Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleLewis acid-catalyzed (3 + 2) annulation of bicyclobutanes with ynamides: access to 2-amino-bicyclo[2.1.1]hexenes†
Deeptanu
Sarkar
,
Shiksha
Deswal
,
Rohan
Chandra Das
and
Akkattu T.
Biju
 *
*
Department of Organic Chemistry, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore-560012, India. E-mail: atbiju@iisc.ac.in; Web: https://atbiju.in/
First published on 10th September 2024
Abstract
Strain-release driven annulations with bicyclo[1.1.0]butanes (BCBs) have become an attractive area of research for the synthesis of bioisosteric bicyclohexane derivatives, which play a vital role in drug discovery. Interestingly, the utilization of the inherent strain in BCBs for the synthesis of functionalized amino-bicyclo[2.1.1]hexenes, which may spatially mimic substituted benzenes and anilines, has received only scant attention. Herein, we report the Sc(OTf)3-catalyzed (3 + 2) annulation of BCBs with ynamides for the facile synthesis of 2-amino-bicyclo[2.1.1]hexenes in one step under mild conditions. The reaction likely proceeds via nucleophilic addition facilitated by the nitrogen lone pair from the alkynyl group of the ynamides to the unsubstituted side of the BCBs, followed by the annulation of the resulting enolate with the keteniminium species. For the first time, the C–C triple bond of ynamides was utilized as the coupling partner for BCBs, resulting in products adorned with a functionalizable amino group and an integrated strained alkene moiety.
Introduction
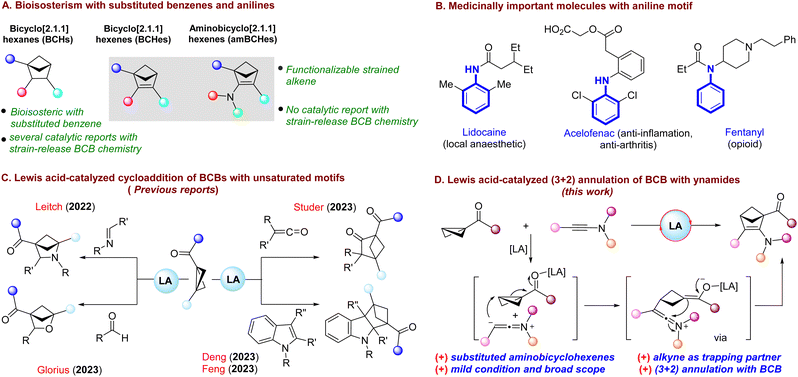
The construction of highly strained hydrocarbons is synthetically challenging and has always attracted the interest of organic and physical chemists.1 The incorporation of saturated building blocks into target molecules has become one of the key strategies in the fields of drug delivery and medicinal chemistry.2 Over the years, there has been growing interest in the synthesis of different strained bicyclic scaffolds3 and these three-dimensional architectures with conformationally restricted C(sp3)-rich skeletons are becoming increasingly relevant in bioisosterism.4 Among them, the synthesis of bicyclo[2.1.1]hexanes (BCHs) is of great interest as they can serve as bioisosteres of benzene rings (Scheme 1A).5The well-known synthetic route to BCHs is the intramolecular [2 + 2] cycloaddition of 1,5-dienes.6 Apart from that, chemists have become more interested in utilizing the strain-release driven cycloaddition of bicyclo[1.1.0]butanes (BCBs) for the synthesis of BCHs and other bicyclic frameworks.7 But there is only one known example of the utilization of this strain-driven cycloaddition strategy for the synthesis of bicyclohexenes.8 These bicyclohexenes may also serve as bioisosteres of benzene derivatives, and the presence of a strained alkene group in bicyclohexenes makes them synthetically more valuable as they can be further functionalized to synthesize various BCHs. Especially, an amino group directly attached to the bicyclohexene core might replicate the properties of aniline, which is medicinally important.9–11 Therefore, we envisioned a strain-release driven annulation of BCBs with ynamides, which could lead to the synthesis of amino-bicyclohexenes in one step, thereby rendering the methodology more atom- and step-economic.
Recently, BCBs have received significant attention from organic chemists for the synthesis of strained bicyclic scaffolds owing to their higher strain energy (66.3 kcal mol−1) and strained butterfly shape.7 The most commonly utilized mode of reactivity of BCBs is the cycloaddition reaction originating from the breaking of the strained σ-bond. Among these cycloaddition processes, strain-release driven [2π + 2σ] cycloaddition has been extensively investigated for the synthesis of BCH frameworks. In this context, Glorius,12 Brown13 and Procter14 groups achieved independent breakthroughs by uncovering intermolecular [2π + 2σ] cycloaddition between BCBs and alkenes using photocatalysis. Moreover, Li15 and Wang16 groups showcased the utilization of a pyridine-boryl radical system to catalyze formal [2π + 2σ] cycloaddition.
Although significant advances have been made using photocatalytic and radical-based approaches, Lewis acid catalysis has recently emerged as a simple yet effective method for catalyzing the annulation reactions of BCBs. Considering this, Leitch and co-workers17 pioneered Lewis acid catalysis for the formal [2π + 2σ] cycloaddition reaction, employing N-arylimines and BCBs to synthesize azabicyclo[2.1.1]hexanes (Scheme 1C). Later, the Studer group18 utilized a Lewis acid-catalyzed approach to illustrate the formal [2π + 2σ] cycloaddition of ketenes with BCBs, yielding BCHs. Subsequently, the Glorius group19 demonstrated the incorporation of aldehydes as coupling partners in the formal [2π + 2σ] cycloaddition of BCBs. Moreover, Deng20 and Feng21 groups independently disclosed the dearomative [2π + 2σ] cycloaddition of indoles with BCBs via Lewis acid catalysis for the synthesis of bicyclo[2.1.1]hexanes.
Despite the advent of strain release-driven cycloadditions of BCBs, in most cases, the coupling partners are limited to moieties with either C–C, C–N or C–O double bonds leading to saturated BCHs, where the bicyclic skeleton cannot be further functionalized. Interestingly, the use of C–C triple bond containing coupling partners for annulation with BCBs has received only scant attention.22 Encouraged by this, we envisaged a Lewis acid-catalyzed annulation of BCBs with the C–C triple bond of ynamides, which could lead to the formation of functionalized 2-amino-bicyclo[2.1.1]hexenes with a strained alkene integrated in the bicyclic scaffold readily available for further synthetic transformations. This is likely to open a new synthetic avenue in drug development and drug design, providing a straightforward route to multisubstituted 2-amino-bicyclohexenes.
The choice of ynamides was based on their versatility as building blocks in different organic transformations specifically in the field of cycloaddition reactions.23 The uniqueness of ynamides comes from the presence of a nitrogen atom directly attached to the alkyne moiety, which makes them more active towards the cycloaddition reaction. Also, regioselectivity can be attributed to the zwitterionic resonance structure of ynamides. While this manuscript was under preparation, Chen, Zhou and co-workers have reported an elegant Lewis acid-catalyzed (3 + 2) annulation of BCBs with ynamides for the synthesis of polysubstituted 2-amino-bicyclo[2.1.1]hexenes.24 Notably, Chen, Zhou and co-workers used N-mesyl ynamide substrates along with a Na2SO4 additive under their optimized conditions, and we utilized N-tosyl ynamides without additives, and both reactions are catalyzed by Sc(OTf)3.
Results and discussion
Inspired by the idea of using ynamides as the olefin partner, the present studies were initiated by treating 2-naphthyl substituted BCB 1a with N-tosyl substituted ynamide 2a in the presence of Sc(OTf)3 (10 mol%) in CH2Cl2 at 30 °C (Table 1, entry 1).25 Interestingly, the desired (3 + 2) annulation product 3a was obtained in 61% yield. Intrigued by this result, various Lewis acids were examined for this (3 + 2) annulation. Disappointingly, the Lewis acid screening did not improve the yield of 3a (entries 2–5). Switching the reaction solvent to CHCl3 resulted in 60% yield of the desired 2-amino-bicyclohexene product (entry 6). However, changing to other solvents such as toluene and dichloroethane (DCE) did not enhance the yield of 3a (entries 7 and 8). Since the ynamide 2a is prone to degradation to the corresponding amide in the presence of a Lewis acid, an experiment was performed with 4 Å MS as an additive.26 This reaction also did not help in improving the yield of 3a (entry 9). Reducing the reaction concentration by half led to a 49% yield of 3a (entry 10). Moreover, reducing or increasing the loading of Sc(OTf)3 did not enhance the yield of 3a (entries 11 and 12). Notably, when Sc(OTf)3 was added at the end to the reaction flask, 3a was formed in an improved yield of 65% (entry 13). This condition was used for substrate scope studies.27| Entry | Variation of the initial conditionsa | Yield of 3ab (%) |
|---|---|---|
| a Initial conditions: 1a (0.1 mmol), 2a (2.0 equiv., addition at the end), Sc(OTf)3 (10 mol%), CH2Cl2 (0.1 M), 30 °C, and 18 h. b The 1H NMR yield of the crude products determined with the aid of 1,3,5-trimethoxybenzene as an internal standard. Isolated yield in parentheses. c Sc(OTf)3 was added at the last; see the ESI for details. | ||
| 1 | None (2a was added at the end) | 62 (61) |
| 2 | Yb(OTf)3 instead of Sc(OTf)3 | 50 |
| 3 | Bi(OTf)3 instead of Sc(OTf)3 | 20 |
| 4 | TMS-OTf instead of Sc(OTf)3 | 51 |
| 5 | Eu(OTf)3 instead of Sc(OTf)3 | 38 |
| 6 | CHCl3 instead of CH2Cl2 | 60 |
| 7 | Toluene instead of CH2Cl2 | 53 |
| 8 | DCE instead of CH2Cl2 | 43 |
| 9 | 4 Å MS as the additive | 56 |
| 10 | 0.05 M CH2Cl2 instead of 0.1 M CH2Cl2 | 49 |
| 11 | 5 mol% Sc(OTf)3 instead of 10 mol% | 59 |
| 12 | 15 mol% Sc(OTf)3 instead of 10 mol% | 62 |
| 13c | Sc(OTf)3 added at the end | 65 (65) |
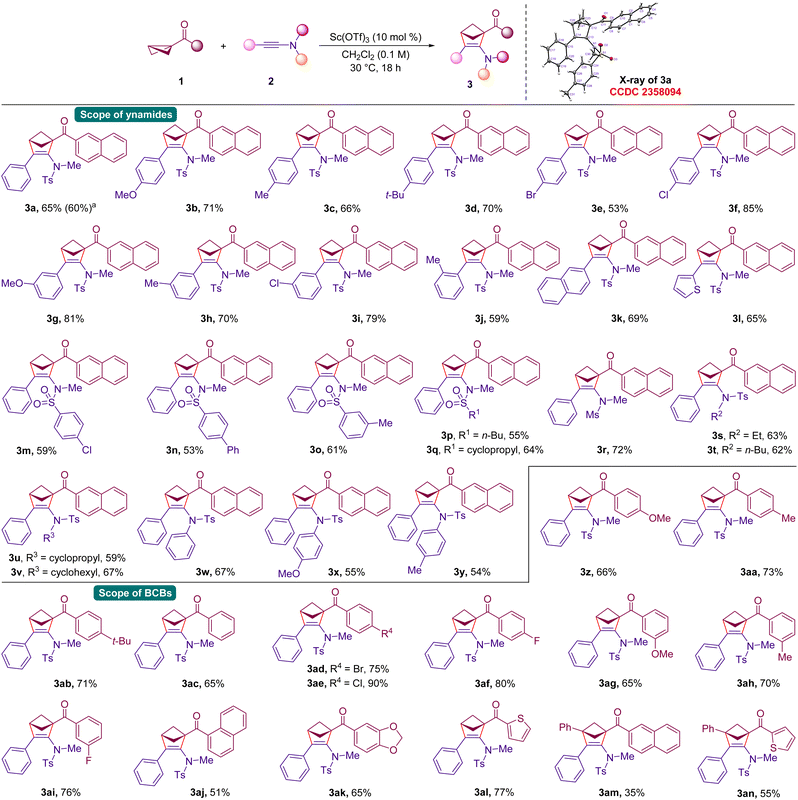
With the identified reaction conditions, we proceeded to evaluate the scope and limitations of the reaction of ynamides with BCBs. Initially, the scope of substituted ynamides was tested (Scheme 2). A reaction with ynamides bearing electronically different groups at the 4-position of the aryl ring readily afforded the (3 + 2) annulation product in good yields (3a–3f). The reaction leading to the formation of 3a was scalable on a 2.0 mmol scale in 60% yield, indicating the practical nature of the present annulation. In the case of the unsubstituted product 3a, the structure was further confirmed by the X-ray analysis of the crystals.28 Ynamides with strongly electron-withdrawing groups such as –NO2 at the 4-position of the ring returned a reduced yield of the annulated product. Moreover, –OMe, –Me and –Cl groups at the 3-position of the ring were also well tolerated producing (3 + 2) adducts in good yields (3g–3i). Substituting the 2-position of the ring with a methyl group produced the product 3j in 59% yield. The reaction conducted using 2-naphthyl and 2-thienyl substituted ynamides afforded the expected products 3k and 3l in 69% and 65% yields, respectively. Additionally, the N-tosyl moiety of the ynamides can be changed to differently substituted aryl sulphonamides and linear as well as cyclic alkyl sulphonamides and in all cases, the (3 + 2) annulated products were formed in reasonable yields (3m–3q). The protecting group on ynamides can be varied using mesyl (Ms) instead of the tosyl group, and the desired product 3r was formed in 72% yield.29 Notably, the methyl group on ynamide nitrogen can also be varied with ethyl, n-butyl, cyclopropyl, cyclohexyl and substituted aryl moieties without affecting the reactivity, and in all cases, the target products were formed in moderate to good yields (3s–3y).
Next, the tolerance of (3 + 2) annulation with substituted BCBs was tested. Instead of the 2-naphthyl moiety in 1a, a variety of BCBs bearing aryl ketones having electron-releasing and neutral groups and halides at the 4-position of the ring underwent smooth (3 + 2) annulation with ynamide 2a, and in all cases, the target products were formed in moderate to good yields (3z–3af). Moreover, substitution at the 3-position of the aryl ring was also tolerated well and the corresponding 2-amino-bicyclo[2.1.1]hexenes were formed in good yields (3ag–3ai). In addition, disubstitution on the aryl ring did not affect the reactivity of the (3 + 2) annulation (3aj and 3ak). Further, the 2-thienyl ketone-derived BCB reacted with 2a to afford the (3 + 2) annulation product 3al in 77% yield. Interestingly, 1,3-disubstituted BCB ketones also afforded the target (3 + 2) annulated products in moderate yields under the present conditions (3am and 3an). Disappointingly, BCBs with phenyl and –CO2Me moieties at the 1,3-positions did not afford the desired (3 + 2) annulated products under the optimized conditions.
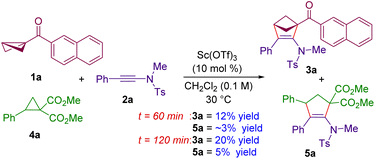
Given the similarity in the reactivity of BCBs with donor–acceptor cyclopropanes under Lewis acid conditions,30 a competition experiment was performed with ynamide 2a with BCB 1a and cyclopropane 4a (Scheme 3). Performing the reaction under optimized conditions and quenching the reaction after 60 minutes revealed that the (3 + 2) annulation product 3a from BCB 1a was formed in 12% yield, whereas the annulation product 5a derived from cyclopropane 4a was formed in ∼3% yield. Moreover, 3a and 5a were formed in 20% and 5% yields respectively when the reaction was quenched after 120 minutes. This is an indication that the BCB 1a works ∼4 times faster than the DA cyclopropane 4a in its reaction with ynamides, thereby shedding light on the better reactivity of BCBs over DA cyclopropanes. This is because of the high strain energy of BCBs compared to DA cyclopropanes.
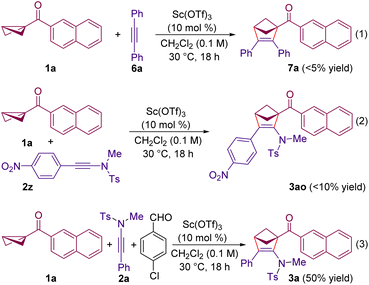
To gain insight into the mechanism of the reaction, a few experiments were performed. When the reaction of BCB 1a was carried out with diphenyl acetylene 6a instead of the ynamide 2a, the desired (3 + 2) annulation product 7a was not formed (Scheme 4, eqn (1)). This study indicates that 6a is not nucleophilic enough to add to the Lewis acid activated BCB and sheds light on the importance of the nucleophilicity of ynamides in the present (3 + 2) annulation. Moreover, when using 4-nitrophenyl substituted ynamide 2z, the reaction furnished the (3 + 2) annulated product 3ao in <10% yield (eqn (2)). It is reasonable to believe that the presence of the –NO2 group makes 2z less nucleophilic for the addition to a Lewis acid activated BCB and thus reduces its reactivity. In addition, our efforts to intercept the enolate formed after the initial addition of the ynamide to the BCB (Scheme 1D) with a third component failed, and the annulated product 3a was formed in 50% yield without the formation of a product incorporating the aldehyde moiety. Notably, the (3 + 2) annulated product from 1a and the aldehyde were also not observed in this case.19
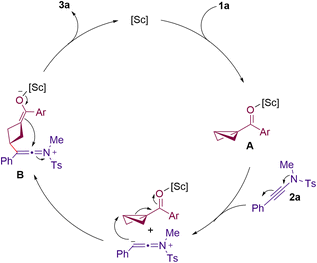
Based on the preliminary mechanistic experiments and literature precedents,20,21 a plausible mechanism is presented in Scheme 5. It is reasonable to assume that the BCB 1a is activated by Sc(OTf)3 to form the Lewis acid–BCB complex A. This activation facilitates a nitrogen lone pair assisted nucleophilic attack (most likely an SN2-type pathway) from the alkynyl moiety of the ynamide 2a, onto the unsubstituted side of the activated BCB. This results in the formation of intermediate B, which possesses an enolate BCB fraction and a keteniminium moiety. Subsequently, the keto-enolate undergoes an intramolecular addition to the keteniminium ion to afford the desired 2-amino-bicyclo[2.1.1]hexene product 3a. Our preliminary studies on trapping the enolate B with electrophiles such as aldehydes failed.
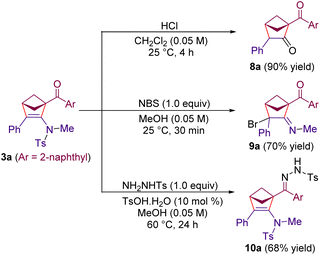
The functionalized 2-amino-bicyclo[2.1.1]hexenes synthesized using the present method can easily be engaged in further transformations. The hydrolysis of the enamine moiety of 3a under acidic conditions resulted in the formation of the 1,3-diketone 8a in 90% yield (Scheme 6). Moreover, the treatment of 3a with N-bromosuccinimide resulted in the formation of the bromoimine derivative 9a in 70% yield. In addition, the reaction of 3a with tosyl hydrazine afforded the hydrazone derivative 10a in 68% yield. Notably, the hydrogenation of the C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C double bond and the reduction of the ketone moiety in related N-mesylated 2-amino-bicyclo[2.1.1]hexene products are reported by Chen, Zhou and co-workers.24
C double bond and the reduction of the ketone moiety in related N-mesylated 2-amino-bicyclo[2.1.1]hexene products are reported by Chen, Zhou and co-workers.24
Conclusions
In conclusion, we have demonstrated the Sc(OTf)3-catalyzed (3 + 2) annulation of BCBs with ynamides leading to the formation of biologically relevant 2-amino-bicyclo[2.1.1]hexenes under mild conditions in a one-pot process. The reaction likely proceeds in a stepwise manner initiated by the nucleophilic addition of ynamides to the unsubstituted side of the BCBs, followed by the annulation of the ensuing enolate with the keteniminium species. Differently substituted keto-BCBs and a variety of electronically dissimilar ynamides underwent this smooth (3 + 2) annulation. Further studies on related annulation reactions involving BCBs are currently ongoing in our laboratory.Data availability
Details on experimental procedures, mechanistic experiments, characterization data of all the 2-amino-bicyclo[2.1.1]hexenes and X-ray data of 3a. The details are available in the ESI† of the manuscript.Author contributions
D. S. and A. T. B. designed the project. D. S. optimized the reaction conditions. D. S., S. D. and R. C. D. examined the substrate scope and analysed the data. D. S. performed the mechanistic experiments. R. C. D. wrote the first draft of the manuscript with inputs from D. S. and S. D., and A. T. B. edited the manuscript. All authors have given approval to the final version of the manuscript. A. T. B. directed the research.Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.Acknowledgements
Generous financial support by the Science and Engineering Research Board (SERB), Government of India (File Number: SCP/2022/000837) is greatly acknowledged. D. S. thanks IISc for the fellowship and S. D. and R. C. D. thank MHRD for the PMRF scholarship. We thank Mr Khush Jain and Ms Safa Shajahan for their help in preparing the ynamide substrates. We thank Mr Kishorkumar Sindogi (IISc) for collecting the X-ray data of 3a. We thank Dr Avishek Guin and Dr Subrata Bhattacharjee for their useful discussions.Notes and references
- A. Greenberg and J. F. Liebman, Strained Organic Molecules, Academic Press, New York, 1978 Search PubMed.
- (a) M. A. Subbaiah and N. A. Meanwell, J. Med. Chem., 2021, 64, 14046 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) M. R. Bauer, P. Di Fruscia, S. C. C. Lucas, I. N. Michaelides, J. E. Nelson, R. I. Storer and B. C. Whitehurst, RSC Med. Chem., 2021, 12, 448 RSC; (c) M. A. Dallaston, S. D. Houston and C. M. Williams, Chem.–Eur. J., 2020, 26, 11966 CrossRef CAS.
- For recent reviews on BCBs, see: (a) Q.-Q. Hu, J. Chen, Y. Yang, H. Yang and L. Zhou, Tetrahedron Chem, 2024, 9, 100070 CrossRef CAS; (b) M. Golfmann and J. C. L. Walker, Commun. Chem., 2023, 6, 9 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) C. B. Kelly, J. A. Milligan, L. J. Tilley and T. M. Sodano, Chem. Sci., 2022, 13, 11721 RSC ; for examples on bicyclic pentanes and other bicyclic scaffolds, see:; (d) J. M. Anderson, N. D. Measom, J. A. Murphy and D. L. Poole, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2021, 60, 24754 CrossRef CAS; (e) X. Ma and P. Luu Nhat, Asian J. Org. Chem., 2020, 9, 8 CrossRef CAS; (f) G. M. Locke, S. S. R. Bernhard and M. O. Senge, Chem.–Eur. J., 2019, 25, 4590 CrossRef CAS; (g) B. A. Chalmers, H. Xing, S. Houston, C. Clark, S. Ghassabian, A. Kuo, B. Cao, A. Reitsma, C.-E. P. Murray, J. E. Stok, G. M. Boyle, C. J. Pierce, S. W. Littler, D. A. Winkler, P. V. Bernhardt, C. Pasay, J. J. De Voss, J. McCarthy, P. G. Parsons, G. H. Walter, M. T. Smith, H. M. Cooper, S. K. Nilsson, J. Tsanaktsidis, G. P. Savage and C. M. Williams, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2016, 55, 3580 CrossRef CAS; (h) M. D. Levin, P. Kaszynski and J. Michl, Chem. Rev., 2000, 100, 169 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (i) T. Iida, J. Kanazawa, T. Matsunaga, K. Miyamoto, K. Hirano and M. Uchiyama, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2022, 144, 21848 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) F. Lovering, MedChemComm, 2013, 4, 515 RSC; (b) F. Lovering, J. Bikker and C. Humblet, J. Med. Chem., 2009, 52, 6752 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) J. Tsien, C. Hu, R. R. Merchant and T. Qin, Nat. Rev. Chem, 2024, 8, 605 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) P. K. Mykhailiuk, Org. Biomol. Chem., 2019, 17, 2839 RSC.
- (a) A. Denisenko, P. Garbuz, N. M. Voloshchuk, Y. Holota, G. Al-Maali, P. Borysko and P. K. Mykhailiuk, Nat. Chem., 2023, 15, 1155 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) S. Paul, D. Adelfinsky, C. Salome, T. Fessard and M. K. Brown, Chem. Sci., 2023, 14, 8070 RSC; (c) A. Denisenko, P. Garbuz, Y. Makovetska, O. Shablykin, D. Lesyk, G. AlMaali, R. Korzh, I. V. Sadkova and P. K. Mykhailiuk, Chem. Sci., 2023, 14, 14092 RSC; (d) A. Denisenko, P. Garbuz, S. V. Shishkina, N. M. Voloshchuk and P. K. Mykhailiuk, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2020, 59, 20515 CrossRef CAS.
- For reviews, see: (a) A. Fawcett, Pure Appl. Chem., 2020, 92, 751 CrossRef CAS; (b) J. Turkowska, J. Durka and D. Gryko, Chem. Commun., 2020, 56, 5718 RSC; (c) M. A. A. Walczak, T. Krainz and P. Wipf, Acc. Chem. Res., 2015, 48, 1149 CrossRef CAS PubMed ; for examples, see:; (d) Q. Fu, S. Cao, J. Wang, X. Lv, H. Wang, X. Zhao and Z. Jiang, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2024, 146, 8372 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (e) Y. Liang, R. Nematswerani, C. G. Daniliuc and F. Glorius, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2024, 63, e202402730 CrossRef CAS; (f) J. Zhang, J.-Y. Su, H. Zheng, H. Li and W.-P. Deng, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2024, 63, e202318476 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (g) T. V. T. Nguyen, A. Bossonnet, M. D. Wodrich and J. Waser, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2023, 145, 25411 CrossRef CAS; (h) T. Yu, J. Yang, Z. Wang, Z. Ding, M. Xu, J. Wen, L. Xu and P. Li, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2023, 145, 4304 CrossRef CAS; (i) H. Wang, H. Shao, A. Das, S. Dutta, H. T. Chan, C. Daniliuc, K. N. Houk and F. Glorius, Science, 2023, 381, 75 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (j) Y. Zheng, W. Huang, R. K. Dhungana, A. Granados, S. Keess, M. Makvandi and G. A. Molander, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2022, 144, 23685 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (k) P. Wipf and M. A. A. Walczak, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2006, 45, 4172 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Xu, Z. Wang, Z. Sun, Y. Ouyang, Z. Ding, T. Yu, L. Xu and P. Li, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2022, 61, e202214507 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) T. M. Sodano, L. A. Combee and C. R. J. Stephenson, ACS Med. Chem. Lett., 2020, 11, 1785 CrossRef CAS; (b) D. Staveness, T. M. Sodano, K. Li, E. A. Burnham, K. D. Jackson and C. R. J. Stephenson, Chem, 2019, 5, 215 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) T. Kahl, K. W. Schröder, F. Lawrence, W. Marshall, H. Höke and R. Jäckh, Aniline, in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2012, vol. 3, p. 465 Search PubMed; (b) J. Schranck and A. Tlili, ACS Catal., 2018, 8, 405 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) A. S. Kalgutkar and D. Dalvie, Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol., 2015, 55, 35 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) A. S. Kalgutkar, J. Med. Chem., 2020, 63, 6276 CrossRef CAS.
- R. Kleinmans, T. Pinkert, S. Dutta, T. O. Paulisch, H. Keum, C. G. Daniliuc and F. Glorius, Nature, 2022, 605, 477 CrossRef CAS.
- R. Guo, Y.-C. Chang, L. Herter, C. Salome, S. E. Braley, T. C. Fessard and M. K. Brown, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2022, 144, 7988 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Agasti, F. Beltran, E. Pye, N. Kaltsoyannis, G. E. M. Crisenza and D. J. Procter, Nat. Chem., 2023, 15, 535 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. Yu, J. Yang, Z. Wang, Z. Ding, M. Xu, J. Wen, L. Xu and P. Li, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2023, 145, 4304 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Liu, S. Lin, Y. Li, J.-H. Xue, Q. Li and H. Wang, ACS Catal., 2023, 13, 5096 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Dhake, K. J. Woelk, J. Becica, A. Un, S. E. Jenny and D. C. Leitch, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2022, 61, e202204719 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- N. Radhoff, G. C. Daniliuc and A. Studer, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2023, 62, e202304771 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Liang, F. Paulus, C. G. Daniliuc and F. Glorius, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2023, 62, e202305043 CrossRef CAS.
- D. Ni, S. Hu, X. Tan, Y. Yu, Z. Li and L. Deng, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2023, 62, e202308606 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) L. Tang, Y. Xiao, F. Wu, J.-L. Zhou, T.-T. Xu and J.-J. Feng, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2023, 62, e202310066 CrossRef CAS PubMed ; see also: ; (b) J.-J. Wang, L. Tang, Y. Xiao, W.-B. Wu, G. Wang and J.-J. Feng, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2024, 63, e202405222 CrossRef CAS.
- For a single example of the annulation of pyridinyl BCBs with phenyl acetylene proceeding in a radical pathway, see ref. 8. For a (3 + 2) annulation involving BCBs to access aminobicyclo[2.1.1]hexanes, see: H. Ren, T. Li, J. Xing, Z. Li, Y. Zhang, X. Yu and J. Zheng, Org. Lett., 2024, 26, 1745 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Ynamide reviews: (a) J. Ficini, Tetrahedron, 1976, 32, 1449 CrossRef CAS; (b) C. A. Zificsak, J. A. Mulder, R. P. Hsung, C. Rameshkumar and L. Wei, Tetrahedron, 2001, 57, 7575 CrossRef CAS; (c) K. A. Dekorver, H. Li, A. G. Lohse, R. Hayashi, Z. Lu, Y. Zhang and R. P. Hsung, Chem. Rev., 2010, 110, 5064 CrossRef CAS; (d) Y.-B. Chen, P.-C. Qian and L.-W. Ye, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2020, 49, 8897 RSC; (e) L. Hu and J. Zhao, Acc. Chem. Res., 2024, 57, 855 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (f) C. C. Lynch, A. Sripada and C. Wolf, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2020, 49, 8543 RSC.
- During the preparation of this manuscript, Chen, Zhou and co-workers reported the Lewis acid-catalyzed (3 + 2) annulation of BCBs with ynamides for the synthesis of polysubstituted 2-amino-bicyclo[2.1.1]hexenes. For details, see: Q.-Q. Hu, L.-Y. Wang, X.-H. Chen, Z.-X. Geng, J. Chen and L. Zhou, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2024, 63, e202405781 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- For related BCB studies from our group, see: (a) A. Guin, S. Bhattacharjee, M. S. Harariya and A. T. Biju, Chem. Sci., 2023, 14, 6585 RSC; (b) A. Guin, S. Deswal, M. S. Harariya and A. T. Biju, Chem. Sci., 2024, 15, 12473 RSC.
- W. D. Mackay, M. Fistikci, R. M. Carris and J. S. Johnson, Org. Lett., 2014, 16, 1626 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- For details, see the ESI†.
- CCDC 2358094 (3a) contains the supplementary crystallographic data for this paper.
- The reaction of 1a with an N-benzyl N-mesyl ynamide substrate used by Chen, Zhou and co-workers (ref. 24) under the optimized conditions afforded a 2-amino-bicyclo[2.1.1]hexene product in 50% yield.
- (a) A. U. Augustin and D. B. Werz, Acc. Chem. Res., 2021, 54, 1528 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) V. Pirenne, B. Muriel and J. Waser, Chem. Rev., 2021, 121, 227 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) D. B. Werz and A. T. Biju, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2020, 59, 3385 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (d) P. Singh, R. K. Varshnaya, R. Dey and P. Banerjee, Adv. Synth. Catal., 2020, 362, 1447 CrossRef CAS; (e) T. F. Schneider, J. Kaschel and D. B. Werz, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2014, 53, 5504 CrossRef CAS; (f) H.-U. Reissig and R. Zimmer, Chem. Rev., 2003, 103, 1151 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available: Details on experimental procedures and characterization data of all compounds. CCDC 2358094. For ESI and crystallographic data in CIF or other electronic format see DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/d4sc03893b |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2024 |