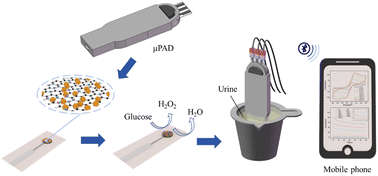
Urine biomarker detection with high accuracy and sensitivity is crucial for advancing point-of-care diagnostics. This paper developed a microfluidic paper-based analytical device (μPAD) for electrochemical glucose detection in urine. The proposed μPAD employs a filter paper substrate to enable pump-free sample transport to a detection zone integrated with the screen-printed electrode (SPE), allowing rapid quantification within 60 seconds. A composite of reduced graphene oxide (RGO)/platinum-palladium nanoparticles (Pt-Pd NPs) with good analytical performance has been electrodeposited on the surface of SPEs and subsequently combined with glucose oxidase (GOx) to create a glucose biosensor (GOx/Pt-Pd NPs/RGO/SPE). Under optimized conditions, the Pt-Pd NPs/RGO/SPE shows good performance, showing a 17.4-fold sensitivity enhancement over bare SPEs in H2O2 detection. The developed μPAD achieves wide linear ranges of 5 μM–20 mM (H2O2) and 20 μM–5 mM (glucose), with low detection limits of 0.97 μM and 8.1 μM, respectively. Furthermore, the μPAD shows wide linear ranges covering required detection ranges of glucose in urine, demonstrating its great potential in personal health monitoring and clinical applications requiring reliable glucose measurement in urine.