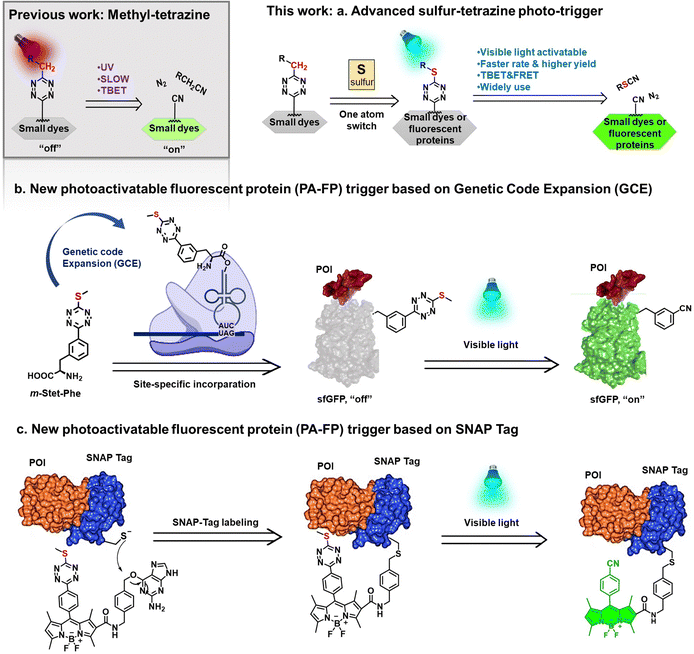
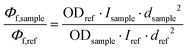Sulfur–tetrazine as highly efficient visible-light activatable photo-trigger for designing photoactivatable fluorescence biomolecules†
Shudan
Yang‡
 a,
Mengxi
Zhang‡
a,
Axel
Loredo
a,
David
Soares
a,
Mengxi
Zhang‡
a,
Axel
Loredo
a,
David
Soares
 a,
Yulun
Wu
a and
Han
Xiao
a,
Yulun
Wu
a and
Han
Xiao
 *abcd
*abcd
aDepartment of Chemistry, Rice University, 6100 Main Street, Houston, Texas 77005, USA. E-mail: han.xiao@rice.edu
bDepartment of Biosciences, Rice University, 6100 Main Street, Houston, Texas 77005, USA
cDepartment of Bioengineering, Rice University, 6100 Main Street, Houston, Texas 77005, USA
dSynthX Center, Rice University, 6100 Main Street, Houston, Texas 77005, USA
First published on 9th October 2024
Abstract
Light-activated fluorescence represents a potent tool for investigating subcellular structures and dynamics, offering enhanced control over the temporal and spatial aspects of the fluorescence signal. While alkyl-substituted tetrazine has previously been reported as a photo-trigger for various fluorophore scaffolds, its limited photochemical efficiency and high activation energy have constrained its widespread application at the biomolecular level. In this study, we demonstrate that a single sulfur atom substitution of tetrazine greatly enhances the photochemical properties of tetrazine conjugates and significantly improves their photocleavage efficiency. Notably, the resulting sulfur–tetrazine can be activated using a lower-energy light source, thus transforming it into a valuable visible-light photo-trigger. To introduce this photo-trigger into biological systems, we have developed a series of visible-light activatable small molecular dyes, along with a photoactivatable noncanonical amino acid containing sulfur–tetrazine. Using the Genetic Code Expansion technology, this novel amino acid is genetically incorporated into fluorescent protein molecules, serving as a phototrigger to create an innovative photoactivatable protein. These advancements in tetrazine-scaffold photo-trigger design open up new avenues for generating photoactivatable biomolecules, promising to greatly facilitate the exploration of biological functions and structures.
Introduction
Photoactivatable fluorophores are renowned for their ability to rigorously control their photophysical properties through a photochemical reaction that transforms a non-emitting precursor into a fluorescent dye.1–18 Typically, the precursor molecule is a well-known fluorophore modified with a photoremovable protecting group, commonly referred to as a “photo-trigger,” which quenches dye fluorescence through two distinct mechanisms. One mechanism involves Förster resonance energy transfer (FRET), a distance-dependent physical process in which the energy transfer from the excited molecular fluorophore (the donor) is captured by the acceptor, represented by the intimately attached cage group. Upon exposure to light, the caged fluorophores undergo photochemical reactions that remove the “cage,” thus restoring the active fluorophores.19–24 In contrast, through-bond energy transfer (TBET) does not necessitate spectral overlap between donors and acceptors. In this context, the phototriggers are conjugated to fluorophore donors through a conjugated linker, enabling faster energy transfer through bonds compared to nonradiative decay processes.25–29In recent decades, tetrazine has emerged as an effective trigger in the design of fluorogenic fluorophores.30–36 Its visible light absorbance overlaps with the emissions of numerous dyes, and its ability to participate in the Inverse Electron Demand Diels–Alder (IEDDA) cycloaddition reaction with strained hydrophobic alkenes makes it a valuable tool for eliminating quenching functionality.33–45 Even though the wide use of bioorthogonal click reaction, photoactivation offers much more distinct advantages in terms of being ‘bio-friendly’ and easy to manipulate, facilitating precise spatiotemporal remote control and programmed manipulation in a non-invasive manner.14,15,46–53 In 2020, our research group introduced tetrazine as a photocleavable trigger for various fluorophore cores, employing the through-bond energy transfer (TBET) mechanism.31 However, despite these efforts, the relatively low efficiency, and the reliance on ultraviolet light for tetrazine removal in most cases have limited its applicability to biological molecules. Consequently, there is a growing need for a more efficient tetrazine photo-trigger that can be applied to both small molecule dyes and proteins of interest.
In this study, we first compare the photolysis rates of alkyl-substituted and sulfur-substituted tetrazine photo-triggers. We found that introduction of a thioether cap to tetrazine fluorescent probes significantly enhanced the photoactivation efficiency at longer wavelengths that were previously inaccessible with alkyl-based tetrazines.31 Next, these improved phototriggers were employed in the development of a series of visible-light activatable small molecular dyes. In comparison to traditional tetrazine-based dyes, those sulfur–tetrazine photo-triggers exhibited significantly faster photolysis reaction rates in live cell imaging. To create sulfur–tetrazine-based photoactivatable proteins, we designed the first noncanonical amino acid (ncAA) containing the sulfur–tetrazine moiety. This ncAA was precisely incorporated in close proximity to the chromophore of a fluorescent protein using Genetic Code Expansion (GCE) technology, enabling precise control of the fluorescence of the affiliated protein and yielding a novel photoactivatable fluorescent protein. These innovative molecules were employed for studying protein localization and dynamics through live-cell or fixed-cell imaging (Fig. 1).
Results and discussion
Photochemical reactivity comparison between tetrazine and sulfur–tetrazine photo-triggers
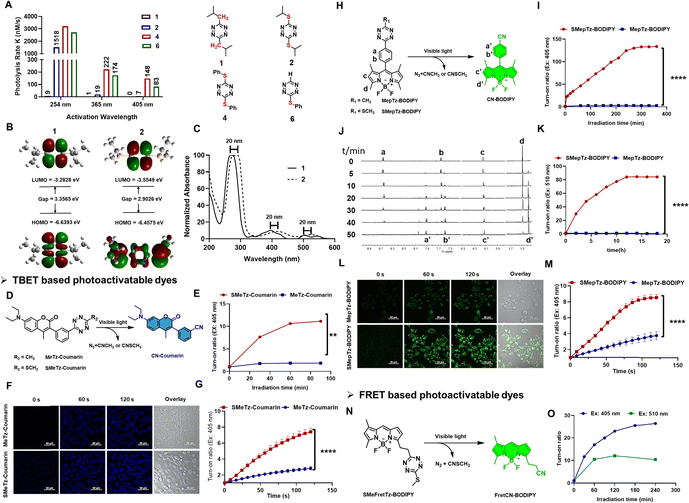
Sulfur-substituted tetrazines exhibit a redshifted energy transition, enabling their photolysis using longer wavelengths of light. This shift has been attributed to either a distinct n–π* transition or a charge transfer involving sulfur.54,55 Such tetrazines have been developed as amino acid-based derivatives, where the tetrazine is incorporated between two cysteine groups, and have been employed in the study of peptide folding dynamics.32,56–58 Therefore, tetrazines containing a sulfur atom at the 3- or 6-position may offer a superior class of photo-triggers for designing photoactivatable fluorescence molecules. To investigate this, we first synthesized various alkyl and sulfur-substituted tetrazine derivatives with different substituent sizes (Fig. 2(A) and Table S3, Fig. S3, ESI†). Alkyl-substituted tetrazines were synthesized using zinc triflate-catalyzed conditions, followed by oxidation with sodium nitrite in aqueous HCl (1 M).59 Sulfur-substituted tetrazines, on the other hand, were prepared by reacting thiols with pyrazole-substituted tetrazine in acetonitrile with triethylamine. Photocleavage experiments were conducted in the presence of UV 254, 365 handheld light sources, or 405 nm LED light. The rate constants, calculated based on the characteristic absorption bands of each compound monitored during the photoirradiation process, revealed that compounds incorporating sulfur atoms, exhibited higher photolysis rates compared to those without a sulfur substituent when exposed to either 254 nm or 365 nm light (1 and 2). Upon LED 405 nm, only sulfur-substituted tetrazine can be photolyzed (2, 4, 6). Furthermore, the presence of a phenyl group facilitated faster dissociation compared to aliphatic substituents (4 and 6).Computational calculations on the frontier molecular orbitals of model compounds 1 and 2 revealed that the introduction of a sulfur-based electron-donating group onto the carbon of s-tetrazine results in the addition of a new π-type orbital. This new orbital is observed to raise the energy of the Highest Occupied Molecular Orbital (HOMO) while lowering the energy of the Lowest Unoccupied Molecular Orbital (LUMO), thereby reducing the band gap energy. This reduction in the band gap energy is expected to lead to a red shift in the excitation wavelength (Fig. 2(B) and (C)). Hochstrasser and his research group also corroborated the enhanced photochemical yield of sulfur tetrazine based on their study of di-cysteine S,S-tetrazines, attributing it to vibrational energy redistribution.32 As they indicated, the presence of the sulfur atom can decelerate the rate at which energy dissipates from the tetrazine ring, thereby opening up a new photochemical pathway.
Design of photoactivatable fluorophores for live cell image using sulfur–tetrazine photo-trigger
Based on the data above, we expect the sulfur–tetrazine to represent a new class of ultra-fast photo-triggers for the design of photoactivatable fluorophores. To demonstrate the sulfur–tetrazine motif can be used as a general photo-trigger of various fluorophore conjugates with highly improved photolysis efficiency, sulfur–tetrazine BODIPY (SMepTz-BODIPY, SMeFretTz-BODIPY, Fig. 2(H) and (N)) and coumarin (SMeTz-Coumarin, Fig. 2(D)) conjugates were designed based on through bond energy transfer (TBET) or Förster resonance energy transfer (FRET) mechanism. These conjugates were prepared through a one-pot conversion of (3-methyloxetan-3-yl) methyl carboxylic esters into asymmetrical 3-thiomethyltetrazines by condensing oxabicyclo[2.2.2] octyl orthoester intermediates reported by Fox in 2010.60 Although phenyl–sulfur tetrazine exhibited a higher photo reactivity (Fig. 1(A)), effective synthetic methods for conjugating it to other structures are still lacking. In addition, the bulky and hydrophobic benzene ring limits its applicability in biological systems. All resulting sulfur–tetrazine conjugates, SMepTz-BODIPY, SMeTz-Coumarin, and SMeFretTz-BODIPY exhibit negligible fluorescence (Table S5, ESI†). Compared with their corresponding methyl–tetrazine conjugates, sulfur–tetrazine conjugated fluorophores underwent much more rapid and complete conversion to give highly fluorescent cyano-fluorophores upon irradiation with UV or visible light (Fig. 2(E), (I), (K) and Fig. S2, S4, ESI†). Spectro-fluorometer was used to monitor the fluorescence increasing, and 1H-NMR (Fig. 2(J)) analysis of the reaction mixtures revealed the reaction processes and characterized the resulting products generated during the irradiation process. The signals corresponding to the phenyl protons a and b at 8.63 and 7.62 gradually shift to 7.91 (a′) and 7.58 (b′); and proton c slightly upfield shifts to c′, and the methyl proton d shift from 1.47 to 1.39 (d′). All the new signals were identical to those observed with synthesized cyanophenyl-BODIPY (CN-BODIPY).31 Upon irradiation with a 405 nm LED, the turn-on ratio of SMepTz-BODIPY was 134, significantly higher than the 3-fold increase observed with MepTz-BODIPY (Fig. 2(I) and Table S4, ESI†). Under 510 LED, the fluorescence intensity of SMepTz-BODIPY increased 84 folds while no fluorescence changes of MepTz-BODIPY were detected within 20 hours (Fig. 2(K)). Similar results were observed with the coumarin conjugates, wherein the turn-on ratio of SMeTz-Coumarin (12 folds) was 6-fold higher than that of MeTz-Coumarin (2 folds) after irradiation with 405 nm LED for 90 minutes (Fig. 2(E) and Table S4, ESI†).To investigate whether sulfur–tetrazine can act as a photoactivatable FRET quencher, we examined the photoactivation process of SMeFretTz-BODIPY. In this setup, the BODIPY dye is quenched by sulfur–tetrazine through the FRET mechanism (Fig. 2(N)). Photoactivation of SMeFretTz-BODIPY was carried out in acetonitrile under the same conditions, resulting in a 27-fold and 12-fold increase in fluorescence intensity under 405 nm and 510 nm irradiation, respectively (Fig. 2(O)).
Encouraged by the significantly improved photoactivation efficiency, we proceeded to evaluate the compatibility of the sulfur–tetrazine conjugated probes, SMeTz-Coumarin and SMepTz-BODIPY, for live imaging (Fig. 2(F) and (L)). These were compared with their methyl tetrazine counterparts, MeTz-Coumarin and MepTz-BODIPY. The probes were incubated with A431 cells in darkness for one hour, followed by three washes with PBS (1×, pH7.4) and imaging with confocal microscopy. To assess the turn-on ratio and speed of these photo-triggers in live cells within a limited time frame, we employed a 405 nm laser, commonly available in commercial microscopes and capable of activating methyl–tetrazine photo triggers. Continuous scanning of the cells was performed using this laser. Before laser scanning, no noticeable fluorescent signals were observed in cells incubated with different probes. However, after scanning with the 405 nm microscopy laser for 2 minutes, we observed a 7- and 9-fold enhancement of intracellular fluorescence signals from SMeTz-Coumarin and SMepTz-BODIPY, compared to 3- and 4-fold increased fluorescence observed in the corresponding methyl–tetrazine conjugates, MeTz-Coumarin and MepTz-BODIPY (Fig. 2(G) and (M)). These results confirm the outstanding photo-dissociation properties of sulfur–tetrazine photo-triggers, along with their good dark stability and cell permeability, rendering them compatible with live-cell imaging in the visible region.
Genetic incorporation of sulfur–tetrazine photo-trigger into proteins using genetic code expansion (GCE)
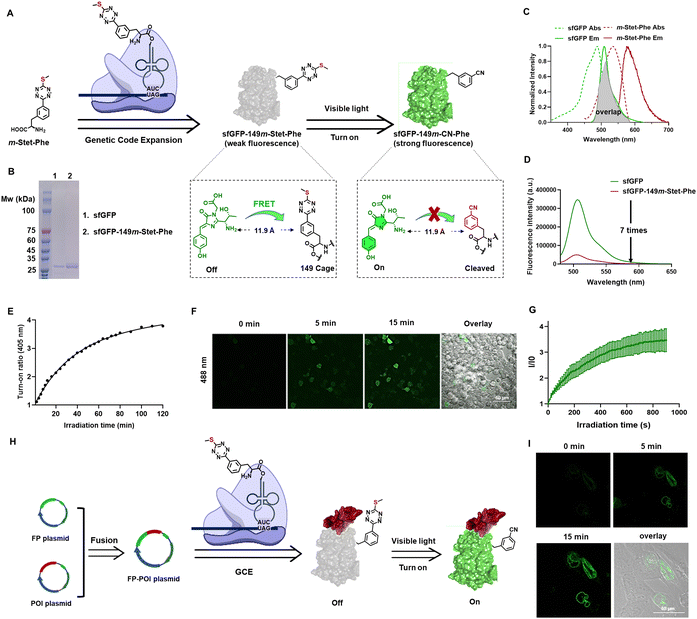
To introduce the sulfur–tetrazine photo-trigger into proteins, we utilized GCE technology, which allows for the site-specific incorporation of ncAAs with distinct physical, chemical, and biological properties and endow the modified proteins with new functions.61–65 The desired ncAA is encoded by a nonsense or frameshift codon, using a bioorthogonal aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase (aaRS)/tRNA pair that is specific for the ncAA but does not cross-react with endogenous host aaRSs, tRNAs, or amino acids. In designing an ncAA with a sulfur–tetrazine photo trigger, we investigated tetrazine-containing ncAAs reported previously. To address the slow reaction rates of traditional bioorthogonal reactions, several phenylalanine-based tetrazine ncAAs have been developed and genetically incorporated into proteins using GCE technology.66–69 Given the reported aaRS's selectivity for the position of the tetrazine ring, which enables the genetic incorporation of tetrazine-based amino acids in eukaryotic cells,66 we conjugated the sulfur–tetrazine moiety with phenylalanine at the meta position, naming it m-Stet-Phe (Fig. 3(A)).To demonstrate the genetic incorporation and photoactivation capabilities of m-Stet-Phe, we utilized super-folded green fluorescent protein (sfGFP) as our model. This model was chosen due to its inherent brightness and emission wavelength that significantly overlaps with the absorbance spectrum of sulfur–tetrazine, ensuring efficient Förster resonance energy transfer (FRET) (Fig. 3(C)). Besides the spectral overlap, the distance between the FRET donor and acceptor pair is crucial for FRET efficiency.24 To maximize FRET efficiency, we site-specifically introduced m-Stet-Phe into position 149 of sfGFP using a previously reported mutant Methanosarcina barkeri pyrrolysyl-tRNA synthetase/tRNACUA pair (Table S2, ESI†).66 Next, we assessed the efficiency and fidelity of m-Stet-Phe incorporation by expressing the resulting sfGFP protein with m-Stet-Phe at residue 149 (sfGFP-149m-Stet-Phe) in E. coli, followed by purification and characterization using electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (ESI-MS) and SDS-PAGE analysis. ESI-MS analysis of sfGFP-149m-Stet-Phe confirmed the expected mass of 27![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 755 Da (Fig. S5, ESI†). Combined with SDS-PAGE analysis, this demonstrated the high fidelity and efficient incorporation of m-Stet-Phe at the desired site within sfGFP (Fig. 3(B)). Purified sfGFP-149m-Stet-Phe emitted pretty weak fluorescence signal in PBS (1×, pH 7.4) solution, seven times lower than sfGFP (Fig. 3(D)). While upon activation with 405 nm LED, its fluorescence continuously increases within 2 hours (Fig. 3(E)).
755 Da (Fig. S5, ESI†). Combined with SDS-PAGE analysis, this demonstrated the high fidelity and efficient incorporation of m-Stet-Phe at the desired site within sfGFP (Fig. 3(B)). Purified sfGFP-149m-Stet-Phe emitted pretty weak fluorescence signal in PBS (1×, pH 7.4) solution, seven times lower than sfGFP (Fig. 3(D)). While upon activation with 405 nm LED, its fluorescence continuously increases within 2 hours (Fig. 3(E)).
We next investigated the photoactivation properties of this photoactivatable sfGFP when expressed in living mammalian cells. HEK293T cells were transfected with both the suppression plasmid pAcBac1-R2-84-MbRs-Tet-v3.0 and the reporter plasmid pAcBac-sfGFP-C1-149TAG, in the presence of 50 μM m-Stet-Phe. Following a 24-hour incubation period and three washes with PBS (1×, pH 7.4), Nikon confocal microscopy was employed to monitor changes in cell fluorescence during 405 nm laser scanning. Before photoactivation, minimal green fluorescence was observed at 488 nm excitation in HEK293T cells expressing sfGFP-149m-Stet-Phe, while it obviously intensified during the photoactivation process (Fig. 3(F)). After continuous scanning for 15 minutes, the green fluorescence had increased by up to 4-fold, indicating gradual photolysis of the sulfur–tetrazine cage and restoration of sfGFP fluorescence within the cells (Fig. 3(G)).
The successful construction of the novel photoactivatable sfGFP renders it an appealing candidate for live-cell imaging. Its advantages include a potentially low signal-to-background ratio, specific localization, excellent photo-switching properties with no side-product formation during photoconversion, and improved solubility compared to conventional large organic dyes. Consequently, we expand its application to visualize other proteins in live cells, particularly structural or functional proteins. Nuclear Lamin plays a pivotal role in various nuclear functions, with its expression level crucial in determining nuclear size.70 Additionally, positive Lamin B1 expression levels have been correlated with tumor formation and progression in various cancer types.71 To further investigate Lamin B1, we fused it with sfGFP-149m-Stet-Phe (Fig. 3(H)). By co-transfecting this newly fused-protein expression plasmid with the suppression plasmid pAcBac1-R2-84-MbRs-Tet-v3.0 into U2OS cells and incubating them with 20 μM m-Stet-Phe, we observed a concentrated signal of Lamin B1 at the nuclear envelope surface during photoactivation with 10% 405 nm confocal laser scanning, as expected (Fig. 3(I)).
Labeling proteins with sulfur–tetrazine photo-trigger using SNAP-tag technology
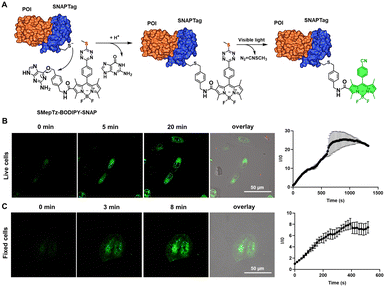
Besides fluorescent protein–protein fusion, small fluorescent probes are also able to label the proteins to be studied and realize fluorogenic imaging through self-labeling protein tags.72 Considering the remarkable photoactivation speed and efficiency of sulfur–tetrazine on small molecule conjugates, we synthesized SMepTz-BODIPY-SNAP (Fig. 4(A)) featuring a benzylguanine moiety attached to the SMepTz-BODIPY scaffold. This design allows for the covalent binding of the probe to the cysteine of the SNAP Tag, enabling the labeling of proteins of interest with a photoactivatable fluorescent probe. To assess the performance of SMepTz-BODIPY-SNAP in protein labeling, we incubated it at 20 μM in complete DMEM medium with both live and fixed U2OS cell lines expressing the NUP96-SNAP Tag fusion protein for 45 minutes. Following three washes with PBS (1×, pH 7.4), we utilized a 40% 405 nm confocal microscope laser to activate the sulfur–tetrazine conjugated probe. The labeling of NUP96, a protein of the nuclear core complex, exhibited a 25-fold increase in brightness within 20 minutes for live cells (Fig. 4(B)) and an 8-fold increase in 5 minutes for fixed cells (Fig. 4(C)).Conclusions
In conclusion, we have developed sulfur–tetrazine as a versatile, ultrafast visible-light activated photo-trigger, demonstrating superior photochemical kinetics and photoproduct yields compared to traditional tetrazine photo-triggers. Its longer activating wavelength and lower photo-transferring energy contribute to enhanced biocompatibility compared to its methyl tetrazine counterpart. Through genetic incorporation of sulfur–tetrazine-based ncAAs using the GCE technology, we successfully controlled the fluorescence of green fluorescent proteins. Moreover, by incorporating this photoactivatable ncAA into structural and functional proteins, we have laid the groundwork for studying various subcellular structures in future research with photoactivatable fluorescent proteins. Additionally, in conjunction with small molecule fluorophores, sulfur–tetrazine was utilized to photoactivate protein labels through the SNAP Tag. Leveraging their exceptional spectroscopic properties, we conducted both live-cell and fixed-cell imaging, yielding a clear visualization of the nuclear envelope. Currently, we are investigating other heteroatom-substituted tetrazine photo-triggers, aiming to expand the range of light wavelengths available for photochemical reactions and to facilitate the construction of additional photoactivatable fluorescent macro biomolecules in future studies.Experimental
Materials
Chemical reagents were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich, Oakwood Chemical, TCI Chemicals, and used without further purification. LB agar and 2YT were ordered from BD Difco TM. Isopropyl-β-D-thiogalactoside (IPTG) was purchased from Anatrace. 4-12% bis-tris gels for SDS-PAGE were purchased from Invitrogen. QuickChange Lightning Multi Site-Directed Mutagenesis Kit was purchased from Agilent Technologies (Cat. 210515). Oligonucleotide primers were purchased from Integrated DNA Technologies and Eurofins Genomics. Plasmid DNA preparation was carried out with the GenCatch TM Plus Plasmid DNA. Miniprep Kit and GenCatch TM Advanced Gel Extraction Kit. FastBreak™ Cell Lysis Reagent 10× was purchased from Promega (Cat. V8572). Ni-NTA Agarose was obtained from Qiagen (Cat. 30230). 1H and 13C NMR spectra were measured on a Bruker AVANCE III HD 600 MHz spectrometer. UV-vis absorption spectra were measured on a Thermo Scientific Evolution 220 UV-Vis Spectrophotometer. Fluorescence measurements were conducted on a Horiba FluoroMax-4 spectrofluorometer. ESI mass spectroscopy was performed on a Bruker MicroToF ESI LC-MS System. Confocal fluorescent images were performed using Nikon A1R-si Laser Scanning Confocal Microscope (Japan), equipped with lasers of 405/488/561/638 nm.Fluorescence measurements
Stock solutions of small molecular probes in acetonitrile were diluted into 1 μM in the corresponding solvent and purified protein was diluted into 0.04 μM in the pH 7.4 1× PBS buffer in a 1 cm × 1 cm quartz cuvette. Measurements of emission spectra were recorded before light irradiation. Activation ratios were calculated from the peak emission intensity of the photolyzed tetrazine and the pre-irradiation intensity. Light irradiation was stopped at the corresponding time points to record emission spectra and continued until a plateau was reached.Photolysis rate calculation
Compounds were dissolved in acetonitrile (1 mM) and irradiated by 254 and 365 nm light. The decrease in absorption was monitored over time to obtain the zero-order reaction rate as follows:| k = −([A])/t | (1) |
Quantum yield determination
Quantum yield measurements were determined using fluorescein73 (fluorescence quantum yield of 0.79 in 0.1 M NaOH) and Quinine sulfate74 (fluorescence quantum yield of 0.546 in H2SO4 0.5 M). The fluorescence quantum yield, Φf (sample), was calculated according to the equation as follows:Φf: quantum yield of fluorescence; I: integrated emission intensity; OD: optical density at the excitation wavelength; d: refractive index of solvents, dCH3CN = 1.34; dethanol = 1.36; dwater = 1.33.
Cell culture
A431 cells, HEK293T cells and U2OS cells were incubated in complete medium Dulbecco's modified Eagle's Medium (DMEM), supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) and 1% penicillin–streptomycin at 37 °C in atmosphere containing 5% CO2.Confocal image of small molecular probes
The stock solution of SMepTz-BODIPY, MepTz-BODIPY, SMeTz-Coumarin and MeTz-Coumarin in anhydrous DMSO was prepared to a concentration of 2 mM. The solution was diluted to a final concentration of 5 μM by complete growth medium in 35 mm glass bottom mattek dishes with A431 cells. After incubation of SMepTz-BODIPY, MepTz-BODIPY, SMeTz-Coumarin and MeTz-Coumarin for 30 minutes under dark conditions, cells were washed with PBS (pH 7.4, 1×) twice and turned to confocal laser scanning microscope (CLSM). Cell imaging was performed with a Nikon Instruments A1 Confocal Laser Microscope. BODIPY dyes were activated using 405 nm light at 100% laser intensity. Coumarin dyes were activated using 405 nm light at 50% laser intensity. Differential interference contrast (DIC) and fluorescent images were processed and analyzed using NIS-Elements.Plasmid construction
Plasmid pUltra-Tet3.0-R2-84-MmPylT was generated from pUltra-MbPylRS-MmPylT by two rounds of mutations N311G, C313S (by primer mz167, mz168) and L270G (by primer mz165, mz166) via Gibson assembly. DNA sequence of Tet3.0-R2-84 is listed in ESI,† Table S2.Plasmid sfGFP-WT-LaminB1-10 was constructed by a two-piece Gibson assembly of sfGFP-WT (cloned from addgene plasmid #54579 with primers mz324, mz325) and LaminB1-10 (cloned from addgene plasmid 57141 with primers mz326, mz327). Plasmid sfGFP-149TAG-LaminB1-10 was generated by sfGFP-WT-LaminB1-10 single mutation with primers mz163, mz164. All primers are listed in Table S1 (ESI†).
Protein expression and purification
E. coli. DH10B cells were co-transformed with protein expression plasmid (pET22b-T5-sfGFP149TAG) and ncAA incorporation plasmids (pUltra-Tet3.0-R2-84-MmPylT) and grown in 2YT medium at 37 °C. The protein expression was carried out in Luria-Bertani (LB) medium supplemented with or without 1 mM m-Stet-Phe (prepared as 100 mM DMSO stock solution). Expression was induced by the addition of isopropyl-β-D-thiogalactoside (IPTG) to a final concentration of 1 mM at OD 0.6 and cells were grown for an additional 18 h at 30 °C. Cells were harvested by centrifugation at 4750 × g for 10 min. The cell pellets were suspended in lysis buffer (cell lysis reagent 10× at 1× pH 7.4 PBS) and lysed for 2 h at 18 °C. The resulting cell lysate was clarified by centrifugation at 14![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 × g for 30 min, and protein was purified on Ni-NTA resin (Qiagen) following the manufacturer's instructions. The purified protein was used for SDS-PAGE and ESI-MS analysis.
000 × g for 30 min, and protein was purified on Ni-NTA resin (Qiagen) following the manufacturer's instructions. The purified protein was used for SDS-PAGE and ESI-MS analysis.
Transfection and confocal image of photoactivatable fluorescent protein
HEK293T cells were plated in a 35 mm glass bottom mattek dishes at about 40% confluency so that they reach 70–90% confluency at the time of transfection. Cells were transfected using PolyJet (Thermo Fisher) 2000 ng of plasmid DNA was diluted in 125 μl of serum-free DMEM and 6 μl of PolyJet reagent was diluted in 125 μl of serum-free DMEM. They were combined and incubated for 10 min at RT before adding to cells. m-Stet-Phe amino acid was added to the cells immediately and incubated for 24 hours before washing with PBS (1×, pH 7.4) three times. Fluorescent images and differential interference contrast (DIC) images were captured using Nikon A1 confocal laser microscope system with 60× oil len. Sulfur tetrazine caged sfGFP was activated using 405 nm light at 5–10% laser intensity and the sfGFP signals were collected with 488 nm channel. The captured images were processed and analyzed using NIS-Elements.Confocal image of SMepTz-BODIPY-SNAP stain
After inubation with SMepTz-BODIPY-SNAP 20 μM in complete DMEM medium, cells being able to express NUP96-SNAP tag were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde PBS (1×, pH 7.4) solution in a 35 mm glass bottom mattek dishes and washed three times with PBS (1×, pH 7.4). Imaging was performed at room temperature on the Nikon A1 confocal laser microscope. Activation used 405 nm light at 40% laser intensity and signals from BODIPY were collected using 488 nm channel. Differential interference contrast (DIC) and fluorescent images were processed and analyzed using NIS-Elements.Author contributions
S. Y., A. L., and H. X. designed all the experiments; S. Y., A.L., M. Z. and D. S. performed all the experiments; S. Y., A. L., M. Z. and Y. L. analysed the data; and S. Y., A. L. and H. X. wrote the manuscript.Data availability
All the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article and its ESI.†Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Anna-Karin Gustavsson for kindly providing the U2OS cell line which stably expresses NUP96-SNAP Tag protein. This work was supported by the NIH (R01-CA277838, R35-GM133706, and R01-AI165079 to H. X.), the Robert A. Welch Foundation (C-1970 to H. X.), US Department of Defense (HT9425-23-1-0494 and W81XWH-21-1-0789 to H. X.) and SynthX Seed Award (SYN-IN-2024-002 to H. X.). H. X. is a Cancer Prevention & Research Institute of Texas (CPRIT) Scholar in Cancer Research.Notes and references
- W. Li and G. Zheng, Photoactivatable Fluorophores and Techniques for Biological Imaging Applications, Photochem. Photobiol. Sci., 2012, 11(3), 460–471, 10.1039/c2pp05342j.
- F. M. Raymo, Photoactivatable Synthetic Fluorophores, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2013, 15(36), 14840, 10.1039/c3cp51822a.
- L. M. Wysocki, J. B. Grimm, A. N. Tkachuk, T. A. Brown, E. Betzig and L. D. Lavis, Facile and General Synthesis of Photoactivatable Xanthene Dyes, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2011, 50(47), 11206–11209, DOI:10.1002/anie.201104571.
- Z. Yu, L. Y. Ho and Q. Lin, Rapid, Photoactivatable Turn-On Fluorescent Probes Based on an Intramolecular Photoclick Reaction, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2011, 133(31), 11912–11915, DOI:10.1021/ja204758c.
- Y. Zhang, Y. Zheng, Y. Meana and F. M. Raymo, BODIPYs with Photoactivatable Fluorescence, Chem. – Eur. J., 2021, 27(44), 11257–11267, DOI:10.1002/chem.202101628.
- G. Lukinavičius and K. Johnsson, Switchable Fluorophores for Protein Labeling in Living Cells, Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol., 2011, 15(6), 768–774, DOI:10.1016/j.cbpa.2011.10.015.
- K. D. Piatkevich and V. V. Verkhusha, Advances in Engineering of Fluorescent Proteins and Photoactivatable Proteins with Red Emission, Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol., 2010, 14(1), 23–29, DOI:10.1016/j.cbpa.2009.10.011.
- J. Tang, M. A. Robichaux, K.-L. Wu, J. Pei, N. T. Nguyen, Y. Zhou, T. G. Wensel and H. Xiao, Single-Atom Fluorescence Switch: A General Approach toward Visible-Light-Activated Dyes for Biological Imaging, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2019, 141(37), 14699–14706, DOI:10.1021/jacs.9b06237.
- L. Wang, S. Wang, J. Tang, V. B. Espinoza, A. Loredo, Z. Tian, R. B. Weisman and H. Xiao, Oxime as a General Photocage for the Design of Visible Light Photo-Activatable Fluorophores, Chem. Sci., 2021, 12(47), 15572–15580, 10.1039/D1SC05351E.
- L. Gai, R. Zhang, X. Shi, Z. Ni, S. Wang, J.-L. Zhang, H. Lu and Z. Guo, BOINPYs: Facile Synthesis and Photothermal Properties Triggered by Photoinduced Nonadiabatic Decay, Chem. Sci., 2023, 14(6), 1434–1442, 10.1039/D2SC06435A.
- X. Zhang and S. J. Booker, Seeing Is Believing: Advances in Biological Imaging, ACS Bio. Med. Chem. Au, 2024, 4(1), 1–3, DOI:10.1021/acsbiomedchemau.3c00075.
- J. Ma, R. Sun, K. Xia, Q. Xia, Y. Liu and X. Zhang, Design and Application of Fluorescent Probes to Detect Cellular Physical Microenvironments, Chem. Rev., 2024, 124(4), 1738–1861, DOI:10.1021/acs.chemrev.3c00573.
- D.-C. Chiu and J. M. Baskin, Imaging and Editing the Phospholipidome, Acc. Chem. Res., 2022, 55(21), 3088–3098, DOI:10.1021/acs.accounts.2c00510.
- W. Yu and J. M. Baskin, Photoaffinity Labeling Approaches to Elucidate Lipid–Protein Interactions, Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol., 2022, 69, 102173, DOI:10.1016/j.cbpa.2022.102173.
- P. Shrestha, D. Kand, R. Weinstain and A. H. Winter, Meso-Methyl BODIPY Photocages: Mechanisms, Photochemical Properties, and Applications, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2023, 145(32), 17497–17514, DOI:10.1021/jacs.3c01682.
- P. Shrestha, A. Mukhopadhyay, K. C. Dissanayake and A. H. Winter, Efficiency of Functional Group Caging with Second-Generation Green- and Red-Light-Labile BODIPY Photoremovable Protecting Groups, J. Org. Chem., 2022, 87(21), 14334–14341, DOI:10.1021/acs.joc.2c01781.
- W. Ren, A. Ji and H. Ai, Light Activation of Protein Splicing with a Photocaged Fast Intein, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2015, 137(6), 2155–2158, DOI:10.1021/ja508597d.
- Y. Pang; Y. Zhang; J. Zhang; Z. Li; Y. He; Y. Wang; J. Oberholzer and H. Ai SHRIMP: Genetically Encoded mScarlet-Derived Red Fluorescent Hydrogen Peroxide Sensor with High Brightness and Minimal Photoactivation. bioRxiv, 2023, preprint, 2023.08.09.552302 DOI:10.1101/2023.08.09.552302.
- G. Zheng, Y.-M. Guo and W.-H. Li, Photoactivatable and Water Soluble FRET Dyes with High Uncaging Cross Section, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2007, 129(35), 10616–10617, DOI:10.1021/ja071427.
- A. C. E. Shibata, H. H. Ueda, K. Eto, M. Onda, A. Sato, T. Ohba, J. Nabekura and H. Murakoshi, Photoactivatable CaMKII Induces Synaptic Plasticity in Single Synapses, Nat. Commun., 2021, 12(1), 751, DOI:10.1038/s41467-021-21025-6.
- S. Peng, R. Sun, W. Wang and C. Chen, Single-Molecule Photoactivation FRET: A General and Easy-To-Implement Approach To Break the Concentration Barrier, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2017, 56(24), 6882–6885, DOI:10.1002/anie.201702731.
- K. Mutoh, N. Miyashita, K. Arai and J. Abe, Turn-On Mode Fluorescence Switch by Using Negative Photochromic Imidazole Dimer, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2019, 141(14), 5650–5654, DOI:10.1021/jacs.9b01870.
- V. Gatterdam, T. Stoess, C. Menge, A. Heckel and R. Tampé, Caged Glutathione – Triggering Protein Interaction by Light, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2012, 51(16), 3960–3963, DOI:10.1002/anie.201108073.
- W. R. Algar, N. Hildebrandt, S. S. Vogel and I. L. Medintz, FRET as a Biomolecular Research Tool – Understanding Its Potential While Avoiding Pitfalls, Nat. Methods, 2019, 16(9), 815–829, DOI:10.1038/s41592-019-0530-8.
- Y.-J. Gong, X.-B. Zhang, C.-C. Zhang, A.-L. Luo, T. Fu, W. Tan, G.-L. Shen and R.-Q. Yu, Through Bond Energy Transfer: A Convenient and Universal Strategy toward Efficient Ratiometric Fluorescent Probe for Bioimaging Applications, Anal. Chem., 2012, 84(24), 10777–10784, DOI:10.1021/ac302762d.
- C. Duxia, Z. Linlin, L. Zhiqiang and L. Weiying, Through Bond Energy Transfer (TBET)-Based Fluorescent Chemosensors, J. Photochem. Photobiol., C, 2020, 44, 100371, DOI:10.1016/j.jphotochemrev.2020.100371.
- S. K. Padhan, V. K. Mishra, N. Murmu, S. Mishra and S. N. Sahu, Through Bond Energy Transfer (TBET)-Operated Fluoride Ion Sensing via Spirolactam Ring Opening of a Coumarin–Fluorescein Bichromophoric Dyad, RSC Adv., 2020, 10(47), 28422–28430, 10.1039/D0RA05357K.
- G. Lu, Y. Guo, J. Zhuo, X. Li, H. Chi and Z. Zhang, A General Strategy for Through-Bond Energy Transfer Fluorescence Probes Combining Intramolecular Charge Transfer: A Silyl Ether System for Endogenous Peroxynitrite Sensing, Chem. – Eur. J., 2019, 25(71), 16350–16357, DOI:10.1002/chem.201903880.
- G.-S. Jiao, L. H. Thoresen and K. Burgess, Fluorescent, Through-Bond Energy Transfer Cassettes for Labeling Multiple Biological Molecules in One Experiment, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2003, 125(48), 14668–14669, DOI:10.1021/ja037193l.
- A. Wieczorek, P. Werther, J. Euchner and R. Wombacher, Green- to Far-Red-Emitting Fluorogenic Tetrazine Probes – Synthetic Access and No-Wash Protein Imaging inside Living Cells, Chem. Sci., 2017, 8(2), 1506–1510, 10.1039/C6SC03879D.
- A. Loredo, J. Tang, L. Wang, K.-L. Wu, Z. Peng and H. Xiao, Tetrazine as a General Phototrigger to Turn on Fluorophores, Chem. Sci., 2020, 11(17), 4410–4415, 10.1039/D0SC01009J.
- M. J. Tucker, J. R. Courter, J. Chen, O. Atasoylu, A. B. Smith and R. M. Hochstrasser, Tetrazine Phototriggers: Probes for Peptide Dynamics, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2010, 49(21), 3612–3616, DOI:10.1002/anie.201000500.
- L. G. Meimetis, J. C. T. Carlson, R. J. Giedt, R. H. Kohler and R. Weissleder, Ultrafluorogenic Coumarin-Tetrazine Probes for Real-Time Biological Imaging, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2014, 53(29), 7531–7534, DOI:10.1002/anie.201403890.
- J. C. T. Carlson, L. G. Meimetis, S. A. Hilderbrand and R. Weissleder, BODIPY-Tetrazine Derivatives as Superbright Bioorthogonal Turn-on Probes, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2013, 52(27), 6917–6920, DOI:10.1002/anie.201301100.
- G. Knorr, E. Kozma, A. Herner, E. A. Lemke and P. Kele, New Red-Emitting Tetrazine-Phenoxazine Fluorogenic Labels for Live-Cell Intracellular Bioorthogonal Labeling Schemes, Chem. – Eur. J., 2016, 22(26), 8972–8979, DOI:10.1002/chem.201600590.
- H. Wu, J. Yang, J. Šečkutė and N. K. Devaraj, In Situ Synthesis of Alkenyl Tetrazines for Highly Fluorogenic Bioorthogonal Live-Cell Imaging Probes, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2014, 53(23), 5805–5809, DOI:10.1002/anie.201400135.
- A. Aktalay, R. Lincoln, L. Heynck, M. A. D. R. B. F. Lima, A. N. Butkevich, M. L. Bossi and S. W. Hell, Bioorthogonal Caging-Group-Free Photoactivatable Probes for Minimal-Linkage-Error Nanoscopy, ACS Cent. Sci., 2023, 9(8), 1581–1590, DOI:10.1021/acscentsci.3c00746.
- K. Kikuchi and A. Kaur, Picture Perfect Precision: Biorthogonal Photoactivatable Tools Achieve Imaging with Molecular-Scale Precision, ACS Cent. Sci., 2023, 9(8), 1518–1521, DOI:10.1021/acscentsci.3c00945.
- N. K. Devaraj and R. Weissleder, Biomedical Applications of Tetrazine Cycloadditions, Acc. Chem. Res., 2011, 44(9), 816–827, DOI:10.1021/ar200037t.
- N. K. Devaraj, S. Hilderbrand, R. Upadhyay, R. Mazitschek and R. Weissleder, Bioorthogonal Turn-On Probes for Imaging Small Molecules inside Living Cells, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2010, 49(16), 2869–2872, DOI:10.1002/anie.200906120.
- B. L. Oliveira, Z. Guo, O. Boutureira, A. Guerreiro, G. Jiménez-Osés and G. J. L. Bernardes, A Minimal, Unstrained S-Allyl Handle for Pre-Targeting Diels–Alder Bioorthogonal Labeling in Live Cells, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2016, 55(47), 14683–14687, DOI:10.1002/anie.201608438.
- D. N. Kamber, Y. Liang, R. J. Blizzard, F. Liu, R. A. Mehl, K. N. Houk and J. A. Prescher, 1,2,4-Triazines Are Versatile Bioorthogonal Reagents, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2015, 137(26), 8388–8391, DOI:10.1021/jacs.5b05100.
- R. D. Row and J. A. Prescher, Tetrazine Marks the Spot, ACS Cent. Sci., 2016, 2(8), 493–494, DOI:10.1021/acscentsci.6b00204.
- D. N. Kamber, S. S. Nguyen, F. Liu, J. S. Briggs, H.-W. Shih, R. D. Row, Z. G. Long, K. N. Houk, Y. Liang and J. A. Prescher, Isomeric Triazines Exhibit Unique Profiles of Bioorthogonal Reactivity, Chem. Sci., 2019, 10(39), 9109–9114, 10.1039/C9SC01427F.
- D. Liang, K. Wu, R. Tei, T. W. Bumpus, J. Ye and J. M. Baskin, A Real-Time, Click Chemistry Imaging Approach Reveals Stimulus-Specific Subcellular Locations of Phospholipase D Activity, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2019, 116(31), 15453–15462, DOI:10.1073/pnas.1903949116.
- S. A. Chechetka, E. Yuba, K. Kono, M. Yudasaka, A. Bianco and E. Miyako, Magnetically and Near-Infrared Light-Powered Supramolecular Nanotransporters for the Remote Control of Enzymatic Reactions, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2016, 55(22), 6476–6481, DOI:10.1002/anie.201602453.
- J. Lu, E. Choi, F. Tamanoi and J. I. Zink, Light-Activated Nanoimpeller-Controlled Drug Release in Cancer Cells, Small, 2008, 4(4), 421–426, DOI:10.1002/smll.200700903.
- L. Chen, Y. Liu, W. Guo and Z. Liu, Light Responsive Nucleic Acid for Biomedical Application, Exploration, 2022, 2(5), 20210099, DOI:10.1002/EXP.20210099.
- M. A. Priestman and D. S. Lawrence, Light-Mediated Remote Control of Signaling Pathways, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, Proteins Proteomics, 2010, 1804(3), 547–558, DOI:10.1016/j.bbapap.2009.09.005.
- E. Contreras-García, C. Lozano, C. García-Iriepa, M. Marazzi, A. H. Winter, C. Torres and D. Sampedro, Controlling Antimicrobial Activity of Quinolones Using Visible/NIR Light-Activated BODIPY Photocages, Pharmaceutics, 2022, 14(5), 1070, DOI:10.3390/pharmaceutics14051070.
- N. P. Toupin, K. Arora, P. Shrestha, J. A. Peterson, L. J. Fischer, E. Rajagurubandara, I. Podgorski, A. H. Winter and J. J. Kodanko, BODIPY-Caged Photoactivated Inhibitors of Cathepsin B Flip the Light Switch on Cancer Cell Apoptosis, ACS Chem. Biol., 2019, 14(12), 2833–2840, DOI:10.1021/acschembio.9b00711.
- R. Tei, J. Morstein, A. Shemet, D. Trauner and J. M. Baskin, Optical Control of Phosphatidic Acid Signaling, ACS Cent. Sci., 2021, 7(7), 1205–1215, DOI:10.1021/acscentsci.1c00444.
- S. Yang, L. Wang, A. Loredo, S. Wang, N. Ada and H. Xiao, Visible Light-Activated Prodrug System with a Novel Heavy-Atom-Free Photosensitizer, Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 2023, 91, 129365, DOI:10.1016/j.bmcl.2023.129365.
- J. Sandstrom, The True Dithio-p-Urazine and Some Related Sym-Tetrazine Derivatives, Acta Chem. Scand., 1961, 15, 1575–1582 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Waluk, J. Spanget-Larsen and E. W. Thulstrup, Electronic States of Symmetrically Disubstituted S-Tetrazines, Chem. Phys., 1995, 200(1–2), 201–213, DOI:10.1016/0301-0104(95)00179-R.
- M. Abdo, S. P. Brown, J. R. Courter, M. J. Tucker, R. M. Hochstrasser and A. B. Smith, Design, Synthesis, and Photochemical Validation of Peptide Linchpins Containing the S,S -Tetrazine Phototrigger, Org. Lett., 2012, 14(13), 3518–3521, DOI:10.1021/ol301490h.
- M. J. Tucker, M. Abdo, J. R. Courter, J. Chen, A. B. Smith and R. M. Hochstrasser, Di-Cysteine S,S-Tetrazine: A Potential Ultra-Fast Photochemical Trigger to Explore the Early Events of Peptide/Protein Folding, J. Photochem. Photobiol., A, 2012, 234, 156–163, DOI:10.1016/j.jphotochem.2012.02.014.
- J. R. Courter, M. Abdo, S. P. Brown, M. J. Tucker, R. M. Hochstrasser and A. B. Smith III, The Design and Synthesis of Alanine-Rich α-Helical Peptides Constrained by an S,S-Tetrazine Photochemical Trigger: A Fragment Union Approach, J. Org. Chem., 2014, 79(2), 759–768, DOI:10.1021/jo402680v.
- J. Yang, M. R. Karver, W. Li, S. Sahu and N. K. Devaraj, Metal-Catalyzed One-Pot Synthesis of Tetrazines Directly from Aliphatic Nitriles and Hydrazine, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2012, 51(21), 5222–5225, DOI:10.1002/anie.201201117.
- Y. Xie, Y. Fang, Z. Huang, A. M. Tallon, C. W. Ende and J. M. Fox, Divergent Synthesis of Monosubstituted and Unsymmetrical 3,6-Disubstituted Tetrazines from Carboxylic Ester Precursors, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2020, 59, 16967–16973, DOI:10.1002/anie.202005569.
- J. W. Chin, Expanding and Reprogramming the Genetic Code, Nature, 2017, 550(7674), 53–60, DOI:10.1038/nature24031.
- C. C. Liu and P. G. Schultz, Adding New Chemistries to the Genetic Code, Annu. Rev. Biochem., 2010, 79(1), 413–444, DOI:10.1146/annurev.biochem.052308.105824.
- J. W. Chin, Expanding and Reprogramming the Genetic Code, Nature, 2017, 550(7674), 53–60, DOI:10.1038/nature24031.
- L. Wang, J. Xie and P. G. Schultz, Expanding the Genetic Code, Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct., 2006, 35, 225–249, DOI:10.1146/annurev.biophys.35.101105.121507.
- H. Xiao and P. G. Schultz, At the Interface of Chemical and Biological Synthesis: An Expanded Genetic Code, Cold Spring Harbor Perspect. Biol., 2016, 8(9), a023945, DOI:10.1101/cshperspect.a023945.
- H. S. Jang, S. Jana, R. J. Blizzard, J. C. Meeuwsen and R. A. Mehl, Access to Faster Eukaryotic Cell Labeling with Encoded Tetrazine Amino Acids, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2020, 142(16), 7245–7249, DOI:10.1021/jacs.9b11520.
- J. L. Seitchik, J. C. Peeler, M. T. Taylor, M. L. Blackman, T. W. Rhoads, R. B. Cooley, C. Refakis, J. M. Fox and R. A. Mehl, Genetically Encoded Tetrazine Amino Acid Directs Rapid Site-Specific in Vivo Bioorthogonal Ligation with Trans -Cyclooctenes, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2012, 134(6), 2898–2901, DOI:10.1021/ja2109745.
- R. J. Blizzard, D. R. Backus, W. Brown, C. G. Bazewicz, Y. Li and R. A. Mehl, Ideal Bioorthogonal Reactions Using A Site-Specifically Encoded Tetrazine Amino Acid, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2015, 137(32), 10044–10047, DOI:10.1021/jacs.5b03275.
- Y. Wang, J. Zhang, B. Han, L. Tan, W. Cai, Y. Li, Y. Su, Y. Yu, X. Wang, X. Duan, H. Wang, X. Shi, J. Wang, X. Yang and T. Liu, Noncanonical Amino Acids as Doubly Bio-Orthogonal Handles for One-Pot Preparation of Protein Multiconjugates, Nat. Commun., 2023, 14(1), 974, DOI:10.1038/s41467-023-36658-y.
- R. D. Moir, M. Yoon, S. Khuon and R. D. Goldman, Nuclear Lamins A and B1: Different Pathways of Assembly during Nuclear Envelope Formation in Living Cells, J. Cell Biol., 2000, 151 Search PubMed.
- A. Fracchia, T. Asraf, M. Salmon-Divon and G. Gerlitz, Increased Lamin B1 Levels Promote Cell Migration by Altering Perinuclear Actin Organization, Cells, 2020, 9(10), 2161, DOI:10.3390/cells9102161.
- C. A. Hoelzel and X. Zhang, Visualizing and Manipulating Biological Processes by Using HaloTag and SNAP-Tag Technologies, ChemBioChem, 2020, 21(14), 1935–1946, DOI:10.1002/cbic.202000037.
- J. Q. Umberger and V. K. LaMer, The Kinetics of Diffusion Controlled Molecular and Ionic Reactions in Solution as Determined by Measurements of the Quenching of Fluorescence1,2, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1945, 67(7), 1099–1109, DOI:10.1021/ja01223a023.
- W. H. Melhuish, Quantum efficiencies of fluorescence of organic substances: effect of solvent and concentration of the fluorescent solute1, J. Phys. Chem., 1961, 65(2), 229–235, DOI:10.1021/j100820a009.
Footnotes |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available. See DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/d4tb01817f |
| ‡ These authors contributed equally. |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2024 |