Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleBisquinoline-based fluorescent cadmium sensors
Yuji
Mikata
 abcd
abcd
aLaboratory for Molecular & Functional Design, Department of Engineering, Nara Women's University, Nara 630-8506, Japan. E-mail: mikata@cc.nara-wu.ac.jp; Fax: +81-742-20-3095; Tel: +81-742-20-3095 Web: https://eng.nara-wu.ac.jp/mikata/
bCooperative Major in Human Centered Engineering, Nara Women's University, Nara 630-8506, Japan
cDepartment of Chemistry, Biology, and Environmental Science, Faculty of Science, Nara Women's University, Nara 630-8506, Japan
dKYOUSEI Science Center, Nara Women's University, Nara 630-8506, Japan
First published on 17th December 2024
Abstract
Rational molecular design afforded fluorescent Cd2+ sensors based on bisquinoline derivatives. Introduction of three methoxy groups at the 5,6,7-positions of the quinoline rings of BQDMEN (N,N′-bis(2-quinolylmethyl)-N,N′-dimethylethylenediamine) resulted in the reversal of metal ion selectivity in fluorescence enhancement from zinc to cadmium. Introduction of bulky alkyl groups and an N,N-bis(2-quinolylmethyl)amine structure, as well as replacement of one of the two tertiary amine binding sites with an oxygen atom and the use of a 1,2-phenylene backbone significantly improved the Cd2+ specificity. The fluorescent cadmium ion selectivity could be explained by the differential binding with Cd2+ and Zn2+, and the formation of a bis(μ-chloro) dinuclear cadmium complex in contrast to the mononuclear zinc complex.
1. Introduction
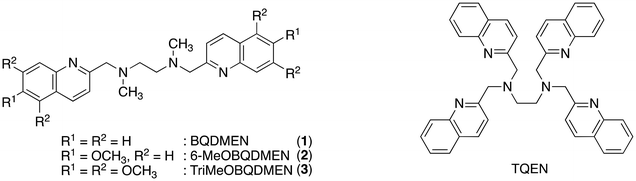
Detection and quantification of toxic heavy metal ions are currently important objectives in regulation of environmental pollutants. Fluorescence sensing provides high selectivity and sensitivity toward targeted metal ions via a rapid analytical protocol using relatively inexpensive equipment. One of the most important issues in the detection of toxic metal ions is discrimination of Cd2+ from naturally abundant Zn2+, both of which are group 12 elements in the periodic table and exhibit only a 21 pm difference in their ionic radii. Since recent human activities in industry increase the exposure of cadmium to air, water and soil, continuous development of fluorescent probes for strict detection of cadmium, especially in environmental water, is in high demand. Many research groups have been investigating quinoline-based molecules for this purpose considering that the long coordination distances and softness of the quinoline nitrogen atom in comparison with conventional pyridine ligands would be suitable for selective binding with Cd2+.1–10 In this Frontier article, several modifications of the molecular structure of BQDMEN (N,N′-bis(2-quinolylmethyl)-N,N′-dimethylethylenediamine (1), Fig. 1)11 for better Cd2+-selectivity in the fluorescence response are discussed (Table 1). A preceding Frontier article by the present author, dealing with a related hexadentate tetrakisquinoline ligand TQEN (N,N,N′,N′-tetrakis(2-quinolylmethyl)ethylenediamine, Fig. 1), contains other examples for fluorescence sensing of Zn2+, Cd2+, Hg2+ and phosphate species.12| λ ex (nm) | λ em (nm) | I Cd/I0 (eq.) | I Zn/ICd (eq.) | K d (metal ion) (M) | ϕ Cd | Ref. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
a In DMF-H2O (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1).
b In DMF-HEPES buffer (1 1).
b In DMF-HEPES buffer (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1). 1).
|
|||||||
| TriMeOBQDMEN (3)a | 339 | 472 | 15 (1) | 0.22 (1) | ∼10−8 (Cd) | 0.29 | 25 |
| ∼10−7 (Zn) | |||||||
3![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) b b |
335 | 458 | 25 (3) | 0.24 (3) | 3 × 10−7 (Cd) | — | 29 |
| 3 × 10−6 (Zn) | |||||||
| TriMeOBQDIEN (5)a | 339 | 459 | 23 (20) | 0.04 (20) | 4 × 10−6 (Cd) | 0.37 | 26 |
| 5 × 10−5 (Zn) | |||||||
| TriMeOBQDBEN (6)a | 337 | 459 | 27 (3) | 0.20 (3) | ∼10−7 (Cd) | 0.33 | 26 |
| 8 × 10−6 (Zn) | |||||||
| TriMeOBQDMPHEN (9)b | 341 | 467 | 51 (1) | 0.26 (1) | 8 × 10−7 (Cd) | 0.43 | 27 |
| 6 × 10−6 (Zn) | |||||||
| TriMeOBQDIPHEN (10)b | 343 | 480 | 427 (40) | 0.05 (40) | 1 × 10−3 (Cd) | — | 27 |
| 4 × 10−2 (Zn) | |||||||
| TriMeO-N,O-BQMAE (11)b | 338 | 470 | 10 (3) | 0.34 (3) | 1 × 10−5 (Cd) | 0.28 | 29 |
| 8 × 10−5 (Cd) | |||||||
| TriMeO-N,N-BQMAE (12)b | 340 | 465 | 12 (3) | 0.26 (3) | ∼10−7 (Cd) | 0.23 | 29 |
| 2 × 10−5 (Zn) | |||||||
| TriMeOBQMOA (14)b | 341 | 464 | 90 (5) | 0.02 (5) | 1 × 10−5 (Cd) | 0.18 | 30 |
2. Polymethoxy substitution on the quinoline ring
The BQDMEN 1 has been reported as a tetranitrogen ligand supporting mononuclear and dinuclear metal complexes including Fe2+, Co2+, Ni2+, Pd2+, Cu2+/+, Ru2+, Cr0 and Mn3+/2+ centres.13–20 We utilized this skeleton for fluorescent Zn2+ sensors and improved the fluorescence quantum yield by introducing a methoxy group to the quinoline rings.11 The fluorescence turn-on mechanism includes the inhibition of photo-induced electron transfer (PeT) and chelation enhanced fluorescence (CHEF).21–23 Thus-obtained 6-MeOBQDMEN (2) (Fig. 1) exhibits sufficient fluorescence intensity and Zn2+ selectivity (ϕZn = 0.28 and IZn/ICd = 2.2 in DMF–H2O (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
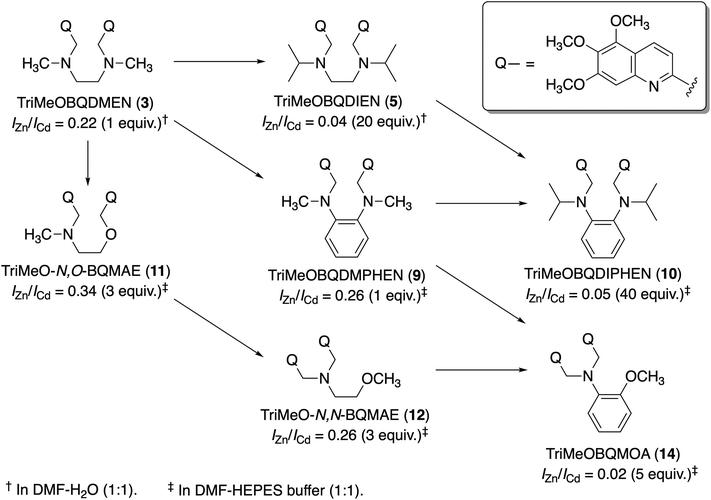
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1)†) for intracellular study. On the other hand, the unsubstituted BQDMEN 1 exhibits dim fluorescence (ϕZn = 0.017) but slightly higher Zn2+ selectivity (IZn/ICd = 3.9) than 2. Although we have known that further methoxy substitution does not improve the quantum yield from our study on TQEN derivatives,24 we expected that the fluorescence metal ion selectivity could shift (or even reverse) to the Cd2+ side. This estimation is indeed true, in which TriMeOBQDMEN 3 (Fig. 1) exhibits Cd2+ selectivity (IZn/ICd = 0.22) with similar fluorescence quantum yield (ϕCd = 0.29) to the Zn2+ complex with 2 (Table 1).25 Interestingly, the extension of the carbon chain in the molecular skeleton from ethylenediamine to propanediamine also shifted the fluorescence response toward the Cd2+ side.
1)†) for intracellular study. On the other hand, the unsubstituted BQDMEN 1 exhibits dim fluorescence (ϕZn = 0.017) but slightly higher Zn2+ selectivity (IZn/ICd = 3.9) than 2. Although we have known that further methoxy substitution does not improve the quantum yield from our study on TQEN derivatives,24 we expected that the fluorescence metal ion selectivity could shift (or even reverse) to the Cd2+ side. This estimation is indeed true, in which TriMeOBQDMEN 3 (Fig. 1) exhibits Cd2+ selectivity (IZn/ICd = 0.22) with similar fluorescence quantum yield (ϕCd = 0.29) to the Zn2+ complex with 2 (Table 1).25 Interestingly, the extension of the carbon chain in the molecular skeleton from ethylenediamine to propanediamine also shifted the fluorescence response toward the Cd2+ side.
The fluorescence titration revealed that TriMeOBQDMEN (3) binds an equimolar amount of metal ions. The Cd2+ complex with 3 exhibits significantly long fluorescence lifetime (τ = ∼30 ns) in comparison with the Zn2+ complex (∼20 ns), indicating the different complex structure and/or fluorescence pathway. X-ray crystallography revealed the structures of the bis(μ-chloro) dinuclear cadmium complex and mononuclear zinc complex with BQDMEN (1) (Fig. 2). ESI-MS also confirmed the formation of [(μ-Cl)2Cd2(3)2](ClO4)+ species under the spectral measurement conditions. The metal binding affinity of 3 is high enough to saturate the ligand in the presence of 1 equiv. of Cd2+ and Zn2+ under our experimental conditions (Table 1). These observations clearly indicate that the BQDMEN ligand discriminates Cd2+ and Zn2+ by differential complexation, and the introduction of three methoxy groups on the quinoline rings successfully highlights the difference in the complex structure via fluorescence outputs. The next step would be an improvement of the insufficient Cd2+ selectivity of 3. Several modifications of the molecular structure were explored to selectively reduce the Zn2+-induced fluorescence signal.
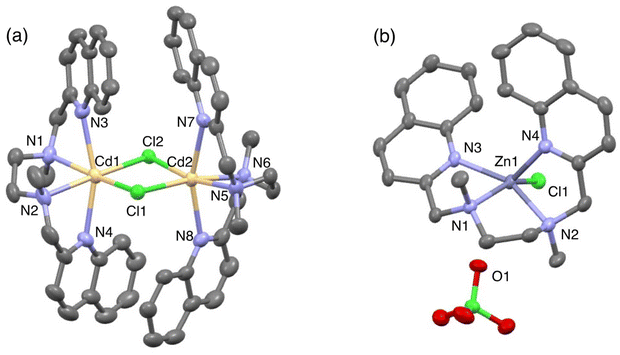 | ||
| Fig. 2 Perspective view of (a) [(μ-Cl)2Cd2(1)2]2+ (CSD refcode CIBKOR) and (b) [Zn(1)Cl]ClO4 (CSD refcode CIBKUX). Reproduced from ref. 25 with permission from the Royal Society of Chemistry. | ||
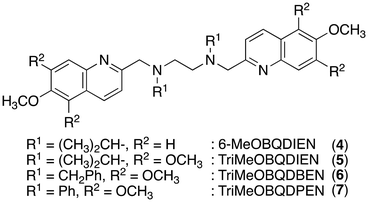
3. Introduction of bulky alkyl groups
Two methyl groups of TriMeOBQDMEN (3) attached to the aliphatic nitrogen atoms were replaced with isopropyl groups to afford TriMeOBQDIEN (N,N′-bis(5,6,7-trimethoxy-2-quinolylmethyl)-N,N′-diisopropylethylenediamine (5), Fig. 3).26 This sterically hindered bisquinoline derivative exhibits weak metal binding affinity (Table 1) and shows characteristic fluorescence titration profiles responding to Cd2+ and Zn2+ (Fig. 4). The highly fluorescent Cd2+ complex with 5 (ϕCd = 0.37) was formed by the addition of ∼5 equiv. of Cd2+ and was stable in the excess amount of metal ions; however, the gradual addition of Zn2+ to 5 exhibited small fluorescence enhancement around 5 equiv. of metal ions, and then, the fluorescence significantly decreased in the presence of an excess amount of zinc salt, Zn(ClO4)2. The monomethoxy derivative (4) (Fig. 3) also exhibits similar profiles. After careful investigations, this observation was explained by the selective decomplexation of the zinc complex by protons generated by excess Zn(ClO4)2 used in the titration experiment. Cd(ClO4)2 did not drop the pH significantly, and the use of Zn(NO3)2 or DMF-HEPES buffer (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) as a solvent did not disrupt the Zn2+-induced fluorescence even in the presence of a large amount of metal ions. Nevertheless, the excellent Cd2+ specificity in fluorescence enhancement achieved in 5 (IZn/ICd = 4% in the presence of 20 equiv. of metal ions) in DMF–H2O (1
1) as a solvent did not disrupt the Zn2+-induced fluorescence even in the presence of a large amount of metal ions. Nevertheless, the excellent Cd2+ specificity in fluorescence enhancement achieved in 5 (IZn/ICd = 4% in the presence of 20 equiv. of metal ions) in DMF–H2O (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) is of significant interest.
1) is of significant interest.
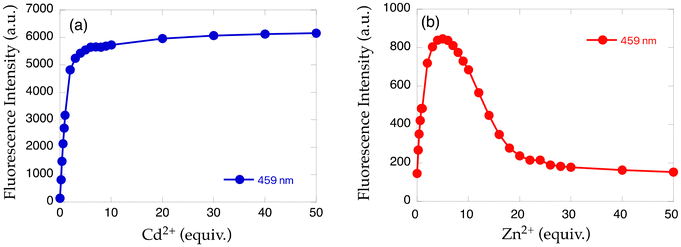 | ||
| Fig. 4 Fluorescence intensity plot of 5 with increasing amounts of (a) Cd2+ and (b) Zn2+.26 | ||
Although X-ray crystallography employing 4 afforded only mononuclear Cd2+ complexes, the long fluorescence lifetime (τ = ∼30 ns) for the Cd2+ complex with 5 suggested the possible formation of bis(μ-chloro) dicadmium species assembled in the excited state even in the isopropyl derivative. The corresponding benzyl (TriMeOBQDBEN (6)) and phenyl (TriMeOBQDPEN (7)) derivatives (Fig. 3) resulted in similar metal ion selectivity and fluorescence stability with 3 and an extremely poor fluorescence response with any metal ions, respectively.
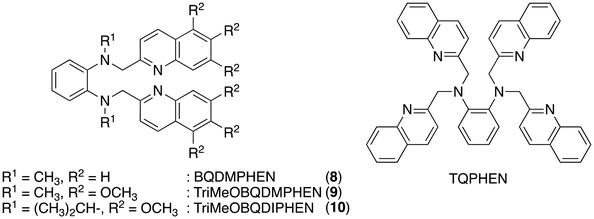
4. Introduction of a benzene skeleton
Instead of the introduction of bulky substituents, replacement of an ethylenediamine backbone of BQDMEN (1) with a 1,2-phenylenediamine also reduces metal binding affinity because the anilinic nitrogen atoms of BQDMPHEN (N,N′-bis(2-quinolylmethyl)-N,N′-dimethyl-1,2-phenylenediamine (8), Fig. 5) have weaker basicity than the aliphatic nitrogen binding site of 1.27 This approach has been successful for the TQEN-based tetrakisquinoline compound, TQPHEN (N,N,N′,N′-tetrakis(2-quinolylmethyl)-1,2-phenylenediamine, Fig. 5), which scarcely binds to Zn2+ under the spectral measurement conditions and therefore exhibits Cd2+-specific fluorescence enhancement.28 Upon addition of metal ions in DMF-HEPES buffer (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1),‡ the ligand 8 exhibited similar fluorescence enhancement with Cd2+ and Zn2+ (IZn/ICd = 0.90 in the presence of 1 equiv. of metal ion), but apparent Cd2+ selectivity (IZn/ICd = 0.26 in the presence of 1 equiv. of metal ions) was achieved in the trimethoxy derivative (TriMeOBQDMPHEN (9), Fig. 5). The insufficient metal ion selectivity was further improved by introducing isopropyl groups as discussed above, affording high fluorescent Cd2+ specificity in TriMeOBQDIPHEN (10) (IZn/ICd = 0.05 in the presence of 40 equiv. of metal ions) (Fig. 5).
1),‡ the ligand 8 exhibited similar fluorescence enhancement with Cd2+ and Zn2+ (IZn/ICd = 0.90 in the presence of 1 equiv. of metal ion), but apparent Cd2+ selectivity (IZn/ICd = 0.26 in the presence of 1 equiv. of metal ions) was achieved in the trimethoxy derivative (TriMeOBQDMPHEN (9), Fig. 5). The insufficient metal ion selectivity was further improved by introducing isopropyl groups as discussed above, affording high fluorescent Cd2+ specificity in TriMeOBQDIPHEN (10) (IZn/ICd = 0.05 in the presence of 40 equiv. of metal ions) (Fig. 5).
Considering the extremely weak metal binding affinity of the isopropyl ligand 10 (Kd(Cd) = 1 × 10−3 M), the methyl counterpart 9 (Kd(Cd) = 8 × 10−7 M) is more suitable for practical use (Table 1). This high metal binding affinity causes diminished Cd2+/Zn2+ selectivity estimated from the ratio of binding constants (Kd(Zn)/Kd(Cd) = 8 and 32 for 9 and 10, respectively); however, the high fluorescence quantum yield (ϕCd = 0.43) and wide pH window (pH = 4–10) of 9 are worth exploring. The structures of Cd2+ and Zn2+ complexes with 8 are both mononuclear but, here again, the long fluorescence lifetime (τ = ∼30 ns) for Cd2+ complexes with 9 and 10 suggests the excimer-like fluorescence mechanism including quinoline–quinoline interactions in the excited state.
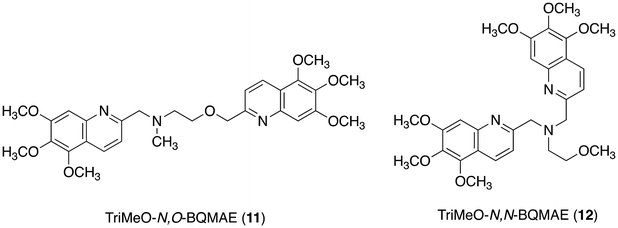
4. Replacement of a nitrogen atom with an oxygen atom
Another strategy to reduce the metal binding affinity of the tetranitrogen ligand TriMeOBQDMEN (3), aiming at the improvement of fluorescent Cd2+ selectivity, is the replacement of one of the two aliphatic ethylenediamine nitrogen atoms of 3 with an oxygen atom. Thus-designed 2-aminoethanol-based N3O1 ligand, TriMeO-N,O-BQMAE (N,O-bis(5,6,7-trimethoxy-2-quinolylmethyl)-2-methylaminoethanol (11), Fig. 6) exhibited two order lower metal binding affinity and slightly decreased Cd2+ preference in fluorescence enhancement in comparison with 3 (IZn/ICd = 0.34 and 0.24 for 11 and 3, respectively, in the presence of 3 equiv. of metal ions in DMF-HEPES buffer (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1)) (Table 1).29 Interestingly, TriMeO-N,N-BQMAE (12) (Fig. 6), the regioisomer of 11, in which both quinoline moieties are attached to the same aliphatic nitrogen atom of the aminoethanol skeleton, exhibits one order higher metal binding affinity than 11 and similar fluorescent Cd2+ selectivity to 3 (IZn/ICd = 0.26 for 12). The fluorescence quantum yield of 12 (ϕCd = 0.23) is slightly smaller in comparison with those of 3 (0.29) and 11 (0.28) under the same experimental conditions. This difference is also reflected by the fluorescence lifetimes, where long fluorescence lifetimes (τ = ∼30 ns) with a possible intramolecular excimer emission for the Cd2+ complex were observed only for 3 and 11. For the N,N-isomer 12, no difference in fluorescence lifetimes of Zn2+ and Cd2+ complexes was detected (τ = ∼18 ns), indicating the monomer emission for both metal complexes with this ligand. The ligand structure of 12 strictly controls the metal binding affinity, possibly due to the difference in the complex structures, affording the fluorescent Cd2+ selectivity. It is important to note that the two order difference in dissociation constants between Cd2+ and Zn2+ complexes was achieved in the N,N-bisquinoline structure of 12 (Table 1). The corresponding N,N-isomer for 3 has not been examined due to problems in its synthesis.
1)) (Table 1).29 Interestingly, TriMeO-N,N-BQMAE (12) (Fig. 6), the regioisomer of 11, in which both quinoline moieties are attached to the same aliphatic nitrogen atom of the aminoethanol skeleton, exhibits one order higher metal binding affinity than 11 and similar fluorescent Cd2+ selectivity to 3 (IZn/ICd = 0.26 for 12). The fluorescence quantum yield of 12 (ϕCd = 0.23) is slightly smaller in comparison with those of 3 (0.29) and 11 (0.28) under the same experimental conditions. This difference is also reflected by the fluorescence lifetimes, where long fluorescence lifetimes (τ = ∼30 ns) with a possible intramolecular excimer emission for the Cd2+ complex were observed only for 3 and 11. For the N,N-isomer 12, no difference in fluorescence lifetimes of Zn2+ and Cd2+ complexes was detected (τ = ∼18 ns), indicating the monomer emission for both metal complexes with this ligand. The ligand structure of 12 strictly controls the metal binding affinity, possibly due to the difference in the complex structures, affording the fluorescent Cd2+ selectivity. It is important to note that the two order difference in dissociation constants between Cd2+ and Zn2+ complexes was achieved in the N,N-bisquinoline structure of 12 (Table 1). The corresponding N,N-isomer for 3 has not been examined due to problems in its synthesis.
5. Use of a benzene skeleton with an oxygen binding site
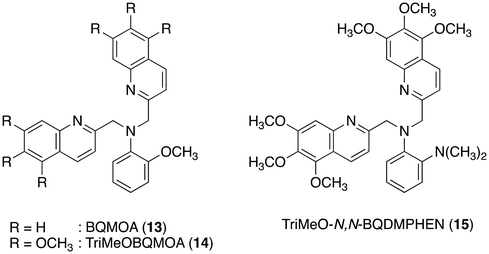
Finally, the N3O1 ligand with a 1,2-phenylene skeleton was explored. Considering the synthetic accessibility, only the N,N-isomer was examined here. Thus-designed TriMeOBQMOA (N,N-bis(5,6,7-trimethoxy-2-quinolylmethyl)-2-methoxyaniline (14), Fig. 7) exhibits excellent Cd2+ specificity in fluorescence enhancement (IZn/ICd = 0.02 in the presence of 5 equiv. of metal ions) with moderate metal binding affinity (Kd(Cd) = 1 × 10−5 M) and fluorescence quantum yield (ϕCd = 0.18) (Table 1).30 The binding affinity of 14 with Zn2+ is extremely weak. The LOD (limit of detection) for Cd2+ was estimated to be 25 nM, which is lower than the environmental limit of water in Japan (3 ppb, 27 nM).Both Cd2+ and Zn2+ complexes with BQMOA (13) (Fig. 7) were structurally characterized by X-ray crystallography (Fig. 8) where the bis(μ-chloro) dinuclear cadmium complex ([(μ-Cl)2Cd2(13)2]2+) and mononuclear zinc complex ([Zn(13)Cl2]) with an uncoordinated quinoline moiety were revealed. These complex structures clearly explain the reason for the short fluorescence lifetime (τ = ∼13 ns) for the Cd2+ and Zn2+ complexes with 14 because of the lack of interquinoline stacking interaction even in the bis(μ-chloro) dicadmium complex. The fluorescent Cd2+ specificity is a result of the extremely weak binding affinity of this ligand with Zn2+.
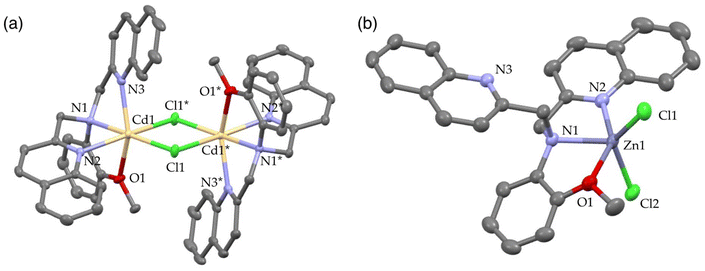 | ||
| Fig. 8 Perspective view of (a) [(μ-Cl)2Cd2(13)2]2+ (CSD refcode YOMQOK) and (b) [Zn(13)Cl2] (CSD refcode YOMQUQ). Adapted from ref. 30 with permission from American Chemical Society, copyright 2024. | ||
The importance of chloride ions in HEPES buffer was also disclosed in this study. As shown in Fig. 9, chloride ions exclusively enhance the fluorescence intensity of 14 in the presence of Cd2+via enhanced complexation, but no such effect was observed for Zn2+ with 14 and dimethylamino derivative TriMeO-N,N-BQDMPHEN (N,N-bis(5,6,7-trimethoxy-2-quinolylmethyl)-N′,N′-dimethyl-1,2-phenylenediamine (15), Fig. 7) with Cd2+ and Zn2+. Not only the moderate metal binding affinity but also the appropriate size and coordination environment of the metal binding cavity of the methoxy derivative 14 in the presence of chloride ions are necessary for fluorescence discrimination of Cd2+ from Zn2+.
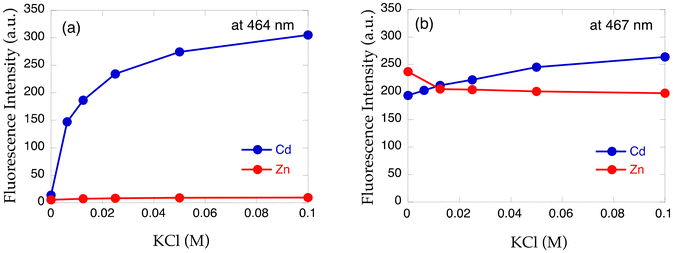 | ||
| Fig. 9 Fluorescence intensity plot of (a) 14 and (b) 15 in the presence of Cd2+ (blue) or Zn2+ (red) with increasing amount of KCl. Adapted from ref. 30 with permission from American Chemical Society, copyright 2024. | ||
6. Conclusions
Based on the structure of BQDMEN (1), a set of fluorescent Cd2+ sensors were rationally designed (Fig. 10). The extensive use of polymethoxy-substituted quinolines as a metal binding motif and chromophore provides several unique characteristics suitable for strict discrimination of Cd2+ from Zn2+via fluorescence signals. Unprecedented fluorescence enhancement mechanisms including intramolecular excimer emission from the bis(μ-chloro) dinuclear cadmium complex were clarified by X-ray crystallography. Tiny changes in the molecular structure of the fluorescent probe largely affect the structure and stability of the resulting metal complexes, affording significant improvement in fluorescent metal ion selectivity and optical properties. In particular, the size and flexibility of the metal binding pocket with a carefully organized coordination geometry are crucial for selective accommodation of the target metal ion. This Frontier article may provide a useful dataset for future molecular design of new fluorescent sensors targeting a wide variety of metal ions.Data availability
No primary research results, software or code have been included and no new data were generated or analysed as part of this review.Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.Acknowledgements
The author expresses sincere thanks to his students and collaborators for their valuable help in the exploration of BQDMEN-based ligands. This work was also supported by the JSPS KAKENHI Grant Number JP23K04808 and the Nara Women's University Intramural Grant for Project Research.References
- X.-L. Tang, X.-H. Peng, W. Dou, J. Mao, J.-R. Zheng, W.-W. Qin, W.-S. Liu, J. Chang and X.-J. Yao, Org. Lett., 2008, 10, 3653–3656 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Xue, G. Li, Q. Liu, H. Wang, C. Liu, X. Ding, S. He and H. Jiang, Inorg. Chem., 2011, 50, 3680–3690 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Mameli, M. C. Aragoni, M. Arca, C. Caltagirone, F. Demartin, G. Farruggia, G. De Filippo, F. A. Devillanova, A. Garau, F. Isaia, V. Lippolis, S. Murgia, L. Prodi, A. Pintus and N. Zaccheroni, Chem. – Eur. J., 2010, 16, 919–930 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Zhou, P. Li, Z. Shi, X. Tang, C. Chen and W. Liu, Inorg. Chem., 2012, 51, 9226–9231 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Tian, B. Li, J. Zhu, H. Wang, Y. Li, J. Xu, J. Wang, W. Wang, Z. Sun, W. Liu, X. Huang, X. Yan, Q. Wang, X. Yao and Y. Tang, Dalton Trans., 2012, 41, 2060–2065 RSC.
- Y. Li, H. Chong, X. Meng, S. Wang, M. Zhu and Q. Guo, Dalton Trans., 2012, 41, 6189–6194 RSC.
- Y. Ma, F. Wang, S. Kambam and X. Chen, Sens. Actuators, B, 2013, 188, 1116–1122 CrossRef CAS.
- X.-J. Jiang, M. Li, H.-L. Lu, L.-H. Xu, H. Xu, S.-Q. Zang, M.-S. Tang, H.-W. Hou and T. C. W. Mak, Inorg. Chem., 2014, 53, 12665–12667 CrossRef CAS.
- E. Hrishikesan, R. Manjunath and P. Kannan, J. Solution Chem., 2016, 45, 907–919 CrossRef CAS.
- D. Udhayakumari, J. Mol. Struct., 2023, 1287, 135715 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Mikata, A. Yamashita, A. Kawamura, H. Konno, Y. Miyamoto and S. Tamotsu, Dalton Trans., 2009, 3800–3806 RSC.
- Y. Mikata, Dalton Trans., 2020, 49, 17494–17504 RSC.
- B. Rieger, A. S. Abu-Surrah, R. Fawzi and M. Steiman, J. Organomet. Chem., 1995, 497, 73–79 CrossRef CAS.
- A. S. Abu-Surrah, U. Thewalt and B. Rieger, J. Organomet. Chem., 1999, 587, 58–66 CrossRef CAS.
- A. S. Abu-Sarrah, Asian J. Chem., 2002, 14, 1251–1256 Search PubMed.
- Y. Mikata, H. So, A. Yamashita, A. Kawamura, M. Mikuriya, K. Fukui, A. Ichimura and S. Yano, Dalton Trans., 2007, 3330–3334 RSC.
- L. S. Morris, M. P. Girouard, M. H. Everhart, W. E. McClain, J. A. van Paridon, R. D. Pike and C. Goh, Inorg. Chim. Acta, 2014, 413, 149–159 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Saga, T. Anamushi, W. Miyahara, S. Yamazaki and K. Saito, Anal. Sci., 2015, 31, 185–189 CrossRef CAS.
- N. Singh, J. Niklas, O. Poluektov, K. M. Van Heuvelen and A. Mukherjee, Inorg. Chim. Acta, 2017, 455, 221–230 CrossRef CAS.
- R. V. Ottenbacher, A. G. Medvedev, A. A. Nefedov and K. P. Bryliakov, Inorg. Chem. Commun., 2023, 156, 111282 CrossRef CAS.
- A. P. de Silva, H. Q. N. Gunaratne, T. Gunnlaugsson, A. J. M. Huxley, C. P. McCoy, J. T. Rademacher and T. E. Rice, Chem. Rev., 1997, 97, 1515–1566 CrossRef CAS.
- B. Daly, J. Ling and A. P. de Silva, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2015, 44, 4203–4211 RSC.
- D. Escudero, Acc. Chem. Res., 2016, 49, 1816–1824 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Mikata, M. Wakamatsu, A. Kawamura, N. Yamanaka, S. Yano, A. Odani, K. Morihiro and S. Tamotsu, Inorg. Chem., 2006, 45, 9262–9268 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Mikata, M. Tanaka, S. Yasuda, A. Tsuruta, T. Hagiwara, H. Konno and T. Matsuo, Dalton Trans., 2023, 52, 7411–7420 RSC.
- Y. Mikata, S. Yasuda, T. Hagiwara, H. Konno and S. Shoji, Inorg. Chim. Acta, 2024, 571, 122218 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Mikata, K. Kawakami, M. Nagaoka, S. Shoji, H. Konno and T. Matsuo, Inorg. Chim. Acta, 2024, 565, 121968 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Mikata, A. Kizu and H. Konno, Dalton Trans., 2015, 44, 104–109 RSC.
- Y. Mikata, A. Tsuruta, H. Koike, S. Shoji and H. Konno, Molecules, 2024, 29, 369 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Mikata, N. Tosaka, S. Yasuda, Y. Sakurai, S. Shoji, H. Konno and T. Matsuo, Inorg. Chem., 2024, 63, 8026–8037 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
Footnotes |
† The DMF-H2O (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) was used as a solvent for spectroscopic measurements in the first half (Sections 2 and 3) of this article. 1) was used as a solvent for spectroscopic measurements in the first half (Sections 2 and 3) of this article. |
‡ The DMF-HEPES buffer (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1, 50 mM HEPES, 0.1 M KCl, pH = 7.5) was used as a solvent for spectroscopic measurements in the second half (Sections 4–6) of this article, considering the pH change in the presence of large amount of metal salts. 1, 50 mM HEPES, 0.1 M KCl, pH = 7.5) was used as a solvent for spectroscopic measurements in the second half (Sections 4–6) of this article, considering the pH change in the presence of large amount of metal salts. |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2025 |