Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleBifunctional Na–Ru on gamma-alumina for CO2 capture from air and conversion to CH4: impact of the regeneration method and support on monolithic contactors†
Enrique García-Bordejé *a,
José M. Conesa
*a,
José M. Conesa b,
Antonio Guerrero-Ruiz
b,
Antonio Guerrero-Ruiz cd and
Inmaculada Rodríguez-Ramos
cd and
Inmaculada Rodríguez-Ramos b
b
aInstituto de Carboquímica (ICB-CSIC), Miguel Luesma Castán 4, E-50018 Zaragoza, Spain. E-mail: jegarcia@icb.csic.es
bInstituto de Catálisis y Petroleoquímica (CSIC), 28049, Madrid, Spain
cDepartamento de Química Inorgánica y Química Técnica, UNED, 28040, Madrid, Spain
dGrupo de Diseño y Aplicación de Catalizadores Heterogéneos, UNED, Unidad Asociada al CSIC por el ICP, Spain
First published on 6th May 2025
Abstract
Dual functional materials (DFMs) have the potential to improve the process of CO2 capture and subsequent conversion to fuel. Materials consisting of Na and Ru supported on alumina have been investigated for cyclic direct CO2 air capture and conversion to CH4. We have studied the regeneration conditions, specifically the target temperature and gas composition (inert or hydrogen-containing gas) during heating. The effect of air humidity and Na loading on the effectiveness of CO2 capture has also been assessed. Finally, the DFMs have been successfully implemented as structured contactors with a low pressure drop, which is an unavoidable requirement for practical application.
Keywords: Dual functional materials; Direct air CO2 capture; Methanation; Monoliths.
1 Introduction
The capture of CO2 directly from ambient air (DAC) is a CO2 removal technology that can lead to negative CO2 carbon emissions,1 which is currently foreseen as the only path to meet the Paris agreement targets.2 Likewise, this technology is gaining recent impetus as evidenced by the US Government investment of $3.5 billion in DAC technology.3 Compared to physisorbents, CO2 chemisorbents may have higher adsorption kinetics at low CO2 partial pressures, higher selectivity to CO2, and improved performance in the presence of humidity. The main CO2 chemisorbents can be divided into alkaline metals and amines. Several chemisorbents have been used in direct air capture (DAC), such as supported amines or aqueous alkaline solutions. The former is known as solid-DAC and is commercialized by Climeworks4 and the latter is known as liquid-DAC and is commercialised by carbon engineering.5 Recent reviews compare the energy efficiency and processing steps in both technologies.6,7 Solid-DAC processes require two solid reactors in parallel, while liquid-DAC consists of several steps that can be performed continuously. Supported amines have the advantage that they can be regenerated by low-grade heat like steam, while alkaline carbonates usually require higher regeneration temperatures. However, supported amines have the drawback of low thermal stability, high cost, corrosion of equipment and inactivation by contaminants in air. The main drawback of liquid-DAC based on alkaline salts is the large water consumption and energy requirements to heat the solutions and regenerate the alkaline metal.8 To overcome the excessive use of water and heat, one possible solution is solid alkaline metals. Micrometer-sized Na2CO3 particles were used for CO2 capture at low temperature from flue gases, showing cyclic stability.9,10 It is expected that stabilising small alkali nanoparticles on a high surface area support will increase the kinetics and efficiency of CO2 capture.Generally, CO2 capture and utilisation are performed as separate processes. This entails intermediate steps of CO2 concentration, compression and transportation, which are high-cost operations. These processes can be circumvented by combining the capture with utilisation in the same reactor and material, which is called a dual functional material (DFM).11–13 In this type of material, the capture function (usually an alkaline metal) is mixed at the nanometric scale with a catalyst for the conversion of CO2 to a valuable fuel. DFMs provide the opportunity to intensify the process because the nanometric distance between the capture and catalytic function enhances the heat and mass transfer. For instance, the heat produced in the exothermic catalytic reaction is used for the CO2 desorption and sorbent regeneration. This is enabled because the decomposition temperature of the alkaline metal carbonates formed after CO2 capture matches the temperature for the catalytic CO2 reduction.
One particularity of DAC is that it requires processing high volumes and flow rates of gas due to the extremely low CO2 concentration (400 ppm). For the process to be economically viable, the pumping costs should be minimal. This calls for effective contactors that impose low resistance to the air flow such as structured contactors.14 The low pressure drop of macroporous structured contactors enables the flowing of air through the contactor with marginal pumping costs, potentially negligible if effective movement of air occurs via natural currents such as wind or if contactors are installed in mobile carriers with suitable fluid dynamics. It has also been proposed to implement DAC contactors in trains,15 whose velocity provides a suitable driving force, thus avoiding the need for fans. Moreover, engineering advances achieved in DAC technology (400 ppm CO2) can be also applied to the CO2 capture from flue gases (5–15 v%) and vice versa. Different structures of macroporous contactors have been used for DAC such as pellets,16,17 fibers,18 films,19,20 or monoliths.21 Structure contactors for DAC are prepared from different materials (carbon, MOFs, and ceramic) and by different techniques like extrusion,22 3D-printing23 or coating of preformed structures.21 Honeycomb monoliths have been investigated for DAC after supporting physisorbents such as zeolites24 or chemisorbents such as amines21 or alkali metals.25 The performance of the monolith impregnated with poly-ethylene imine (PEI)21 was similar to powder sorbent across a range of PEI contents, resulting in an optimised CO2 gravimetric capacity of 0.7 mmol g−1 and a volumetric capacity of 350 mol m−3. However, amines are thermally unstable and very hazardous.26,27 Alkali metal carbonates appear to be a cheaper and less hazardous material than volatile amines. Activated carbon monoliths impregnated with alkali carbonates such as Na2CO3![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 25 and K2CO3
25 and K2CO3![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 28 have been also used in DAC. Nevertheless, the use of structured reactors based on DFM for combined DAC capture and conversion is very scarce. The few reports about DFM-based structured reactors are limited to a spin-off company that develops these materials29 and some articles from the Farrauto's group30,31 using monoliths. This group recently reported aging studies of monoliths for 100 cycles of DAC and methanation, showing a stable performance32 even with a low amount of Ru of 0.25 wt%.33 The selected metals in all these articles are Na/Ru on Al2O3. Na is the alkali metal of choice because it is inexpensive and requires lower regeneration temperatures than other metals, such as Ca.34 Among the methanation metal catalysts, Ru is preferred due to its high selectivity for the Sabatier reaction and its resistance to oxidation compared to nickel.35 Several articles suggest the capture from air at high temperature.36,37 However, the large volumes of air and the long capture times required due to the high dilution of CO2 suggest that performing the capture at atmospheric conditions, without any heating or dehumidification pretreatment may be more feasible.
28 have been also used in DAC. Nevertheless, the use of structured reactors based on DFM for combined DAC capture and conversion is very scarce. The few reports about DFM-based structured reactors are limited to a spin-off company that develops these materials29 and some articles from the Farrauto's group30,31 using monoliths. This group recently reported aging studies of monoliths for 100 cycles of DAC and methanation, showing a stable performance32 even with a low amount of Ru of 0.25 wt%.33 The selected metals in all these articles are Na/Ru on Al2O3. Na is the alkali metal of choice because it is inexpensive and requires lower regeneration temperatures than other metals, such as Ca.34 Among the methanation metal catalysts, Ru is preferred due to its high selectivity for the Sabatier reaction and its resistance to oxidation compared to nickel.35 Several articles suggest the capture from air at high temperature.36,37 However, the large volumes of air and the long capture times required due to the high dilution of CO2 suggest that performing the capture at atmospheric conditions, without any heating or dehumidification pretreatment may be more feasible.
Herein we prepared dual functional materials based on Ru–Na supported on alumina. To gain insight into the regeneration process, two regenerating methods were used: one involving heating in inert gas up to 200 °C and then introducing H2, and the other introducing H2 during the temperature ramp. Different Na loadings were prepared and studied using the two regeneration methods. Finally, as a proof of concept, the DFMs were supported on alumina washcoated cordierite monoliths and compared with the powder DFMs.
2 Results and discussion
2.1 Characterization
DFMs with different Na loadings were prepared and characterised by N2 physisorption (Fig. S1 in the ESI† and Table 1). The alumina support is completely mesoporous with negligible micropore volume, as determined by the t-plot method (Fig. S2 in the ESI†). After the impregnation of the metals, no microporosity is created and the materials are still mainly mesoporous. Comparing the DFMs to the bare alumina support, the surface area and pore volume remained almost unvaried up to a Na/Ru ratio of 3.7 and then decreased for higher Na loadings. For the highest loading, that is NaRu (14.6![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1), the total pore volume decreases pronouncedly while keeping similar average pore sizes for all loadings, indicating some pore plugging due to alkali metal accumulation for the highest loadings.
1), the total pore volume decreases pronouncedly while keeping similar average pore sizes for all loadings, indicating some pore plugging due to alkali metal accumulation for the highest loadings.
| Material | BET surface area | Total pore volume | Average pore width (4 V/A)a | dp (XRD)b | dp (TEM) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| m2 g−1 | cm3 g−1 | nm | nm | nm | |
| a Calculated using the BJH desorption branch of the pore size distribution.b Calculated from the XRD diffraction maximum of Ru0 at 2θ ≈ 44° (PDF-06-0663). | |||||
| Alumina sup. | 218 | 0.29 | 4.6 | — | — |
NaRu (2.5![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) 1) |
217 | 0.27 | 3.8 | 9.3 | 10.4 ± 4.8 |
NaRu (3.7![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) 1) |
213 | 0.31 | 5.2 | 9.4 | 9.4 ± 3.2 |
NaRu (7.4![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) 1) |
206 | 0.23 | 4.3 | 9.9 | 14.4 ± 5.7 |
NaRu (10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) 1) |
131 | 0.21 | 4.3 | 10.5 | 13.9 ± 6 |
NaRu (14.6![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) 1) |
161 | 0.17 | 4.1 | 9.6 | 8.9 ± 3.5 |
XRD measurements (Fig. 1) and TEM analysis (Fig. S3 ESI†) of DFMs were also performed. The diffraction peaks of Ru0 (PDF 00-06-0663) were visible for all the samples. From the more intense peak at 2θ ≈ 44°, the average Ru particle size was calculated (Table 1). The average particle sizes determined by XRD are in the same range as those determined from TEM image analysis (Table 1). Using TEM, the average size is more uncertain because it depends on the selected images. In fact, larger particles were detected in some images, leading to a slightly larger average particle size than those determined by XRD. Comparing the different DFMs, no significant differences in Ru particle size as a function of the Na loading could be seen. The particle size of Na could not be determined by TEM due to the absence of contrast. The XRD peaks due to Na are very weak or absent, indicating an amorphous nature. Only some peaks could be ascribed to the alkaline for the highest loading of NaRu (14.6![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) as Na2O (PDF 03-1074) or Na aluminates (PDF 01-079-1560). For this latter loading, some fibrous structures were also observed (Fig. S3e†), which were absent in the rest of the DFMs. The EDS mapping (Fig. S4†) showed that the alkaline is distributed closely around the Ru nanoparticles for the lowest loadings. In contrast, Na is distributed homogeneously throughout all the alumina surface for the highest loadings. This fact and the formation of aluminates suggest a good interaction between the alkaline metal and the alumina support. In contrast, the distribution of Ru is less uniform, which could be attributed to the combination of two effects: the weaker interaction with the alumina support, which facilitates the nucleation and growth of metal nanoparticles and the fact that the precursor has been impregnated in the second step of successive impregnation after the Na, thus on a more irregular surface consisting of Na and uncovered alumina.
1) as Na2O (PDF 03-1074) or Na aluminates (PDF 01-079-1560). For this latter loading, some fibrous structures were also observed (Fig. S3e†), which were absent in the rest of the DFMs. The EDS mapping (Fig. S4†) showed that the alkaline is distributed closely around the Ru nanoparticles for the lowest loadings. In contrast, Na is distributed homogeneously throughout all the alumina surface for the highest loadings. This fact and the formation of aluminates suggest a good interaction between the alkaline metal and the alumina support. In contrast, the distribution of Ru is less uniform, which could be attributed to the combination of two effects: the weaker interaction with the alumina support, which facilitates the nucleation and growth of metal nanoparticles and the fact that the precursor has been impregnated in the second step of successive impregnation after the Na, thus on a more irregular surface consisting of Na and uncovered alumina.
2.2 Testing in CO2 capture and subsequent methanation
Fig. 2 illustrates the process operation at the macroscale (top) and a simplified mechanism at the nanometric scale (bottom) for CO2 capture from air at room temperature and subsequent conversion to CH4 at higher temperature. In the first step, CO2 is captured from air, emitting a CO2-free effluent. The alkaline metal retains CO2 in the form of carbonates and hydrogen carbonates, and the noble metal surface oxidises in contact with the air. The mechanism of reaction of H2 for DFMs at medium temperature (200–300 °C) has been studied in the literature.34,38 In brief, the H2 feedstock reduces the partially oxidised Ru nanoparticles, where H2 is subsequently dissociated. The H– on Ru reacts with the alkali carbonates and hydrogen carbonate to produce CH4 at the interface between the alkali and the noble metal. During the heating ramp, the transients make the process more complex, giving a mixture of products such as CO2 from bicarbonates and carbonate decomposition at different temperatures or also CH4 when the temperature is high enough to activate the methanation reaction. Moreover, the heat produced by the exothermic methanation reaction contributes further to the decomposition of carbonates, releasing reactive COx intermediates. The intimate contact between Ru and Na favours the mass and heat transport to produce CH4, increasing the efficiency and intensification of the process.39 | ||
| Fig. 2 A scheme of the mechanism of CO2 capture from air and methanation. Top: macroscopic scale; bottom: mechanism at the nanoscopic scale of DFM. | ||
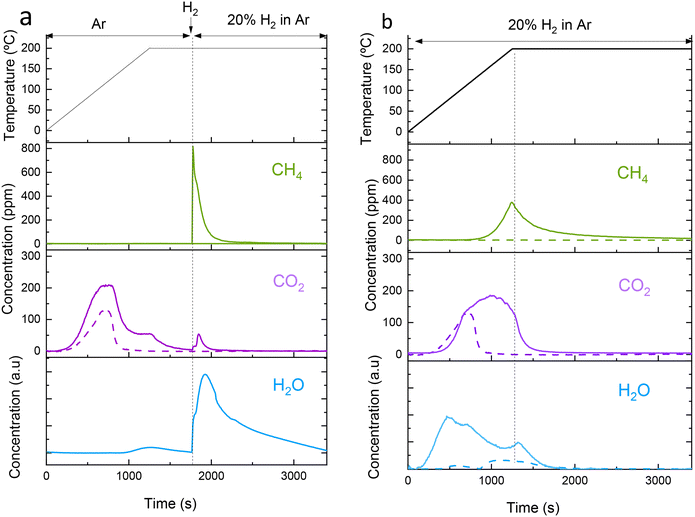
To study the effect of the regeneration method, we selected a sample with a low Na loading, i.e. NaRu (3.7![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1). In a low-loaded sample, Na is expected to be more dispersed as surface Na, hence highly exposed to the gas phase. The two regeneration methods were performed by heating at the same target temperature but varying the feed gas composition during heating. One method consists of heating in Ar flow and introducing H2 flow when the target temperature is reached and holding for 30 min (method A, Fig. 3a) and the other method (method B) consists of feeding H2 from the beginning of the heating to the desired temperature and holding for 30 min (method B, Fig. 3b). Fig. 3 shows the temporal evolution of gases during regeneration heating up to 200 °C using the two regeneration methods. CO2 evolves at low temperatures from 50 °C up to 200 °C with a maximum at ∼125 °C. A similar low-temperature CO2 desorption was also observed for monometallic Ru/Al2O3 (the discontinuous line in Fig. 3), indicating that it corresponds mainly to CO2 physisorbed on alumina pores or weakly chemisorbed on Ru or HO-groups of alumina support. A CO2 desorption shoulder was present at higher temperatures (Fig. 3a) for DFM coinciding with a H2O peak, which can be attributed to the decomposition of sodium hydrogen carbonate to sodium carbonate according to eqn (1). Using method A, CH4 started to be produced only when H2 is fed at 200 °C and the amount of CO2 released concomitantly is negligible, hence avoiding costs of separation. Along with CH4 emission, the other main product is H2O. Therefore, method A can potentially obtain two separate streams of purified gas, i.e. CO2 stream during heating and CH4 stream in the isothermal step at high temperature. Using method B, CH4 started to be produced from temperatures as low as 130 °C with a peak at ∼200 °C. This method produces more total CH4, but it is mixed initially with significant amounts of CO2, which incurs high separation costs. To reduce the separation costs using method B, it would be necessary to develop DFMs that either do not desorb CO2 at low temperatures or with high catalytic activity to reduce CO2 at lower temperatures, thus preventing the release of a gas containing a mixture of unconverted CO2 and CH4.
1). In a low-loaded sample, Na is expected to be more dispersed as surface Na, hence highly exposed to the gas phase. The two regeneration methods were performed by heating at the same target temperature but varying the feed gas composition during heating. One method consists of heating in Ar flow and introducing H2 flow when the target temperature is reached and holding for 30 min (method A, Fig. 3a) and the other method (method B) consists of feeding H2 from the beginning of the heating to the desired temperature and holding for 30 min (method B, Fig. 3b). Fig. 3 shows the temporal evolution of gases during regeneration heating up to 200 °C using the two regeneration methods. CO2 evolves at low temperatures from 50 °C up to 200 °C with a maximum at ∼125 °C. A similar low-temperature CO2 desorption was also observed for monometallic Ru/Al2O3 (the discontinuous line in Fig. 3), indicating that it corresponds mainly to CO2 physisorbed on alumina pores or weakly chemisorbed on Ru or HO-groups of alumina support. A CO2 desorption shoulder was present at higher temperatures (Fig. 3a) for DFM coinciding with a H2O peak, which can be attributed to the decomposition of sodium hydrogen carbonate to sodium carbonate according to eqn (1). Using method A, CH4 started to be produced only when H2 is fed at 200 °C and the amount of CO2 released concomitantly is negligible, hence avoiding costs of separation. Along with CH4 emission, the other main product is H2O. Therefore, method A can potentially obtain two separate streams of purified gas, i.e. CO2 stream during heating and CH4 stream in the isothermal step at high temperature. Using method B, CH4 started to be produced from temperatures as low as 130 °C with a peak at ∼200 °C. This method produces more total CH4, but it is mixed initially with significant amounts of CO2, which incurs high separation costs. To reduce the separation costs using method B, it would be necessary to develop DFMs that either do not desorb CO2 at low temperatures or with high catalytic activity to reduce CO2 at lower temperatures, thus preventing the release of a gas containing a mixture of unconverted CO2 and CH4.
| 2NaHCO3 → Na2CO3 + CO2 + H2O | (1) |
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1). In some cases, the carbon balance is not closed, more remarkably for 150 °C. This deviation must be due to some unconverted carbonates that remain in the DFM. For the two regeneration methods, 150 °C provides lower values while 200 °C gives similar regeneration values as 300 °C (Fig. 4) for both regeneration methods. Therefore, 200 °C was selected as the regeneration temperature because of cost-efficiency and the possibility of using waste heat for the process. When the regeneration is performed with method B, that is, feeding H2 from the beginning (Fig. 3b), more CH4 is produced, and the carbon balance is well closed in contrast to the regeneration method A. Therefore, the regeneration method B proved to be more effective than the regeneration method A. The reason is that, during the heating ramp, CH4 is produced only when using method B (Fig. 3b), while more CO2 is released using method A, which is not converted to CH4 due to the absence of H2 in the gas (Fig. 3a). However, when using method A at 200 or 300 °C (Fig. 4a), pure CO2 is obtained during the ramp and almost pure CH4 is obtained in the isothermal step. This is not the case for 150 °C, at which the methanation activity is lower. The CH4 peak in Fig. 3 is the result of the interplay of several processes such as the thermal decomposition of the solid carbonates/bicarbonates, the Sabatier reaction that leads to CH4 and the diffusion of the gas in the bulk solid which follows a shrinking core model. This makes the estimation of an average rate very ambiguous because after a fast peaking of CH4 there is a tail controlled by the slower diffusion. In any case, the lower CH4 yield at 150 °C can be attributed to the fact that all the processes (decomposition, Sabatier reaction and diffusion) are activated by temperature.
1). In some cases, the carbon balance is not closed, more remarkably for 150 °C. This deviation must be due to some unconverted carbonates that remain in the DFM. For the two regeneration methods, 150 °C provides lower values while 200 °C gives similar regeneration values as 300 °C (Fig. 4) for both regeneration methods. Therefore, 200 °C was selected as the regeneration temperature because of cost-efficiency and the possibility of using waste heat for the process. When the regeneration is performed with method B, that is, feeding H2 from the beginning (Fig. 3b), more CH4 is produced, and the carbon balance is well closed in contrast to the regeneration method A. Therefore, the regeneration method B proved to be more effective than the regeneration method A. The reason is that, during the heating ramp, CH4 is produced only when using method B (Fig. 3b), while more CO2 is released using method A, which is not converted to CH4 due to the absence of H2 in the gas (Fig. 3a). However, when using method A at 200 or 300 °C (Fig. 4a), pure CO2 is obtained during the ramp and almost pure CH4 is obtained in the isothermal step. This is not the case for 150 °C, at which the methanation activity is lower. The CH4 peak in Fig. 3 is the result of the interplay of several processes such as the thermal decomposition of the solid carbonates/bicarbonates, the Sabatier reaction that leads to CH4 and the diffusion of the gas in the bulk solid which follows a shrinking core model. This makes the estimation of an average rate very ambiguous because after a fast peaking of CH4 there is a tail controlled by the slower diffusion. In any case, the lower CH4 yield at 150 °C can be attributed to the fact that all the processes (decomposition, Sabatier reaction and diffusion) are activated by temperature.
The effect of the presence of humidity in the air on the amount of captured CO2 was positive for all the Na contents. Fig. 5 is an illustrative example for the sample NaRu (3.7![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1), in which Na is expected to be well dispersed on the surface. Fig. 5a shows the capture from dry air and Fig. 5b from air containing ∼3% water vapour. Four cycles were performed regenerating at 200 °C following method A. In both cases, the first cycle exhibited higher CO2 capture and hence higher CH4 and CO2 emissions during regeneration than subsequent cycles. The difference between the first and next cycles is shorter under humid conditions, suggesting that the carbonate species formed under humid conditions are less stable and thus the regeneration is more effective. The species formed under humid conditions are likely alkali hydrogen carbonates that decompose more easily than carbonates. In contrast, the larger difference between the first and subsequent cycles under dry conditions indicates that a significant amount of unreacted carbonate remains on the DFM surface, limiting the amount of adsorbed CO2 in the following cycle. The values of capture are stabilised from cycles two to four. For this reason, hereinafter we compared the performances of DFMs after stabilisation in 4th cycle. Fig. 5 shows that the values of CO2 capture are higher in the presence of moisture than in its absence, which is mainly attributed to the favoured regeneration. This is a competitive advantage compared to other capture technologies, which are affected negatively by H2O presence.40
1), in which Na is expected to be well dispersed on the surface. Fig. 5a shows the capture from dry air and Fig. 5b from air containing ∼3% water vapour. Four cycles were performed regenerating at 200 °C following method A. In both cases, the first cycle exhibited higher CO2 capture and hence higher CH4 and CO2 emissions during regeneration than subsequent cycles. The difference between the first and next cycles is shorter under humid conditions, suggesting that the carbonate species formed under humid conditions are less stable and thus the regeneration is more effective. The species formed under humid conditions are likely alkali hydrogen carbonates that decompose more easily than carbonates. In contrast, the larger difference between the first and subsequent cycles under dry conditions indicates that a significant amount of unreacted carbonate remains on the DFM surface, limiting the amount of adsorbed CO2 in the following cycle. The values of capture are stabilised from cycles two to four. For this reason, hereinafter we compared the performances of DFMs after stabilisation in 4th cycle. Fig. 5 shows that the values of CO2 capture are higher in the presence of moisture than in its absence, which is mainly attributed to the favoured regeneration. This is a competitive advantage compared to other capture technologies, which are affected negatively by H2O presence.40
Fig. 6 depicts the effect of different Ru![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) Na ratios on the capture parameters at 4th cycle, i.e. after stabilisation, using the two regeneration methods. The amount of captured CO2 is lower using method A (Fig. 6a) than method B (Fig. 6b) because the regeneration is worse using the former method. The values of captured CO2 increased as the loading of Na increased up to a Na
Na ratios on the capture parameters at 4th cycle, i.e. after stabilisation, using the two regeneration methods. The amount of captured CO2 is lower using method A (Fig. 6a) than method B (Fig. 6b) because the regeneration is worse using the former method. The values of captured CO2 increased as the loading of Na increased up to a Na![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) Ru ratio of 7.4
Ru ratio of 7.4![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1. For larger Na loadings, the captured CO2 does not increase or even decrease. According to the N2 adsorption results above (Table 1), it can be hypothesized that for the highest Na loadings, Na forms larger aggregates that clog or are buried in the pores. Larger Na particles pose more diffusional limitations for the CO2 gas to diffuse inside/outside the nanoparticles. Accordingly, larger aggregates are more difficult to regenerate than highly dispersed Na in the DFMs of lower Na loadings. In addition, Na aluminates found by XRD (Fig. 1) for the higher loadings do not participate in CO2 capture. Thus, highly loaded DFMs exhibit lower efficiency in CO2 capture from air due to incomplete regeneration and likely larger Na particles, according to N2 physisorption. Comparing the two regeneration methods, using the regeneration method A, released CO2, CH4 and captured CO2 follow the same profile as a function of Na loading. This suggests that the carbonate decomposed, releasing CO2 during heating up to 200 °C, is a fixed percentage of the captured CO2. The remaining CO2 is hydrogenated to CH4 when H2 is added at 200 °C. However, when using method B, in which H2 is added from the beginning, surprisingly, the CO2 released in regeneration decreases from a Na
1. For larger Na loadings, the captured CO2 does not increase or even decrease. According to the N2 adsorption results above (Table 1), it can be hypothesized that for the highest Na loadings, Na forms larger aggregates that clog or are buried in the pores. Larger Na particles pose more diffusional limitations for the CO2 gas to diffuse inside/outside the nanoparticles. Accordingly, larger aggregates are more difficult to regenerate than highly dispersed Na in the DFMs of lower Na loadings. In addition, Na aluminates found by XRD (Fig. 1) for the higher loadings do not participate in CO2 capture. Thus, highly loaded DFMs exhibit lower efficiency in CO2 capture from air due to incomplete regeneration and likely larger Na particles, according to N2 physisorption. Comparing the two regeneration methods, using the regeneration method A, released CO2, CH4 and captured CO2 follow the same profile as a function of Na loading. This suggests that the carbonate decomposed, releasing CO2 during heating up to 200 °C, is a fixed percentage of the captured CO2. The remaining CO2 is hydrogenated to CH4 when H2 is added at 200 °C. However, when using method B, in which H2 is added from the beginning, surprisingly, the CO2 released in regeneration decreases from a Na![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) Ru ratio of 4.7 upwards, with almost negligible unreacted CO2 released for the Na
Ru ratio of 4.7 upwards, with almost negligible unreacted CO2 released for the Na![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) Ru ratios of 10 and 14.6. This is very relevant because the purity of the produced CH4 avoids the need for an additional gas separation process. The CH4 produced is maximized for NaRu (10
Ru ratios of 10 and 14.6. This is very relevant because the purity of the produced CH4 avoids the need for an additional gas separation process. The CH4 produced is maximized for NaRu (10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1), reaching 300 μmol g−1 with negligible CO2 emissions. Some hypotheses can be put forward to explain this behaviour. Since a substantial part of CO2 evolving at low temperatures comes mainly from the adsorption on the alumina support (Fig. 4b), the higher Na coverage on the alumina support (EDS analysis in Fig. S4d and e of ESI†) may prevent the CO2 evolution at low temperatures, at which the catalyst is not active yet to convert CO2 to CH4. Another possible explanation is that when the Na loading increases, the proximity between the capture and catalytic function increases, enhancing the supply of –H to COx ad-species and hence the kinetics of the conversion of CO2 to CH4, making the catalyst more active at lower temperatures. The elucidation of the reason or mechanisms cooperating for the enhanced CO2 conversion for Na/Ru ratios above 7.4 would require the use of operando techniques. Among similar materials reported in the literature for DAC, higher CO2 uptakes, between 500–1300 μmol gDFM−1, were reported for a DFM consisting of 1% Ru, 10% Na2O on γ-Al2O3.30,32 However, a significant amount of CO2 was reported during heating, leading to CH4 yields between 60–80%. To our knowledge, the absence of significant CO2 desorption during heating as found here for NaRu (1
1), reaching 300 μmol g−1 with negligible CO2 emissions. Some hypotheses can be put forward to explain this behaviour. Since a substantial part of CO2 evolving at low temperatures comes mainly from the adsorption on the alumina support (Fig. 4b), the higher Na coverage on the alumina support (EDS analysis in Fig. S4d and e of ESI†) may prevent the CO2 evolution at low temperatures, at which the catalyst is not active yet to convert CO2 to CH4. Another possible explanation is that when the Na loading increases, the proximity between the capture and catalytic function increases, enhancing the supply of –H to COx ad-species and hence the kinetics of the conversion of CO2 to CH4, making the catalyst more active at lower temperatures. The elucidation of the reason or mechanisms cooperating for the enhanced CO2 conversion for Na/Ru ratios above 7.4 would require the use of operando techniques. Among similar materials reported in the literature for DAC, higher CO2 uptakes, between 500–1300 μmol gDFM−1, were reported for a DFM consisting of 1% Ru, 10% Na2O on γ-Al2O3.30,32 However, a significant amount of CO2 was reported during heating, leading to CH4 yields between 60–80%. To our knowledge, the absence of significant CO2 desorption during heating as found here for NaRu (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10), leading to CH4 yields above 95%, has no precedent in the literature.
10), leading to CH4 yields above 95%, has no precedent in the literature.
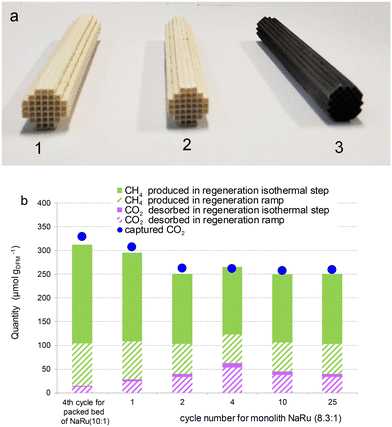
As explained in the introduction, due to the high air volume to be treated, the application of DFM for direct air capture can only be economically competitive if the contactor has a low pressure drop to minimize or even suppress the pumping costs. As a proof of concept, we supported Na–Ru DFM on alumina washcoated cordierite monoliths and tested it in cycles of CO2 captured from air and subsequent hydrogenation to methane. The nominal stoichiometry selected to support in the monolith was NaRu (10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1), as it provided higher CH4 productivity and minimizes the desorption of unreacted CO2 in experiments in packed bed (Fig. 6b). Fig. 7a shows a photograph illustrating the different steps of monolith preparation: the 1 cm diameter × 6.5 cm length cordierite monolith washcoated with alumina (monolith 1), this monolith was loaded with Na and treated with N2 at 500 °C (monolith 2), and this latter monolith was impregnated with Ru and subsequently calcined in N2 and reduced in H2 at 500 °C (monolith 3). Monolith 3 takes a black colour due to the reduction of ruthenium. The uniform distribution of the colour throughout the monolith is indicative of the homogeneous distribution of Ru and alumina coating on the cordierite surface. Ultrasonic treatment during 20 min showed negligible weight loss (∼0.2 wt% of the total monolith, which characterizes 3 wt% of the coating), indicating a good adhesion of alumina and DFM. This is due to the fact that alumina penetrates the macropores of cordierite, as can be observed in SEM images (Fig. S5†). Except for some accumulations of alumina in the mouth of macropores, the alumina coating was very uniform on all the channel surfaces. The alumina thickness is below the resolution of SEM, and in previous works,41 we determined that it was ∼0.1 μm. The N2 physisorption characterization showed that the cordierite monolith has a negligible surface area (Table S1†), and it increases to 6.1 m2 g−1 when coated with Al2O3. As this is due to the alumina, when normalized per the alumina weight, it is 215 m2 g−1, in agreement with that of the powdered material. 12 monolithic DFMs were prepared, exhibiting good repeatability in the preparation. The average alumina loading after step 1 was 6.1 ± 0.3 wt%, calculated by weight difference between the monolith before and after alumina coating. The monolith + DFM weighed about ∼2.6 g, and the DFM amounted to ∼6.7% of the total monolith weight. This results in a total DFM weight in each monolith between 120–160 mg. Therefore, the amount of DFM in an experiment with the monolith was almost double that used in packed bed experiments (70 mg). The NaNO3 and Ru nitrosyl nitrate precursors were weighed to provide nominal loadings equal to the stoichiometry NaRu (10
1), as it provided higher CH4 productivity and minimizes the desorption of unreacted CO2 in experiments in packed bed (Fig. 6b). Fig. 7a shows a photograph illustrating the different steps of monolith preparation: the 1 cm diameter × 6.5 cm length cordierite monolith washcoated with alumina (monolith 1), this monolith was loaded with Na and treated with N2 at 500 °C (monolith 2), and this latter monolith was impregnated with Ru and subsequently calcined in N2 and reduced in H2 at 500 °C (monolith 3). Monolith 3 takes a black colour due to the reduction of ruthenium. The uniform distribution of the colour throughout the monolith is indicative of the homogeneous distribution of Ru and alumina coating on the cordierite surface. Ultrasonic treatment during 20 min showed negligible weight loss (∼0.2 wt% of the total monolith, which characterizes 3 wt% of the coating), indicating a good adhesion of alumina and DFM. This is due to the fact that alumina penetrates the macropores of cordierite, as can be observed in SEM images (Fig. S5†). Except for some accumulations of alumina in the mouth of macropores, the alumina coating was very uniform on all the channel surfaces. The alumina thickness is below the resolution of SEM, and in previous works,41 we determined that it was ∼0.1 μm. The N2 physisorption characterization showed that the cordierite monolith has a negligible surface area (Table S1†), and it increases to 6.1 m2 g−1 when coated with Al2O3. As this is due to the alumina, when normalized per the alumina weight, it is 215 m2 g−1, in agreement with that of the powdered material. 12 monolithic DFMs were prepared, exhibiting good repeatability in the preparation. The average alumina loading after step 1 was 6.1 ± 0.3 wt%, calculated by weight difference between the monolith before and after alumina coating. The monolith + DFM weighed about ∼2.6 g, and the DFM amounted to ∼6.7% of the total monolith weight. This results in a total DFM weight in each monolith between 120–160 mg. Therefore, the amount of DFM in an experiment with the monolith was almost double that used in packed bed experiments (70 mg). The NaNO3 and Ru nitrosyl nitrate precursors were weighed to provide nominal loadings equal to the stoichiometry NaRu (10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) and 3 wt% Ru loading. The actual loadings measured by ICP-OES were comparable to the nominal loading for Ru (total Ru in a monolith ∼5 mg) but slightly lower for Na, resulting in an actual ratio NaRu (8.3
1) and 3 wt% Ru loading. The actual loadings measured by ICP-OES were comparable to the nominal loading for Ru (total Ru in a monolith ∼5 mg) but slightly lower for Na, resulting in an actual ratio NaRu (8.3![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) and a total fraction of DFM in the monolith of 6.7%. The discrepancy in the ratio relates to the idiosyncrasy of the different impregnation methods, i.e. incipient wetness impregnation for the powdered DFM and equilibrium adsorption for the monolithic one. The former method allows a straightforward and accurate adjustment of the loading, while the adjustment is more difficult for the latter. Therefore, the preparation process of the DFM monolith requires further optimization. This should also include the characterization of the metal distribution on the monolith surface and through the washcoating cross-section.
1) and a total fraction of DFM in the monolith of 6.7%. The discrepancy in the ratio relates to the idiosyncrasy of the different impregnation methods, i.e. incipient wetness impregnation for the powdered DFM and equilibrium adsorption for the monolithic one. The former method allows a straightforward and accurate adjustment of the loading, while the adjustment is more difficult for the latter. Therefore, the preparation process of the DFM monolith requires further optimization. This should also include the characterization of the metal distribution on the monolith surface and through the washcoating cross-section.
Using the DFM coated monolith, up to 25 cycles of capture and regeneration at 200 °C following method B were performed. The performances for selected cycles of the monolith are shown in Fig. 7b, which also includes for comparison the performance of a packed bed of particulated DFM NaRu (10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1). The performance of the monolith decays from the first to the second cycle, like in the packed bed experiments. For further cycles, the performance was stable up to the 25th tested cycle. At steady state, the CO2 capture per DFM weight for the monolith was about 20% smaller than for the packed bed. However, when it is normalized per actual Na loading, the values become comparable for the monolith and the packed bed of particulate DFM, corroborating the effectiveness of DFM incorporation into the monolith and the good gas diffusion to the monolith DFM coating.
1). The performance of the monolith decays from the first to the second cycle, like in the packed bed experiments. For further cycles, the performance was stable up to the 25th tested cycle. At steady state, the CO2 capture per DFM weight for the monolith was about 20% smaller than for the packed bed. However, when it is normalized per actual Na loading, the values become comparable for the monolith and the packed bed of particulate DFM, corroborating the effectiveness of DFM incorporation into the monolith and the good gas diffusion to the monolith DFM coating.
We also performed the capture step in a rotating system, as depicted in Fig. 8a. The set-up consists of 1 cm diameter quartz reactor tubes fixed by clamps to the edges of a 10 cm length bar. The bar is fixed by the middle perpendicular to the rotating shaft connected to a rotor. The tube was open so that air could enter inside the tube thanks to the speed or the rotation. Either the monolith or 150 mg of powder NaRu (10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) in the packed bed with SiC was fixed inside a quartz tube, as in previous force flow experiments. The capture was performed at room temperature (∼25 °C) by rotating at 100 rpm for 15 min either with the monolith or with the packed bed. Subsequently, the reactor was placed in the furnace, and it was regenerated under a force flow of 20% H2 in Ar, as previously described in method B. This concept of a rotating system is not intended to design a small-scale prototype but to test and prove the feasibility of our DFM in equipment working with a low pressure drop. Hypothetical implementation of the system could involve the coupling to an aerogenerator where a renewable energy such as wind is used to move the aerogenerator blades together with the monolith. Subsequently, the monolith is regenerated with green hydrogen from an electrolyser powered also by Eolic energy.
1) in the packed bed with SiC was fixed inside a quartz tube, as in previous force flow experiments. The capture was performed at room temperature (∼25 °C) by rotating at 100 rpm for 15 min either with the monolith or with the packed bed. Subsequently, the reactor was placed in the furnace, and it was regenerated under a force flow of 20% H2 in Ar, as previously described in method B. This concept of a rotating system is not intended to design a small-scale prototype but to test and prove the feasibility of our DFM in equipment working with a low pressure drop. Hypothetical implementation of the system could involve the coupling to an aerogenerator where a renewable energy such as wind is used to move the aerogenerator blades together with the monolith. Subsequently, the monolith is regenerated with green hydrogen from an electrolyser powered also by Eolic energy.
The rotation generates air flowing at atmospheric pressure through the tube, in contrast to the reactor experiments, in which synthetic air was forced to flow through by pressurized cylinders. Fig. 8b shows that the monolith captures similar CO2 amounts as when the capture was performed under force flow (Fig. 7b), while the packed bed captures significantly lower CO2 amounts in the rotating system. This contrast in behaviour can be ascribed to the distinct fluid dynamic properties of the monolith and packed bed. The low pressure drop of the monolith enables the generation of air ducts through monolith channels by rotation. In contrast, the air cannot diffuse inside the bed because the rotation is not able to overcome the higher resistance to flow through the packed bed. In the experimental system, an electrical motor drives the rotation but the turning can also be propelled by renewable energy like wind, e.g. by implementing the monolith in a system with wind blades.
3 Conclusions
The impact of the two regeneration methods was tested as a function of the Na loading. The regeneration method A, in which H2 is introduced when a high temperature is reached, leads to pure CO2 being released during the temperature ramp in Ar and an almost pure CH4 emission when adding H2 at the target temperature. In regeneration method B, H2 is introduced from the beginning, and a mixture of desorbed CO2 and CH4 is emitted. In general, the regeneration using method B is more effective than method A. The optimum regeneration method depends on the Na loading. For the lowest loadings up to NaRu (7.4![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1), a significant amount of CO2 is desorbed during the heating ramp using the two methods. Therefore, method A could reduce separation costs because it avoids the simultaneous emission of CO2 and CH4. For the highest Na loadings, the method of heating under H2 leads to negligible release of unreacted CO2. Accordingly, for the Na
1), a significant amount of CO2 is desorbed during the heating ramp using the two methods. Therefore, method A could reduce separation costs because it avoids the simultaneous emission of CO2 and CH4. For the highest Na loadings, the method of heating under H2 leads to negligible release of unreacted CO2. Accordingly, for the Na![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) Ru (10
Ru (10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) DFM, method B is a more effective regeneration method, which does not require further gas separation steps. The CO2 capture increases as the Na
1) DFM, method B is a more effective regeneration method, which does not require further gas separation steps. The CO2 capture increases as the Na![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) Ru ratio increases up to a maximum of 330 μmol g−1 for a 10
Ru ratio increases up to a maximum of 330 μmol g−1 for a 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 Na
1 Na![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) Ru ratio, and then it decreases for higher Na loadings. The lowest efficiency for the highest loading of NaRu (14.6
Ru ratio, and then it decreases for higher Na loadings. The lowest efficiency for the highest loading of NaRu (14.6![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) can be attributed to the aggregation of Na, which entails incomplete regeneration at 200 °C. Moreover, the presence of humidity in the air had a beneficial effect on the CO2 capture and regeneration, in contrast to other capture materials in the literature. Finally, the DFMs were successfully incorporated into alumina washcoated monoliths, showing similar efficiency to the powder catalyst but imparting a lower pressure drop to the flow of air, paving the way to practical applications in renewable energy.
1) can be attributed to the aggregation of Na, which entails incomplete regeneration at 200 °C. Moreover, the presence of humidity in the air had a beneficial effect on the CO2 capture and regeneration, in contrast to other capture materials in the literature. Finally, the DFMs were successfully incorporated into alumina washcoated monoliths, showing similar efficiency to the powder catalyst but imparting a lower pressure drop to the flow of air, paving the way to practical applications in renewable energy.
4 Experimental
4.1 Preparation of the DFM
Both the monolith alumina coating layer and the alumina particles in powder form were prepared from the same colloidal sol prepared from pseudoboehmite (AlOOH, Pural from Sasol) according to a previously described procedure.41 Pseudoboehmite at neutral pH forms a colloidal sol that can be easily coated on a substrate such as a monolith, and it becomes a solid after gelation and drying. This solid, which can be in the form of a monolith coating layer or ground into unsupported particles, is transformed to mesoporous alumina by calcination as described below.![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1
1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 5. The sol was gelled and calcined at 600 °C in air at a 1 °C min−1 heating rate. The calcined γ-Al2O3 was ground and sieved into particles smaller than 100 μm. A calculated amount of NaNO3 (Merck) was weighed to achieve the desired final Na
5. The sol was gelled and calcined at 600 °C in air at a 1 °C min−1 heating rate. The calcined γ-Al2O3 was ground and sieved into particles smaller than 100 μm. A calculated amount of NaNO3 (Merck) was weighed to achieve the desired final Na![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) Ru ratio and diluted in the water volume needed to impregnate the alumina powder by incipient wetness impregnation. The powder was dried at room temperature for 12
Ru ratio and diluted in the water volume needed to impregnate the alumina powder by incipient wetness impregnation. The powder was dried at room temperature for 12![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) h and calcined in N2 at 500 °C (1 °C min−1, 1 h dwell time). Subsequently, 3 wt% of Ru with respect to the alumina weight was impregnated by incipient wetness impregnation using Ru nitrosyl nitrate (Johnson Matthey) as a precursor. The impregnated powder was dried at room temperature for 12
h and calcined in N2 at 500 °C (1 °C min−1, 1 h dwell time). Subsequently, 3 wt% of Ru with respect to the alumina weight was impregnated by incipient wetness impregnation using Ru nitrosyl nitrate (Johnson Matthey) as a precursor. The impregnated powder was dried at room temperature for 12![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) h, calcined in N2 at 500 °C (1 °C min−1, 1 h dwell time), reduced in H2 under the same conditions, and reserved for testing. Five Na contents were impregnated, keeping constant Ru loading (3 wt%). The Na to Ru ratios prepared were 2.5, 3.7, 7.4, 10 and 14.6.
h, calcined in N2 at 500 °C (1 °C min−1, 1 h dwell time), reduced in H2 under the same conditions, and reserved for testing. Five Na contents were impregnated, keeping constant Ru loading (3 wt%). The Na to Ru ratios prepared were 2.5, 3.7, 7.4, 10 and 14.6.4.2 Characterization and testing in cycles of CO2 capture and methanation
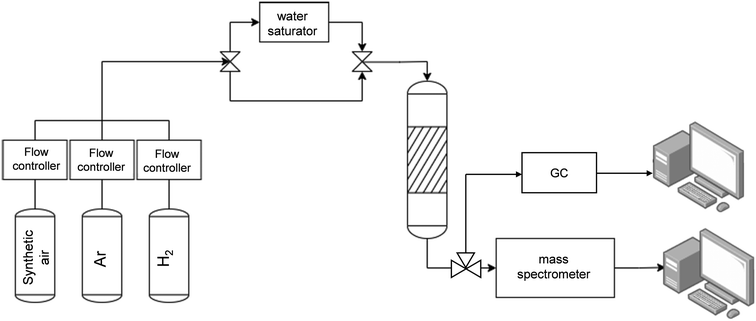
The layout of the experimental set up is shown in Fig. 9. The CO2 capture/methanation experiments for the powdered DFM were carried out by mixing 70 mg of DFM powder with the same amount of SiC and placed on top of quartz wool fixed in the middle of a cylindrical quartz reactor (6 mm OD–4 mm ID) inside a vertical furnace equipped and connected to stainless steel tubing. A thermocouple was introduced inside the catalytic bed and connected to a temperature controller (Eurotherm). The gas flow rates were controlled using a Bronkhorst flow meter. Prior to each catalytic test, the catalyst was prereduced in H2 (60 mL![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) min−1) at 500 °C for 1 h using a heating rate of 10 °C
min−1) at 500 °C for 1 h using a heating rate of 10 °C![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) min−1. The experiment consists of the following steps:
min−1. The experiment consists of the following steps:
1. CO2 capture step: 60 mL min−1 (STP) of a simulated air containing 400 ppm CO2, 21% O2 in Ar was fed to the reactor, kept at a constant set-point temperature of 40 °C for 30 min. In the experiments with humid air, the air was saturated with water by bubbling it through a humidifier kept at a constant temperature of 30 °C, leading to a H2O partial pressure of ∼3%.
2. Sweeping with Ar: after the breakthrough of CO2, the reactor was flushed with 60 mL min−1 of Ar to remove weakly physisorbed species (CO2, H2O) for 30 min.
3. Methanation/regeneration: this was carried out by heating at different temperatures, following two different methodologies. Method A: heating to the setpoint temperature under Ar and then feeding 60 mL min−1 of 20% H2 in Ar; method B: feeding 60 mL min−1 of 20% H2 in Ar from the beginning of the heating ramp. In both methods, the total time of regeneration was maintained for 60 min. Three setpoint temperatures were used: 150 °C, 200 °C and 300 °C, finally leaving 200 °C as the standard for all samples. Diluted H2 was used instead of 100% H2 because of the limitations of the mass spectrometer for high H2 concentrations. However, it was verified experimentally that the H2 concentration did not affect the methanation temperature by varying the H2 concentration from 10 to 60%.
The monolithic DFM was tested in a reactor of 1.2 cm internal diameter. The 1 cm diameter monolith was fitted to the walls with quartz strips. Due to the larger diameter of the reactor compared to the packed bed experiments, the flow rate was increased up to 147 mL min−1 to keep the same gas linear velocity of 20 cm min−1 in both reactors.
In all the steps, the outlet gas was analyzed with a Pfeiffer vacuum mass spectrometer. The main m/z signals monitored in the mass spectrometer were 2 (H2), 15 (CH4), 18 (H2O), 28 (CO), 40 (Ar) and 44 (CO2). All the m/z signals were corrected by the baseline of argon. The concentrations of CO2 and CH4 were calculated by calibrating the m/z = 44 and m/z = 15, respectively. To calculate the CO concentration, the contribution of CO2 was subtracted from m/z = 28. The correct calibration of the mass spectrometer was double-checked by analyzing the gases with a gas chromatograph (ARNEL CLARUS 690). The CO2 capture capacity (in mmol g−1) was calculated by integrating the CO2 breakthrough curve.
The DFM with different Na loadings was characterised by N2 adsorption at 77 K (BET). This was performed using a Micromeritics ASAP 2020 apparatus, after outgassing for 4 h at 473 K. From the physisorption measurements with N2, the surface area (SN2) was calculated by the BET (Brunauer, Emmet, and Teller) theory in the relative pressure range 0.05–0.30. Pore volume was calculated from the amount of N2 adsorbed at a relative pressure of 0.99. The pore-size distribution was obtained from the desorption branch of the N2 isotherm according to the BJH method (Barrett–Joyner–Halenda) using the DataMaster V4.0 software and assuming slit pore geometry. The model fitted quite well to the isotherm with a standard deviation of ∼0.05 cm3 g−1 STP. The micropore surface area (Smic) was calculated by the t-plot method, and the external surface area (Smes) was obtained by subtraction from the total surface area.
The structural properties of the DFM were studied by powder X-ray diffraction (XRD) using a Polycristal X'Pert Pro Panalytical diffractometer employing Cu Kα radiation (λ = 1.54 Å). XRD patterns were recorded with a step size of 0.04° s−1, covering a 2θ range between 4° and 90°. High-resolution transmission microscopy (TEM) images were obtained on a JEOL JEM-2100 microscope with a field emission gun operated at 200 kV. The reduced samples were ground, ultrasonically dispersed in ethanol and deposited on carbon-coated Cu grids. The statistical treatment of the recorded images was carried out by measuring a minimum of 200 particles, using the following equation to calculate the mean diameter: dp = Σni·di/Σni, where ni refers to the number of particles with a di averaged diameter, along with the standard deviation of the values used. Additionally, local elemental analysis of selected zones was carried out by energy dispersive X-ray analysis (EDS) in scanning transmission mode with an x-Max80 detector (Oxford Instruments) using a spot size of 1 nm.
Data availability
The data supporting this article have been included as part of the ESI.†Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.Acknowledgements
The financial support from MICIU/AEI/10.13039/501100011033 and by FEDER, UE through grant PID2023-146481OB-I00, Gobierno de Aragón (Grupo Reconocido DGA T03_17R), and associated EU Regional Development Funds is gratefully acknowledged.References
- E. S. Sanz-Pérez, C. R. Murdock, S. A. Didas and C. W. Jones, Direct capture of CO2 from ambient air, Chem. Rev., 2016, 116, 11840–11876 CrossRef PubMed.
- IEA World Energy Outlook 2022, https://iea.blob.core.windows.net/assets/830fe099-5530-48f2-a7c1-11f35d510983/WorldEnergyOutlook2022.pdf, (accessed October 2024).
- https://www.energy.gov/articles/biden-administration-launches-35-billion-program-capture-carbon-pollution-air-0, (accessed july 2022).
- V. Gutknecht, S. Ó. Snæbjörnsdóttir, B. Sigfússon, E. S. Aradóttir and L. Charles, Creating a carbon dioxide removal solution by combining rapid mineralization of CO2 with direct air capture, Energy Procedia, 2018, 146, 129–134 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Wang, S. Li, S. Deng, X. Zeng, K. Li, J. Liu, J. Yan and L. Lei, Energetic and life cycle assessment of direct air capture: A review, Sustain. Prod. Consum., 2023, 36, 1–16 CrossRef.
- A. Sodiq, Y. Abdullatif, B. Aissa, A. Ostovar, N. Nassar, M. El-Naas and A. Amhamed, A review on progress made in direct air capture of CO2, Environ. Technol. Innovation, 2023, 29, 102991 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Erans, E. S. Sanz-Pérez, D. P. Hanak, Z. Clulow, D. M. Reiner and G. A. Mutch, Direct air capture: Process technology, techno-economic and socio-political challenges, Energy Environ. Sci., 2022, 15, 1360–1405 RSC.
- A. Kiani, K. Jiang and P. Feron, Techno-economic assessment for CO2 capture from air using a conventional liquid-based absorption process, Front. Energy Res., 2020, 8, 92 CrossRef.
- Y. Liang, D. P. Harrison, R. P. Gupta, D. A. Green and W. J. McMichael, Carbon dioxide capture using dry sodium-based sorbents, Energy Fuels, 2004, 18, 569–575 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Park, D. Sung, B. Choi, K. Oh and K. Moon, Sorption of carbon dioxide onto sodium carbonate, Sep. Sci. Technol., 2006, 41, 2665–2684 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Hu and A. Urakawa, Continuous CO2 capture and reduction in one process: CO2 methanation over unpromoted and promoted Ni/ZrO2, J. CO2 Util., 2018, 25, 323–329 CrossRef CAS.
- M. S. Duyar, M. A. A. Treviño and R. J. Farrauto, Dual function materials for CO2 capture and conversion using renewable H2, Appl. Catal., B, 2015, 168–169, 370–376 CrossRef CAS.
- E. García-Bordejé, A. B. Dongil, J. Moral, J. M. Conesa, A. Guerrero-Ruiz and I. Rodríguez-Ramos, Cyclic performance in CO2 capture-methanation of bifunctional Ru with different base metals: Effect of the reactivity of COx ad-species, J. CO2 Util., 2023, 68, 102370 CrossRef.
- M.-Y. Low, L. V. Barton, R. Pini and C. Petit, Analytical review of the current state of knowledge of adsorption materials and processes for direct air capture, Chem. Eng. Res. Des., 2023, 189, 745–767 CrossRef CAS.
- E. Bachman, A. Tavasoli, T. A. Hatton, C. T. Maravelias, E. Haites, P. Styring, A. Aspuru-Guzik, J. MacIntosh and G. Ozin, Rail-based direct air carbon capture, Joule, 2022, 6, 1368–1381 CrossRef CAS.
- R. P. Wijesiri, G. P. Knowles, H. Yeasmin, A. F. A. Hoadley and A. L. Chaffee, CO2 capture from air using pelletized polyethylenimine impregnated MCF silica, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2019, 58, 3293–3303 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Park, Y. S. Chae, D. W. Kang, M. Kang, J. H. Choe, S. Kim, J. Y. Kim, Y. W. Jeong and C. S. Hong, Shaping of a metal–organic framework–polymer composite and its CO2 adsorption performances from humid indoor air, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2021, 13, 25421–25427 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. R. Sujan, S. H. Pang, G. Zhu, C. W. Jones and R. P. Lively, Direct CO2 capture from air using poly(ethylenimine)-loaded polymer/silica fiber sorbents, ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng., 2019, 7, 5264–5273 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Seok Chae, S. Park, D. Won Kang, D. Won Kim, M. Kang, D. San Choi, J. Hyeak Choe and C. Seop Hong, Moisture-tolerant diamine-appended metal–organic framework composites for effective indoor CO2 capture through facile spray coating, Chem. Eng. J., 2022, 433, 133856 CrossRef CAS.
- R. Castro-Muñoz, M. Zamidi Ahmad, M. Malankowska and J. Coronas, A new relevant membrane application: CO2 direct air capture (DAC), Chem. Eng. J., 2022, 446, 137047 CrossRef.
- M. A. Sakwa-Novak, C.-J. Yoo, S. Tan, F. Rashidi and C. W. Jones, Poly(ethylenimine)-functionalized monolithic alumina honeycomb adsorbents for CO2 capture from air, ChemSusChem, 2016, 9, 1859–1868 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. Rodríguez-Mosqueda, J. Rutgers, E. A. Bramer and G. Brem, Low temperature water vapor pressure swing for the regeneration of adsorbents for CO2 enrichment in greenhouses via direct air capture, J. CO2 Util., 2019, 29, 65–73 CrossRef.
- H. Thakkar, S. Eastman, Q. Al-Naddaf, A. A. Rownaghi and F. Rezaei, 3D-printed metal–organic framework monoliths for gas adsorption processes, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2017, 9, 35908–35916 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Sinha, H. Thakkar, F. Rezaei, Y. Kawajiri and M. J. Realff, Direct air capture of CO2 in enclosed environments: design under uncertainty and techno-economic analysis, in Computer Aided Chemical Engineering, ed. M. R. Eden, M. G. Ierapetritou and G. P. Towler, Elsevier, 2018, pp. 2179–2184 Search PubMed.
- R. Rodríguez-Mosqueda, E. A. Bramer and G. Brem, CO2 capture from ambient air using hydrated Na2CO3 supported on activated carbon honeycombs with application to CO2 enrichment in greenhouses, Chem. Eng. Sci., 2018, 189, 114–122 CrossRef.
- A. Wagner, B. Steen, G. Johansson, E. Zanghellini, P. Jacobsson and P. Johansson, Carbon dioxide capture from ambient air using amine-grafted mesoporous adsorbents, Int. J. Spectrosc., 2013, 2013, 690186 Search PubMed.
- C. Gebald, J. A. Wurzbacher, P. Tingaut and A. Steinfeld, Stability of amine-functionalized cellulose during temperature-vacuum-swing cycling for CO2 capture from air, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2013, 47, 10063–10070 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. Rodríguez-Mosqueda, E. A. Bramer, T. Roestenberg and G. Brem, Parametrical study on CO2 capture from ambient air using hydrated K2CO3 supported on an activated carbon honeycomb, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2018, 57, 3628–3638 CrossRef PubMed.
- https://www.susteon.com/technology#05DFM, (accessed July 2023).
- C. Jeong-Potter, M. Abdallah, C. Sanderson, M. Goldman, R. Gupta and R. Farrauto, Dual function materials (Ru+Na2O/Al2O3) for direct air capture of CO2 and in situ catalytic methanation: The impact of realistic ambient conditions, Appl. Catal., B, 2022, 307, 120990 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Goldman, S. Kota, X. Gao, L. Katzman and R. Farrauto, Parametric and laboratory aging studies of direct CO2 air capture simulating ambient capture conditions and desorption of CO2 on supported alkaline adsorbents, Carbon Capture Sci. Technol., 2023, 6, 100094 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Abdallah, Y. Lin and R. J. Farrauto, Laboratory aging of a dual function material (DFM) washcoated monolith for varying ambient direct air capture of CO2 and in situ catalytic conversion to CH4, Appl. Catal., B, 2023, 339, 123105 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Lin, M. J. Abdallah, J. E. Peters, T. Luo, H. Sheng, Y. L. Chen and R. J. Farrauto, Aging studies of dual functional materials for CO2 direct air capture with in situ methanation under simulated ambient conditions: Ru thrifting for cost reduction, Chem. Eng. J., 2024, 479, 147495 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Bermejo-López, B. Pereda-Ayo, J. A. González-Marcos and J. R. González-Velasco, Mechanism of the CO2 storage and in situ hydrogenation to CH4. Temperature and adsorbent loading effects over Ru-CaO/Al2O3 and Ru-Na2CO3/Al2O3 catalysts, Appl. Catal., B, 2019, 256, 117845 CrossRef.
- M. A. Arellano-Treviño, Z. He, M. C. Libby and R. J. Farrauto, Catalysts and adsorbents for CO2 capture and conversion with dual function materials: Limitations of Ni-containing DFMs for flue gas applications, J. CO2 Util., 2019, 31, 143–151 CrossRef.
- T. Tatsumichi, R. Okuno, H. Hashimoto, N. Namiki and Z. Maeno, Direct capture of low-concentration CO2 and selective hydrogenation to CH4 over Al2O3-supported Ni–La dual functional materials, Green Chem., 2024, 26, 10842–10850 RSC.
- F. Kosaka, T. Sasayama, Y. Liu, S.-Y. Chen, T. Mochizuki, K. Matsuoka, A. Urakawa and K. Kuramoto, Direct and continuous conversion of flue gas CO2 into green fuels using dual function materials in a circulating fluidized bed system, Chem. Eng. J., 2022, 450, 138055 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Proaño, E. Tello, M. A. Arellano-Trevino, S. Wang, R. J. Farrauto and M. Cobo, In-situ DRIFTS study of two-step CO2 capture and catalytic methanation over Ru,“Na2O”/Al2O3 dual functional material, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2019, 479, 25–30 CrossRef.
- E. García-Bordejé and R. González-Olmos, Advances in process intensification of direct air CO2 capture with chemical conversion, Prog. Energy Combust. Sci., 2024, 100, 101132 CrossRef.
- L. Joos, J. A. Swisher and B. Smit, Molecular simulation study of the competitive adsorption of H2O and CO2 in Zeolite 13X, Langmuir, 2013, 29, 15936–15942 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- E. García-Bordejé, I. Kvande, D. Chen and M. Rønning, Carbon nanofibers uniformly grown on γ-alumina washcoated cordierite monoliths, Adv. Mater., 2006, 18, 1589–1592 CrossRef.
- A. Bustinza, M. Frías, Y. Liu and E. García-Bordejé, Mono- and bimetallic metal catalysts based on Ni and Ru supported on alumina-coated monoliths for CO2 methanation, Catal. Sci. Technol., 2020, 10, 4061–4071 RSC.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available. See DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/d5im00030k |
| This journal is © Institute of Process Engineering of CAS 2025 |