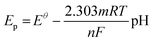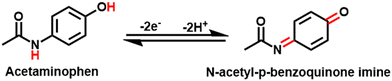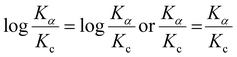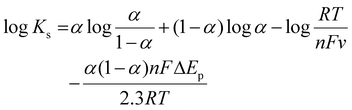In situ synthesis of a UIO-66-NH2@Ti3C2 composite for advanced electrochemical detection of acetaminophen†
Muhammad Hussnain
Afzal
a,
Wajeeha
Pervaiz
b,
Zhuo
Huang
c,
Zhengyun
Wang
a,
Guangfang
Li
 *a and
Hongfang
Liu
*a and
Hongfang
Liu
 *a
*a
aHubei Key Laboratory of Material Chemistry and Service Failure, Key Laboratory of Material Chemistry for Energy Conversion and Storage (Ministry of Education), Hubei Engineering Research Center for Biomaterials and Medical Protective Materials, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 1037 Luoyu Rd, Wuhan, China. E-mail: guangFL@hust.edu.cn; liuhf@hust.edu.cn
bCollege of Food Science and Technology, Huazhong Agricultural University, 1 Shizishan Street, Wuhan, China
cChangjiang River Scientific Research Institute of Changjiang Water Resources Commission, 289 Huangpu Street, Wuhan, Hubei, China
First published on 14th January 2025
Abstract
Acetaminophen (AP) is a widely used analgesic and antipyretic drug, but its excessive use poses health risks and contributes to environmental contamination. In response to the need for rapid, accurate, and cost-effective detection methods, we developed a highly sensitive and selective electrochemical sensor for AP. The sensor was based on a composite of UIO-66-NH2 (UN) and an MXene (Ti3C2). UIO-66-NH2 was in situ synthesized onto the MXene via a one-step hydrothermal process with a varying MXene content, followed by calcination at 300 °C under an argon (Ar) flow. This treatment induced the formation of TiO2 on the MXene surface and increased the interlayer spacing, which enhanced its electrochemical performance. The resulting UN@Ti3C2-C electrode exhibited remarkable electrochemical activity due to the high surface area and excellent conductivity of the MXene. The fabricated sensor demonstrated a simple yet effective approach for the rapid and quantitative detection of AP, with a linear detection range of 0.032–160 μM and a low detection limit of 10 nM. Moreover, the sensor was successfully applied to detect AP in different water samples, validating its potential as a reliable and efficient tool for AP monitoring.
1. Introduction
The global outbreak of the novel coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) has posed unprecedented challenges to public health systems worldwide. Amidst the urgency to identify effective therapeutic strategies to combat the pandemic, existing drugs with potential repurposing opportunities have garnered significant attention. Among these, AP has emerged as a frontline candidate for managing symptoms associated with COVID-19.AP also known as paracetamol is a commonly available over-the-counter drug with antipyretic and analgesic properties.1 Its affordability, accessibility and relative safety profile have contributed to its widespread usage during the COVID-19 pandemic. AP therapy has a low side-effect frequency, but an overdose can cause liver damage2,3 and lead to acute hepatic injury.4,5 In addition, AP has been identified as an aquatic pollutant with traces commonly found in water bodies and fish, stemming from both pharmaceutical manufacturing and human consumption.6 The concentrations of AP found in the coastal area samples were 75.7–169.8 ngL−1 which was twice as high as the previously reported concentration before COVID-19 (4.7–72.3 ngL−1).7 Evaluating toxicity in fish stands out as one of the most reliable approaches for comprehending the harmful impacts of environmental pollutants on aquatic ecosystems.8,9 Therefore, simple, reliable, and sensitive methods need to be developed for AP detection.
There are many commonly used techniques for the detection of AP, including high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC),10 gas chromatography (GC),11 spectrophotometry,12 thermogravimetric analysis, and electrochemical methods.13,14 However, these methods have drawbacks, including low selectivity, complex procedures, high costs and the need for sample pre-treatment. In contrast, researchers are increasingly attracted to electrochemical sensing technology due to its extensive applicability in the analysis of environmental and biological data. This fascination stems from its notable advantages, including sensitivity and excellent selectivity, rapid analytical response, straightforward equipment requirements, cost-effectiveness and the absence of sample pre-treatment requirements.15–17
So far, a variety of materials with distinctive electrochemical properties have been explored for the development of electrochemical sensors aimed at detecting AP. These materials include graphene,18 graphene oxide,19 carbon nanotubes,20 metal nanoparticles,21 and MXenes,22,23 as well as metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) and MOF-derived carbon materials.24,25 Among these options, MOFs have gained attention due to their diverse structure, ample specific surface area and uniformly structured cavities. MOFs have proven to be excellent sacrificial templates for creating innovative metal or metal oxide nano-porous carbon composites. However, the low electrical conductivity of MOFs hinders electron transfer, restricting their use in certain applications such as electrochemical sensors. Several works have recently shown the potential of MOFs for electrochemical sensing. For example, Tang et al.26 developed a Co-based MOF which shows good electrocatalytic performance for AP with a glassy carbon electrode. Among all the MOFs, UIO-66-NH2 (Zr-MOF) is the promising candidate for electrochemical sensing in aqueous media, the property of the material to be considered should be its water stability.27,28 Its highly porous nature provides sites for the analyte molecules and consequently improves the sensitivity of the electrochemical sensing system. Zhang et al.29 developed an electrochemical sensor using Zr-MOF and carbon derived from walnut shells (WC) as modified materials. This sensor is highly sensitive and selective for detecting paracetamol (Para) and para-aminophenol (PAP). Furthermore, Li et al.24 further improved the sensing performance for AP and dopamine by combining Zr-MOF with carbon nanotubes.
MXenes are novel two-dimensional (2D) nanomaterials similar to graphene, consisting of multiple layers. They have excellent electrical conductivity, a large specific surface area and numerous functional groups making them highly attractive in the field of electrochemistry.30 MXenes are typically represented by the formula Mn+1XnTx, where “M” stands for transition metals, “X” refers to carbon or nitrogen atoms, and “Tx” indicates surface functional groups like –OH, –O, and –F. MXenes can establish strong interactions with the organic ligands found in MOFs and some inorganic compounds due to their multiple active sites.31 They are particularly effective as a conductive platform to support materials that have high catalytic activity but low electrical conductivity. As a result, Ti3C2Tx-MXene is widely used in electrochemical sensing applications.32 For example, Zhao et al.33 developed a disposable electrochemical biosensor using multi-dimensional nanocomposites (MXene/Au–Pd) to detect organophosphorus pesticides. In another study, Wang and colleagues created an electrochemical sensor based on a reduced graphene oxide (rGO) and Ti3C2Tx-MXene composite, specifically for the detection of AP.34 These examples demonstrate the versatility and effectiveness of Ti3C2Tx-MXene in enhancing the sensor performance in various applications.
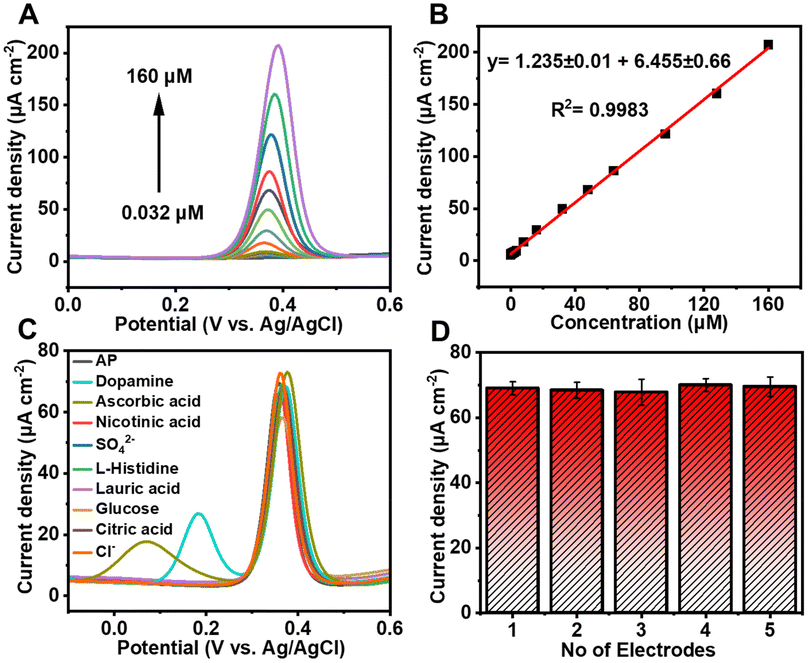
In this study, UN@Ti3C2-C was synthesized by a hydrothermal method with a varying content of MXene (20, 30, 50 and 70% by weight) and then calcined to 300 °C under an argon atmosphere resulting in the formation of TiO2 on the MXene surface as presented in Fig. 1. This process improved its conductivity and increased its surface area. The electrochemical behavior of AP was tested using the UIO-66-NH2 and MXene composites. The results showed that this electrochemical sensor could detect AP with high sensitivity, selectivity, and stability. Moreover, it was effective in detecting AP in real-world samples.
 | ||
| Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of the various steps in UIO-66-NH2@Ti3C2-C synthesis and the electrochemical sensing mechanism. | ||
2. Experimental section
2.1 Chemicals and materials
MAX phase (Ti3AlC2), lithium fluoride (LIF), hydrochloric acid (HCl), zirconium chloride (ZrCl4), 2-amino terephthalic acid (2-NH2-BDC), acetic acid (CH3COOH), dimethylformamide (DMF), and methanol (CH3OH) reagents were purchased from Sinopharm Group Chemical Reagent Co. Ltd (Shanghai, China). All of the chemicals were analytically pure and used without any further purification. Double distilled water was used to make all of the solutions. The supporting electrolyte of 0.1 M phosphate buffer solution (PBS, pH = 7) was composed of KH2PO4 and K2HPO4·3H2O in a suitable amount, and it was used throughout the experiment.2.2 Instrumentation
X-ray diffraction patterns (XRD) were obtained using a Rigaku D/max-rA diffractometer (Japan) with a Ni filter using Cu Kα radiation (40 kV, 200 mA), and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) was carried out on an AXISULTRA DLD-600 W X spectrometer (Shimadzu Company). Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) was performed on a HITACHI X-650 (Hitachi Co., Japan). An acceleration voltage of 200 kV was used to capture the images of transmission electron microscopy (TEM) with a TECNAI G220 U-Twin instrument (Netherlands). Cyclic voltammetry (CV), differential pulse voltammetry (DPV), and electron impedance spectroscopy (EIS) were performed on a CHI760E electrochemical workstation (CH Instrument Company, Shanghai, China), and fitted with GCE, Ag/AgCl/saturated KCl, and platinum as the working, reference, and counter electrodes respectively, in a traditional three-electrode system at room temperature with deoxygenated 10 mL of 0.1 M PBS (pH = 7). The working potential range was used from −0.6 to 1.2 V in CV and DPV, while a frequency range of 0.1 to 105 Hz and 0.005 V of sinusoidal potential amplitude were established for EIS.2.3 Preparation of MXene (Ti3C2)
MXene was prepared by etching 1 g Ti3AlC2 powder with a mixture of 1 g LiF and HCl (10 mol L−1, 20 ml) in a container for 30 h under stirring for removal of the Al layer based on previous literature.35 Afterwards, deionized water was utilized to wash the mixture, effectively removing any remaining acid and impurities. Subsequently, the obtained solid sample was added to deionized water again using a sonication process for 6 h under N2 flow. Finally, after freeze-drying for 24 h, the final product was obtained.2.5 Preparation of UN@Ti3C2
Preparation of UN@Ti3C2 was as follows: 50 mg of ZrCl4 and 50 mg of 2-NH2-BDC were dissolved in 20 ml DMF by vigorously stirring and it was named solution A. Then 20, 30, 50 and 70% by weight of the above-mentioned Ti3C2 were dispersed ultrasonically in 20 mL DMF separately for 30 minutes and named solution B. Solution A was added to solution B to obtain solution C. Then, 10 ml of acetic acid was further added to solution C under persistent mechanical stirring for 30 minutes. Next, these four suspensions were transferred to a Teflon-lined stainless-steel autoclave and heated for 16 h at 120 °C. After that, the powder form was separated and methanol was used to wash it several times and dried at 60 °C overnight. This process yielded various compositions of UN@Ti3C2 with ratios of 20%, 30%, 50%, and 70%. Additionally, UiO-66-NH2 was synthesized using the same procedure but without the inclusion of MXene.2.5 Preparation of UiO-66-NH2@Ti3C2-C
The UN@Ti3C2-C composite was obtained by a simple calcination method. Typically, the above-prepared (20, 30, 50 and 70%) UN@Ti3C2 was calcined at 300 °C at a ramping rate of 5 °C min−1 in an Ar flow to obtain UN@Ti3C2-C. Finally, the obtained samples were collected and ground.2.6 Modification of the glassy carbon electrode (GCE)
An alumina slurry with particle sizes of 0.3 and 0.05 μm was poured onto micro cloth pads and used to polish and modify the surface of the GCE, which has a diameter of 3 mm. In the next step, it was washed with distilled H2O and ethanol for one minute ultrasonically and finally, N2 was purged to dry it. Afterward, 5 μL of each suspension (3 mg mL−1), UN, 20% UN@Ti3C2-C, 30% UN@Ti3C2-C, 50% UN@Ti3C2-C, and 70% UN@Ti3C2-C were cast on a polished GCE surface at ambient temperature.3. Results and discussion
3.1 Characterization of 50% UN@Ti3C2-C
Firstly, we performed SEM and TEM to investigate the morphology of UIO-66-NH2, UN@Ti3C2, and 50% UN@Ti3C2-C samples, as shown in Fig. 2(A–E). Fig. 2(A) shows the successful synthesis of octahedral UIO-66-NH2 with particle sizes ranging from 0.33 μm to 0.52 μm and an average size of 0.45 μm. Fig. 2(B) demonstrates the successful integration of octahedral UIO-66-NH2 onto the MXene surface. Fig. 2(C) shows the SEM images of 50% UN@Ti3C2-C, revealing MXene layers with octahedral UIO-66-NH2 positioned on and between these layers. A significant amount of TiO2 was observed on the surface of MXene, which increased the thickness of the layers and the interlayer spacing, and the MXene surface became rougher due to the conversion of Ti3C2 into TiO2.36,37Fig. 2(D and E) display the TEM image of 50% UN@Ti3C2-C which shows TiO2 particles on the MOF surface. Additionally, Fig S1† presents the EDX spectrum of 50% UN@Ti3C2-C, while Table S1† shows the relative concentrations of different elements present in the material. | ||
| Fig. 2 SEM image of UIO-66-NH2 (A), UN@Ti3C2 (B), 50% UN@Ti3C2-C (C), TEM image of 50% UN@Ti3C2-C (D), the corresponding elemental mapping of 50% UN@Ti3C2-C (E). | ||
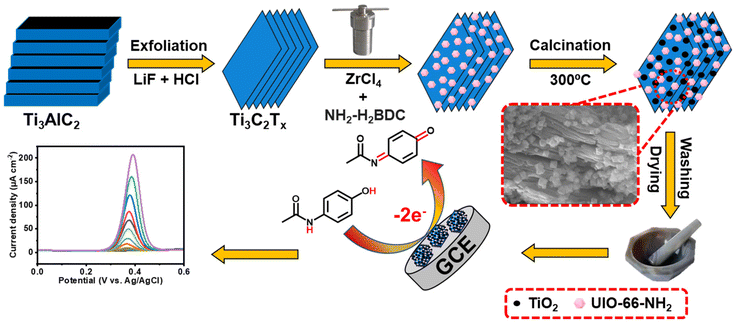
Furthermore, XRD analysis was used to examine the crystalline structure of UIO-66-NH2, Ti3C2 and composite materials UN@Ti3C2 and 50% UN@Ti3C2-C as displayed in Fig. 3(F). The major diffraction peaks at 7.36°, 8.55°, and 25.68° are assigned to the (111), (200), and (422) crystal planes which indicate the successful synthesis of UIO-66-NH2.38 In Ti3C2, the diffraction peaks at 8.79°, 18.23°, and 27.62° are assigned to the (002), (004), and (006) planes respectively.35,39 After calcination of 50% UN@Ti3C2 at 300 °C, the diffraction peak at 7.6° slightly shifted to 7.25° indicating an increase in interlayer spacing. In addition to the presence of main characteristic peaks from Ti3C2, many other peaks are observed for anatase TiO2 like 25.3°, 37.8°, 48.1°, 53.9°, 55.0°, and 62.7° which were ascribed to the (101), (004), (200), (105), (211), and (204) planes.40 The XRD patterns of UN@Ti3C2 and 50% UN@Ti3C2-C indicate the successful incorporation of UIO-66-NH2 on the Ti3C2 surface.41
 | ||
| Fig. 3 (A) XPS wide-scan survey spectrum of 50% UN@Ti3C2-C. (B) Ti 2p. (C) Zr 3d. (D) O 1s. (E) N 1s. (F) XRD patterns of the samples UIO-66-NH2, Ti3C2, UN@Ti3C2, and UN@Ti3C2-C. | ||
Next, the metallic composition and valence bond configuration of Ti3C2 and UIO-66-NH2 were studied using XPS. The wide-scan XPS spectrum in Fig. 3(A) indicates the existence of elements like Zr, Ti, N, C and O. Fig. 3(B) depicts the Ti 2p spectrum of 50% UN@Ti3C2-C which could be fitted into two peaks (Ti 2p3/2 and Ti 2p1/2) that can be ascribed to Ti–O (457.9 and 463.7). The doublet of Ti–O shows the presence of TiO2 particles. As for the Zr 3d spectrum in Fig. 3(C), two peaks could be attributed to Zr 3d5/2 and Zr 3d3/2 with binding energies of 181.9 and 184.2 eV respectively. As for the O 1s spectrum shown in Fig. 3(D), the peak at approximately 529.5 eV is attributed to lattice oxygen (O2−) in metal oxides, which likely arises from the partial oxidation of the Ti3C2 surface to form TiO2 during calcination. Additionally, Zr–O bonds from the UIO-66-NH2 framework contribute to this peak, indicating the presence of zirconium oxide. The second peak, located around 531.1 eV, is assigned to surface hydroxyl groups (–OH), which are commonly found on the surface of Ti3C2 as termination groups and may also be present due to interactions between the UIO-66-NH2 framework and atmospheric moisture. The peak at 532 eV is likely due to carbonyl groups (C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O) from the organic linker in the UIO-66-NH2 structure, which contains functional groups such as amides or carboxyls.41,42 As for the N 1s spectrum shown in Fig. 3(E), two peaks are observed at 399.2 eV and 400.1 eV, which can be attributed to the –NH2 group bonded to the phenyl ring (PhNH2) and the protonated amidogen form (PhNH3+), respectively.43,44 These peaks confirm the presence of the –NH2 group in the material.
O) from the organic linker in the UIO-66-NH2 structure, which contains functional groups such as amides or carboxyls.41,42 As for the N 1s spectrum shown in Fig. 3(E), two peaks are observed at 399.2 eV and 400.1 eV, which can be attributed to the –NH2 group bonded to the phenyl ring (PhNH2) and the protonated amidogen form (PhNH3+), respectively.43,44 These peaks confirm the presence of the –NH2 group in the material.
3.2 Electrochemical performance of 50% UiO-66-NH2@Ti3C2-C
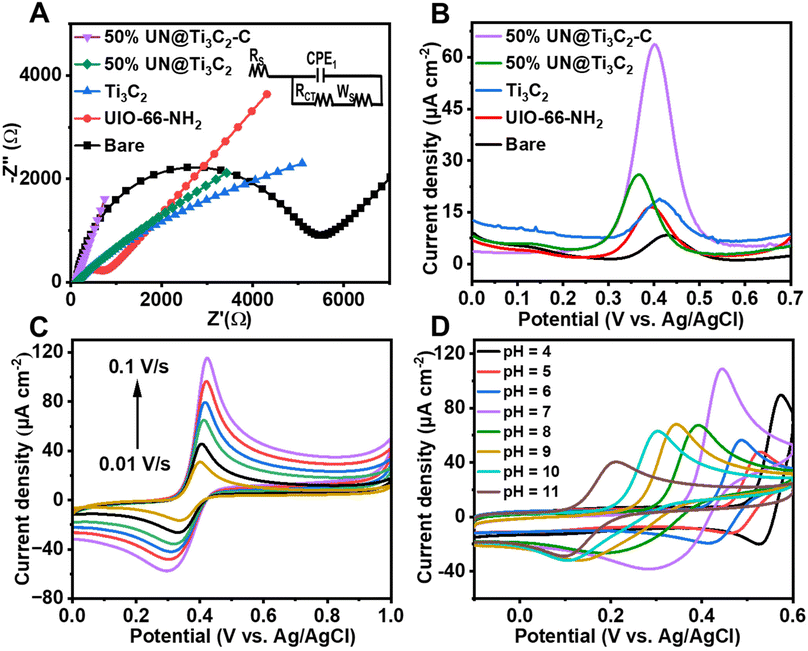
Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) was conducted to assess the interfacial properties of different modified electrodes immersed in a [Fe(CN)6]3−/4− redox probe solution containing 0.1 M KCl. The electrodes investigated included unmodified bare GCE, UIO-66-NH2/GCE, Ti3C2/GCE, 50% UN@Ti3C2/GCE and 50% UN@Ti3C2-C/GCE. This method was chosen due to its effectiveness in characterizing electrode interfaces. Fig. 4(A) shows different characteristics of Nyquist-plots fitted for the Randle's equivalent circuit (inset of Fig. 4(A)) where ‘Rct’ stands for the charge transfer resistance of the semicircle, and it controls the kinetics of electrons on the electrode surface while ‘Rs’ stands for the resistance of solution, ‘Cdl’ stands for double layer capacitance and ‘W’ denotes the Warburg constant. It can be noticed that the bare GCE shows a large charge transfer resistance with an Rct value of 4972.4 Ω. The Rct value for UIO-66-NH2/GCE is found to be 591.5.7 Ω, reflecting the improved electron transfer due to the MOF's high surface area and porous structure, which facilitate a better interaction between the electrode and electrolyte. For Ti3C2, the Rct value was found to be 130 Ω. When Ti3C2 was incorporated into the composite, the charge transfer resistance decreased with the 50% UN@Ti3C2 composite showing an Rct of 105 Ω and the 50% UN@Ti3C2-C composite further decreasing it to 87 Ω, indicating the optimal balance between the MOF and MXene leading to excellent electron transfer capability. These results highlight the synergistic effect between UIO-66-NH2 and Ti3C2 in enhancing the electrochemical performance of the electrode. The excellent conductivity and large specific surface area of Ti3C2 combined with the porous nature of UIO-66-NH2 provide abundant active sites for electron transfer and analyte adsorption. This significantly improves the electrode's sensitivity and efficiency in electrochemical sensing applications. The optimal performance observed with the 50% UN@Ti3C2 composite suggests that balancing the proportion of MXene is crucial for maximizing sensor performance. CV curves of numerous modified electrodes in the redox solution comprising [Fe(CN)6]3−/4− were recorded and the same results were obtained as shown in Fig S2.† To calculate the effective electroactive surface area of the modified electrode we use the Randles–Sevcik equation.15,45| Ip = (2.69 × 105)n3/2AC × D1/2v1/2 |
To further assess the performance of the electrochemical sensor using six different types of modified electrodes, DPV responses of various modified electrodes, including bare GCE, UiO-66-NH2, 50% UN@Ti3C2 and 50% UN@Ti3C2-C, in 48 μM acetaminophen solution at pH 7 (PBS) are shown in Fig. 4(B). The current density (μA cm−2) is plotted against the applied potential (V), demonstrating a clear enhancement in the current response with the addition of MXene. The bare electrode shows the lowest current response, indicating poor sensitivity for acetaminophen detection. The UiO-66-NH2 modified electrode slightly improves the current signal but the highest sensitivity is observed with the 50% UN@Ti3C2-C modified electrodes suggesting that this specific composition optimizes the balance between conductivity and active surface area. The incorporation of Ti3C2 improves electron transfer kinetics, while UiO-66-NH2 provides additional active sites for acetaminophen interaction, resulting in higher sensitivity. Increasing the MXene content from 20% to 50% improves the sensor performance, but beyond 50%, the increase in MXene does not result in further enhancement, as seen in Fig S3.† This suggests that 50% MXene provides the optimal composition for AP sensing.
3.3 Influence of pH
The pH of the supporting electrolyte significantly influences the electrochemical characteristics of the working electrode in sensing the target analyte. Hence, we investigated the impact of pH on the response of AP (48 μM) using CV with the 50% UN@Ti3C2-C/GCE sensor. pH was controlled using 0.1 M PBS, ranging from 4.0 to 11 in CV voltammograms as shown in Fig. 4(D). Notably, the oxidation peak current response for AP was found to be maximal at pH 7.0. Consequently, pH 7.0 was selected as the optimal value for further AP sensing research in this study. Additionally, as illustrated in Fig S4(B),† the oxidation peak potential (Ep) of AP exhibited a linear relationship with pH. Specifically, as the pH increased, the linear equations describing this relationship are as follows:| Ep = −0.049 ± 0.002 pH + 0.7821 ± 0.01 (R2 = 0.9936) |
The slope values of −0.049 V pH−1 were also observed, which is smaller than the Nernst equation calculated value of 0.059 V pH−1 suggesting that the electrooxidation of AP is a two proton and two electron system.3,46
Nernst equation:
However, according to the results, the possible mechanism of AP electrochemical sensing is demonstrated in Scheme 1.
Furthermore, for the peak current change, Ipc firstly decreases from 4 to 5 and then increases and at pH 7 it shows the maximum current, and thereafter by increasing the pH to 11 the current decreases, as shown in Fig S4(A).†
3.4 Influence of scan rate
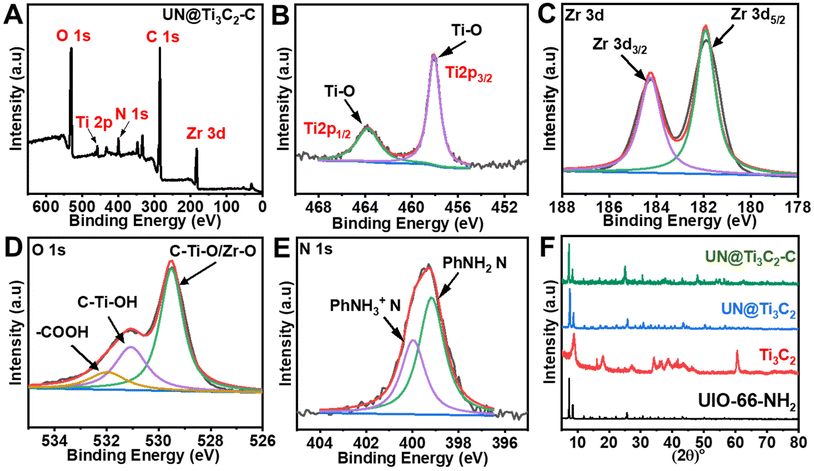
The effect of scan rate on the current values of AC is investigated at different scan rates from 0.01 to 0.1 V s−1 with 50% UN@Ti3C2-C/GCE. As shown in Fig. 4(C), both anodic and cathodic currents increase with the increase in scan rate from 0.01 to 0.1 V s−1. To understand how electrode reactions work, a calibration plot is drawn between scan rates and peak current values, as shown in Fig S5(A).† These results confirm that a mass diffusion-controlled process is involved in the AP redox reactions at the surface of 50% UN@Ti3C2-C/GCE. Moreover, the oxidation peak potential is linearly related to the log of the scan rate and follows the equations Epa = 0.042 ± 0.001 + 0.446 ± 0.002 (R2 = 0.9875) and Epc = 0.065 ± 0.005 + 0.257 ± 0.007 (R2 = 0.9714), as shown in Fig S5(B).† Based on47 theory, the value of charge transfer coefficient (α) could be found using the following equation.48where Ka is the slope of Epavs. log
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) v (0.04271) and Kc is the slope of Epavs. log
v (0.04271) and Kc is the slope of Epavs. log![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) v (0.0651). According to the formula, α was calculated to be 0.37. According to47 theory, the slopes of the lines were equal to 2.3RT/(1 − α)nF and −2.3RT/αnF for the anodic and cathodic peaks, respectively. The number of electrons involved in the reaction of AP is 2. Furthermore, the heterogeneous electron transfer rate constant (ks) was evaluated according to the following equation:
v (0.0651). According to the formula, α was calculated to be 0.37. According to47 theory, the slopes of the lines were equal to 2.3RT/(1 − α)nF and −2.3RT/αnF for the anodic and cathodic peaks, respectively. The number of electrons involved in the reaction of AP is 2. Furthermore, the heterogeneous electron transfer rate constant (ks) was evaluated according to the following equation:where ‘R’ stands for the ideal gas constant, F is Faraday's constant, ΔEp is the value for peak potential shift, and n indicates the number of electron transfers. The value of ks was calculated to be 1.6745 s−1 and 1.5936 s−1 for ΔEpa and ΔEpc respectively. The high value of ks indicates that 50% UN@Ti3C2-C/GCE could effectively improve the electron transfer between the surface of the electrode and electrolyte solution.20,45
3.5 Determination of AP (sensitivity)
To investigate the sensitivity of 50% UN@Ti3C2-C/GCE under optimal conditions following the addition of AP (PBS, pH = 7.0), DPV has been employed. By increasing the concentration of AP, the oxidation peak current values increased constantly as shown in Fig. 5(A). Moreover, Fig. 5(B) shows the calibration plot between AP concentrations and oxidation peak current which matches the linear regression equation y = 1.235 ± 0.01 + 6.455 ± 0.66 from 0.032 μM to 160 μM linear range with R2 = 0.9983. The limit of detection (LOD) and limit of quantification (LOQ) were calculated to be 0.010 μM and 0.15 μM using equations of IUPAC, LOD = 3S/m and LOQ = 10S/m respectively. In these equations, S is the standard deviation of blank (no analyte) and m is the slope of the calibration curve. The sensitivity was estimated to be 1.235 μA μM−1 cm−2 which can be calculated by dividing the slope of the calibration plot by the surface area of the electrode. Furthermore, the analytical performance of the proposed electrochemical sensor based on the 50% UN@Ti3C2-C composite for AP sensing was compared with traditional methods and previously reported electrochemical sensors in terms of detection method, LOD, and linear range (Table 1). This comparison highlights the superior sensitivity and broader linear range of the proposed sensor, demonstrating its effectiveness in AP detection. By integrating the unique properties of UIO-66-NH2 and MXene, the sensor exhibits enhanced electrochemical performance providing improved detection limits and selectivity compared to traditional sensors.| Traditional methods | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Method | LOQ | LOD | Linear range | Ref. |
| UV spectrophotometry | 0.0869 μg mL−1 | 0.0287 μg ml−1 | 2–10 μg ml−1 | 49 |
| GC-MS | 20.00 μg mL−1 | 6.00 μg mL−1 | 75–500 μg mL−1 | 50 |
| HPLC | 1.7 × 106 M | 5 × 107 M | 10 μg L−1–5 mg L−1 | 51 |
| HPLC | 0.11 μg mL−1 | 0.04 μg mL−1 | 1–300 μg/mL | 52 |
| HPLC | 0.2 μg mL−1 | 0.067 μg mL−1 | 0.2 μg mL−1–75 μg mL−1 | 53 |
| HPLC | 2.13 μg mL−1 | 0.64 μg mL−1 | 10–400 μg mL−1 | 50 |
| Electrochemical sensors | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sensor material | Detection method | LOD (μM) | Linear range (μM) | Ref. |
| Co–N–C@PC/GCE | DPV | 0.034 | 0.1–25 | 54 |
| N-HKUST-1/Au/GCE | DPV | 0.16 | 1–4448.4 | 55 |
| ZnO-MoO3-C/SPE | DPV | 1.14 | 2.5–2000 | 56 |
| MXene/SPE | DPV | 0.048 | 0.25–2000 | 57 |
| Ti3C2Tx/MWCNT/GCE | DPV | 0.23 | 1.0–90.1 | 58 |
| UiO-66-NH2/CNTs/GCE | DPV | 0.009 | 0.03–2.0 | 24 |
| 50% UN@Ti3C2-C/GCE | DPV | 0.010 | 0.032–160 | This work |
3.6 Selectivity, reproducibility, and stability
To determine the selectivity of 50% UN@Ti3C2-C/GCE, we perform DPV measurements against different possible interfering species including dopamine, ascorbic acid, nicotinic acid, L-histidine, lauric acid, glucose, citric acid, anions and cations that may cause interference. A distinctive response can be seen in Fig. 5(C) upon the addition of 48 μM AP in 0.1 M PBS at pH 7.0. In the potential window of −0.1 to 0.6, a 10-fold higher concentration of each of the species does not show any significant interference. Dopamine and ascorbic acid show peaks but they do not show a significant effect on AP's current peak. So, the mentioned results confirmed that this sensor is highly selective. The reproducibility tests were carried out in 0.1 PBS containing 40 μM AP under the same experimental conditions. Ipa was measured at the five different electrodes through DPV and relative standard deviation (RSD) was calculated to be 1.34% as illustrated in Fig. 5(D). Furthermore, the sensor's stability was examined by storing the electrode for periods of 7, 15, and 21 days before use, and the peak currents achieved were 98.1% (RSD = 0.72%), 97.6% (RSD = 1.09) and 96.8% (RSD = 1.62%) of the initial current signal, respectively, as shown in Fig S6.† The results demonstrate the good reproducibility and stability of this sensor.3.7 Mechanism
The synthesis of a UN/Ti3C2 composite, followed by calcination at 300 °C under an argon atmosphere, offers an efficient approach for the electrochemical detection of AP. UIO-66-NH2, a MOF formed by Zr4+ ions and 2-aminoterephthalic acid, provides high porosity and amine groups that enhance AP adsorption. Ti3C2 contributes superior conductivity and functional groups (–OH,![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O) that improve electron transfer during sensing.
O) that improve electron transfer during sensing.
During synthesis, MXene integrates with or attaches to the MOF, enhancing dispersion and performance. Calcination stabilizes the composite, retaining the MOF's porosity and amine functionality while dehydrating MXene and partially modifying its surface groups. Minor TiO2 formation during calcination strengthens the composite via Zr–O–Ti bonds, with additional hydrogen bonding enhancing structural stability.
The composite's high surface area and functional groups enable effective AP adsorption through hydrogen bonding and π–π interactions, and the amine groups (–NH2) in UIO-66-NH2 act as adsorption sites for acetaminophen. The –NH2 groups form hydrogen bonds with the hydroxyl (–OH) group on the AP molecule. The aromatic ring of the 2-aminoterephthalic acid linker interacts with the aromatic ring of AP through π–π stacking, further stabilizing the adsorption. Zr4+ ions act as catalytic sites in this system due to their Lewis acidic properties, which enables coordination with the electron-rich hydroxyl and amino groups of acetaminophen. This coordination enhances the electrophilicity of the AP molecule, facilitating the oxidation process to the reactive metabolite N-acetyl-p-benzoquinone imine (NAPQI). The Zr4+ ions can also stabilize the transition states during oxidation, lowering the activation energy and promoting faster electron transfer.59,60 Moreover, Ti3C2 ensures fast electron transfer during the oxidation of AP to NAPQI as presented in Fig. 6. The presence of TiO2, formed during calcination, further enhances the catalytic activity by providing additional sites for electron transfer, contributing to the overall efficiency of the sensor. This combination creates a robust, reusable sensor material with high sensitivity and selectivity, suitable for practical applications and further optimization.
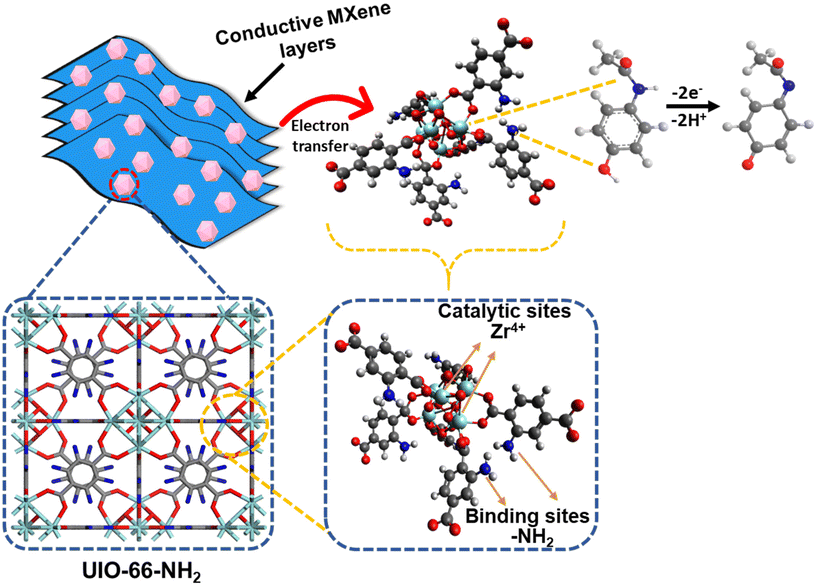 | ||
| Fig. 6 Schematic representation of the sensing mechanism for AP using the UN@Ti3C2-C composite electrode. | ||
3.8 Determination of acetaminophen in real samples
To assess the practical utility of the fabricated 50% UN@Ti3C2-C sensor, recovery experiments were conducted using real-world water samples collected from tap water, the Yangtze River, and East Lake. The standard addition method was employed for the recovery experiments, where two concentrations of AP (10 μM and 20 μM) were added to three different water samples. As shown in Table 2, the recovery rates for AP ranged from 98.5% to 111.5%, with RSD values below 5%. These findings confirm the feasibility and reliability of the designed sensor for the electrochemical detection of AP in real-world water samples.| Samples | Added (μM) | Found (μM) | Recovery (%) | RSD (%, n = 3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tap water | 10 | 9.85 | 98.5 | ±1.69 |
| 20 | 19.82 | 99.1 | ±1.87 | |
| Yangtze river | 10 | 10.3 | 103 | ±2.63 |
| 20 | 20.7 | 102.7 | ±1.98 | |
| East lake | 10 | 11.15 | 111.5 | ±3.52 |
| 20 | 21.45 | 107.2 | ±2.83 |
4. Conclusion
In conclusion, a highly sensitive and selective electrochemical sensor for AP was successfully developed using a composite of UIO-66-NH2 and Ti3C2, synthesized via a one-step hydrothermal process. The calcination at 300 °C under argon resulted in enhanced electrochemical properties, driven by TiO2 formation and increased interlayer spacing on the MXene surface. The 50% UN@Ti3C2-C electrode demonstrated excellent electrochemical activity, enabling rapid and quantitative detection of AP with a broad linear range (0.032–160 μM) and an ultra-low detection limit of 10 nM. The sensor's successful application in real water and pharmaceutical tablet samples highlights its practicality and potential for real-world monitoring of AP, offering a reliable and efficient approach for environmental and pharmaceutical analysis.Data availability
The data supporting this article have been included as part of the ESI.† Additional data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.Conflicts of interest
The authors report no declarations of interest.Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support from the National Key Research and Development Program of China Sino-Austrian intergovernmental industry-university-research cooperation project (Project No. 2022YFE0117000), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (HUST: YCJJ202203008), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (52171069 and 22005109), and the Open Project Program of Hubei Key Laboratory of Materials Chemistry and Service Failure (2020MCF02).References
- S. Sekar, J.-S. Yun and S. Lee, Environ. Res., 2023, 239, 117293 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- F. S. Larsen and J. Wendon, Intensive Care Med., 2014, 40, 888–890 Search PubMed.
- Y. Yan, Z. Liu, P. Xie, S. Huang, J. Chen, F. Caddeo, X. Liu, Q. Huang, M. Jin and L. Shui, J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2023, 634, 509–520 Search PubMed.
- R. Clark, V. Borirakchanyavat, A. Davidson, R. Williams, R. Thompson, B. Widdop and R. Goulding, Lancet, 1973, 301, 66–70 CrossRef PubMed.
- P. T. T. Ninh, N. D. Dat, M. L. Nguyen, N. T. Dong, H.-P. Chao and H. N. Tran, Environ. Res., 2023, 218, 114927 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- N. O. Erhunmwunse, I. Tongo and L. I. Ezemonye, Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf., 2021, 208, 111482 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- I. Cipriani-Avila, J. Molinero, M. Cabrera, E. J. Medina-Villamizar, M. V. Capparelli, E. Jara-Negrete, V. Pinos-Velez, S. Acosta, D. L. Andrade and M. Barrado, Sci. Total Environ., 2023, 866, 161340 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. Van der Oost, J. Beyer and N. P. Vermeulen, Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol., 2003, 13, 57–149 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- G. Sivarasan, V. Manikandan, S. Periyasamy, M. S. AlSalhi, S. Devanesan, P. S. M. Kumar, R. Rao Pasupuleti, X. Liu and H.-M. Lo, Environ. Res., 2023, 227, 115723 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. Tonoli, E. Varesio and G. Hopfgartner, J. Chromatogr. B:Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci., 2012, 904, 42–50 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Trettin, A. A. Zoerner, A. Böhmer, F.-M. Gutzki, D. O. Stichtenoth, J. Jordan and D. Tsikas, J. Chromatogr. B:Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci., 2011, 879, 2274–2280 Search PubMed.
- A. R. Khaskheli, A. Shah, M. I. Bhanger, A. Niaz and S. Mahesar, Spectrochim. Acta, Part A, 2007, 68, 747–751 Search PubMed.
- T. S. H. Pham, P. J. Mahon, G. Lai, L. Fu, C. T. Lin and A. Yu, Electroanalysis, 2019, 31, 1758–1768 CrossRef CAS.
- R. Manjunatha, D. H. Nagaraju, G. S. Suresh, J. S. Melo, S. F. D'Souza and T. V. Venkatesha, Electrochim. Acta, 2011, 56, 6619–6627 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Iftikhar, A. Aziz, G. Ashraf, Y. Xu, G. Li, T. Zhang, M. Asif, F. Xiao and H. Liu, Food Chem., 2022, 395, 133642 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. C. N. Ngwem, J. C. Kemmegne-Mbouguen, H. W. Langmi, N. M. Musyoka and R. Mokaya, ChemistrySelect, 2022, 7, e202202308 Search PubMed.
- S. B. Matt, S. Raghavendra, M. Shivanna, M. Sidlinganahalli and D. M. Siddalingappa, J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater., 2021, 31, 511–519 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Kang, J. Wang, H. Wu, J. Liu, I. A. Aksay and Y. Lin, Talanta, 2010, 81, 754–759 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. J. Ahmed, S. Perveen, S. G. Hussain, A. A. Khan, S. M. W. Ejaz and S. M. A. Rizvi, Chem. Pap., 2023, 77, 2275–2294 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. U. Alam, Y. Qin, M. M. Howlader, N.-X. Hu and M. J. Deen, Sens. Actuators, B, 2018, 254, 896–909 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Kenarkob and Z. Pourghobadi, Microchem. J., 2019, 146, 1019–1025 CrossRef CAS.
- P. K. Kalambate, Dhanjai, A. Sinha, Y. Li, Y. Shen and Y. Huang, Microchim. Acta, 2020, 187, 1–12 CrossRef PubMed.
- E. Mari, M. Duraisamy, M. Eswaran, S. Sellappan, K. Won, P. Chandra, P.-C. Tsai, P.-C. Huang, Y.-H. Chen and Y.-C. Lin, Microchim. Acta, 2024, 191, 1–14 CrossRef PubMed.
- Y. Li, Y. Shen, Y. Zhang, T. Zeng, Q. Wan, G. Lai and N. Yang, Anal. Chim. Acta, 2021, 1158, 338419 Search PubMed.
- A. Mir, M. Shabani-Nooshabadi and N. Ziaie, Chemosphere, 2023, 338, 139427 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Tang, Z.-Z. Hui, T. Hu, X. Cheng, J.-H. Guo, Z.-R. Li and H. Yu, Rare Met., 2022, 41, 189–198 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Wang, X. Liu, N. K. Demir, J. P. Chen and K. Li, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2016, 45, 5107–5134 Search PubMed.
- R. Rani, A. Deep, B. Mizaikoff and S. Singh, J. Electroanal. Chem., 2022, 909, 116124 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Zhang, H. Guo, J. Zhang, L. Sun, Z. Pan, B. Liu and W. Yang, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2022, 169, 016517 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Pan, S. Li, L. Zhang, F. Li, Z. Zhang, T. Yu and D. Zhang, J. Energy Storage, 2022, 55, 105415 CrossRef.
- Y. Li, Y. Liu, Z. Wang, P. Wang, Z. Zheng, H. Cheng, Y. Dai and B. Huang, Chem. Eng. J., 2021, 411, 128446 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Zhang, C. Li, Y. Chen, S. Li, F. Li, X. Wu, T. Gui, Z. Cao and Y. Wang, Microchim. Acta, 2023, 190, 267 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- F. Zhao, Y. Yao, C. Jiang, Y. Shao, D. Barceló, Y. Ying and J. Ping, J. Hazard. Mater., 2020, 384, 121358 Search PubMed.
- J. Zhang, S. Xu, W. Liu, Q. Wang and J. Qu, Talanta, 2024, 275, 126192 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- F. Liu, A. Zhou, J. Chen, J. Jia, W. Zhou, L. Wang and Q. Hu, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2017, 416, 781–789 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Wang, Y. Wu, J. Zhang, G. Li, H. Huang, X. Zhang and Q. M. L. Jiang, Mater. Lett., 2015, 160, 537–540 CrossRef CAS.
- P. A. Maughan, V. R. Seymour, R. Bernardo-Gavito, D. J. Kelly, S. Shao, S. Tantisriyanurak, R. Dawson, S. J. Haigh, R. J. Young and N. Tapia-Ruiz, Langmuir, 2020, 36, 4370–4382 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Z. Man, Y. Meng, X. Lin, X. Dai, L. Wang and D. Liu, Chem. Eng. J., 2022, 431, 133952 Search PubMed.
- R. Kang, Z. Zhang, L. Guo, J. Cui, Y. Chen, X. Hou, B. Wang, C.-T. Lin, N. Jiang and J. Yu, Sci. Rep., 2019, 9, 9135 CrossRef PubMed.
- W. Zhong, J. Zou, Q. Yu, Y. Gao, F. Qu, S. Liu, H. Zhou and L. Lu, Food Chem., 2023, 402, 134379 Search PubMed.
- J. Wang, Q. Xu, Y. Yang, J. Liu, W. Kong and L. Shi, Talanta, 2024, 268, 125344 Search PubMed.
- M. Liu, Z. Zhang, M. Yang, P. Li, Y. Wang, Y. He and J. Yuan, Composites, Part A, 2022, 161, 107122 Search PubMed.
- M. Peñas-Garzón, M. J. Sampaio, Y. L. Wang, J. Bedia, J. J. Rodriguez, C. Belver, C. G. Silva and J. L. Faria, Sep. Purif. Technol., 2022, 286, 120467 CrossRef.
- J. Dong, X. Li, L. Wen, Y. Ma, J. Xu, H. Luo, J. Hou, C. Hou and D. Huo, Food Chem., 2024, 437, 137835 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Chen, M. Zhang, H. Zhang, X. Yan, J. Xie, J. Qi, X. Sun and J. Li, Environ. Res., 2021, 201, 111500 Search PubMed.
- X. Kong, Y. Wang, Q. Zhang, T. Zhang, Q. Teng, L. Wang, H. Wang and Y. Zhang, J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2017, 505, 615–621 Search PubMed.
- E. Laviron, J. Electroanal. Chem. Interfacial Electrochem., 1979, 101, 19–28 CrossRef CAS.
- J. R. Santos, D. S. Viégas, I. C. B. Alves, A. D. Rabelo, W. M. Costa, E. P. Marques, L. Zhang, J. Zhang and A. L. Marques, Electrocatalysis, 2019, 10, 560–572 Search PubMed.
- M. S. Kondawar, R. R. Shah, J. J. Waghmare, N. Shah and M. K. Malusare, Int. J. PharmTech Res., 2011, 3, 1603–1608 CAS.
- T. Belal, T. Awad and R. Clark, J. Chromatogr. Sci., 2009, 47, 849–854 CAS.
- J. Meyer and U. Karst, Chromatographia, 2001, 54, 163–167 CrossRef CAS.
- A. A. Mouhamed, B. M. Eltanany, N. M. Mostafa and A. H. Nadim, J. Chromatogr. Sci., 2024, 62(7), 627–634 CAS.
- T. A. Fernandes, J. P. Aguiar, A. I. Fernandes and J. F. Pinto, J. Pharm. Anal., 2017, 7, 401–405 CrossRef PubMed.
- K. Yang, H. Yang, Y. Zheng, H. Chen, W. Liu and X. Yang, Microchem. J., 2024, 110874 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Chen, C. Wang, M. Wang, L. Pan, D. Xu and J. Li, J. Environ. Chem. Eng., 2024, 12, 113448 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Liu, N. Zhang, X. Huang, Q. Wang, X. Wang and S. Wang, Microchem. J., 2021, 161, 105719 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Zhang, X. Jiang, J. Zhang, H. Zhang and Y. Li, Biosens. Bioelectron., 2019, 130, 315–321 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- E. Mari, M. Duraisamy, M. Eswaran, S. Sellappan, K. Won, P. Chandra, P.-C. Tsai, P.-C. Huang, Y.-H. Chen and Y.-C. Lin, Microchim. Acta, 2024, 191, 212 Search PubMed.
- X. He, F. Yin, X. Yi, T. Yang, B. Chen, X. Wu, S. Guo, G. Li and Z. Li, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2022, 14, 26571–26586 Search PubMed.
- J. Hajek, M. Vandichel, B. Van de Voorde, B. Bueken, D. De Vos, M. Waroquier and V. Van Speybroeck, J. Catal., 2015, 331, 1–12 Search PubMed.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available. See DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/d4nr04388j |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2025 |