Unravelling the different pathways of cyclohexene oxidation via a peroxyl radical generated from tert-butyl hydroperoxide (TBHP) by various metal salts†
Lu-Jian
Zhou
a,
Xiao-Hui
Liu
*a,
Han-Wen
Zhang
 a,
Can
Xue
a,
Can
Xue
 a,
Han-Kang
Zhong
a and
Xian-Tai
Zhou
a,
Han-Kang
Zhong
a and
Xian-Tai
Zhou
 *ab
*ab
aSchool of Chemical Engineering and Technology, Sun Yat-sen University, Zhuhai, 519082, P.R. China. E-mail: zhouxtai@mail.sysu.edu.cn
bHuizhou Research Institute, Sun Yat-sen University, Huizhou, 516081, P.R. China
First published on 18th October 2024
Abstract
Selective oxidation of cyclohexene is rather challenging due to its two bond reactive centers: allylic C–H and C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C. It is of great significance to achieve highly selective oxidation towards the two reactive centers by regulating the catalytic system. Herein, the selective oxidation towards the allylic C–H and C
C. It is of great significance to achieve highly selective oxidation towards the two reactive centers by regulating the catalytic system. Herein, the selective oxidation towards the allylic C–H and C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C bond reactive sites of cyclohexene was achieved by using CuCl2 and VCl3 as the catalyst, respectively, in the presence of tert-butyl hydroperoxide (TBHP). The CuCl2-catalyzed oxidation of cyclohexene mainly yielded oxidation products at the allylic position, while the VCl3-catalyzed oxidation of cyclohexene mainly yielded epoxidation products at the C
C bond reactive sites of cyclohexene was achieved by using CuCl2 and VCl3 as the catalyst, respectively, in the presence of tert-butyl hydroperoxide (TBHP). The CuCl2-catalyzed oxidation of cyclohexene mainly yielded oxidation products at the allylic position, while the VCl3-catalyzed oxidation of cyclohexene mainly yielded epoxidation products at the C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C bond. The two different reaction mechanisms are mainly due to the different roles of the t-BuOO˙ radical in the respective catalytic systems. Electron paramagnetic resonance characterizations showed that the amount of t-BuOO˙ radicals in the CuCl2 catalytic system is much lower than that in the VCl3 system. The two different mechanisms were proposed by the means of 18O2 experiments, KIE kinetics and EPR. These mechanisms revealed that the CuCl2 catalyst could rapidly generate the t-BuOO˙ radical, which undergoes bimolecular decay to produce O2. The oxygen then combines with the allyl radical of cyclohexene to produce the oxidized product at the allylic reactive center. In contrast, the VCl3 catalyst promoted the generation of the t-BuOO˙ radical, which reacted with the C
C bond. The two different reaction mechanisms are mainly due to the different roles of the t-BuOO˙ radical in the respective catalytic systems. Electron paramagnetic resonance characterizations showed that the amount of t-BuOO˙ radicals in the CuCl2 catalytic system is much lower than that in the VCl3 system. The two different mechanisms were proposed by the means of 18O2 experiments, KIE kinetics and EPR. These mechanisms revealed that the CuCl2 catalyst could rapidly generate the t-BuOO˙ radical, which undergoes bimolecular decay to produce O2. The oxygen then combines with the allyl radical of cyclohexene to produce the oxidized product at the allylic reactive center. In contrast, the VCl3 catalyst promoted the generation of the t-BuOO˙ radical, which reacted with the C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C bond of cyclohexene to directly yield the epoxide.
C bond of cyclohexene to directly yield the epoxide.
Introduction
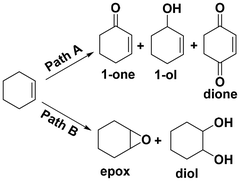
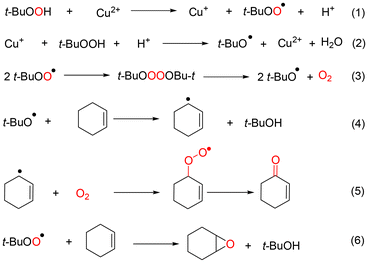
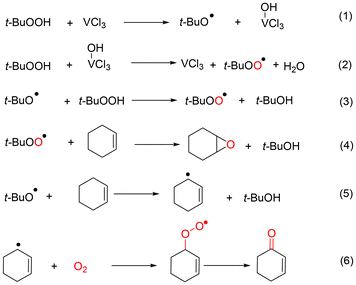
Selective oxidation of alkenes has always attracted the attention of fundamental and applied research due to the high added value of the oxidized products.1–4 As a readily available industrial alkene, cyclohexene can be oxidized to oxygenate compounds that are widely used in fields such as chemistry, agriculture and medicine.5–7 As cyclohexene has two active sites—the allyl site and the carbon–carbon double bond—it can undergo two oxidation pathways, as shown in Fig. 1. One is the allylic oxidation pathway, which produces 2-cyclohexen-1-ol and 2-cyclohexen-1-one (Path A, Scheme 1). The other is the epoxidation pathway, which produces epoxide, with excessive hydrolysis leading to 1,2-cyclohexadiol (Path B, Scheme 1).8–10 However, the two branched pathways cannot be clearly distinguished, which usually results in reaction products from both these pathways. Therefore, it is difficult to obtain a desired single product via cyclohexene oxidation.Many efforts have been made in recent years to improve the selectivity of some desired products from cyclohexene oxidation by developing various catalytic protocols with environmentally friendly oxidants, such as molecular oxygen, H2O2 or TBHP (tert-butyl hydroperoxide).11–14 In general, cyclohexene was oxidized with molecular oxygen catalyzed by various metal catalysts, such as copper,15 cobalt,16 manganese salts,17 and the main obtained products were generated from the allylic position, such as 2-cyclohexen-1-ol and 2-cyclohexen-1-one (Path A). This could be ascribed to the cyclohexenyl radical, which could be generated smoothly using a metal catalyst or via thermal dehydrogenation. Subsequently, an allylic hydroperoxide radical (ROO˙) intermediate generated easily from the reaction between the cyclohexenyl radical and O2.18 The oxidation of cyclohexene with O2 is subject to radical chain reactions, with ROO˙ radicals being the main chain carriers.19
Different product distributions in cyclohexene oxidation could be obtained when H2O2 was used as the oxidant.20 The decomposition mechanism of H2O2 is closely related to the type of catalyst. Efficient catalysts for the oxidation of cyclohexene using H2O2, such as Nb silicates,21 Mn/Al2O3,22 Ag/TiO2/SiO2,23 achieved a high selectivity for the epoxide products. Such catalysts promote the heterolytic cleavage of H2O2 to HOO˙ radicals, which can coordinate at the catalytic metal center to selectively transfer one oxygen atom to the C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C bond of cyclohexene, forming epoxides. However, various catalysts, such as Cu-zeolite-Y,24 Fe-based MOF MIL-88A (Fe),25 CoW composite oxides,26 promoted the homolytic cleavage of H2O2 to ˙OH, which resulted in products from the allylic oxidation pathway (Path A).
C bond of cyclohexene, forming epoxides. However, various catalysts, such as Cu-zeolite-Y,24 Fe-based MOF MIL-88A (Fe),25 CoW composite oxides,26 promoted the homolytic cleavage of H2O2 to ˙OH, which resulted in products from the allylic oxidation pathway (Path A).
Compared with H2O2, TBHP exhibits a higher stability and is widely used in the large-scale production of propylene oxide, such as the Halcon processes, which simultaneously produce tert-butanol as a byproduct.27–29 The type of catalyst also plays a key role in the selectivity of products for cyclohexene oxidation with TBHP as the oxidant. For example, VO2-SiO230 and Mo-based catalysts31 showed an excellent epoxidation selectivity for cyclohexene oxidation in the presence of TBHP; most other metal–base catalysts, such as Cu, Co and Mn, exhibit dominant selectivity for allylic products.32–34 The homolytic decomposition of the O–O bond in the TBHP molecule could generate t-BuO˙ and ˙OH radicals, while ROO˙ radicals are the main radicals in the heterolytic cleavage of TBHP. The difference in product selectivity could be ascribed to the generation of different types of reactive oxygen species by various catalysts.
Thus, the oxidation of cyclohexene is highly complicated, which involves a complex reaction network of various free radicals and chain reactions. Especially for TBHP, three kinds of reactive oxygen radicals (t-BuO˙, ˙OH and t-BuOO˙) could be produced via the cleavage of the TBHP molecule, which directly affect the selectivity of the products. Therefore, achieving selective generation of reactive oxygen radicals in the cleavage of TBHP is of great significance for selective control of cyclohexene oxidation products.
With this idea in mind, the selective oxidation of cyclohexene was achieved by using CuCl2 and VCl3 as catalysts in the presence of TBHP. Two distinct mechanisms, namely the allylic oxidation pathway and the epoxidation pathway, were obtained, respectively. A series of characterizations, such as EPR, KIE kinetics and 18O2 experiments, showed that the different roles of the t-BuOO˙ radical in the respective catalytic systems yielded two distinct mechanisms. This work would provide the potential application prospects for improving the product selectivity of the alkene with the allyl site and C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C bond as two active sites.
C bond as two active sites.
Results and discussion
Selective oxidation of cyclohexene catalyzed by various metal chloride salt catalysts with TBHP as the oxidant were explored. The main products of the allyl position (Path A) are 2-cyclohexen-1-one (1), 2-cyclohexen-1-ol (2) and 2-cyclohexen-1,4-dione (3). The main products of the C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C bond position (Path B) are cyclohexene epoxide (4) and 1,2-cyclohexane-diol (5). In addition, there are other products that contain both allyl and C
C bond position (Path B) are cyclohexene epoxide (4) and 1,2-cyclohexane-diol (5). In addition, there are other products that contain both allyl and C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C bond positions, such as 2,3-epoxy-1-cyclohexanone and 2,3-epoxy-1-cyclohexanol (Fig. S1†).
C bond positions, such as 2,3-epoxy-1-cyclohexanone and 2,3-epoxy-1-cyclohexanol (Fig. S1†).
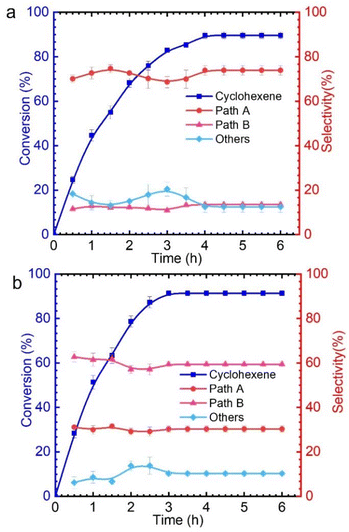
As shown in Table S1,† only 9% cyclohexene was converted in the absence of catalyst. It is known that there are significant differences in the catalytic performance of different metal chlorides. This is mainly related to the different abilities of various metal chlorides to activate TBHP for generating reactive oxygen species. Among these, CuCl2 and VCl3 exhibit excellent catalytic performances, with conversion rates of 93% and 90%, respectively. The effect of reaction conditions, such as the solvent and reaction temperature, on cyclohexene oxidation was explored (Tables S2–S4†). Upon closer observation, it was found that when copper chloride was used as the catalyst, the products obtained from cyclohexene oxidation were mainly via pathway A, while using vanadium chloride mainly produced pathway B products (Fig. 1 and Fig. S2†). However, for other metal chlorides, there seems to be no significant difference in the products that are generated from the two pathways. Therefore, we attempted to explore the different mechanisms for catalytic oxidation of cyclohexene catalyzed by CuCl2 and VCl3.
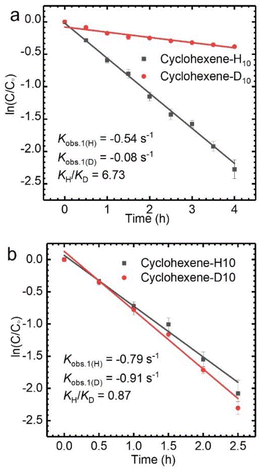
The allyl position of cyclohexene is an active reaction site, which can be determined by kinetic isotope effect (KIE) experiments (Fig. S3†).35 A KIE value of 6.73 (KH/KD) was obtained for the oxidation of cyclohexene-H10 and cyclohexene-D10 with TBHP catalyzed by CuCl2, which indicates that the allyl-H activation step is the rate-determining step. However, the KIE value of 0.87 demonstrates that the oxidation mechanism of cyclohexene when using VCl3 as a catalyst is completely different from that when using CuCl2 as the catalyst (Fig. 2). The findings obtained from the KIE tests are consistent with the above catalytic performances.
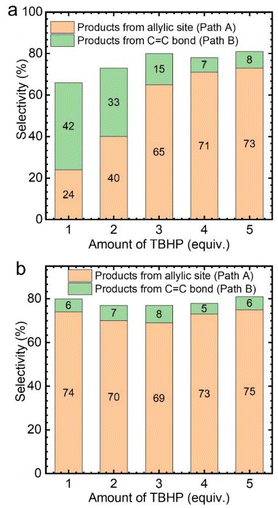
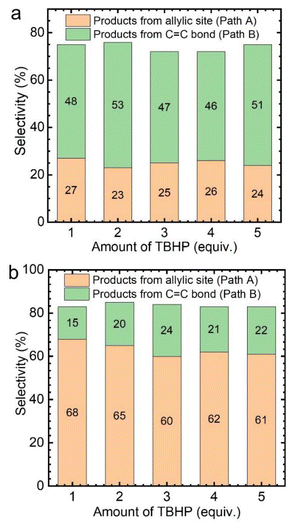
Subsequently, the effect of TBHP oxidant dosage on the reaction was further investigated by using CuCl2 as the catalyst. As a result, it was found that with the increase of TBHP dosage, the oxidation products at the allyl position gradually increased, while the products from epoxidation gradually decreased (Fig. 3a). Meanwhile, numerous gas bubbles were observed in the reaction solution during the experiments (Fig. S4b†). After collection and analysis, the generated gas in the solution was confirmed to be molecular oxygen (Fig. S5a†). The generated dioxygen content is much higher than the oxygen content in air and a standard gas containing 21% oxygen (Fig. S5b†). Therefore, it could be deduced that the produced dioxygen originates from TBHP.36
Afterwards, while using different amounts of TBHP as the oxidant, a certain amount of oxygen (flow rate: 5 mL min−1) was introduced into the reaction system. It was found that, regardless of the amount of TBHP used, the selectivity of Path A products remained unchanged (Fig. 3b). This indicates that the role of TBHP is to promote the generation of dioxygen, which is an important participant in this catalytic process. Cyclohexene oxidation catalyzed by CuCl2 with TBHP was then carried out under an 18O2 atmosphere. Apart from products containing 16O, products containing 18O at the allyl position were observed by CSI-MS (18O-labeled 2-cyclohexen-1-one, m/z = 98.0618; 18O-labeled 2-cyclohexen-1,4-dione, m/z = 114.0453) (Fig. S6†).
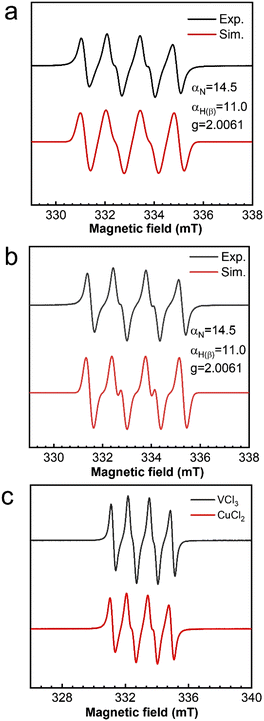
Similarly, the effect of TBHP oxidant dosage on the oxidation of cyclohexene was also investigated with VCl3 as the catalyst. However, the selectivity of the product hardly changed with the amount of TBHP, with the main generated products corresponding to the C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C bond position (Path B) (Fig. 4a). Meanwhile, no gas bubbles were observed in the reaction solution. After introducing oxygen at a 5 mL min−1 flow rate, the selectivity of the product changed significantly. The oxidized products were transformed to those generated at the allyl position (Path A) (Fig. 4b). This also indicates that the reaction rate between allyl radicals and oxygen is much higher than that of epoxidation.
C bond position (Path B) (Fig. 4a). Meanwhile, no gas bubbles were observed in the reaction solution. After introducing oxygen at a 5 mL min−1 flow rate, the selectivity of the product changed significantly. The oxidized products were transformed to those generated at the allyl position (Path A) (Fig. 4b). This also indicates that the reaction rate between allyl radicals and oxygen is much higher than that of epoxidation.
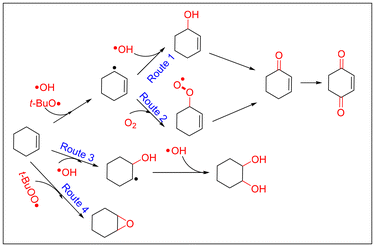
Both in CuCl2- and VCl3-catalyzed oxidations of cyclohexene with TBHP, EPR signals corresponding to radical adducts of dimethyl pyridine N-oxide (DMPO) were observed. The adducts determined by hyperfine coupling constant (HFCC) values (αN = 14.5 G, αH(β) = 11 G, and g = 2.0061) can be attributed to DMPO spin adducts of the peroxyl radical (t-BuOO˙) (Fig. 5a and b).37 Comparing the peak intensity of peroxide radicals in the two catalytic systems, it can be seen that the amount of peroxide radicals in the CuCl2 catalytic system is much lower than that in the VCl3 system (Fig. 5c). The kinetics of the consumption of the peroxide radical indicated that the consumption of t-BuOO˙ radicals in the CuCl2 reaction system was much faster than that in the VCl3 reaction system (Fig. S7†). Combining the TBHP consumption rate curves of the two catalytic systems, it is evident that the role of the peroxide radicals is significantly different in the two systems (Fig. S8†). To further investigate whether the epoxidation of olefins is a mechanism of peroxyacids or the peroxyl radical, the epoxidations of cis-styrene catalyzed by CuCl2 and VCl3 were investigated. The results showed that both in the VCl3 and CuCl2 systems, the peroxide radical is the main species for olefin epoxidation. However, the efficiency of the CuCl2 catalyst for catalytic cis-styrene epoxidation was much lower that of VCl3. In addition, peroxyacids were the main species for epoxidation in the absence of catalyst (Table S5†).38
Three types of oxygen-containing radicals, including the tert-butylperoxyl radical (t-BuOO˙), tert-butoxyl radical (t-BuO˙) and hydroxyl radical (˙OH), could be generated from the decomposition of TBHP. The adducts determined by hyperfine coupling constant (HFCC) values (αN = 13.19 G, αH(β) = 8.16 G, and g = 2.0059) could be attributed to DMPO spin adducts of t-BuO˙ (Fig. S9a†).39 The adducts determined by hyperfine coupling constant (HFCC) values (αN = 14.8 G, αH(β) = 14.8 G, and g = 2.0059) can be attributed to DMPO spin adducts of ˙OH (Fig. S9b†).40 On the basis of the literature, TBHP is induced by Cu2+ to generate t-BuOO˙ and simultaneously Cu2+ is reduced to Cu+. Conversely, t-BuO˙ can be formed via the reductive decomposition of TBHP, which is accompanied by the regeneration of the Cu2+ catalyst from Cu+.41 Certainly, the bimolecular decay of t-BuOO˙ is another way to provide t-BuO˙, and more significantly, the oxygen produced in this process plays a key role in this reaction as the unique oxygen source.
In addition, the adducts of the cyclohexenyl radical and cyclohexenyl peroxyl radical by DMPO were detected at a mass to charge ratio (m/z) of 194.1535 and 226.1429, respectively (Fig. S10d and Fig. S10f†). Therefore, the t-BuOO˙ radical undergoes a self-polymerization reaction catalyzed by CuCl2 to produce O2. The generated dioxygen could combine with the cyclohexenyl radical to generate the corresponding oxidation products (Scheme 2).42
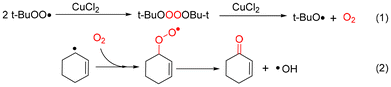 | ||
| Scheme 2 Pathway for dioxygen and 2-cyclohexen-1-one generation in the CuCl2 catalytic oxidation of cyclohexene. | ||
According to DFT calculations, the decomposition of O–O bond homolysis to ˙OH is favored over heterolysis to the ROO˙ radical, as it requires less energy.43 The O–O bond homolysis of di-tert-butyl peroxide (DTBP) produces the tert-butoxyl radical (t-BuO˙), while the O–O bond homolysis of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) produces the hydroxyl radical (˙OH). Using DTBP and H2O2 as oxidants, some control experiments catalyzed by CuCl2 were carried out to determine the roles of the t-BuO˙ and ˙OH radicals.
As a substrate, cyclohexane epoxide was not converted at all, regardless of the oxidant used among TBHP, DTBP and H2O2. This indicates that the generation of 1,2-cyclohexane-diol (5) is not obtained via the deep oxidation or hydration of epoxide (entries 1–3 in Table S6†). In contrast, cyclohexene could be converted with various conversions when using any of the three oxidants (entries 4–6 in Table S6†). The conversion was 35% and the main products were generated through Path A when H2O2 was used as the oxidant (entry 6 in Table S6†). However, the conversion was only 10% and the only product was the combination of the cyclohexenyl radical and t-BuO˙ when DTBP was used as the oxidant (entry 5 in Table S6†). These results indicate that both t-BuO˙ and ˙OH radicals can abstract the hydrogen atom from the α-position of cyclohexene to generate the cyclohexene radical.
No conversion was obtained in the oxidation of both cyclohexen-1-one and 2-cyclohexen-1-ol using DTBP as the oxidant (entry 8 and 10 in Table S6†). However, when using TBHP and H2O2 as the oxidant, the main products were 1-one and 1,4-dione in the oxidation of cyclohexen-1-ol and 2-cyclohexen-1-one, respectively. Such observations indicate that ˙OH radicals are active species that promote further oxidation of cyclohexen-1-ol and 2-cyclohexen-1-one.
From Table S2 (entry 1†), it can be seen that the main product of cyclohexene oxidation was diol in the absence of catalyst, with a selectivity of up to 43%. When adding VCl3 catalyst into the solution, the selectivity of the diols decreased from 43% to 7%, while the selectivity of epoxide increased from 5% to 51%. Combining the results of cis-styrene epoxidation (Table S5†), the promoted generation of t-BuOO˙ by VCl3 could be concluded, thereby enhancing the selectivity of epoxide. In addition, cyclohexanol radicals were observed in CSI-MS spectra of DMPO spin adducts at a mass to charge ratio (m/z) of 212.1640 (Fig. S10h†), which were the products of the addition reaction between the ˙OH radical and double bond of cyclohexene. Subsequently, diol was generated from the combination of the cyclohexanol radical and ˙OH radical, not the hydration of epoxide.
Based on above observations and discussions, the roles of the three kind radicals—t-BuOO˙, t-BuO˙ and ˙OH—can be summarized as shown in Fig. 6. When the oxidation of cyclohexene was catalyzed by CuCl2, the cyclohexenyl radical was promoted to generate through t-BuO˙ and ˙OH radicals. Therefore, the main products were generated from the allyl position of cyclohexene (Route 1 and Route 2 in Fig. 6). However, the t-BuOO˙ radical was the active species when cyclohexene oxidation was catalyzed by VCl3, which resulted in the main products being generated from the C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C bond of cyclohexene (Route 4 in Fig. 6). In addition, the ˙OH radical was the active species for generating 1,2-cyclohexane-diol when the oxidation was conducted in the absence of catalyst (Route 3 in Fig. 6).44
C bond of cyclohexene (Route 4 in Fig. 6). In addition, the ˙OH radical was the active species for generating 1,2-cyclohexane-diol when the oxidation was conducted in the absence of catalyst (Route 3 in Fig. 6).44
The different pathways of cyclohexene oxidation catalyzed by CuCl2 and VCl3 could be well demonstrated, according to the above discussion. A tentative mechanism of cyclohexene oxidation via Path A in the CuCl2/TBHP system was proposed, as shown in Scheme 3. Initially, TBHP is induced by Cu2+ to generate t-BuOO˙ and the Cu2+ was reduced to Cu+ (eqn (1) in Scheme 3). Conversely, t-BuO˙ can be formed via the reductive decomposition of TBHP, which is accompanied by the regeneration of Cu2+ from Cu+ (eqn (2) in Scheme 3). Certainly, the oxygen was produced via the bimolecular decay of t-BuOO˙, also providing t-BuO˙ in the presence of CuCl2 (eqn (3) in Scheme 3). Next, the oxygen combines with the cyclohexenyl radical to generate the cyclohexenyl peroxyl radical, and then to provide the corresponding products at the allyl position of cyclohexene (Path A) (eqn (4) and (5) in Scheme 3).
As mentioned above (Table S5†), trans-stilbene oxide was the predominant product in the epoxidation of cis-styrene catalyzed by VCl3, which suggested that the t-BuOO˙ radical was the active species. Therefore, a plausible mechanism of cyclohexene oxidation via Path B in the VCl3/TBHP system was proposed as shown in Scheme 4. The peroxyl radical (t-BuOO˙) could be generated by both the oxidation and reduction of VCl3 (eqn (1) and (2) in Scheme 4). In addition, t-BuOO˙ can be formed via the decomposition of TBHP by t-BuO˙, which is accompanied by the generation of t-BuOH (eqn (3) in Scheme 4). Then, the t-BuOO˙ radical reacted with cyclohexene to yield the epoxide directly (eqn (4) in Scheme 4).45–47
Conclusions
In summary, two different mechanisms were obtained in the selective oxidation of cyclohexene catalyzed by CuCl2 and VCl3, respectively, in the presence of TBHP. The CuCl2-catalyzed oxidation of cyclohexene mainly yielded allylic products, but the VCl3-catalyzed oxidation of cyclohexene mainly yielded epoxidation products. The two opposed mechanisms are mainly caused by the different roles of the t-BuOO˙ radical in their respective catalytic oxidations, which were demonstrated by means of 18O2 experiments, KIE kinetics and EPR characterizations. CuCl2 could rapidly generate the t-BuOO˙ radical, which undergoes a bimolecular decay to produce O2. The oxygen combines with the allyl radical of cyclohexene that is generated by the attack of t-BuO˙ or ˙OH radicals on cyclohexene to produce the oxidized products at the allylic site. In contrast, the t-BuOO˙ radical could react with the C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C bond of cyclohexene to yield the epoxide directly in the VCl3 catalytic system. This work provides potential application prospects for improving the product selectivity of alkene with AN allyl site and C
C bond of cyclohexene to yield the epoxide directly in the VCl3 catalytic system. This work provides potential application prospects for improving the product selectivity of alkene with AN allyl site and C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C bond as two active sites.
C bond as two active sites.
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.Data for this paper, including reactions screening and optimization experiments, detailed experimental procedures, spectral data, and computational study details, are provided in the ESI.†
Author contributions
L. Z. and X. L. developed the concept, designed these experiments, analyzed experimental data and wrote the paper. H. Z, C. X and H. Z. contributed to the catalyst synthesis, catalytic experiments and the analyzed experimental data. X. Z. directed the project. All the authors discussed the results and provided comments during the manuscript preparation.Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 22278451, 22378436 and 21938001), Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation (2022B1515120057, 2023A1515012710 and 2023A1515111144) and Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, Sun Yat-sen University (24lgqb014).References
- S. C. Hammer, G. Kubik, E. Watkins, S. Huang, H. Minges and F. H. Arnold, Anti-Markovnikov alkene oxidation by metal-oxo-mediated enzyme catalysis, Science, 2017, 358, 215–218 CrossRef CAS.
- S. J. Ma, C. K. Hill, C. L. Olen and J. F. Hartwig, Ruthenium-catalyzed hydroamination of unactivated terminal alkenes with stoichiometric amounts of alkene and an ammonia surrogate by sequential oxidation and reduction, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2021, 143, 359–368 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Nodzewska, A. Wadolowska and M. Watkinson, Recent advances in the catalytic oxidation of alkene and alkane substrates using immobilized manganese complexes with nitrogen containing ligands, Coord. Chem. Rev., 2019, 382, 181–216 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Sankaralingam, M. Balamurugan and M. Palaniandavar, Alkane and alkene oxidation reactions catalyzed by nickel(II) complexes: Effect of ligand factors, Coord. Chem. Rev., 2020, 403, 213085 CrossRef.
- J. H. Tong, W. H. Wang, L. D. Su, Q. Li, F. F. Liu, W. M. Ma, Z. Q. Lei and L. L. Bo, Highly selective oxidation of cyclohexene to 2-cyclohexene-1-one over polyoxometalate/metal-organic framework hybrids with greatly improved performances, Catal. Sci. Technol., 2017, 7, 222–230 RSC.
- J. Büker, X. B. Huang, J. Bitzer, W. Kleist, M. Muhler and B. X. Peng, Synthesis of Cu single atoms supported on mesoporous graphitic carbon nitride and their application in liquid-phase aerobic oxidation ofcyclohexene, ACS Catal., 2021, 11, 7863–7875 CrossRef.
- H. G. Cao, B. R. Zhu, Y. F. Yang, L. Xu, L. Yu and Q. Xu, Recent advances on controllable and selective catalytic oxidation of cyclohexene, Chin. J. Catal., 2018, 39, 899–907 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Büker, M. Muhler and B. X. Peng, Concepts of heterogeneously catalyzed liquid-phase oxidation of cyclohexene with tert-butyl hydroperoxide, hydrogen peroxide and molecular oxygen, ChemCatChem, 2023, 15, e202201216 CrossRef.
- B. X. Guang, Y. W. Zhang, Y. H. Xiao, M. J. Su and Y. Liu, Cu(II) coordinated N-bearing heteropolyacid-based poly(ionic liquid)s for allylic oxidation of cyclohexene to 2-cyclohexene-1-one with O2 under mild conditions, New J. Chem., 2023, 47, 3936–3944 RSC.
- T. Zhang, Y. Q. Hu, T. Han, Y. Q. Zhai and Y. Z. Zheng, Redox-active cobalt(II/III) metal-organic framework for selective oxidation of cyclohexene, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2018, 10, 15786–15792 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Y. Wu, H. H. Lin, Y. C. Jin, D. X. Liu, Y. K. Yu and Y. M. Liu, Efficient allylic oxidation of cyclohexene catalyzed by Ti-MCM-41 using H2O2 as oxidant, Microporous Mesoporous Mater., 2024, 378, 113263 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Tumuluri, J. K. Abu-Dahrieh, K. Mathiyalagan, A. M. Kalidhas, T. Perumal, S. Srinivasan, V. L. Mangesh, N. S. Kumar, S. B. Alreshaidan, K. Chandrasekaran, V. Arunachalam and A. S. Al-Fatesh, Selective oxidation of cyclohexene over the mesoporous H-beta zeolite on copper/nickel bimetal catalyst in continuous reactor, ACS Omega, 2024, 9, 25800–25811 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. F. Wu, M. J. Su, Y. H. Xiao, B. X. Guang and Y. Liu, Heteropolyacid-based poly(ionic liquid)s for the selective oxidation of cyclohexene to 2-cyclohexene-1-one, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2022, 61, 299–306 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Y. Zhu and G. W. Diao, High catalytic activity of CuO nanorods for oxidation of cyclohexene to 2-cyclohexene-1-one, Catal. Sci. Technol., 2012, 2, 82–84 RSC.
- D. D. Mal, J. Kundu and D. Pradhan, CuO{001} as the most active exposed facet for allylic oxidation of cyclohexene via a greener route, ChemCatChem, 2021, 13, 362–372 CrossRef CAS.
- G. Flores, J. Aguilar-Pliego, N. Martin-Guaregua, I. A. Ibarra and M. Sanchez-Sanchez, Room-temperature prepared bimetallic nanocrystalline MOF-74 as catalysts in the aerobic oxidation of cyclohexene, Catal. Today, 2022, 394, 295–303 CrossRef.
- A. R. Faraji, S. Mosazadeh and F. Ashouri, Synthesis and characterization of cobalt-supported catalysts on modified magnetic nanoparticle: Green and highly efficient heterogeneous nanocatalyst for selective oxidation of ethylbenzene, cyclohexene and oximes with molecular oxygen, J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2017, 506, 10–26 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Büker, S. Angel, S. Salamon, J. Landers, T. Falk, H. Wende, H. Wiggers, C. Schulz, M. Muhler and B. X. Peng, Structure-activity correlation in aerobic cyclohexene oxidation and peroxide decomposition over CoxFe3(-xO4 spinel oxides, Catal. Sci. Technol., 2022, 12, 3594–3605 RSC.
- R. L. Luck and N. K. Newberry, Free-radical catalyzed oxidation reactions with cyclohexene and cyclooctene with peroxides as initiators, J. Phys. Org. Chem., 2022, 35, e4326 CrossRef CAS.
- P. Ponchai, K. Adpakpang and S. Bureekaew, Selective cyclohexene oxidation to allylic compounds over a Cu-triazole framework via homolytic activation of hydrogen peroxide, Dalton Trans., 2021, 50, 7917–7921 RSC.
- N. E. Thornburg, A. B. Thompson and J. M. Notestein, Periodic trends in highly dispersed groups IV and V supported metal oxide catalysts for alkene epoxidation with H2O2, ACS Catal., 2015, 5, 5077–5088 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Salavati-Niasari, P. Salemi and F. Davar, Oxidation of cyclohexene with tert-butylhydroperoxide and hydrogen peroxide catalysted by Cu(II), Ni(II), Co(II) and Mn(II) complexes of N,N′-bis-(α-methylsalicylidene)-2,2-dimethylpropane-1,3-diamine, supported on alumina, J. Mol. Catal. A: Chem., 2005, 238, 215–222 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Wang, J. Y. Xue, X. Y. Wang and X. H. Liu, Heterogeneous Ag-TiO2-SiO2 composite materials as novel catalytic systems for selective epoxidation of cyclohexene by H2O2, PLoS One, 2017, 12, e0176332 CrossRef PubMed.
- M. Lashanizadegan, S. Rayati and Z. D. Derakhshan, Heterogeneous green catalyst for oxidation of cyclohexene and cyclooctene with hydrogen peroxide in the presence of host (nanocavity of Y-zeolite)/guest (N4-Cu(II) Schiff base complex) nanocomposite material, Chin. J. Chem., 2011, 29, 2439–2444 CrossRef CAS.
- N. Li, C. P. Jian, Y. P. Song, L. Wang, A. U. Rehman, Y. H. Fu, F. M. Zhang, D. L. Chen and W. D. Zhu, Scalable synthesis of MIL-88A(Fe) for efficient aerobic oxidation of cyclohexene to 2-cyclohexene-1-ol, Mol. Catal., 2023, 535, 112899 CrossRef CAS.
- P. Dong, T. N. Shao, J. L. Li, J. P. Xie, X. H. Zhang, Y. Xin, X. R. Wang, Y. Zhao and G. X. Li, The tandem catalysis of porous CoW composite oxide: Intensified allylic oxidation of cyclohexene to 2-cyclohexene-1-one, Mol. Catal., 2024, 556, 113955 CrossRef CAS.
- J. M. Yang, S. L. Liu, Y. Y. Liu, L. M. Zhou, H. Wen, H. J. Wei, R. F. Shen, X. L. Wu, J. C. Jiang and B. J. Li, Review and perspectives on TS-1 catalyzed propylene epoxidation, iScience, 2024, 27, 109064 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- N. Kapil, T. Weissenberger, F. Cardinale, P. Trogadas, T. A. Nijhuis, M. M. Nigra and M. O. Coppens, Precisely engineered supported gold clusters as a stable catalyst for propylene epoxidation, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2021, 60, 18185–18193 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Marimuthu, J. W. Zhang and S. Linic, Tuning selectivity in propylene epoxidation by plasmon mediated photo-switching of Cu oxidation state, Science, 2013, 339, 1590–1593 CrossRef CAS.
- S. El-Korso, I. Khaldi, S. Bedrane, A. Choukchou-Braham, F. Thibault-Starzyk and R. Bachir, Liquid phase cyclohexene oxidation over vanadia based catalysts with tert-butyl hydroperoxide: Epoxidation versus allylic oxidation, J. Mol. Catal. A: Chem., 2014, 394, 89–96 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Xiong, Y. R. He, D. J. Xu, X. H. Liu, C. Xue, X. T. Zhou and H. B. Ji, Enhanced oxygen transfer over bifunctional Mo-based oxametallacycle catalyst for epoxidation of propylene, J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2022, 611, 564–577 CrossRef CAS.
- D. Habibi and A. R. Faraji, Synthesis, characterization and application of a nano-manganese-catalyst as an efficient solid catalyst for solvent free selective oxidation of ethylbenzene, cyclohexene, and benzylalcohol, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2013, 276, 487–496 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Büker, B. Alkan, Q. Fu, W. Xia, J. Schulwitz, D. Waffel, T. Falk, C. Schulz, H. Wiggers, M. Muhler and B. X. Peng, Selective cyclohexene oxidation with O2, H2O2 and tert-butyl hydroperoxide over spray-flame synthesized LaCo1(-xFexO nanoparticles, Catal. Sci. Technol., 2020, 10, 5196–5206 RSC.
- M. Salavati-Niasari and A. Amiri, Synthesis and characterization of alumina-supported Mn(II), Co(II), Ni(II) and Cu(II) complexes of bis(salicylaldiminato)hydrazone as catalysts for oxidation of cyclohexene with tert-buthylhydroperoxide, Appl. Catal., A, 2005, 290, 46–53 CrossRef CAS.
- X. H. Liu, H. Y. Yu, J. Y. Huang, J. H. Su, C. Xue, X. T. Zhou, Y. R. He, Q. He, D. J. Xu, C. Xiong and H. B. Ji, Biomimetic catalytic aerobic oxidation of C-sp(3)-H bonds under mild conditions using galactose oxidase model compound CuIIL, Chem. Sci., 2022, 13, 9560–9568 RSC.
- M. F. Zhao, K. X. Zhang, J. X. Xu and J. Z. Li, FeIII/TBHP mediated remote C-O bond construction of 8-aminoquinolines: access to methoxylation and cyanomethoxylation, Org. Chem. Front., 2022, 9, 4063–4069 RSC.
- R. Lo Scalzo, EPR free radical scavenging activity on superoxide, hydroxyl and tert-butyl hydroperoxide radicals by common hydrophilic antioxidants: effect of mixing and influence of glucose and citric acid, Eur. Food Res. Technol., 2021, 247, 2253–2265 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Chen, J. Y. Zhang, Y. Sun, Y. K. Xu, Y. A. Yang, Y. M. Lee, W. H. Ji, B. J. Wang, W. Nam and B. Wang, Mononuclear non-heme manganese-catalyzed enantioselective cis-dihydroxylation of alkenes modeling rieske dioxygenases, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2023, 145, 27626–27638 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. De Cooman, E. Pauwels, H. Vrielinck, E. Sagstuen, M. Waroquier and F. Callens, Oxidation and reduction products of X irradiation at 10 K in sucrose single crystals: Radical identification by EPR, ENDOR, and DFT, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2010, 114, 666–674 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- U. Hochkirch, W. Herrmann, R. Stösser, K. P. Moll, J. G. Llerena, M. Linscheid and H. H. Borchert, Determination of spin concentrations in ESR tomography as applied for the spatial distribution of spin labels inhuman skin, Appl. Magn. Reson., 2008, 35, 173–184 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Y. Zhu and G. W. Diao, High catalytic activity of CuO nanorods for oxidation of cyclohexene to 2-cyclohexene-1-one, Catal. Sci. Technol., 2012, 2, 82–84 RSC.
- Y. L. Su, L. De Angelis, L. Tram, Y. Yu and M. P. Doyle, Catalytic oxidative cleavage reactions of arylalkenes by tert-butyl hydroperoxide - A mechanistic assessment, J. Org. Chem., 2020, 85, 3728–3741 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. N. Xu, A. Draksharapu, W. Rasheed and L. Que, Acid pKa dependence in O-O bond heterolysis of a nonheme FeIII-OOH intermediate to form a potent FeIV=O oxidant with herne compound I-like reactivity, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2019, 141, 16093–16107 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. T. Zhang, D. D. Xiao, H. Tan and W. B. Liu, Highly selective synthesis of 2-tert-butoxy-1-arylethanones via copper(I)-catalyzed oxidation/tert-butoxylation of aryl olefins with TBHP, J. Org. Chem., 2020, 85, 3929–3935 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. R. Langeslay, D. M. Kaphan, C. L. Marshall, P. C. Stair, A. P. Sattelberger and M. Delferro, Catalytic applications of vanadium: A mechanistic perspective, Chem. Rev., 2019, 119, 2128–2191 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. H. Liu, J. Y. Huang, L. M. Tao, H. Y. Yu, X. T. Zhou, C. Xue, Q. Han, W. Zou and H. B. Ji, Oxygen atom transfer mechanism for vanadium-oxo porphyrin complexe mediated aerobic olefin epoxidation, Chin. J. Chem., 2022, 40, 115–122 CrossRef CAS.
- X. H. Liu, H. Y. Yu, C. Xue, X. T. Zhou and H. B. Ji, Cyclohexene promoted efficient biomimetic oxidation of alcohols to carbonyl compounds catalyzed by manganese porphyrin under mild conditions, Chin. J. Chem., 2020, 38, 458–464 CrossRef CAS.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available: Experimental procedures, spectral data, and computational study details. See DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/d4qo01681e |
| This journal is © the Partner Organisations 2025 |