A novel therapeutic strategy utilizing EpCAM aptamer-conjugated gemcitabine for targeting bladder cancer and cancer stem cells†
Jiahao
Liu‡
 a,
Long
Wang‡
a,
Yongbo
Peng‡
a,
Long
Wang‡
a,
Yongbo
Peng‡
 b,
Shuyang
Long
c,
Hongliang
Zeng
d,
Minhua
Deng
ef,
Wei
Xiang
a,
Biao
Liu
a,
Xing
Hu
a,
Xuewen
Liu
g,
Jianfei
Xie
h,
Weibin
Hou
a,
Jin
Tang
a and
Jianye
Liu
b,
Shuyang
Long
c,
Hongliang
Zeng
d,
Minhua
Deng
ef,
Wei
Xiang
a,
Biao
Liu
a,
Xing
Hu
a,
Xuewen
Liu
g,
Jianfei
Xie
h,
Weibin
Hou
a,
Jin
Tang
a and
Jianye
Liu
 *a
*a
aDepartment of Urology, The Third Xiangya Hospital of Central South University, No. 138, Tongzipo Road, Changsha, 410013, Hunan, China. E-mail: 602536@csu.edu.cn
bChongqing Key Laboratory for Pharmaceutical Metabolism Research, College of Pharmacy, Chongqing Medical University, No. 1, Yixueyuan Road, Chongqing, 400016, China
cSchool of Medicine, Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, Grade 2024, China
dInstitute of Chinese Materia Medica, Hunan Academy of Chinese Medicine, No. 8, Yuehua Road, Changsha 410013, China
eDepartment of Urology, Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center, No. 651, Dongfeng Road East, Guangzhou, 510060, Guangdong, China
fState Key Laboratory of Oncology in Southern China, Collaborative Innovation Center for Cancer Medicine, No. 651, Dongfeng Road East, Guangzhou, 510060, Guangdong, China
gDepartment of Oncology, The Third Xiangya Hospital of Central South University, No. 138, Tongzipo Road, Changsha, 410013, Hunan, China
hDepartment of Nursing, The Third Xiangya Hospital of Central South University, No. 138, Tongzipo Road, Changsha, 410013, Hunan, China
First published on 10th January 2025
Abstract
Gemcitabine (GEM) is a first line chemotherapy drug for bladder cancer (BCa). GEM's lack of specificity has led to disadvantages, resulting in low efficiency, especially when combined with the targeted treatment of BCa stem cells (CSCs), which is considered the cause of BCa recurrence and progression. To enhance the anti-cancer effect and reduce the side effects of GEM targeting of BCa cells/CSCs, an aptamer drug conjugate (ApDC) targeted delivery system was used to improve the efficiency of GEM in BCa therapy using EpCAM aptamer-GEM conjugates based on the epithelial cell adhesion molecule (EpCAM), which is highly expressed on the cell membrane of BCa cells/CSCs. We designed and synthesized EpCAM aptamer gemcitabine conjugates (EpCAM-GEMs, one aptamer carried three GEMs). The targeting effect of EpCAM-GEMs was examined in a xenograft model using an in vivo imaging system. To evaluate the antitumor activity and mechanism of EpCAM-GEMs, Cell Counting Kit-8, apoptosis and colony formation assays; BCa CSC xenotransplantation; xenotransplantation of subcutaneous tumors; a lung metastasis model; an in situ model; and biosafety assessment were used in vitro and in vivo. EpCAM is highly expressed on the surface of BCa cells/CSCs. EpCAM-GEMs were automatically synthesized using a DNA synthesizer, were stable in serum, and selectively delivered GEM to kill BCa cells/CSCs. EpCAM-GEMs entered BCa cells via macropinocytosis, released GEM to inhibit DNA synthesis, and degraded all BCa cells under the action of a BCa cell intracellular phosphatase; however, they did not kill normal cells because of their low EpCAM expression. EpCAM-GEMs inhibited BCa growth and metastasis in three bladder tumor models, with good biosafety. These results demonstrated the targeted anti-tumor efficiency and good biosafety of EpCAM-GEMs in BCa treatment, which will provide a new therapeutic strategy in BCa biomarker targeted therapy.
1. Introduction
Bladder cancer (BCa) ranks among the top ten most common malignancies worldwide. Based on how deep the tumor grows, it is divided into non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC) and muscle-invasive bladder cancer (MIBC).1 The global Age Standardized Incidence Rate (ASR) for male mortality from BCa is 3.2 per 100![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 people per year and for women it is 0.9 per 100
000 people per year and for women it is 0.9 per 100![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 per year.2 A combination of surgery and chemotherapy is commonly used to treat BCa. However, a lack of specificity, the high rate of postoperative recurrence and progression, the serious loss of quality of life, and intolerance to the side effects of chemotherapy hinder the efficacy of these treatments.3–5 With the development of the molecular biology and genetics of BCa, the applications of immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs), antibody drug conjugates (ADC), and gene therapy have emerged as treatments for BCa. ICIs target checkpoint proteins on the cell surface to stimulate the immune system to recognize and destroy cancer cells, and are indicated for patients with advanced BCa and those who are not eligible for platinum therapy.6 ADC drugs are monoclonal antibodies that target tumor antigens in combination with cytotoxic drugs.7 Gene therapy is represented by fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) inhibition, which is used for advanced BCa.8 Although the above treatments bring hope for the treatment of BCa, clinical responses are not obvious, there are significant limitations, and they cannot benefit all patients, and hence these are not ideal treatments for BCa. Therefore, BCa treatment urgently requires new treatment methods.
000 per year.2 A combination of surgery and chemotherapy is commonly used to treat BCa. However, a lack of specificity, the high rate of postoperative recurrence and progression, the serious loss of quality of life, and intolerance to the side effects of chemotherapy hinder the efficacy of these treatments.3–5 With the development of the molecular biology and genetics of BCa, the applications of immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs), antibody drug conjugates (ADC), and gene therapy have emerged as treatments for BCa. ICIs target checkpoint proteins on the cell surface to stimulate the immune system to recognize and destroy cancer cells, and are indicated for patients with advanced BCa and those who are not eligible for platinum therapy.6 ADC drugs are monoclonal antibodies that target tumor antigens in combination with cytotoxic drugs.7 Gene therapy is represented by fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) inhibition, which is used for advanced BCa.8 Although the above treatments bring hope for the treatment of BCa, clinical responses are not obvious, there are significant limitations, and they cannot benefit all patients, and hence these are not ideal treatments for BCa. Therefore, BCa treatment urgently requires new treatment methods.
An aptamer is a single-stranded oligonucleotide that specifically binds to a target antigen, and is frequently produced using an in vitro selection process termed systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment (SELEX).9–12 Conventional chemotherapeutics are toxic to healthy tissue because of their non-targeting effects and suffer from dosage limitation because of side effects. It is hoped that these problems could be solved using aptamer drug conjugates (ApDC), which can specifically deliver chemotherapy drugs to cancer cells, but do not damage normal cells, and can be used at higher doses for maximum effect.13–16 Modification of the aptamer with hydrophobic groups solves the problem of high solubility and weak affinity of chemotherapeutics in water. Aptamers also have obvious advantages, such as small size, easy synthesis, good stability, and lack of immunogenicity.11,16–18
The epithelial cell adhesion molecule (EpCAM) is a biomarker expressed in cancer cells and cancer stem cells (CSCs), and is considered a tumor-associated antigen. EpCAM is involved in regulating cell adhesion, and mediates signal transduction, cell migration, proliferation, and differentiation.19–21 Studies have shown that knockout of EpCAM can lead to downregulation of the expression of CSC markers (octamer-binding protein 4 (OCT4), SRY-box transcription factor 2 (SOX2), and NANOG).22 EpCAM has been reported in colon cancer, prostate cancer, breast cancer, ovarian cancer, retinoblastoma cancer, and gallbladder cancer.23–29 Gemcitabine (GEM) is an analog of cytarabine, which can interfere with DNA synthesis and replication to induce cell death. However, GEM has poor pharmacokinetics, cannot clearly distinguish between normal cells and cancer cells, and causes adverse effects, such as abnormal liver function and bone marrow suppression.30,31
Compared with non-CSCs, CSCs have increased drug resistance, stronger invasiveness, and higher metastasis potential, and it is generally considered that the existence of CSCs is the root cause of cancer incurability, progression, and recurrence.32 Therefore, anti-cancer drug research should be directed towards developing a targeted drug system for CSCs. The combination of an EpCAM aptamer with chemotherapeutics has been shown to be effective against CSCs.33
Consequently, we first synthesized EpCAM aptamer-gemcitabine (EpCAM-GEMs) conjugates to treat BCa. The EpCAM aptamer sequence was connected to three GEMs via phosphodiester bonds. EpCAM-GEMs target both BCa cells and CSCs, with no toxicity toward normal cells. EpCAM-GEMs can enter cells through macropinocytosis. Under the acidic conditions of intracellular lysosomes, phosphatase shearing releases GEM into the nucleus, where it inhibits DNA synthesis and thus exerts cytotoxicity. Moreover, three animal models were established to carry out in vivo studies of the potential antitumor effects and biosafety of EpCAM-GEMs. The result proved that EpCAM-GEMs are an effective ApDC-mediated targeting system to treat BCa.
2. Results
2.1. Overexpression of EpCAM in BCa tissue and cell lines
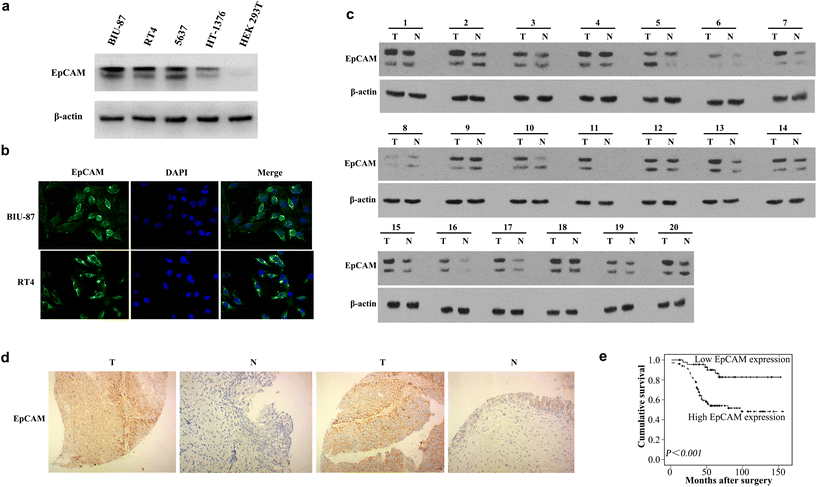
To confirm EpCAM as a biomarker that is highly expressed in BCa, we measured the EpCAM protein levels in four BCa cell lines (BIU-87, RT4, 5637, and HT-1376) and the human embryonic kidney HEK293T cell line. The results showed that EpCAM is overexpressed in BCa cells, but was not expressed in HEK293T cells (Fig. 1a). Furthermore, immunofluorescence analysis showed that EpCAM was primarily expressed in the membranes of BCa cells (Fig. 1b). Compared with that in adjacent normal tissue, EpCAM protein expression was upregulated significantly in human BCa tissues (Fig. 1c). Immunohistochemical findings showed high expression of EpCAM in 102/148 (68.9%) of BCa tissues, and in only 10/45 (22.2%) of adjacent noncancerous tissues (P < 0.001, Fig. 1d and Fig. S2‡).2.2. EpCAM expression, clinicopathological variables, and survival outcome
Table S1‡ shows the significant association between the clinicopathological variables and EpCAM expression. There was a significant association between high EpCAM expression and advanced stages (P = 0.032) and positive lymph nodes (P = 0.006). Kaplan–Meier analysis revealed that patients with high expression of EpCAM had poorer survival (P < 0.001, Fig. 1e). Consideration of all other clinicopathological features together showed that histological grade, pT stage, lymph node metastasis, and overexpression of EpCAM were associated significantly with survival (P < 0.05, Table S2‡). Using the stepwise selection method in the Cox regression survival analysis showed that EpCAM overexpression (P = 0.001) was an independent predictor of survival (Table S3‡).2.3. Synthesis of aptamer EpCAM-GEMs
To construct EpCAM-GEMs using automatic solid-phase DNA synthesis, GEM phosphoramide building blocks were first synthesized using one-step coupling of GEM and N,N-diisopropyl chlorophosphoramide (yield ∼80.0%). Specifically, three GEM molecules and the EpCAM aptamer SYL3C sequence were synthesized from the 3′ end to the 5′ end of the oligonucleotide; the first base-CpG was selected as the solid-phase carrier, and its 5′ -OH dimethoxytrityl tetrafluoroborate protection group was deprotected using trichloroacetic acid. SYL3C is a truncated and optimized sequence of SYL3, removing unnecessary nucleotides. SYL3C has an important three-hairpin structure that preserves targeted binding capabilities.21 After oligonucleotide synthesis activation, trichloroacetic acid was eluted using anhydrous acetonitrile, phosphoramide was used to form a phosphite bond at the 5′-OH through tetrazole activation, and then its phosphate (III) was oxidized to phosphate (V) using I2 to obtain a stable phosphodiester bond of the oligonucleotide. Acetyl blocked a small amount of 5′-OH that was not involved in the coupling reaction, and one base was added to each cycle reaction until the target sequence was completed. In the end, these CpG-carried EpCAM-GEMs and other conjugates were deprotected, and then the target oligonucleotides were purified using high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), at a purity >95% (Table S4 and Fig. S1, S3–S18‡).2.4. The EpCAM-GEMs in vitro targeting and stability in serum
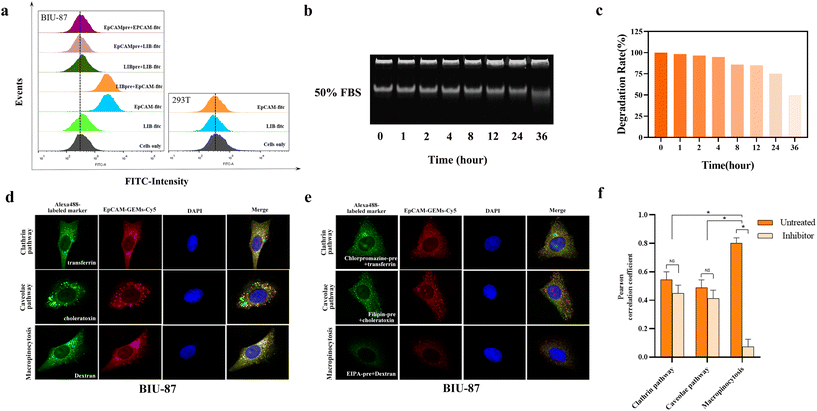
FITC-labeled sequences of EpCAM-GEMs and LIB-GEMs (control) were used to study the targeting of EpCAM-GEMs to BCa cells and the HEK293T cell line. Among them, LIB, serving as a random control sequence for the EpCAM aptamer, does not bind to EpCAM. The results showed that EpCAM-GEMs could target BIU-87 cells via high binding affinity with EpCAM. For the HEK293T normal human embryonic kidney cells, EpCAM-GEMs and LIB-GEMs showed no significant fluorescence intensity, which indicated that EpCAM-GEMs cannot target HEK293T cells because these cells lack EpCAM protein expression. Competitive experiments further demonstrated that EpCAM could target BIU-87 cells by incubating with EpCAM and LIB successively (Fig. 2a). In the immunofluorescence experiment, BIU-87 cells markedly bound EpCAM-GEMs, but hardly bound LIB-GEMs (Fig. S19‡). These results confirmed that EpCAM-GEMs can target cancer cells that overexpress EpCAM. Then, to evaluate the stability of EpCAM-GEMs in biological medium, DMEM cell culture medium supplemented with 50% FBS was prepared to simulate the growth environment of tumor cells. The results showed that EpCAM-GEMs did not significantly degrade in the first 6 h in 50% FBS, which indicated that EpCAM-GEMs can maintain a certain stability in serum, and could maintain an ideal plasma concentration, with a resulting anti-cancer effect on BCa cells (Fig. 2b and c).2.5. Critical cellular events and molecular interactions
To observe whether the BIU-87 cell took up EpCAM-GEMs through endocytosis, Alexa fluor-488 labeled endocytosis markers were examined using confocal microscopy. In contrast to transferrin and cholera toxin, EpCAM-GEMs-Cy5 (red) and dextran (green, a macropinocytosis marker) were significantly colocalized in BIU-87 cells (Fig. 2d), indicating that EpCAM-GEMs-Cy5 was mainly absorbed by BIU-87 cells through large cell phagocytosis. This deduction was supported by the significant reduction in colocalization between EpCAM-GEMs-Cy5 and dextran in the presence of EIPA (5-[N-ethyl-N-isopropyl] amiloride, an inhibitor of macropinocytosis) (Fig. 2e). The Pearson correlation coefficient of large cell phagocytosis was approximately 0.8, which decreased to approximately 0.2 after the addition of the inhibitor (Fig. 2f). These results confirmed that EpCAM-GEMs-Cy5 mainly entered BIU-87 cells through the macropinocytosis pathway. In addition, we studied the co-localization of LIB-GEMs-Cy5 and endocytic markers in BIU-87 cells (Fig. S20‡), and no co-localization signal was observed, suggesting that the entry of LIB-GEMs into BIU-87 cells might not involve endocytosis. This further clarified the targeting effect of EpCAM-GEMs on BIU-87 cells.2.6. Drug release in vitro
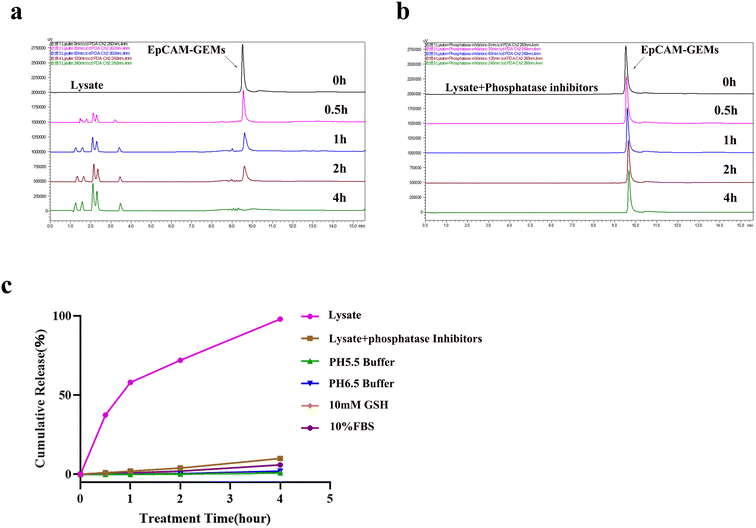
To clarify the intracellular release of GEM from EpCAM-GEMs, HPLC analysis of substance release was carried out under different conditions, such as low pH 5.5 buffer (simulating the tumor microenvironment), pH 6.5 buffer (simulating the acid endonuclease/lysosomal system), 10% FBS (cell culture medium), 10 × 10−3 M glutathione (simulating a reduced tumor microenvironment), and cell lysate or lysate added with phosphatase inhibitors. The phosphodiester bond used as an ApDC bridge indicates that the drug is released through the action of an intracellular phosphatase. When EpCAM-GEMs were treated with crude cell lysate of BIU-87 cells at 37 °C, the time-dependent release of GEM from EpCAM-GEMs (retention time: 9.7 minutes) and aptamer fragments of different sizes (retention time: 1.2 minutes, 1.6 minutes, 2.1 minutes, 2.3 minutes, and 3.5 minutes) were observed (Fig. 3a). About 50% of EpCAM-GEMs were degraded within 1 h and almost all had degraded by 4 h. In addition, the presence of phosphatase inhibitors significantly hindered the release of GEM from EpCAM-GEMs within 4 h (Fig. 3b), with only about 10% of EpCAM-GEMs being degraded. Other factors caused little or no significant degradation within 4 h (Fig. 3c and Fig. S21–S24‡). These results supported the design hypothesis that GEM release is achieved through phosphatase-mediated degradation.2.7. Effect of EpCAM-GEMs on BCa cell growth
A cell counting kit 8 (CCK-8) test was used to evaluate the cytotoxicity of EpCAM-GEMs toward BIU-87 cells and HEK293T normal human embryonic kidney cells. The data showed that GEM alone did not have good selectivity for BIU-87 and HEK293T cells because the IC50 values of these two cells were 109.7 nM and 99.32 nM, respectively (Fig. 4a and b). In contrast, EpCAM-GEMs showed similar cytotoxicity to GEM on BIU-87 cells (IC50, 96.19 nM vs. 109.7 nM, Fig. 4a and c). However, the IC50 value of EpCAM-GEMs for the HEK293T cell line was about eight times higher than that for BIU-87 cells (Fig. 4b). Similar results were observed in terms of the cell cycle. Compared with GEM, EpCAM-GEMs increased the G1/S phase ratio of BIU-87 cells, and LIB-GEMs showed equivalent results to untreated cells in terms of the cell cycle. However, there was no significant difference in the G1/S phase ratio of EpCAM-GEMs for HEK293T compared with the untreated group and the LIB-GEM-treated group (Fig. 4d and e), which further verified the specific binding of EpCAM-GEMs to EpCAM and their low cytotoxicity toward normal cells. These results also showed that EpCAM-GEMs had better selectivity than LIB-GEMs, and their anticancer effect was equivalent to that of GEM alone.2.8. In vivo imaging and anti-tumor activity of EpCAM-GEMs in xenotransplanted subcutaneous tumors
To verify the BCa targeting of EpCAM-GEMs-Cy5 in vivo, the tissue distribution of EpCAM-GEMs-Cy5 in a BIU-87 cell xenograft tumor model was measured using in vivo imaging technology. In Fig. 5a, EpCAM-GEMs-Cy5 shows a stronger fluorescence signal than the LIB-GEMs-Cy5 control group at 1 h after injection (right nude mouse). After 4 hours, the other group of nude mice that underwent the same treatment were euthanized, and their tumors and primary organs were collected for optical imaging. The tumors treated with EpCAM GEMs-Cy5 exhibited significant fluorescence signals (Fig. 5b). The above results showed that EpCAM-GEMs have good tumor targeting in vivo. To further determine the in vivo antitumor effect of EpCAM-GEMs, BIU-87 cells were used to evaluate the inhibitory effect of EpCAM-GEMs on tumor growth in a xenograft subcutaneous tumor model (Fig. 5c). Administration was stopped when the nude mice lost more than 20% of their body weight. EpCAM-GEMs significantly reduced the tumor weight and volume (Fig. 5d and e). Compared with the PBS, EpCAM, and LIB groups, EpCAM-GEMs reduced the tumor weight and volume by nearly 80%, while GEM or LIB-GEMs only reduced the tumor weight and volume by about 40% and 50%, respectively. The EpCAM, LIB, and PBS groups did not show an antitumor effect (Fig. 5f). The weight of the mice in the GEM and LIB-GEMs groups decreased significantly because of the toxicity and side effects of GEM, while the weight of the mice in the EpCAM-GEM group did not decrease markedly, probably because of their in vivo targeting ability (Fig. 5g). These results showed that using the EpCAM aptamer as a targeted drug carrier reduced the systemic toxicity of GEM and greatly improved its therapeutic effect. In addition, Ki67 antigen (brown) and terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase nick end labeling (TUNEL) signals indicated that EpCAM-GEMs could induce significant BCa cell apoptosis and produce a greater antitumor effect than the other treatments. Consistently, nuclear concentration and vacuolation were observed after hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining of tumor tissues treated with EpCAM-GEMs (Fig. S25a–c‡).2.9. Selectivity and toxicity of EpCAM-GEMs to bladder CSCs
To verify that EpCAM-GEMs have the same targeting and toxicity to bladder CSCs, two groups of BIU-87 cells were selected and cultured in DMEM and serum free medium (SFM), respectively. The BIU-87 cells in SFM medium adopted a spherical state (Fig. 6a). The expression of the stem cell markers of BIU-87 spheres was similar to that of PA1, a positive control human teratoma cell line; while BIU-87 cells cultured in DMEM did not express stem cell markers, indicating that the BIU-87 spheres were CSCs (Fig. 6b). The limited dilution assay (LDA) was used to study the effect of EpCAM-GEMs on the self-renewal potential of bladder CSCs. BIU-87 cells were successively diluted in stem cell culture and subjected to different treatments to evaluate the sensitivity of the tumor-ball assay system to detecting self-renewing cell elimination. Cells treated with EpCAM-GEMs produced significantly fewer tumor pellets than those treated with PBS, EpCAM, LIB, free GEM, and LIB-GEMs (Fig. 6c, d and ESI Fig. S26‡). Then, BIU-87 sphere cells were treated with LIB-GEMs, GEM, or EpCAM-GEMs. The number of apoptotic cells among the BIU-87 CSCs treated with EpCAM-GEMs was higher than that in those treated with LIB-GEMs (Fig. 6e). To further determine whether EpCAM-GEMs can affect the ability of CSCs to form tumors in immunocompromised mice, free BIU-87 cells were injected subcutaneously into nude mice at a cellular dose of 1 × 105 or 1 × 104 per site, as shown in Fig. 6f, Fig. S27 and Table S5.‡ In terms of the tumor number and size, the EpCAM-GEM group had significantly fewer and smaller sized tumors. Furthermore, when 1 × 104 EpCAM-GEM-treated cells were implanted in mice, there was no tumor formation, in contrast to mice that received the same dose of free GEM-treated cells or PBS, or the control only. These results strongly suggest that EpCAM aptamer-guided GEM successfully targeted and effectively eradicated CSCs in vivo, thereby inhibiting tumor growth. Thus, EpCAM-GEMs show targeting and killing ability toward BIU-87 CSCs. In addition, the expression of CSC surface markers in the EpCAM-GEM group decreased significantly compared with those treated with PBS, GEM, and EpCAM-GEMs (Fig. 6g), which indicated that EpCAM-GEMs killed CSCs in transplanted tumors in vivo. These results further proved that EpCAM-GEMs could not only specifically kill BCa cells, but also kill bladder CSCs, thus ameliorating tumor progression, recurrence, and metastasis.2.10. Antitumor activity of EpCAM-GEMs in a lung metastasis model induced by tail vein injection
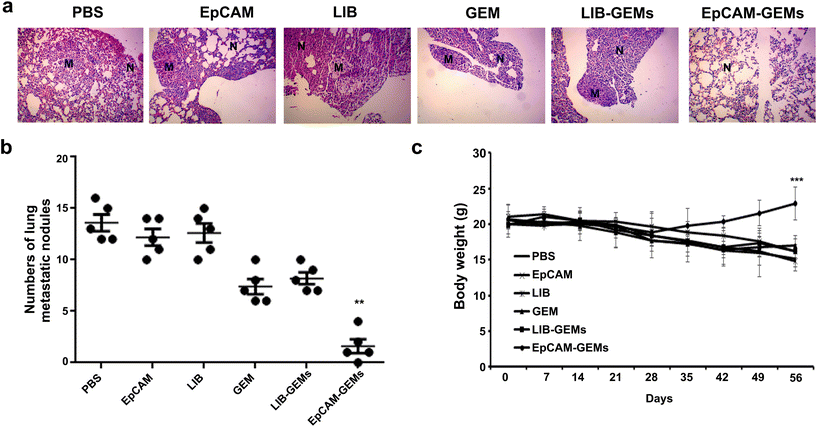
The in vivo antitumor effect of EpCAM-GEMs was evaluated in a lung metastasis model induced by tail vein injection of human BCa cells. The EpCAM-GEM group exhibited a significantly lower rate of lung metastasis compared with the GEM group and other groups (Fig. 7a). Moreover, the number of pulmonary metastatic nodules in the EpCAM-GEM-treated group was significantly lower than that in the groups with GEM treatment and other treatments (Fig. 7b). Notably, no significant loss in body weight was observed in the EpCAM-GEM group (Fig. 7c). These data suggested that EpCAM-GEMs could inhibit tumor metastatic progression through their targeted delivery of antitumor reagents to BCa cells.2.11. Antitumor activity of EpCAM-GEMs in an in situ bladder cancer model
Urinary bladder instillation chemotherapy is one of the main approaches used to treat BCa. Consequently, we further assessed the tumor suppressive effect of EpCAM-GEMs in an in situ model of BCa. Among the various groups, significant differences in the bladder histopathology were observed between the EpCAM-GEM treatment group and the other treatment groups (Table S6‡). In the majority of the examined BCa tissues, EpCAM-GEM treatment resulted in the lowest tumor stage (stage pT0/Tis/Ta), whereas in the other groups, the stage of the majority of the tumors was higher than pT2. Histological examination of H&E stained tissue slices and excised bladders confirmed these results (Fig. 8).2.12. The in vivo biosafety assessment of EpCAM-GEMs
Considering the adverse side effects caused by GEM in the clinic, it was necessary to evaluate the biosafety of EpCAM-GEMs in vivo via pathological sections, and whole blood and biochemical examination. In liver H&E staining, the GEM and LIB-GEM groups showed varying degrees of hepatic cord loss and structural disorder, while EpCAM-GEMs did not cause obvious liver tissue damage, with a clear liver tissue structure. There was no obvious structural damage detected in the other main organs in each group (Fig. S28‡). The levels of alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) in the GEM and LIB-GEM groups were higher, indicating hepatotoxicity, and lower levels of white blood cells (WBCs) and platelets (PLTs) were observed, which were consistent with the clinical observations. However, the ALT, AST, WBC, and PLT levels in the EpCAM-GEM group were similar to those in the PBS group, indicating no hepatotoxicity or bone marrow suppression (Table S7 and Fig. S29, S30‡). Notably, no significant differences were observed in red blood cells (RBCs), hemoglobin (HGB), creatinine (CREA), myocardial enzymes (creatine kinase (CK)) and urea in all treatment groups (Table S7 and Fig. S29, S30‡). These results showed that EpCAM-GEMs could overcome some of the side effects of GEM and achieve ideal antitumor efficiency, which is likely to benefit from the precise targeting of EpCAM-GEMs. In short, the above data showed that EpCAM-GEMs have good biosafety while exerting a significant anti-cancer effect.3. Discussion
In recent years, although new therapies have emerged in the field of BCa treatment, represented by ICIs, ADC, and gene therapy, they still do not work across the board for a variety of reasons. Since the introduction of ICI drugs, drug resistance, off-target effects, and immune-related adverse events have been frequently reported. Most patients with BCa do not respond to ICIs, and among those patients who do initially respond, many show a significantly reduced response to ICIs or develop resistance, resulting in tumor recurrence and progression. ICIs induce off-target effects through a variety of mechanisms, with heart and kidney injury being the most common.34,35 Although ADC drugs can target BCa cells, the effect–toxicity ratio and response rate can be further improved because of the high immunogenicity of antibodies and the occurrence of adverse events, including hematological diseases caused by toxicity and off-target effects, as well as the periodic changes of antigens.17,36 Most importantly, it has been reported that ADC drugs cannot achieve an effective concentration in tumor tissues because of their weak penetration ability and limited distribution, which allow BCa cells to escape and cause tumor recurrence.37–39 Aberrations in FGFR are present in only a subset of patients with BCa and thus patients should be screened; however, the screening criteria are unclear.40 It has also been reported that only a small percentage of FGFR aberrant BCa cancers are responsive to FGFR inhibitors, and that the sensitivity of different FGFR receptors to drugs is highly variable.41 FGFR inhibitors can also be resistant to drugs and produce adverse reactions, such as hyperphosphatemia, because of off-target effects.42,43 In addition, the indications for these drugs are mostly for patients with advanced BCa or patients who are insensitive to platinum chemotherapy, and there is no new treatment for patients with early BCa. Another reason is that these treatments only target cancer cells, ignoring the crucial role of CSCs. There is evidence that CSCs are involved in the occurrence, development, and treatment resistance of cancer. In cancer treatment, uncleared cells are often the key factor in cancer recurrence, while standard cancer treatment can only eliminate non-cancer stem cells, and the relatively static CSCs can escape and are even enriched. Failure to kill CSCs often leads to eventual treatment failure.44As a novel treatment for BCa, EpCAM-GEMs have potential clinical applications. EpCAM-GEMs target both BCa cells and CSCs via EpCAM, carrying three GEM molecules that specifically act on cells and accumulate at effective drug concentrations. EpCAM-GEMs improved the drug targeting of cancer cells to reduce toxicity to normal tissue, and enabled the drug to act on CSCs to reduce drug resistance and inhibit tumor progression and recurrence. EpCAM expression is stable and no EpCAM mutations have been reported in cancer cells; therefore, EpCAM-GEMs might be useful in treating patients with different stages of BCa.
In this study, the EpCAM aptamer and gemcitabine were linked using a 3′, 5′-phosphodiester bond, which is not easy to degrade in the blood because of its very long half-life.45 However, in the presence of intracellular acid and phosphatase, the cleavage rate of the phosphate diester bond can be increased 1017 times,46 ensuring the rapid release of GEM in the cell. We proved that the EpCAM-GEMs entered cells mainly through the macropinocytosis pathway, which was consistent with a previous report that aptamer conjugates enter cells via the macropinocytosis pathway.47 We confirmed the high expression of EpCAM in BCa using western blotting, immunofluorescence, and clinical sample detection; however, almost no expression was observed in normal cells. To explore their clinical research value, we explored the targeting, toxicity, and biosafety of EpCAM-GEMs in a subcutaneous xenografted tumor model, a lung metastasis tumor model, and an in situ bladder tumor model, and obtained promising results.
This is the first report on the synthesis of EpCAM-GEMs and their use in treating BCa. Our findings indicated that EpCAM-GEMs enhanced GEM's affinity for BCa cells, accelerated GEM's cellular accumulation, reduced the side effects of damaging normal cells, and decreased the drug resistance mediated by surviving CSCs. Taken together, our results revealed the use of EpCAM-GEMs as a promising strategy that offers a new direction for the precision treatment of BCa.
4. Conclusions
Overall, the results suggested that EpCAM-GEMs targeted BCa and could effectively inhibit the progression of BCa. These observations deepen our understanding of ApDC treatment strategies for BCa. The results of the present study suggested that EpCAM-GEMs could be an innovative treatment for BCa.5. Experimental section
5.1. Gemcitabine phosphonamidite and EpCAM-GEM oligonucleotide synthesis
The reported method and synthesis procedure to prepare gemcitabine phosphoramidite are shown in Fig. S1.‡48,49 EpCAM-GEM oligonucleotide sequence synthesis was run automatically using a DNA synthesizer, and the specific reactions and purification are shown in the ESI.‡5.2. Primary bladder tissue samples
All 148 primary tumor samples of BCa and 45 adjacent nonmalignant epithelium bladder specimens were obtained from patients with BCa treated at the 3rd Xiangya Hospital of Central South University and Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center between 2002 and 2012. The specimens were fixed in formalin for 24 h and then embedded in paraffin.50 Clinicopathological information on the patients was obtained from patient records and is summarized in Table S1.‡ Twenty paired urothelial cell BCa specimens and adjacent normal tissues were collected from patients who received radical cystectomy surgery and used for western blotting analysis.5.3. Immunohistochemical (IHC) analysis
Tumor samples were subjected to fixation using 10% formaldehyde in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), paraffin embedded, sectioned at 4 μm, and processed for EpCAM immunohistochemistry using the avidin–biotin-peroxidase method.51 In brief, the sections were incubated in 3% H2O2 for 20 min to quench endogenous peroxidases. The samples were heated at 120 °C for 15 min in 10 mM citrate buffer (pH 6.0) using an autoclave to retrieve the antigens. The samples were treated using Block Ace (Dainippon Sumitomo Pharmaceutical, Osaka, Japan) at room temperature for 30 min and then incubated overnight at 4 °C with anti-EpCAM antibodies (Abcam, Cambridge, MA, USA; 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 500 dilution). Color development was then achieved using the avidin–biotin-peroxidase complex system (Vectastain Elite ABC kit; Vector Laboratories, Burlingame, CA, USA) with diaminobenzidine tetrahydrochloride. Mayer's hematoxylin was used to counterstain the sections.
500 dilution). Color development was then achieved using the avidin–biotin-peroxidase complex system (Vectastain Elite ABC kit; Vector Laboratories, Burlingame, CA, USA) with diaminobenzidine tetrahydrochloride. Mayer's hematoxylin was used to counterstain the sections.
Two independent observers reviewed and scored the degree of immunostaining of the sections. The EpCAM-expressing cell proportion varied from 0% to 100%, and the staining intensity was scored as 0 (no staining), 1 (weak staining, light yellow), 2 (moderate staining, yellowish brown), and 3 (strong staining, brown). This method of assessment was used to evaluate EpCAM expression in BCa tissue and normal bladder tissue. Tumors were classified as of high expression if they had an intensity score ≥2 with at least 50% EpCAM-positive cells; low expression tumors had an intensity score of <2 with <50% EpCAM-positive cells.
5.4. Specific binding assay
After 0.02% EDTA digestion of BIU-87 and HEK293T cells, about 2 × 105 cells in each group were incubated on ice for 50 min in 200 μL of binding buffer containing 200 nM EpCAM-fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC), LIB-FITC, and cells only (binding buffer containing 10% fetal bovine serum). LIB (the TDO-5 sequence) is a control sequence of EpCAM that cannot bind to the target cells. The binding buffer consisted of 0.1 mg ml−1 tRNA (Sigma, St Louis, MO, USA), 1 mg ml−1 BSA (Sigma), and 5 nM MgCl2. For the competitive binding experiment, EpCAM and LIB were preincubated at a concentration of 1000 nM and incubated on ice for 1 h. Each group was washed with 700 μL PBS three times, and then suspended again in 300 μL of PBS for flow cytometry detection using the BD FACSVerse™ system (San Jose, CA, USA).5.5. Endocytic pathway study
BIU-87 cells were seeded into 15 mm confocal dishes overnight to allow the cells to adhere to the wall. While the cells were blocked with 5% BSA for 1 h, 200 nM EpCAM-GEMs were incubated with Alexa fluor 488-labeled endocytic markers (5 μg mL−1 transferrin, 25 μg mL−1 cholera toxin, and 25 μg mL−1 dextran) for 2 h, 2 μg mL−1 Hoechst 33342 was added, and the cells were washed with washing buffer and observed under a confocal microscope. To study the endocytic pathway, chlorpromazine (0.1 mM, a clathrin pathway inhibitor), filipin (1 mM, a caveolae pathway inhibitor) and EIPA (0.1 mM, a macropinocytosis pathway inhibitor) were preincubated with BIU-87 cells for 2 h. Then, 200 nM Cy5-labeled EpCAM-GEMs and Alexa fluor 488-labeled endocytosis markers were added, and the cells were washed and observed under a confocal microscope.5.6. GEM release study
To investigate the release of GEM from EpCAM-GEMs in the cell lysate, BIU-87 cells were seeded into a 10 cm large dish, and then radioimmunoprecipitation assay (RIPA) cell lysis buffer was added, with or without phosphatase inhibitors. After sufficient lysis, the cell lysate was treated with 50 μM EpCAM-GEMs for 0–4 h, respectively, in a 37 °C water bath. The GEM fractions were then extracted by adding acetonitrile and mixing fully. The cells were centrifuged at 12![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 rpm for 10 minutes at 4 °C. The supernatant was retained and determined using HPLC at 260 nm. Meanwhile, in the other groups EpCAM-GEMs were added into buffer, 10% FBS, or glutathione (GSH) solutions, respectively, according to the above method.52 To eliminate the influence of other factors on the experiment, the above experiments underwent standardization.
000 rpm for 10 minutes at 4 °C. The supernatant was retained and determined using HPLC at 260 nm. Meanwhile, in the other groups EpCAM-GEMs were added into buffer, 10% FBS, or glutathione (GSH) solutions, respectively, according to the above method.52 To eliminate the influence of other factors on the experiment, the above experiments underwent standardization.
5.7. Cell apoptosis analysis
BIU-87 sphere cells were added to 6-well plates, grown for 24 h to allow the cells to adhere to the wall, treated with 100 nM GEM, LIB-GEMs, or EpCAM-GEMs, respectively, for 12 h, and then cultured in complete medium for 72 h. The untreated cells formed the control. According to the instructions of the AnnexinV PE/7-AAD apoptosis detection kit, the cells were washed with PBS, collected, and resuspended in 5 μL of Annexin-V FITC with 195 μL of binding buffer and 5 μL of 7-aminoactinomycin D (7-AAD), and then incubated for 15 min in the dark at room temperature. Analysis was then performed using flow cytometry (Beckman Instruments, Inc., Brea, CA, USA).5.8. Screening of CSCs
The CSC culture medium was prepared by adding 0.4% bovine serum, 5% horse serum, epidermal growth factor (EGF; 20 ng mL−1), basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF; 10 ng mL−1), and human insulin (5 ng mL−1) into serum-free medium DMEM/F12. BIU-87 cells were grown in normal complete DMEM containing 5% carbon dioxide at 37 °C. When cells reached 70% aggregation, they were digested and collected. 1000 cells per mL in CSC culture medium were added to a 6-well plate. The culture was completed after about 10 days and the pellet-forming morphology was observed. The above cells comprised the first pellet-forming cells. The first pellet-forming cells were digested and cultured again in the same way to form the second pellet-forming cells,53,54 which could be considered as CSCs.555.9. Colony formation assay for BCa CSCs
BIU-87 cells were subcutaneously inoculated into nude mice and treated with PBS, EpCAM, LIB, GEM, LIB-gems, and EpCAM-gems (dissolved in PBS at an equivalent GEM dosage of 16 mg kg−1 every 2 days for a total of 6 administrations). One day after the final treatment, the nude mice were euthanized, and their tumors were excised. The tumors were then cut into small pieces, digested with enzymes (containing RPMI-1640, 20% FBS, 6 mg mL−1 collagenase II, 3 mg mL−1 neutral protease, and 75 μg mL−1 hyaluronidase), and prepared into a single-cell suspension. Subsequently, the BIU-87 cells from the single-cell suspension were subcutaneously injected into new nude mice at concentrations of 1 × 105 cells per injection (n = 6 for each group). Tumor growth was observed daily, and after eight weeks, the tumors were resected to compare their formation and size differences. CSC frequency in vivo was calculated using ELDA. All animal procedures were performed in accordance with the Guidelines for Care and Use of Laboratory Animals of Central South University and approved by the Animal Ethics Committee of The Third Xiangya Hospital.5.10. Tumor formation of BCa CSCs in vivo
BIU-87 cells were inoculated subcutaneously into nude mice and treated with PBS, EpCAM, LIB, GEM, LIB-GEMs, and EpCAM-GEMs (n = 6), respectively. One day after the last treatment, the tumor was removed to prepare a single-cell suspension, and the single-cell prepared BIU-87 cells were injected subcutaneously into nude mice at 1 × 104 and 1 × 105 (n = 6). Tumor growth was observed daily and analyzed via the ELDA website.5.11. Biological imaging of EpCAM-GEMs in vivo
When the volume of subcutaneous transplanted tumor in nude mice was >600 mm3, EpCAM-GEMs-Cy5 and LIB-GEMs-Cy5 (50 μM, 200 μL) were injected into the tail vein of mice, separately. After anesthesia with isoflurane, the tumor bearing mice were imaged before injection and at 0.5–4 h after injection using the in vivo imaging system (IVIS) Lumina XR optical imaging system (PerkinElmer, Waltham, MA, USA). After 4 h, we euthanized the nude mice, and dissected out the tumors, heart, liver, spleen, lungs, and kidneys for tissue imaging. The nude mice were euthanized in a manner that minimized or eliminated pain and distress. The Ethics Committee of the 3rd Xiangya Hospital of Central South University approved all the animal experiments.5.12. Anti-tumor activity of EpCAM-GEMs in xenotransplanted subcutaneous tumors
When the volume of subcutaneous transplanted tumors in the nude mice exceeded 100 mm3, the mice were assigned randomly to six groups (n = 5 per group). The groups received 200 μL of PBS, EpCAM, LIB, GEM, LIB-GEMs, or EpCAM-GEMs (dissolved in PBS, equivalent GEM dosage of 16 mg kg−2 days, six times) through injection into the caudal vein, respectively. Two days after the last administration, the nude mice were euthanized, their blood was collected for blood and biochemical analysis, and the tumors, heart, liver, spleen, lungs, and kidneys of each mouse were taken for immunohistochemical and histological examination.5.13. In vivo antitumor effects of EpCAM-GEMs in a lung metastasis model
To further investigate the in vivo antitumor activity of EpCAM-GEM, a severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) mouse model of lung metastasis from a tail vein injection of BCa cells was used. BCa cells (2.5 × 106 cells per 100 μL, in cold PBS) were injected into the tail veins of BALB/c nude mice. Four weeks later, the mice were assigned randomly to six groups. PBS, EpCAM, LIB, GEM, LIB-GEMs, or EpCAM-GEMs (with an equivalent GEM dosage of 16 mg kg−1) were given to mice of the six groups via i.v. once a week for 5 weeks. After 5 weeks, the mice were killed humanely using CO2 and their lung tumor tissues were excised for histological analysis.5.14. Intravesical instillation to assess EpCAM-GEMs’ in vivo anti-tumor effects
We further assessed EpCAM-GEMs’ in vivo antitumor activity using an in situ model of BCa. Ether inhalation was used to anesthetize female SD rats, whose bladders were infused with 0.2 mL N-methyl-nitrosurea (MNU) (10 mg mL−1; Sigma) via a 22-gage angiocatheter once every two weeks, five times. Spontaneous micturition was avoided by keeping the rats under anesthesia for 45 min post-catheterization. After checking for successful tumor induction, 72 rats were classified into 6 groups (12 rats per group). The rats were anesthetized and then their bladders were instilled with PBS, EpCAM, LIB, GEM, LIB-GEMs, or EpCAM-GEMs (with an equivalent GEM dosage of 5 mg kg−1). Spontaneous micturition was avoided by keeping the rats under anesthesia for 45 min post-catheterization. Repeated treatments were administered once weekly for five weeks. The rats were killed humanely at two days after the last treatment. Their bladders were removed, weighed, fixed for 24 h in 4% paraformaldehyde, embedded in paraffin, and examined histopathologically. Transverse sections were cut from the midportion of the bladder and stained using hematoxylin and eosin (H&E).5.15. Statistical analysis
For the colocalization analysis, ImageJ software (NIH, Bethesda, MD, USA) was used to calculate Pearson's correlation coefficient (PCC). Fisher's exact test was used to determine the correlation between clinicopathological features and the immunohistochemical data. The survival rate was calculated using the Kaplan–Meier method. Significant prognostic factors were identified using univariate and multivariate Cox proportional hazard models, which included backward and forward elimination of variables. The log-rank test was used to assess statistical differences. SPSS WIN program package 20.0 (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA) was used to carry out all statistical analyses. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM or mean ± SD. Statistical significance was accepted at P < 0.05.Abbreviations
| GEM | Gemcitabine |
| BCa | Bladder cancer |
| CSCs | Cancer stem cells |
| EpCAM | Epithelial cell adhesion molecule |
| ApDC | Aptamer drug conjugates |
| EpCAM-GEMs | EpCAM aptamer gemcitabine conjugates |
| ASR | Age-standardized rate |
| ICIs | Immune checkpoint inhibitors |
| ADC | Antibody drug conjugates |
| FGFR | Fibroblast growth factor receptor |
| SELEX | Systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment |
| OCT4 | Octamer-binding protein 4 |
| SOX2 | SRY-box transcription factor 2 |
| DNA | Deoxyribonucleic acid |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline |
| RIPA | Radioimmunoprecipitation assay |
| GSH | Glutathione |
| EGF | Epidermal growth factor |
| bFGF | Basic fibroblast growth factor |
| SCID | Severe combined immunodeficiency |
| H&E | Hematoxylin and eosin |
| HPLC | High performance liquid chromatography |
| LDA | Limited dilution assay |
| WBCs | White blood cells |
| RBCs | Red blood cells |
| HGB | Hemoglobin |
| PLTs | Platelets |
| ALT | Alanine aminotransferase |
| AST | Aspartate aminotransferase |
| CREA | Creatinine |
| CK | Creatine phosphokinase. |
Author contributions
Jianye Liu, Jiahao Liu, Long Wang, and Yongbo Peng: conceptualization, methodology, investigation, formal analysis, writing – original draft, and writing – review & editing. Hongliang Zeng, Wei Xiang, Biao Liu, and Xing Hu: formal analysis and investigation. Minhua Deng, Xuewen Liu, and Jianfei Xie: formal analysis and investigation. Weibin Hou, Jin Tang, and Shuyang Long: resources and formal analysis. Jianye Liu, Jiahao Liu, Long Wang, and Yongbo Peng: supervision and project administration. Jianye Liu: conceptualization, writing – review & editing, supervision, project administration, and funding acquisition. All authors reviewed the manuscript.Ethics approval
All animal procedures were performed in accordance with the Guidelines for Care and Use of Laboratory Animals of Central South University and approved by the Animal Ethics Committee of The Third Xiangya Hospital.Data availability
All data needed to evaluate the conclusions in the paper are present in the paper and/or the ESI.‡ Additional data related to this paper may be requested from the authors.Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (2023YFC2507000), Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province (2023JJ10092), Science and Technology Innovation Leader of Hunan Province (2023RC1033), Hunan Provincial Health High-Level Talent Scientific Research Project (R2023048), and The Wisdom Accumulation and Talent Cultivation Project of the Third Xiangya Hospital of Central South University (YX202204).References
- H. Moch, A. L. Cubilla, P. A. Humphrey, V. E. Reuter and T. M. Ulbright, Eur. Urol., 2016, 70(1), 93–105, DOI:10.1016/j.eururo.2016.02.029.
- A. Richters, K. K. H. Aben and L. Kiemeney, World J. Urol., 2020, 38(8), 1895–1904, DOI:10.1007/s00345-019-02984-4.
- M. Babjuk, M. Burger, E. M. Comperat, P. Gontero, A. H. Mostafid, J. Palou, B. W. G. van Rhijn, M. Roupret, S. F. Shariat, R. Sylvester, R. Zigeuner, O. Capoun, D. Cohen, J. L. D. Escrig, V. Hernandez, B. Peyronnet, T. Seisen and V. Soukup, Eur. Urol., 2019, 76(5), 639–657, DOI:10.1016/j.eururo.2019.08.016.
- A. Lopez-Beltran, M. S. Cookson, B. J. Guercio and L. Cheng, BMJ., 2024 DOI:10.1136/bmj-2023-076743.
- J. Alfred Witjes, H. Max Bruins, A. Carrión, R. Cathomas, E. Compérat, J. A. Efstathiou, R. Fietkau, G. Gakis, A. Lorch, A. Martini, L. S. Mertens, R. P. Meijer, M. I. Milowsky, Y. Neuzillet, V. Panebianco, J. Redlef, M. Rink, M. Rouanne, G.N. Thalmann, S. Sæbjørnsen, E. Veskimäe and A.G. van der Heijden, Eur. Urol., 2024 DOI:10.1016/j.eururo.2024.03.002.
- K. Sury, M. A. Perazella and A. C. Shirali, Nat. Rev. Nephrol., 2018, 14(9), 571–588, DOI:10.1038/s41581-018-0035-1.
- J. Z. Drago, S. Modi and S. Chandarlapaty, Nat. Rev. Clin Oncol., 2021, 18(6), 327–344, DOI:10.1038/s41571-021-00470-8.
- M. Touat, E. Ileana, S. Postel-Vinay, F. Andre and J. C. Soria, Clin. Cancer Res., 2015, 21(12), 2684–2694, DOI:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-2329.
- L. Kelly, K. E. Maier, A. Yan and M. Levy, Nat. Commun., 2021, 12(1), 6275, DOI:10.1038/s41467-021-26463-w.
- J. Zhong, D. Liu, Q. Yang, J. Ding and X. Chen, Drug Des., Dev. Ther., 2024, 18, 859–870, DOI:10.2147/DDDT.S444988.
- F. Radom, P. M. Jurek, M. P. Mazurek, J. Otlewski and F. Jelen, Biotechnol. Adv., 2013, 31(8), 1260–1274, DOI:10.1016/j.biotechadv.2013.04.007.
- J. Xuan, Z. Wang, Y. Huang, Y. Liu, Y. Han, M. Li and M. Xiao, Biomater Sci., 2024 10.1039/d4bm00138a.
- A. D. Keefe, S. Pai and A. Ellington, Nat. Rev. Drug Discovery, 2010, 9(7), 537–550, DOI:10.1038/nrd3141.
- X. Li, X. Zhu and L. Qiu, Acta Biomater., 2016, 35, 269–279, DOI:10.1016/j.actbio.2016.02.012.
- C. H. Wang, S. T. Kang, Y. H. Lee, Y. L. Luo, Y. F. Huang and C. K. Yeh, Biomaterials, 2012, 33(6), 1939–1947, DOI:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2011.11.036.
- G. Zhu and X. Chen, Adv. Drug Delivery Rev., 2018, 134, 65–78, DOI:10.1016/j.addr.2018.08.005.
- S. Panowski, S. Bhakta, H. Raab, P. Polakis and J. R. Junutula, mAbs, 2014, 6(1), 34–45, DOI:10.4161/mabs.27022.
- S. Sun, H. Liu, Y. Hu, Y. Wang, M. Zhao, Y. Yuan, Y. Han, Y. Jing, J. Cui, X. Ren, X. Chen and J. SuBioact. Mater. 202220166–178, DOI:10.1016/j.bioactmat.2022.05.016. Erratum in: Bioact Mater. 2024, DOI:10.1016/j.bioactmat.2024.06.006.
- W. Alshaer, N. A. Ababneh, M. Hatmal, H. Izmirli, M. Choukeife, A. Shraim, N. Sharar, A. Abu-Shiekah, F. Odeh, A. Al Bawab, A. Awidi and S. Ismail, PLoS One, 2018 DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0194529.
- S. Shigdar, J. Lin, Y. Yu, M. Pastuovic, M. Wei and W. Duan, Cancer Sci., 2011, 102(5), 991–998, DOI:10.1111/j.1349-7006.2011.01897.x.
- Y. Song, Z. Zhu, Y. An, W. Zhang, H. Zhang, D. Liu, C. Yu, W. Duan and C. J. Yang, Anal. Chem., 2013, 85(8), 4141–4149, DOI:10.1021/ac400366b.
- N. Subramanian, J. R. Kanwar, R. K. Kanwar, J. Sreemanthula, J. Biswas, V. Khetan and S. Krishnakumar, PLoS One, 2015, 10(7), e0132407, DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0132407.
- R. T. Bryan, N. J. Shimwell, W. Wei, A. J. Devall, S. J. Pirrie, N. D. James, M. P. Zeegers, K. K. Cheng, A. Martin and D. G. Ward, Br. J. Cancer, 2014, 110(3), 679–685, DOI:10.1038/bjc.2013.744.
- M. Saeinasab, S. Iranpour, N. Hosseini-Giv, A. S. Saljooghi and M. M. Matin, Int. J. Biol. Macromol., 2024, 259(Pt 1), 129233, DOI:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.129233.
- O. Gires, M. Pan, H. Schinke, M. Canis and P. A. Baeuerle, Cancer Metastasis Rev., 2020, 39(3), 969–987, DOI:10.1007/s10555-020-09898-3.
- M. Mashreghi, P. Zamani, S. A. Moosavian and M. R. Jaafari, Nanoscale Res. Lett., 2020, 15(1), 101, DOI:10.1186/s11671-020-03334-9.
- J. Yao, J. Feng, X. Gao, D. Wei, T. Kang, Q. Zhu, T. Jiang, X. Wei and J. Chen, Biomaterials, 2017, 113, 1–17, DOI:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2016.10.033.
- Q. Zhang, R. Ma, Y. Zhang, J. Zhao, Y. Wang and Z. Xu, ACS Sens., 2023, 8(2), 875–883, DOI:10.1021/acssensors.2c02587.
- J. Zheng, S. Zhao, X. Yu, S. Huang and H. Y. Liu, Theranostics, 2017, 7(5), 1373–1388, DOI:10.7150/thno.17826.
- L. Zhu, S. Lin, W. Cui, Y. Xu, L. Wang, Z. Wang, S. Yuan, Y. Zhang, Y. Fan and J. Geng, Biomater Sci., 2022, 10(13), 3624–3636, 10.1039/d2bm00437b.
- S. Paroha, J. Verma, R. D. Dubey, R. P. Dewangan, N. Molugulu, R. A. Bapat, P. K. Sahoo and P. Kesharwani, Int. J. Pharm., 2021, 592, 120043, DOI:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2020.120043.
- E. Batlle and H. Clevers, Nat. Med., 2017, 23(10), 1124–1134, DOI:10.1038/nm.4409.
- D. Xiang, S. Shigdar, A. G. Bean, M. Bruce, W. Yang, M. Mathesh, T. Wang, W. Yin, P. H. Tran, H. Al Shamaileh, R. A. Barrero, P. Z. Zhang, Y. Li, L. Kong, K. Liu, S. F. Zhou, Y. Hou, A. He and W. Duan, Theranostics, 2017, 7(17), 4071–4086, DOI:10.7150/thno.20168.
- S. Bagchi, R. Yuan and E. G. Engleman, Annu. Rev. Phytopathol., 2021, 16, 223–249, DOI:10.1146/annurev-pathol-042020-042741.
- A. J. Schoenfeld and M. D. Hellmann, Cancer Cell, 2020, 37(4), 443–455, DOI:10.1016/j.ccell.2020.03.017.
- P. M. Drake and D. Rabuka, BioDrugs, 2017, 31(6), 521–531, DOI:10.1007/s40259-017-0254-1.
- C. H. Chau, P. S. Steeg and W. D. Figg, Lancet, 2019, 394(10200), 793–804, DOI:10.1016/s0140-6736(19)31774-x.
- P. J. Vlachostergios, C. D. Jakubowski, M. J. Niaz, A. Lee, C. Thomas, A. L. Hackett, P. Patel, N. Rashid and S. T. Tagawa, Bladder Cancer, 2018, 4(3), 247–259, DOI:10.3233/BLC-180169.
- D. Xiang, C. Zheng, S. F. Zhou, S. Qiao, P. H. Tran, C. Pu, Y. Li, L. Kong, A. Z. Kouzani, J. Lin, K. Liu, L. Li, S. Shigdar and W. Duan, Theranostics, 2015, 5(10), 1083–1097, DOI:10.7150/thno.11711.
- I. S. Babina and N. C. Turner, Nat. Rev. Cancer, 2017, 17(5), 318–332, DOI:10.1038/nrc.2017.8.
- M. Katoh, Y. Loriot, G. Brandi, S. Tavolari, ZA. Wainberg and M. Katoh, Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol., 2024, 312–329, DOI:10.1038/s41571-024-00869-z.
- P. R. Gavine, L. Mooney, E. Kilgour, A. P. Thomas, K. Al-Kadhimi, S. Beck, C. Rooney, T. Coleman, D. Baker, M. J. Mellor, A. N. Brooks and T. Klinowska, Cancer Res., 2012, 72(8), 2045–2056, DOI:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-3034.
- G. Zhao, W. Y. Li, D. Chen, J. R. Henry, H. Y. Li, Z. Chen, M. Zia-Ebrahimi, L. Bloem, Y. Zhai, K. Huss, S. B. Peng and D. J. McCann, Mol. Cancer Ther., 2011, 10(11), 2200–2210, DOI:10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-11-0306.
- N. K. Lytle, A. G. Barber and T. Reya, Nat. Rev. Cancer, 2018, 18(11), 669–680, DOI:10.1038/s41568-018-0056-x.
- S. Mikkola, T. Lonnberg and H. Lonnberg, Beilstein J. Org. Chem., 2018, 14, 803–837, DOI:10.3762/bjoc.14.68.
- G. K. Schroeder, C. Lad, P. Wyman, N. H. Williams and R. Wolfenden, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2006 DOI:10.1073/pnas.0510879103.
- E. M. Reyes-Reyes, Y. Teng and P. J. Bates, Cancer Res., 2010, 70(21), 8617–8629, DOI:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-0920.
- R. Wang, G. Zhu, L. Mei, Y. Xie, H. Ma, M. Ye, F. L. Qing and W. Tan, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2014, 136(7), 2731–2734, DOI:10.1021/ja4117395.
- W. Xiang, Y. Peng, H. Zeng, C. Yu, Q. Zhang, B. Liu, J. Liu, X. Hu, W. Wei, M. Deng, N. Wang, X. Liu, J. Xie, W. Hou, J. Tang, Z. Long, L. Wang and J. Liu, Biomater. Res., 2022, 26(1), 74, DOI:10.1186/s40824-022-00328-9.
- J. Y. Liu, Y. B. Dai, X. Li, K. Cao, D. Xie, Z. T. Tong, Z. Long, H. Xiao, M. K. Chen, Y. L. Ye, B. Liu, J. Tan, J. Tang, Z. Z. Xu, Y. Gan, Y. H. Zhou, F. Deng and L. Y. He, Cell Death Dis., 2017, 8(3), e2691, DOI:10.1038/cddis.2017.118.
- Y. Naoi, Y. Miyoshi, T. Taguchi, S. J. Kim, T. Arai, N. Maruyama, Y. Tamaki and S. Noguchi, Cancer Lett., 2008, 262(2), 248–256, DOI:10.1016/j.canlet.2007.12.008.
- A. Sathiyaseelan, K. Saravanakumar, A. V. A. Mariadoss and M. H. Wang, Carbohydr Polym., 2021, 117907, DOI:10.1016/j.carbpol.2021.117907.
- T. Sharif, E. Martell, C. Dai, M. S. Ghassemi-Rad, K. Lee, S. K. Singh, I. C. G. Weaver and S. Gujar, Cell Death Dis., 2018, 9(10), 990, DOI:10.1038/s41419-018-0997-8.
- X. Yang, S. K. Sarvestani, S. Moeinzadeh, X. He and E. Jabbari, Tissue Eng., Part A, 2013, 19(5–6), 669–684, DOI:10.1089/ten.TEA.2012.0333.
- G. Su, Y. Zhao, J. Wei, J. Han, L. Chen, Z. Xiao, B. Chen and J. Dai, Biomaterials, 2013, 34(13), 3215–3222, DOI:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2013.01.044.
Footnotes |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available. See DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/d4bm01471e |
| ‡ These authors contributed equally to this work. |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2025 |