Imine-linked donor–acceptor metal–organic frameworks for an efficient photocatalytic oxidative coupling reaction†
Ri-Qin
Xia
 ,
Tian-E.
Zhang
,
Zhen-Na
Liu
,
Rong-Jia
Wei
,
Tian-E.
Zhang
,
Zhen-Na
Liu
,
Rong-Jia
Wei
 *,
Guo-Hong
Ning
*,
Guo-Hong
Ning
 * and
Dan
Li
* and
Dan
Li

College of Chemistry and Materials Science, Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Functional Supramolecular Coordination Materials and Applications, Jinan University, Guangzhou, Guangdong 510632, P. R. China. E-mail: rjwei@jnu.edu.cn; guohongning@jnu.edu.cn
First published on 15th November 2023
Abstract
Donor–acceptor metal–organic frameworks (D–A MOFs) are promising platforms for photocatalytic organic transformation and energy conversion due to their controllable chemical structures and tunable energy band gaps. Herein, we report two imine-linked D–A MOFs, namely JNM-18 and JNM-19, containing both Cu(I) cyclic trinuclear units (CTUs) as an electron acceptor (A) and triphenylbenzene (TPB) or hexaphenylbenzene (HPB) as an electron donor (D) synthesized by Schiff base condensations. With precise spatial distribution of donor and acceptor moieties within the two-dimensional (2D) networks, the obtained D–A MOFs exhibited efficient photocatalytic activity for the aerobic oxidation reaction of benzylamines upon irradiation with a violet LED. Interestingly, JNM-18 with planar TPB moieties showed better photo-electrochemical properties, and thus better photocatalytic performance than JNM-19 containing nonplanar HPB units with propeller arrangement which was possibly due to the stronger electron-donating abilities of the associated building units. This work illustrates a convenient approach to reticularly prepare D–A MOFs as photocatalysts by linkage of dynamic covalent bonds.
Introduction
Metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) constructed from metal ions/clusters and bridging ligands based on reticular chemistry are rapidly developing porous crystalline materials.1–3 Due to the high surface areas and well-defined nanopores, MOFs are highly attractive and have been broadly studied in many research fields such as guest sensing, energy storage, gas separation, and heterogeneous catalysis.4–8 In particular, donor–acceptor MOFs (D–A MOFs) with precise spatial distribution of donor and acceptor moieties are attractive platforms for photocatalyzed organic transformation and energy conversion due to their controllable chemical structures and tunable energy band gaps.9–11 Upon photo-irradiation, D–A MOFs can generate effectively separate electron–hole pairs that turn O2 into reactive oxygen species (ROS) which can be further used to initiate the photocatalyzed oxidative reaction.12,13 Although the photocatalyzed aerobic oxidation reactions have been widely explored using homogeneous catalysts of coordination complexes with noble metal ions in the past few decades, it is desired to develop non-noble-metal D–A MOFs as heterogeneous photocatalysts with high efficiency and recyclability.14–17Cyclic trinuclear units (CTUs) are a class of functional metal clusters with coordinatively unsaturated d10 metal ions showing unique properties such as luminescence, metallophilic attraction, π-acidity/basicity and catalytic properties.18,19 Recently, by combining the chemistry of MOFs and covalent organic frameworks (COFs),20 we and other groups have successfully synthesized various functional CTU-based MOFs linked by dynamic covalent bonds, which allows us to bring the merits from MOFs and COFs.21–29 Due to the built-in characteristics, CTU-based MOFs exhibit not only highly ordered structures and controllable porosities, but also unique catalytic activity for various organic transfer reactions.26–29 It has been found that Cu(I) CTUs exhibited an electron-deficient surface,30 which can be used as electron acceptor building blocks to construct D–A MOFs via dynamic covalent chemistry. We envision that the photocatalytic performance of Cu(I) CTU based MOFs can be boosted through fine-tuning of organic linkers with different electron-donating capacities.31
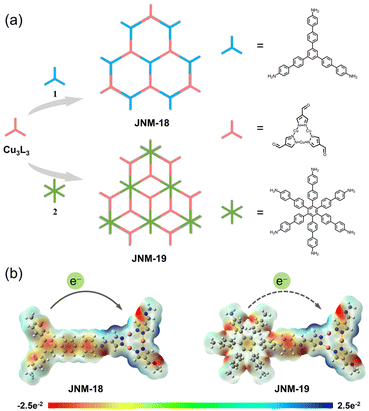
In this work, we report two imine-linked two-dimensional (2D) D–A MOFs, JNM-18 and JNM-19 (JNM = Jinan materials), which were reticularly constructed by Schiff base reactions between a carboxaldehyde functionalized Cu(I) CTU as an electron acceptor and triphenylbenzene (TPB)32,33 or hexaphenylbenzene (HPB)34,35 moieties as electron donors, respectively (Fig. 1a). The Cu(I) CTU-based MOFs showed similar imine-linked D–A pair structures yet different framework topologies due to the varied connecting number of the donor units. With the precise spatial distribution of donor and acceptor moieties in the skeleton, JNM-18 and JNM-19 delivered efficient photocatalytic activity for the aerobic oxidation reaction of benzylamines. Owing to the stronger electron donating ability of the planar TPB core compared to the nonplanar HPB unit with propeller arrangement, JNM-18 showed better photo-electrochemical properties than JNM-19, such as superior visible-light absorption, enhanced charge separation, and higher ROS generation efficiency, resulting in higher photocatalytic activity. This research provides a convenient approach to construct reticular D–A MOF photocatalysts by linkage of dynamic covalent bonds.
Results and discussion
Syntheses and characterization
Two imine-linked D–A MOFs, namely JNM-18 and JNM-19, were prepared under solvothermal conditions at 120 °C for 72 h by Schiff base condensation between the Cu-CTU, Cu3L3 (HL = pyrazole-4-carboxaldehyde), and the corresponding amino organic linkers, 5′′-(4′-amino-[1,1′-biphenyl]-4-yl)-[1,1′:4′,1′′:3′′,1′′′:4′′′,1′′′′-quinquephenyl]-4,4′′′′-diamine (1) and 3′′,4′′,5′′,6′′-tetrakis(4′-amino[1,1′-biphenyl]-4-yl)-[1,1′:4′,1′′:2′′,1′′′:4′′′,1′′′′-quinquephenyl]-4,4′′′′-diamine (2), respectively (Fig. S1 and S2, see the ESI† for details). Electrostatic potential (ESP) surface maps of JNM-18 and JNM-19 calculated based on their optimized structures revealed the positive potential focus on the Cu ions and the negative potential centered on the TPB and HPB cores, suggesting that a donor–acceptor heterojunction can be generated when they are linked with a covalent bond (Fig. 1b and see the ESI† for details). Moreover, the TPB core is much flatter than the HPB units with propeller arrangement.36 This superior integrity of π-conjugation is strongly related to the electron donating ability, which leads to a stronger donor–acceptor interaction in JNM-18 than that in JNM-19, influencing their photo-electrochemical properties and photocatalytic activity.37The formations of imine linkages of the products were confirmed using Fourier Transform Infrared (FT-IR) spectra, as evidenced by the disappearance of the N–H stretching bands21 ranging from 3466–3203 cm−1 and the appearance of the C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N stretching signals22 located at 1621 and 1624 cm−1 for JNM-18 and JNM-19, respectively (Fig. S5 and S6†). The solid-state 13C cross-polarization/magic-angle spinning nuclear magnetic resonance (CP/MAS NMR) spectra revealed the characteristic imine carbon16 resonance peaks at 156 and 157 ppm for JNM-18 and JNM-19, respectively, demonstrating the successful formation of C
N stretching signals22 located at 1621 and 1624 cm−1 for JNM-18 and JNM-19, respectively (Fig. S5 and S6†). The solid-state 13C cross-polarization/magic-angle spinning nuclear magnetic resonance (CP/MAS NMR) spectra revealed the characteristic imine carbon16 resonance peaks at 156 and 157 ppm for JNM-18 and JNM-19, respectively, demonstrating the successful formation of C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N linkages within the frameworks (Fig. S7 and S8†). Energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS) elemental analyses of JNM-18 and JNM-19 revealed a uniform distribution of Cu ions in the networks (Fig. S9 and S10†). X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) spectra of JNM-18 and JNM-19 revealed symmetrical Cu(I) 2p3/2 peaks at 932.98 and 932.82 eV without satellite peaks,38 suggesting the monovalent state of copper ions within the skeleton (Fig. S11 and S12†). Thermal gravimetric analyses (TGA) and various temperature PXRD experiments revealed moderate thermal stability of JNM-18 and JNM-19 which remained crystalline up to 200 °C (Fig. S13–16†). The materials also showed good stabilities towards water and various organic solvents (Fig. S17 and S18†).
N linkages within the frameworks (Fig. S7 and S8†). Energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS) elemental analyses of JNM-18 and JNM-19 revealed a uniform distribution of Cu ions in the networks (Fig. S9 and S10†). X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) spectra of JNM-18 and JNM-19 revealed symmetrical Cu(I) 2p3/2 peaks at 932.98 and 932.82 eV without satellite peaks,38 suggesting the monovalent state of copper ions within the skeleton (Fig. S11 and S12†). Thermal gravimetric analyses (TGA) and various temperature PXRD experiments revealed moderate thermal stability of JNM-18 and JNM-19 which remained crystalline up to 200 °C (Fig. S13–16†). The materials also showed good stabilities towards water and various organic solvents (Fig. S17 and S18†).
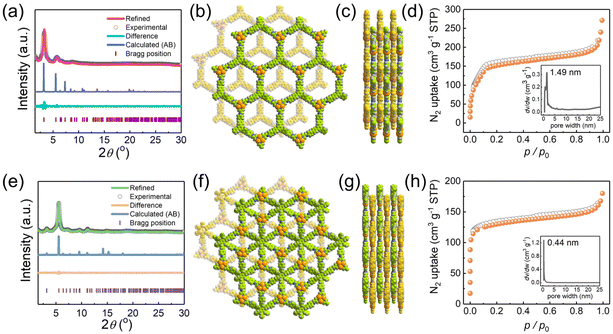
The high crystallinities of JNM-18 and JNM-19 were confirmed by powder X-ray diffraction (PXRD) shown in Fig. 2a and d, respectively, of which the structures were studied by PXRD experiments combined with theoretical simulations. For example, JNM-18 exhibited an intense peak at 3.20° and three small peaks at 5.78°, 6.70°, and 8.78°, which could be assigned to the (1![[1 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif) 0), (1
0), (1![[2 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0032_0304.gif) 0), (2
0), (2![[2 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0032_0304.gif) 0), and (210) planes, respectively. We further calculated the eclipsed (AA) and staggered packing (AB) modes of the 2D lamellar layers of JNM-18 with hcb topology using Materials Studio (Fig. 2b and S21†). The calculated PXRD patterns based on the two possible stacking models of JNM-18 are shown in Fig. S19,† which clearly revealed the good matching of the experimental PXRD pattern with the calculated one obtained from the AB stacking structure. Pawley refinement was thus performed based on the AB packing model, which gave a trigonal space group of P3 with unit cell parameters of a = b = 31.9432 Å, and c = 13.3836 Å, and refinement parameters of Rp = 3.40% and Rwp = 4.23% (Fig. 2a). Similarly, structural simulation and PXRD experiment suggested that JNM-19 employed AB staggered stacking mode of the 2D lamellar kgd layers, and Pawley refinement resulted in a hexagonal space group of P63 with unit cell parameters of a = b = 31.6707 Å, and c = 12.5253 Å, and refinement parameters of Rp = 2.08% and Rwp = 2.62% (Fig. 2d and e). Nitrogen adsorption measurements were performed at 77 K to study the porosities of JNM-18 and JNM-19, where type I adsorption curves were found for both materials, indicating their microporous nature. Analyses of the Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) surface areas afforded values of 761 and 596 m2 g−1 with total pore volumes of 0.4555 and 0.2836 ml g−1 (P/P0 = 0.99) for JNM-18 and JNM-19, respectively. Moreover, narrow pore size distributions with peak values of 1.49 nm and 0.44 nm given by nonlocal density functional theory (NLDFT) for JNM-18 and JNM-19, respectively, well agreed with the theoretical values of 1.47 and 0.42 nm found for the staggered AB stacking models of JNM-18 and JNM-19, respectively (Fig. 2c and f).
0), and (210) planes, respectively. We further calculated the eclipsed (AA) and staggered packing (AB) modes of the 2D lamellar layers of JNM-18 with hcb topology using Materials Studio (Fig. 2b and S21†). The calculated PXRD patterns based on the two possible stacking models of JNM-18 are shown in Fig. S19,† which clearly revealed the good matching of the experimental PXRD pattern with the calculated one obtained from the AB stacking structure. Pawley refinement was thus performed based on the AB packing model, which gave a trigonal space group of P3 with unit cell parameters of a = b = 31.9432 Å, and c = 13.3836 Å, and refinement parameters of Rp = 3.40% and Rwp = 4.23% (Fig. 2a). Similarly, structural simulation and PXRD experiment suggested that JNM-19 employed AB staggered stacking mode of the 2D lamellar kgd layers, and Pawley refinement resulted in a hexagonal space group of P63 with unit cell parameters of a = b = 31.6707 Å, and c = 12.5253 Å, and refinement parameters of Rp = 2.08% and Rwp = 2.62% (Fig. 2d and e). Nitrogen adsorption measurements were performed at 77 K to study the porosities of JNM-18 and JNM-19, where type I adsorption curves were found for both materials, indicating their microporous nature. Analyses of the Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) surface areas afforded values of 761 and 596 m2 g−1 with total pore volumes of 0.4555 and 0.2836 ml g−1 (P/P0 = 0.99) for JNM-18 and JNM-19, respectively. Moreover, narrow pore size distributions with peak values of 1.49 nm and 0.44 nm given by nonlocal density functional theory (NLDFT) for JNM-18 and JNM-19, respectively, well agreed with the theoretical values of 1.47 and 0.42 nm found for the staggered AB stacking models of JNM-18 and JNM-19, respectively (Fig. 2c and f).
The scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images of JNM-18 showed ball-shape microcrystals with a nanometer size, while JNM-19 exhibited flake-like morphologies in the micrometer range (Fig. 3a and d). High-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HR-TEM) images clearly exhibited highly crystalline nanolayers for the two materials (Fig. 3b and e), showing order lattice fringes with distances of 1.53 and 1.57 nm, respectively, associated with the (1![[1 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif) 0) and (110) planes for JNM-18 and JNM-19, respectively (Fig. 3c and f).
0) and (110) planes for JNM-18 and JNM-19, respectively (Fig. 3c and f).
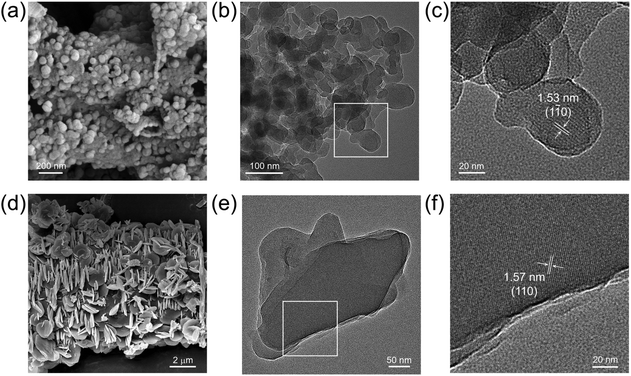 | ||
| Fig. 3 SEM images of JNM-18 (a) and JNM-19 (d). HR-TEM images of JNM-18 (b) and JNM-19 (e). Enlarged images of selected areas in part b (c) and e (f). | ||
Optical and electrochemical properties
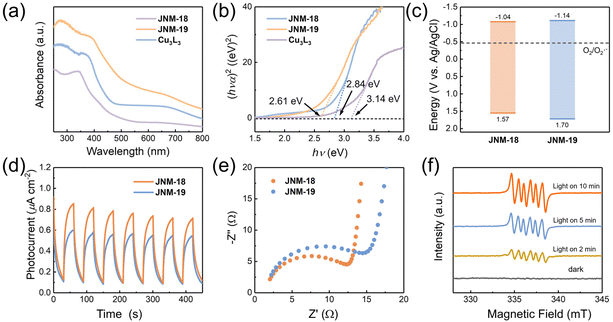
The photocatalytic activities are significantly related to the relative energies of the band gap and their charge separation efficiency. While Cu3L3 showed light yellow color (Fig. S25†), JNM-18 and JNM-19 were obtained as yellow and green powder (Fig. S26 and S27†), respectively, suggesting stronger absorption of visible light for the D–A MOFs. The UV-Vis diffuse reflectance spectra of JNM-18 and JNM-19 exhibit more bathochromic absorption bands (Fig. 4a), resulting in reduced values of 2.61 and 2.84 eV, respectively, for the band gap energy, compared to that of Cu3L3 (3.14 eV) based on the Kubelka–Munk equation (Fig. 4b). In addition, Mott–Schottky measurements showed positive slopes for JNM-18 and JNM-19, indicative of typical n-type semiconductors, and the lowest unoccupied molecular orbital (LUMO) levels of JNM-18 and JNM-19 are estimated to be −1.04, and −1.14 eV versus Ag/AgCl, respectively (Fig. S28 and S29†). In consideration of the bandgaps obtained from the UV-vis spectra, the corresponding highest occupied molecular orbital (HOMO) levels of JNM-18 and JNM-19 are calculated to be +1.57, and +1.70 eV versus Ag/AgCl, respectively. The resulting band structures of JNM-18 and JNM-19 are therefore obtained, which clearly suggest they are capable of activating O2 to superoxide anion radicals (O2˙−) which can be used in photocatalytic aerobic oxidation reactions (Fig. 4c).25 Moreover, transient photocurrent responses were observed for JNMs, indicating the photo-induced charge separation (Fig. 4d). In contrast, Cu3L3 showed negligible photocurrent response (Fig. S29†), suggesting that the construction of D–A networks with precise spatial distribution of donor and acceptor moieties could efficiently enhance the photo-induced charge separation.15 Interestingly, the photocurrent intensity of JNM-18 was higher than that of JNM-19, implying higher photo-induced charge separation efficiency of JNM-18. Furthermore, the electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) of JNM-18 exhibited a smaller radius than that of JNM-19, suggesting a lower internal resistance for the charge transfer in JNM-18 (Fig. 4e). Those optical and electrochemical experiments clearly reveal that the construction of D–A MOFs via direct imine linkage could reduce the band gap energy, resulting in the decrease of photocarrier transfer barrier and the increase of the charge separation efficiency.39 Notably, JNM-18 showed better photo-electrochemical properties than JNM-19 that might be due to the stronger electron donating ability of the planar TPB units in the 2D networks, compared to the nonplanar HPB moieties with propeller arrangement in JNM-19, which may enhance the photocatalytic activity of the materials.37Photocatalytic studies
With the remarkable photoelectronic properties of imine-linked D–A MOFs in hand, we elucidated their photocatalytic performance for the aerobic oxidation of amines to imines. Initially, the aerobic oxidation of benzylamine (3a) under light irradiation was chosen as a model reaction. As shown in Table 1 (entry 1), when benzylamine (0.3 mmol) and 3 mol% (based on Cu) JNM-18 were mixed in 2 mL CH3CN and reacted at room temperature (rt) for 12 h under irradiation with a violet LED, compound 3a underwent the oxidative coupling reaction to give the imine product (4a) with 94% yield confirmed by 1H NMR. To optimize the reaction conditions, several control experiments were conducted. In the absence of JNM-18 or light irradiation, low conversion of 3a was observed, suggesting the indispensability of catalysts and light in the aerobic oxidation reaction (Table 1, entries 2 and 3). Filled with Ar, the imine product 4a was barely detected (Table 1, entry 4). With the use of O2 instead of air, the conversion of 3a could be increased to 99%, indicating the crucial role of O2 as the terminal oxidant (Table 1, entry 5). Reaction solvents were found to strongly influence the photocatalytic efficiency, where the use of MeOH or EtOH instead of MeCN gave much lower yields (Table 1, entries 6 and 7). The use of a blue LED also resulted in much lower yield (Table 1, entry 8). The decrease of catalyst loading from 3 to 1.5 mol% reduced the coupling product yield to 61%, while the use of 6 mol% catalyst loading could not increase the yield (Table 1, entries 9 and 10). Reactions using Cu3L3 afforded low yield, evidencing the significance of constructing D–A MOFs for improving the photocatalytic activity (Table 1, entry 11). Notably, when JNM-19 was employed as a photocatalyst, 4a with 75% or 92% yield can be obtained within 12 h or 24 h, respectively, suggesting a lower photocatalytic efficiency compared to JNM-18 (Table 1, entries 12 and 13). This may due to the stronger electron donating ability arising from the planar TPB units in JNM-18 frameworks than the nonplanar HPB moieties in JNM-19, which results in a larger photocarrier transfer barrier and lower charge separation efficiency, and thus enhanced photocatalytic performance.40| Entry | Change from the “standard conditions” | Yield (%) |
|---|---|---|
| a Reaction conditions: benzylamine (0.3 mmol), JNM-18 (3 mol%), CH3CN (2 mL), r.t., a violet LED (12 W), air. The reported yields presented are based on 1H NMR spectra. | ||
| 1 | None | 94 |
| 2 | No catalyst | 14 |
| 3 | No light | 4 |
| 4 | Under Ar, instead of air | Trace |
| 5 | Under O2, instead of air | 99 |
| 6 | MeOH, instead of MeCN | 30 |
| 7 | EtOH, instead of MeCN | 34 |
| 8 | A blue LED, instead of a violet LED | 11 |
| 9 | 1.5 mol% JNM-18 | 61 |
| 10 | 6 mol% JNM-18 | 93 |
| 11 | Cu3L3 instead of JNM-18 | 10 |
| 12 | JNM-19, instead of JNM-18 | 75 |
| 13 | JNM-19, instead of JNM-18, 24 h | 92 |
| 14 | NaN3 as the 1O2 scavenger | 92 |
| 15 | Benzoquinone as the O2˙− scavenger | 5 |
| 16 | AgNO3 as the e− scavenger | 5 |
Superoxide anion radical (O2˙−) and singlet oxygen (1O2) are the ROS involved in the photocatalytic aerobic oxidation reaction.25 Here, various control experiments were performed to study the generated ROS and the mechanism of the photocatalytic oxidation of 3a. The addition of NaN3 (5.0 equiv.) as the 1O2 scavenger to the reaction solution did not change the conversion of 3a, suggesting that 1O2 was not involved in the reaction process (Table 1, entry 14). In contrast, the addition of benzoquinone (5.0 equiv.) as a O2˙− scavenger remarkably lowered the yield to 5% (Table 1, entry 15). Besides, the use of AgNO3 as an e− scavenger also impeded the oxidation of 3a by disturbing the generation of O2˙− from O2 (Table 1, entry 16). Therefore, O2˙− is the dominant ROS for JNM-18 photocatalyzed aerobic oxidation reaction.
Moreover, we applied electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) spectra to further investigate the ROS by spin trapping.41 With the addition of 5,5-dimethyl-pyrroline-N-oxide (DMPO), the characteristic peaks of the DMPO–O2˙− radical were found, of which the intensities were remarkably enhanced by prolonging the irradiation time, confirming the generation of O2˙− active species by the JNM-18 photocatalyst (Fig. 4f). Besides, the O2˙− generation of JNM-18 was further evaluated by the use of nitro blue tetrazolium (NBT), of which the absorption band at 259 nm was dramatically decreased upon the addition of JNM-18 upon violet LED irradiation (Fig. S34†). The generation of O2˙− ROS was also observed in JNM-19 by EPR with DMPO and UV-vis spectroscopy with NBT (Fig. S31 and S34†), but with less efficiency than JNM-18. These results were consistent with the observation of lower conversion for the JNM-19 photocatalyzed aerobic oxidation reaction.
We also evaluate the reusability of JNM-18 for heterogeneous photocatalyzed benzylamine oxidation reactions. Remarkably, the yields for the oxidative coupling products barely decreased (Fig. S35†). In addition, inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) revealed that copper ions were not present in the reaction supernatant, suggesting that the photocatalyst JNM-18 was not damaged after catalytic cycles (see the ESI† for details). Moreover, XPS analysis and PXRD measurement demonstrated the monovalent state of the Cu ions and high crystallinity of JNM-18 remained during the recycle catalytic experiments (Fig. S36 and S37†). Furthermore, FT-IR spectra and SEM images of JNM-18 before and after photocatalysis did not show obvious differences, implying the structural integrity (Fig. S38 and S39†).
Furthermore, we expanded the photocatalytic application using JNM-18 by exploring various benzylamine derivatives with a broad range of substituents under the standard reaction conditions (Table 2). In general, the JNM-18 photocatalyzed reaction was tolerant to different substituted primary amines, which were oxidized to the associated imines with excellent yields. Notably, the benzyl amines with electron-withdrawing groups exhibited higher yields (Table 2, entries 2–5), compared with those with electron-donating substituents (Table 2, entries 6–8), as a result of the enhanced electronegativity on the benzyl moieties. Moreover, the steric effect using benzylamine substituted with a long alkyl chain was also tested, showing good yields for the corresponding imine product (Table 2, entry 9). Benzyl amines with reactive functional substituents, such as vinyl and thiophene, that may disturb the oxidation reactions were also applicable to the JNM-18 photocatalyzed oxidation (Table 2, entries 10 and 11). We also investigated several secondary amines for the photocatalyzed oxidation to further explore the reaction scope (Table S5†). Though the yields were shown to be inferior to the reactions based on primary amines, the secondary amines could be oxidized to the corresponding imines, suggesting the good toleration in the aerobic oxidation of amines using the JNM-18 photocatalyst.
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) a
a
| a Reaction conditions: amine (0.3 mmol), JNM-18 (3 mol%), CH3CN (2 mL), rt, a violet LED (12 W), air. The reported yields presented are based on 1H NMR spectra. |
|---|
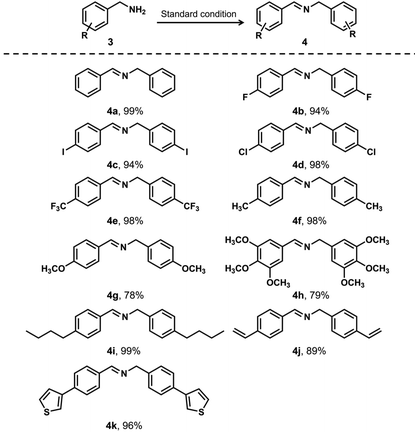
|
Gradually, a plausible mechanism for the photocatalyzed aerobic oxidation of benzylamine by the CTU-based D–A MOFs is proposed on the basis of the above experimental data and reported results in the literature (Fig. S40†).14,15,38,41–45 Taking JNM-18 as an example, the D–A MOF plays a role as a transfer channel that accelerates the separation of electron–hole systems (e−–h+) upon irradiation with violet light, following the singlet electron transfer (SET) which migrated e− from the HOMO to the LUMO in JNM-18 and generated O2˙− by reduction of O2. Secondly, benzylamine was rapidly transformed to the amine radical cation by h+ drifted on the JNM-18 surface, which subsequently reacted with O2˙− to form the benzaldimine intermediate that further condenses with benzylamine to generate the target product.
Conclusions
In summary, two imine-linked D–A MOFs, JNM-18 and JNM-19, were reticularly synthesized by covalent networking of Cu(I) CTUs and an organic linker functionalized with TPB and HPB electron-donating moieties, respectively. The obtained D–A MOFs show high crystallinity and uniform porosity. In addition, due to the precise spatial distribution of donor and acceptor units within the extended networks, the D–A MOFs exhibited excellent photocatalytic performance for the aerobic oxidation reaction of benzylamines upon photo-irradiation. Moreover, JNM-18 exhibited stronger visible-light absorption, higher charge separation efficiency, and higher ROS generation efficiency compared to JNM-19, thus resulting in higher photocatalytic activity. This work demonstrates a facile approach to synthesize D–A MOFs by reticular chemistry of dynamic covalent bonds, which is helpful for developing and designing efficient MOF photocatalysts.Author contributions
R.-J. W., G.-H. N. and D. L. designed the research; R.-Q. X., T.-E. Z. and Z.-N. L. conducted the experiments and data analysis; R.-Q. X., R.-J. W., G.-H. N. and D. L. co-wrote the manuscript. All authors read and commented on the manuscript.Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.Acknowledgements
G. H. N. is thankful for the financial support from the Guangzhou Science and Technology Project (202201020038). This study was supported financially by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 22371091, 21975104, 22150004 and 21731002), the Guangdong Major Project of Basic and Applied Research (no. 2019B030302009), and the Open Fund of Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Functional Supramolecular Coordination Materials and Applications (no. 2020B121201005).References
- O. M. Yaghi, M. O'Keeffe, N. W. Ockwig, H. K. Chae, M. Eddaoudi and J. Kim, Reticular Synthesis and the Design of New Materials, Nature, 2003, 423, 705–714 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Li, D. Li, M. O'Keeffe and O. M. Yaghi, Topological Analysis of Metal–Organic Frameworks with Polytopic Linkers and/or Multiple Building Units and the Minimal Transitivity Principle, Chem. Rev., 2014, 114, 1343–1370 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Schoedel, M. Li, D. Li, M. O'Keeffe and O. M. Yaghi, Structures of Metal–Organic Frameworks with Rod Secondary Building Units, Chem. Rev., 2016, 116, 12466–12535 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Zeng, M. Xie, T. Wang, R.-J. Wei, X.-J. Xie, Y. Zhao, W. Lu and D. Li, Orthogonal-Array Dynamic Molecular Sieving of Propylene/Propane Mixtures, Nature, 2021, 595, 542–548 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R.-B. Lin, S. Xiang, W. Zhou and B. Chen, Microporous Metal–Organic Framework Materials for Gas Separation, Chem, 2020, 6, 337–363 CAS.
- A. J. Rieth, A. M. Wright and M. Dincă, Kinetic Stability of Metal–Organic Frameworks for Corrosive and Coordinating Gas Capture, Nat. Rev. Mater., 2019, 4, 708–725 CrossRef CAS.
- Z. Han, Z. Yan, K. Wang, X. Kang, K. Lv, X. Zhang, Z. Zhou, S. Yang, W. Shi and P. Cheng, Observation of Oxygen Evolution over a {Ni12}-Cluster Based Metal-Organic Framework, Sci. China: Chem., 2022, 65, 1088–1093 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Fiankor, J. Nyakuchena, R. S. H. Khoo, X. Zhang, Y. Hu, S. Yang, J. Huang and J. Zhang, Symmetry-Guided Synthesis of N, N′-Bicarbazole and Porphyrin-Based Mixed-Ligand Metal–Organic Frameworks: Light Harvesting and Energy Transfer, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2021, 143, 20411–20418 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Miyasaka, Control of Charge Transfer in Donor/Acceptor Metal–Organic Frameworks, Acc. Chem. Res., 2013, 46, 248–257 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- B. Zhang, J. Xu, C. T. Li, H. L. Huang, M. X. Chen, M. H. Yu, Z. Chang and X. H. Bu, Facile Tuned TSCT-TADF in Donor-Acceptor MOF for Highly Adjustable Photonic Modules Based on Heterostructures Crystals, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2023, 62, e202303262 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. S. Zhang, Q. Gao, Z. Chang, X. T. Liu, B. Zhao, Z. H. Xuan, T. L. Hu, Y. H. Zhang, J. Zhu and X. H. Bu, Rational Construction of Highly Tunable Donor-Acceptor Materials Based on a Crystalline Host-Guest Platform, Adv. Mater., 2018, 30, 1804715 CrossRef PubMed.
- E. Romero, J. R. Gómez Castellanos, G. Gadda, M. W. Fraaije and A. Mattevi, Same Substrate, Many Reactions: Oxygen Activation in Flavoenzymes, Chem. Rev., 2018, 118, 1742–1769 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- F. Zhang, J. Ma, Y. Tan, G. Yu, H. Qin, L. Zheng, H. Liu and R. Li, Construction of Porphyrin Porous Organic Cage as a Support for Single Cobalt Atoms for Photocatalytic Oxidation in Visible Light, ACS Catal., 2022, 12, 5827–5833 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Wu, X.-Y. Liu, P.-W. Cheng, M. Xie, W. Lu and D. Li, Metal-Organic Frameworks as Photocatalysts for Aerobic Oxidation Reactions, Sci. China: Chem., 2023, 66, 1634–1653 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Wu, X.-Y. Liu, P.-W. Cheng, Y.-L. Huang, J. Zheng, M. Xie, W. Lu and D. Li, Linker Engineering for Reactive Oxygen Species Generation Efficiency in Ultra-Stable Nickel-Based Metal–Organic Frameworks, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2023, 145, 18931–18938 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Z. W. Jiang, Y. C. Zou, T. T. Zhao, S. J. Zhen, Y. F. Li and C. Z. Huang, Controllable Synthesis of Porphyrin-Based 2D Lanthanide Metal–Organic Frameworks with Thickness– and Metal–Node–Dependent Photocatalytic Performance, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2020, 59, 3300–3306 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J.-K. Jin, K. Wu, X.-Y. Liu, G.-Q. Huang, Y.-L. Huang, D. Luo, M. Xie, Y. Zhao, W. Lu and X.-P. Zhou, Building a Pyrazole–Benzothiadiazole–Pyrazole Photosensitizer into Metal–Organic Frameworks for Photocatalytic Aerobic Oxidation, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2021, 143, 21340–21349 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Zheng, Z. Lu, K. Wu, G. H. Ning and D. Li, Coinage-Metal-Based Cyclic Trinuclear Complexes with Metal-Metal Interactions: Theories to Experiments and Structures to Functions, Chem. Rev., 2020, 120, 9675–9742 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y.-M. Wang, K.-M. Mo, X. Luo, R.-Q. Xia, J.-Y. Song, G.-H. Ning and D. Li, An Anthraquinone-Based Cu(I) Cyclic Trinuclear Complex for Photo-Catalyzing C-C Coupling Reactions, Sci. China: Chem., 2023, 66 DOI:10.1007/s11426-023-1777-y.
- A. P. Côté, A. I. Benin, N. W. Ockwig, M. O'Keeffe, A. J. Matzger and O. M. Yaghi, Porous, Crystalline, Covalent Organic Frameworks, Science, 2005, 310, 1166–1170 CrossRef PubMed.
- R.-J. Wei, H.-G. Zhou, Z.-Y. Zhang, G.-H. Ning and D. Li, Copper(I)–Organic Frameworks for Catalysis: Networking Metal Clusters with Dynamic Covalent Chemistry, CCS Chem., 2020, 2, 2045–2053 Search PubMed.
- H.-G. Zhou, R.-Q. Xia, J. Zheng, D. Yuan, G.-H. Ning and D. Li, Acid-Triggered Interlayer Sliding of Two-Dimensional Copper(I)–Organic Frameworks: More Metal Sites for Catalysis, Chem. Sci., 2021, 12, 6280–6286 RSC.
- X.-C. Lin, Y.-M. Wang, X. Chen, P.-Y. You, K.-M. Mo, G.-H. Ning and D. Li, A Photosensitizing Metal-Organic Framework as a Tandem Reaction Catalyst for Primary Alcohols from Terminal Alkenes and Alkynes, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2023, 62, e202306497 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. L. Nguyen, F. Gándara, H. Furukawa, T. L. Doan, K. E. Cordova and O. M. Yaghi, A Titanium–Organic Framework as an Exemplar of Combining the Chemistry of Metal– and Covalent–Organic Frameworks, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2016, 138, 4330–4333 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Luo, X. Luo, M. Xie, H.-Z. Li, H. Duan, H.-G. Zhou, R.-J. Wei, G.-H. Ning and D. Li, Selective and Rapid Extraction of Trace Amount of Gold from Complex Liquids with Silver(I)-Organic Frameworks, Nat. Commun., 2022, 13, 7771 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Zhou, J. Li, L. Kan, L. Zhang, Q. Huang, Y. Yan, Y. Chen, J. Liu, S.-L. Li and Y.-Q. Lan, Linking Oxidative and Reductive Clusters to Prepare Crystalline Porous Catalysts for Photocatalytic CO2 Reduction with H2O, Nat. Commun., 2022, 13, 4681 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J.-N. Lu, J.-J. Liu, L.-Z. Dong, J.-M. Lin, F. Yu, J. Liu and Y.-Q. Lan, Synergistic Metal–Nonmetal Active Sites in a Metal–Organic Cage for Efficient Photocatalytic Synthesis of Hydrogen Peroxide in Pure Water, Angew. Chem., 2023, 63, e202308505 Search PubMed.
- X. Wang, X. Ding, Y. Jin, D. Qi, H. Wang, Y. Han, T. Wang and J. Jiang, Post-Nickelation of a Crystalline Trinuclear Copper Organic Framework for Synergistic Photocatalytic Carbon Dioxide Conversion, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2023, 62, e202302808 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R.-J. Wei, M. Xie, R.-Q. Xia, J. Chen, H.-J. Hu, G.-H. Ning and D. Li, Gold(I)-Organic Frameworks as Catalysts for Carboxylation of Alkynes with CO2, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2023, 145, 22720–22727 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Zheng, H. Yang, M. Xie and D. Li, The π-Acidity/Basicity of Cyclic Trinuclear Units (CTUs): From a Theoretical Perspective to Potential Applications, Chem. Commun., 2019, 55, 7134–7146 RSC.
- R.-Q. Xia, J. Zheng, R.-J. Wei, J. He, D.-Q. Ye, M.-D. Li, G.-H. Ning and D. Li, Strong Visible Light-Absorbing Bodipy-Based Cu(I) Cyclic Trinuclear Sensitizer for Photocatalysis, Inorg. Chem. Front., 2022, 9, 2928–2937 RSC.
- C. Mejuto, G. Guisado-Barrios, D. Gusev and E. Peris, First Homoleptic MIC and Heteroleptic NHC–MIC Coordination Cages from 1,3,5-Triphenylbenzene-Bridged Tris-MIC and Tris-NHC Ligands, Chem. Commun., 2015, 51, 13914–13917 RSC.
- Y. Zhang, G. Wu, H. Liu, R. Tian, Y. Li, D. Wang, R. Chen, J. Zhao, S. Liu and Z. Li, Donor–Acceptor Based Two-Dimensional Covalent Organic Frameworks for near-Infrared Photothermal Conversion, Mater. Chem. Front., 2021, 5, 6575–6581 RSC.
- S. Pramanik, H. Deol, V. Bhalla and M. Kumar, Aiee Active Donor–Acceptor–Donor-Based Hexaphenylbenzene Probe for Recognition of Aliphatic and Aromatic Amines, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2017, 10, 12112–12123 CrossRef PubMed.
- H. Liu, Z. Zhang, C. Mu, L. Ma, H. Yuan, S. Ling, H. Wang, X. Li and M. Zhang, Hexaphenylbenzene-Based Deep Blue-Emissive Metallacages as Donors for Light-Harvesting Systems, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2022, 61, e202207289 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. Rathore, C. L. Burns and S. A. Abdelwahed, Hopping of a Single Hole in Hexakis [4-(1, 1, 2-Triphenyl-Ethenyl) Phenyl] Benzene Cation Radical through the Hexaphenylbenzene Propeller, Org. Lett., 2004, 6, 1689–1692 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. Xiong, Y. Wang, F. Zhang, X. Li and X. Lang, Linker Length-Dependent Photocatalytic Activity of β-Ketoenamine Covalent Organic Frameworks, Appl. Catal., B, 2023, 322, 122135 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Duan, X. Chen, Y.-N. Yang, J. Zhao, X.-C. Lin, W.-J. Tang, Q. Gao, G.-H. Ning and D. Li, Tailoring Stability, Catalytic Activity and Selectivity of Covalent Metal–Organic Frameworks Via Steric Modification of Metal Nodes, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2023, 11, 12777–12783 RSC.
- P. You, R. Wei, G. Ning and D. Li, An Eosin Y Encapsulated Cu(I) Covalent Metal Organic Framework for Efficient Photocatalytic Sonogashira Cross-Coupling Reaction, Chem. Res. Chin. Univ., 2022, 38, 415–420 CrossRef CAS.
- J.-D. Yi, R. Xu, Q. Wu, T. Zhang, K.-T. Zang, J. Luo, Y.-L. Liang, Y.-B. Huang and R. Cao, Atomically Dispersed Iron–Nitrogen Active Sites within Porphyrinic Triazine-Based Frameworks for Oxygen Reduction Reaction in Both Alkaline and Acidic Media, ACS Energy Lett., 2018, 3, 883–889 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Wu, X.-Y. Liu, M. Xie, P.-W. Cheng, J. Zheng, W. Lu and D. Li, Rational Design of D-π-A-π-D Porous Organic Polymer with Polarized π for Photocatalytic Aerobic Oxidation, Appl. Catal., B, 2023, 334, 122847 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Wei, Z. Guo, X. Liang, P. Chen, H. Liu and H. Xing, Selective Photooxidation of Amines and Sulfides Triggered by a Superoxide Radical Using a Novel Visible-Light-Responsive Metal–Organic Framework, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2019, 11, 3016–3023 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Liu, Z. Guo, H. Lv, X. Liu, Y. Che, Y. Mei, R. Bai, Y. Chi and H. Xing, Visible-Light-Driven Self-Coupling and Oxidative Dehydrogenation of Amines to Imines via a Mn(II)-Based Coordination Polymer, Inorg. Chem. Front., 2020, 7, 1016–1025 RSC.
- K. Gao, H. Li, Q. Meng, J. Wu and H. Hou, Efficient and Selective Visible-Light-Driven Oxidative Coupling of Amines to Imines in Air over CdS@ Zr-MOFs, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2021, 13, 2779–2787 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- W.-J. Xu, B.-X. Huang, G. Li, F. Yang, W. Lin, J.-X. Gu, H.-G. Deng, Z.-G. Gu and H.-G. Jin, Donor–Acceptor Mixed-Naphthalene Diimide-Porphyrin MOF for Boosting Photocatalytic Oxidative Coupling of Amines, ACS Catal., 2023, 13, 5723–5732 CrossRef CAS.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available: General procedures, detailed experimental methods, FT-IR spectra, NMR, XPS, structural simulation, PXRD patterns and TGA. See DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/d3qi02118a |
| This journal is © the Partner Organisations 2024 |