Open Access Article
Open Access Article3,4-Dimethoxy phenyl thiosemicarbazone as an effective corrosion inhibitor of copper under acidic solution: comprehensive experimental, characterization and theoretical investigations
Naima Benachoura,
Amel Delimib,
Hamza Allal cd,
Abir Boublia
cd,
Abir Boublia e,
Amel Sedikf,
Hana Ferkous*b,
Amel Djedouanif,
Smail Briouaa,
Chérifa Boulechfarb,
Hichem Benzouidg,
Abdelkrim Houssouh,
Ayhan Oralij,
Barbara Ernstk,
Manawwer Alam
e,
Amel Sedikf,
Hana Ferkous*b,
Amel Djedouanif,
Smail Briouaa,
Chérifa Boulechfarb,
Hichem Benzouidg,
Abdelkrim Houssouh,
Ayhan Oralij,
Barbara Ernstk,
Manawwer Alam l and
Yacine Benguerba
l and
Yacine Benguerba m
m
aDepartment of Chemistry, Faculty of Science, Université de Skikda, Skikda, 21000, Algeria
bLaboratory of Mechanical Engineering and Materials, Faculty of Technology, University of 20 Aout 1955, Skikda, 21000, Algeria. E-mail: h.ferkous@univ−skikda.dz
cUnit of Research CHEMS, Chemistry Department, University of Mentouri Brothers, Constantine 1, Algeria
dDepartment of Process Engineering, Faculty of Process Engineering, Salah Boubnider Constantine 3 University, Constantine, Algeria
eLaboratoire de Physico-Chimie des Hauts Polymères (LPCHP), Département de Génie des Procédés, Faculté de Technologie, Université Ferhat ABBAS Sétif-1, Sétif, 19000, Algeria
fScientific and Technical Research, Center in Physico-chemical Analysis (CRAPC), BP 384, Bou-Ismail Industrial Zone, Tipaza, RP 42004, Algeria
gLaboratory of Metallurgy and Materials Engineering, Badji Mokhtar University (UBMA), 23000 Annaba, Algeria
hLaboratory of Nanomaterials-Corrosion and Surface Treatments, University Badji Mokhtar Annaba, Algeria
iScience, Technology, Application, and Research Center, CanakkaleOnsekiz Mart University, Terzioglu Campus, Canakkale, Turkey
jDepartment of Chemistry, Faculty of Sciences, CanakkaleOnsekiz Mart University, Terzioglu Campus, Canakkale, Turkey
kUniversité de Strasbourg, CNRS, IPHC UMR 7178, Laboratoire de Reconnaissance et Procédés de Séparation Moléculaire (RePSeM), ECPM 25 Rue Becquerel, Strasbourg, F-67000, France
lDepartment of Chemistry, College of Science, King Saud University, PO Box 2455, Riyadh, 11451, Saudi Arabia
mLaboratoire de Biopharmacie Et Pharmacotechnie (LBPT), Université Ferhat ABBAS Sétif-1, Sétif, Algeria. E-mail: yacinebenguerba@univ−setif.dz
First published on 30th April 2024
Abstract
This study investigates the corrosion inhibition potential of 3,4-dimethoxy phenyl thiosemicarbazone (DMPTS) for copper in 1 M hydrochloric acid (HCl) solutions, aiming to disclose the mechanism behind its protective action. Through an integrative methodology encompassing electrochemical analyses—such as weight loss measurements, potentiodynamic polarization, and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS)—we quantitatively evaluate the corrosion protection efficacy of DMPTS. It was determined that the optimal concentration of DMPTS markedly boosts the corrosion resistance of copper, achieving an impressive inhibition efficiency of up to 89% at 400 ppm. The formation of a protective layer on the copper surface, a critical aspect of DMPTS's inhibitory action, was characterized using Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) and Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM). These techniques provided empirical evidence of surface morphology modifications and roughness changes, affirming the formation of a protective barrier against corrosion. A significant advancement in our study was the application of Attenuated Total Reflectance Fourier Transform Infrared (ATR-FTIR) spectroscopy, which identified chemical adsorption as the definitive mechanism of corrosion inhibition by DMPTS. The ATR-FTIR results explicitly demonstrated the specific interactions between DMPTS molecules and the copper surface, indicative of a robust protective adsorbed layer formation. This mechanistic insight, crucial to understanding the inhibitory process, aligns with the protective efficacy observed in electrochemical and surface analyses. Theoretical support, provided by the Quantum Theory of Atoms in Molecules (QTAIM) and quantum chemical computations, further validated the strong molecular interaction between DMPTS and copper, corroborating the experimental findings. Collectively, this research not only confirms the superior corrosion inhibition performance of DMPTS in an acidic setting but also elucidates the chemical adsorption mechanism as the foundation of its action, offering valuable insights for the development of effective corrosion inhibitors in industrial applications.
1. Introduction
Copper is highly regarded as a key metallic material, celebrated for its outstanding electrical, thermal, and mechanical properties.1 It is crucial across various sectors, including military, transportation, electronics, automotive, marine, and construction, where its alloys are indispensable in numerous applications.2–4 However, despite its impressive qualities under normal conditions, copper is susceptible to corrosion in severe environmental conditions, especially in acidic contexts containing chloride and sulfate ions.5–7 This corrosion risk poses significant safety and financial implications, making it imperative to develop effective copper protection methods to counter these risks.8 The corrosion challenge underscores the urgency for robust strategies to shield against corrosive agents' potential damages and substantial economic impacts.9–11Various corrosion inhibition techniques have been explored in response, including using corrosion inhibitors designed to mitigate metal corrosion in acidic settings.12,13 Traditional organic corrosion inhibitors, while effective, are hampered by their high cost, toxicity, complicated production processes, and environmental hazards.14,15 This has created an urgent want for environmentally friendly and effective substitutes for these conventional inhibitors. Green inhibitors have gained significant recognition as an effective remedy in the industrial domain due to their non-toxic characteristics and ability to stop corrosion.16–18
Understanding the mechanisms of adsorption and inhibition is essential for developing effective corrosion inhibitors. Organic molecules, particularly those with heteroatoms (N, O, S) or polar functional groups, are known to adsorb onto metal surfaces through physical or chemical interactions.19–21 This adsorption forms protective barrier-type coatings that prevent corrosion by blocking electrochemical reactions at both cathodic and anodic sites on the metal surface.22,23 The efficiency of this protective layer in reducing redox reactions at the metal–solution interface is critical for corrosion inhibition.
The displacement of water molecules by organic inhibitors and the subsequent formation of a robust protective layer are central to this process.22,24,25 The effectiveness of an inhibitor depends on various factors, including the presence of polar groups, a conjugated system,26 and steric effects,27 as well as the charge distribution, molecular size, type of adsorption, and the specific characteristics of both the metal surface and the corrosive environment.28,29
Schiff bases are particularly noted for their efficiency as corrosion inhibitors due to their simple synthesis, strong adsorption capacity on copper surfaces, and significant corrosion resistance, attributed to their structural features that enhance adsorption.13,30 Their efficacy has been widely recognized, with Self-Assembled Monolayers (SAMs) of Schiff bases providing considerable protection against corrosion in aggressive electrolytes.31–34 Notably, Al-Amiery et al. highlighted a Schiff base derivative that exhibited an impressive inhibition efficiency of 90.8% at minimal concentrations.35 Further investigations have demonstrated Schiff bases' potential to achieve up to 94.0% corrosion inhibition in 1 M HCl at a concentration of 5 × 10−3 M, showcasing the characteristics of an efficient corrosion inhibitor.31
Molecular simulations have significantly deepened our understanding by elucidating the atomic-level interactions and bonding energies between Schiff base inhibitors and copper surfaces.36 These simulations offer invaluable insights into the chemical characteristics of organic inhibitors and their interactions with metal surfaces, highlighting the role of electron correlation effects in these processes.20,21,23,37–39 Furthermore, the application of Density Functional Theory (DFT) has been instrumental in exploring the inhibitory capacities and ground-state geometries of various substances, underscoring the theory's computational efficiency in capturing electron correlation effects vital for analyzing chemical interactions.16,40,41 This computational approach complements experimental findings by providing a detailed molecular perspective, thereby enhancing our comprehension of corrosion inhibition mechanisms. However, achieving a holistic understanding of corrosion inhibition necessitates integrating molecular modeling with in situ nanoscale investigations and evaluating macroscopic efficacy. This comprehensive approach ensures a thorough grasp of the inhibitor's performance, from molecular interactions to practical application in preventing corrosion. Such an integrated methodology is crucial for developing more effective corrosion inhibitors, leveraging both theoretical insights and empirical evidence to guide the design and optimization of new corrosion prevention strategies.
This investigation aims to assess the corrosion inhibition effectiveness of 3,4-dimethoxy phenyl thiosemicarbazone (DMPTS) on copper in a 1 M hydrochloric acid (HCl) solution. The selection of a 1 M HCl solution as the corrosion environment holds significance due to its relevance to real-world scenarios. HCl solutions, especially at a concentration of 1 M, are commonly encountered in various industrial processes such as oil well acidification, steel and iron pickling, chemical cleaning, and processing. This acidic environment accelerates the corrosion process, enabling the observation of significant corrosion effects within a reasonable experimental timeframe.42,43 To comprehensively examine the effects of DMPTS on copper corrosion, a range of experimental and computational methodologies will be employed. These methodologies include electrochemical impedance spectroscopy, gravimetric analysis, open circuit potential (OCP), potentiodynamic polarization (PDP), atomic force microscopy (AFM), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy with an attenuated total reflectance accessory (ATR-FTIR) spectroscopy. Additionally, analyses utilizing density functional theory (DFT) simulations, the COSMO-RS approach, non-covalent interaction (NCI) studies, and the quantum theory of atoms in molecules (QTAIM) will provide insights into the atomic-level interactions between DMPTS and copper.
Our study delves into the effects of DMPTS on copper corrosion in a 1 M HCl solution, aiming to provide crucial insights for the development of corrosion-resistant materials and protective coatings in industrial applications. We emphasize the significance of comprehending metal corrosion behavior in acidic environments and the necessity for effective corrosion inhibition strategies to mitigate associated risks. Additionally, we aim to offer a novel perspective on the acidic corrosion control capabilities of Schiff base compounds, with a focus on elucidating their mechanisms and highlighting DMPTS's potential as a robust inhibitor. Furthermore, we advocate for further research into Schiff base compounds and other materials, stressing the importance of understanding inhibitory mechanisms in designing corrosion inhibitors. Through the integration of theoretical and experimental approaches, we anticipate a more comprehensive understanding of inhibition processes, paving the way for the development of safe, effective, and environmentally friendly inhibitors Fig. 1.
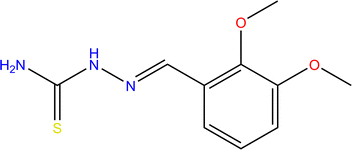 | ||
| Fig. 1 Chemical structure of DMPTS; molecular weight = 239.293 g mol−1, chemical formula = C10H13N3O2S. | ||
2. Experimental
2.1. Copper samples preparation
The working electrode was cut from a cylindrical copper rod (98.9%) and covered with epoxy resin (excluding the bottom exposed surface area of 0.35 cm2). The electrode's surface was smoothed using several grades of emery paper (ranging from 600 to 2400) and polished with 3 mm diamond paste. After degreasing with acetone, rinsing with distilled water to remove any impurities. Following cleaning, the samples were dried, and their initial weights were recorded. Additionally, the weight percent chemical composition of copper sample is revealed in Table 1.| Element | O | H | Mn | Fe | Cu | Zn | Pb | Bi |
| Content (wt%) | 0.39–0.45 | 2 × 10−5 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 99.03 | 0.12 | 0.02 | 0.03 |
2.2. DMPTS synthesis
The synthesis of DMPTS begins with the mixing of equimolar amounts (9 mmol) of 3,4-dimethoxy benzaldehyde and thiosemicarbazide (obtained from Sigma-Aldrich) in 30 ml of absolute ethanol, facilitated by two drops of glacial acetic acid as a catalyst. Refluxing the mixture for three hours ensures complete reaction, yielding a yellow precipitate upon cooling. Filtration and ethanol washing are employed to remove impurities, followed by recrystallization using a solvent mixture of 75% ethanol and 25% water to enhance purity. This meticulous process yields a high-quality DMPTS product with a yield of 68%.2.3. Test solution
To evaluate the inhibitory impact of DMPTS, a prevalent corrosive agent, a 1 M HCl solution, was used for the corrosion inhibition investigation. A range of inhibitor concentrations was evaluated to ascertain the most cost-effective concentration of DMPTS that effectively inhibits corrosion. For this purpose, 100, 200, 300, and 400 ppm concentrations were added to the HCl solution. The experimental procedure began with the preparation of a stock solution. This involved dissolving the required amount of DMPTS to achieve a concentration of 400 ppm in a 1 M HCl solution. This stock solution served as the basis for preparing other required concentrations. By appropriately diluting the stock solution with more 1 M HCl solution, the desired concentrations of 100, 200, and 300 ppm were obtained. This method ensured consistency in the concentration of DMPTS across different test solutions—each set of experiments utilized freshly prepared test solutions to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the results. During the experiments, these solutions were left exposed to air without stirring. This approach was chosen to mimic a more natural and uncontrolled environment, as it would occur in practical applications where stirring or closed systems might not always be feasible. The experiments were conducted at a controlled temperature of 298 K (approximately 25 °C). The choice of 25 °C as the experimental temperature was made to closely resemble standard room temperature conditions, which are commonly encountered in numerous real-world scenarios. These scenarios include indoor environments such as offices, homes, laboratories, and industrial facilities where temperature control is typically maintained around 25 °C. Additionally, ambient outdoor temperatures in many regions often hover around this range, especially in temperate climates. Therefore, selecting 25 °C allows for the simulation of corrosion behaviors under conditions that are representative of a wide range of practical applications and environmental exposures. In general, the objective of this experimental design was to methodically assess the efficacy of DMPTS as a corrosion inhibitor in a frequently encountered corrosive environment (1 M HCl). The primary focus was identifying the optimal DMPTS concentration that balances inhibitory performance and economic viability.2.4. Weight loss method
In this study, we utilized the gravimetric method to evaluate the efficacy of the synthesized DMPTS compound as a corrosion inhibitor for copper in a 1 M HCl solution. Renowned for its simplicity and reliability, this method entails monitoring the metal's weight loss over time to quantify the corrosion rate accurately. Following meticulous sample preparation, involving polishing to ensure surface uniformity and cleaning to eliminate contaminants, the prepared samples underwent immersion in the 1 M HCl solution for 5 hours at room temperature. This immersion period was selected based on its common usage in corrosion studies, providing sufficient time for measurable corrosion effects while maintaining practicality in laboratory settings. During the immersion, exposure was conducted both in the absence and presence of various concentrations of DMPTS to facilitate a comparative analysis of corrosion rates. Following the immersion period, the samples were removed from the solution, cleaned, dried, and weighed again to determine the weight loss incurred due to corrosion.The corrosion rates Wcorr (in the absence of the inhibitor) and 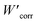 (in the presence of the inhibitor) were calculated in terms of mg cm−2 h−1, reflecting the material lost per unit area per hour due to corrosion. The inhibition efficiency (IEwl) based on weight loss was calculated using the formula:
(in the presence of the inhibitor) were calculated in terms of mg cm−2 h−1, reflecting the material lost per unit area per hour due to corrosion. The inhibition efficiency (IEwl) based on weight loss was calculated using the formula:
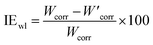 | (1) |
This formula provides a percentage reduction in corrosion rate due to the presence of the inhibitor, offering a quantitative measure of DMPTS's effectiveness as a corrosion inhibitor. A higher IEwl value indicates greater effectiveness at reducing the rate of copper corrosion in an acidic environment.
2.5. Electrochemical measurements
In this study, electrochemical analysis was employed to assess the corrosion inhibiting properties of the synthesized DMPTS compound on copper in an acidic setting. The experiments were conducted with a sophisticated setup, employing the widely recognized Gamry software for precise control and data acquisition in electrochemical research. The experimental configuration featured a three-electrode cell comprising a working electrode, counter electrode, and reference electrode. The working electrode, crafted from copper, served as the substrate for studying corrosion behavior in the presence and absence of the DMPTS inhibitor. For the counter electrode, a platinum (Pt) sheet with a surface area of 2 cm2 was chosen due to its inert nature and excellent conductivity in electrochemical setups. All potential measurements were referenced against an Ag/AgCl (3 M KCl) electrode, a standard choice in electrochemistry known for its stability. Before beginning measurements, the copper electrode underwent a 60 minutes immersion in corrosive solutions (1 M HCl with and without DMPTS). This pre-conditioning step was crucial for establishing a steady-state open-circuit potential (OCP), ensuring that the surface achieved a stable condition representative of the corrosion environment. The use of this carefully designed electrochemical cell and protocol allowed for a comprehensive investigation into the inhibitory effects of DMPTS on copper corrosion.Two main types of electrochemical measurements were performed to comprehensively evaluate the corrosion inhibition capabilities of DMPTS on copper in acidic environments. Potentiodynamic polarization (PD) involved plotting the current density against the applied potential, with polarization curves recorded over a range from −200 mV to +200 mV relative to the Ag/AgCl reference electrode, and a potential sweep rate set at 1 mV s−1. The polarization resistance (Rp), indicative of the material's resistance to corrosion, was calculated using the Tafel extrapolation method. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS) measurements were conducted over a frequency range from 100 kHz to 0.01 Hz, using a signal amplitude of 10 mV peak-to-peak at the OCP. The frequency points per decade for the EIS measurements were set at 10 points per decade. The experimental EIS data were analyzed by fitting them to suitable electrical equivalent circuit diagrams (EECDs) using EClab software. Collectively, these electrochemical techniques provided a holistic comprehension of copper corrosion behavior when exposed to DMPTS, thereby offering valuable insights into its potential as an effective corrosion inhibitor in acidic environments.
2.6. Characterization of a metal surface
This study employed various surface characterization techniques to understand well the corrosion inhibition effect of 3,4-dimethoxy phenyl thiosemicarbazone (DMPTS) on copper surfaces. These techniques were crucial for examining the physicochemical changes on the copper surface after exposure to a corrosive environment (1 M HCl medium) with and without DMPTS at a concentration of 400 ppm.The Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) used was a Jeol JSM-6460LAV model. SEM is an advanced tool for examining the surface morphology of materials at a microscale. It provides high-resolution images that reveal details about the surface texture, morphology, and any corrosion products or protective layers formed on the copper surface. In this study, SEM was used to compare the surface state of the copper samples after being submerged in the corrosive medium with and without the inhibitor.
Coupled with SEM, Energy Dispersive X-ray Spectrometry (EDS) was utilized to analyze the surface's elemental composition. EDS is a technique used to detect and quantify the presence of different elements on the sample's surface. It is particularly useful in corrosion studies to identify the elements involved in corrosion products or inhibitor layers.
The Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM) equipment used was the Integrated Dynamics Engineering D-65479 Raunheimnanoscope model. AFM is a scanning probe microscopy that provides a 3D topographical map of the surface at the nanoscale. It is extremely sensitive to surface features and can provide detailed information about surface roughness, texture, and any changes due to corrosion or the formation of protective layers.
The identification of DMPTS functional groups was carried out using Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy with an attenuated total reflectance accessory (FT-IR/ATR) spectroscopy. ATR-FTIR spectra were collected within the range of 4000–400 cm−1 using the FT/IR 4200 Jasco instrument.
By submerging the copper samples in 1 M HCl for 24 hours, both with and without the DMPTS inhibitor, these techniques allowed for a comparative analysis of the copper surface's condition. SEM and AFM analyses provided detailed surface morphology images, while EDS offered insights into the elemental composition and the nature of any corrosion products or inhibitor films formed. This comprehensive approach to surface characterization is essential for understanding corrosion inhibition mechanisms and the effectiveness of DMPTS in protecting copper surfaces in corrosive environments.
2.7. Theoretical study
In this research, DFT computations play a pivotal role in analyzing the molecular electronic structure of the studied compound, 3,4-dimethoxy phenyl thiosemicarbazone (DMPTS), and its potential protonated forms (N–H and S–H). The quantum chemical computations necessary for this analysis were carried out using the ORCA software package (version 4.2.1).44 These computations utilized the def2-TZVPP triple-quality basis sets45 and the B3LYP functional,46–48 recognized for their accuracy in molecular electronic structure analysis.The geometry-optimized structures of the molecules, along with their frontier molecular orbitals – HOMO (highest occupied molecular orbital energy) and LUMO (lowest unoccupied molecular orbital energy) – were visualized using the Avogadro graphical software (version 23).49 This visualization helps us understand the inhibitor compounds' molecular reactivity and interaction potentials. Additionally, the study included an analysis of the atomic charges within these molecules using the natural population analysis (NPA) approach, with computations performed via the JANPA software package.50 Understanding these charge distributions is essential in predicting molecular interactions, particularly in corrosion inhibition.
The molecular electrostatic potential (MEP) of these compounds was generated using the ORCA package44 and visualized using the UCSF Chimera program (version 1.10.2).51 Furthermore, the Visual Molecular Dynamics (VMD) interface52 was used to compute the Fukui isosurface maps, which depict the areas of maximum reactivity inside the molecules. These maps were constructed using cube files produced by the Multiwfn program.53
The researchers used a conductor-like screening model that was applied to real solutions to examine better the inhibitors' properties and interactions (COSMO-RS). Turbomole 7.4 54 with the def2-TZVPP basis set and B3LYP-DFT for protonated and neutral compounds were used in the optimization procedure. Further analysis of the inhibitor's properties in solution was facilitated using the COSMOThermx program,55 which was employed to compute relevant parameters.
Using approaches such as Reduced Density Gradient (RDG) and the Quantum Theory of Atoms in Molecules (QTAIM),56,57 the investigation also included an intricate analysis of non-covalent interactions (NCI) within a three-dimensional framework. Using reduced density gradients and electron density (ρ), the RDG analysis is delineated as follows:
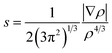 | (2) |
Weak non-covalent interactions, including hydrogen bonds, van der Waals forces, and steric repulsions, are very easy to detect with this approach. Comprehending the behavior of the system requires such interactions.58,59
These NCI investigations used the computational program Multiwfn53 to investigate and identify probable weak interactions within the system. The findings were represented visually using RDG plots and QTAIM maps generated using the VMD interface.52 Furthermore, supplementary color scatter plots were constructed for the components utilizing gnuplot.60 Using these advanced computational methods, a comprehensive analysis of the weak interactions within the molecular system was conducted, yielding significant knowledge on the molecular inhibitory mechanism of DMPTS.
3. Results and discussion
3.1. Weight loss tests
In this section, weight loss tests were conducted to evaluate the corrosion rate of copper and assess the efficacy of the corrosion inhibitor, DMPTS on copper corrosion in 1 M HCl solutions. Fig. 2 summarizes the findings derived from weight loss experiments, providing insights into both the corrosion rate and the efficiency of the corrosion inhibition process at various DMPTS concentrations. This experimental approach offers a straightforward methodology that requires minimal specialized equipment, aligning with its practical feasibility.61–63 Copper samples were submerged in 100 ml of 1 M HCl solution, with and without the presence of DMPTS inhibitor. The immersion duration and inhibitor concentrations were carefully controlled to ensure accurate measurements.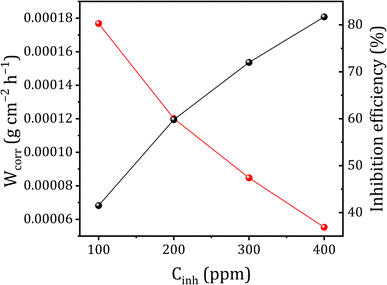 | ||
| Fig. 2 Variation of the corrosion rate inhibition efficiency of DMPTS as a function of concentration for different copper corrosion in 1 M HCl solution. | ||
Fig. 2 depicts the variation in corrosion rate inhibition efficiency of DMPTS across different concentrations in 1 M HCl solution. The corrosion rate was calculated based on the mass loss of the sample surface over a specified time period, expressed in milligrams per square centimeter per hour (mg cm−2 h−1) using the equation:
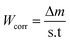 | (3) |
Therefore, the results depicted in Fig. 2 demonstrate a noteworthy trend: as the concentration of DMPTS increases, the percentage of the inhibition efficiency also rises, ranging from 41.5% to 81.7%. This observation indicates that the inhibitor molecules effectively formed a protective coating on the surfaces of copper specimens through adsorption mechanisms.64 The significant enhancement in corrosion inhibition efficiency with increasing DMPTS concentration underscores its potential as an effective corrosion inhibitor for copper in acidic environments. The protective coating formed on the copper surface serves as a barrier against corrosive attack, resulting in reduced corrosion rates. These findings highlight the promising application of DMPTS in corrosion control strategies, particularly in industrial settings where copper components are exposed to aggressive environments.
3.2. Open circuit potential analysis
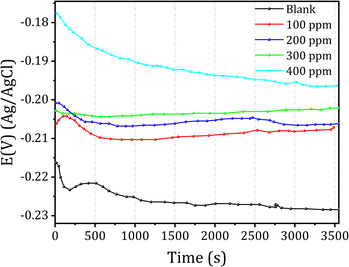
During a corrosion test, changes in the open-circuit potential (OCP) serve as an initial indicator of the extent of deterioration caused by exposure to harsh environments. Fig. 3 depicts the relationship between immersion duration and the OCP of copper in 1 M HCl, both with and without the DMPTS inhibitor, across various concentration levels.As seen in Fig. 3, in the absence of DMPTS, the OCP shows a minimum free corrosion potential. Subsequently, the potential gradually decreases from 80 mV to relatively stable values. This decline corresponds to the dissolution of the metal, with the potential shifting towards less noble values until it reaches a point of relative stability. This stabilization is likely attributed to the formation of protective layers from surface corrosion deposits.65,66 Upon the addition of DMPTS to the 1 M HCl solution, a noticeable shift in the OCP towards more positive potential values is observed, as depicted in Fig. 3. Throughout the measurement period, no substantial fluctuations in the OCP were detected. While OCP data offer valuable insights into the corrosion behavior, it is crucial to emphasize that determining the inhibitor type solely based on OCP measurements is not conclusive.67,68 To gain a comprehensive understanding of the inhibitor's mechanism of action, additional analyses, including polarization and EIS studies, will be essential and will be further discussed in subsequent sections.
3.3. Potentiodynamic polarization
Fig. 4 displays both anodic and cathodic polarization curves obtained from a copper electrode immersed in 1 M HCl, both in the presence and absence of DMPTS. Notably, the inhibitor demonstrates consistent resistance to polarization across all concentrations (Table 2). Moreover, the profiles of both the anodic and cathodic curves remain unchanged, suggesting that the inhibitors selectively impede reaction sites on the copper surface without affecting the anodic and cathodic processes. The lack of a clear pattern in the variation of Ecorr values with increasing inhibitor concentration implies that these compounds function as mixed-type inhibitors. As stated in ref. 69, the anodic reaction of copper in an HCl medium is copper dissolution. This occurs as a result of the oxidation of Cu to Cu+ and Cu+ to Cu2+, as described by eqn (4) and (5).| Cu → Cuads+ + e− (Fast) | (4) |
| Cuads+ → Cusol2+ + e− (Slow) | (5) |
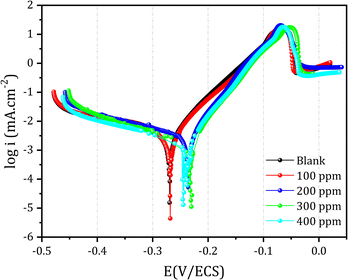 | ||
| Fig. 4 Polarization curves of copper in 1 M HCl in various concentrations of DMPTS inhibitor at 25 °C. | ||
| C (ppm) | icorr (μA cm−2) | Ecorr (mV) | Ba (mV dec−1) | Bc (mV dec−1) | Rp (Ω) | EI% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blank | 3.71 | −268.98 | 53.7 | 227.7 | 4.53 | — |
| 100 ppm | 2.76 | −235.45 | 42.1 | 127.1 | 4138 | 25.39 |
| 200 ppm | 2.14 | −236.10 | 43.2 | 155.9 | 8100 | 42.10 |
| 300 ppm | 1.76 | −239.85 | 42.6 | 200.0 | 13![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 158 158 |
52.53 |
| 400 ppm | 0.45 | −272.22 | 47.2 | 106.74 | 27![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 747 747 |
87.89 |
Cu+ interacts rapidly with Cl− in the electrolyte to yield CuCl, which changes into the soluble CuCl2− complex and has poor adhesion to the copper surface.
| Cu+ + Cl− ↔ CuCl | (6) |
| CuCl + Cl− ↔ CuCl2− | (7) |
Bacarella and Griess70 state that the anodic dissolution of copper in an acidic chloride solution is regulated by diffusion of CuCl2 to the solution bulk and electro-dissolution of copper. The mechanism of the cathodic corrosion process is as follows:
| 1/2O2 + 2H+ + 2e− → H2O | (8) |
Copper corrosion is facilitated by the breakdown of corrosion products and the creation of chloride complexes in chloride-containing environments. An overabundance of Cl− ions results in additional complexes, including CuCl2− and CuCl3−. Furthermore, the dissolution of copper occurs through the formation of CuCl, which is not adequately protective and undergoes a reaction with excess chloride to convert into the soluble form CuCl2−.71,72 Observing the anodic processes makes it possible to see that the copper substrate readily generates cuprous ions on the electrode surface when submerged in HCl. Consequently, the corrosion inhibitor molecules on the copper electrode surface undergo the following reaction process:73
| Cuads+ + nInh → [Cu − Inhh]ads+ | (9) |
As shown in Table 3, the value of corrosion current density is 3.145 μA cm−2 in 1 M HCl environment without DMPTS. When the concentration of inhibitor is 400 ppm in a HCl environment, the corrosion current density of the entire copper electrode surface drops sharply to 0.42 μA cm−2. The inhibition efficiency can arrive up to 87% when the concentration of DMPTS is 400 ppm, which can be considered a high-performance corrosion inhibitor. Studying its application as a copper inhibitor in an acid medium is significant.
| C ppm | Rs | CPEf (μF) × 10−4 | a1 | Rcf (Ω cm2) | W1 (Ohm s−1/2) | σ2 | EI% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blank | 0.7600 ± 0.2 | 3.650 ± 1.56 | 0.680 | 600 ± 0.7 | 50 ± 0.31 | 2.16 | — |
| 100 | 0.7331 ± 0.2 | 3.270 ± 2.14 | 0.741 | 678 ± 0.92 | 50 ± 0.31 | 1.5 | 64.27 |
| 200 | 0.7305 ± 0.2 | 1.730 ± 0.90 | 0.745 | 923.2 ± 0.95 | 72 ± 0.26 | 1.3 | 73.35 |
| 300 | 0.7348 ± 0.2 | 2.400 ± 1.47 | 0.744 | 950 ± 1.20 | 100 ± 0.30 | 2.7 | 70.57 |
| 400 | 0.7510 ± 0.2 | 1.960 ± 0.7 | 0.758 | 1848 ± 3.00 | 600 ± 0.20 | 1.5 | 89.20 |
3.4. EIS measurements
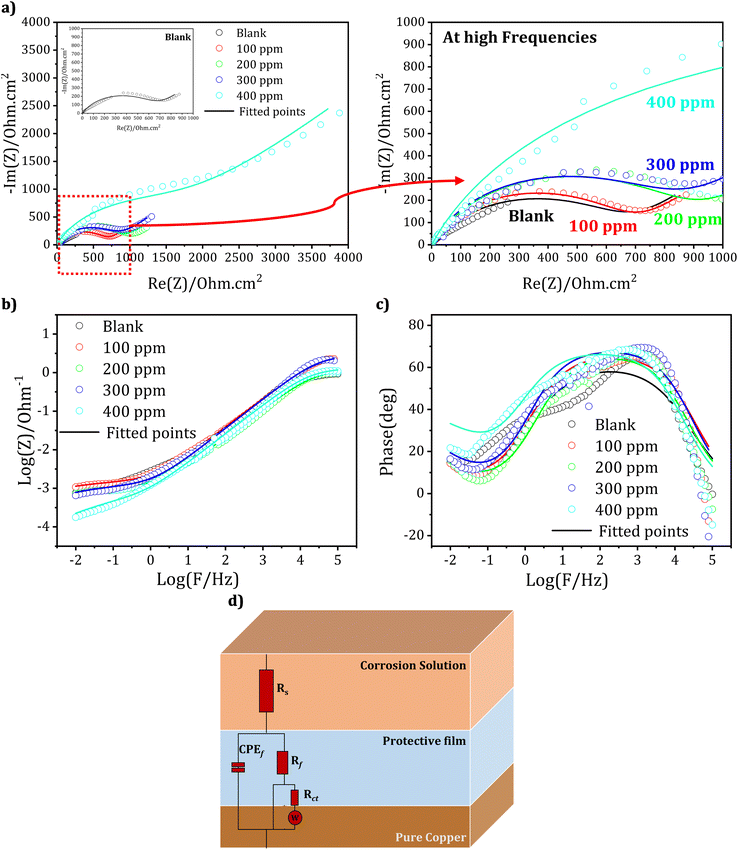
EIS serves as a powerful tool for scrutinizing electrochemical processes occurring at the electrode/electrolyte interface, providing valuable insights into the resistance and capacitance associated with corrosion phenomena. Through the application of low-amplitude alternating current to the working electrode, EIS facilitates a comprehensive exploration of the metal's corrosive behavior.In this study, EIS was employed to assess the corrosion protection capabilities of DMPTS molecules on copper surfaces immersed in a 1 M HCl solution at 25 °C. To examine the impact of inhibitor concentration on inhibition effectiveness, DMPTS was applied at concentrations ranging from 100 to 400 ppm. Fig. 5a and b present representative Nyquist and Bode plots without and with varying concentrations of the inhibitor, respectively. Additionally, Electrical Equivalent Circuit Diagrams (EECD) models (Fig. 5c) were implemented to simulate the Cu/HCl solution interface and interpret EIS data.
The consistent shape of the impedance behavior across different inhibitor concentrations suggests a potentially similar corrosion inhibition mechanism for DMPTS. The Nyquist plot as shown in Fig. 5a revealed two capacitive loops representing charge transfer resistance, double layer capacitance, and Warburg impedance associated with diffusion processes.
In Fig. 5b, the Bode plots for DMPTS exhibit two peaks corresponding to distinct relaxation time constants linked to processes occurring on the copper surface, specifically related to the double layer and the surface inhibitor film.14,74 The EECD model comprises two constant phase elements (CPE) connected in series with uncompensated resistance (Rs), representing solution resistance and electrical connections. Rct represents charge transfer resistance during copper dissolution.67 The deviation from ideal semicircles in Nyquist plots may be attributed to surface inhomogeneity and inhibitor adsorption.75
Parameters derived from EIS measurements are detailed in Table 3, showcasing significant increases in Rs and Rf with DMPTS incorporation, while CPEf exhibits notable reductions compared to the blank condition.65,66,76,77 The diminished CPEf after the addition of DMPTS, attributed to its large size and lower dielectric constant than water, suggests effective inhibition of mass transfer from the metal surface.78–80
The comparative analysis in Table 3 provides a comprehensive understanding of the impact of DMPTS on key parameters, highlighting its pivotal role in modifying the corrosion resistance characteristics of copper in acidic environments. The constant phase angle component CPEf represent Cf, while w signifies the Warburg impedance. The CPE impedance, denoted as ZCPE, is calculated using the formula:
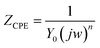 | (10) |
The fitted findings for DMPTS inhibitor concentrations at 1 M HCl, derived from the equivalent electrical circuit modeling of the experimental impedance data and shown in Fig. 5c, are summarized in Table 3. The parameters exhibit a satisfactory fit within experimental error and data repeatability limitations. At 400 ppm, the Rp values (polarization resistance, Rp = Rct + Rf) attain a magnitude of 2319 Ω cm2. Additionally, this resistance is greater when DMPTS is present instead of being blank. The value of fitting to the equivalent circuit was evaluated by the chi square value (χ2).81,82 The achieved chi square values without and with DMPTS compounds respectively (Table 3) reveal an excellent fitting to the suggested circuit. Generally, a rise in polarization resistance corresponds to a reduction in bilayer capacity, a novel corrosion inhibitor for preserving copper.65 Creating an inhibitor layer at the interface between copper and solution is accountable for the experimental outcomes.24,29,81,82 The inhibition efficiency hits 89.20% at 400 ppm, which leads to an increase in electrode surface coverage.
The obtained inhibition efficiency, EI, for the different concentrations of DMPTS inhibitors tested at 1 M HCl reached a maximum of 89.20%. EI was calculated using the equation:
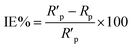 | (11) |
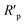 denote the polarization resistance without and with inhibitor addition, respectively.
denote the polarization resistance without and with inhibitor addition, respectively.
3.5. AFM analysis
AFM is quite beneficial to investigate surface morphologies at the nano to microscale. An innovative method has emerged for investigating the impact of the inhibitor on the initiation and advancement of corrosion at the interface between the metal and solution. AFM experiments can illustrate the local corrosion behavior of metals in hostile electrolytes at this level. It is extremely sensitive to surface features and can provide detailed information about surface roughness, texture, and any changes due to corrosion or the formation of protective layers.83 The surface roughness (Sa) and associated copper surface morphologies after polishing are shown in Fig. 6.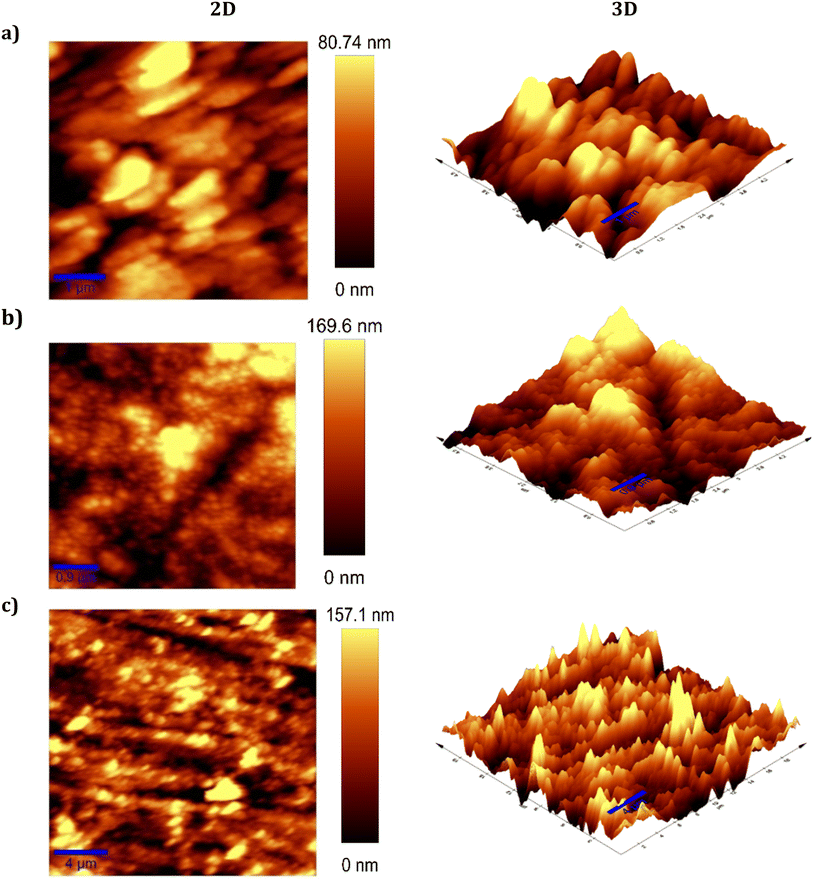 | ||
| Fig. 6 2D and 3D AFM images: (a) for polished copper steel, (b) for immersed in 1 M HCl (blank), and (c) in 1 M HCl containing 400 ppm of DMPTS inhibitors. | ||
The formation of many corrosion pits on the copper surface after polishing with a basic slurry devoid of corrosion inhibitors is seen in Fig. 6a. Sa values for surface roughness reach 0.29 nanometers. In contrast, as seen in Fig. 6b and c, the addition of 400 ppm DMPTS results in a comparatively smoother surface on the copper. The decrease in surface roughness Sa to an estimated value of 0.15 nm is seen in Fig. 6b. According to the findings, DMPTS may effectively produce a passivating coating to protect the copper surface, particularly the concave area, enhancing surface quality Table 4.62,84,85
| RMS (Rq) (nm) | Average roughness (Ra) (nm) | |
|---|---|---|
| Polished metal | 52.7263 | 40.9791 |
| Uninhibited metal | 125.935 | 103.532 |
| Inhibited metal/DMPTS | 45.3064 | 35.0403 |
3.6. SEM analysis
SEM is a powerful tool for examining the surface morphology of materials at a microscale. It provides high-resolution images that reveal details about the surface texture, morphology, and any corrosion products or protective layers formed on the metal surface.EDS was utilized to analyze the surface's elemental composition. EDS is a technique used to detect and quantify the presence of different elements on the sample's surface. It is particularly useful in corrosion studies to identify the elements involved in corrosion products or inhibitor layers. Fig. 7 displays SEM micrographs illustrating the surfaces of copper samples before and after introducing DMPTS at a concentration of 400 ppm in the corrosive medium. SEM micrographs are examined at the same magnification to see the alterations during the corrosion process. The SEM image in Fig. 7a illustrates that the copper surface incurred significant damage due to a quick corrosion attack without an inhibitor after exposure to a 1 M HCl medium. As shown in Fig. 7b, adding DMPTS at a concentration of 400 ppm to the pickling solution results in a comparatively smoother surface with a few minor notches. The adsorption of organic inhibitors may elucidate the latter onto the surface of the substrate. Effective adsorption of DMPTS on copper surfaces might significantly impede the corrosive assault, according to these findings.
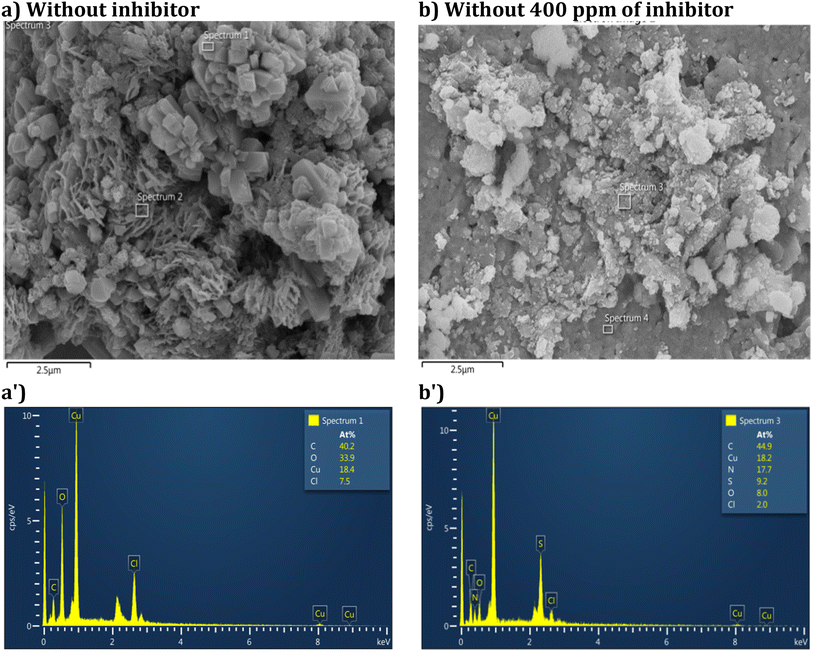 | ||
| Fig. 7 SEM images and EDS spectra of copper surface: after immersion in HCl without DMPTS (a & a') and after immersion in HCl and 400 ppm DMPTS (b & b'). | ||
3.7. ATR-FTIR spectroscopy
ATR-FTIR spectroscopy stands as a critical analytical tool in surface chemistry, offering deep insight into molecular interactions at the metal–inhibitor interface. This technique is particularly crucial for confirming the adsorption of organic inhibitors onto metal surfaces—a fundamental aspect of corrosion science. The examination of vibrational modes of chemical bonds through ATR-FTIR facilitates the identification of functional groups and sheds light on adsorption mechanisms, which are imperative in the design and optimization of corrosion inhibitor.In the present study, ATR-FTIR spectroscopy was utilized to probe the surface chemistry of copper upon treatment with DMPTS in an acidic medium. The spectrum of DMPTS, as illustrated in Fig. 8, shows distinctive peaks which correspond to the functional groups intrinsic to its structure. The N–H stretching vibrations, generally observed in the region of 3300–3500 cm−1, are indeed noted, albeit slightly shifted, possibly due to the electron-withdrawing influence of the adjacent sulfur atom. The aromatic C–H stretches are evident near 3000 cm−1. The characteristic C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N stretch of the thiosemicarbazone framework, typically found around 1600 cm−1, is present and shows a notable shift in the spectrum of the inhibitor-treated copper surface. This shift may signify the involvement of the C
N stretch of the thiosemicarbazone framework, typically found around 1600 cm−1, is present and shows a notable shift in the spectrum of the inhibitor-treated copper surface. This shift may signify the involvement of the C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N group in the coordination to the copper atoms. Additionally, the C–O stretch vibrations of the methoxy groups, expected in the range of 1250–1000 cm−1, exhibit changes in intensity, suggesting their engagement in the adsorption process.
N group in the coordination to the copper atoms. Additionally, the C–O stretch vibrations of the methoxy groups, expected in the range of 1250–1000 cm−1, exhibit changes in intensity, suggesting their engagement in the adsorption process.
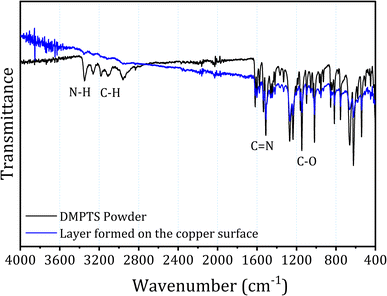 | ||
| Fig. 8 ATR spectrum of the copper surface after immersion in 1 M HCl solution containing 400 ppm of DMPTS. | ||
The ATR-FTIR results, particularly the shifts in peak positions and changes in intensities, provide compelling evidence of the adsorption of DMPTS onto the copper surface. These molecular interactions likely result in the formation of a complex with the metal, which is indicative of a protective layer that could contribute to the observed inhibition of corrosion. These findings not only offer a chemical context for the physical characterization conducted via SEM and AFM but also lay the foundation for understanding the morphological alterations and the protective film's beginning. As such, the ATR-FTIR analysis confirms the efficacy of DMPTS as a corrosion inhibitor, complementing the morphological evidence provided by subsequent analyses including AFM and SEM.
3.8. Theoretical studies
| Parameters | Molecules | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Neutral | Protonated (S–H) | Protonated (N–H) | |
| EHOMO (eV) | −7.978 | −11.302 | −11.777 |
| ELUMO (eV) | 0.213 | −3.536 | −4.816 |
| ΔEgap (eV) | 8.191 | 7.766 | 6.961 |
| μ (Debye) | 7.807 | 8.609 | 5.809 |
| ET (a.u.) | −1102.2 | −1102.6 | −1102.6 |
| η (eV) | 4.095 | 3.883 | 3.480 |
| σ (eV) | 0.244 | 0.258 | 0.287 |
| ω (eV) | 1.840 | 7.088 | 9.888 |
The visual examination of the frontier molecular orbitals corresponding to the optimized structures of the neutral forms of the investigated molecule (Fig. 9) reveals that the HOMO orbitals are delocalized in all areas of the molecule, with the sulfur atom exhibiting a comparatively higher density. In addition, LUMO delocalizes the majority of the molecule with a greater emphasis on the phenyl ring portion. This discovery implies that the potential for adsorption of the investigated neutral molecule is parallel to the metallic surface. The sulfur atom of the C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) S group will be the most reactive location of the molecule and may give electrons to the surface in this configuration. On the contrary, the aromatic ring's carbon atoms will be the most reactive locations in the molecule, capable of accepting electrons from the surrounding surface.
S group will be the most reactive location of the molecule and may give electrons to the surface in this configuration. On the contrary, the aromatic ring's carbon atoms will be the most reactive locations in the molecule, capable of accepting electrons from the surrounding surface.
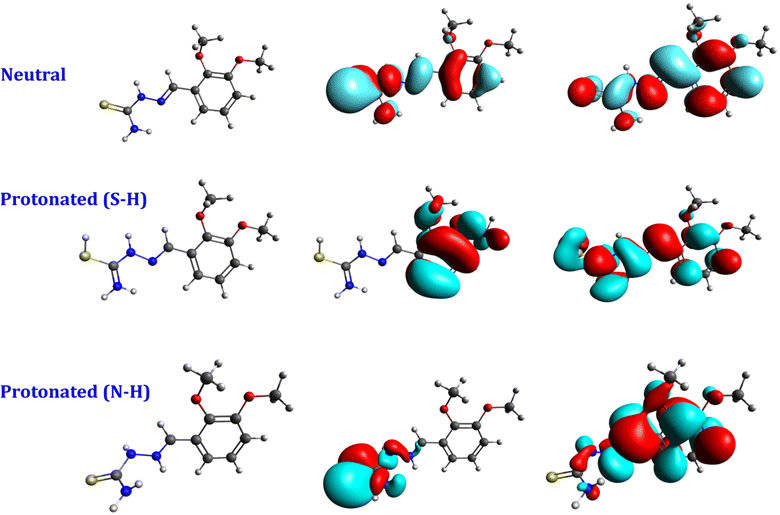 | ||
| Fig. 9 The optimized geometries, HOMO, and LUMO orbitals of the neutral and protonated structure of DMPTS. | ||
Nonetheless, following the DFT calculations, two potential protonated forms were recognized. Both are protonated at the nitrogen atom N3 (protonated N–H), as seen in Fig. 9, with the first protonated at the sulfur atom S1 (protonated S–H).
It is crucial to emphasize that the introduction of a hydrogen atom at the S or N2 position, as seen in the protonated S–H or N–H analogs, respectively, has a notable impact on the HOMO. In the protonated N–H form, the HOMO distribution is delocalized around the C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) S group. In contrast, in the protonated S–H form, the HOMO state is delocalized over the phenyl ring moiety. This observation shows that the protonated molecule at the nitrogen atom N3 (protonated N–H) can adsorb onto the metal surface with perpendicular orientation via the sulfur atom of the C
S group. In contrast, in the protonated S–H form, the HOMO state is delocalized over the phenyl ring moiety. This observation shows that the protonated molecule at the nitrogen atom N3 (protonated N–H) can adsorb onto the metal surface with perpendicular orientation via the sulfur atom of the C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) S group, whereas, through the phenyl ring, the protonated S–H molecule (protonated S1) can cling to metal surfaces.
S group, whereas, through the phenyl ring, the protonated S–H molecule (protonated S1) can cling to metal surfaces.
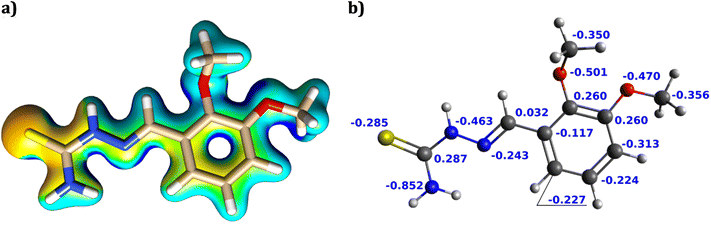 | ||
| Fig. 10 Molecular electrostatic potential (MEP) (a) and the studied neutral molecule's natural population analysis (NPA) (b). | ||
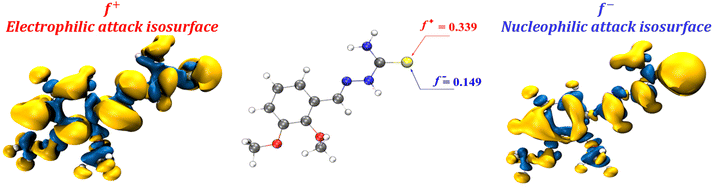
The findings of the atomic charge calculation indicate that heteroatoms have a greater concentration of highly charged electrons, with the nitrogen atom in the NH2 group possessing the most nucleophilic site and the largest negative charge. Additionally, a larger negative electrostatic potential is discernible near the sulfur atoms. This conclusion is consistent with our prior findings about HOMO orbitals, which indicate that the sulfur atom situated inside the C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) S group exhibits the most reactivity toward nucleophilic attack. Nevertheless, it is worth noting that the isosurface of Fukui indices, which represents reactive sites for nucleophilic and electrophilic attacks, is predominantly distributed across the entire molecule (refer to Fig. 11). This suggests that every atom within the molecule has the potential to function as a reactive site for such attacks.
S group exhibits the most reactivity toward nucleophilic attack. Nevertheless, it is worth noting that the isosurface of Fukui indices, which represents reactive sites for nucleophilic and electrophilic attacks, is predominantly distributed across the entire molecule (refer to Fig. 11). This suggests that every atom within the molecule has the potential to function as a reactive site for such attacks.
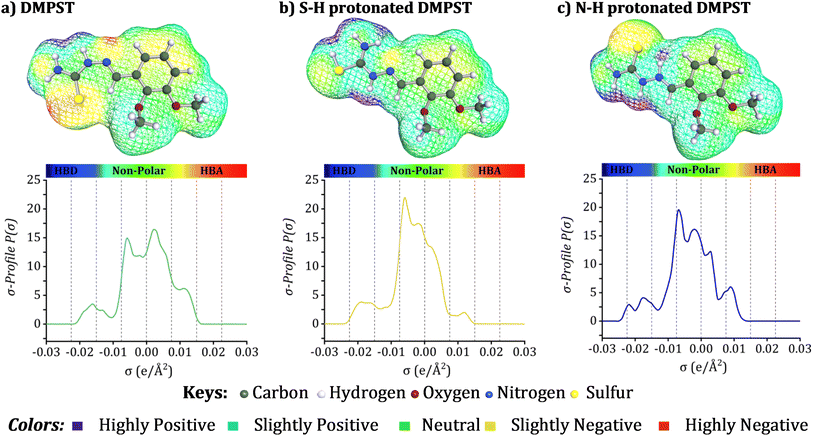 | ||
| Fig. 12 3D surface charge density distribution and σ-profiles of the modeled neutral and protonated DMPTS structures. | ||
The COSMO-RS surfaces clearly illustrate the charge distribution throughout the neutral, SH-protonated, and NH-protonated states of the DMPTS molecule, as shown in Fig. 12. The visual depiction illustrates the following: regions designated as hydrogen bond acceptors (HBA) are colored red, while non-polar areas are represented by green; hydrogen bond donor sites (HBD) are represented by blue.89–92 The σ-profile, as used in COSMO-RS analysis, represents a probability distribution of surface area vs. charge density.93–95 Graphically depicted, the σ-profile is commonly divided into three discrete regions: (1) the HBA region, which signifies positive charge densities; (2) the non-polar region, which signifies nearly neutral charge densities; and (3) the HBD region, which represents negative charge densities.96–99 As a result, the σ-profiles indicate that DMPTS molecules are largely non-polar, except for particular O atoms and localized HBA areas associated with S and N atoms within the DMPTS structures.100,101 This comprehensive analysis of charge distribution and σ-profiles offers significant insights into the characteristics of DMPTS molecules and their possible interactions, improving our capacity to develop efficacious corrosion inhibitors.102
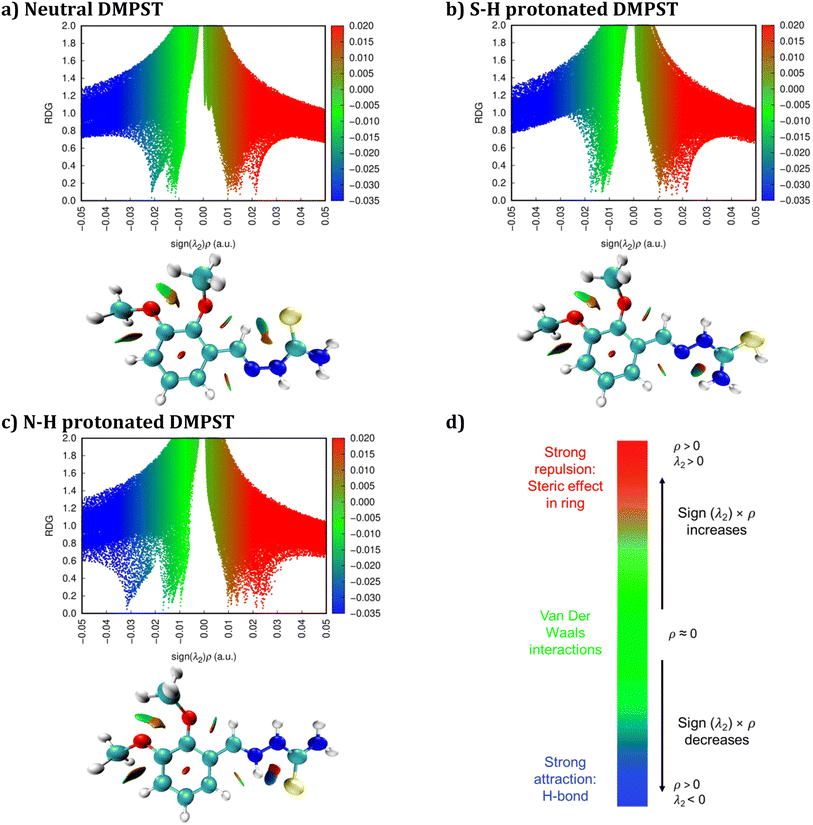
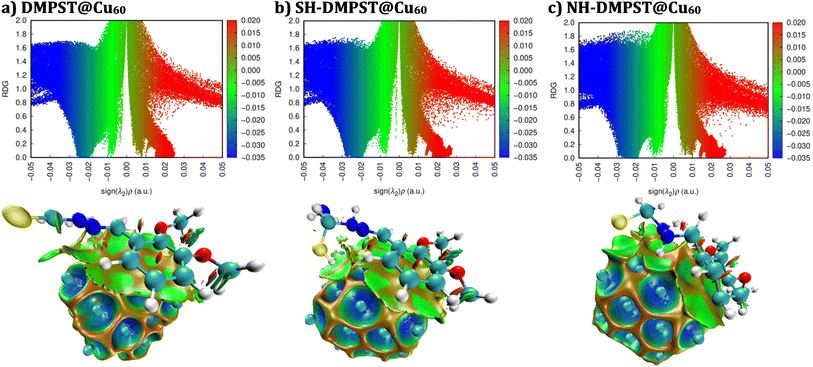
Significantly, the electron clouds in these locations demonstrate stability when interacting with appropriate acceptors. The red scatter plot illustrates the efficient mitigation of steric-repellent interactions between the desired copper surfaces and the DMPTS inhibitors. The corrosion-inhibitory molecules' chemical structure includes heteroatoms, such as N and S, in addition to methoxy or aromatic groups, which contribute to the facilitation of this accomplishment. The NCI-RDG plots provide significant visual depictions, shedding light on the complex intermolecular interactions inside the DMPTS structures. Furthermore, an extensive inquiry was conducted to examine the interactions between the Cu60 cluster surface and DMPTS inhibitors, including neutral and protonated DMPTS. To obtain a more comprehensive understanding of the pertinent interactions and physical characteristics of bonding, the interfaces between DMPTS@Cu60, SH-DMPTS@Cu60, and NH-DMPTS@Cu60 isosurfaces were optimized and analyzed utilizing Turbomole 7.4 software. Additionally, NCI analysis was performed using Multiwfn software.53 Fig. 14 illustrates these complexes' RDG vs. sign (λ2) × ρ plots. These plots differentiate between attractive and non-bonded interactions occurring at the interfaces between the metal surface and the inhibitor. A green zone separating the compound from the copper surface indicates that weak van der Waals interactions make a substantial impact. These interactions are of the utmost importance in reducing steric-repellent forces at the interfaces between the DMPTS and the copper surfaces of interest. This interaction is facilitated by high electron density heteroatoms (e.g., N and S) and certain functional groups (e.g., phenolic or methoxy groups) in the molecular arrangement of corrosion-inhibitory compounds. N and S atoms, in particular, contribute to this. The corrosion inhibition process is highly influenced by van der Waals interactions, as shown by green zones contingent upon the protonation state and coverage of DMPTS. These components enhance the efficacy of corrosion inhibition synergistically.106,107 An assortment of intramolecular and intermolecular interactions, such as repulsive and attractive forces, are represented by coloration. As seen by the green zones in Fig. 14, the NCI studies give vital insights into the critical roles of interactions between the Cu60 surface and adsorption inhibitors in the corrosion inhibition process. DMPTS protonated with SH− and NH− are notable among the structures investigated for their strong electron-donating and accepting properties.36,101,108 These characteristics enhance the establishment of a successful adsorption layer, fortifying the bonds between the material and the copper surface. This insight is consistent with previous discussions that focused on the results of the COSMO−RS, FMO, MEP, and Fukui investigations, which jointly highlighted the bonding and reactivity properties of DMPTS molecules. A more profound appreciation of the inhibitory process elucidates how this molecule efficiently averts corrosion on copper surfaces.
| BCP | X⋯Y | ρ(r) | ∇2ρ(r) | V(r) | G(r) | |V(r)|/G(r) | H(r) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DMPTS@Cu60 | |||||||
| 214 | 33(Cu)⋯19(H) | 0.00841 | 0.01765 | −0.00482 | 0.00461 | −1.04387 | −0.00020 |
| 272 | 37(Cu)⋯2(O) | 0.00971 | 0.02180 | −0.00789 | 0.00667 | −1.18270 | −0.00122 |
| 297 | 41(Cu)⋯15(O) | 0.00757 | 0.01668 | −0.00548 | 0.00483 | −1.13585 | −0.00066 |
| 339 | 13(C)⋯45(Cu) | 0.00805 | 0.01350 | −0.00363 | 0.00350 | −1.03610 | −0.00013 |
| 352 | 70(Cu)⋯28(H) | 0.00906 | 0.01705 | −0.00597 | 0.00512 | −1.16716 | −0.00086 |
| 359 | 64(Cu)⋯7(C) | 0.00952 | 0.01548 | −0.00500 | 0.00444 | −1.12732 | −0.00056 |
| 422 | 44(Cu)⋯12(S) | 0.00754 | 0.01076 | −0.00430 | 0.00350 | −1.23063 | −0.00081 |
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) |
|||||||
| SH-DMPTS@Cu60 | |||||||
| 246 | 5(Cu)⋯72(N) | 0.00820 | 0.01358 | −0.00507 | 0.00423 | −1.19808 | −0.00084 |
| 265 | 8(Cu)⋯75(S) | 0.01083 | 0.01898 | −0.00800 | 0.00637 | −1.25556 | −0.00163 |
| 307 | 13(Cu)⋯70(C) | 0.00991 | 0.01738 | −0.00629 | 0.00532 | −1.18281 | −0.00097 |
| 324 | 13(Cu)⋯94(H) | 0.00874 | 0.01779 | −0.00401 | 0.00423 | −0.94874 | 0.00022 |
| 331 | 9(Cu)⋯78(O) | 0.00821 | 0.01849 | −0.00664 | 0.00563 | −1.17908 | −0.00101 |
| 381 | 43(Cu)⋯68(C) | 0.00696 | 0.00988 | −0.00237 | 0.00242 | −0.97900 | 0.00005 |
| 388 | 91(H)⋯41(Cu) | 0.00911 | 0.01594 | −0.00529 | 0.00464 | −1.14069 | −0.00065 |
| 393 | 41(Cu)⋯66(C) | 0.00913 | 0.01463 | −0.00472 | 0.00419 | −1.12645 | −0.00053 |
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) |
|||||||
| NH-DMPTS@Cu60 | |||||||
| 130 | 91(H)⋯51(Cu) | 0.00778 | 0.01453 | −0.00388 | 0.00376 | −1.03305 | −0.00012 |
| 133 | 69(C)⋯21(Cu) | 0.01270 | 0.01871 | −0.00829 | 0.00648 | −1.27871 | −0.00181 |
| 138 | 78(O)⋯53(Cu) | 0.01041 | 0.02027 | −0.00732 | 0.00620 | −1.18216 | −0.00113 |
| 141 | 67(C)⋯1(Cu) | 0.00869 | 0.01237 | −0.00386 | 0.00348 | −1.11009 | −0.00038 |
| 146 | 93(H)⋯5(Cu) | 0.01249 | 0.02107 | −0.00852 | 0.00689 | −1.23578 | −0.00162 |
| 147 | 89(H)⋯51(Cu) | 0.00964 | 0.01611 | −0.00514 | 0.00458 | −1.12175 | −0.00056 |
| 148 | 72(N)⋯21(Cu) | 0.01094 | 0.01253 | −0.00505 | 0.00409 | −1.23384 | −0.00096 |
| 159 | 74(S)⋯7(Cu) | 0.01088 | 0.01234 | −0.00609 | 0.00459 | −1.32758 | −0.00150 |
| 170 | 74(S)⋯37(Cu) | 0.01033 | 0.00991 | −0.00507 | 0.00377 | −1.34327 | −0.00129 |
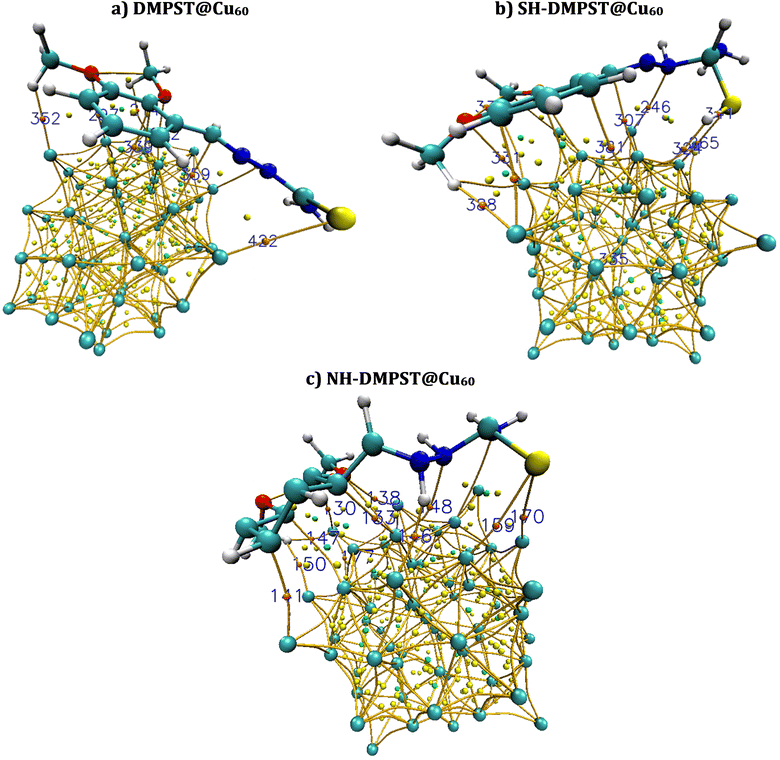
Based on the observed results, positive ρ(r) values were consistently identified across all complexes, namely DMPTS@Cu60, SH-DMPTS@Cu60, and NH-DMPTS@Cu60. Simultaneously, positive Δ2ρ(r) values indicated hydrogen bond interactions involving various pairs, such as N–Cu, S–Cu, O–Cu, and H–Cu. For instance, specific BCPs (e.g., 214, 272, 297, 393, 352, 359, and 422) in DMPTS@Cu60 exhibited positive Δ2ρ(r) and negative H(r) values. This suggests that the interactions between atoms in these complexes possess a partially covalent character. The observation aligns with the fact that the ability to share electrons, represented by V(r), is relatively smaller than their tendency to diffuse, denoted by G(r), evident in |V(r)|/G(r) < 1. Furthermore, the confirmation of weak hydrogen bonding, supported by EHB < 0, for specific bonds like 13(Cu)⋯94(H) and 78(O)⋯53(Cu) in SH-DMPTS and NH-DMPTS, respectively, indicates a physical nature of interaction without a significant covalent character. These results collectively highlight that the interactions within DMPTS@Cu60, SH-DMPTS@Cu60, and NH-DMPTS@Cu60 complexes predominantly involve hydrogen bonding, with some displaying a partially covalent character.112 This comprehension offers valuable insights into the bonding interactions' nature within these systems, emphasizing their potential as effective corrosion inhibitors for Cu60 surfaces. Identifying such interactions is pivotal for understanding the inhibitory mechanism and provides a foundation for further exploration of these compounds as corrosion protection agents for copper-based materials.
3.9. Proposed mechanism for the corrosion inhibition
Investigating the mechanism of inhibition at the interface of copper and hydrochloric acid has played a crucial role in elucidating the complex mechanisms behind the suppression of corrosion. As seen in Fig. 16, this mechanical examination combines theoretical ideas with experimental studies. The complexities of this process begin when the acidic medium, HCl, is introduced, which aids in the protonation of the sulfur or amine function of DMPTS. As shown in the computational section, this protonation happens primarily at the main sulfur atom, followed by protonation at the third nitrogen atom. The copper surface rapidly oxidizes when exposed to this harsh environment, producing a positively charged metal surface that draws negatively charged Cl− ions from the HCl solution.113,114 As a consequence, the metal surface becomes negatively charged. The physical adsorption of protonated inhibitor molecules is accelerated by this electrostatic attraction, resulting in a rapid initial adsorption phase.74,85,115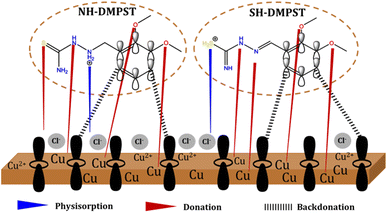 | ||
| Fig. 16 Proposed schematic diagram of the corrosion inhibition mechanism of the studied DMPTS inhibitors. | ||
Furthermore, in addition to conjugated double bonds, the adsorption process is facilitated by the active involvement of electron-rich lone pairs of nitrogen, sulfur, and oxygen.61,68 Using a donor–acceptor contact, this partnership facilitates chemisorption and activates two crucial processes that underlie the inhibitory effect. Initially, electrons are transferred from the active sites of the inhibitor to unoccupied d orbitals of the copper atom (donation). Subsequently, lone pairs in the d orbitals of the copper atom are back donated to electron-poor C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C bonds (Fig. 16). To summarize, water molecules on the copper surface are displaced by DMPTS molecules, distinguished by their polar groups and heteroatoms in their structural makeup via adsorption processes.113,116,117
C bonds (Fig. 16). To summarize, water molecules on the copper surface are displaced by DMPTS molecules, distinguished by their polar groups and heteroatoms in their structural makeup via adsorption processes.113,116,117
Chemisorption is repeatedly confirmed as the predominant adsorption process by experimental and theoretical research,118–121 while the potential of little physisorption cannot be completely ruled out. After careful consideration, it can be deduced that the adsorption of DMPTS on the copper metal surface in the corrosive environment of 1 M HCl is governed by the interdependent mechanisms of physisorption, chemisorption via donation and back-donation.122,123 Compared to the SH-protonated state, the NH-protonated form of DMPTS exhibits a more robust ability to prevent copper corrosion in acidic environments. By presenting a thorough mechanistic depiction of the corrosion inhibition process, this article offers valuable insights into the complex series of occurrences that culminate in the adsorption of inhibitors onto the metal surface.
3.10. Comparative analysis with literature data
In our study, we conducted a comparative analysis of the corrosion inhibition efficiency of DMPTS in comparison to selected literature findings, as presented in Table 7. This analysis aimed to contextualize the performance of DMPTS in relation to other inhibitors reported in the literature and highlight the unique characteristics of DMPTS as a corrosion inhibitor for copper. As shown in Table 7, DMPTS exhibits remarkable corrosion inhibition efficiency across a range of evaluation techniques, including weight loss, PDP, and EIS measurements. The inhibition efficiency of DMPTS varies between 81.70% and 89.20%, depending on the specific evaluation method and experimental conditions employed. Upon comparison with literature data, DMPTS demonstrates comparable or superior inhibition efficiency when tested under similar conditions. For instance, DMPTS exhibits higher inhibition efficiency than N-(4-N,N-dimethylaminobenzal)-p-anisidine (SB1)124 and Chitosan Thiophene carboxaldehyde Schiff base (ChTSB)125 in weight loss measurements, indicating its effectiveness in mitigating copper corrosion in 1 M HCl solution. Furthermore, DMPTS outperforms 2-amino-5-ethylthio-1,3,4-thiadiazole (AETD)126 in both weight loss and electrochemical techniques, highlighting its versatility and effectiveness across different evaluation methods. This superior performance underscores the potential of DMPTS as a promising corrosion inhibitor for copper in acidic environments. The comparative analysis with literature data emphasizes the efficacy of DMPTS as a corrosion inhibitor and underscores its competitive advantage in terms of inhibition efficiency. These findings contribute valuable insights to the existing body of knowledge on corrosion inhibition and underscore the potential of DMPTS as a viable solution for mitigating copper corrosion in industrial applications. As a results, our comparative analysis reaffirms the effectiveness of DMPTS as a corrosion inhibitor for copper. The promising results obtained in our study warrant further exploration of DMPTS and its derivatives for corrosion mitigation purposes, paving the way for the development of novel and efficient inhibitors with applications in various industrial settings.| Inhibitor | Structure | Metal/alloy | Solution | Efficiency (%) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N-(4-N,N-Dimethylaminobenzal)-p-anisidine (SB1) |  |
Mild steel | 1 M HCl | 84.93 WL | 124 |
| Chitosan thiophene carboxaldehyde Schiffbase (ChTSB) | 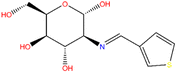 |
Mild steel | 1 M HCl | 81.64 WL | 125 |
| 78.45 PDP | |||||
| 75.22 EIS | |||||
| 2-Amino-5-ethylthio-1,3,4-thiadiazole (AETD) | 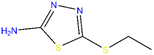 |
Copper | 0.5 M HCl | 77.00 WL | 126 |
| 73.30 PDP | |||||
| 78.50 EIS | |||||
| DMPTS | 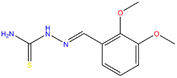 |
Copper | 1 M HCl | 81.70 WL | This work |
| 87.89 PDP | |||||
| 89.20 EIS |
4. Conclusion
In conclusion, this study has successfully investigated the use of 3,4-dimethoxy phenyl thiosemicarbazone (DMPTS), a Schiff base compound, as a cost-effective corrosion inhibitor for copper in 1 M HCl solution. Through a comprehensive suite of experimental and theoretical approaches, the efficacy of DMPTS was thoroughly evaluated, leading to the following salient findings:• DMPTS was employed as a corrosion inhibitor for copper in a 1 M HCl solution, exhibiting concentration-dependent effectiveness up to 89% at 400 ppm.
• Electrochemical studies, specifically EIS analysis, demonstrated an increase in charge transfer resistance, which is indicative of the effective adsorption of DMPTS molecules and the consequent formation of a protective film on the copper surface.
• The surface morphology assessments via AFM, SEM, and corroborative elemental analysis through EDS revealed that the inhibitor molecules confer a significant protective effect. The presence of the inhibitor on the copper surface was further verified by EDS, which showed distinct changes in surface composition compared to the untreated samples.
• ATR-FTIR spectroscopy was introduced as an essential tool for confirming the adsorption of DMPTS onto the copper surface. The spectroscopic data provided definitive evidence of the inhibitor's interaction with the metal, through observable shifts in key vibrational frequencies corresponding to the functional groups in DMPTS.
• Theoretical calculations, including the use of Fukui indices, offered deep insights into the reactive sites of DMPTS molecules, detailing the electron donation and acceptance processes integral to the interaction with the copper surface. A strong agreement was found between the experimental results and the global quantum chemical descriptors, further substantiating the corrosion inhibition mechanism proposed for DMPTS.
The integrated experimental and theoretical framework presented in this study not only underscores the viability of DMPTS as a corrosion inhibitor but also enhances our understanding of the molecular interactions at play. Such knowledge paves the way for the development of more effective and economically feasible corrosion inhibitors for industrial applications.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have not any conflict of interestAcknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the funding from Researchers Supporting laboratoire de Génie mécanique et Matériaux, Faculté de Technologie, University 20 Août 1955-Skikda, Skikda, 21000, Algeria, and the Ministry of Higher Education and Scientific Research, Ferhat ABBAS Setif 1 University, the Directorate General for Scientific Research and Technological Development (DGRSDT), Algeria. The authors are thankful to the Researchers Supporting Project (RSP2024R113), King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.References
- A. Sedik, S. Athmani, A. Saoudi, H. Ferkous, N. Ribouh, D. Lerari, K. Bachari, S. Djellali, M. Berredjem, R. Solmaz, M. Alam, B.-H. Jeon and Y. Benguerba, RSC Adv., 2022, 12, 23718–23735 RSC.
- L. Gao, S. Peng, X. Huang and Z. Gong, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2020, 511, 145446 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Tian, Y. F. Cheng, W. Li and B. Hou, Corros. Sci., 2015, 100, 341–352 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Boublia, Z. Guezzout, N. Haddaoui, M. Badawi, A. S. Darwish, T. Lemaoui, S. E. I. Lebouachera, K. K. Yadav, M. A. Alreshidi, J. S. Algethami, M. Abbas, F. Banat, I. M. AlNashef, B. H. Jeon and Y. Benguerba, Crit. Rev. Solid State Mater. Sci., 2023, 0, 1–25 Search PubMed.
- E. E. El-Katori, M. Ahmed and H. Nady, Colloids Surf., A, 2022, 649, 129391 CrossRef CAS.
- M. E. Belghiti, Y. El Ouadi, S. Echihi, A. Elmelouky, H. Outada, Y. Karzazi, M. Bakasse, C. Jama, F. Bentiss and A. Dafali, Surf. Interfaces, 2020, 21, 100692 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Qiang, S. Zhang, L. Guo, X. Zheng, B. Xiang and S. Chen, Corros. Sci., 2017, 119, 68–78 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Wu, F. Wiame, V. Maurice and P. Marcus, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2020, 527, 146814 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Dehghani, G. Bahlakeh, B. Ramezanzadeh and M. Ramezanzadeh, J. Mol. Liq., 2020, 299, 112220 CrossRef CAS.
- U. M. Angst, Mater. Struct., 2018, 51, 1–20 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Delimi, H. Ferkous, M. Alam, S. Djellali, A. Sedik, K. Abdesalem, C. Boulechfar, A. Belakhdar, K. K. Yadav and M. M. S. Cabral-Pinto, RSC Adv., 2022, 12, 15601–15612 RSC.
- L. Hamadi, S. Mansouri, K. Oulmi and A. Kareche, Egypt. J. Pet., 2018, 27, 1157–1165 CrossRef.
- A. Fateh, M. Aliofkhazraei and A. R. Rezvanian, Arabian J. Chem., 2020, 13, 481–544 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Qiang, H. Li and X. Lan, J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2020, 52, 63–71 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Ramezanzadeh, G. Bahlakeh and B. Ramezanzadeh, J. Mol. Liq., 2020, 304, 112750 CrossRef.
- C. Boulechfar, H. Ferkous, S. Djellali, M. A. Amin, S. Boufas, A. Djedouani, A. Delimi, Y. Ben Amor, K. Kumar Yadav, B.-H. Jeon and Y. Benguerba, J. Mol. Liq., 2021, 344, 117874 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Gabsi, H. Ferkous, A. Delimi, A. Boublia, C. Boulechfar, A. Kahlouche, A. S. Darwish, T. Lemaoui and Y. Benguerba, Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res., 2023, 1–25 Search PubMed.
- A. Peter, I. B. Obot and S. K. Sharma, Int. J. Ind. Chem., 2015, 6, 153–164 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Zarrouk, B. Hammouti, A. Dafali, M. Bouachrine, H. Zarrok, S. Boukhris and S. S. Al-Deyab, J. Saudi Chem. Soc., 2014, 18, 450–455 CrossRef.
- S. Djellali, H. Ferkous, R. Sahraoui and S. Meharga, Recent Advances in Environmental Science from the Euro-Mediterranean and Surrounding Regions (2nd Edition) Proceedings of 2nd Euro-Mediterranean Conference for Environmental Integration (EMCEI-2), Tunisia 2019, Springer, 2021, pp. 1379–1384 Search PubMed.
- A. Delimi, H. Ferkous, M. Alam, S. Djellali, A. Sedik, K. Abdesalem, C. Boulechfar, A. Belakhdar, K. K. Yadav, M. M. S. Cabral-Pinto, B. H. Jeon and Y. Benguerba, RSC Adv., 2022, 12, 15601–15612 RSC.
- H. S. Bahari, F. Ye, E. A. T. Carrillo, C. Leliopoulos, H. Savaloni and J. Dutta, Int. J. Biol. Macromol., 2020, 162, 1566–1577 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Madaci, H. Ferkous, A. Sedik, A. Delimi, C. Boulechfar, A. Belakhdar, M. Berredjem, M. A. Chaouch, M. Alam, H. Majdoub, N. Jaffrezic-Renault and Y. Benguerba, J. Mol. Liq., 2023, 384, 122272 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Sedik, S. Abderrahmane and A. Himour, Sens. Lett., 2011, 9, 2219–2222 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Galai, M. Rbaa, H. Serrar, M. Ouakki, A. Ech-chebab, A. S. Abousalem, E. Ech-chihbi, K. Dahmani, S. Boukhris and A. Zarrouk, Colloids Surf., A, 2021, 613, 126127 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Mo, H. Q. Luo and N. B. Li, J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2017, 505, 929–939 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. Farahati, A. Ghaffarinejad, S. M. Mousavi-Khoshdel, J. Rezania, H. Behzadi and A. Shockravi, Prog. Org. Coat., 2019, 132, 417–428 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Chetouani, B. Hammouti, T. Benhadda and M. Daoudi, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2005, 249, 375–385 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Sedik, S. Abderrahmane, S. Boukerche, A. Himour and A. Gharbi, Sens. Transducers, 2014, 27, 326 Search PubMed.
- C. Verma and M. A. Quraishi, Coord. Chem. Rev., 2021, 446, 214105 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Issaadi, T. Douadi and S. Chafaa, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2014, 316, 582–589 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Zhang, Z. Liu, G.-C. Han, S.-L. Chen and Z. Chen, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2016, 389, 601–608 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Mathiyarasu, S. S. Pathak and V. Yegnaraman, Corros. Rev., 2006, 24, 307–322 CAS.
- P. Zarras and J. D. Stenger-Smith, Intell. Coat. Corros. Control, 2015, 59–91 CAS.
- A. Al-Amiery, T. A. Salman, K. F. Alazawi, L. M. Shaker, A. A. H. Kadhum and M. S. Takriff, Int. J. Low-Carbon Technol., 2020, 15, 202–209 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Boulechfar, H. Ferkous, A. Delimi, A. Djedouani, A. Kahlouche, A. Boublia, A. S. Darwish, T. Lemaoui, R. Verma and Y. Benguerba, Inorg. Chem. Commun., 2023, 110451 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Ferkous, S. Djellali, R. Sahraoui, H. Behloul, K. Saoud and A. Çukurovali, Recent Advances in Environmental Science from the Euro-Mediterranean and Surrounding Regions (2nd Edition) Proceedings of 2nd Euro-Mediterranean Conference for Environmental Integration (EMCEI-2), Tunisia 2019, Springer, 2021, pp. 53–58 Search PubMed.
- A. Kokalj, S. Peljhan, M. Finsgar and I. Milosev, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2010, 132, 16657–16668 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. F. Khaled, Corros. Sci., 2010, 52, 3225–3234 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Ferkous, S. Djellali, R. Sahraoui, H. Behloul, K. Saoud and A. Çukurovali, Recent Advances in Environmental Science from the Euro-Mediterranean and Surrounding Regions (2nd Edition) Proceedings of 2nd Euro-Mediterranean Conference for Environmental Integration (EMCEI-2), Tunisia 2019, Springer, 2021, pp. 1473–1478 Search PubMed.
- F. Bouchareb, M. Berredjem, D. A. Dehmchi, R. Kadri, M. Kadri, H. Ferkous, A. Mansouri, S. Bouyegh, S. A. Ahmed and T. Ben Hadda, J. Mol. Struct., 2023, 1294, 136503 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Bilgiç, Int. J. Corros. Scale Inhib., 2021, 10, 145–175 Search PubMed.
- H. S. Aljibori, O. H. Abdulzahra, A. J. Al Adily, W. K. Al-Azzawi, A. A. Al-Amiery and A. A. H. Kadhum, Int. J. Corros. Scale Inhib., 2023, 12, 842–866 CAS.
- F. Neese, Wiley Interdiscip. Rev.: Comput. Mol. Sci., 2012, 2, 73–78 CAS.
- F. Furche and D. Rappoport, Comput. Photochem., 2005, 16, 93–128 CAS.
- S. Boudjelida, S. Djellali, H. Ferkous, Y. Benguerba, I. Chikouche and M. Carraro, Polymers, 2022, 14, 1505 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Houssou, S. Amirat, H. Ferkous, S. Alleg, K. Dadda, R. Boulechfar, L. Abadlia, W. Bouchelaghem, J.K. Bhutto, M.A. Alreshidi, K.K. Yadav, N. Elboughdiri, A. Erto and Y. Benguerba, Powder Technol., 2024, 433, 10439–10452 CrossRef.
- T. Yasmin, A. Mahmood, M. Farooq, U. Rehman, R. M. Sarfraz, H. Ijaz, M. R. Akram, A. Boublia, M. M. S. Bekhit and B. Ernst, Int. J. Biol. Macromol., 2023, 127032 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. D. Hanwell, D. E. Curtis, D. C. Lonie, T. Vandermeersch, E. Zurek and G. R. Hutchison, J. Cheminf., 2012, 4, 1–17 Search PubMed.
- H. Benzouid, S. Boudebane, H. Ferkous, F. Lekoui, N. Bin Nayan, A. Delimi, M.A. Alreshidi, M. Arshad, K.K. Yadav, B. Ernst, N. Elboughdiri and Y. Benguerba, Mater. Today Commun., 2023, 37, 107405 CrossRef CAS.
- D. Lee, P. M. Chen, J. Flinn and S. Narayanasamy, Proceedings of the 33rd ACM SIGPLAN Conference on Programming Language Design and Implementation, 2012, pp. 463–474 Search PubMed.
- W. Humphrey, A. Dalke and K. Schulten, J. Mol. Graphics, 1996, 14, 33–38 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. Lu and F. Chen, J. Comput. Chem., 2012, 33, 580–592 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- F. Furche, R. Ahlrichs, C. Hättig, W. Klopper, M. Sierka and F. Weigend, Wiley Interdiscip. Rev.: Comput. Mol. Sci., 2014, 4, 91–100 CAS.
- C. Loschen and A. Klamt, 2013.
- S. Kr, M. Murmu, N. Chandra and P. Banerjee, J. Mol. Liq., 2022, 364, 120033 CrossRef.
- E. R. Johnson, S. Keinan, P. Mori-Sánchez, J. Contreras-García, A. J. Cohen and W. Yang, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2010, 132, 6498–6506 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Mandal, S. Bej and P. Banerjee, J. Mol. Liq., 2023, 381, 121789 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Boutouil, M. R. Laamari, I. Elazhary, L. Bahsis, H. Anane and S.-E. Stiriba, Mater. Chem. Phys., 2020, 241, 122420 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Williams, C. Kelley, H. B. Bröker, J. Campbell, R. Cunningham, D. Denholm, E. Elber, R. Fearick, C. Grammes and L. Hart, An interactive plotting program, 2023, available online: http://http//www.gnuplot.info Search PubMed.
- H. Ferkous, A. Delimi, A. Kahlouche, C. Boulechfar, S. Djellali, A. Belakhdar, K. K. Yadav, I. H. Ali, A. Ahmad, H. J. Ahn, M. H. Abdellattif, B. H. Jeon and Y. Benguerba, Polymers, 2022, 14, 1–20 Search PubMed.
- A. Belakhdar, H. Ferkous, S. Djellali, R. Sahraoui, H. Lahbib and Y. Ben Amor, Biomater. Sci., 2020, 3, 46–53 Search PubMed.
- C. Boulechfar, H. Ferkous, S. Boufas, M. Berredjem, A. Delimi, S. Djellali, A. Djedouani, R. Bahadi, S. Laamari, K. K. Yadav, B.-H. Jeon, W. Bouchelaghem, M. Alam and Y. Benguerba, J. Mol. Struct., 2023, 1271, 134007 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Belakhdar, H. Ferkous, S. Djellali, H. Lahbib and Y. Ben Amor, Recent Advances in Environmental Science from the Euro-Mediterranean and Surrounding Regions (2nd Edition) Proceedings of 2nd Euro-Mediterranean Conference for Environmental Integration (EMCEI-2), Tunisia 2019, Springer, 2021, pp. 1479–1483 Search PubMed.
- Z. Jebali, H. Ferkous, M. Zerroug, A. Boublia, A. Delimi, A. Bouzid, H. Majdoub, B. Ernst, N. Elboughdiri and Y. Benguerba, Unveiling the potent corrosion-inhibiting power of Ammophila arenaria aqueous extract for mild steel in acidic environments: An integrated experimental and computational study, J. Environ. Chem. Eng., 2024, 12 DOI:10.1016/j.jece.2024.112374.
- J. He, Q. Li, X. Li, J. An, G. Chen, L. Zhao and W. Li, J. Mol. Liq., 2020, 320, 114494 CrossRef CAS.
- R. Solmaz, G. Kardaş, M. Çulha, B. Yazıcı and M. Erbil, Electrochim. Acta, 2008, 53, 5941–5952 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Boukerche, H. Ferkous, A. Delimi, A. Sedik, A. Djedouani, K. O. Rachedi, H. Bouchoukh, M. Berredjem, M. Zahzouh and A. Himour, Arabian J. Chem., 2023, 16, 105061 CrossRef CAS.
- D.-Q. Zhang, Q.-R. Cai, X.-M. He, L.-X. Gao and G.-D. Zhou, Mater. Chem. Phys., 2008, 112, 353–358 CrossRef CAS.
- A. L. Bacarella and J. C. Griess, J. Electrochem. Soc., 1973, 120, 459 CrossRef CAS.
- K. F. Khaled, M. N. H. Hamed, K. M. Abdel-Azim and N. S. Abdelshafi, J. Solid State Electrochem., 2011, 15, 663–673 CrossRef CAS.
- D. S. Chauhan, M. A. Quraishi, C. Carrière, A. Seyeux, P. Marcus and A. Singh, J. Mol. Liq., 2019, 289, 111113 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Damous, H. Allal, Y. Belhocine, S. Maza and H. Merazig, J. Mol. Liq., 2021, 340, 117136 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Ferkous, M. Zerroug, M. Radjai, M. A. Chaouch, Z. jebali and H. Majdoub, Recent Advances in Environmental Science from the Euro-Mediterranean and Surrounding Regions: Proceedings of Euro-Mediterranean Conference for Environmental Integration (EMCEI-1), Tunisia 2017, Springer, 2018, pp. 1291–1292 Search PubMed.
- A. Popova, M. Christov and A. Vasilev, Corros. Sci., 2011, 53, 1770–1777 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Zhang, L. Yang, Y. Zhang, B. Tan, X. Zheng and W. Li, J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng., 2022, 136, 104408 CrossRef CAS.
- R. Solmaz, A. Salcı, Y. A. Dursun and G. Kardaş, Colloids Surf., A, 2023, 674, 131908 CrossRef CAS.
- E. Altunbaş Şahin, F. Tezcan, R. Solmaz and G. Kardaş, J. Adhes. Sci. Technol., 2020, 34, 135–152 CrossRef.
- M. Shabani-Nooshabadi and F. Karimian-Taheri, RSC Adv., 2015, 5, 96601–96610 RSC.
- K. El Mouaden, B. El Ibrahimi, R. Oukhrib, L. Bazzi, B. Hammouti, O. Jbara, A. Tara, D. S. Chauhan and M. A. Quraishi, Int. J. Biol. Macromol., 2018, 119, 1311–1323 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Wan, H. Chen, B. Liao and X. Guo, Prog. Org. Coat., 2024, 186, 108089 CrossRef CAS.
- Z. G. Luo, Y. Zhang, H. Wang, S. Wan, L. F. Song, B. K. Liao and X. P. Guo, Corros. Sci., 2024, 227, 111705 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Sedik, D. Lerari, A. Salci, S. Athmani, K. Bachari, İ. H. Gecibesler and R. Solmaz, J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng., 2020, 107, 189–200 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Zerroug, H. Ferkous, M. Radjai, M. A. Chaouch, A. Madaci, H. Majdoub and A. Bouzid, Recent Advances in Environmental Science from the Euro-Mediterranean and Surrounding Regions: Proceedings of Euro-Mediterranean Conference for Environmental Integration (EMCEI-1), Tunisia 2017, Springer, 2018, pp. 1337–1339 Search PubMed.
- M. Radjai, H. Ferkous, M. Zerroug, S. Djellali, M. A. Chaouch, B. Hattabi, H. Majdoub and M. Boutahala, Recent Advances in Environmental Science from the Euro-Mediterranean and Surrounding Regions: Proceedings of Euro-Mediterranean Conference for Environmental Integration (EMCEI-1), Tunisia 2017, Springer, 2018, pp. 1379–1381 Search PubMed.
- S. Bousba, H. Allal, M. Damous and S. Maza, Comput. Theor. Chem., 2023, 1225, 114168 CrossRef CAS.
- B. Sakki, M. E. Said, B. Mezhoud, H. Allal, Y. Larbah, A. Kherrouba, A. Chibani and A. Bouraiou, J. Adhes. Sci. Technol., 2022, 36, 2245–2268 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Acidi, A. Sedik, A. Rizi, R. Bouasla, K. O. Rachedi, M. Berredjem, A. Delimi, A. Abdennouri, H. Ferkous and K. K. Yadav, J. Mol. Liq., 2023, 391, 123423 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Boublia, T. Lemaoui, G. Almustafa, A. S. Darwish, Y. Benguerba, F. Banat and I. M. AlNashef, ACS Omega, 2023, 8(14), 13177–13191 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. Lemaoui, A. Boublia, A. S. Darwish, M. Alam, S. Park, B.-H. Jeon, F. Banat, Y. Benguerba and I. M. AlNashef, ACS Omega, 2022, 7(36), 32194–32207 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Mouffok, D. Bellouche, I. Debbous, A. Anane, Y. Khoualdia, A. Boublia, A. S. Darwish, T. Lemaoui and Y. Benguerba, J. Mol. Liq., 2023, 375, 121321 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Boublia, T. Lemaoui, J. AlYammahi, A. S. Darwish, A. Ahmad, M. Alam, F. Banat, Y. Benguerba and I. M. AlNashef, ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng., 2023, 11(1), 208–227 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Lemaoui, A. S. Darwish, G. Almustafa, A. Boublia, P. R. Sarika, N. A. Jabbar, T. Ibrahim, P. Nancarrow, K. K. Yadav, A. M. Fallatah, M. Abbas, J. S. Algethami, Y. Benguerba, B. H. Jeon, F. Banat and I. M. AlNashef, Energy Storage Mater., 2023, 59, 102795 CrossRef.
- D. Uka, B. Blagojević, O. Alioui, A. Boublia, N. Elboughdiri, Y. Benguerba, T. Jurić and B. M. Popović, J. Mol. Liq., 2023, 123411 CrossRef CAS.
- J. AlYammahi, A. S. Darwish, T. Lemaoui, A. Boublia, Y. Benguerba, I. M. AlNashef and F. Banat, ACS Omega, 2023, 8(29), 26533–26547 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- E. Słupek, P. Makoś-Chełstowska and J. Gębicki, Materials, 2021, 14, 1–20 CrossRef PubMed.
- A. Boublia, T. Lemaoui, F. Abu Hatab, A. S. Darwish, F. Banat, Y. Benguerba and I. M. AlNashef, J. Mol. Liq., 2022, 366, 120225 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Lemaoui, A. Boublia, S. Lemaoui, A.S. Darwish, B. Ernst, M. Alam, Y. Benguerba, F. Banat and I.M. AlNashef, ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng., 2023, 11, 9564–9580 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Boublia, Z. Guezzout, N. Haddaoui, M. Badawi, A. S. Darwish, T. Lemaoui, F. Banat, K. K. Yadav, B.-H. Jeon, E. Noureddine, Y. Benguerba and I. AlNashef, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2024, 12, 2209–2236 RSC.
- A. Belakhdar, H. Ferkous, S. Djellali, R. Sahraoui, H. Lahbib, Y. Ben Amor, A. Erto, M. Balsamo and Y. Benguerba, Colloids Surf., A, 2020, 606, 125458 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Behloul, H. Ferkous, N. Bougdah, S. Djellali, M. Alam, C. Djilani, A. Sedik, D. Lerari, B.-H. Jeon and Y. Benguerba, J. Mol. Liq., 2022, 364, 119956 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Kahlouche, H. Ferkous, A. Delimi, S. Djellali, K. K. Yadav, A. M. Fallatah, B.-H. Jeon, K. Ferial, C. Boulechfar, Y. Ben Amor and Y. Benguerba, J. Mol. Liq., 2022, 347, 118397 CrossRef CAS.
- M. E. Said, H. Allal, B. Mezhoud, M. Bouchouit, A. Chibani and A. Bouraiou, Int. J. Corros. Scale Inhib., 2023, 12, 679–695 CAS.
- Q. H. Zhang, B. S. Hou, Y. Y. Li, Y. Lei, X. Wang, H. F. Liu and G. A. Zhang, Corros. Sci., 2021, 189, 109596 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Murmu, N. C. Murmu, M. Ghosh and P. Banerjee, J. Adhes. Sci. Technol., 2022, 36, 2732–2760 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Ferkous, A. Sedik, A. Delimi, R. Redjemia, K. Abdesalem, C. Boulechfar, A. Abdennouri, A. Madaci, M. Berredjem, A. Boublia, M. Sajid Ali, B.-H. Jeon, K. Kumar Yadav and Y. Benguerba, J. Mol. Liq., 2023, 123781 Search PubMed.
- C. Gattinoni and A. Michaelides, Faraday Discuss., 2015, 180, 439–458 RSC.
- C. Boulechfar, H. Ferkous, A. Delimi, M. Berredjem, A. Kahlouche, A. Madaci, S. Djellali, S. Boufas, A. Djedouani and A. Errachid, J. Mol. Liq., 2023, 121637 CrossRef CAS.
- F. Fuster and S. J. Grabowski, J. Phys. Chem. A, 2011, 115, 10078–10086 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. L. A. Popelier, Chem. Bond Fundam. Asp. Chem. Bond., 2014, pp. 271–308 Search PubMed.
- O. Moumeni, M. Mehri, R. Kerkour, A. Boublia, F. Mihoub, K. Rebai, A. A. Khan, A. Erto, A. S. Darwish, T. Lemaoui, N. Chafai and Y. Benguerba, J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng., 2023, 147, 104918 CrossRef CAS.
- P. S. V. Kumar, V. Raghavendra and V. Subramanian, J. Chem. Sci., 2016, 128, 1527–1536 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Ferkous, M. Zerroug, M. A. Chaouch, M. Radjai, H. Majdoub and A. Bouzid, Advances in Science, Technology and Innovation, 2018, pp. 1293–1296 Search PubMed.
- H. Ferkous, S. Djellali, R. Sahraoui, Y. Benguerba, H. Behloul and A. Çukurovali, J. Mol. Liq., 2020, 307, 112957 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Ferkous, A. Dilemi, A. Abdennouri and S. I. R. Malha, Synthèse: Revue des Sciences et de la Technologie, 2023, 29, 36–43 Search PubMed.
- H. Ferkous, A. Delimi, A. Kahlouche, C. Boulechfar, S. Djellali, A. Belakhdar, K. K. Yadav, I. H. Ali, A. Ahmad and H.-J. Ahn, Polymers, 2022, 14, 3288 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Rizi, A. Sedik, A. Acidi, K. O. Rachedi, H. Ferkous, M. Berredjem, A. Delimi, A. Abdennouri, M. ALAM, B. Ernst and Y. Benguerba, ACS Omega, 2023, 8, 47224–47238 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- G. L. Dotto, L. A. A. Pinto, M. A. Hachicha and S. Knani, Food Chem., 2015, 171, 1–7 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Pang, L. Sellaoui, D. Franco, M. S. Netto, J. Georgin, G. Luiz Dotto, M. K. Abu Shayeb, H. Belmabrouk, A. Bonilla-Petriciolet and Z. Li, Chem. Eng. J., 2020, 391, 123617 CrossRef CAS.
- G. S. dos Reis, B. Grigore Cazacliu, C. Rodriguez Correa, E. Ovsyannikova, A. Kruse, C. Hoffmann Sampaio, E. C. Lima and G. L. Dotto, J. Environ. Chem. Eng., 2020, 8, 103605 CrossRef CAS.
- H. N. Tran, H. C. Nguyen, S. H. Woo, T. V. Nguyen, S. Vigneswaran, A. Hosseini-Bandegharaei, J. Rinklebe, A. Kumar Sarmah, A. Ivanets and G. L. Dotto, Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol., 2019, 49, 2155–2219 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Rouibah, H. Ferkous, A. Delimi, T. Himeur, M. Benamira, M. Zighed, A. S. Darwish, T. Lemaoui, K. K. Yadav, J. K. Bhutto, A. Ahmad, S. Chaiprapat and Y. Benguerba, J. Environ. Manage., 2023, 326, 116742 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Ferkous, K. Rouibah, N.-E.-H. Hammoudi, M. Alam, C. Djilani, A. Delimi, O. Laraba, K. K. Yadav, H.-J. Ahn, B.-H. Jeon and Y. Benguerba, Polymers, 2022, 14, 2396 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. Sethi, A. Chaturvedi, R. K. Upadhyay and S. P. Mathur, J. Chil. Chem. Soc., 2007, 52, 1206–1213 CAS.
- R. Menaka and S. Subhashini, Polym. Int., 2017, 66, 349–358 CrossRef CAS.
- E. M. Sherif and S.-M. Park, Electrochim. Acta, 2006, 51, 6556–6562 CrossRef CAS.
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2024 |