elastase as an Indicator of Periodontal Disease Progression, J. Periodontol., 1992, 63(4), 237–242 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. S. Kinney, T. Morelli, M. Oh, T. M. Braun, C. A. Ramseier and J. V. Sugai, et al., Crevicular fluid biomarkers and periodontal disease progression, J. Clin. Periodontol., 2014, 41(2), 113–120 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. C. Baliban, D. Sakellari, Z. Li, Y. A. Guzman, B. A. Garcia and C. A. Floudas, Discovery of biomarker combinations that predict periodontal health or disease with high accuracy from GCF samples based on high-throughput proteomic analysis and mixed-integer linear optimization, J. Clin. Periodontol., 2013, 40(2), 131–139 CrossRef PubMed.
- L. F. de Castro, S. V. de Freitas, L. C. Duarte, J. A. C. de Souza, T. R. L. C. Paixão and W. K. T. Coltro, Salivary diagnostics on paper microfluidic devices and their use as wearable sensors for glucose monitoring, Anal. Bioanal. Chem., 2019, 411(19), 4919–4928 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- N. Rathnayake, D. R. Gieselmann, A. M. Heikkinen, T. Tervahartiala and T. Sorsa, Salivary Diagnostics—Point-of-Care diagnostics of MMP-8 in dentistry and medicine, Diagnostics, 2017, 7(1), 7 CrossRef PubMed.
- S. Wignarajah, G. A. R. Y. Suaifan, S. Bizzarro, F. J. Bikker, W. E. Kaman and M. Zourob, Colorimetric Assay for the Detection of Typical Biomarkers for Periodontitis Using a Magnetic Nanoparticle Biosensor, Anal. Chem., 2015, 87(24), 12161–12168 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- B. H. Lee, S. H. Kim, Y. Ko, J. C. Park, S. Ji and M. B. Gu, The sensitive detection of ODAM by using sandwich-type biosensors with a cognate pair of aptamers for the early diagnosis of periodontal disease, Biosens. Bioelectron., 2019, 126, 122–128 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- G. Bae, M. Kim, A. Lee, S. Ji, M. Jang and S. Yim, et al., Nanometric lamination of zinc oxide nanofilms with gold nanoparticles for self-perceived periodontal disease sensors, Composites, Part B, 2022, 230, 109490 CrossRef CAS.
- E. H. Yee, S. Lathwal, P. P. Shah and H. D. Sikes, Detection of Biomarkers of Periodontal Disease in Human Saliva Using Stabilized, Vertical Flow Immunoassays, ACS Sens., 2017, 2(11), 1589–1593 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. E. Herr, A. V. Hatch, D. J. Throckmorton, H. M. Tran, J. S. Brennan and W. V. Giannobile, et al., Microfluidic immunoassays as rapid saliva-based clinical diagnostics, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2007, 104(13), 5268–5273 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. T. V. Kung, B. Ochs and J. M. Goodson, Temperature as a periodontal diagnostic, J. Clin. Periodontol., 1990, 17(8), 557–563 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. S. Mannoor, H. Tao, J. D. Clayton, A. Sengupta, D. L. Kaplan and R. R. Naik, et al., Graphene-based wireless bacteria detection on tooth enamel, Nat. Commun., 2012, 3(1), 763 CrossRef PubMed.
- T. Arakawa, Y. Kuroki, H. Nitta, P. Chouhan, K. Toma and S.-I. Sawada, et al., Mouthguard biosensor with telemetry system for monitoring of saliva glucose: A novel cavitas sensor, Biosens. Bioelectron., 2016, 84, 106–111 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. García-Carmona, A. Martín, J. R. Sempionatto, J. R. Moreto, M. C. González and J. Wang, et al., Pacifier Biosensor: Toward Noninvasive Saliva Biomarker Monitoring, Anal. Chem., 2019, 91(21), 13883–13891 CrossRef PubMed.
- J. Kim, S. Imani, W. R. de Araujo, J. Warchall, G. Valdés-Ramírez and T. R. L. C. Paixão, et al., Wearable salivary uric acid mouthguard biosensor with integrated wireless electronics, Biosens. Bioelectron., 2015, 74, 1061–1068 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Joe, B. H. Lee, S. H. Kim, Y. Ko and M. B. Gu, Aptamer duo-based portable electrochemical biosensors for early diagnosis of periodontal disease, Biosens. Bioelectron., 2022, 199, 113884 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. Hix-Janssens, S. Shinde, R. Abouhany, J. Davies, J. Neilands and G. Svensäter, et al., Microcontact-Imprinted Optical Sensors for Virulence Factors of Periodontal Disease, ACS Omega, 2023, 8(17), 15259–15265 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- E. E. Totu, I. Isildak, A. C. Nechifor, C. M. Cristache and M. Enachescu, New sensor based on membranes with magnetic nano-inclusions for early diagnosis in periodontal disease, Biosens. Bioelectron., 2018, 102, 336–344 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- B. H. Lee, S. H. Kim, Y. Ko, J. C. Park, S. Ji and M. B. Gu, The sensitive detection of ODAM by using sandwich-type biosensors with a cognate pair of aptamers for the early diagnosis of periodontal disease, Biosens. Bioelectron., 2019, 126, 122–128 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- W. Hong and W. Gu Lee, Wearable sensors for continuous oral cavity and dietary monitoring toward personalized healthcare and digital medicine, Analyst, 2020, 145(24), 7796–7808 RSC.
- R. B. Tattersall, The History of Diabetes Mellitus, in Textbook of Diabetes [Internet], John Wiley & Sons, Ltd, 2017, pp. 1–22, Available from: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/9781118924853.ch1 Search PubMed.
- A. H. Free and H. M. Free, Urinalysis, Critical Discipline of Clinical Science, Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci., 1972, 3(4), 481–531 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. F. Clarke and J. R. Foster, A history of blood glucose meters and their role in self-monitoring of diabetes mellitus, Br. J. Biomed. Sci., 2012, 69(2), 83–93 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Tricoli, N. Nasiri and S. De, Wearable and Miniaturized Sensor Technologies for Personalized and Preventive Medicine, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2017, 27(15), 1605271 CrossRef.
- M. Vettoretti, G. Cappon, A. Facchinetti and G. Sparacino, Advanced Diabetes Management Using Artificial Intelligence and Continuous Glucose Monitoring Sensors, Sensors, 2020, 20(14), 3870 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Nomura, M. Noguchi, M. Kometani, K. Furukawa and T. Yoneda, Artificial Intelligence in Current Diabetes Management and Prediction, Curr. Diabetes Rep., 2021, 21(12), 61 CrossRef PubMed.
- S. S. Ramachandra, D. Mehta, N. Sandesh, V. Baliga and J. Amarnath, Periodontal probing systems: a review of available equipment, Compend. Contin. Educ. Dent., 2011, 32(2), 71–77 Search PubMed.
- M. S. Reddy, Radiographic Methods in the Evaluation of Periodontal Therapy, J. Periodontol., 1992, 63(12S), 1078–1084 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Tugnait, V. Clerehugh and P. N. Hirschmann, The usefulness of radiographs in diagnosis and management of periodontal diseases: a review, J. Dent., 2000, 28(4), 219–226 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. G. Gröndahl, K. Gröndahl and R. L. Webber, A digital subtraction technique for dental radiography, Oral Surg., Oral Med., Oral Pathol., 1983, 55(1), 96–102 CrossRef PubMed.
- S. Reddy, S. Kaul, M. G. S. Prasad, J. Agnihotri, H. G. Asutkar and N. Bhowmik, Biomarkers In Periodontal Diagnosis: “What The Future Holds…”, International Journal of Clinical Dental Science, 2011, 2(1), 76–83 Search PubMed.
- W. He, M. You, W. Wan, F. Xu, F. Li and A. Li, Point-of-Care Periodontitis Testing: Biomarkers, Current Technologies, and Perspectives, Trends Biotechnol., 2018, 36(11), 1127–1144 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- 510(k) Premarket Notification [Internet] [cited 2024 May 27], Available from: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cdrh/cfdocs/cfpmn/pmn.cfm?ID=K223296.
- 510(k) Premarket Notification [Internet] [cited 2024 May 27], Available from: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cdrh/cfdocs/cfpmn/pmn.cfm?ID=K232440.
- Use of cone beam computed tomography in periodontology – PMC [Internet] [cited 2023 Dec 18], Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4037540/.
- R. Mohan, A. Singh and M. Gundappa, Three-dimensional imaging in periodontal diagnosis - Utilization of cone beam computed tomography, J. Indian Soc. Periodontol., 2011, 15(1), 11–17 CrossRef PubMed.
- R. Chifor, A. F. Badea, I. Chifor, D. A. Mitrea, M. Crisan and M. E. Badea, Periodontal evaluation using a non-invasive imaging method (ultrasonography), Med. Pharm. Rep., 2019, 92(Suppl 3), S20–S32 Search PubMed.
- S. Ramani, R. Vijayalakshmi, J. Mahendra, C. B. NalinaKumari and N. Ravi, Artificial intelligence in periodontics – An overview, IP Int. J. Periodontol. Implantol., 2023, 8(2), 71–74 CrossRef.
- E. H. Kim, S. Kim, H. J. Kim, H.-O. Jeong, J. Lee and J. Jang, et al., Prediction of Chronic Periodontitis Severity Using Machine Learning Models Based On Salivary Bacterial Copy Number, Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol., 2020, 10, 1–13 CrossRef PubMed , Available from: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fcimb.2020.571515.
- V. L. Kouznetsova, J. Li, E. Romm and I. F. Tsigelny, Finding distinctions between oral cancer and periodontitis using saliva metabolites and machine learning, Oral Dis., 2021, 27(3), 484–493 CrossRef PubMed.
- T. Shan, F. R. Tay and L. Gu, Application of Artificial Intelligence in Dentistry, J. Dent. Res., 2021, 100(3), 232–244 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Patil, S. Albogami, J. Hosmani, S. Mujoo, M. A. Kamil and M. A. Mansour, et al., Artificial Intelligence in the Diagnosis of Oral Diseases: Applications and Pitfalls, Diagnostics, 2022, 12(5), 1029 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. C. Radha, B. S. Raghavendra, B. V. Subhash, J. Rajan and A. V. Narasimhadhan, Machine learning techniques for periodontitis and dental caries detection: A narrative review, Int. J. Med. Eng. Inf., 2023, 178, 105170 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Chang, M. F. Chang, N. Angelov, C. Y. Hsu, H. W. Meng and S. Sheng, et al., Application of deep machine learning for the radiographic diagnosis of periodontitis, Clin. Oral Investig., 2022, 26(11), 6629–6637 CrossRef PubMed.
- A. E. Herr, A. V. Hatch, W. V. Giannobile, D. J. Throckmorton, H. M. Tran and J. S. Brennan, et al., Integrated Microfluidic Platform for Oral Diagnostics, Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci., 2007, 1098(1), 362–374 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. M. Ardila, G. A. Jiménez-Arbeláez and A. M. Vivares-Builes, Potential Clinical Application of Organs-on-a-Chip in Periodontal Diseases: A Systematic Review of In Vitro Studies, Dent. J., 2023, 11(7), 158 CrossRef PubMed.
- L. Steigmann, S. Maekawa, C. Sima, S. Travan, C. W. Wang and W. V. Giannobile, Biosensor and Lab-on-a-chip Biomarker-identifying Technologies for Oral and Periodontal Diseases, Front. Pharmacol., 2020, 11, 1–18 CrossRef PubMed , Available from: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2020.588480.
- N. Christodoulides, P. N. Floriano, C. S. Miller, J. L. Ebersole, S. Mohanty and P. Dharshan, et al., Lab-on-a-Chip Methods for Point-of-Care Measurements of Salivary Biomarkers of Periodontitis, Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci., 2007, 1098(1), 411–428 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. M. França, A. Tahayeri, N. S. Rodrigues, S. Ferdosian, R. M. P. Rontani and G. Sereda, et al., The tooth on-a-chip: a microphysiologic model system mimicking the biologic interface of the tooth with biomaterials, Lab Chip, 2020, 20(2), 405–413 RSC.
- A. L. Gard, R. J. Luu, R. Maloney, M. H. Cooper, B. P. Cain and H. Azizgolshani, et al., A high-throughput, 28-day, microfluidic model of gingival tissue inflammation and recovery, Commun. Biol., 2023, 6(1), 1–12 CrossRef PubMed.
- P. Pataranutaporn, A. Jain, C. M. Johnson, P. Shah and P. Maes, Wearable Lab on Body: Combining Sensing of Biochemical and Digital Markers in a Wearable Device, in 2019 41st Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), 2019, pp. 3327–3332 Search PubMed.
- J. Andreu-Perez, D. R. Leff, H. M. D. Ip and G. Z. Yang, From Wearable Sensors to Smart Implants-–Toward Pervasive and Personalized Healthcare, IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng., 2015, 62(12), 2750–2762 Search PubMed.
- A. J. Furkart, S. B. Dove, W. D. McDavid, P. Nummikoski and S. Matteson, Direct digital radiography for the detection of periodontal bone lesions, Oral Surg., Oral Med., Oral Pathol., 1992, 74(5), 652–660 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Drolshagen, L. Keilig, I. Hasan, S. Reimann, J. Deschner and K. T. Brinkmann, et al., Development of a novel intraoral measurement device to determine the biomechanical characteristics of the human periodontal ligament, J. Biomech., 2011, 44(11), 2136–2143 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. L. Shen, C. L. Huang, Y. C. Lin, J. K. Du, F. L. Chen and Y. Kabasawa, et al., Effects of artificial intelligence-assisted dental monitoring intervention in patients with periodontitis: A randomized controlled trial, J. Clin. Periodontol., 2022, 49(10), 988–998 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- N. Bostanci and G. N. Belibasakis, Precision periodontal care: from omics discoveries to chairside diagnostics, Clin. Oral Investig., 2023, 27(3), 971–978 CrossRef PubMed.
- E. Pappa, E. Kousvelari and H. Vastardis, Saliva in the “Omics” era: A promising tool in paediatrics, Oral Dis., 2019, 25(1), 16–25 CrossRef PubMed.
- G. N. Güncü, D. Yilmaz, E. Könönen and U. K. Gürsoy, Salivary Antimicrobial Peptides in Early Detection of Periodontitis, Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol., 2015, 5, 1–6 Search PubMed , Available from: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fcimb.2015.00099.
- J. J. W. Mikkonen, S. P. Singh, M. Herrala, R. Lappalainen, S. Myllymaa and A. M. Kullaa, Salivary metabolomics in the diagnosis of oral cancer and periodontal diseases, J. Periodontal Res., 2016, 51(4), 431–437 CrossRef PubMed.
- S. Huang, T. He, F. Yue, V. Xu, S. Wang and P. Zhu, et al., Longitudinal multi-omics and microbiome meta-analysis identify an asymptotmatic gingival state that links gingivitis, periodontitis, and aging, mBio, 2021, 12(2), e03281-20 CrossRef PubMed.
- K. J. Califf, K. Schwarzberg-Lipson, N. Garg, S. M. Gibbons, J. G. Caporaso and J. Slots, et al., Multi-omics Analysis of Periodontal Pocket Microbial Communities Pre- and Posttreatment, mSystems, 2017, 2(3), 00016–00017 CrossRef PubMed.
- C. J. Seneviratne, T. Suriyanarayanan, A. S. Widyarman, L. S. Lee, M. Lau and J. Ching, et al., Multi-omics tools for studying microbial biofilms: current perspectives and future directions, Crit. Rev. Microbiol., 2020, 46(6), 759–778 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
Footnote |
| † Equally contributing authors. |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2024 |
