Engineering the next generation of MXenes: challenges and strategies for scalable production and enhanced performance
Weizhai
Bao
 *ab,
Hao
Shen
a,
Guozhao
Zeng
a,
Yangyang
Zhang
a,
Yaoyu
Wang
*ab,
Hao
Shen
a,
Guozhao
Zeng
a,
Yangyang
Zhang
a,
Yaoyu
Wang
 a,
Dingyu
Cui
a,
Jingjie
Xia
a,
King
Jing
a,
He
Liu
ab,
Cong
Guo
ab,
Feng
Yu
a,
Dingyu
Cui
a,
Jingjie
Xia
a,
King
Jing
a,
He
Liu
ab,
Cong
Guo
ab,
Feng
Yu
 ab,
Kaiwen
Sun
ab,
Kaiwen
Sun
 *c and
Jingfa
Li
*c and
Jingfa
Li
 *ab
*ab
aInstitute of Advanced Materials and Flexible Electronics (IAMFE), School of Chemistry and Materials Science, Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology, Nanjing, 210044, China
bDepartment of Materials Physics, School of Chemistry and Materials Science, Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology, Nanjing, 210044, China. E-mail: weizhai.bao@nuist.edu.cn
cAustralian Centre for Advanced Photovoltaics, School of Photovoltaic and Renewable Energy Engineering, University of New South Wales, Sydney, 2052, Australia
First published on 13th February 2025
Abstract
Two-dimensional nanomaterials, such as MXenes, have garnered significant attention due to their excellent properties, including electrical conductivity, mechanical strength, and thermal stability. These properties make them promising candidates for energy storage and catalysis applications. However, several challenges impede their large-scale production and industrial application. Issues such as high production costs, safety concerns related to toxic etching agents, instability in oxidative environments, and the complex synthesis process must be addressed. In this review, we systematically analyze current methodologies for scaling up MXene production, focusing on the synthesis and etching of MAX phases, delamination strategies, and the production of MXene derivatives. We explore strategies for overcoming challenges like aggregation, oxidation, and cost, presenting optimization techniques for enhancing electrochemical performance and stability. The review also discusses the applications of MXenes in batteries and supercapacitors, emphasizing their potential for large-scale use. Finally, we provide an outlook on future research directions for MXene to develop safer and more cost-effective production methods to improve the performance of MXene in order to realize its commercial potential in energy technologies.
1. Introduction
Two-dimensional nanomaterials derived from van der Waals and non-van der Waals solids possess excellent physical and chemical properties brought about by the size effect, attracting widespread attention from researchers in the fields of large-scale energy storage. The atomic layers from van der Waals solids such as graphene and transition metal disulfides without dangling bonds can be facilely produced based on their van der Waals counterparts.1–4 In contrast, producing atomic layers from non-van der Waals solids is difficult owing to their strong chemical bonds in bulk. As non-van der Waals solids, MXenes are novel transition metal carbon/nitrides, two-dimensional materials with hexagonal compact crystal structures typically obtained by selective etching of the A-atom layer of the MAX phase, followed by ion intercalation and ultrasound-assisted stripping.5–8 Compared with other 2D materials, MXene has: (1) Superior electrical conductivity: Enables rapid charge transfer. (2) Large specific surface area: Provides abundant active sites and enhances storage capacity. (3) Robust mechanical properties: High flexibility and mechanical strength, ideal for flexible devices. (4) Excellent thermal stability: Suitable for high/variable-temperature applications. (5) Tunable surface chemistry: Controllable functional groups allow electrochemical property modulation via surface modification. (6) Rich interlayer chemistry: Intercalation chemical modulation further optimizes electrochemical performance. (7) High ionic conductivity: Improves ion transport efficiency in batteries. (8) Chemical stability: Maintains structural integrity for long-term applications. (9) Environmental friendliness: Reduced ecological impact during synthesis and utilization. Therefore, MXenes show promising applications in energy storage and catalysis.9–12So far, more than 30 kinds of MXene with different chemical and physical properties have been synthesized, and the current mainstream synthesis method is to produce MXene with hydrofluoric acid (HF) or in situ HF generation to etch MAX.13–15 However, the cost of managing highly toxic and corrosive HF and its associated chemical waste may be highly challenging at the industrial scale.16,17 In addition, the A atomic layer can be selectively etched by the high-temperature molten salt method, but due to the lack of hydrophilic functional groups (–OH/–O), it is difficult to obtain multilayer or single-layer MXene. In addition, MXene can also be obtained by etching the A-atom layer using electrochemical methods, but the low yield and the use of MAX as the electrode limit its large-scale production.18 Although streamlined pilot-scale production of MXenes, with comprehensive safety controls, has been demonstrated, there is still a strong requirement for a safe, environmentally friendly, and cost-effective method to reduce the toxic chemical waste, drive down the production cost of MXenes, and realize their wide industrial applicability.19–21
In order to realize the industrialization of MXene electrode materials, it is necessary to ensure the safety, environmental protection, low cost, simple process and large-scale replication of the synthesis process. At the same time, the shortcomings of MXene's poor stability in an oxygen environment should be solved. It is gratifying that the integration of MXenes with other materials effectively combines the engineering properties of different materials in a complementary way. Wei's team22 developed a continuous and controllable preparation strategy to construct high-density MXene fiber nanocomposites with high mechanical strength, high toughness and high electrical conductivity. Based on the high-density MXene fiber nanocomposites prepared, large-area MXene fabric was prepared by weaving and artificial weaving. Professor Han's team23 has developed a simple, continuously controllable and additive/binder-free method for the preparation of pure MXene fibers by large-scale wet spinning. MXene nanosheets (average transverse size 5.11 μm2) are highly concentrated in water and do not form aggregates or undergo phase separation. The introduction of ammonium ions during coagulation can successfully assemble the MXene nanosheets into soft, meter-length fibers with very high electrical conductivity (7713 S cm−1). In recent years, the research on large-scale production of MXene materials has been increasing, and a more comprehensive and systematic summary of large-scale preparation methods and applications of MXene is urgently needed.7,24,25
This review examines the research progress and future prospects of MXene composite materials from an industrialization perspective, focusing on the developments in the scaling up of MXene precursors, MXenes, and their derivatives. The article systematically summarizes various aspects of scaling up MXene production, including the large-scale synthesis and etching of the parent MAX phases, the large-scale delamination strategies for MXenes, and the mass production of MXene derivatives. Additionally, we discuss the roles and optimization strategies for MXenes and their derivatives to achieve the desired electrochemical performance and stability. The potential applications of MXenes in energy applications are also assessed (Fig. 1). Finally, we explore future directions for research on the large-scale production of MXenes from various perspectives and envision the commercial potential of MXenes.
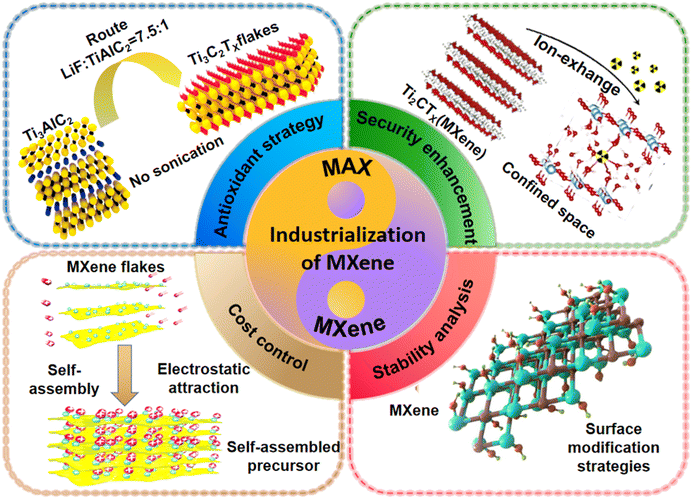 | ||
| Fig. 1 Optimization strategy of MXene scale preparation. Figure used in the top left corner: reproduced from ref. 14 with permission from Wiley-VCH, copyright 2016. Figure used in the top right corner: reproduced from ref. 15 with permission from Elsevier, copyright 2019. Figure used in the lower left corner: reproduced from ref. 20 with permission from Wiley-VCH, copyright 2018. Figure used in the lower right corner: reproduced from ref. 24 with permission from Elsevier, copyright 2023. | ||
2. Industrialization of MXene
MXenes have emerged as highly promising two-dimensional materials, primarily due to their unique two-dimensional structure, functional surface properties, exceptional conductivity, and robust stability. These characteristics have enabled their application across a diverse array of fields, including rechargeable batteries, supercapacitors, catalysts, electromagnetic shielding, electrochromic materials, antennas, and beyond. The industrialization of MXenes is propelled by the robust market demand for these materials. However, ensuring a sufficient and stable supply of raw materials remains a fundamental prerequisite for the successful industrialization of MXenes. Consequently, the pursuit of cost-effective industrial production methods for the MAX phase is imperative. A suitable synthesis process forms the cornerstone of MXene industrialization, necessitating the selection of a cost-effective, safe, high-yielding, and straightforward equipment-based synthesis process.26 The ultimate goal of MXene industrialization is the development of mature commercial products. While MXenes are more conducive to scientific exploration, the development of MXene-based products—such as inks, laminated papers, films, aerogels, and foams—that meet market demands is essential. Therefore, it is imperative to develop MXene-based products with mature markets while ensuring their superior performance.272.1. Synthesis of MAX
The large-scale preparation of MXenes requires the production of high-purity MAX phases capable of ensuring a stable and reliable supply. Research demonstrates that the selection of precursors and synthesis techniques significantly impacts the properties of MXenes. For example, in the synthesis of Ti3AlC2, an increase in aluminum content is correlated with higher yields of Ti3C2Tx and enhanced stability and electrical conductivity.28 Consequently, it is imperative to investigate and optimize the synthesis processes of the MAX phase to achieve the desired characteristics for MXene production.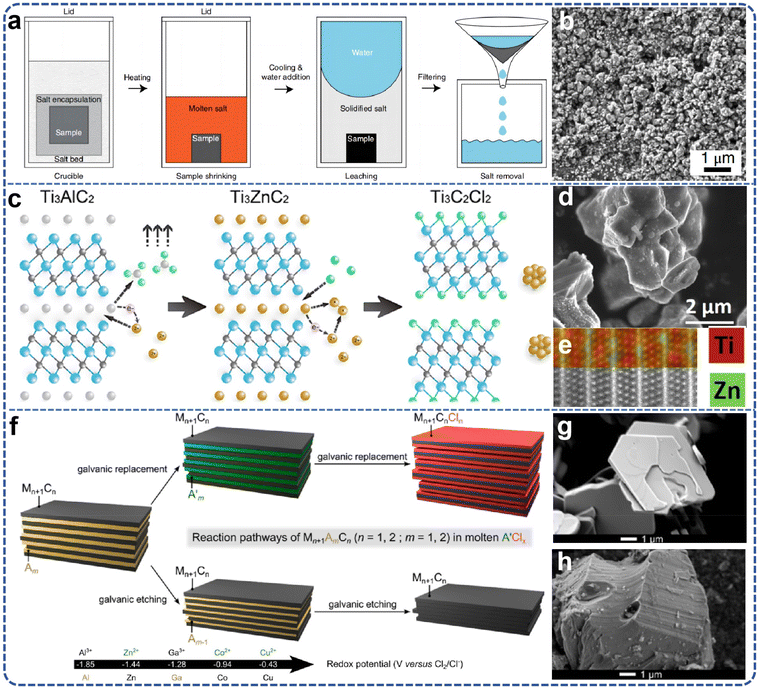 | ||
| Fig. 2 (a) The “molten salt protected synthesis/sintering” process; (b) scanning electron micrograph of synthesized Ti3SiC2. Reproduced from ref. 39 with permission from Nature, copyright 2019. (c) Synthesis roadmap of Ti3C2Cl2; (d) SEM image of Ti3ZnC2; (e) HR-STEM and the corresponding EDS map of Ti3ZnC2. Reproduced from ref. 40 with permission from American Chemical Society, copyright 2019. (f) Scheme of the galvanic reactivity of MAX-related phases in molten salts; the top branch corresponds to galvanic replacement, evidenced for Ti3AlC2; the bottom branch corresponds to galvanic etching, evidenced for Mo2Ga2C; SEM images of (g) Mo2Ga2C and (h) Ti3AlC2. Reproduced from ref. 42 with permission from American Chemical Society, copyright 2023. | ||
The demonstration of combined etching and insertion of Ti3AlC2 into molten zinc chloride potentially relates to “decompression” processes observed in organic material insertion into clay and mixed materials. The Mo2Ga2C case elucidates that, in addition to displacement, electrical etching can degrade layered structures, highlighting the interplay between the relative stabilities of the intercalated and etched phases and suggesting the potential for fine-tuning this reactivity via the parent phase composition and structure and the molten salt composition. Researchers identified significant interactions between MAX phase ceramic materials and particular oxides within chloride molten salts, observing distinctive A-site atomic lattice displacement behaviors. These findings underscore the intricate reactivity dynamics within molten salt environments and the potential for precise modulation of these interactions through judicious selection of phase compositions and molten salt chemistries.40–42 Due to the presence of non-conductive aluminum oxide within the product, the synthesized new material exhibits a low yield, and atomic resolution characterization poses significant challenges. Through a comprehensive investigation of a series of traditional MAX phase materials, including Ti3AlC2, Ti2AlC, V2AlC, Cr2AlC, and various high-temperature molten salt chlorides, it has been determined that aluminum chloride, owing to its low boiling point, is easily separated from MAX phase products at elevated temperatures. Consequently, a series of novel MAX phase materials, namely Ti3ZnC2, Ti2ZnC, V2ZnC, and Cr2ZnC, has been synthesized for the first time with high quality (Fig. 2f–h). Portehault et al.'s43 research has elucidated the intrinsic relationship between the displacement process, the chemical bond characteristics of the MAX phase, and the coordination structure of ZnCl2 molten salts. Transition metal chloride molten salts, represented by ZnCl2, are generally recognized as strong Lewis acids due to the presence of coordinately unsaturated Zn2+ ions within the molten ZnCl2. These Zn2+ ions serve as potent electron acceptors, akin to the role played by H+ ions in acid solutions. The Zn2+ ions interact with the weakly bonded A-layer atoms (Al) in the MAX phase materials, such as Ti3AlC2, converting them into low-boiling-point AlCl3, which subsequently volatilizes. The in situ-reduced zinc atoms further occupy the vacancies left by the aluminum atoms, resulting in the formation of a MAX phase with zinc occupying the A site. The MAX phase material, characterized by zinc in the A position, is inherently unstable at 1300 °C and can only exist at lower temperatures (e.g., 550 °C). Low-temperature powder metallurgy sintering synthesis does not provide sufficient energy for atomic rearrangement in accordance with the MAX phase atomic stacking, which accounts for the limitation in the composition of MAX phase materials. The synthesis strategy involving precise substitution of A-site atoms circumvents the high thermodynamic barriers and competitive phase formation typically associated with traditional powder metallurgy methods for MAX phase synthesis. Thus, this approach is anticipated to represent a general pathway for the synthesis of additional novel MAX phase materials.
2.2. Synthesis of MXene
The primary obstacle in achieving large-scale synthesis of MXene lies in the development of non-hazardous etching routes. The kinetics of etching are contingent upon the composition of the etchant, temperature, and particle size, all of which contribute to the distinct properties of the resultant MXene. The preparation of monolayer MXene necessitates careful consideration of stripper selection and operation method, as these factors significantly influence the final layer size, adsorbed molecules/ions, and performance across a broad spectrum of devices. As early as 2015, research endeavors were embarked upon to explore the large-scale preparation of 2D MXene.45 Large-scale production of few-layer MXene nanosheets was successfully achieved through organic base intercalation following etching with hydrofluoric acid, followed by manual shaking and ultrasonic stripping (Fig. 3a). The organic bases employed, such as TMAOH and TBAOH, are macromolecules that intercalate between the MXene layers, thereby increasing interlayer spacing and reducing interlayer forces. This results in uniformly dispersed MXene nanosheets after manual shaking or instrumental ultrasonic stripping. Subsequent to simple filtration, flexible, self-supported MXene films can be obtained. Other organic bases, such as n-butylamine, have also demonstrated efficacy in stripping MXene materials like V2CxTx and Ti3CNTx. Unlike the dimethyl sulfoxide intercalation–peeling method, which is limited to Ti3C2Tx, this organic base intercalation–peeling method is applicable to various MXene material systems. Given the simplicity of this preparation method and its versatility in peeling a wide array of MXenes, it facilitates the large-scale preparation of MXene aqueous solutions.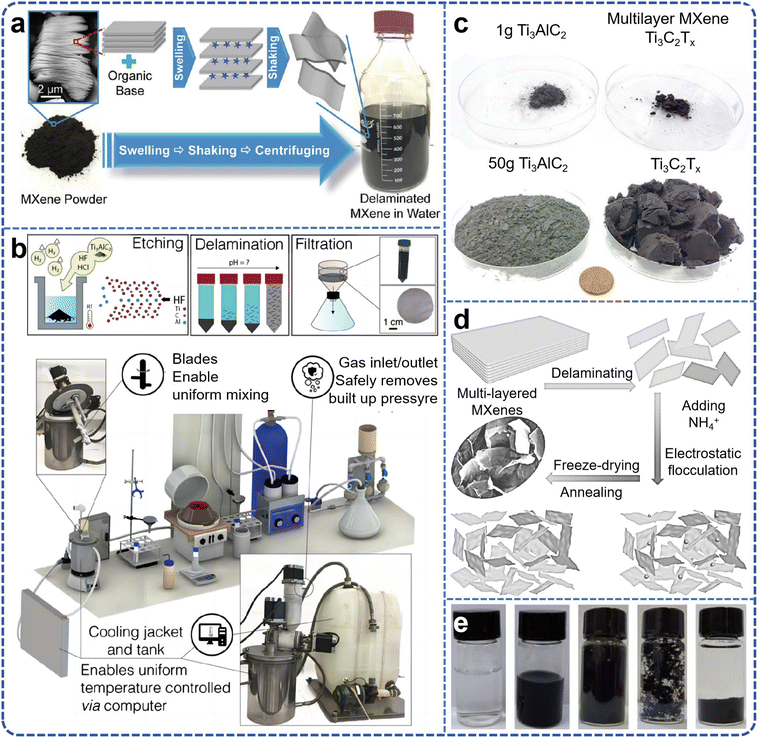 | ||
| Fig. 3 (a) Schematic for MXene delamination process by reacting MXenes with an organic base that causes multilayered MXene powder to swell significantly. Reproduced from ref. 45 with permission from The Royal Society of Chemistry, copyright 2015. (b) Schematic of MXene synthesis and 3D model of synthesis setup; (c) images of the precursor Ti3AlC2 MAX used in synthesis of the 1 and 50 g Ti3C2Tx batch sizes. Reproduced from ref. 46 with permission from Wiley-VCH, copyright 2020. (d) Schematic preparation process of few-layered Ti3C2Tx MXene powders; (e) sample example photo of preparation. Reproduced from ref. 53 with permission from American Chemical Society, copyright 2020. | ||
The initial synthesis of MXenes involved the selective removal of aluminum from Ti3AlC2via the use of concentrated hydrofluoric acid (HF, 50 wt%). Subsequent studies elucidated that variations in etching duration result in a concomitant decline in HF concentration, subsequently influencing the morphological characteristics of the MXenes produced. Furthermore, the exfoliation of MXenes achieved exclusively through fluoride-ion solution etching is deemed inefficient and fraught with practical application shortcomings. In practical contexts, there is a greater propensity for the material to be in a reduced layering state (typically fewer than five layers of 2D material) to optimize its performance.48,49 Currently, the exfoliation of multilayer MXenes predominantly relies on the incorporation of organic bases or lithium ions, followed by the application of ultrasound to induce substantial material delamination. However, the use of ultrasound invariably results in the fragmentation of single-layer MXene material, generating a significant number of surface defects. This phenomenon leads to a diminution in material conductivity and stability, concurrently undermining the yield of the material.50 Li et al.51 devised a power-focused delamination strategy by scrutinizing the resistance and dynamics of delamination during MXene peeling, leveraging the distinctive structure of MXene. In essence, MXene's etched multilayer structure is sedimented via centrifugal precipitation, rendering it more amenable to peeling. Simultaneously, the impact force engendered by the vortex motion of the water flow is concentrated on a singular surface of the MXene sheet, effectively overcoming the interlayer forces of the MXene sheet and facilitating useful work. Conversely, in the minimally intensive layer delamination process, the energy derived from hand cranking predominantly transforms into the kinetic energy of the multilayer MXene block, with minimal provision to the lamellar layers to surmount the interlayer force. In the Power-Focused Delamination (PFD) process, the impact force induced by eddy currents is focused on the surface of MXene precipitates. Consequently, this methodology permits the application of concentrated shear to strip a single layer of MXene from the surface of multiple layers, yielding significantly higher outputs than those achieved through minimally intensive layer delamination. Upon completion of five PFD cycles, the yield of large layer defect-free Ti3C2Tx MXene nanosheets reached 61.2%, with a colloidal concentration of 20.4 mg mL−1, without any sonication. Wu et al.52 exploited the expansion phenomenon during water freezing, and the yield of MXene (Ti3C2Tx) nanosheets was notably augmented through a straightforward and repetitive freeze–thaw (FAT) technique. Via this approach, conspicuous microfolds emerged on the surface of large-sized MXene whilst its yield attained 39%. When FAT was integrated with ultrasound, albeit small-sized MXene nanosheets were yielded, the output soared to 81.4%, surpassing that of any previously reported synthesis methods. Han et al.53 systematically elucidated a strategy for liquid-phase flocculation (encompassing the ammonium ion method and its enhanced variant) based on the fundamental property of MXene (surface electronegativity).54 The infusion of positively charged ammonium ions disrupts the electrostatic equilibrium state of the MXene solution, leading to the spontaneous electrostatic aggregation and sedimentation of MXene nanosheets, accompanied by the decantation of water from the upper layer. This substantially abbreviates the cooling, drying, and lyophilization periods of the flocculated precipitate, ultimately expediting the preparation of less-layered MXene powders (as illustrated in Fig. 3d and e). MXene nanosheets are susceptible to oxidative degradation in aqueous solution, and the resultant MXene materials are ideally in a less-layered powder form, facilitating storage in an anhydrous and oxygen-free milieu. While freeze-drying can transform the MXene solution into a powder state, the entire procedure is time-consuming, yields are notably diminished, and agglomeration persists. Yang et al.26 innovated a supercritical rapid stripping method for the bulk preparation of diverse MXenes, supported by supercritical carbon dioxide. Under supercritical conditions (critical temperature Tc = 31.04 °C, critical pressure Pc = 7.38 MPa), CO2 molecules transition into a liquid phase.55 Enhanced molecular collisions between these CO2 molecules and the in situ-generated HF from NH4HF2 significantly accelerated HF's penetration into the MAX phase. Subsequently, the M–Al bonds within the MAX phase are severed to form aluminum salts, AlF3 and (NH4)3AlF6. These formed aluminum salts are progressively extruded from the MXene layer's interior, expediting the etching process. Ultimately, over a kilogram of MXene powder was synthesized within a mere four hours.
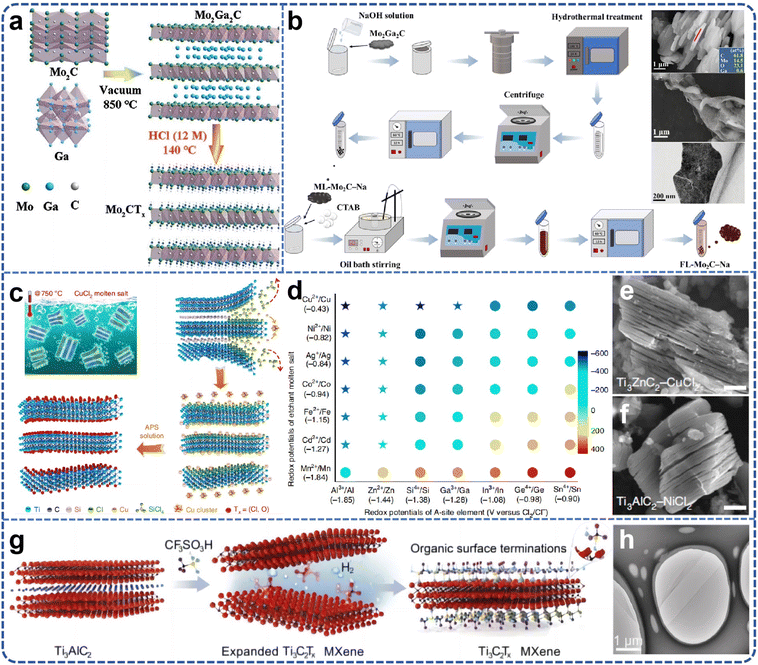 | ||
| Fig. 4 (a) Schematic illustration of the preparation procedure for fluoride-free Mo2CTx. Reproduced from ref. 56 with permission from Wiley-VCH, copyright 2021. (b) The schematic diagram and SEM and TEM images of Mo2C MXene synthesized from Mo2Ga2C by NaOH etching method. Reproduced from ref. 58 with permission from Tsinghua University Press, copyright 2023. (c) Schematic of Ti3C2Tx MXene preparation; (d) Gibbs free energy mapping (700 °C) guiding the selection of Lewis acid Cl salts according to the electrochemical redox potentials of A-site elements in MAX phases (x axis) and molten salt cations (y axis) in Cl melts; SEM images reveal the typical accordion morphology of MXenes from different MAX phases etched by various Lewis acid Cl salts, such as (e), Ti3AlCN by CuCl2 and (f) Ti3AlC2 by NiCl2. Reproduced from ref. 61 with permission from Nature, copyright 2020. (g) Schematic illustration of the synthetic route; (h) TEM images of CF3SO3H–Ti3C2Tx. Reproduced from ref. 62 with permission from Wiley-VCH, copyright 2024. | ||
In 2019, laboratory researchers ascertained that the Ti3AlC2 MAX phase exhibits significant reactivity within ZnCl2 molten salts, with the Zn2+ cation functioning analogously to the H+ ion in HF acids, and the Cl− anion mimicking the behavior of F− to ultimately coordinate with M atoms. Consequently, this A-site elemental substitution reaction not only yielded a series of Mn+1ZnXn phases but also facilitated the realization of Mn+1XnCl2 MXene two-dimensional materials with Cl groups on the surface.59,60 However, the formation mechanism of Ti3C2Cl2 MXene from a chemical perspective remains inadequately elucidated. Li et al.61 proposed a generalized method for etching the MAX phases through direct redox coupling of elemental A and cations in Lewis acid molten salts (Fig. 4c). By modulating the chemistry of the MAX precursor and the composition of the Lewis acid melt, this synthetic pathway was extended to encompass, in addition to Zn, A-site elements such as Al, Si, and Ga derived from various MAX-phase precursors. For the first time, MXene synthesis was achieved from unconventional MAX-phase precursors, including Ti3SiC2 and Ta2AlC, via this method. Gibbs free-energy calculations guided the formation of various Lewis acids, and MAX phases were matched based on these calculations, thereby expanding the range of MAX phases available for MXene synthesis and offering more options for scalable preparation (Fig. 4d–f). The Ti3C2–MXene anode produced by this molten salt synthesis method can deliver a lithium storage capacity of up to 738 C g−1 (205 mA h g−1), characterized by a high charge/discharge rate and pseudocapacitance-like electrochemical properties. Most etching methods entail multi-step delamination reactions, high temperatures, and intricate separation steps, which constrain the scalable preparation and direct application of single or low-layer MXene nanosheets. Even with the aid of an insertion agent, producing single nanosheets from MXenes with an accordion-like structure remains a formidable challenge. Lu et al.62 developed a novel scheme for the synthesis of high-quality single- or few-layered 2D MXene using organic Lewis acid (trifluoromethanesulfonic acid) etching (Fig. 4g). This scheme demonstrates that the etching reaction at room temperature can form single- or few-layered Ti3C2Tx, which can be further converted into –CF3SO3-terminated Ti3C2Tx nanosheets with moderate size (approximately 4 μm), monolayer thickness of about 1.6 nm, and a single-to-few-layer yield exceeding 70% (Fig. 4h). Simultaneously, the encapsulation of the –CF3SO3 group endows the Ti3C2Tx nanosheets with excellent colloidal stability, enabling stable dispersion in aqueous solution for at least one month. The study found that the proposed etching strategy is likely to facilitate the development of other types of MXenes in the future, suggesting that surface engineering may be a viable strategy for synthesizing functional MXenes with enhanced stability. Lin et al.63 combined the molten salt method for MAX phase preparation with the two-dimensional MXene preparation via molten salt Lewis acid etching, using elemental monomers as raw materials. They utilized molten salt to prepare the MAX phase in situ at high temperature and then cooled down to 700 degrees Celsius to add Lewis acid salt for in situ etching of two-dimensional MXene materials. The etching holding time is only 10 minutes to achieve a superior etching effect (Fig. 5a and b). The total preparation time is less than 8 hours, including the heating and cooling processes, which is significantly shorter than previous MXene preparation strategies. Furthermore, the process employed low-melting-point eutectic salt melting to isolate the reactants from the air, eliminating the need for inert gas protection and greatly simplifying the preparation conditions. The high-temperature molten salt etching strategy usually takes tens to hundreds of hours, the preparation conditions are harsh, and not only is the preparation efficiency low, but also difficult to expand. Yang et al.64 proposed a scalable low-temperature molten salt etching strategy (LTMS), using 130 °C NH4HF2 molten salt as the etching agent, capable of achieving high-quality ultrafast preparation of Ti3C2Tx MXene within 5 minutes. Compared with other traditional preparation methods, this strategy not only improves the preparation speed of MXene by 1–2 orders of magnitude, but also avoids the use of corrosive acids under mild preparation conditions. The enhanced thermal motion and improved diffusion of molten NH4HF2 molecules significantly accelerated the etching process of the MAX phase, resulting in the preparation of Ti3C2Tx MXene in as little as 5 minutes. The versatility of the LTMS method makes it a valuable method for the rapid synthesis of various MXenes, including V4C3Tx, Nb4C3Tx, Mo2TiC2Tx, and Mo2CTx. The LTMS method is easy to scale up and can yield more than 100 grams of Ti3C2Tx in a single reaction. The obtained LTMS–MXene shows excellent electrochemical performance in supercapacitors, which strongly proves the effectiveness of the LTMS method. Multilayered MXene prepared by the Lewis acid molten salt etching method is highly challenging to delaminate into monolayers due to hydrophobicity and strong interactions between MXene sheets caused by halogen end groups. The currently employed delamination methods do not involve hazardous chemicals such as n-butyllithium or sodium hydride, which poses difficulties for scale-up applications and restricts the practical application of such MXenes. Lithium chloride (LiCl) effectively delaminates MXene while preserving its surface chemistry. LiCl is a benign, abundant, and inexpensive salt. The use of LiCl as an intercalator ensures that the intrinsic properties of Ti3C2Cl2 MXene remain unchanged, especially its prepared monolayers exhibiting an electrical conductivity of 8000 S cm−1, which is maintained even after one week of exposure to 95% humidity.65
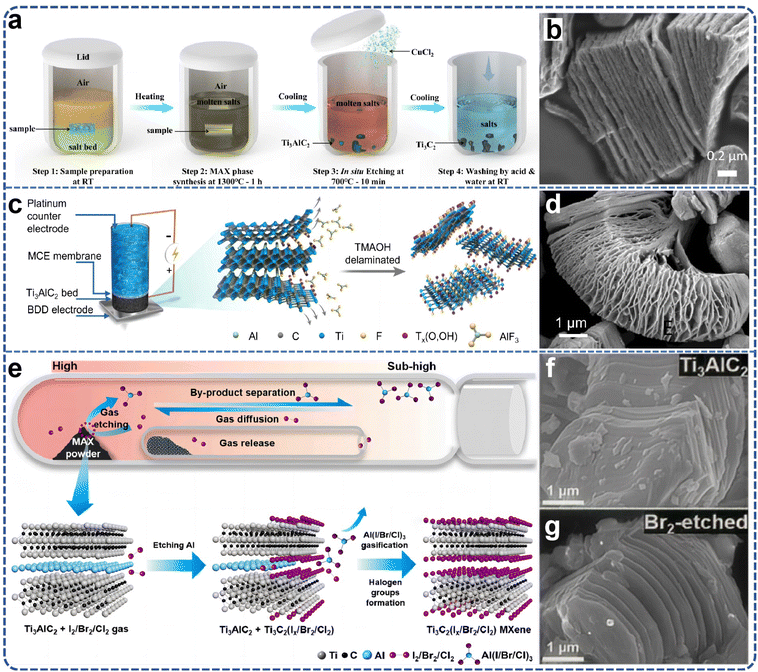 | ||
| Fig. 5 (a) Lin et al. synthesized Ti3C2Tx MXene from elemental Ti, Al and C powders in a one-pot process; (b) related SEM images of Ti3C2Tx prepared. Reproduced from ref. 63 with permission from Nature, copyright 2021. (c) Schematic diagram of a small packed-bed electrochemical reactor for the electrochemical preparation of MXenes; (d) SEM image of MXene prepared by electrochemistry. Reproduced from ref. 66 with permission from Wiley-VCH, copyright 2023. (e) Schematic of gases etching to prepare MXenes; (f) and (g) SEM image of Ti3AlC2 prepared by gas etching. Reproduced from ref. 68 with permission from Elsevier, copyright 2024. | ||
2.3. Synthesis of MXene derivatives
Currently, traditional fibers, gels, films, and other raw materials hold a significant position in the market, being extensively utilized in energy storage, environmental governance, biomedical applications, and electronic devices. However, the practical application of these materials exhibits numerous deficiencies, including insufficient mechanical strength, limited electrical conductivity, inferior chemical stability, and other issues, which constrain their deployment in higher-end applications. The integration of MXene into fibers, gels, and films can markedly enhance the overall properties of these materials. For instance, MXene incorporated into fibers can bolster the strength and electrical conductivity of the fibers, MXene-infused gels can elevate the electrochemical properties and flexibility of the gels, and MXene-reinforced films can enhance the electrical conductivity and stability of the films. Thus, advancing the large-scale production of high-performance MXene-enhanced products can not only effectively augment the properties of existing materials and address the pressing demand for high-performance materials in the market but also catalyze the industrialization trajectory of MXene materials themselves. The scale-up of production can result in cost reductions via improvements in economic efficiency, facilitate the optimization and standardization of technology, and consequently, foster the extensive application and dissemination of MXene materials across diverse application domains.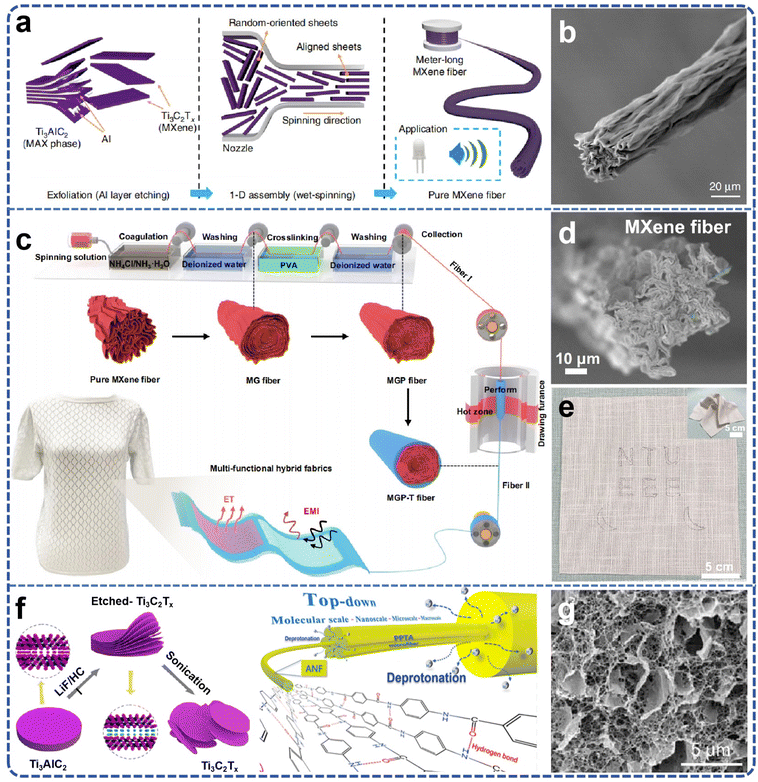 | ||
| Fig. 6 (a) Schematic illustration of the reconstruction of MXene single layers into MXene fibers; (b) SEM images of Ti3C2Tx MXene fiber. Reproduced from ref. 23 with permission from Nature, copyright 2020. (c) Fabrication of MGP-T fiber via continuous wet spinning and thermal drawing, and the formation of MXene-based textiles; (d) pure MXene fibers; (e) designed patterns woven into the cotton cloth under complex deformations (inset). Reproduced from ref. 22 with permission from Nature, copyright 2022. (f) ANF diagram of MXene preparation and stripping from aramid fibers; (g) SEM image of freeze-dried hydrogel, presenting a 3D ANF network with evenly distributed MXene nanosheets. Reproduced from ref. 75 with permission from American Chemical Society, copyright 2022. | ||
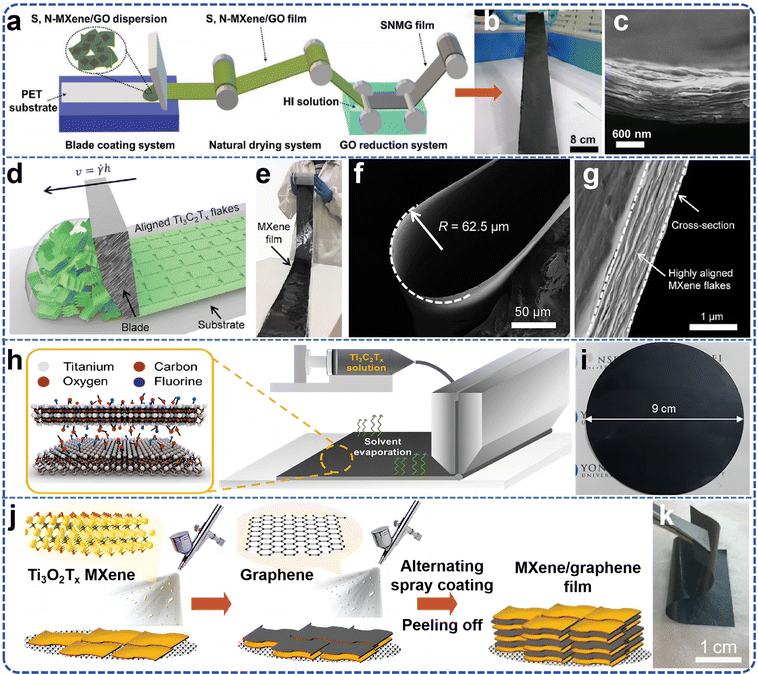 | ||
| Fig. 7 (a) Process flow chart of large-scale production of independent S, N co-doped m xenon hybrid film; (b) large area hybrid membrane photograph; (c) cross-section SEM image. Reproduced from ref. 81 with permission from Wiley-VCH, copyright 2021. (d) Schematic illustration of the blade coating process; (e) digital photograph of a 1 m long and 10 cm wide film produced from large MXene flakes that was blade coated onto a Celgard membrane (thickness of the Ti3C2Tx film is 940 nm); (f) SEM image of blade coated film made from large flakes folded at 180° forming a radius of ≈62.5 μm; (g) SEM image shows the cross-section of a blade coated film containing highly aligned large MXene flakes. Reproduced from ref. 82 with permission from Wiley-VCH, copyright 2020. (h) Schematic illustration of Ti3C2Tx coating procedure using a slot-die coater; (i) photographic image of an as-prepared Ti3C2Tx membrane. Reproduced from ref. 83 with permission from American Chemical Society, copyright 2021. (j) Schematic showing the manufacturing of free-standing and flexible 2D MXene/graphene heterostructured films by a spray-assisted LbL process; (k) digital images of a spraycoated M/G-20 film showing the flexibility. Reproduced from ref. 84 with permission from Wiley-VCH, copyright 2019. | ||
The use of organic compounds, surfactants, or metal ions as cross-linking agents is a common strategy for constructing MXene gels. However, the inclusion of such agents can negatively impact the electrical conductivity and lubricity of MXene, posing a challenge to their overall performance. Therefore, further research is necessary to develop scalable methods for producing MXene gels while maintaining their key functional properties. Liu et al.86 proposed a strategy for the rapid preparation of MXene gels using low-intensity centrifugation assistance (Fig. 8a). This method eliminates the need for the addition of high-concentration MXene nanosheet dispersions and cross-linking agents. By adjusting the pH, MXene nanosheets rapidly and spontaneously form gels at a very low dispersion concentration of 0.5 mg mL−1, creating multifunctional structures (Fig. 8b). With optimized surface terminations and internal microstructure, the resulting gel proved to be an ideal candidate material for high-performance semi-solid lubricants, offering excellent viscoelasticity, thixotropy, superior yield stress, and adjustable near-infrared emissivity and photothermal conversion capacity. This approach provides a simple and cost-effective paradigm for the preparation of MXene-based gels. Moreover, Dong's team87 team employed Ti3C2Tx MXene as a dynamic cross-linking agent to achieve rapid and universal gelation of various monomers and polymers by carefully regulating the intermolecular forces between the MXene and the cross-linking network. Using acrylic acid (AA) monomer as an example, the mechanism of rapid gelation is as follows: the polar groups on the surface of Ti3C2Tx MXene chelate with the –COOH group of AA, releasing significant heat in a short period, which accelerates the decomposition of ammonium persulfate. This greatly increases the generation rate of free radicals, promoting rapid cross-linking. The chain growth reaction of free radical polymerization is accompanied by intense heat release, which further accelerates the reaction, thus fostering free radical formation. The –OH, –F, and –O groups on the surface of Ti3C2Tx MXene form multiple hydrogen bonds with the –COOH groups of polyacrylic acid (PAA) and the –OH groups of glycerol, promoting strong heat release during the reaction. The differences between MXene and various monomers are mainly attributed to the steric hindrance and hydrophilicity of the side groups in the monomers, which to some extent weaken the intermolecular forces between MXene sheets. This study lays a foundation for the practical application of hydrogels.
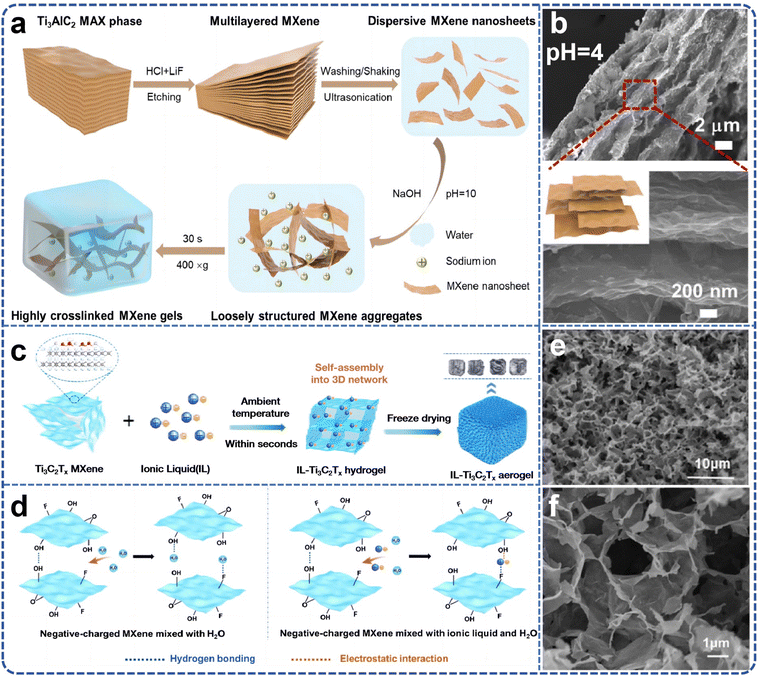 | ||
| Fig. 8 (a) Schematic illustration of producing Ti3C2Tx MXene gelators and centrifugation-assisted MXene gels; (b) pH-dependent internal structures of the MXene gel. Reproduced from ref. 86 with permission from Springer, copyright 2024. (c) Schematic illustration of synthesis of ionic liquids–Ti3C2Tx aerogel; (d) schematic of the interaction between Ti3C2Tx MXene in solution with and without ILs; (e and f) SEM of IL–Ti3C2Tx. Reproduced from ref. 88 with permission from American Chemical Society, copyright 2024. | ||
During the investigation into the rapid gelation of Ti3C2Tx MXene, it was found that certain divalent metal ions could effectively interact with MXene nanosheets to assemble three-dimensional structures. In contrast, univalent metal ions led to MXene solidification, and trivalent metal ions caused MXene oxidation. However, the small size and limited variety of metal ions are not conducive to the fine control and large-scale production of three-dimensional porous MXene structures. To address this issue, Zhao et al.88 reported a fast, simple, scalable, and gentle strategy for constructing a series of three-dimensional porous Ti3C2Tx MXene gels by inducing rapid gelation of Ti3C2Tx within seconds using various ionic liquids (ILs) (Fig. 8c). During the gelation process, ionic liquids were introduced into the Ti3C2Tx colloidal dispersion to disrupt the electrostatic repulsion between the nanosheets, and the ILs acted as cross-linking agents to connect the nanosheets, forming a three-dimensional porous structure (Fig. 8d). Density functional theory (DFT) calculations further revealed the cross-linking behavior of different ILs on Ti3C2Tx. By adjusting the concentration and type of IL, the pore structure and interlayer spacing of individual blocks could be precisely controlled. Notably, the [C2VIm]Br-induced Ti3C2Tx monomer exhibited a higher specific surface area and optimal pore size, reducing ion transport distances and providing more active sites for ion storage (Fig. 8e and f). This approach offers a general strategy for the large-scale preparation of MXene gels.
3. Optimization strategy for MXene industrial production
3.1. Anti-oxidation
MXene materials exhibit vast potential for diverse applications, owing to their distinctive structural characteristics and exceptional electrochemical properties. However, a notable challenge lies in their susceptibility to oxidation during synthesis, processing, and storage, which consequently results in diminished performance. This oxidation not only adversely affects the material's conductivity and electrochemical stability but also restricts its reliability and operational lifespan in practical applications. The synthesis of MXenes is generally accomplished through the selective extraction of an atomic layer from layered ternary metal carbides or nitrides, known as MAX phases. While the Mn+1Xn backbone of MXenes is inherited from the MAX precursor, the nature of their surface terminations is predominantly dictated by the synthesis methodology employed. Conventionally, wet chemical etching using fluorinated or chlorinated aqueous acids yields MXenes with a heterogeneous mixture of –OH, –O, –F, and –Cl termination groups. In contrast, Lewis acid molten salt etching can produce MXenes with single-atomic layer halogen terminations (–Cl, –Br, or –I), which may subsequently be altered through conversion processes. Nevertheless, these functional groups remain prone to oxidation upon exposure to air or during washing, thereby preventing the formation of a stable and ordered functional architecture. Furthermore, although alternative synthetic techniques—such as hydrothermal etching, electrochemical etching, and iodine-assisted etching—along with post-treatment strategies like annealing and chemical conversion offer supplementary options for functional groups, they remain constrained by the aforementioned limitations in terms of group types. The inherent instability and disorder of surface functional groups represent a significant obstacle to the broader application of MXenes. Consequently, there is an urgent need for the development of synthetic methodologies and post-treatment approaches that can yield MXenes with intact structures and superior quality, thereby enhancing their stability and functional integrity for advanced applications.In the preparation of MXene, it is critical to select an appropriate reactor and maintain a stable argon environment. Typically, a highly sealed reactor is employed to prevent the ingress of external air. To ensure a consistent concentration of argon within the reactor, it is subjected to vacuum treatment to remove residual air prior to initiation of the reaction, followed by the introduction of high-purity argon (typically 99.999% purity). The argon atmosphere must be maintained consistently throughout the reaction to avert oxidation induced by oxygen infiltration. When Ti3AlC2 (MAX phase) powder is introduced into the reactor, the flow of argon serves to block oxygen, thereby preventing surface oxidation during the subsequent etching process. Within the argon atmosphere, the MAX phase material is mixed with the etching agent (such as HF or LiF + HCl), and the etching reaction typically involves a mixture of HF or lithium fluoride (LiF) and HCl. The duration of etching is contingent upon specific experimental conditions, usually ranging from several hours to ten hours. During this process, argon safeguards the highly reactive material from reacting with oxygen in the air, thereby ensuring that MXene remains non-oxidized during the etching. The function of these chemicals is to etch the Al layer in the Ti3AlC2 to produce the layered Ti3C2Tx MXene. Post-etching, the resultant product may contain unreacted byproducts such as HF or LiF. To enhance the purity of MXene, the etched product requires multiple cleaning cycles. The cleaning process is also conducted under argon to prevent oxidation upon exposure to air. Cleaning is typically executed with deionized water until the pH of the product approximates neutrality (typically 6–7). Following each cleaning cycle, the MXene is separated from the cleaning solution via centrifugation to eliminate residual etching solution and byproducts. The cleaned MXene material must subsequently be dried, which should also be performed under an argon atmosphere or in a vacuum. Traditional drying methods expose MXene to air, leaving it prone to oxidation during the drying process; thus, vacuum drying or drying in a flowing argon environment is especially crucial. Generally, the drying temperature is regulated within a lower range (e.g., 40 °C to 60 °C) to prevent high-temperature-induced oxidation reactions. Maintaining a continuous argon flow or vacuum throughout the entire drying process is an effective means to prevent oxidation.89
Hydrogen, as a reducing gas, also effectively protects MXene materials from oxidation. Mo2Ga2C (MAX phase) powder was introduced into a reactor protected by a hydrogen atmosphere. In a hydrogen environment, Mo2Ga2C was etched with a HF solution to remove the Ga layer, forming Mo2CTx MXene. Following etching, the product underwent a reduction treatment under a hydrogen atmosphere to further eliminate residual oxides and restore the electrical conductivity of Mo2CTx. This method leveraged the reducibility of hydrogen to ensure the high antioxidant properties of Mo2CTx MXene during synthesis and post-synthesis treatments.90
Ammonia (NH3), a gas with both reducing and nitrogen source capabilities, is utilized in the synthesis of MXene not only to prevent oxidation but also to achieve nitrogen doping. Consequently, in the preparation of Ti2Tx MXene, employing ammonia as the reaction atmosphere proves to be a dual-purpose strategy. High-purity ammonia gas is continuously injected into the reactor to ensure the stability of the ammonia atmosphere throughout the reaction. Prior to operation, the reactor undergoes vacuum treatment to remove residual oxygen, after which ammonia is introduced to create a protective atmosphere. The flow rate and pressure of ammonia during the reaction process must be strictly controlled to prevent air infiltration and ensure the material remains non-oxidized. The Ti2Tx MXene is placed within a reactor protected by an ammonia atmosphere. The Ti3AlC2Tx MXene is subsequently produced by etching the aluminum layer using a mixed solution of HF or LiF + HCl, thereby forming layered Ti2Tx MXene. The ammonia atmosphere effectively isolates oxygen, preventing the oxidation of Ti2Tx MXene during the etching process. The etching reaction typically lasts for several hours, contingent upon the etching rate. Post-etching, the Ti2Tx MXene material may still contain residual oxides or remnants that are not completely removed. The material is subsequently cleaned and placed in a high-temperature furnace protected by ammonia gas, where the material undergoes heating, usually at a temperature between 500 °C and 800 °C. The specific temperature and duration can be adjusted according to the desired depth of nitrogen doping and the electrochemical performance requirements of the material. During this process, ammonia serves not only as a reducing atmosphere to prevent further oxidation of the material but also reacts with Ti3C2Tx as a nitrogen source, causing nitrogen atoms to be embedded within the material's lattice, forming Ti3C2TxN MXene. Upon completion of the heat treatment, the material requires further cleaning and drying to remove potential by-products and enhance the material's purity.91 The cleaning process is typically conducted in an ammonia environment using deionized water until the material's pH approximates neutrality. Additionally, post-cleaning, the material is dried either under vacuum or within an ammonia atmosphere to prevent contact with atmospheric oxygen during the drying process. Nitrogen doping imparts a novel electronic structure and chemical activity to the material by substituting some surface terminal groups (such as –O, –OH, –F) or directly embedding nitrogen atoms into the lattice structure. The doped materials exhibit superior electrochemical properties, particularly in energy storage devices like supercapacitors and lithium-ion batteries.
The application of protective atmosphere synthesis in the industrial production of MXene materials demonstrates significant advantages. By operating within an inert or reducing atmosphere, the oxidation of MXene material during synthesis and treatment is prevented, enhancing the material's stability, avoiding the formation of oxidation by-products, and improving the purity of the MXene material. By regulating the composition of the atmosphere and reaction conditions, the electrochemical and physical properties of MXene materials can also be optimized.
Ti3C2Tx MXene is typically derived from the MAX phase material (Ti3AlC2) through chemical etching. Specifically, Ti3AlC2 powder is immersed in a solution containing HF or LiF + HCl and etched under controlled temperature and time conditions to eliminate the Al layer within the MAX phase, ultimately yielding Ti3C2Tx MXene. During this etching procedure, fluorine ions (F−) play a dual role: they react with the Al layer to expedite its removal and form stable Ti–F bonds with Ti atoms, leading to fluorine group modification on the material's surface. The fluorine groups, firmly bonded to Ti atoms via chemical bonds, constitute Ti–F bonds with remarkable chemical stability. The presence of these Ti–F bonds effectively blocks oxygen, thereby reducing the occurrence of oxidation reactions. In contrast, unfluorinated MXene materials are more susceptible to reacting with oxygen in the air, resulting in the formation of TiO2 and subsequent degradation of the material's structure and performance. However, with fluoride modification, the surface Ti–F bonds exhibit stable existence, providing robust oxidation resistance. Furthermore, the introduction of fluorine groups mitigates the interaction between water and the material's surface through hydrophobic action, enhancing the material's resistance to hydrolysis. This hydrophobic effect reduces the degradation of MXene properties triggered by water-induced hydrolysis reactions. Fluorine groups not only prevent oxidation and hydrolysis but also enhance the material's stability under elevated temperatures or other harsh conditions, thereby extending its service life. Notably, fluoridation primarily aims to enhance the antioxidant properties of MXene materials while preserving their electrical conductivity. The introduction of fluoro groups does not significantly alter the electronic structure of Ti3C2Tx, allowing it to maintain its original excellent electrical conductivity. This retention of conductivity enables fluorinated MXene materials to continue exploiting their high electrical conductivity in various applications, particularly in electrochemical and energy storage devices.
Additionally, the presence of fluoro groups modulates the surface chemical properties of the material, enhancing MXene's selectivity and reactivity in specific electrochemical reactions. To further optimize fluorination treatment effects, etching conditions can be fine-tuned. For instance, adjusting the concentration of etching agents influences the fluoro group coverage and the uniformity of surface modification. Precise control over etching temperature and time avoids excessive etching, thereby minimizing damage to the layered structure of MXene and ensuring material integrity and functionality. Lastly, fluorinated MXene can undergo moderate heat treatment to reinforce the binding force of fluorophoric groups, further improving its oxidation resistance and stability. MXene materials treated with surface fluoridation exhibit broad promise in numerous applications, especially in scenarios requiring prolonged exposure to air, moisture, or other challenging environments. Fluorination not only prolongs the service life of MXene but also preserves its high conductivity and electrochemical properties, making it particularly suitable for energy storage devices, electrocatalysis, sensors, and environmental protection applications.92
Polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) is a universally employed water-soluble polymer material distinguished by its exceptional film-forming capabilities and stability. The carbonyl and pyrrolidone rings intrinsic to its chemical architecture facilitate the establishment of stable bonds with adjacent material surfaces, mediated by hydrogen bonding or electrostatic interactions. Integration of PVP onto the surface of MXene serves to effectually cloak the exposed regions of MXene, thereby forming a uniform protective membrane. Initially, the Ti3AlC2 MAX phase undergoes etching via HF or a LiF + HCl mixed solution to eliminate the Al layer, resulting in the layered Ti3C2Tx MXene. Post-etching, the material is meticulously cleansed to eliminate by-products, followed by drying under vacuum or in an inert gas milieu to forestall oxidation. Preceding surface modification, a PVP solution is formulated. Typically, a PVP solution of suitable concentration (ranging from 0.1 wt% to 1 wt%) is selected as the modification agent, with polar solvents like water or ethanol commonly chosen to ascertain uniform dissolution and complete contact with the MXene surface. The prepared Ti3C2Tx MXene is dispersed within the PVP solution, subsequently stirred over an extended duration—several hours to a full day—to allow PVP to progressively adsorb and coalesce onto the MXene surface via hydrogen bonding or electrostatic action. During this process, the carbonyl moiety of PVP engages in hydrogen bonding with the oxygen and hydroxyl groups on the MXene surface, while the polymer chain of PVP conjoins to constitute a continuous, uniform protective film. The resultant MXene material is then subjected to drying under vacuum or at low temperatures to expunge the solvent, thereby ensuring firm adherence of PVP to the MXene surface. Control over temperature during the drying phase is paramount, typically maintained between 40 °C to 60 °C to avert PVP degradation due to excessive temperatures. The PVP layer enveloping the Ti3C2Tx MXene surface forms a dense protective film, which effectively segregates oxygen, curtails direct interaction between Ti atoms and oxygen, inhibits the formation of oxide layers (such as TiO2), and preserves the structural integrity of the material. PVP exhibits commendable water-barrier properties, with the polar constituents within its molecular framework capable of engaging with water molecules to preclude reactions with the MXene surface, thereby diminishing the risk of hydrolysis and ensuing performance deterioration. Over prolonged usage, the PVP coating substantively safeguards the MXene material from significant property degradation due to oxidation or moisture erosion in the ambient environment. Despite PVP, as a polymeric material, being conventionally regarded as an insulator, its modification does not notably impact the electrical conductivity of MXene. The electrical conductivity of MXene is predominantly governed by the metallic bond and elevated electron mobility within its two-dimensional layered structure, and the introduction of PVP does not undermine this overall configuration. Given that the PVP coating layer is primarily superficial, its thin profile does not impede the electron conduction pathways within MXene. Consequently, the modified MXene material retains its inherent electrical conductivity while concurrently exhibiting superior dispersion properties, which prevent aggregation of MXene in solution or electrode constructs. This uniform dispersion effect sustains the material's efficient electrical conductivity, particularly in energy storage applications, where enhanced dispersion contributes to elevating the material's electrochemical activity.93
The introduction of a TiO2 coating on the surface of MXene serves to effectively mitigate the ingress of oxygen and moisture, thereby impeding the oxidation of MXene materials in ambient air. Simultaneously, the distinct photocatalytic attributes of TiO2 endow it with promising potential in applications pertaining to photocatalytic degradation of pollutants and photoelectric devices. Initially, the synthesis of Ti3C2Tx MXene is achieved through a conventional method, typically involving the etching of the Ti2AlC phase with HF or a LiF + HCl solution to eliminate the aluminum layer, resulting in the formation of two-dimensional Ti3C2Tx MXene. Post-synthesis, the MXene material undergoes multiple washing cycles to purge residual acids and by-products, followed by vacuum drying to prevent oxidation in atmospheric conditions. To effectuate the deposition of TiO2 onto the MXene surface, a solution containing titanium precursors must be meticulously prepared. Commonly employed titanium precursors encompass tetrabutyltitanate (TBT) or tetraisopropyl titanate (TTIP), which, upon hydrolysis, yield TiO2. In the experimental protocol, an appropriate quantity of the titanium precursor is solubilized in an organic solvent, such as ethanol or isopropyl alcohol, with incremental introduction of water to modulate the hydrolysis rate. The synthesized Ti3C2Tx MXene is then dispersed within the titanium precursor solution and thoroughly agitated to ensure comprehensive contact between the MXene surface and the precursor. Within the solution milieu, the titanium precursor undergoes a hydrolysis reaction, the rate of which is precisely regulated by adjusting the volume of water added and the reaction temperature. Moderate hydrolysis contributes to the uniform deposition of TiO2, thereby averting uneven or excessive coating formation, culminating in the deposition of TiO2 on the MXene surface, thereby establishing an initial coating. The thickness of this coating can be modulated by varying the concentration of the titanium precursor and the duration of the reaction. A thinner coating confers robust antioxidant protection without compromising the material's electrical conductivity. Post-deposition, the TiO2 coating necessitates thermal curing. This heat treatment is typically conducted under an air or argon atmosphere. Temperatures that are too low may result in insufficient densification of the coating, whereas excessively high temperatures may precipitate the oxidation of MXene. Consequently, the selection of the temperature is critical, often chosen to range between 300 °C and 500 °C, to ensure the complete crystallization and robust adhesion of the TiO2 coating to the MXene surface.94
In the context of organic acid molecules, such as oxalic acid, citric acid, and glycolic acid, the presence of multiple carboxyl (–COOH) groups enables the formation of coordination bonds with titanium atoms on the MXene surface, thereby establishing a stable organic molecular layer. This molecular layer not only proficiently obstructs the infiltration of external oxygen and moisture but also maintains the electrical conductivity of MXene by modulating the chemical properties of its surface, further augmenting the interaction of MXene with other materials, such as polymers or metals. Initially, the Ti3C2Tx MXene is synthesized using a suitable organic acid, such as oxalic acid (C2H2O4), citric acid (C6H8O7), or glycolic acid (H2C2O4), which is dissolved in deionized water to create an organic acid solution. The choice of different organic acids exerts a discernible influence on the surface modification efficacy of MXene. Oxalic acid, characterized by robust acidity and high coordination capability, rapidly forms a stable coordination structure with the MXene surface. Conversely, citric acid, owing to its polycarboxyl structure, forms a thick and stable organic layer on the MXene surface, thereby rendering it suitable for applications requiring sustained antioxidant protection. Considering that oxalic acid operates as a simple dicarboxylic acid and provides swift and effective antioxidant protection through thin organic molecular layers, the appropriate type of organic acid can be selected based on the specific application requirements. The Ti3C2Tx MXene material is subsequently immersed in the organic acid solution, undergoing treatment via stirring or ultrasound to facilitate the reaction between the organic acid molecules and the MXene surface. The carboxyl groups form stable coordination bonds by coordinating with the titanium atoms on the MXene surface, thereby uniformly distributing across the MXene surface. Typically, the immersion duration varies according to the specific characteristics of the organic acids and MXene, ranging from several hours to tens of hours, to ensure the comprehensive binding of the organic acid molecules to the MXene surface. The concentration of the organic acid solution is also modulated in accordance with the material's requirements; higher concentrations facilitate the formation of a thicker protective layer, whereas lower concentrations are more adept at fine-tuning the modification effect. Upon completion of the modification process, the MXene is extracted from the organic acid solution and subjected to multiple rinses with deionized water to eliminate unreacted organic acid molecules and solvents. Subsequently, vacuum drying is employed to eradicate residual water and solvent from the material's surface, thereby ensuring the stability of the modified layer.95 In a recent study, Zhang et al.96 reported that tartaric acid, acting as both an organic capping agent and a multifunctional antioxidant, successfully inhibited the oxidation of MXenes and facilitated its composite formation with PEDOT:PSS (Ti3C2Tx/PEDOT:PSS) (Fig. 9a). Consequently, even at high temperatures of 60 °C, 25 wt% of tartaric acid can effectively limit oxidation in water dispersions, a capability not achievable with untreated MXene. Here, the multifunctional properties of tartaric acid encompass not only the inhibition of Ti ion edges and defects but also induce partial dissociation, replacing the insulation of PSS and promoting crosslinking between PEDOT nanomaterials and resins, thereby enhancing the structural stability of the composite in water for over two weeks. Compared with untreated MXenes (conductivity of 552 S cm−1), the resulting composite (ta-MXene/PEDOT:PSS) exhibits a conductivity increase to 2240 S cm−1 with no physicochemical alterations. Specifically, citric acid, tartaric acid, and oxalic acid were notably effective in inhibiting the oxidation of Ti3C2Tx and Ti2CTx MXene nanosheets, whereas a few polycarboxylic acids and phenolic compounds promoted oxidation (Fig. 9b).97 The structure–phase relationship is predicated on the fact that effective antioxidants like citric acid or tartaric acid and oxalate-based MXene dispersions exhibit a significant negative zeta potential and a lower hydrodynamic diameter, leading to higher colloidal dispersion. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) analyses revealed that high-quality MXenes (Ti3C2) remained unoxidized for up to 4 months, until 10 months later when pinholes were clearly formed in the pseudo-crystal (Fig. 9c and d), indicating the onset of oxidation.98 Generally, MXenes synthesized via the EN-MILD method exhibit higher electrical conductivity than MILD MXene (Fig. 9e and f).99 The results for 18-hour and 24-hour MXenes (using EN-MILD) significantly surpass any previously reported conductivity values for Ti3C2Tx MXenes. Parameters such as wafer size, morphology, surface chemistry, and inserted lithium ions are the primary components to be considered. AFM and SEM characterizations showed that the EN-MILD method produced larger slices of MXenes at 18-hour and 24-hour etching times. Controlling the size of MXene sheets is crucial for achieving higher electrical conductivity. The underlying mechanism involves lower inter-flake contact resistance in films containing larger MXene sheets, as well as better alignment in separate MXene sheets. Therefore, the enhanced conductivity can be attributed to the reduction and better arrangement of inter-flake resistance in films prepared by EN-MILD 18-hour and EN-MILD 24-hour MXenes.
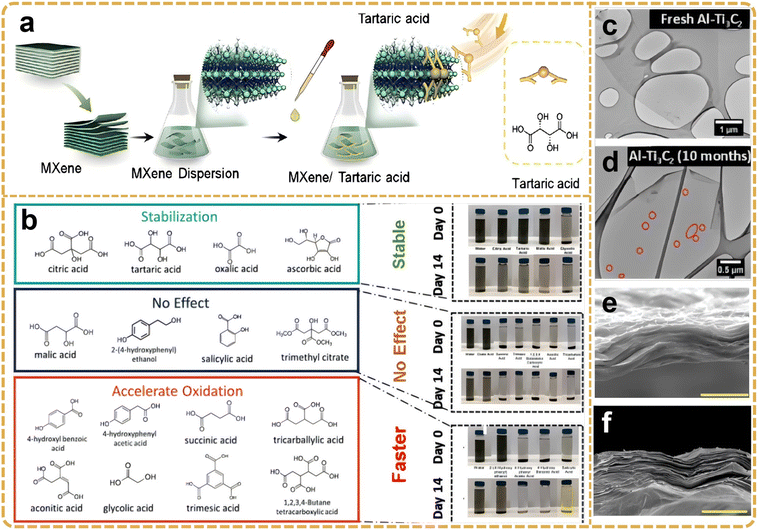 | ||
| Fig. 9 (a) The formation of the MXene–tartrate complex is illustrated. Reproduced from ref. 96 with permission from Elsevier, copyright 2021. (b) Various antioxidant Ti3C2Tx molecules and their antioxidant capacity and corresponding digital photos in 14 days of storage. Reproduced from ref. 85 with permission from Wiley-VCH, copyright 2022. (c and d) TEM images of high-quality fresh Al-Ti3C2 MXene and after 10 months of storage. Reproduced from ref. 98 with permission from American Chemical Society, copyright 2021. Employing the EN-MILD approach increased the electrical conductivity to 6 times higher than that MILD approach; cross-sections of MXene films prepared by (e) MILD approach and (f) EN-MILD after 24 h etching, respectively. The scale bar is 3 μm. Reproduced from ref. 99 with permission from The Royal Society of Chemistry, copyright 2021. | ||
The surface modification strategy in MXene industrial production optimization demonstrates significant advantages. (1) Effective oxidation prevention: surface modification forms a chemical or physical barrier, effectively preventing direct contact between oxygen, water in the external environment, and MXene material, thereby significantly extending its service life. (2) Enhanced material stability: surface modification not only augments the oxidation resistance of MXene but also improves the physicochemical stability of the material by introducing functional groups or polymers. (3) Maintenance of excellent performance: reasonably designed surface modification strategies can markedly enhance antioxidant properties while maintaining or even improving the electrical conductivity, energy storage, and catalytic properties of MXene materials.
Vitamin C exhibits potent reductive properties, and the ester group (C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O) and hydroxyl group (OH) within its molecule can donate electrons, thereby preventing MXene from oxidizing due to environmental factors such as oxygen and water. Vitamin C functions as a reducing agent by binding to the surface active site of MXene, inhibiting the oxidation of Ti atoms to TiO2 and averting the formation of surface oxides. The reduction of vitamin C curtails the infiltration of oxygen and water, thereby delaying the oxidation process of MXene. The inclusion of this antioxidant provides protection during both the material synthesis and storage phases. Initially, the Ti3AlC2 MAX phase is etched using HF or LiF + HCl solutions to eliminate the Al layer, yielding a two-dimensional Ti3C2Tx MXene. During the synthesis or cleaning of MXene, a vitamin C solution of a specified concentration is prepared. Typically, vitamin C is dissolved in deionized water, with the concentration adjusted according to experimental requirements, commonly ranging from 0.1 to 1 M. The selected concentration impacts the antioxidative effect; a higher concentration of vitamin C solution supplies more reducing molecules, effectively inhibiting MXene oxidation but potentially affecting the material's surface structure. Appropriate concentration adjustment ensures MXene protection while maintaining structural integrity and electrochemical properties. During the synthesis of Ti3C2Tx MXene, a vitamin C solution is added under nitrogen or argon protection to minimize atmospheric oxygen interference and optimize the antioxidative process. This can be achieved by using the vitamin C solution as a post-etching cleaning agent or by directly adding a specified amount of vitamin C to the solution to prevent oxidation. The soaking time is generally regulated between a few minutes to several hours to ensure complete binding of vitamin C molecules to the MXene surface and to exert antioxidative effects. Upon completion of the vitamin C treatment, the MXene material is rinsed with deionized water to eliminate unreacted vitamin C and residues.
O) and hydroxyl group (OH) within its molecule can donate electrons, thereby preventing MXene from oxidizing due to environmental factors such as oxygen and water. Vitamin C functions as a reducing agent by binding to the surface active site of MXene, inhibiting the oxidation of Ti atoms to TiO2 and averting the formation of surface oxides. The reduction of vitamin C curtails the infiltration of oxygen and water, thereby delaying the oxidation process of MXene. The inclusion of this antioxidant provides protection during both the material synthesis and storage phases. Initially, the Ti3AlC2 MAX phase is etched using HF or LiF + HCl solutions to eliminate the Al layer, yielding a two-dimensional Ti3C2Tx MXene. During the synthesis or cleaning of MXene, a vitamin C solution of a specified concentration is prepared. Typically, vitamin C is dissolved in deionized water, with the concentration adjusted according to experimental requirements, commonly ranging from 0.1 to 1 M. The selected concentration impacts the antioxidative effect; a higher concentration of vitamin C solution supplies more reducing molecules, effectively inhibiting MXene oxidation but potentially affecting the material's surface structure. Appropriate concentration adjustment ensures MXene protection while maintaining structural integrity and electrochemical properties. During the synthesis of Ti3C2Tx MXene, a vitamin C solution is added under nitrogen or argon protection to minimize atmospheric oxygen interference and optimize the antioxidative process. This can be achieved by using the vitamin C solution as a post-etching cleaning agent or by directly adding a specified amount of vitamin C to the solution to prevent oxidation. The soaking time is generally regulated between a few minutes to several hours to ensure complete binding of vitamin C molecules to the MXene surface and to exert antioxidative effects. Upon completion of the vitamin C treatment, the MXene material is rinsed with deionized water to eliminate unreacted vitamin C and residues.
Tetrabutylammonium ion (TBA+) is a larger organic ion with a strong electrostatic effect capable of ion exchange with the MXene surface, forming a protective coating. Through this electrostatic interaction, TBA+ ion stabilizes the MXene surface structure, preventing oxygen or moisture from binding with Ti atoms on the surface, thereby inhibiting the oxidation process. The ammonium-based protective layer formed by TBA+ ions on the MXene surface effectively shields the material from external environmental effects, significantly enhancing MXene's antioxidative properties and extending its storage life. Initially, the Ti3AlC2 MAX phase is etched using HF or LiF + HCl solutions to eliminate the Al layer, yielding a two-dimensional Ti3C2Tx MXene. Following the etching, a TBA+ solution is prepared, typically using a TBA+ salt (e.g., tetrabutylammonium hydroxide, tetrabutylammonium bromide) dissolved in deionized water or another suitable solvent, with the concentration adjusted according to experimental needs, commonly ranging from 0.01 to 1 M. The prepared TBA+ solution is added to the MXene suspension obtained post-etching for an ion exchange reaction. TBA+ ions bind to the MXene surface via electrostatic action, replacing the original surface ions (such as H+ or Li+) to form a stable ammonium-based protective layer. The reaction time generally spans 30 minutes to several hours, with the reaction temperature adjustable between room temperature and 50 °C to ensure full binding of TBA+ ions to the MXene surface to form a uniform protective layer. To ensure uniform distribution of TBA+ ions on the MXene surface, magnetic agitation or ultrasonic oscillation can be employed to expedite the ion exchange process. After the ion exchange is complete, the treated MXene suspension is rinsed multiple times with deionized water to remove excess TBA+ ions and unreacted by-products. The cleaned MXene is subsequently vacuum-dried to produce MXene material encased in a protective TBA layer.100
Urea (CO(NH2)2) is a compound possessing notable reducing properties and is extensively employed in industrial and chemical synthesis. The amino (–NH2) and –C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O groups within its structure can interact with metal atoms, such as Ti, on the surface of MXene, thereby forming hydrogen bonds or coordination bonds. Through this interaction, urea can establish a stable protective film on the surface of MXene, effectively precluding the infiltration of oxygen or water and thereby inhibiting the onset of oxidation reactions. Specifically, the amino group within urea can form hydrogen bonds with the titanium atom (Ti) on the MXene surface, whereas the carbonyl group coordinates with the surface metal atom through its oxygen atom. This dual binding mechanism not only stabilizes the MXene surface structure but also effectively curbs oxidation reactions typical in humid environments, thus endowing MXene with enhanced antioxidant properties during prolonged storage. In the preparation of MXene, the Ti3AlC2 MAX phase is typically etched using HF or a LiF + HCl solution to eliminate the Al layer, yielding a two-dimensional Ti3C2Tx MXene. Urea is dissolved in deionized water or an appropriate solvent, usually at a concentration ranging from 0.1 M to 1 M. To ensure the uniform distribution of urea, magnetic or ultrasonic agitation can be employed to facilitate its complete dissolution and to create favorable conditions for subsequent MXene modification. Following etching and initial cleaning, MXene is immersed in a urea solution for surface modification. Urea molecules bond to metal atoms (such as Ti) on the MXene surface via their amino and carbonyl groups, forming a stable network of hydrogen and coordination bonds, thereby creating a protective film on the MXene surface. The urea surface modification is typically performed at room temperature, with the reaction duration ranging from 30 minutes to several hours, contingent upon experimental parameters, to ensure uniform and stable adsorption of urea molecules on the MXene surface. During the reaction, magnetic or ultrasonic assistance can be utilized to ensure uniform distribution of urea molecules within the MXene suspension and to maximize contact with the MXene surface. Post-modification, the material is repeatedly rinsed with deionized water to remove unbound urea molecules and any reaction by-products. Subsequently, the modified MXene material is subjected to vacuum drying to obtain a stable material with a urea-modified surface.101
O groups within its structure can interact with metal atoms, such as Ti, on the surface of MXene, thereby forming hydrogen bonds or coordination bonds. Through this interaction, urea can establish a stable protective film on the surface of MXene, effectively precluding the infiltration of oxygen or water and thereby inhibiting the onset of oxidation reactions. Specifically, the amino group within urea can form hydrogen bonds with the titanium atom (Ti) on the MXene surface, whereas the carbonyl group coordinates with the surface metal atom through its oxygen atom. This dual binding mechanism not only stabilizes the MXene surface structure but also effectively curbs oxidation reactions typical in humid environments, thus endowing MXene with enhanced antioxidant properties during prolonged storage. In the preparation of MXene, the Ti3AlC2 MAX phase is typically etched using HF or a LiF + HCl solution to eliminate the Al layer, yielding a two-dimensional Ti3C2Tx MXene. Urea is dissolved in deionized water or an appropriate solvent, usually at a concentration ranging from 0.1 M to 1 M. To ensure the uniform distribution of urea, magnetic or ultrasonic agitation can be employed to facilitate its complete dissolution and to create favorable conditions for subsequent MXene modification. Following etching and initial cleaning, MXene is immersed in a urea solution for surface modification. Urea molecules bond to metal atoms (such as Ti) on the MXene surface via their amino and carbonyl groups, forming a stable network of hydrogen and coordination bonds, thereby creating a protective film on the MXene surface. The urea surface modification is typically performed at room temperature, with the reaction duration ranging from 30 minutes to several hours, contingent upon experimental parameters, to ensure uniform and stable adsorption of urea molecules on the MXene surface. During the reaction, magnetic or ultrasonic assistance can be utilized to ensure uniform distribution of urea molecules within the MXene suspension and to maximize contact with the MXene surface. Post-modification, the material is repeatedly rinsed with deionized water to remove unbound urea molecules and any reaction by-products. Subsequently, the modified MXene material is subjected to vacuum drying to obtain a stable material with a urea-modified surface.101
Tea polyphenols (TP), a class of natural antioxidant compounds extracted from tea, comprising catechin, gallic acid, and epigallocatechin, possess a molecular structure rich in multiple phenolic –OH. These groups can form stable hydrogen bonds or covalent bonds with functional groups on the MXene surface, such as –OH and carboxylic (–COOH) groups, thereby preventing direct contact between oxygen, water, and the MXene surface. This chemical bonding enables tea polyphenols to form an antioxidant protective film on the MXene surface, effectively inhibiting oxidation reactions. Additionally, the phenolic hydroxyl groups in tea polyphenols exhibit notable antioxidant reducing properties, capable of neutralizing oxidants on the material surface and further diminishing the oxidation rate of MXene. Initially, a MAX phase material such as Ti3AlC2 is etched using a HF or LiF + HCl mixture to eliminate the Al layer, yielding Ti3C2Tx MXene. Tea polyphenols are dissolved in deionized water or an appropriate organic solvent, typically at a concentration ranging from 0.01 M to 0.1 M. To ensure uniformity in the tea polyphenol solution, magnetic stirring or ultrasonic treatment can be employed to enhance the dispersion of tea polyphenol molecules. Following MXene preparation and preliminary cleaning, it is immersed in the tea polyphenol solution for surface modification. Tea polyphenol molecules interact with functional groups on the MXene surface via their phenolic hydroxyl groups, forming hydrogen bonds or covalent bonds. This bonding method stabilizes the MXene surface and forms a stable antioxidant film. Tea polyphenol modification is generally conducted at room temperature, with a reaction period ranging from 30 minutes to several hours, adjustable based on experimental conditions, to ensure uniform adsorption of tea polyphenol molecules on the MXene surface. Magnetic or ultrasonic assistance can be employed during the reaction to ensure thorough mixing of MXene with the tea polyphenol solution, enhancing the uniformity of surface modification. Post-modification, the material surface is repeatedly rinsed with deionized water to remove unbound tea polyphenol molecules and other by-products.102
Advantages of the antioxidant addition strategy: (1) effective oxidation delay: antioxidants can effectively prevent the oxygen and water-induced erosion of materials and delay the oxidation of materials through chemical combination or electrostatic interaction with the MXene surface. (2) Retention of material properties: many antioxidants act as protective agents without significantly compromising the electrical conductivity and other physicochemical properties of MXene, which is critical for its application in energy storage, catalysis, and other fields. (3) Simple and easy: the incorporation of antioxidants can typically be accomplished through straightforward solution treatment or surface modification, offering the advantages of a simple process and low cost, making it suitable for industrial production.
In an open system, the active surface sites of MXene are susceptible to reacting with oxygen and moisture in the air, leading to material oxidation. In contrast, in a closed system the oxygen in the air is removed by filling with an inert gas (such as argon or nitrogen), which effectively prevents oxidation reactions. The tightness of the closed reactor ensures an oxygen-free environment during synthesis, allowing the material to remain stable in a highly active state. The inert gas, being chemically inert and non-reactive with the reactants, also acts as a “barrier” that prevents oxygen diffusion, thereby safeguarding the surface structure of the MXene material. Firstly, Ti3AlC2 (MAX phase) is selected as the precursor material. The MAX phase material, a layered metal carbide, contains an Al layer that is readily etched to form the MXene material. To prevent oxidation during the reaction, the MAX phase material must be processed in a closed system. Closed reactors are typically fabricated from high-strength materials capable of maintaining seal integrity in high-temperature, corrosive environments. The reactor is filled with an inert gas, such as argon or nitrogen, to displace the oxygen in the air. To ensure an oxygen-free state in the system, the reactor can be purged multiple times before the reaction to remove residual oxygen. Argon is commonly used as an inert gas due to its strong chemical inertness and high density, which effectively covers the reaction system and prevents oxygen ingress. Argon gas is introduced into the reactor to create a stable protective environment, effectively preventing the infiltration of external oxygen. The tightness of the closed system is critical. During the reaction, it is necessary to ensure that no air leaks to maintain an oxygen-free state in the system. Sealing gaskets or sealing rubber rings can be employed to enhance tightness, and pressure changes in the reactor can be monitored in real-time by pressure detection devices to ensure system stability. The Ti3AlC2 MAX phase material is placed in the reactor and etched by injecting HF solution. The HF solution reacts with the Al layer in the MAX phase to remove the Al atoms and form the layered structure of Ti3C2Tx MXene. The entire reaction process is conducted in a closed system to ensure that oxygen in the air does not react with the highly active MXene surface. Typically, the etching reaction is carried out at or slightly above room temperature, depending on the amount of reactants and the concentration of the etching solution. The control of reaction time significantly impacts the number of layers and surface functional groups of MXene, and an appropriate etching time is conducive to the formation of high-quality MXene materials. During the etching process, the flow rate of argon can be controlled to further eliminate trace oxygen or by-products that may be generated in the system, ensuring that the material surface is unaffected by oxidation.92 The synthesis of MXene materials within a closed tube reactor is a prevalent industrial method. The reaction, under the protection of an inert gas such as argon or nitrogen, can effectively inhibit oxidation. Ti3C2Tx MXene can be synthesized using a closed tubular reactor. In the etching reaction, argon gas is continuously filled to ensure that the oxygen concentration in the reactor is close to zero. Precise control of the reactor's pressure and gas flow ensures the stability of the reaction process. The combination of the closed system and inert gas significantly reduces the surface oxidation degree of the synthesized MXene material, thereby maintaining its electrical conductivity. Research indicates that this method enhances the long-term stability of MXene materials, particularly increasing their application potential in energy storage equipment.103
A microenclosed nanoreactor is a device capable of precisely controlling the reaction environment at the micron or nanometer scale. By encapsulating reactants and isolating them from oxygen and water in the external environment, the nanoreactor provides a highly controlled chemical environment for MXene synthesis. The nanoreactor effectively isolates oxygen and water from the outside air through the physical closure of the nanostructure. This physical barrier prevents external environmental changes from affecting the material's surface during synthesis, reducing the likelihood of oxidation. Within the nanoreactor, the reactants are controlled in a highly refined chemical environment, which further inhibits oxidation through the use of inert gases (such as argon) and antioxidant agents (such as tetrabutylammonium, vitamin C, etc.). This dual protective mechanism, combining physical and chemical methods, significantly enhances the antioxidant capacity of MXene materials. First, Ti3AlC2 powder is placed in a microenclosed nanoreactor. The reactor is designed to achieve a closed environment at the micron or nanometer level. Through the physical isolation provided by the nanoreactor, the reactants are encapsulated in an environment completely isolated from external air, thereby ensuring that the entire reaction process remains unaffected by oxygen or water. The nanoreactor utilizes micromachining technology to precisely encapsulate the MAX phase material. The encapsulated reactants not only isolate external air but also maintain a stable chemical environment during the etching process. Within the nanoreactor, the etching reaction of Ti3AlC2 is conducted by adding HF solution. The HF solution reacts with the aluminum (Al) layer in the MAX phase to remove aluminum atoms and form the layered structure of Ti3C2 MXene. The entire etching process is performed in a micro-closed reaction environment, ensuring that oxygen and water do not enter the system, thereby reducing surface oxidation of the material. The temperature, pressure, and chemical environment of the reaction can be precisely controlled due to the high accuracy of the nanoreactor's closure. This environment aids in maintaining the uniformity of the etching process, resulting in a more regular interlayer structure and a more abundant surface functional group composition in the MXene materials. Upon completion of the cleaning process, further heat treatment, surface modification, or other subsequent treatment operations can be performed on the MXene material according to specific needs. Due to the high stability of the environment within the nanoreactor, these operations can be carried out in an oxygen-free condition, ensuring that the electrochemical properties and electrical conductivity of MXene are not compromised.104
Advantages of the closed-system synthesis strategy: (1) Effective isolation of oxygen: the closed system significantly inhibits the ingress of oxygen into the reactor through both physical and chemical mechanisms, thereby preventing surface oxidation of MXene materials and ensuring the retention of their high conductivity. (2) Maintain material properties: closed system synthesis not only enhances the antioxidant capabilities of the material but also preserves the electrochemical properties of MXene under large-scale production conditions, thereby guaranteeing its performance in applications such as energy storage and catalysis. (3) Suitable for industrial production: the closed system synthesis process offers precise control over the synthesis parameters, making it highly suitable for large-scale industrial applications. This approach ensures high production stability and reproducibility.
During low-temperature storage, effective sealing and moisture-proof measures must also be implemented to prevent condensation resulting from temperature fluctuations. MXene materials should be packaged in sealed bags that may be purged with nitrogen or subjected to vacuum conditions to further minimize exposure to moisture and atmospheric oxygen.104 The essence of vacuum storage is to mitigate the influence of oxygen and moisture by placing MXene materials in an oxygen-depleted environment. This is achieved by evacuating the air from the storage container or filling it with an inert gas (such as nitrogen or argon), effectively isolating the materials from external oxygen and water to inhibit oxidation reactions. Inert gases (e.g., nitrogen and argon) do not engage in chemical reactions, enabling their use to fill the storage containers and obstruct the ingress of atmospheric moisture and oxygen, thus creating a protective inert environment. In such conditions, the reactive sites on the surface of MXenes are shielded from oxygen, effectively reducing surface oxidation reactions. Studies have demonstrated that MXene materials are particularly susceptible to oxidation in open-air environments, where titanium atoms oxidize to form a TiO2 layer, resulting in decreased conductivity and specific capacity. However, by storing the materials in a vacuum or inert gas atmosphere, the infiltration of oxygen can be effectively curtailed, leading to a significant reduction in the oxidation rate. Experimental data reveal that MXene materials stored in argon maintain their initial conductivity for several months, with the oxidation rate diminished by over 90% compared with open-air conditions. Researchers who placed Ti3C2Tx MXene materials in sealed containers filled with argon for extended periods observed only a slight decrease in conductivity after six months of storage. In stark contrast, samples stored under open-air conditions at room temperature exhibited a significant conductivity decline and evident signs of oxidation during the same timeframe. Both vacuum and inert gas storage strategies not only prolong the oxidation process but also preserve the high electrical conductivity and favorable electrochemical properties of MXene materials. This is crucial for applications in energy storage devices, sensors, and other fields. Storing MXene materials in inert gas environments allows for sustained stability in electron mobility and specific capacity over extended durations. For instance, Ti3C2Tx MXene stored in vacuum or argon retained 98% of its initial conductivity after several months of storage, whereas the electrical conductivity of air-stored samples decreased by approximately 40% during the same interval. Electrochemical performance assessments indicated that the specific capacity of MXene materials stored in argon showed only minor declines, contrasting starkly with the significant drop in specific capacity observed for samples stored in air, thus affirming the efficacy of antioxidant protection in an inert gas environment.105
Humidity exerts a direct and accelerating effect on the oxidation of MXene materials. Water molecules present in the air can react with active sites on the MXene surface, facilitating the oxidation of Ti atoms to form TiO2. In particularly humid environments, water molecules penetrate the material's interior, gradually thickening the surface oxide layer. This process compromises the material's stability and performance. Under high-humidity conditions, water molecules expedite the hydration oxidation of MXene. In Ti2Tx MXene, Ti atoms are more prone to oxidation, forming TiO2 and significantly diminishing the material's conductivity. Prolonged exposure to high humidity causes gradual alterations in the interlayer structure of MXene, severely affecting its mechanical and electrochemical properties. To mitigate the impact of humidity, desiccants are commonly employed to control the storage environment. By placing a desiccant, such as silica gel, in the storage container, moisture is absorbed, effectively reducing humidity and minimizing contact between MXene and water molecules, thereby decelerating oxidation. Silica gel, known for its high hygroscopic efficiency, is frequently used. When MXene material is sealed in a container with silica gel, the humidity is maintained at a low level, significantly slowing the oxidation process. Experimental results indicate that silica gel can reduce storage humidity to below 10%, thereby substantially retarding MXene oxidation. Molecular sieves are another class of desiccants utilized for their strong moisture absorption capacity and thermal stability. By capturing water molecules from the air and trapping them within their internal structures, molecular sieves further reduce humidity levels in the storage environment. To ensure continuous desiccation, regular replacement or regeneration of the desiccant is necessary. Regeneration typically involves heating to eliminate adsorbed water, thereby restoring the desiccant's moisture absorption capability. Research has demonstrated that storing Ti3C2Tx MXene with a silica gel desiccant in a sealed container significantly reduces the oxidation rate. After six months of storage in low humidity, the material's electrical conductivity decreased by less than 5%, whereas samples stored in high-humidity conditions exhibited a conductivity decline of over 30%.106
The oxidation of MXene materials primarily results from reactions with oxygen and moisture in the air, leading to the formation of a surface oxide layer that adversely affects electrical conductivity and chemical activity. Dispersing MXene in an appropriate anhydrous organic solvent can isolate it from air moisture, preventing oxidation. Anhydrous organic solvents provide a moisture-free environment, substantially reducing the risk of hydration oxidation. These solvents also offer excellent dispersion stability, preventing MXene aggregation and precipitation during storage. The selection of a suitable solvent is critical for implementing effective antioxidant strategies for MXene storage. Studies indicate that anhydrous organic solvents such as acetonitrile and dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) can significantly delay MXene oxidation. Acetonitrile, a low-viscosity, anhydrous polar solvent, effectively inhibits MXene's contact with water molecules, providing a relatively oxygen-free storage environment. Research has shown that Ti3C2Tx MXene dispersed in anhydrous acetonitrile maintained stable conductivity and structure over several months, with a significantly reduced oxidation rate. MXene materials stored in acetonitrile exhibited a lower oxidation degree compared with those stored in aqueous solutions or air. Acetonitrile not only extends the storage duration but also ensures uniform dispersion, which is crucial for applications in energy storage devices. DMSO, a highly polar anhydrous solvent, is widely utilized in chemical reactions and material storage. With extremely low oxygen content, DMSO effectively isolates MXene from oxygen and water, preserving its electrical conductivity and structural stability over extended storage periods. Studies have shown that MXene materials dispersed in DMSO experience minimal changes in electrochemical properties, with a significantly reduced oxidation rate compared with materials stored in aqueous solutions or air. DMSO not only prevents oxidation but also ensures good dispersion, avoiding aggregation issues. This solvent is particularly suitable for long-term storage and applications requiring high performance retention, such as supercapacitors and lithium-ion batteries.107
The advantages of storage environment optimization strategy: (1) prolong the life of MXene: by optimizing the storage environment, the operational life of MXene materials can be significantly extended, thereby mitigating the deleterious effects of oxidation on their performance. (2) Maintain electrochemical performance: MXene materials, when stored under conditions of low temperature, vacuum, inert gas, or in solution dispersion, can sustain their high electrical conductivity and electrochemical activity over prolonged periods. (3) Suitable for large-scale storage: The optimized storage environment not only extends MXene's service life and maintains its electrochemical performance, but also ensures that it can maintain its efficient performance in large-scale storage processes.
Upon exposure to oxygen in the air, MXene materials tend to develop a thin oxide layer on their surfaces. This oxide layer not only impairs the electrical conductivity and electrochemical properties of the material but also leads to further oxidation during prolonged storage. Heating the material under an inert atmosphere enables low-temperature annealing to effectively remove these surface oxides without damaging the layered structure of the MXene material. Through low-temperature annealing treatment, the oxide layer on the surface of MXene can be reduced or eliminated, restoring its inherent surface chemical properties. Given the low annealing temperature (typically between 200 and 300 °C), this treatment does not substantially alter the layered structure of MXene, nor does it compromise its electrical conductivity and other properties. To achieve optimal antioxidant effects, low-temperature annealing is typically conducted under an inert atmosphere to prevent secondary oxidation by oxygen during the treatment process. Commonly employed inert gases include argon and nitrogen, which provide an oxygen-free environment to ensure the material's oxidation resistance is improved during annealing. Research indicates that the temperature range of 200–300 °C is the most effective for removing surface oxides, as it is sufficiently high to eliminate the oxide layer without causing structural collapse or degradation of the MXene material. The annealing duration is usually controlled within a few hours (e.g., 2–4 hours) to ensure complete removal of the oxide layer while minimizing exposure to high temperatures. Annealing in argon guarantees that the entire process occurs in the absence of oxygen, thus preventing secondary oxidation. In experimental settings, researchers have employed a sealed annealing furnace with argon gas flow to treat MXene. Results revealed that the material's surface oxide was significantly reduced post-treatment, and its electrical conductivity was restored. Low-temperature annealing is an effective post-treatment method for MXene synthesis, significantly enhancing the material's oxidation resistance by removing surface oxides under an inert atmosphere while maintaining its structural stability and electrical conductivity. Experimental outcomes demonstrated that the oxidation rate of MXene material after low-temperature annealing treatment at 200–300 °C was markedly reduced, electrical conductivity was restored, and storage life was substantially extended. The method described is both operationally straightforward and cost-effective, rendering it suitable for large-scale industrial applications. It furnishes technical support for the broad application of MXene materials in energy storage, catalysis, and other domains.
By establishing a protective layer on the surface of the MXene material, the antioxidant solvent effectively mitigates direct contact between oxygen and water with the material's surface, thereby diminishing oxidation reactions. The antioxidant solvent is capable of forming a protective film on the MXene surface, which serves to isolate against it oxygen and water in the atmosphere and decrease the incidence of oxidation. Certain antioxidant solvents possess chemical reducibility and can interact with the surface active sites to stabilize the material's chemical state, further enhancing its antioxidative properties. Ethanol, a prevalent organic solvent, exhibits favorable solubility and low toxicity. The hydroxyl group within its molecule can form hydrogen bonds with the MXene surface, thereby creating a protective film. The volatile nature of ethanol ensures that it leaves no residue during processing. Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), a polar solvent, effectively dissolves MXene and forms a stable protective layer on its surface. DMSO also boasts commendable antioxidant properties, providing supplementary chemical protection. Acetonitrile, an anhydrous organic solvent, effectively prevents water contact with MXene, thereby diminishing oxidation reactions. Acetonitrile demonstrates excellent dispersibility and stability throughout the treatment process. Selecting an appropriate antioxidant solvent, such as ethanol, DMSO, or acetonitrile, and preparing its solution entails adjusting the concentration according to the specific characteristics and processing requirements of MXene, typically within the range of 1–5%. The synthesized MXene material is dispersed in the antioxidant solvent. Ultrasonic treatment or agitation ensures a uniform dispersion of MXene. The MXene material should be thoroughly immersed in the solvent during processing. The dispersed MXene suspension is soaked in the antioxidant solvent for a stipulated duration, usually 1–2 hours, with the soaking time adjusted based on the specific reaction between the material and solvent. Post-treatment, the MXene is washed with a pure antioxidant solvent to eliminate unreacted solvents and other impurities. This washing process can be accomplished via centrifugal separation or filtration. The washed MXene material is then dried in a vacuum drying oven, typically at temperatures between 60 and 80 °C for several hours, until the material is fully dry. This drying process eradicates residual solvents and maintains the material's stability. Treating MXene materials with antioxidant solvents constitutes an efficacious synthetic post-treatment method, capable of forming a protective layer on the material's surface, thereby significantly augmenting its antioxidative properties. By judiciously selecting the solvent and fine-tuning the treatment parameters, the optimal antioxidative effect can be achieved while preserving the electrochemical properties and structural stability of MXene. This method's simplicity and cost-effectiveness render it apt for industrial production and large-scale application of MXene.
3.2. Safety
The MXene material has garnered increasing attention from both scientific research and industry due to its exceptional electrochemical performance and extensive application potential. However, the synthesis and processing of MXenes entail various inherent safety risks, including the use of toxic chemicals, high reactivity, and concerns regarding the safety of the material itself. Consequently, it is imperative to optimize the industrial production process of MXenes to ensure safety.By utilizing a composite acid system through the combination of other acids or fluorides, the quantity of HF required can be significantly reduced without compromising the etching efficacy. The components of the acid and fluoride in the composite acid system synergistically work to limit direct contact with HF, thereby decreasing its toxicity and corrosive potential. For instance, a composite acid system comprising LiF and HCl can be employed to etch the MAX phase. In this setup, LiF releases fluorine ions during the reaction, while HCl provides an acidic environment. This combination minimizes the dependence on HF while achieving efficient etching. LiF and HCl should be mixed in predetermined proportions, typically within a concentration range of 0.1 M to 1 M for LiF and between 1 M and 3 M for HCl, adjusted as per specific etching requirements. The MAX phase, such as Ti3AlC2, is then etched using the composite acid solution. It may be necessary to optimize reaction conditions (e.g., temperature, duration) to guarantee the desired etching results. Additionally, post-treatment of the waste liquid is essential to ensure that it does not contain high concentrations of HF, thereby minimizing environmental pollution.108
The synthesis of Ti3C2Tx involves a multi-step process, commencing with the treatment of combustible powders, such as aluminum and titanium carbide, or graphite, to synthesize the Ti3AlC2 MAX phase. The hazards inherent in the synthesis of MAX phases are applicable to various components, primarily involving the handling and storage of reactive powders, the operation of high-temperature furnaces, and the use of hydrochloric acid for cleaning MAX powder (Fig. 10b and c). The Ti3AlC2 phase is subsequently chemically etched using a strong oxidant in a highly exothermic process to yield the desired Ti3C2Tx. A general schematic detailing the step-by-step synthesis of Ti3AlC2 and Ti3C2Tx materials from raw materials is illustrated in Fig. 10a, along with the principal hazards associated with each step.47 MXenes are produced by the selective removal of layer A from the MAX phase powder, as depicted in Fig. 10d. In the most conventional case involving Ti3AlC2, the aluminum layer is removed using an aqueous solution of HF, which can be either introduced at different concentrations or generated in situ via fluoride-based compounds and acids, such as lithium fluoride and hydrochloric acid, respectively. The etching reaction is highly exothermic, yielding H2 gas and water vapor. This section reviews the process safety aspects of this step, with a particular focus on the exothermic nature of the reaction and the formation of by-products. As shown in Fig. 10e, the HF synthesis route employing 10 wt% or higher concentrations is the most hazardous, whereas the route utilizing lithium fluoride and hydrochloric acid, or F3Fe and hydrochloric acid to produce HF in situ, poses relatively lower risks. Etching with hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide is considered the least harmful. However, it is important to note that there are substantial differences in the quality and yield of Ti3C2Tx produced by these methods. There is currently no standardized method for reporting Ti3C2Tx yields; in this study, however, the yield of each synthetic route is estimated based on experimental mass and the reported final concentration, with the end group composition and final volume derived from XPS resulting images using previously reported similar etching methods and yields. Yields are categorized as high (>55%), medium (15% to 55%), and low (<15%). The synthetic routes involving HF and in situ HF (i.e., HCl/LiF and F3Fe/HCl) exhibit the highest yield, the sodium hydroxide method yields moderately, and the hydrochloric acid and NH4NF3 method yields comparatively the least. The most prevalent method for synthesizing Ti3C2Tx from Ti3AlC2 involves the use of hydrochloric acid and lithium fluoride, as this approach maintains high MXene yields while minimizing HF treatment during etching. Nonetheless, it is crucial to recognize that HF remains as a by-product of this method, necessitating appropriate precautions. This process is summarized in Fig. 10f, wherein a 6 M hydrochloric acid solution is introduced into a 5 M Teflon reactor containing lithium fluoride, and powdered Ti3AlC2 is gradually added to the solution to minimize bubbling during the reaction.109,110
 | ||
| Fig. 10 (a) Schematic diagram of Ti3C2Tx synthesis from raw materials. (b) Describes the safe synthesis of MXenes, from its precursor (MAX) to the end product (layered MXene); (c) as shown in the figure, steps associated with the production of MAX: ball milling, air oxygen passivation, high-temperature reaction, pickling to remove unreacted precursors and by-products. Reproduced from ref. 47 with permission from American Chemical Society, copyright 2021. (d) Schematic of Ti3AlC2 MAX phase etched to Ti3C2Tx MXene; (e) relative hazards of various etchant used to etch Al from Ti3AlC2 phase to Ti3C2Tx phase; (f) schematic of Ti3C2Tx MXene synthesis using LiF/HCl etchant and the hazards associated with these steps. Reproduced from ref. 108 with permission from American Chemical Society, copyright 2019. | ||
The synthesis process often involves the use of substantial amounts of acidic solutions, such as hydrofluoric and hydrochloric acids, which generate waste liquids containing acidic residues and heavy metal ions. If not properly treated, these waste products can lead to environmental pollution, disrupt ecosystems, and pose health risks to personnel. Consequently, effective waste treatment and neutralization are critical for enhancing production safety and environmental protection. Waste liquids produced during MXene preparation should be collected in dedicated containers to prevent leakage and cross-contamination. Solid particles and sediments in the waste liquids are separated through sedimentation or centrifugation, reducing the burden on subsequent treatment processes. Neutralization is achieved using alkaline substances such as NaOH or Na2CO3. These neutralizers react with acidic components in the waste, forming salts and water, thereby neutralizing the acidity. Sodium hydroxide or sodium carbonate is gradually added to the waste liquid while continuously stirring to ensure uniform reaction. The pH of the waste liquid is continuously monitored to ensure neutrality (pH ∼ 7). Over-addition of neutralizers can lead to waste and secondary pollution, necessitating careful and gradual adjustment. Following the neutralization process, precipitates such as sodium sulfate or ferric hydroxide may form in the waste solution. These are separated via precipitation or filtration to remove them from the waste liquid. The neutralized waste liquid should undergo further treatment, such as the elimination of residual harmful substances and heavy metal ions through activated carbon adsorption or membrane separation technologies, to comply with environmental regulations. The sediment (waste residue) must be managed in accordance with local environmental regulations, typically involving safe landfill or high-temperature incineration processes. Post-treatment, both the waste liquid and residue should be tested for compliance to confirm adherence to discharge standards and prevent new environmental pollution.
In the industrial production of MXene, the use of hazardous chemicals such as HF necessitates stringent safety measures, even when risks are mitigated via low concentrations or alternatives. These measures include the design and implementation of secure storage systems to prevent leakage and accidental exposure to chemical agents. Containers made from corrosion-resistant materials, such as polyvinyl fluoride (PTFE) or high-density polyethylene (HDPE), should be selected to withstand the erosion of highly corrosive chemicals like HF. A dual sealing system should be employed to prevent volatilization and leakage, with regular checks and maintenance of the seal status ensuring proper containment. Automated feeding systems should be utilized to minimize manual handling, thereby reducing the risk of operator exposure to hazardous chemicals. These systems should feature precise control and monitoring functionalities to ensure accuracy in the transfer of chemicals from storage to reaction equipment. The waste liquid treatment system should incorporate neutralization, precipitation, and filtration processes. Acidic waste should be neutralized using automated systems, employing alkaline substances such as NaOH or Na2CO3 to adjust the waste to a safe pH range. The by-products are then separated via precipitation, and the treated waste is ultimately transported to an environmentally friendly treatment facility. Real-time monitoring systems should be installed to track pressure, temperature, and chemical concentrations during storage and reactions. These systems should include an alarm function to alert operators to abnormalities. An emergency response system, featuring automated leak detection and isolation devices, should be established. The emergency response plan should encompass spill-handling procedures, evacuation plans, and training for emergency personnel.111
Researchers have also investigated alternative green or non-toxic reagents for MXene preparation, beyond direct replacement or optimization of conventional etching agents. For instance, organic acid-based etching methods are being developed to entirely avoid corrosive inorganic acids. Utilizing relatively mild organic acids such as oxalic or citric acid as etching agents, the reaction conditions are regulated to effectively etch MAX phase materials and produce MXene. This organic acid etching method not only enhances operator safety but also simplifies waste liquid disposal. Although still in developmental stages, this method holds significant potential for toxicity reduction and environmental protection. Further optimization could facilitate its industrial application, thereby mitigating overall production risks.
Advantages of safe chemical selection and handling: (1) by opting for low-concentration or green alternative reagents, the exposure risk of operators to harmful chemicals is substantially diminished. (2) Reduce environmental pollution: optimizing the waste liquid treatment and neutralization process minimizes chemical waste liquid pollution and enhances production process sustainability. (3) Increased industrial adaptability: the development of safer reagents and automated processing systems ensures the safety and sustainability of MXene industrial production, paving the way for large-scale applications.
The automatic control system plays an important role in the precise regulation of key parameters such as temperature, pressure and reactant addition. By reducing manual intervention, the system not only reduces the operator's risk of direct contact with corrosive acids, such as hydrofluoric acid, but also avoids the dangers caused by overheating or excessive reactant use. In addition, automated technology enables real-time monitoring of reaction conditions, such as pH, gas concentration and temperature, and automatically adjusts or stops the reaction once anomalies are detected, ensuring that the production process is always safe and controlled.112 In industrial production, automated systems further improve production efficiency and product consistency by remotely monitoring and regulating reaction parameters such as acid injection volume, reaction time, etc. At the same time, the automated waste gas and liquid waste treatment system can treat acid waste gas and liquid waste in real time, through neutralization, precipitation and other processes to restore them to a safe range, thereby reducing the harm to the environment and operators.113 To further improve security, the system is equipped with a real-time warning mechanism. Through gas leak sensors, temperature and pressure monitoring equipment, the system is able to immediately alert when anomalies are detected and automatically perform emergency measures, such as shutting down the reaction system or activating emergency ventilation. These features significantly improve the safety and reliability of production, ensuring rapid response in emergency situations and preventing safety incidents.111
The advantages of automated reaction equipment: (1) by utilizing enclosed and automated reaction systems, operators are not directly exposed to hazardous chemicals, thereby minimizing safety risks associated with accidental leaks and operational errors. (2) Automation control technology enables precise management of reaction conditions, accelerates production rates, reduces human intervention time in the production process, and improves the stability and reproducibility of output. (3) Environmental friendliness: with an automated waste gas and liquid treatment system, by-products are processed in real time during the reaction process, thereby reducing environmental pollution and promoting greener, more sustainable production practices.
During MXene production, particularly in the fluorination etching stage, the environmental control system should monitor and regulate the temperature, humidity, and gas concentration of the reaction environment to ensure the stability and safety of the reaction. For instance, the temperature control system maintains the reaction room's temperature within the predetermined range to prevent reaction instability due to excessive heat or the release of harmful gases. By installing high-precision temperature and humidity sensors in the reaction chamber, these sensors continuously monitor the environmental parameters and automatically adjust the air conditioning or heating devices through the feedback control system to ensure that the environmental conditions consistently meet production requirements. Additionally, gas detectors monitor the concentration of harmful gases in the reaction chamber, and the ventilation system can be promptly adjusted to prevent the accumulation of gases to dangerous levels. The environmental control system effectively maintains the stability of the production environment, preventing reaction fluctuations or equipment failures caused by environmental factors. By controlling temperature and humidity, the impact on the material is minimized, thereby enhancing the consistency and quality of the product.114
Ventilation systems are crucial in MXene production, particularly in managing harmful gases generated during the reaction. For example, during the etching stage in the reaction chamber, the ventilation system effectively expels toxic gases (such as HF) from the reaction area, safeguarding both the operator and the environment. Utilizing efficient exhaust systems and gas handling devices, such as activated carbon filters or chemical scrubbers, these systems manage the harmful gases released during the reaction. The ventilation system maintains the gas concentration within the safe range by continually exchanging the air in the reaction room with fresh outside air. Additionally, airflow simulation technology optimizes the ventilation design to ensure that harmful gases are effectively captured and disposed of. Enhanced ventilation systems significantly reduce the concentration of harmful gases, protecting operator health and minimizing environmental pollution. An efficient gas capture and treatment system also improves the safety and stability of the production process. In large-scale MXene production facilities, integrated environmental control and ventilation systems enable automated management, further enhancing production safety. For example, by linking the environmental control system with the ventilation system, the reaction environment is comprehensively monitored and regulated. In the event of an anomaly, the system can automatically implement countermeasures, such as increasing the ventilation rate or adjusting the ambient temperature. The integrated system manages environmental control and ventilation functions through a central control unit, which automatically adjusts the ventilation rate when harmful gas concentrations are detected to be abnormal or when environmental conditions are suboptimal. It also maintains production stability by controlling environmental parameters such as temperature and humidity. Real-time data transmission and monitoring systems provide operators with instant feedback, ensuring a swift response to any situation. This integrated system can achieve complete automatic management of the production environment, thereby improving both the safety and efficiency of the production process. Real-time monitoring and automatic regulation can effectively mitigate the impact of environmental conditions on the production process while ensuring the safety of the reaction.115
In the industrial production of MXene, systematic toxicity assessments represent a crucial step in ensuring production safety. This encompasses a comprehensive evaluation of both the biocompatibility and potential toxicity of MXene materials. In vitro cellular assays are commonly employed to evaluate the effects of MXene on biological cells. Various cell lines, including human skin cells (such as HaCaT) and liver cells (such as HepG2), can be selected for experimentation as they represent different biological systems and facilitate a comprehensive evaluation of MXene cytotoxicity. Cells are treated with MXene at varying concentrations, with a control group established for comparison. Treatment methods may include direct addition to the culture medium or utilization of cell contact tests. Cell counting kits (such as CCK-8 or MTT) are utilized to assess cell survival and proliferation, with these kits indirectly reflecting cellular health by measuring metabolic activity. Microscopic observations are performed to identify morphological changes, including cell contraction, deformation, or apoptosis. Membrane permeability assays, utilizing flow cytometry or fluorescent staining techniques, are employed to determine whether MXene induces damage to cell membranes. In vivo animal studies provide further insights into the toxicity of MXene across an entire organism. Typically, mouse or rat models are employed, with exposure routes selected based on the study's requirements, which may include oral administration, injection, or inhalation. Animals may be exposed to MXene through various methods, such as gastric tube injection of a MXene solution or intraperitoneal injection of a MXene suspension. The evaluation encompasses the distribution, metabolism, and potential toxicity of MXene in vivo, involving monitoring of weight changes, blood biochemical markers, and histopathological alterations. Additionally, it is essential to analyze whether MXene accumulates in specific tissues, as this may lead to long-term biological toxicity. The safe dosage range is established by gradually escalating the MXene dosage while continuously monitoring the animals’ health status to ensure the absence of severe toxic reactions.116 Moreover, environmental impact assessments are essential to ensure ecological protection throughout the MXene production process. Through environmental risk evaluations, researchers can determine the potential environmental impact of emissions resulting from the MXene production process, which includes the treatment and disposal of gaseous, liquid, and solid waste. These assessments can assist in identifying and managing harmful substances potentially released during production, thereby facilitating the implementation of effective control measures. For environmental impact assessments, samples of exhaust gases, liquids, and solids generated during production can be collected for chemical composition analysis and toxicity testing. Environmental monitoring instruments should be employed to measure emission levels from production facilities, comparing them against national or regional environmental standards to ascertain their environmental impact. A comprehensive environmental impact assessment can identify production-related environmental risks and aid in the development of appropriate environmental protection measures, ensuring compliance with environmental regulations and minimizing adverse impacts.117 Lastly, the long-term stability of MXene materials is a vital consideration in safety assessments within both production and application contexts. Researchers can evaluate the stability of MXene under various environmental conditions, including elevated temperatures, high humidity, and acidic or alkaline environments. This can be conducted through long-term storage tests and accelerated aging experiments to assess the structural stability and performance retention of MXene under these conditions. For long-term stability assessments, MXene samples can be subjected to different environmental scenarios (such as high temperature, high humidity, or strong acids/bases), with periodic testing of their structure and properties. Techniques such as XRD, SEM, and TEM are employed to monitor structural changes and properties of MXene. Through long-term stability evaluations, the durability and reliability of MXene in practical applications can be determined, thereby providing foundational insights for material selection and process optimization in industrial production.118
3.3. Cost
In the industrial production process of MXene materials, cost control is a critical factor for achieving large-scale application and commercialization. To facilitate the broad industrial application of MXene, it is essential to optimize the production process and reduce production costs.In industrial production of MXene, the transition metal constitutes the core raw material for synthesis. Particularly in the fabrication of Ti3C2 MXene, the selection of the titanium source is critical for controlling production costs and ensuring the quality of the final product. Optimizing the selection of raw materials, particularly titanium sources, can significantly reduce costs and enhance production efficiency. The traditional synthesis of Ti3C2 MXene has predominantly relied on high-purity titanium compounds such as TiCl4 or titanates (e.g., barium titanate). These high-purity titanium compounds exhibit favorable reactivity and ensure the high quality of MXene but are costly, significantly inflating production costs. In large-scale industrial applications, the high cost of high-purity titanium compounds, compounded by the uneven distribution of global titanium resources, leads to fluctuations in production costs, thereby limiting the widespread application of MXene in various fields. To mitigate production costs, researchers have investigated more economical alternatives for titanium sources, including titanium ores and TiO2. These alternatives are substantially less expensive than high-purity titanium compounds yet can yield product quality comparable to traditional sources through process optimization. Recent studies have demonstrated that high-quality Ti3C2 MXene can be successfully produced using titanium oxide (TiO2) as a titanium source in the presence of reducing agents (e.g., hydrogen). TiO2 is initially reacted with carbides or other elements to form titanium carbides (TiC), which are subsequently reduced under a hydrogen atmosphere to remove excess oxides. This process not only lowers raw material costs but also renders the production process more environmentally friendly, as TiO2 is more readily available and less environmentally impactful than conventional titanium compounds. By regulating the temperature, hydrogen flow rate, and reaction time of the reduction process, high-efficiency titanium reduction can be achieved, enhancing the utilization rate of the titanium source and minimizing by-product generation. As natural titanium resources, titanium ores (e.g., rutile, ilmenite) are inexpensive and abundant, offering a potential source of raw materials. In production, titanium ore requires preliminary purification to remove impurities before being used in the synthesis of Ti3C2 MXene. Not only is titanium ore inexpensive, but it can also further reduce purification costs through existing ore refining processes. Given that titanium ores may contain more impurities, additional pretreatment steps are essential to ensure the final quality and purity of MXene. Comparative experiments on various titanium sources have revealed that optimized low-cost titanium sources (e.g., TiO2), combined with an appropriate reducing agent, can produce high-quality MXene with key performance indicators such as electrical conductivity and specific surface area comparable to that produced using high-purity titanium compounds. By integrating considerations of raw material cost, process complexity, and final product performance, researchers conducted a series of experiments to optimize production parameters, ultimately identifying a cost-effective raw material selection scheme. This scheme not only reduced raw material costs but also enhanced overall production efficiency.119
Etching agents are employed in the synthesis of MXene to remove the A layer from the MAX phase, a critical process that significantly influences the final quality of MXene. Traditionally, HF has been extensively utilized in etching processes; however, its high cost and substantial environmental impact have garnered increasing attention. To mitigate these issues, the exploration of low-cost, environmentally benign alternative etching agents has become imperative. For instance, researchers have suggested the use of ammonium fluoride (NH4HF2) as a viable alternative. Ammonium fluoride exhibits lower toxicity and safer operational conditions compared with hydrofluoric acid, while effectively etching the A layer in the MAX phase. Utilizing ammonium fluoride not only reduces production costs but also diminishes the risk of environmental pollution. Furthermore, this substitutional approach holds the potential to enhance the quality and performance of MXene, thereby increasing overall production efficiency.120
In the surface modification of MXene, the carbon source serves to provide carbon-based functional groups to the material, significantly affecting its electrical conductivity and electrochemical properties. Carbon sources such as acetylene and methane, due to their high carbon content and manageable reactivity, can effectively react with the surface of MXene materials to form carbon-based functional groups suitable for energy storage applications. Nonetheless, these carbon sources are more expensive and require sophisticated control systems during synthesis, thereby increasing overall production costs. The expenses associated with carbon sources like acetylene and methane are challenging to control in large-scale production, and their stringent reaction conditions (such as high temperature and high pressure) necessitate additional energy consumption and equipment investment, further escalating production costs. Consequently, identifying alternative carbon sources has become a pivotal strategy to reduce costs. To mitigate production costs, researchers are exploring the use of low-cost carbon sources, such as biomass carbon. Biomass carbon, a type of carbon material derived from renewable resources (such as wood and crop residues) through pyrolysis or carbonization processes, has become a strong candidate to replace traditional carbon sources due to its easy availability and low raw material cost. Biomass carbon possesses a porous structure and a large specific surface area, which can effectively enhance the density of surface functional groups and electrochemical activity of MXene. Given its porous nature, biomass carbon can also improve ion transport performance within the material, contributing to enhanced application performance in electrochemical energy storage. Moreover, the preparation process of biomass carbon is relatively straightforward, does not require a complex gas control system, and can be conducted under normal or low pressure, further reducing energy consumption and equipment investment. When utilized as the carbon source for MXene, the optimization of pyrolysis conditions can enhance the energy storage capacity and cycling stability of MXene materials while maintaining their original electrochemical performance. Studies have demonstrated that the specific capacitance and conductivity of MXene remain high after substituting traditional carbon sources with biomass carbon, with a significant reduction in material costs.
The nitrogen source serves to adjust the nitrogen-based functional groups of MXene material, which can markedly enhance its electronic structure and catalytic activity. Nitrogen sources such as ammonia and ammonium nitride can effectively provide nitrogen atoms during the synthesis process, conferring the MXene surface with favorable nitrogen-doping properties. However, gaseous nitrogen sources like ammonia are costly and impose stringent requirements on transportation, storage, and reaction conditions, thereby elevating costs in the production process. The use of ammonia and ammonium nitride not only incurs higher costs but also imposes specific demands on reaction equipment. For example, the use of ammonia necessitates high-pressure gas equipment and robust piping systems, increasing the complexity and safety risks of the production facility. Consequently, identifying a cost-effective and operable nitrogen source has become an urgent issue to address in MXene industrial production.121
MXene is typically synthesized through chemical etching, which entails the removal of the A layer from MAX phase materials. This process predominantly employs wet chemistry techniques, utilizing strong acids, such as hydrofluoric acid, to etch the MAX phase. However, conventional wet chemical methods present several drawbacks, including prolonged reaction times, elevated consumption of chemical reagents, and substantial waste disposal costs. In traditional wet chemistry, HF commonly acts as the etching agent to eliminate the A layer (the metallic element layer) within the MAX phase, resulting in the formation of MXene with a two-dimensional layered structure. The MXene process involves dissolving lithium fluoride in 6 M hydrochloric acid, gradually adding Ti3AlC2 powder, and heating the mixture at 40 °C for 45 hours. Following the etching, the resulting sediment is thoroughly washed to eliminate reaction byproducts and increase the pH through multiple cycles of water addition, centrifugation, and decantation. This results in a deposition that resembles a clay-like paste, which, when wet (Fig. 11a), can be rolled between permeable films using a roller mill, generating a flexible independent film within minutes, in contrast to previous labor-intensive methods involving insertion, delamination, and filtration. The XRD pattern of the etched material exhibits a marked increase in the intensity and sharpness of the (000l) peaks in its air-dried multilayer state (Fig. 11b, pink). In certain cases, the full width at half maximum (FWHM) is as small as 0.188°, as opposed to the broader peaks typically associated with HF-etched MXenes. When the “clay” material is subjected to rolling into films, the XRD pattern subsequently reveals a robust order in the c-axis direction (Fig. 11b, blue). The thickness of the resulting thin films ranges from sub-microns to approximately 100 μm, and this method facilitates their straightforward production. Notably, there is a significant reduction in the intensity of the particle shear peak (110) at an angle of 61°, indicating a decrease in ordering in the non-fundamental direction while maintaining order in the c-axis direction (refer to the blue XRD pattern in Fig. 11b and the SEM images in Fig. 11d). Morphologically, the cross-sectional view (Fig. 11c) of the sheet reveals integral shear among multiple layers of particles, demonstrating remarkable flexibility even upon complete drying. The etching process using lithium fluoride and hydrochloric acid is considerably milder than HF, resulting in an increased transverse expansion size (Fig. 11d) and a lack of nanoscale defects commonly observed in HF-etched samples. TEM analysis indicates that over 70% of the 321 sheets examined possess dimensions ranging from 0.5 to 1.5 μm. A single layer, approximately 10 Å thick, was visualized via TEM (Fig. 11e), confirming the material's two-dimensional nature. An examination of 332 sheets revealed that approximately 70% were 1 to 2 layers thick.122 It is important to note that this 70% estimate is conservative, as restacking or folding of the sheets may result in an apparent increase in thickness. The structural similarities between MXene and graphene are noteworthy, including the exfoliation of 2D Ti3C2 layers (Fig. 11f and g) into multilayer flakes akin to exfoliated graphite, as well as the formation of scrolls (Fig. 11i and j). Additionally, as demonstrated in the TEM images (Fig. 11j), certain nanosheets can bend to radii of less than 20 nm without fracturing, providing evidence of the strength and flexibility of the Ti3C2 layers. A similar scrolling effect was also achieved through ultrasonic treatment of graphene.123 It was hypothesized that the ultrasonic treatment employed during the exfoliation process induces the rolling of some nanosheets into scroll-like structures, as illustrated in Fig. 11k.2 For instance, a multilayer architecture can serve as a host for lithium storage. Density functional theory (DFT) calculations at 0 K in Li-rich environments reveal the formation of Ti3C2Li2 due to the insertion of Li into the vacancies created by the removal of Al atoms (Fig. 11h). However, the use of HF, a highly corrosive and hazardous substance, necessitates high concentrations, leading to substantial consumption. The etching process is time-consuming and requires a large quantity of chemical reagents, which not only escalates reagent costs but also imposes stringent safety and handling requirements due to the production environment's potential hazards. Furthermore, the etching process generates significant amounts of toxic by-products, such as fluoride gases and acidic waste liquids, necessitating specialized waste gas treatment systems and liquid waste neutralization equipment. This, in turn, increases the environmental treatment costs associated with the process. The high pollution levels and elevated costs associated with this process pose significant challenges to the large-scale industrial production of MXenes. To mitigate these issues, researchers have proposed the use of NH4HF2 as a safer and more cost-effective alternative etchant. As a fluoride compound, ammonium fluoride releases fluorine ions at lower concentrations, achieving a comparable etching effect to hydrofluoric acid but with reduced toxicity and corrosiveness, making it a more economically viable option. Even at low concentrations, ammonium fluoride demonstrates excellent etching capabilities, significantly reducing fluoride emissions. By substituting hydrofluoric acid with ammonium fluoride, the chemical etching process is markedly improved. The required reagent dosage is reduced, and because ammonium fluoride is less corrosive, the reaction conditions are milder, thereby decreasing equipment corrosion and wear. Moreover, ammonium fluoride effectively removes the A-layer from the MAX phase at low concentrations, shortening reaction times and minimizing overall reagent consumption. The reduced concentration also curtails by-product formation, simplifying subsequent waste treatment procedures. The adoption of ammonium fluoride significantly diminishes the generation of harmful gases, such as hydrogen fluoride, during the etching process, thereby reducing environmental impact. Compared with hydrofluoric acid, the by-products of ammonium fluoride etching exhibit lower toxicity, simplifying waste liquid treatment and effectively lowering waste treatment costs. The use of this more environmentally benign reagent improves both the safety and environmental sustainability of the entire process, offering a more feasible solution for large-scale production. In addition to cost advantages, the ammonium fluoride etching method demonstrates superior product quality. The relatively mild etching process minimizes damage to the MXene layer structure, resulting in materials with higher structural integrity and enhanced performance stability. Experimental results indicate that ammonium fluoride etching reduces interlayer defects in MXenes during exfoliation, thereby improving the electrochemical performance and energy storage capacity of the material. In the ongoing optimization of wet chemistry processes, the recovery and reuse of reagents represent an important avenue for reducing production costs. Researchers are currently investigating methods to chemically recycle ammonium fluoride post-etching to further decrease reagent consumption and waste generation. This recycling strategy not only promises further reductions in reagent costs but also aims to significantly lessen the environmental impact, rendering MXene production more sustainable.102
 | ||
| Fig. 11 (a) Schematic diagram of MXene clay synthesis and electrode preparation. Structural characterization of MXene; (b) XRD patterns of samples produced by etching in LiF 1 HCl solution; (c) SEM image of a fracture surface of a 4 mm-thick film produced by rolling, showing shearing of layers. Fracture surface of a thicker rolled film (30 mm); (d) TEM image of several flakes, showing lateral sizes up to a few hundred nanometres; (e) TEM images of single-and double-layer flakes, respectively. Insets show sketches of these layers. Reproduced from ref. 122 with permission from Nature, copyright 2014. (f) TEM images for stacked layers of Ti–C–O–F. Those are similar to multilayer graphene or exfoliated graphite that finds use in electrochemical storage; (g) The same as (f) but at a higher magnification; (h) model of the Li-intercalated structure of Ti3C2 (Ti3C2Li2); (i) conical scroll of about 20 nm in outer diameter; (j) cross-sectional TEM image of a scroll with an inner radius of less than 20 nm; (k) schematic for MXene scroll (OH-terminated). Reproduced from ref. 2 with permission from Wiley-VCH, copyright 2011. | ||
Microwave-assisted heating technology has gradually emerged as one of the key advancements in material synthesis. During the preparation of MXene, this technology has demonstrated the ability to significantly reduce reaction time, enhance energy utilization, and lower overall production costs. Microwave heating expedites and homogenizes the thermal system by directly interacting with the molecules of the reactants via electromagnetic waves. In contrast to traditional electric furnace heating, microwave heating is characterized by high energy efficiency, as it selectively heats polar molecules within the reaction system, such as water components or other polar solvents. In the synthesis of MXene, microwave heating rapidly elevates the temperature of aqueous substances within the reaction system, circumventing the energy losses inherent in the heat transfer process of traditional heating methods. This capability enables microwave heating to complete chemical reactions in a shorter duration, substantially enhancing reaction efficiency. The chemical etching process of MXene is expedited, and reaction times are markedly shortened through microwave-assisted heating technology. Whereas traditional electric furnace heating typically requires several hours or longer to remove the A layer (metal layer) from the MAX phase material, microwave heating can accomplish the etching process within a few minutes to tens of minutes. The reduction in reaction time not only augments production efficiency but also curtails equipment operation time, diminishes energy consumption and wear, and further lowers production costs. Microwave heating primarily conveys energy through the selective heating of polar molecules within the reaction system. For instance, in systems employing aqueous media or polar solvents, microwaves can directly heat water or other polar molecules within the reactants, rapidly attaining the desired reaction temperature. Compared with conventional heating methods, microwave heating is more uniform, mitigating local overheating or cold spot phenomena and preventing structural defects in materials caused by temperature irregularities. During the etching of MXene, microwave heating accelerates the etching reaction time by enhancing the removal of the A layer from the MAX phase material via fluoride ions. In practical applications, microwave energy acts upon water molecules or fluorine-containing reagents within the reaction system, allowing ions to quickly infiltrate the interior of the MAX phase, thereby accelerating the dissolution and stripping of the metal layer and ultimately forming layered MXene structures. Relative to traditional heating methods, microwave-assisted etching reactions exhibit greater speed and efficiency, significantly improving the uniformity and integrity of the MXene layers. Compared with traditional electric furnace heating, microwave-assisted heating markedly reduces energy consumption. Due to the efficient energy transfer and shortened reaction time inherent in microwave heating, electricity consumption throughout the synthesis process is diminished, resulting in substantial savings in energy costs. Notably, in large-scale production scenarios, the reduction in energy consumption holds significant implications for overall cost management. Additionally, microwave heating mitigates equipment maintenance costs associated with prolonged operation during electric furnace heating processes, further contributing to reduced production expenditures.
Traditional MXene synthesis predominantly employs batch reactions. While this approach is suitable for small-scale laboratory research, large-scale industrial applications necessitate numerous repetitions of batch synthesis, with substantial inter-reaction intervals, leading to low production efficiency and elevated costs. Continuous flow synthesis processes can effectively enhance productivity and minimize downtime. By structuring the MXene synthesis process as a continuous flow reaction within a closed system, reactants can be continuously introduced and MXene material continuously generated, minimizing production delays and simultaneously enhancing reaction uniformity and product quality. The continuous flow process substantially augments MXene's production efficiency, curtails equipment idle time due to batch production, and simplifies operational complexity, rendering it suitable for large-scale production and significantly lowering production costs per unit time. In the synthesis of MXene, the extensive use of organic solvents for washing and separation incurs significant costs, and additional environmental treatment expenses are incurred in managing and discharging these solvents. Consequently, the recovery and reuse of solvents serve to effectively reduce solvent usage costs.124 Within the production process, the design of a solvent recycling system allows for the recovery and reuse of organic solvents from the etching process in subsequent steps. Such systems decrease the need for fresh solvents, mitigate solvent disposal costs and reduce liquid waste discharges. The solvent recovery system notably diminishes organic solvent consumption, lowers production costs and environmental pollution, while ensuring consistent product quality. Through the strategic design of the recycling process, this approach effectively bolsters both environmental protection and economic benefits.125
In the industrial production of MXene materials, energy consumption is particularly high during the processes of heating, stirring, separation, and drying. The adoption of equipment with high energy efficiency can lead to significant reductions in energy usage. Energy-efficient equipment effectively decreases energy costs during production by minimizing unnecessary energy losses and promoting optimal resource utilization. In the drying and heating stages of MXene materials, utilizing efficient reactors and drum drying equipment can prevent heat energy waste and accelerate the drying process. Such devices not only optimize heat energy usage but also minimize the need for repetitive heating processes, thus conserving both time and energy.126 In addition to selecting energy-efficient equipment, the implementation of energy consumption monitoring and management systems throughout the production process can significantly enhance energy efficiency. The energy management system allows for real-time monitoring of the energy consumption of each piece of equipment involved in production. It also regulates the operational status of the equipment based on real-time data to prevent excessive energy usage and resource waste. An intelligent energy management system has been incorporated into MXene's continuous production line. This system monitored the equipment's energy consumption and automatically adjusted parameters, such as heating and stirring speeds, to prevent energy waste during non-critical operational periods. Furthermore, these energy management systems contribute to reduced energy costs by optimizing energy usage times, such as scheduling production during periods of lower electricity rates. By effectively minimizing energy waste during production, the intelligent energy management system enhanced resource allocation and achieved significant cost savings, particularly during peak–valley periods of power consumption. Through real-time monitoring and adjustments, the energy efficiency of the plant markedly improved, ensuring optimal usage throughout all stages of the production process.127
In the industrial production of MXene materials, considerable waste heat is generated during heating and cooling processes. The recovery and reuse of this waste heat for other production processes can substantially decrease energy waste. Waste heat recovery not only diminishes overall energy consumption but also reduces greenhouse gas emissions, thereby enhancing the plant's level of environmentally sustainable production. In the MXene production process, high-temperature residual heat from the synthetic reactor is captured via a heat exchange system and utilized in other heat-requiring processes, such as solvent recovery or material pre-heating. This waste heat recovery technology significantly lowers the external heating demands within the production process, thereby reducing energy expenditures. The waste heat recovery system optimizes the utilization of energy produced during the reaction process, thereby minimizing waste and enhancing overall energy efficiency. This is particularly impactful in large-scale continuous production, where the integration of waste heat recovery systems can lead to a substantial reduction in electricity and fuel consumption, thus significantly lowering production costs.124 Moreover, the incorporation of automation and intelligent technologies not only enhances production accuracy but also reduces errors and energy wastage associated with manual operations. Intelligent equipment can adapt operational parameters to meet production requirements, thereby minimizing energy usage. Furthermore, automation technology maintains the production line in an efficient operational state, thus mitigating energy waste caused by downtimes. The fully automated management of MXene material production, facilitated by intelligent control systems, exemplified during the etching process, allows for precise regulation of temperature and reaction time, reduces human error, and ensures efficient energy utilization. The automatic monitoring system enables equipment adjustments independent of manual intervention, thereby increasing production efficiency. Overall, automation and intelligent equipment significantly enhance production efficiency and diminish energy waste during manufacturing processes, particularly in continuous production scenarios. Such advancements not only lower production costs but also reduce operational expenses and improve the market competitiveness of MXene materials.
The expansion of production scale, coupled with improvements in production line efficiency, can lead to a significant reduction in unit costs. Employing standardized processes and equipment decreases variable production costs, thereby enhancing both the stability and efficiency of the manufacturing process. Moreover, substantial production volumes confer procurement advantages, allowing for bulk purchases of raw materials at reduced prices and further lowering overall production costs. For instance, chemical reagents and raw materials required in the MXene production process, such as HF and LiF, are acquired in bulk quantities, resulting in significantly lower unit prices. Additionally, the utilization of standardized large-scale synthetic apparatus and continuous production lines minimizes both time and equipment maintenance costs throughout the manufacturing process. This scale effect not only optimizes cost structures but also bolsters the market competitiveness of firms. By scaling up production, the unit production costs of MXene materials have been considerably decreased, particularly during the high-purity MXene continuous production process, which has substantially reduced labor, energy consumption, and maintenance expenses. This strategic approach has markedly enhanced the company's profit margins and rendered the market pricing of MXene materials more competitive.128
In the context of large-scale MXene production, traditional batch processes have imposed limitations on production capacity increases; however, the implementation of continuous synthesis processes effectively addresses this challenge. Continuous production not only facilitates increased output but also diminishes equipment idle time and maintenance-related downtime. Moreover, the standardization potential of the continuous synthesis process enhances product quality consistency, thereby reducing defect rates. During the synthesis of MXene materials, continuous flow synthesis technology can vastly improve material yields. For example, the synthesis of Ti3C2Tx MXene utilizing a continuous flow reactor instead of a conventional batch reactor not only boosts yield but also minimizes waste liquid and exhaust gas generation, thus lowering environmental treatment costs. The continuous flow reactor features a high degree of automation, which contributes to reduced labor costs and enhances the overall efficiency of the production line. The continuous process significantly decreases equipment downtime throughout manufacturing while ensuring greater consistency in MXene material quality across batches, thereby minimizing waste and defective product rates. Concurrently, reduced manual intervention in the production process lowers the likelihood of operational errors and further decreases labor costs, enhancing overall economic efficiency.
3.4. Stability
The colloidal dispersion of MXenes in water exhibits remarkable stability due to their negative zeta potential. However, a significant drawback in utilizing MXenes in aqueous mixtures is their relatively short shelf life, which is attributable to the oxidation of titanium layers, resulting in the formation of titanium oxide. This oxidation occurs as a consequence of the interaction between MXene flakes and water. In non-aqueous mixtures, these flakes may also react with dissolved oxygen present in the medium. Hydrolysis of MXenes is pivotal in the complete transformation of Ti3C2 MXenes into TiO2 in aqueous environments. The degradation process is evidenced by a gradual color change in the mixture: it transitions from black (colloidal solution) to light gray (after 3 days), off-white (after 14 days), and ultimately to milky white (after 28 days).129The oxidation of MXenes primarily occurs at active sites on their surfaces, where reactions with oxygen and water gradually lead to the formation of an oxide layer. As oxidation progresses, the electrochemical properties of MXenes decline rapidly, significantly weakening their electrical conductivity and energy storage capacity. This degradation not only undermines the energy storage efficiency of MXenes but may also result in structural collapse during prolonged storage or usage, compromising their unique layered structure. Consequently, the development of technologies to effectively mitigate the oxidation of MXenes has emerged as a crucial avenue for enhancing their stability. Carbon nanotubes, characterized by high strength and excellent conductivity, are a carbon-based material with remarkable chemical stability, making them ideal antioxidants for MXenes. By integrating carbon nanotubes with MXenes, a physical barrier can be established on the MXene surface to impede the ingress of oxygen and water, thereby delaying the oxidation process. This addition not only enhances the oxidation resistance of MXenes but also improves their electrical conductivity and mechanical properties, facilitating the long-term stability of MXenes in energy storage applications. Dopamine, an organic molecule known for its good biocompatibility, can form a uniform protective film on the MXene surface through a self-assembly process. Research indicates that the self-polymerization of dopamine molecules on MXene surfaces effectively blocks external oxygen and moisture, significantly enhancing the antioxidant performance of MXenes. Notably, in the case of Ti2Tx MXenes, the protective layer formed by dopamine not only improves the material's oxidation resistance but also positively impacts its energy storage performance. Polyvinyl alcohol (PVA), an inexpensive and easily processed polymer material, can be bonded to the MXene surface through chemical binding or physical adsorption. The PVA coating provides stable protection by preventing the ingress of oxygen and moisture, thereby significantly delaying the oxidation process. Researchers have found that the introduction of a PVA coating extends the storage time of MXene materials in air from mere days to weeks, or even longer. In addition, the introduction of PVA did not adversely affect the electrochemical properties of MXene, thereby preserving its high electrical and ionic conductivity. A study on Ti2Tx MXene demonstrated that the incorporation of dopamine during the synthesis or post-processing stages significantly enhanced the material's antioxidant properties. Through a self-assembly mechanism, dopamine molecules created a dense protective film on the surface of MXene, effectively thwarting the ingress of oxygen and water. This protective film notably decelerates the oxidation process and augments the physical and chemical attributes of the material. Post-treatment with dopamine, the antioxidant capacity of MXene is markedly enhanced, and its stability in air is prolonged from a few days to weeks, or even months. Owing to dopamine's biocompatibility, this treatment expands the potential applications of MXene in the biomedical and environmental sectors.130 In certain studies, MXene has been combined with antioxidant metals (such as aluminum and nickel) to further bolster the material's stability. These metals form a robust oxidative protective layer with the MXene surface, preventing further oxygen infiltration into the MXene interior. Through this composite approach, the material's long-term oxidation resistance is substantially improved. Furthermore, the addition of metals may enhance MXene's electrical conductivity and mechanical strength, supporting its broad spectrum of industrial applications. In antioxidant coating applications, it is crucial to control the thickness and uniformity of the coating. An excessively thick coating may impair MXene's electrical conductivity and other physical properties, while an overly thin coating may prove insufficient in preventing oxidation. Therefore, optimizing the coating thickness is essential to ensure the material's performance. Techniques such as spin coating, solution dip coating, or spray coating can achieve uniform coatings, ensuring optimal antioxidant effectiveness.
To further enhance oxidation resistance, multi-layer composite coating technology can be employed. For instance, MXene can be encapsulated with a protective layer of dopamine and a layer of polyvinyl alcohol. This multi-layer protection strategy offers more comprehensive shielding and significantly extends the service life of MXene. Multilayer composite coatings also provide superior stability under varying environmental conditions, ensuring the material's performance in diverse application scenarios. Since vacancies are positively charged, adjacent carbon atoms (C4−) are prone to oxidation (electron loss), accumulating electron holes around the defect site and promoting further oxidation. Given that the electron hole is positive and the defect is negative, an internal electric field biases the Ti atom on the negative side, facilitating O2 dissolution (in the form of O2−) with the MXene lattice plane and generating titanium dioxide, while carbon oxidizes in the opposite domain (Fig. 12a).131,132 After five days in ambient air, in STEM images Nb2CTx exhibited a honeycomb-like atomic arrangement with a disordered structure, as evidenced by the corresponding FFT pattern. EELS analysis revealed a higher concentration of oxygen in samples cured for five days (–O/–OH termination), indicating progressive deterioration of Nb2CTx in ambient air. To elucidate this oxidation process at the atomic level, a standard M2X model structure was projected along the C-axis and superimposed it onto STEM images of Nb2CTx. The model accurately matched the STEM images, achieving high-contrast atomic columns and forming a large, honeycomb-like, closed-fill structure. STEM image simulations predict that Nb2C MXene's favorable termination atom position is above the hollow site and oriented toward the Nb atom. Consequently, when situated at the hcp site of the standard MAX phase, a layer of Nb-adsorbed atoms (adatoms) containing O appears on the top surface, followed by subsequent layers on either side. The MAX phase, a precursor to MXenes, is a ternary carbide or nitride with the general formula Mn+1AXn, where M is an early transition metal, A is an A-group element (primarily IIIA or IVA), X is carbon or nitrogen, and n can be 1, 2, or 3. A typical MAX compound consists of a metal A layer and an Mn+1Xn layer. The chemical activity of each layer is more pronounced than that of the Mn+1Xn layer. 2D Ti3C2Tx nanosheets were prepared by etching Ti3AlC2 (MAX) phase using a HF. Fig. 12b displays the schematic illustration of the synthesis of few-layer Ti3C2Tx nanosheets.133 The A layer is removed from the MAX phase through HF etching to produce 2D MXenes. MXene surfaces prepared in HF solutions typically terminate with F and/or OH groups due to their surface energy. Fig. 12c illustrates the chemical structure of a typical OH-terminated MAX phase (Ti3AlC2) and MXene (Ti3C2).134 The latter undergoes high-frequency etching and ultrasound treatment. Ti3C2Tx dispersed in isopropyl alcohol (IPA) exhibits high stability against oxidation in oxygen and argon (Ar) atmospheres, whereas Ti3C2Tx dispersed in water is unstable to oxidation under the same conditions (Fig. 12d).135 The aqueous solution of the Ti3C2Tx MXene dispersion became turbid, whereas the dispersion stored in isopropanol (IPA) retained its original black color under both oxygen and argon atmospheres. UV-vis analysis of Ti3C2Tx MXene was conducted under water/Ar and IPA/O2 conditions for validation. Following careful selection of the MAX phase, the optimal synthesis conditions were found to directly influence the properties of the resulting polyenes. The concentration of the acid etchant was observed to alter the type and density of atomic defects, which initiated the oxidation reaction. A dilute acid solution was found to help maintain the integrity of MXene flakes. The electronic properties and oxidation kinetics of Ti3C2Tx MXene were systematically investigated and synthesized through two distinct pathways: (1) using concentrated hydrofluoric acid (40 wt% HF) at room temperature for 24 hours, and (2) employing a 6 M HCl and LiF solution at 40 °C for 16 hours. The first method produced multi-layered MXene (denoted as M-Ti3C2Tx), while the second method yielded ultra-thin MXene sheets (U-Ti3C2Tx) (Fig. 12e).136
 | ||
| Fig. 12 (a) Schematic of the internal electric field, with the positive side formed around a hole with many Ti-vacancies and the negative side with the accumulation of electrons on the convex particle. Reproduced from ref. 131 with permission from The Royal Society of Chemistry, copyright 2019. (b) Schematic illustration of the preparation of Ti3C2Tx flakes from Ti3AlC2 (MAX) using an HF etching process. Reproduced from ref. 132 with permission from Elsevier, copyright 2024. (c) Chemical structures of Ti3AlC2 (a typical MAX phase), and Ti3C2 (a typical MXene) with OH termination. Ti3C2 is made from Ti3AlC2 by HF etching and sonication. Reproduced from ref. 134 with permission from Elsevier, copyright 2015. (d) Comparative schematic illustration of the oxidation stability of each newly prepared Ti3C2Tx MXene colloidal solution after purging with O2 or Ar. Reproduced from ref. 135 with permission from American Chemical Society, copyright 2019. (e) Synthesis illustration of M-Ti3C2Tx, and U-Ti3C2Tx MXenes. Reproduced from ref. 136 with permission from The Royal Society of Chemistry, copyright 2019. | ||
During MXene synthesis, the naturally formed surface functional groups (such as –OH, –F, and –O) can react with atmospheric oxygen, leading to the formation of oxidation products. This reaction results in a gradual decline in the electrochemical properties of the material. However, these functional groups also provide short-term antioxidant protection, particularly through interactions between surface hydroxyl or fluorine groups and certain environmental components, which help to mitigate the acceleration of oxidation. Surface functionalization strategies can further enhance the antioxidant stability of MXene materials. By introducing organic molecules onto the MXene surface, a stable organic protective layer can be formed. These molecules can establish a dense coating on the MXene surface through chemical bonding or physical adsorption, thereby preventing direct contact with oxygen and water. For example, sodium polystyrene sulfonate (PSS), a commonly used organic molecular modifier, forms a dense protective layer on the MXene surface by interacting with the –OH and –O functional groups. This organic modification not only effectively prevents oxidation but also preserves MXene's high electrical conductivity and other favorable properties. Additionally, due to the high tunability of polymers like PSS, researchers can further optimize their molecular structure to enhance antioxidant effects. Another prevalent surface modification method involves enhancing the antioxidant properties of MXene by applying a polymer coating. Polymer coatings, characterized by high chemical stability and strong mechanical strength, offer long-term protection for MXene. For instance, modifying the MXene surface with polyethylene glycol (PEG) has been shown to improve both antioxidant properties and dispersion in aqueous solutions. Furthermore, certain polymeric materials, such as polystyrene and PVDF, can form stable protective layers through binding to the MXene surface, thereby delaying the oxidation process.
In addition to organic molecule and polymer coating modifications, chemical vapor deposition (CVD) is an effective surface modification technique. CVD can deposit inert gas molecules (such as nitrogen and argon) onto the MXene surface via gas-phase reactions, forming an inert protective film. This inert film effectively isolates the MXene from oxygen and moisture in the environment, significantly enhancing its antioxidant capacity. The advantage of CVD modification lies in its high controllability, allowing precise regulation of the protective film's thickness and uniformity to ensure optimal surface protection for MXene. In a typical experiment, researchers successfully established a stable organic protective layer by combining sodium PSS molecules with the surface functional groups (such as –OH and –O) of Ti3C2Tx MXene. The protective layer significantly mitigates the intrusion of oxygen and water by forming either chemical bonds or physical adsorption with the MXene surface, thereby delaying the oxidation process. Experimental results indicate that the antioxidant properties of PSS-modified MXene materials are markedly enhanced, with the storage duration in air extended to several weeks or even months, in contrast to unmodified MXene materials, which undergo significant oxidation within a few days. Furthermore, the application of the PSS coating does not detrimentally affect the electrical conductivity or energy storage performance of MXene, demonstrating the practical feasibility of this modification method. In a separate investigation, researchers employed chemical CVD technology to deposit inert gases, such as argon, onto the MXene surface, resulting in the formation of a thin, uniform, inert protective layer. This layer effectively prevents the intrusion of oxygen while ensuring the electrochemical properties of the material remain stable. Compared with traditional wet chemical modification, the CVD method achieves uniform protection of the MXene surface without compromising the intrinsic properties of the material, thus presenting promising applications in industrial production.
When conducting surface functional group modifications, ensuring uniformity and appropriate thickness of the coating is crucial. An excessively thin coating fails to provide sufficient antioxidant protection, while an overly thick coating may adversely affect the material's electrical conductivity. Therefore, researchers must optimize processing conditions, such as reaction temperature, duration, and solution concentration, to attain optimal modification outcomes. For instance, in the molecular modification of PSS, the careful regulation of PSS concentration and solution pH can facilitate uniform coverage of the MXene surface. Moreover, to further enhance the antioxidant properties of MXene while considering other functional characteristics, researchers have explored the development of multifunctional modified materials. For example, materials that simultaneously offer oxidation resistance and electrical conductivity can enhance the stability and performance of MXene in applications. Additionally, the development of coating materials endowed with self-healing capabilities can facilitate the repair of functional groups on the surface after minor oxidative damage, thereby extending the material's service life.133
Post-synthetic treatment is a pivotal step in enhancing the antioxidant capacity of MXene materials. Appropriate treatment following synthesis can significantly extend the storage life of these materials. Common post-treatment methods encompass heat treatment and chemical passivation, among others. These techniques can further reduce the active sites on the material's surface, rendering it less susceptible to oxidation reactions. In several studies, Ti3C2Tx MXene underwent a series of heat treatments post-synthesis, revealing that moderate heat treatment at low temperatures effectively passivates the active functional groups on the MXene surface, thereby imparting stronger antioxidant properties in atmospheric environments. Additionally, some experiments have utilized chemical passivation methods (such as vulcanization and fluorination) to form a more stable protective layer, thereby enhancing the oxidation stability of the material.137
The environmental stability of MXene materials is significantly influenced by pH, particularly in aqueous solutions where the material may undergo dissolution, oxidation, or degradation under varying pH conditions, directly affecting its structural integrity and electrochemical performance. Therefore, for different application scenarios, ensuring the stability of MXene materials within a specific pH range is essential to enhance their service life and application efficacy. Research indicates that MXene materials exhibit relatively high stability in acidic environments, notably within pH values of 1–4. Acidic conditions effectively inhibit oxidation reactions, thereby delaying material degradation. In an acidic environment, the chemical reactivity of functional groups (such as –OH, –F) on the MXene surface is reduced under low pH conditions, and penetration and reaction of oxygen and water molecules with the MXene layer are hindered, significantly improving the material's antioxidant properties. By adjusting the pH of the Ti2Tx MXene storage solution to acidic (about pH 3), the oxidation rate of MXene is successfully delayed.138 Experimental results demonstrate that the layered structure of MXene can remain stable for an extended period in pH- 3 solution, with minimal impact on its electrical conductivity and electrochemical properties from oxidation. This indicates that in acidic environments, the oxidation process of MXene materials is significantly slowed, thereby extending storage time from a few days to weeks or even longer. Under acidic conditions, the activity of oxidants (such as dissolved oxygen) in the solution is reduced, and the reaction rate of oxygen with the MXene surface is significantly decreased, thus inhibiting the material's oxidation. Furthermore, the acidic environment can also passivate active sites on the material's surface, further augmenting the environmental stability of MXene. The discovery presents a reliable approach for the storage and utilization of MXene materials, enabling the extension of their service life through the adjustment of the storage environment's pH value during industrial production.
While MXene exhibits high stability in acidic conditions, in alkaline environments (pH > 7), MXene materials are more susceptible to oxidation reactions, leading to a decline in their electrochemical performance. Consequently, maintaining the stability of MXene under alkaline conditions has emerged as another critical research direction. Through appropriate surface modification and structural design, the stability of MXene in alkaline environments can be significantly enhanced, and the oxidation process can be delayed to ensure its electrochemical activity under such conditions. In high-pH alkaline environments, the functional groups on the surface of MXene (e.g., –OH, –F) are more prone to react with oxygen and water molecules, resulting in the disruption of the material's layered structure and a subsequent decline in electrochemical performance. This process typically accelerates material degradation, severely limiting its lifetime in practical applications. To address the oxidation of MXene in alkaline environments, researchers have developed various surface modification techniques. For instance, in a study, researchers successfully delayed the oxidation process of MXene by introducing a protective layer onto the material's surface, allowing it to maintain high electrochemical activity under alkaline conditions. The protective layer is typically introduced through CVD or solution coating, which covers the MXene surface with a stable, antioxidant organic or inorganic material. This method prevents direct contact between oxygen and water molecules with MXene, significantly enhancing the material's antioxidant properties. In one experiment, researchers modified the surface of Ti3C2Tx MXene using a polymer coating as a protective barrier. This coating forms a stable layer in alkaline environments, substantially improving the antioxidant properties of MXene materials. Experimental results indicate that the surface-modified MXene can still maintain excellent electrochemical properties in a pH-9 alkaline environment, with a greatly reduced oxidation rate.118
MXene materials are prone to structural degradation and oxidation at elevated temperatures, making the enhancement of their thermal stability crucial for maintaining stable performance in high-temperature applications. By optimizing the synthesis process and post-treatment methods, the thermal stability of MXene can be significantly improved to meet the demands of more rigorous industrial environments. In MXene's industrial production, heat treatment is a common process step. Researchers have found that following high-temperature treatment, the thermal stability of MXene materials can be significantly enhanced. For example, after MXene was annealed at high temperatures in argon, the layered structure of Ti3C2Tx was preserved, and its thermal oxidation stability was substantially improved. This enhancement is attributed to the high-temperature treatment, which forms a protective layer on the material's surface, preventing further oxidation. Doping technology is an effective method to improve the thermal stability of MXene. By incorporating various doping elements (such as boron, nitrogen) into MXene materials, the antioxidant capacity at high temperatures can be enhanced. For example, the stability of Ti3C2Tx MXene at high temperatures is significantly improved through boron doping technology. Experimental results show that the doped MXene can maintain its structural integrity and electrochemical properties at 400 °C.139
The electrochemical stability of MXene materials is a crucial attribute in electrochemical energy storage applications. The interfacial interaction between the electrolyte and the MXene electrode material directly influences the electrochemical behavior and stability of the electrode, particularly during extended cycling. The solvent composition, additives, and salt concentrations in the electrolyte significantly impact the formation of passivation layers on the MXene electrode surface, ion transport efficiency, and the overall stability of the material. Therefore, optimizing the electrolyte composition can effectively minimize side reactions, prevent the degradation or failure of MXene materials during electrochemical processes, extend their operational lifespan, and enhance their electrochemical performance. High-concentration electrolytes have demonstrated significant advantages in optimizing the electrochemical properties of MXene materials. By increasing the salt concentration in the electrolyte, the stability of the interface between the electrolyte and the MXene electrode is improved, side reactions are reduced, and the electrochemical cycling stability of the material is enhanced. The electrochemical performance of Ti3C2Tx MXene is significantly improved by using a high-concentration LiTFSI (lithium bistrifluoromethane sulfonimide) electrolyte.140 In this study, the researchers applied a high concentration of LiTFSI electrolyte to the Ti3C2Tx MXene electrode, resulting in a substantial extension of the electrode's cycle life and a reduction in the formation of passivation films on the electrode surface. The high-concentration electrolyte effectively mitigated side reactions between the electrode and the electrolyte, such as the production of by-products from redox reactions, thereby enhancing the stability of the electrode material. In high-concentration electrolytes, the interactions between ions and solvent molecules are more complex, leading to reduced solvation and a decreased likelihood of side reactions. This not only minimizes the formation of passivation films on the electrode surface but also improves the efficiency of ion transport at the electrode interface. This optimization strategy significantly enhances the electrochemical cycling stability of MXene materials and boosts their electrochemical activity at high current densities, providing more stable performance for applications in energy storage devices such as supercapacitors and lithium-ion batteries.
Ionic liquids, when used as electrolytes, exhibit numerous advantageous properties in the realm of electrochemical energy storage. Compared with conventional organic electrolytes, ionic liquids offer higher thermal stability, lower volatility, and a wider electrochemical window, thereby effectively enhancing the electrochemical stability of MXene materials. The integration of ionic liquids not only mitigates the incidence of side reactions but also enhances ion transport efficiency and extends the service life of materials. In investigation,141 the researchers significantly enhanced the electrochemical stability of the MXene electrode by employing an ionic liquid electrolyte, such as EMIM-TFSI or 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazole tetrafluoroboric acid. Experimental findings indicate that ionic liquid electrolytes exhibit superior cycle life and more stable electrochemical performance during MXene electrode utilization, particularly at elevated current densities, where MXene materials consistently maintain excellent electrical conductivity and ion transport efficiency. The unique physicochemical properties of ionic liquids, including low volatility and high thermal stability, ensure their stability at high temperatures, thereby minimizing the likelihood of interfacial side reactions between the electrode and electrolyte. Additionally, the presence of large cations and anions in ionic liquids effectively reduces electrolyte viscosity, thereby improving ion transport efficiency. This attribute facilitates the provision of a more stable and efficient operational environment for the MXene electrode, safeguarding its electrochemical performance from degradation or passivation during prolonged use.
In the context of enhancing MXene's electrochemical stability, composite material design represents a pivotal strategy. By incorporating MXene with other conductive materials, such as graphene, carbon nanotubes, and metal oxides, not only can its mechanical strength and electrical conductivity be augmented but also its electrochemical performance can be substantially improved. These composite designs effectively augment MXene's specific surface area, accelerate ion transport rates, enhance structural stability, and mitigate electrode material degradation in electrochemical reactions. As a two-dimensional material boasting exceptional electrical conductivity and a high specific surface area, the composite of graphene and MXene exhibits superior electrochemical properties. By synergizing the attributes of MXene with graphene, the latter effectively addresses the issue of self-stacking in MXene sheets and enhances the overall electrical conductivity of the material. A Ti3C2Tx MXene/reduced graphene oxide (rGO) composite was designed and assembled to form a three-dimensional network structure.142 This architectural configuration aids in expanding the composite's specific surface area and alleviates the self-stacking issue of MXene sheets. Consequently, MXene and graphene composites exhibit markedly improved specific capacitance and superior cycling stability during extended cycle testing. Graphene functions as a supporting structure within the composite, preventing MXene layers from self-stacking and agglomerating in the electrolyte, thus preserving MXene's high specific surface area. Simultaneously, graphene's high electrical conductivity furnishes supplementary electron transport pathways, enhancing the material's charge transport capability at elevated current densities. This composite design substantially bolsters the electrochemical performance of MXene, significantly amplifying its application potential in energy storage devices, such as supercapacitors and lithium-ion batteries.143
3.5 Comprehensive strategy
(1) Integrated antioxidant and safety measures: a combination of antioxidant and safety enhancing measures is used in the production process, such as protective atmosphere synthesis in a closed system, combined with surface modification and the use of antioxidants, to achieve efficient and safe MXene production. (2) Green synthesis technology: develop environmentally friendly green synthesis technology to reduce the use and emission of harmful substances. For example, the use of aqueous synthesis or less toxic etching agents to enhance the green level of MXene production. (3) Whole process optimization: from raw material selection, synthesis process, waste liquid treatment to product application, the whole process is optimized and designed to reduce costs and improve production safety and oxidation resistance.4. Large-scale applications of MXene-base electrode materials
MXene-based electrode materials possess a unique layered structure, high conductivity, and abundant surface functional groups, demonstrating extensive application prospects across various fields. This discussion will explore the large-scale application of MXene-based electrode materials in batteries, supercapacitors, and catalysts, analyzing their performance advantages, practical application challenges, and corresponding solutions.4.1. Battery application
With the progressive advancement of new energy storage technologies, MXene-based electrode materials have garnered extensive attention due to their unique physical and chemical properties within the battery domain. MXene exhibits exceptional electrical conductivity, abundant surface functional groups, and commendable chemical stability, rendering it an optimal candidate for battery electrode materials. Its superior electrical conductivity facilitates an enhanced charge transfer rate, while the surface functional groups offer active sites for interaction with the electrolyte, thereby laying the groundwork for the widespread application of MXene in batteries.Due to the self-stacking issue of pure MXene materials in lithium-ion batteries (LIBs), which hampers the effective diffusion of lithium ions, researchers have developed various MXene-based composites to enhance their electrochemical performance. By combining MXene with other materials, significant improvements in specific capacity, cycling stability, and rate performance have been achieved. In the context of LIBs, the composite strategy of MXene and carbon materials has proved particularly effective. Carbon materials, such as carbon nanotubes (CNTs), possess high electrical conductivity and chemical stability, which can significantly enhance the performance of MXene in batteries. When combined with MXene, CNTs form a stable three-dimensional conductive network, optimizing ion transport and electronic conductivity. For example, Hossain et al.144 studied the application of MXene/CNT composites in LIBs. In their study, the researchers created an electrode material with a three-dimensional conducting network by integrating MXene sheets with CNTs. This network structure effectively mitigates the self-stacking of MXene layers and maintains the spacing between layers, ensuring rapid lithium-ion diffusion in the electrolyte. Moreover, the addition of CNTs provides additional electron conduction paths, improving overall electrical conductivity and electrochemical performance. Electrochemical performance tests demonstrated that MXene/CNT composites exhibit excellent cycling stability and high-rate performance. After multiple charge and discharge cycles, the composite retains high capacity with minimal capacity loss, indicating enhanced long-term stability. At high current densities, the composite maintains high-rate performance due to the efficient three-dimensional conductive network and enhanced electron transport. Zhang et al.145 synthesized a columnar SnS/Ti3C2Tx composite with in situ TiO2 nanoparticles through solvothermal reaction and annealing treatment, as shown in Fig. 13a and b.146 The SnS/Ti3C2Tx composite exhibits 866 mA h g−1 at a current rate of 500 mA g−1 with a composite efficiency of 99%, which is superior to commercial SnS and single Ti3C2. The column effect of Ti3C2Tx xenon improves electrochemical performance. Mesoporous polydopamine (OMPDA)/Ti3C2Tx was prepared by in situ polymerization on the surface of Ti3C2Tx using PS-b-PEO block polymer as a soft template, as shown in Fig. 13b. After 200 cycles, at a current rate of 50 mA g−1, the average discharge capacity of the electrode is 1000 mA h g−1, and the cycle efficiency is 92%. The enhanced electrochemical performance is due to the mesopore, which enhances the overall ability and reversibility of the reaction with Li+. Zhang et al.148 prepared flexible porous Si/Ti3C2Tx composite material MXene through vacuum filtration, and used the composite material Si and Ti3C2Tx MXene (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1, 1
1, 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 and 3
1 and 3![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) to prepare the anode of LIB, as shown in Fig. 13c. The higher the mass content of porous silicon, the higher the electrochemical performance. A carbon-doped TiO2/Fe2O3 composite material based on Ti3C2MXene was named C-TiO2/Fe2O3–Ti3C2, and the performance of the MXene as a LIB anode was analyzed, as shown in Fig. 13d. The initial discharge capacity of the C-TiO2/Fe2O3–Ti3C2 composite anode at 0.1 A g−1 is 538 mA h g−1. In addition, at different current densities of 0.2, 0.5, 1, 2 and 5 A g−1, the supplied discharge capacities of the electrode are 386, 320.5, 274.1, 218.1 and 152.6 mA h g−1, respectively. This remarkable electrochemical performance is attributed to the combined effects of carbon doping, layered titanium dioxide structure, and ferric oxide hybridization, all of which greatly accelerated charge transfer. Xu et al.150 constructed a VNbO5 metal oxide (named VNbC@VNO-500) on the surface of VNbCTx MXene by partial oxidation at 500 °C. Partial oxidation enhanced the binding between VNbO5 and VNbCTx MXene, and effectively improved the electrochemical performance. As the anode of a lithium-ion battery, the prepared VNbC@VNO-500 MXene has a specific capacity of 400.3 mA h g−1 after 100 cycles at a current density of 0.1 A g−1, as shown in Fig. 13e. In addition, the specific capacities of the electrode material at 0.1, 0.2, 0.5, 1.0, 2.0 and 5.0 A g−1 current densities are 327.3, 306.6, 270.7, 222.4, 181.7 and 141.2 mA h g−1, respectively, showing good magnification performance.
1) to prepare the anode of LIB, as shown in Fig. 13c. The higher the mass content of porous silicon, the higher the electrochemical performance. A carbon-doped TiO2/Fe2O3 composite material based on Ti3C2MXene was named C-TiO2/Fe2O3–Ti3C2, and the performance of the MXene as a LIB anode was analyzed, as shown in Fig. 13d. The initial discharge capacity of the C-TiO2/Fe2O3–Ti3C2 composite anode at 0.1 A g−1 is 538 mA h g−1. In addition, at different current densities of 0.2, 0.5, 1, 2 and 5 A g−1, the supplied discharge capacities of the electrode are 386, 320.5, 274.1, 218.1 and 152.6 mA h g−1, respectively. This remarkable electrochemical performance is attributed to the combined effects of carbon doping, layered titanium dioxide structure, and ferric oxide hybridization, all of which greatly accelerated charge transfer. Xu et al.150 constructed a VNbO5 metal oxide (named VNbC@VNO-500) on the surface of VNbCTx MXene by partial oxidation at 500 °C. Partial oxidation enhanced the binding between VNbO5 and VNbCTx MXene, and effectively improved the electrochemical performance. As the anode of a lithium-ion battery, the prepared VNbC@VNO-500 MXene has a specific capacity of 400.3 mA h g−1 after 100 cycles at a current density of 0.1 A g−1, as shown in Fig. 13e. In addition, the specific capacities of the electrode material at 0.1, 0.2, 0.5, 1.0, 2.0 and 5.0 A g−1 current densities are 327.3, 306.6, 270.7, 222.4, 181.7 and 141.2 mA h g−1, respectively, showing good magnification performance.
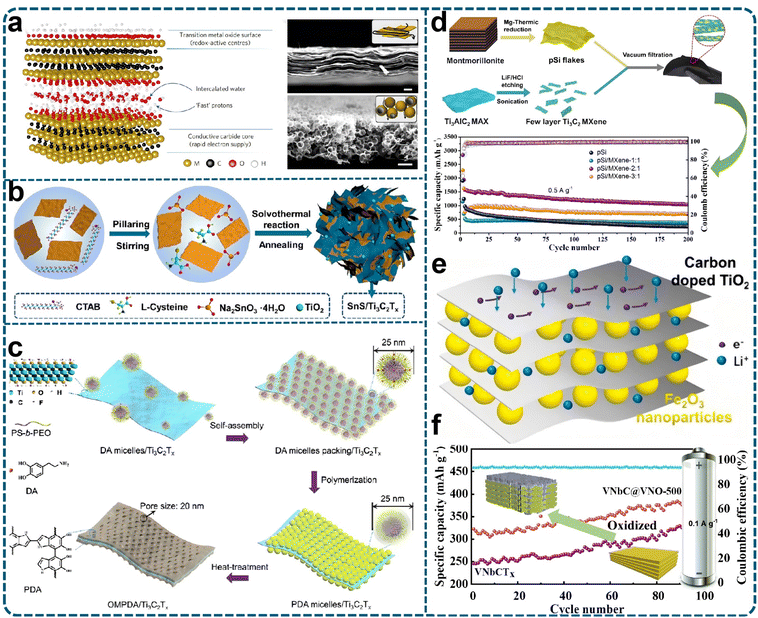 | ||
| Fig. 13 (a) Schematic diagram of MXene structure. Due to its conductive carbide core and transition metal oxide-like surface, MXenes has excellent electrical conductivity. The embedded water molecule allows the proton to be very close to the REDOX active site. SEM image of Ti3C2Tx MXene hydrogel cross section. SEM image of large hole templated Ti3C2Tx electrode section. Reproduced from ref. 145 with permission from Nature, copyright 2017. (b) Schematic illustration of the preparation process of SnS/Ti3C2Tx composites. Reproduced from ref. 146 with permission from American Chemical Society, copyright 2020. (c) Schematic diagram of preparation steps of OMPDA/Ti3C2Tx composites. Reproduced from ref. 147 with permission from American Chemical Society, copyright 2020. (d) Schematic diagram of synthetic and cycling properties of different samples at 0.5 A g−1. Reproduced from ref. 148 with permission from Elsevier, copyright 2023. (e) Schematic diagram of C-TiO2/Fe2O3–Ti3C2 MXene. Reproduced from ref. 149 with permission from Elsevier, copyright 2022. (f) Cycling stability curves of VNbC@VNO-500 and VNbCTx MXene at 0.1 A g−1. Reproduced from ref. 150 with permission from Elsevier, copyright 2023. | ||
In lithium-ion batteries (LIBs), silicon is an attractive anode material due to its extremely high specific capacity (approximately 4200 mA h g−1). However, silicon has significant volume expansion (up to 300%) during charge and discharge, leading to problems such as electrode powder and capacity attenuation, which limits its practical application in lithium-ion batteries. To solve this problem, the researchers developed an MXene/silicon composite with high stability and excellent electrochemical properties by combining MXene with silicon nanoparticles. In the study of Xu et al.,150 Ti3C2Tx MXene was combined with silicon nanoparticles, and the two-dimensional lamellar structure of MXene was used to alleviate the volume expansion stress generated by silicon during the charge–discharge cycle.151 The MXene layer not only provides mechanical support for the silicon, but also builds a stable conductive network that can withstand stress changes in the electrode during cycling, thereby preventing the rupture of the silicon particles and the pulverization of the electrode. In addition, the MXene layer provides an effective channel for the rapid diffusion of lithium ions, ensuring the electrochemical reaction rate of the electrode material, and further improving the magnification performance of the silicon-based electrode. In electrochemical tests, MXene/silicon composites demonstrated significantly improved cycling stability and capacity retention. The experimental results show that the composite can still maintain a higher specific capacity after multiple charge and discharge cycles, and the capacity decay rate is significantly reduced compared with pure silicon materials. This performance improvement is due to the protective effect of the MXene layer, which effectively inhibits the volume expansion of the silicon particles and reduces the mechanical stress of the electrode during the cycle. In addition, MXene's excellent electrical conductivity also improves the overall conductive network of the material, ensuring stable performance at high current densities.
The high conductivity of MXene and its good interfacial interaction with solid electrolyte make its application in the solid state lithium-ion battery a research hotspot. Zheng et al.152 proposed a strategy to enhance the lithium-ion transport performance by introducing Ti3C2Tx MXene into a solid electrolyte. With its unique two-dimensional lamellar structure and excellent electrical conductivity, Ti3C2Tx MXene is able to build an efficient electron transport channel between the solid electrolyte and the electrode material, thereby improving the conductivity and cycle life of the battery. Experiments show that MXene can form a stable conductive network in the solid electrolyte, which significantly improves the diffusion rate of lithium ions. In addition, the abundant functional groups (such as –OH, –F, etc.) on the surface of MXene provide more active sites for lithium ion embedding, and enhance the dynamic process of lithium ion embedding and de-embedding. The interaction between these functional groups and lithium ions not only improves the migration rate of lithium ions, but also enhances the diffusion stability of lithium ions in the electrode material. In the research by Zheng et al.,152 the incorporation of MXene into solid-state lithium-ion batteries led to notable enhancements in performance. Experimental data demonstrated that MXene significantly improved the battery's cycle life and rate capability. Even after numerous charge–discharge cycles, the solid-state batteries maintained a high capacity retention rate, indicating excellent cycling stability. This improvement is attributed to MXene's two-dimensional structure, which enhances the interface contact between the electrode and the solid electrolyte and effectively alleviates the volume changes of the electrode material during charging and discharging, thereby reducing mechanical stress on the electrode. Overall, the application of Ti3C2Tx MXene in solid-state lithium-ion batteries showcases its great potential for improving battery performance. MXene's two-dimensional lamellar structure not only enhances electrical conductivity but also promotes lithium-ion transport through its rich surface functional groups, thus extending the battery's cycle life. This research provides a crucial foundation for the combination of solid electrolytes with MXene composite materials and contributes to the development of high-performance solid-state lithium-ion batteries. Ti3C2Tx MXene, a two-dimensional transition metal carbide, exhibits significant electrochemical properties in lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) due to its unique layered structure. Its lamellar structure provides fast lithium-ion diffusion channels and forms an efficient electron transport network, allowing it to maintain high specific capacity and excellent rate performance over multiple charge–discharge cycles. Experimental confirmations have shown that Ti2Tx MXene retains its structural integrity after 500 charge–discharge cycles, demonstrating exceptional cycling stability. This stability is primarily due to the lamellar structure effectively alleviating volume changes caused by lithium-ion embedding and de-embedding during charging and discharging, thus reducing material pulverization and capacity fading.153 Moreover, the abundant surface functional groups (such as –OH and –F) on MXene provide additional lithium-ion storage sites, further enhancing the material's specific capacity. Ti3C2Tx MXene also exhibits good electrochemical behavior at high current densities due to its high conductivity. The two-dimensional lamellar structure offers a short and fast diffusion path for lithium-ion transport, improving the migration rate of lithium ions within the material. This feature makes it suitable for high-power density battery applications, such as electric vehicles and portable electronic devices. Comparative experiments have shown that Ti2Tx MXene maintains a high capacity retention rate over extended charge–discharge periods and exhibits good cycling stability under high current conditions, making it a promising material for applications requiring rapid charge and discharge capabilities. Even after 500 cycles, Ti2Tx MXene retains more than 80% of its initial capacity, demonstrating robust durability.143
With their unique structure and excellent electrochemical properties, MXene materials bring significant performance improvements to lithium-ion batteries. However, in practical applications, the self-stacking problem of MXene composite materials still needs to be further solved, while cost control and environmental stability in large-scale synthesis and application also need to be paid more attention. By optimizing the composite design of MXene and other materials to improve its interface stability and cycle performance, MXene has a broad application prospect in lithium-ion batteries.
To further enhance the performance of MXenes in sodium-ion batteries, researchers have optimized their sodium storage capabilities by combining them with other materials. For instance, the incorporation of transition metal oxides and carbon materials alongside MXenes has been shown to significantly improve both cycling performance and the diffusion rate of sodium ions. Due to their excellent electrical conductivity and minimal volume expansion, the composites of carbon materials and MXenes can augment the overall performance of electrode materials. In a study by Luo et al.,154 a composite of Ti2Tx MXene and graphene was developed for use as the negative electrode in sodium-ion batteries, demonstrating high efficiency in sodium ion transport and outstanding electrochemical properties. The research indicates that the lamellar structure of graphene within the composite effectively prevents the self-stacking of MXene layers, which not only enhances electrolyte permeability but also accelerates the diffusion rate of sodium ions. During the cycling of the battery, the intercalation and deintercalation of sodium ions frequently cause the electrode material to undergo volume expansion and contraction, potentially compromising structural integrity. Nevertheless, the composite of Ti2Tx MXene and graphene, owing to its high specific surface area and layered structure, effectively alleviates stress associated with volume changes, thereby ensuring structural stability. Moreover, the superior conductivity of graphene further strengthens the conductive network of the electrode material, facilitating efficient charge transfer. This composite not only exhibits high cycling stability but also retains excellent electrochemical performance under conditions of rapid charge and discharge. Luo et al.'s154 experimental results indicated that the composite maintains a high specific capacity even after numerous cycles, significantly extending its cycle life. This demonstrates the considerable potential of Ti3C2Tx MXene and graphene composites for negative electrode applications in sodium-ion batteries, particularly in large-scale production contexts aimed at enhancing energy density and stability.155
In solid-state ion batteries (SIBs), transition metal oxides have garnered significant attention due to their high specific capacity; however, their inherent poor cycling stability hinders practical applications. The integration of MXene materials can effectively enhance the structural stability and electrical conductivity of these metal oxides, thereby improving their electrochemical performance in SIBs. MXene/Fe2O3 composite was applied to the negative electrode of a sodium-ion battery to show good cycling stability and capacity retention.156 Even under high-rate charge–discharge conditions, the composite maintained commendable electrochemical performance. This superior performance is primarily attributed to the two-dimensional lamellar structure of MXene, which provides robust support for Fe2O3, mitigating the volumetric expansion and contraction of transition metal oxides during cycling. Fe2O3 undergoes substantial volume changes during sodium ion intercalation and deintercalation, which often leads to structural damage and capacity decay. Due to its high conductivity and layered architecture, the MXene layer not only mitigates structural damage from Fe2O3's volumetric changes but also facilitates rapid electron and sodium ion transport, thereby enhancing overall charge transfer efficiency. The findings indicated that the MXene/Fe2O3 composite exhibited exceptional cycling stability over numerous charge–discharge cycles. The high conductivity of MXene enables rapid electron transfer within the composite, while Fe2O3 serves as the primary active material with a high sodium storage capacity. This synergistic interaction allows the composite to maintain a high specific capacity at elevated rates, significantly improving the cycle life and structural integrity of the electrode material. The results show that the composite strategy of MXene and transition metal oxides can not only improve the structure and electrochemical stability of the material, but also effectively improve its electrical conductivity and ion transport performance. This design paradigm offers a novel approach for the large-scale application of sodium-ion batteries, advancing the development of high-performance, cost-effective sodium-ion battery electrode materials.
The functional groups present on the surface of MXene are pivotal for sodium storage properties, particularly concerning sodium ion adsorption and diffusion. Manipulating these surface functional groups further enhances the ability of sodium ions to intercalate and deintercalate. The storage capacity of sodium ions was successfully improved by regulating the surface functional group of Ti3C2MXene.157 Enhancing the specific capacity and cycling stability of MXene was achieved by altering its interlayer structure and increasing the intercalation space for sodium ions. Specifically, the researchers expanded the layer spacing of the material by incorporating sulfur into Ti3C2 MXene. This structural modification provides a more spacious channel for sodium ion intercalation and diffusion, reducing ion migration resistance within the electrode material. Additionally, the chemical bond formed between sulfur atoms and titanium atoms enhances the stability of sodium ion intercalation and mitigates structural damage caused by volumetric changes during cycling. Sulfur doping not only improves ion transport performance but also augments the electrical conductivity of the MXene material, thus optimizing overall electrochemical performance. The results demonstrated that the sulfur-doped Ti3C2 MXene exhibited significantly superior performance in sodium-ion batteries compared with untreated materials, particularly maintaining a high specific capacity over multiple charge–discharge cycles and demonstrating excellent cycling stability. Sulfur doping stabilizes the layered structure of MXene during sodium ion intercalation and deintercalation, thereby effectively extending battery lifespan. This study proves that the electrochemical performance of MXene in sodium-ion batteries can be significantly improved through the modification of surface functional groups, especially the introduction of sulfur. This methodology offers a novel approach for enhancing ion storage capacity and structural stability in MXene-based electrode materials, potentially advancing the practical application of sodium-ion batteries in large-scale energy storage systems.157
The application of MXene in sodium-ion batteries showcases its vast potential, as its two-dimensional lamellar structure not only provides abundant active sites for sodium ion storage but also effectively mitigates issues related to volumetric expansion during charge–discharge cycles. Nevertheless, the practical application of MXene in SIBs encounters challenges, including cost control in large-scale synthesis, environmental stability, and self-stacking issues. Future research will focus on optimizing the electrochemical performance of MXene through composite material design and interface engineering, which will be pivotal in advancing its large-scale application in sodium-ion batteries.
4.2. Supercapacitor application
Supercapacitors (SCs), also referred to as electrochemical capacitors or capacitor batteries, have garnered significant attention due to their high power density, rapid charge–discharge capabilities, and extended cycle life. These attributes render them particularly valuable in various applications, including portable electronic devices, electric vehicles, and other sectors. MXene-based electrode materials exhibit considerable promise in the realm of supercapacitors, attributed to their distinctive layered structure, excellent electrical conductivity, and abundant surface functional groups.![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 cycles. Beyond composite strategies, MXene derivatives and surface modifications are also pivotal in enhancing electrochemical performance. Through chemical etching and surface functional group modifications, MXene materials can adopt various structures and surface states to optimize their electrochemical properties. For instance, nitrogen-doped Ti3C2Tx MXene showcases superior capacitive properties, with nitrogen significantly improving the material's electrical conductivity and charge storage capacity. At a current density of 1 A g−1, the nitrogen-doped MXene achieve a specific capacitance of 300 F g−1. Additionally, MXene derivatives, such as hydroxide-coated MXene, exhibit excellent electrochemical properties due to their surface containing numerous electrochemically active sites. Researchers synthesized Ni(OH)2/MXene composites by chemically reducing nickel hydroxide onto the MXene surface, achieving a high specific capacitance of 400 F g−1 at a current density of 3 A g−1 and maintaining excellent capacitance retention after 5000 cycles. The structural stability of CTAB-Sn(IV)@Ti3C2 was verified through 100 cycles at 0.1 A g−1. TEM images of CTAB-Sn(IV)@Ti3C2 reveal a clear hierarchical structure (Fig. 14a and b), affirming the robust nature of the CTAB@Ti3C2 matrix. Despite the alloying process, numerous individual nanoparticles, ranging from 3 to 7 nm in diameter, remain uniformly anchored within the CTAB@Ti3C2 matrix. After cycling, HRTEM images (Fig. 14c) display clear lattice stripes with a d-spacing of 0.210 nm, consistent with previous reports and corresponding to the quadrionic Sn phase of the (220) plane (JCPDS card no. 65-5224). To further confirm Sn insertion within the CTAB@Ti3C2 matrix interlayer, Fig. 14d and f display cross-sectional images of CTAB-Sn(IV)@Ti3C2 after 100 cycles, combined with STEM imaging and element mapping of Ti and Sn, showing a stronger Sn signal in the interlayer compared with the matrix surface. The robust structure of CTAB@Ti3C2 and the columnar effect of Sn within the matrix layer endow the nanocomposites with exceptional electrochemical properties. Based on its superior energy storage performance, CTAB-Sn(IV)@Ti3C2 was employed as the anode electrode, coupled with a conventional commercial AC electrode (Fig. 14g).154 In a half-cell system, AC in an organic electrolyte at potentials above 3.0–4.5 V (versus Li+/Li) exhibits noteworthy electrochemical performance, with a capacity of 34 mA h g−1 at 0.2 A g−1, within the typical range of AC (∼30–60 mA h g−1 at 0.1–0.3 A g−1).
000 cycles. Beyond composite strategies, MXene derivatives and surface modifications are also pivotal in enhancing electrochemical performance. Through chemical etching and surface functional group modifications, MXene materials can adopt various structures and surface states to optimize their electrochemical properties. For instance, nitrogen-doped Ti3C2Tx MXene showcases superior capacitive properties, with nitrogen significantly improving the material's electrical conductivity and charge storage capacity. At a current density of 1 A g−1, the nitrogen-doped MXene achieve a specific capacitance of 300 F g−1. Additionally, MXene derivatives, such as hydroxide-coated MXene, exhibit excellent electrochemical properties due to their surface containing numerous electrochemically active sites. Researchers synthesized Ni(OH)2/MXene composites by chemically reducing nickel hydroxide onto the MXene surface, achieving a high specific capacitance of 400 F g−1 at a current density of 3 A g−1 and maintaining excellent capacitance retention after 5000 cycles. The structural stability of CTAB-Sn(IV)@Ti3C2 was verified through 100 cycles at 0.1 A g−1. TEM images of CTAB-Sn(IV)@Ti3C2 reveal a clear hierarchical structure (Fig. 14a and b), affirming the robust nature of the CTAB@Ti3C2 matrix. Despite the alloying process, numerous individual nanoparticles, ranging from 3 to 7 nm in diameter, remain uniformly anchored within the CTAB@Ti3C2 matrix. After cycling, HRTEM images (Fig. 14c) display clear lattice stripes with a d-spacing of 0.210 nm, consistent with previous reports and corresponding to the quadrionic Sn phase of the (220) plane (JCPDS card no. 65-5224). To further confirm Sn insertion within the CTAB@Ti3C2 matrix interlayer, Fig. 14d and f display cross-sectional images of CTAB-Sn(IV)@Ti3C2 after 100 cycles, combined with STEM imaging and element mapping of Ti and Sn, showing a stronger Sn signal in the interlayer compared with the matrix surface. The robust structure of CTAB@Ti3C2 and the columnar effect of Sn within the matrix layer endow the nanocomposites with exceptional electrochemical properties. Based on its superior energy storage performance, CTAB-Sn(IV)@Ti3C2 was employed as the anode electrode, coupled with a conventional commercial AC electrode (Fig. 14g).154 In a half-cell system, AC in an organic electrolyte at potentials above 3.0–4.5 V (versus Li+/Li) exhibits noteworthy electrochemical performance, with a capacity of 34 mA h g−1 at 0.2 A g−1, within the typical range of AC (∼30–60 mA h g−1 at 0.1–0.3 A g−1).
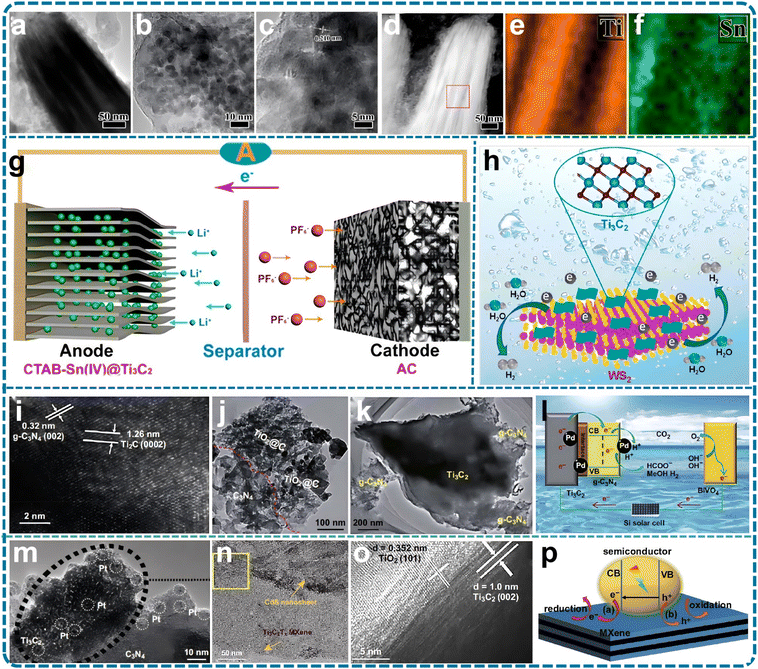 | ||
| Fig. 14 TEM and HRTEM images of (a–c) CTAB-Sn(IV)@Ti3C2 after 100 cycles of charging to 3 V at 0.1 A g−1; (d–f) CTAB-Sn(IV)@Ti3C2 STEM image after 100 cycles and element mapping image of Ti and Sn; (g) CTAB-Sn(IV)@Ti3C2//AC LIC Charging process. Reproduced from ref. 154 with permission from American Chemical Society, copyright 2016. (h) Schematic representation of the mechanism whereby 10% WS2/Ti3C2 achieves electrochemical water splitting. Reproduced from ref. 161 with permission from American Chemical Society, copyright 2023. Photocatalytic composites based on MXene in combination with g-C3N4 formed by in situ decoration. (i) HRTEM images of TiCN-0.4. Reproduced from ref. 165 with permission from The Royal Society of Chemistry, copyright 2017. (j) TEM images of the TiO2@C/g-C3N4. Reproduced from ref. 166 with permission from The Royal Society of Chemistry, copyright 2018. (k) TEM images of Pd-TCCN3; (l) a proposed mechanism for PEC reduction of CO2 into chemical fuels. Reproduced from ref. 167 with permission from The Royal Society of Chemistry, copyright 2018. (m) HR-TEM images of g-C3N4/Ti3C2. Reproduced from ref. 168 with permission from The Royal Society of Chemistry, copyright 2018. (n) TEM image of the as-prepared 2D CdS/Ti3C2Tx sheet-onto-sheet heterostructures. Reproduced from ref. 169 with permission from Elsevier, copyright 2018. (o) HRTEM image of the interface structure of TC-OH and P25 NPs. (p) Schematic of the working mechanism of MXenes applied in photocatalysis. Reproduced from ref. 170 with permission from American Chemical Society, copyright 2019. | ||
To further enhance the electrochemical performance of MXene in supercapacitors, researchers often augment its specific capacity and cyclability by integrating it with other materials. Among various applications, MXene composites with conductive polymers have garnered substantial interest due to their superior electrochemical attributes. Conductive polymers, such as polyaniline (PANI) and polypyrrole (PPy), possess substantial specific capacitance and elevated electrochemical activity. Their combination with MXene can further augment the conductivity and electrochemical performance of the electrode materials. Yuan et al.158 investigated a composite material consisting of Ti2Tx MXene and polyaniline, wherein the PANI was uniformly deposited on the MXene layers via in situ polymerization technology, thereby markedly enhancing the energy storage performance of supercapacitors. In this investigation, the researchers employed an in situ polymerization method to uniformly deposit polyaniline molecules onto the MXene layers, forming a tightly bonded MXene/PANI composite. MXene furnishes an exceptional conductive network, whereas PANI offers high-capacitance electrochemical activity. The synergy of both materials not only mitigates the issue of MXene layers prone to self-stacking but also significantly amplifies the effective specific surface area of the electrode material, fostering ion transport within the electrolyte and, consequently, enhancing the overall electrochemical performance of the electrode material. Experimental results reveal that MXene/PANI composites exhibit a specific capacitance of up to 650 F g−1 at a current density of 1 A g−1, a figure that far surpasses that of single-component MXene or PANI electrode materials. This enhancement primarily stems from the high electrochemical activity of PANI coupled with the swift electron transport pathway provided by the MXene material, which substantially elevates the capacitive properties of the composite. Additionally, the composite demonstrates remarkable cycling stability, retaining high capacitance even after numerous charge and discharge cycles. This attribute underscores its significant potential in supercapacitor applications demanding high energy density and extended longevity. Yuan et al.158 demonstrated that by synergistically integrating a conductive polymer with MXene, the specific capacitance and electrochemical performance of the electrode material can be further enhanced while preserving the high conductivity of the material. The MXene/PANI composite not only delivers superior energy storage performance but also effectively prolongs the service life of supercapacitors, offering robust technical support for future high-efficiency and long-endurance energy storage devices.158
Carbon materials, such as graphene and carbon nanotubes, exhibit extremely high electrical conductivity and exceptional electrochemical stability. When combined with MXene, they not only enhance the conductive network of the material but also significantly improve its rate performance and cycling stability. Ghidiu et al.93 discovered that the integration of Ti3C2Tx MXene with reduced graphene oxide (rGO) could develop an efficient supercapacitor electrode material. Initially, Ghidiu et al. amalgamated Ti3C2Tx MXene with rGO to form a composite featuring a three-dimensional structure. MXene's high electrical conductivity, coupled with rGO's superior mechanical properties, provides the composite with exceptionally high structural stability. In comparison with MXene alone, the composite effectively mitigates the issue of MXene layer self-stacking, a phenomenon that reduces the specific surface area of the electrode material during electrochemical processes and impairs the transport efficiency of charges and ions. By integrating with rGO, the composite material sustains a larger specific surface area and higher electrolyte permeability during charge–discharge cycles, thereby enhancing its electrochemical performance. Experimental results revealed that the Ti3C2Tx MXene/rGO composite maintained a high specific capacitance and exhibited remarkable cycling stability under high current densities. Specifically, the specific capacitance retention of the composite at high magnification significantly surpassed that of single MXene or graphene electrode materials. Furthermore, following thousands of charge–discharge cycles, the composite retained commendable electrochemical stability, underscoring its extended cycle life. This performance enhancement is primarily attributed to the three-dimensional conductive network structure of the composite, which facilitates rapid electron and ion transport while preserving the integrity of the electrode structure throughout the cycle. The composite design of MXene and carbon materials offers a practical solution to augment the magnification performance and cycling stability of supercapacitors. This material not only amalgamates the strengths of MXene and rGO but also addresses their individual limitations, thereby offering new insights and technical support for the advancement of high-performance, long-life supercapacitors.93
Surface modification represents an effective strategy to enhance the electrochemical performance of MXene-based electrode materials. Doping with various elements can significantly improve MXene's electronic structure and surface chemistry, thereby augmenting its charge storage capacity and electrical conductivity. For instance, nitrogen doping is a prevalent surface modification method that enhances the material's electrical conductivity and electrochemical activity by incorporating nitrogen atoms into the MXene structure, thereby improving its performance in supercapacitors. During nitrogen doping, nitrogen atoms can replace part of the carbon or oxygen atoms, altering the surface chemistry of the MXene materials. Nitrogen's strong electronegativity and high electron supply capacity generate more active sites on the material's surface, enhancing the interaction between MXene and the electrolyte and thus improving its charge storage capacity and ion transport efficiency. Studies have demonstrated that nitrogen-doped Ti3C2Tx MXene exhibits excellent electrochemical properties in supercapacitor applications. For example, in acidic electrolytes, the specific capacitance of nitrogen-doped Ti3C2Tx MXene reached 380 F g−1, significantly exceeding that of undoped MXene. Additionally, nitrogen doping notably enhances the capacitance retention of MXene materials. At high current densities, nitrogen-doped MXene materials maintain high capacitance retention during rapid charge–discharge cycles, indicating superior magnification and long-life performance. Another crucial advantage of nitrogen doping is the improvement in electrical conductivity. The incorporation of nitrogen atoms increases the electrical conductivity of MXene, smoothening the electron transport path within the material and thereby enhancing its overall conductivity. This modification renders nitrogen-doped MXene material highly promising for long-life, high-performance energy storage devices. Nitrogen doping also positively impacts the electrochemical stability of MXene. In supercapacitor applications, the cycling life of the electrode material is paramount. Nitrogen doping not only enhances the electrical conductivity of the material but also extends its service life by improving its mechanical stability. Findings indicate that nitrogen-doped Ti3C2Tx MXene retains high electrochemical properties after thousands of charge–discharge cycles, validating its suitability for long-term stable operation in energy storage devices. In summary, nitrogen doping offers an effective means to enhance the electrochemical performance of MXene materials, significantly augmenting their application performance in supercapacitors by optimizing the electronic structure and surface chemistry of the materials. Consequently, nitrogen-doped MXene emerges as a promising electrode material for high-performance energy storage devices, characterized by its high specific capacitance, exceptional magnification performance, and extended lifetime.159
To enhance the electrochemical performance of MXene materials in supercapacitors, researchers have integrated MXene with high specific capacitive materials, such as hydroxides, to augment its energy storage capacity. Among these, Ni(OH)2 has been identified as an optimal component for MXene composites due to its high theoretical capacitance and superior electrochemical properties. By depositing Ni(OH)2 onto the surface of MXene layers, the number of active sites within the electrode material can be significantly increased, thereby enhancing its overall electrochemical performance. The foundation of this composite strategy is the synergistic interaction between MXene and Ni(OH)2. The two-dimensional layered structure of MXene serves as an effective substrate for Ni(OH)2 deposition, while its high conductivity facilitates rapid electron transport. Ni(OH)2, recognized for its high specific capacitance, contributes additional energy storage sites to the composite electrode, further improving both specific capacitance and rate capability. For instance, researchers successfully deposited Ni(OH)2 uniformly onto the surface of Ti(OH)2 Tx MXene, resulting in the preparation of an Ni(OH)2/Ti3C2Tx composite. This composite was subjected to systematic evaluations of its electrochemical performance in supercapacitors. Experimental results indicated that the composite achieved a specific capacitance of up to 500 F g−1 at a current density of 3 A g−1, significantly surpassing the performance of MXene or Ni(OH)2 used independently. This improvement is primarily attributed to Ni(OH)2 providing more reversible REDOX active sites for electrochemical reactions, while MXene's conductive network structure fosters rapid electron and ion transport within the electrode. In addition to its impressive specific capacitance, the Ni(OH)2/Ti3C2Tx composite demonstrates excellent cycle life performance. After 5000 charge–discharge cycles, the composite retains 92% of its capacitance, indicating robust cycling stability. This characteristic suggests substantial potential for the composite material in high energy density and high power density energy storage applications. The lamellar structure of MXene not only facilitates efficient electron transport but also effectively mitigates volume expansion and structural alterations associated with the electrochemical reactions of Ni(OH)2, thereby enhancing the stability and durability of the composite. This composite strategy utilizing MXene and Ni(OH)2 illustrates that integrating MXene with high-specific capacitive materials can greatly enhance electrochemical performance while extending the operational lifespan of the electrode material, positioning it favorably for long-lasting, high-performance energy storage devices.
The electrolyte plays a crucial role in supercapacitors, directly influencing the electrochemical properties and energy storage efficiency of the electrode materials. Due to the diverse range of surface functional groups, MXene-based electrode materials can be combined with various electrolytic liquid phases, including aqueous, organic, and ionic liquids, facilitating the formation of different capacitive storage mechanisms. The pairing of MXene with aqueous electrolytes reveals exceptional electrochemical properties in supercapacitor applications, particularly characterized by high specific capacitance and outstanding power density. The abundant hydroxyl (–OH) and oxygen (–O) functional groups present on the surface of MXene materials create favorable conditions for interaction with water molecules. These functional groups enhance the rapid adsorption and desorption processes of ions in the electrolyte at the electrode surface, significantly improving the energy storage efficiency and charge–discharge rates of supercapacitors. For example, Wang et al.160 developed a supercapacitor material based on Ti3C2Tx MXene utilizing an aqueous electrolyte such as H2SO4. In this study, the MXene material facilitated a much faster and smoother ion transport across the surface of the electrode by generating strong interfacial interactions with water molecules. This mechanism accelerates the electrochemical reaction rates of MXene in aqueous electrolytes and effectively enhances the specific capacitance and power density of supercapacitors. This performance significantly outstrips that of conventional electrode materials, underscoring the considerable potential of MXene materials in energy storage applications. The two-dimensional lamellar architecture of MXene not only provides fast ion transport pathways but also increases the effective interaction area between the electrode and the electrolyte through the functional groups, enhancing the efficiency of ion embedding and de-embedding, and consequently improving overall electrochemical performance. Additionally, the combination of MXene with aqueous electrolytes offers environmental and safety advantages. Aqueous electrolytes exhibit good electrical conductivity and electrochemical stability, alongside lower risks of environmental pollution and reduced costs, thereby signaling broad prospects for MXene-based supercapacitors in large-scale energy storage applications.
Flexible supercapacitors have been extensively studied for their application prospects in portable mobile electronic devices. Designing lightweight flexible electrodes with strong mechanical properties and electrochemical stability is the key to realizing high-energy flexible batteries. 2D MXene films are emerging as ideal electrode materials for flexible and wearable supercapacitors due to their metallic conductivity, tunable chemical properties, unique flexibility and excellent mechanical properties. In addition, MXene can store large amounts of charge through surface Faraday REDOX reactions, providing higher capacitance than conventional electric double-layer capacitors. MXene-based electrodes typically face challenges related to their large aspect ratio and complex and elongated ion diffusion paths resulting from nanosheet recombination, resulting in slow kinetics and low capacitance. The construction of ion transport channels is an effective way to solve the above two-dimensional MXene problem.161 Yang et al.162 proposed a novel strategy to construct 3D interconnected porous MXene/carbon point (p-MC) films with uniformly distributed in-plane large holes on the MXene layer and tightly anchored carbon points between the MXene layers for high-performance flexible supercapacitors. In this novel structure, the large pores in the plane acting as the aorta reduce the vertical path distortion of the rapid diffusion of ions, while the enlarged layer spacing acts as capillaries to rapidly transport ions to each electrochemically active site. Due to its structural advantages, the p-MC electrode has a high capacitance of 688.9 F g−1 at 2 A g−1, which is nearly 2.5 times that of pure MXene. In addition, the p-MC electrode has a much higher pseudocapacitance contribution than the pure MXene electrode. When assembled into solid-state asymmetric flexible supercapacitors, p-MC-based devices can exhibit electrochemical properties with good flexibility. Xu et al.163 proposed to fabricate porous, chemically bonded black phosphene/Ti3C2Tx heterostructured films with co-doped S/N heteroatoms by electrostatic self-assembly followed by thermal foaming. The addition of black phosphene can effectively prevent the recombination of Ti3C2Tx, and the porous structure can enhance ion transport. In addition, the doped heteroatoms significantly increased the electrochemical activity of Ti3C2Tx. A porous film with a thickness of about 50 μm exhibits a high capacitance of 374 F g−1 at 0.5 A g−1 and retains 84% of the capacitance at 20 A g−1, thus giving the assembled flexible supercapacitors excellent magnification performance. This work provides a promising innovative approach for the development of high rate MXene-based flexible supercapacitors.
The investigation of MXene composite materials in supercapacitors reveals significant application potential. Through composite design incorporating conductive polymers and carbon-based materials, MXene-based supercapacitors exhibit high specific capacitance, exceptional magnification performance, and prolonged cycle life. Furthermore, the optimization of the electrolyte substantially enhances the electrochemical performance of the MXene electrode material. Nonetheless, the widespread implementation of MXene in supercapacitors encounters several challenges, including the development of large-area preparation technology, the optimization of material structure, and the enhancement of environmental stability. MXene-based electrode materials offer a novel approach for the advancement of high-performance supercapacitors. Through composite design with conductive polymers and carbon materials, MXene composite materials demonstrate superior energy storage performance. Future research endeavors should focus on further improving the electrochemical stability of MXene materials, reducing production costs, and developing large-scale preparation technology, as these are pivotal in promoting its extensive application within the realm of supercapacitors.
4.3. Catalyst application
MXene composite materials, with their unique structure and excellent physical and chemical properties, show great application potential in the field of electrocatalysis and photocatalysis.Electrocatalytic carbon dioxide reduction (CO2RR) is a green technology that converts CO2 into valuable chemicals or fuels, crucial for mitigating global climate change and reinforcing the carbon cycle. MXene materials, known for their high electrical conductivity and surface-adjustable functional groups, have shown significant potential in CO2RR. Specifically, nitrogen-doped Ti2C2Tx MXene has been developed as a highly efficient CO2RR catalyst. Nitrogen doping not only enhances the conductivity of MXene but also increases the active sites on its surface, effectively promoting CO2 adsorption and reducing the energy required for the reduction reaction. In CO2RR experiments, nitrogen-doped MXene exhibited excellent catalytic selectivity at −0.6 V (vs. RHE), with a Faraday efficiency of 85% for CO generation, accompanied by high current density and stability. The stability in long-term electrolysis tests, with minimal performance decline, suggests its potential for industrial applications. This finding not only validates the potential of MXene materials in CO2 reduction but also provides important insights for developing novel, high-efficiency CO2RR catalysts.
The oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) is a critical process in fuel cells and metal–air batteries, impacting their overall performance. Despite the superior catalytic activity of platinum-based catalysts, their high cost and poor stability limit their widespread use. Non-precious metal catalysts, such as MXene composites, have gained attention for their low cost, high activity, and excellent stability. Ti3C2Tx MXene, compounded with cobalt-based nanoparticles through a solvothermal method, has demonstrated outstanding ORR performance in alkaline electrolytes. The composite exhibits a low initial potential, rapid oxygen reduction kinetics, and high catalytic selectivity. It also shows exceptional stability in long-term cycle tests, maintaining performance with minimal attenuation. The mechanical robustness of MXene and the uniform distribution of cobalt nanoparticles contribute to this stability. Future studies could focus on optimizing the interface structure between cobalt nanoparticles and MXene lamellae, enhancing catalytic activity, and opening new avenues for cost-effective fuel cells.
The oxygen evolution reaction (OER) is a key step in water electrolysis and renewable energy storage, but its slow kinetics require efficient catalysts to reduce overpotential and enhance efficiency. Traditional OER catalysts, often reliant on precious metals like platinum and iridium, are expensive and have limited reserves. Therefore, developing inexpensive and efficient OER catalysts is a priority. MXene, with its superior electrical conductivity and two-dimensional layered structure, serves as an ideal catalyst support. A highly efficient MXene/NiFe LDH composite catalyst, prepared by electrochemically depositing nickel–iron layered double hydroxide (NiFe LDH) onto Ti2C2Tx MXene, has shown outstanding OER performance. Under a current density of 10 mA cm−2, the catalyst displays an overpotential of only 270 mV, significantly lower than many conventional non-precious metal catalysts. The composite also demonstrates exceptional stability in long-term electrolysis tests, maintaining performance due to the mechanical strength of MXene and the uniform distribution of NiFe LDH. This catalyst's performance highlights the potential of MXene as a catalyst carrier and offers new insights for developing efficient and stable non-precious metal catalysts. Future research could optimize MXene's surface modification and recombination techniques, advancing its application in water decomposition and renewable energy storage.166
Photocatalysis technology, which harnesses light energy to drive chemical reactions, plays a pivotal role in environmental remediation and energy conversion. The photocatalytic properties of MXene composite materials have been extensively studied, particularly in the context of pollutant degradation and water decomposition. Water decomposition, a highly researched area in photocatalysis, aims to provide viable solutions for clean energy development by converting water into hydrogen and oxygen through photocatalysis. The key to achieving efficient photocatalytic water decomposition lies in the design of photocatalysts that can absorb sufficient light energy under visible light irradiation and effectively separate photogenerated electrons and holes. However, traditional photocatalysts often suffer from limited light absorption ranges and rapid photogenerated carrier recombination rates, resulting in low overall catalytic efficiency. Therefore, the development of novel and efficient photocatalysts has emerged as a critical aspect of photocatalytic water decomposition research. MXene, with its distinctive structure and remarkable photocatalytic properties, has exhibited promising potential in this field. In a study conducted by Yoon et al.,167 the application of Ti3C2 MXene as a photocatalyst in water decomposition reactions was investigated. The results revealed that Ti3C2 MXene not only exhibits excellent light absorption capacity but also demonstrates superior photogenic carrier separation performance, significantly enhancing photocatalytic efficiency. The layered structure of Ti3C2 MXene is a key factor contributing to its outstanding photocatalytic performance. The material's two-dimensional structure provides a large surface area, enabling it to offer more active sites for photocatalytic reactions. Additionally, the abundant functional groups (such as –OH, –F, etc.) on the surface of Ti3C2 MXene further improve the separation efficiency of photogenerated electrons and holes, reducing their recombination probability and prolonging the lifetime of photogenerated carriers. Under visible light irradiation, Ti3C2 MXene exhibits remarkable photocatalytic properties. Experimental results indicated that the material can effectively utilize visible light energy to catalyze the water decomposition reaction, producing hydrogen and oxygen. Compared with traditional photocatalysts like TiO2, Ti3C2 MXene not only broadens the light absorption range but also effectively increases the photocatalytic reaction rate. Specifically, Ti3C2 MXene is capable of absorbing a broader spectrum of visible light wavelengths, enabling it to harness a greater portion of solar energy and thus enhancing photocatalytic efficiency. Furthermore, the high conductivity of Ti3C2 MXene plays a crucial role in promoting its photocatalytic performance by facilitating the rapid conduction of photogenerated electrons and reducing their recombination probability during photocatalysis. Due to these characteristics, Ti3C2 MXene maintains high catalytic activity during the photocatalytic water decomposition process and exhibits a long service life. In multiple photocatalytic cycle experiments, the material demonstrates excellent stability with almost no attenuation of catalytic performance, highlighting its great potential for practical applications.
The successful application of Ti3C2 MXene also benefits from its strong structural adjustability, making it a versatile and promising material for photocatalytic water decomposition and beyond. The photocatalytic properties of MXene materials can be further optimized by changing the surface functional groups or doping elements. For example, heteratom doping such as nitrogen and sulfur can change the electronic structure of Ti3C2 MXene, thereby enhancing its light absorption and photogenerated carrier separation efficiency. This provides more possibilities for the further optimization and application of Ti3C2 MXene materials. In summary, the successful application of Ti MXene as a photocatalyst in the water decomposition reaction not only shows its excellent photocatalytic performance, but also provides a new idea for the development of photocatalytic materials in the future. Due to its unique structure, efficient electron–hole separation ability and good stability, Ti2 MXene has broad application potential in the areas of photocatalytic water decomposition and photocatalytic CO2 reduction. Future studies can further improve the photocatalytic performance of MXene by further optimizing its structural design and surface chemical modification, and promote its practical application in renewable energy development.
The application efficiency of Ti3C2 MXene in solar-powered water decomposition is expected to be further improved through the combination with other photocatalytic materials or modification of surface functional groups.167 G-C3N4 is a two-dimensional semiconductor material that binds with MXenes as a co-catalyst during photocatalysis (Fig. 14i–l).168–170 MXene can be added during the combustion of precursors, such as melamine and thiourea, but the high calcination temperature (about 550 °C) may result in the oxidation of MXene to titanium dioxide. The high photoactivity of G-C3N4/MXene is attributed to charge separation. In addition, heterojunctions formed by TiO2–C3N4 also play an important role in charge separation. The synergistic effect of Ti3C2 MXene and Pt as double catalysts enhances the hydrogen evolution of g-C3N4 (Fig. 14m–o), and the high-frequency etching strips the composite of Ti3C2 and g-C3N4 mixed in the liquid stirred after the photodeposition of platinum.171,172 The photocatalyst absorbs visible light, and the photogenerated electrons are excited to CB, leaving holes in the valence band (VB). The excited carriers transfer to MXenes at the interface mainly because of the higher potential of MXenes. The electrons are transferred to MXenes without recombination, and H+ is reduced on the surface of MXene, methane and CO produce H2, and ammonia N2 produces H2, as shown in Fig. 14p process (a). As shown in (b) process, holes are transferred to MXenes and react to produce OH˙, which can be used for organic degradation; electrons can also produce OH˙ for organic degradation.173 Due to the good electrical conductivity and large surface area of MXenes, it has been applied to photocatalysis, both replacing the precious metal co-catalyst and improving the charge separation ability of the photocatalyst (Fig. 15a).174–176 The most common methods for preparing photocatalyst combinations include mechanical mixing, self-assembly, in situ decorative quantification, and oxidation, or a combination of all four methods. The findings indicate that ˙O2−, ˙OH, and h+ play an important role in the degradation process. In particular, under visible-light irradiation, N-doped TiO2 is excited to produce photoinduced e− and h+, and e− is quickly transferred to the N-doped C matrix. The relatively conduction band of the TiO2 (−0.3 eV) is greater than that of C (−0.08 eV),177 which enhances surface functional group C as an excellent C conductor to rapidly take the photoinduced e−, enhancing separation capability. Photoinduced e− reacts with O2 to generate ˙O2−, whereas photoinduced h+ reacts with OH− in H2O to produce ˙OH.178 A schematic diagram of photocatalytic phenol removal under visible light irradiation with N-doped TiO2/Ti3C2 MXene is described in Fig. 15d.179 While CO2 conversion produces photocatalytic reaction products, this performance improvement can be attributed to the two-dimensional heterojunction properties of ultra-thin Ti3C2/Bi2WO6 nanocomposites, which have the following benefits: (i) effective transfer of photogenerated e− from Bi2WO6 conduction band across the nanocomposites interface and accumulation on the Ti3C2 surface, owing to the fairly small charge transport space of the very thin structure, (ii) increased effective surface area associated with the addition of Ti3C2, and (iii) superior photothermal conversion features of Ti3C2, which provides energy to stimulate catalyst and improve the confined photocatalytic reactions.180 The photocatalytic process with Ti3C2/Bi2WO6 nanocomposites is demonstrated in detail in Fig. 15e. In addition to the hydrothermal method and calcination, chemical oxidation and high-energy ball milling are also used for oxidation. Cheng et al.181 oxidized Ti3C2 tablets with 30% hydrogen peroxide to form microporous MXene/TiO2-x nanodots (Fig. 15b). The catalyst can be used as a photoFenton bifunctional catalyst for the degradation of rhodamine B under both dark and light conditions, and TiO2@C nanosheets are synthesized from Ti2C by high-energy ball milling and used for methyl blue degradation (Fig. 15c).182
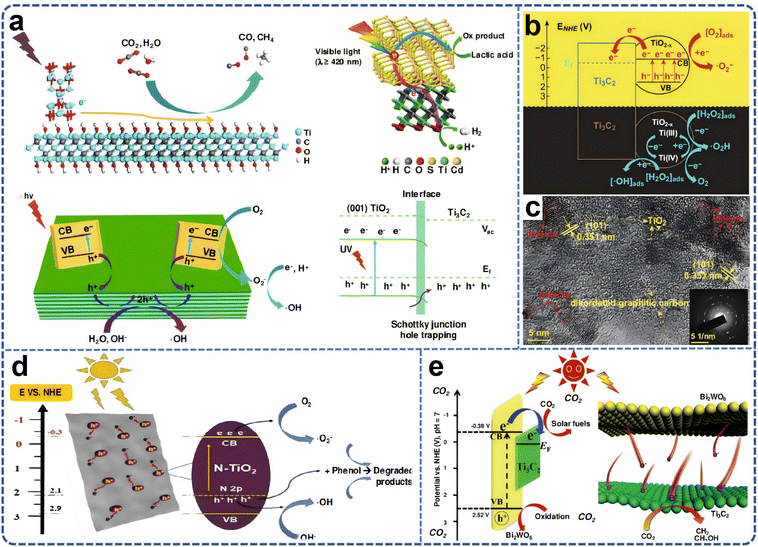 | ||
| Fig. 15 (a) Schematic showing charge separation between MXene co-catalyst and a photocatalyst. Reproduced from ref. 174 with permission from Wiley-VCH, copyright 2018. (b) Mechanisms of degradation over mp-MXene/TiO2−x. Reproduced from ref. 181 with permission from The Royal Society of Chemistry, copyright 2018. (c) HRTEM image of TiO2@C. Bottom right inset is SAED of this area. Reproduced from ref. 182 with permission from Elsevier, copyright 2018. (d) N-TiO2@C photocatalytic degradation of phenol under visible light irradiation. Reproduced from ref. 179 with permission from Elsevier, copyright 2019. (e) Energy level structure diagram of Bi2WO6 and Ti3C2, and photogenerated electron transfer process at the interface of nanocomposites. Reproduced from ref. 180 with permission from Wiley-VCH, copyright 2018. | ||
Photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants is one of the important methods in water treatment technology which can effectively remove harmful organic matter in water. Although traditional photocatalysts such as TiO2 have certain applications in the degradation of organic pollutants, due to its poor response to visible light, the photocatalytic efficiency is low, so it is necessary to develop new efficient photocatalytic materials. In recent years, MXene has become a research hotspot in the field of photocatalysis due to its excellent electrical conductivity, abundant surface active sites and adjustable optical properties. Iravani et al.183 developed a photocatalyst based on Ti3C2 MXene and used it for the degradation of organic pollutants. In the study, Ti3C2 MXene significantly increased its photocatalytic activity through surface doping and modification. The doping process adjusts the electronic structure of MXene by introducing different elements or functional groups, enlarging the photoresponse range, improving the separation efficiency of photogenerated carriers, and reducing the recombination phenomenon of photogenerated electrons and holes. Due to this series of optimizations, Ti3C2 MXene showed good photocatalytic performance, especially in ultraviolet light to degrade dye-based organic pollutants significantly. The results showed that the Ti2 MXene-based photocatalyst was able to rapidly generate photoluminescent electrons and holes under ultraviolet light, and these photoluminescent carriers were further involved in the degradation reaction. In the process of degrading dye-based organic pollutants, photogenic holes react with hydroxyl ions in water to form strong oxidizing hydroxyl radicals (–OH), which can effectively attack the chemical bonds of organic pollutants and promote their decomposition into harmless small molecules or carbon dioxide and water. At the same time, the two-dimensional lamellar structure of MXene provides more active sites for the adsorption and reaction of pollutants, which further promotes the degradation reaction. The photocatalytic water splitting process for the production of H2 and O2, using Ti3C2–TiO2 nanoflowers synthesized at different temperatures (300 °C and 500 °C) as co-catalysts (reaction conditions: 0.02 g catalyst, 100 mL pure water), is shown in Fig. 16a. The photocatalytic mechanisms of Ti3C2–TiO2 nanoflowers and TiO2 nanoribbons under solar light irradiation are also discussed.184 MXene-based structures with large surface area, surface-controlled chemical properties, regular planar structure, unique optical/thermal properties, hydrophilicity, excellent metal conductivity, and abundant derivatives have been extensively studied for the photocatalytic degradation of pollutants (Fig. 16b).185–188 They have good potential for removing contaminants through interfacial chemical conversion and adsorption, as well as catalytic removal and photocatalytic degradation capabilities. After the magnetic heterostructures of α-Fe2O3/ZnFe2O4 were formed by a simple hydrothermal preparation technique, the magnetic heterostructures on the surface of MXene (Ti3C2) were dispersed by ultrasonic assisted self-assembly using MXenes as a co-catalyst (Fig. 16c).189 These photocatalysts show better photocatalytic activity in eliminating rhodamine B and toxic Cr(VI), with advantages of reusability and high conductivity. In another study, MXene (Ti3C2)/MoS2 nanocomposites with a large specific surface area were prepared by the hydrothermal method, showing efficient photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants. The structure of Ti3C2 MXene/O-doped g-C3N4 2D-2D Schottky-junction by in situ electrostatic assembly of negatively charged MXenes and positively charged O-doped g-C3N4 nanosheets was reported. Due to the synergies between the compounds and the formation of Schottky junctions, the obtained photocatalysts exhibited enhanced hydrogen evolution capacity and photocatalytic activity. In one study, a terpolymer Ti3C2Tx/Ti3AlC2@Ag composite photocatalyst was prepared which could catalyse the degradation of methylene blue, rhodamine B and methylene orange with degradation efficiencies of 99.7%, 98.9% and 99.3%, respectively (Fig. 16d).190 The synergistic effect between Ag nanomaterials and partially etched Ti3C2Tx/Ti3AlC2 nanosheets was demonstrated by photogenic carrier transfer and reactive oxygen species (ROS) formation. These effects can also improve the catalytic degradation performance. Kumar et al.191 developed MXene (Ti3C2) coupled g-C3N4 nanosheets based on a plasma photocatalyst with good reusability (up to 3 cycles) for removal of pharmaceutical contaminants (cefixime) under visible light irradiation (Fig. 16e). After optimization, the photocatalyst containing 3 wt% MXenes can effectively remove (∼64.69%) cefixime under 105 min of visible light irradiation. Mechanistic studies have shown that the presence of gold (Au) nanomaterials and MXenes can promote excellent carrier separation and increase the number of active sites due to interface contact with g-C3N4 nanosheets. The Ti3C2 MXene photocatalyst studied by Iravani et al.183 showed excellent degradation efficiency in the process of degrading organic pollutants. Taking Methylene Blue (MB), a common dye pollutant, as an example, the catalyst can degrade MB to a colorless and transparent state in a short time under ultraviolet light, with a degradation efficiency of more than 90%. In addition, the catalyst showed good photocatalytic stability and reusable performance. After repeated use, the activity of the Ti3C2 MXene photocatalyst was almost not significantly decreased, which proved its high durability and economy in practical applications. In addition, the surface modification of MXene also improved its ability to handle different kinds of organic pollutants. It was found that by introducing different functional groups or doping different elements on the surface of MXene, the selectivity of its photocatalytic reaction can be effectively regulated, so as to achieve efficient degradation of specific types of pollutants. This feature provides a broad prospect for the application of MXene materials in water treatment. In conclusion, the Ti3C2 MXene-based photocatalyst developed by Iravani et al.183 showed good potential for photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants. Through doping and surface modification, MXene not only improves its photocatalytic activity, but also shows excellent photostability and reusability, making it suitable for large-scale water treatment systems. In the future, further studies can explore the composite or multifunctional modification of different types of MXene materials to further enhance their catalytic activity in the visible light range and expand their practical applications in pollutant treatment and environmental remediation. This result provides a new idea for developing efficient and low-cost photocatalytic water treatment technology.183
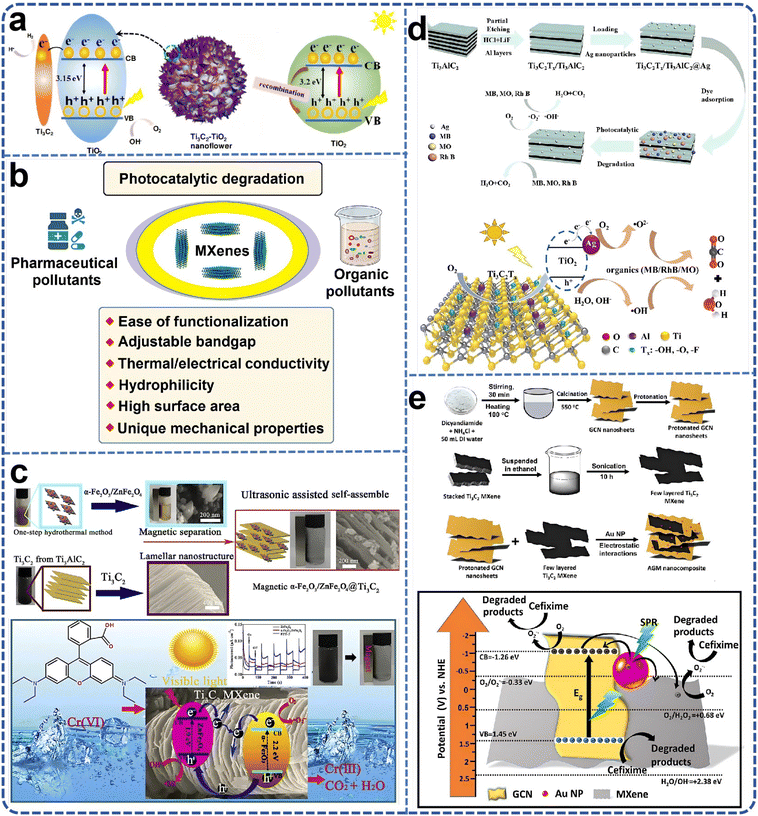 | ||
| Fig. 16 (a) Schematic photocatalytic mechanism for Ti3C2–TiO2 nano-flowers and TiO2 nano-belts under solar light irradiation. Reproduced from ref. 184 with permission from Elsevier, copyright 2018. (b) MXenes has unique photocatalytic degradation of drugs and organic contaminants. Reproduced from ref. 185 with permission from Molecules, copyright 2022. (c) The preparation process of magnetic α-Fe2O3/ZnFe2O4@MXene (Ti3C2) composite material, using rhodamine B and the photocatalytic removal mechanism of toxic Cr(VI) in water. Reproduced from ref. 137 with permission from Elsevier, copyright 2020. (d) Preparation process of three-dimensional Ti3C2Tx/Ti3AlC2@Ag photocatalytic degradation of pollutant terpolymer. Mechanism of reactive oxygen species and photodegradation. MB: methylene blue; RhB: rhodamine B; MO: methylene orange. Reproduced from ref. 190 with permission from Elsevier, copyright 2022. (e) Preparation process of g-C3N4/MXene (AGM) nanocomposites modified by gold nanomaterials. The photocatalytic decomposition mechanism of the designed nanocomposites to the drug contaminant cefixime under visible light irradiation was studied. Reproduced from ref. 191 with permission from Elsevier, copyright 2022. | ||
MXene-based electrode materials show excellent performance in catalyst applications, especially in the field of electrocatalysis and photocatalysis. By studying the application of different MXene-based catalysts in water decomposition, oxygen reduction reaction and degradation of organic pollutants, the great potential of MXene materials in catalytic performance was proved. Future research could further explore the optimization methods and practical applications of MXene composite materials to promote their large-scale application in the field of catalysis.
5. Conclusion
In this paper, we have conducted a comprehensive review on the large-scale production of MXene precursors, MXenes, and their derivatives. Our study systematically examines the methodologies for achieving large-scale MXene production. We analyze the challenges and optimization strategies associated with achieving large-scale production, focusing on four critical aspects: stability, oxidation resistance, safety, and cost. Additionally, we provide an overview of the applications of MXene in the fields of energy storage and catalysis. The potential for large-scale application of MXene-based electrode materials in batteries, supercapacitors, and catalysts is highlighted, demonstrating considerable promise. Through meticulous material design, optimization, composite material preparation, and synthesis process refinement, significant advancements in the electrochemical performance and catalytic activity of MXene composite materials have been achieved.However, several challenges remain to be addressed before MXene composite materials can achieve large-scale applicability. These challenges and potential future research directions include:
Material stability: MXenes tend to aggregate and restack due to van der Waals forces, reducing their effective surface area and accessibility for ions in applications like batteries and supercapacitors. This aggregation can significantly limit their performance in energy storage applications. Development of advanced methods to prevent or minimize aggregation is needed, such as surface functionalization with stabilizing agents, or the use of novel dispersion techniques. The long-term stability of MXenes under various conditions should be investigated and the use of polymer coatings or other protective layers explored to enhance their structural stability over time.
Oxidation resistance: MXenes are prone to oxidation, especially when exposed to air or moisture, which can lead to degradation of their electrochemical properties over time. We need to design and synthesize MXenes with enhanced oxidation resistance, such as through nitrogen or sulfur doping, or by introducing protective layers that can effectively shield the material from environmental factors. Detailed studies should be conducted on the mechanisms of oxidation and predictive models developed to guide the optimization of oxidation-resistant MXene materials.
Cost-effective production: The cost of transition metals used in MXene synthesis can be high, impacting the overall cost-effectiveness of MXene production. The etching process, particularly when using hydrofluoric acid, is both expensive and hazardous. Alternative, less expensive transition metals or development of cheaper synthesis processes should be explored, such as solid-state reactions or mechanochemical methods. The use of non-toxic and environmentally friendly etchants to replace hydrofluoric acid should be investigated, reducing the overall cost and safety risks associated with large-scale production.
Environmental and safety concerns: The chemicals used in the etching process, such as hydrofluoric acid, pose significant safety and environmental risks. The disposal of these chemicals can lead to hazardous waste, which is a major concern for large-scale production. Greener synthesis methods are needed that minimize the use of hazardous chemicals and reduce waste generation. For example, we should investigate the use of ionic liquids or green solvents in the etching process. Additionally, there should be a focus on the recycling and reuse of etchants to create more sustainable production processes. Safety protocols and guidelines should be established to ensure the safe handling and disposal of chemicals used in MXene synthesis.
Manufacturing process refinement: The synthesis of MXenes typically involves a top-down approach, such as selective etching of MAX phases, which can be complex and requires precise control over conditions to ensure high yield and quality. Optimization of the etching conditions can achieve higher yields and better quality MXene materials. Continuous production methods should be developed to scale up the synthesis process, ensuring consistent quality and reduced production times. The integration of MXene synthesis with existing industrial processes to minimize additional capital and operational costs should be investigated.
Application-specific challenges: The performance of MXene composite materials in specific applications, such as batteries and supercapacitors, can vary depending on the fabrication methods and the choice of composite materials. Tailoring the synthesis and composite preparation methods can optimize the performance for specific applications. For example, in battery applications, there should be a focus on improving the cycling stability and rate capability of MXene-based electrodes. In catalytic applications, the role of different dopants and surface modifications in enhancing catalytic activity and selectivity could be investigated.
Author contributions
W. Z. Bao, H. Shen, G. Z. Zeng contributed equally to this work. W. Z. Bao, H. Shen, G. Z. Zeng, and K. W. Sun conceived and designed the structure of the review. H. Shen collected the papers related to the topic of the review. W. Z. Bao co-wrote the paper with input from W. Z. Bao, H. Shen, G. Z. Zeng, D. Y. Cui, J. J. Xia, H. Liu, C. Guo, J. F. Li, F. Yu, and K. W. Sun. The paper was revised by all authors.Data availability
No primary research results, software or code have been included and no new data were generated or analysed as part of this review.Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.Acknowledgements
The work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (22005150) and Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu (BK20200825), and Jiangsu Provincial Scientific Research and Practice Innovation Program (KYCX22_1191). W. B. also acknowledges the financial support of the Startup Foundation for Introducing Talent of NUIST.References
- M. Downes, C. E. Shuck, R. W. Lord, M. Anayee, M. Shekhirev, R. J. Wang, T. Hryhorchuk, M. Dahlqvist, J. Rosen and Y. Gogotsi, ACS Nano, 2023, 17, 17158–17168 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Naguib, M. Kurtoglu, V. Presser, J. Lu, J. Niu, M. Heon, L. Hultman, Y. Gogotsi and M. W. Barsoum, Adv. Mater., 2011, 23, 4248–4253 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- G. Deysher, C. E. Shuck, K. Hantanasirisakul, N. C. Frey, A. C. Foucher, K. Maleski, A. Sarycheva, V. B. Shenoy, E. A. Stach, B. Anasori and Y. Gogotsi, ACS Nano, 2020, 14, 204–217 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- W. Bao, H. Shen, Y. Zhang, C. Qian, D. Cui, J. Xia, H. Liu, C. Guo, F. Yu, J. Li and K. Sun, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2024, 12, 8617–8639 RSC.
- P. Salles, D. Pinto, K. Hantanasirisakul, K. Maleski, C. E. Shuck and Y. Gogotsi, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2019, 29, 1809223 CrossRef.
- A. Lipatov, M. Alhabeb, H. Lu, S. Zhao, M. J. Loes, N. S. Vorobeva, Y. Dall'Agnese, Y. Gao, A. Gruverman, Y. Gogotsi and A. Sinitskii, Adv. Electron. Mater., 2020, 6, 1901382 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Lipatov, H. Lu, M. Alhabeb, B. Anasori, A. Gruverman, Y. Gogotsi and A. Sinitskii, Sci. Adv., 2018, 4, eaat0491 CrossRef PubMed.
- W. Bao, R. Wang, C. Qian, H. Shen, F. Yu, H. Liu, C. Guo, J. Li and K. Sun, Small, 2024, 20, 2307179 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Zhang, Y. Zhao, X. Guo, C. Chen, C.-L. Dong, R.-S. Liu, C.-P. Han, Y. Li, Y. Gogotsi and G. Wang, Nat. Catal., 2018, 1, 985–992 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Ding, Y. Li, M. Li, K. Chen, K. Liang, G. Chen, J. Lu, J. Palisaitis, P. O. Å. Persson, P. Eklund, L. Hultman, S. Du, Z. Chai, Y. Gogotsi and Q. Huang, Science, 2023, 379, 1130–1135 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Rosenkranz, M. C. Righi, A. V. Sumant, B. Anasori and V. N. Mochalin, Adv. Mater., 2023, 35, 2207757 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Qian, R. Wang, H. Shen, J. Xia, D. Cui, K. Sun, H. Liu, C. Guo, F. Yu, J. Li and W. Bao, Small, 2023, 19, 2304045 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. Hantanasirisakul and Y. Gogotsi, Adv. Mater., 2018, 30, 1804779 CrossRef PubMed.
- A. Lipatov, M. Alhabeb, M. R. Lukatskaya, A. Boson, Y. Gogotsi and A. Sinitskii, Adv. Electron. Mater., 2016, 2, 1600255 CrossRef.
- P. Zhang, L. Wang, L.-Y. Yuan, J.-H. Lan, Z.-F. Chai and W.-Q. Shi, Chem. Eng. J., 2019, 370, 1200–1209 CrossRef CAS.
- J. K. El-Demellawi, A. E. Mansour, A. M. El-Zohry, M. N. Hedhili, J. Yin, A.-H. M. Emwas, P. Maity, X. Xu, O. M. Bakr, O. F. Mohammed and H. N. Alshareef, ACS Mater. Lett., 2022, 4, 2480–2490 CrossRef CAS.
- W. Bao, H. Shen, Y. Zhang, C. Qian, G. Zeng, K. Jing, D. Cui, J. Xia, H. Liu, C. Guo, F. Yu, K. Sun and J. Li, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2024, 12, 23179–23201 RSC.
- C. Zhang, L. McKeon, M. P. Kremer, S.-H. Park, O. Ronan, A. Seral-Ascaso, S. Barwich, C. Ó. Coileáin, N. McEvoy, H. C. Nerl, B. Anasori, J. N. Coleman, Y. Gogotsi and V. Nicolosi, Nat. Commun., 2019, 10, 1795 CrossRef PubMed.
- B. Akuzum, K. Maleski, B. Anasori, P. Lelyukh, N. J. Alvarez, E. C. Kumbur and Y. Gogotsi, ACS Nano, 2018, 12, 2685–2694 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- W. Bao, L. Liu, C. Wang, S. Choi, D. Wang and G. Wang, Adv. Energy Mater., 2018, 8, 1702485 CrossRef.
- R. Wang, C. Qian, Z. Zhang, H. Shen, J. Xia, D. Cui, K. Sun, H. Liu, C. Guo, F. Yu, J. Li and W. Bao, Small, 2023, 19, 2206848 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. Zhou, Y. Yu, B. He, Z. Wang, T. Xiong, Z. Wang, Y. Liu, J. Xin, M. Qi, H. Zhang, X. Zhou, L. Gao, Q. Cheng and L. Wei, Nat. Commun., 2022, 13, 4564 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- W. Eom, H. Shin, R. B. Ambade, S. H. Lee, K. H. Lee, D. J. Kang and T. H. Han, Nat. Commun., 2020, 11, 2825 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- G. Li, S. Lian, J. Wang, G. Xie, N. Zhang and X. Xie, J. Materiomics, 2023, 9, 1160–1184 CrossRef.
- W. Bao, R. Wang, K. Sun, C. Qian, Y. Zhang and J. Li, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2022, 14, 38696–38705 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- N. Chen, Z. Duan, W. Cai, Y. Wang, B. Pu, H. Huang, Y. Xie, Q. Tang, H. Zhang and W. Yang, Nano Energy, 2023, 107, 108147 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Li, Z. Huang, C. E. Shuck, G. Liang, Y. Gogotsi and C. Zhi, Nat. Rev. Chem., 2022, 6, 389–404 CrossRef PubMed.
- P. P. Michałowski, M. Anayee, T. S. Mathis, S. Kozdra, A. Wójcik, K. Hantanasirisakul, I. Jóźwik, A. Piątkowska, M. Możdżonek, A. Malinowska, R. Diduszko, E. Wierzbicka and Y. Gogotsi, Nat. Nanotechnol., 2022, 17, 1192–1197 CrossRef PubMed.
- M. Dahlqvist, M. W. Barsoum and J. Rosen, Mater. Today, 2024, 72, 1–24 CrossRef.
- C. Roy, P. Banerjee and S. Bhattacharyya, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2020, 40, 923–929 CrossRef CAS.
- Z. J. Lin, M. J. Zhuo, M. S. Li, J. Y. Wang and Y. C. Zhou, Scr. Mater., 2007, 56, 1115–1118 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Chen, M. Dahlqvist, T. Lapauw, B. Tunca, F. Wang, J. Lu, R. Meshkian, K. Lambrinou, B. Blanpain, J. Vleugels and J. Rosen, Inorg. Chem., 2018, 57, 6237–6244 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- N. Kubitza, R. Xie, I. Tarasov, C. Shen, H. Zhang, U. Wiedwald and C. S. Birkel, Chem. Mater., 2023, 35, 4427–4434 CrossRef CAS.
- Q. Shan, X. Mu, M. Alhabeb, C. E. Shuck, D. Pang, X. Zhao, X.-F. Chu, Y. Wei, F. Du, G. Chen, Y. Gogotsi, Y. Gao and Y. Dall'Agnese, Electrochem. Commun., 2018, 96, 103–107 CrossRef CAS.
- W. Bao, R. Wang, H. Liu, C. Qian, H. Liu, F. Yu, C. Guo, J. Li and K. Sun, Small, 2023, 19, 2303745 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Zhang, Z. Yang, N. Ben, W. Gu, K. Luo and F. Yu, Bull. Mater. Sci., 2024, 47, 31 CrossRef CAS.
- W. Luo, Y. Liu, C. Wang, D. Zhao, X. Yuan, L. Wang, J. Zhu, S. Guo and X. Kong, J. Mater. Chem. C, 2021, 9, 7697–7705 RSC.
- J. Chen, Q. Jin, Y. Li, H. Shao, P. Liu, Y. Liu, P.-L. Taberna, Q. Huang, Z. Lin and P. Simon, Energy Environ. Mater., 2023, 6, e12328 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Dash, R. Vaßen, O. Guillon and J. Gonzalez-Julian, Nat. Mater., 2019, 18, 465–470 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Li, J. Lu, K. Luo, Y. Li, K. Chang, K. Chen, J. Zhou, J. Rosen, L. Hultman, P. Eklund, P. O. Å. Persson, S. Du, Z. Chai, Z. Huang and Q. Huang, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2019, 141, 4730–4737 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Zhang, K. Dasbiswas, N. B. Ludwig, G. Han, B. Lee, S. Vaikuntanathan and D. V. Talapin, Nature, 2017, 542, 328–331 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- W. Bao, R. Wang, C. Qian, M. Li, K. Sun, F. Yu, H. Liu, C. Guo and J. Li, ACS Nano, 2022, 16, 17454–17465 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- E. Defoy, M. Baron, A. Séné, A. Ghoridi, D. Thiaudière, S. Célérier, P. Chartier, F. Brette, V. Mauchamp and D. Portehault, Chem. Mater., 2023, 35, 8112–8121 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Fan, D. Tang, X. Mao, H. Zhu, W. Xiao and D. Wang, Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2018, 49, 2770–2778 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Naguib, R. R. Unocic, B. L. Armstrong and J. Nanda, Dalton Trans., 2015, 44, 9353–9358 RSC.
- C. E. Shuck, A. Sarycheva, M. Anayee, A. Levitt, Y. Zhu, S. Uzun, V. Balitskiy, V. Zahorodna, O. Gogotsi and Y. Gogotsi, Adv. Eng. Mater., 2020, 22, 1901241 CrossRef CAS.
- C. E. Shuck, K. Ventura-Martinez, A. Goad, S. Uzun, M. Shekhirev and Y. Gogotsi, ACS Chem. Health Saf., 2021, 28, 326–338 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Zhang, ACS Nano, 2015, 9, 9451–9469 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Tan, X. Cao, X.-J. Wu, Q. He, J. Yang, X. Zhang, J. Chen, W. Zhao, S. Han, G.-H. Nam, M. Sindoro and H. Zhang, Chem. Rev., 2017, 117, 6225–6331 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Malaki, A. Maleki and R. S. Varma, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2019, 7, 10843–10857 RSC.
- Q. Zhang, R. Fan, W. Cheng, P. Ji, J. Sheng, Q. Liao, H. Lai, X. Fu, C. Zhang and H. Li, Adv. Sci., 2022, 9, 2202748 CrossRef PubMed.
- X. Huang and P. Wu, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2020, 30, 1910048 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Zhang, P. Huang, J. Wang, Z. Zhuang, Z. Zhang and W.-Q. Han, J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2020, 11, 1247–1254 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Zhang, H. Ying, B. Yuan, R. Hu and W.-Q. Han, Nano–Micro Lett., 2020, 12, 78 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Q. Tang, Y. Wang, N. Chen, B. Pu, Y. Qing, M. Zhang, J. Bai, Y. Yang, J. Cui, Y. Liu, B. Zhou and W. Yang, Small Methods, 2024, 8, 2300836 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Wang, H. Shou, S. Chen, S. Wei, Y. Lin, P. Zhang, Z. Liu, K. Zhu, X. Guo, X. Wu, P. M. Ajayan and L. Song, Adv. Mater., 2021, 33, 2101015 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- B. Zhang, J. Zhu, P. Shi, W. Wu and F. Wang, Ceram. Int., 2019, 45, 8395–8405 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Guo, X. Zhang, S. Jin, Q. Xia, Y. Chang, L. Wang and A. Zhou, J. Adv. Ceram., 2023, 12, 1889–1901 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Fürstner, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2019, 141, 11–24 CrossRef PubMed.
- W. Bao, R. Wang, C. Qian, Z. Zhang, R. Wu, Y. Zhang, F. Liu, J. Li and G. Wang, ACS Nano, 2021, 15, 16207–16217 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Li, H. Shao, Z. Lin, J. Lu, L. Liu, B. Duployer, P. O. Å. Persson, P. Eklund, L. Hultman, M. Li, K. Chen, X.-H. Zha, S. Du, P. Rozier, Z. Chai, E. Raymundo-Piñero, P.-L. Taberna, P. Simon and Q. Huang, Nat. Mater., 2020, 19, 894–899 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- F. Wang, F. Tian, X. Xia, Z. Pang, S. Wang, X. Yu, G. Li, Y. Zhao, Q. Xu, S. Hu, L. Ji, X. Zou and X. Lu, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2024, 63, e202405315 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- G. Ma, H. Shao, J. Xu, Y. Liu, Q. Huang, P.-L. Taberna, P. Simon and Z. Lin, Nat. Commun., 2021, 12, 5085 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Wang, B. Zhou, Q. Tang, Y. Yang, B. Pu, J. Bai, J. Xu, Q. Feng, Y. Liu and W. Yang, Adv. Mater., 2024, 36, 2410736 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. Zhang, K. Shevchuk, R. J. Wang, H. Kim, J. Hourani and Y. Gogotsi, Chem. Mater., 2024, 36, 1998–2006 CrossRef CAS.
- Z. Huang, J. Qin, Y. Zhu, K. He, H. Chen, H. Y. Hoh, M. Batmunkh, T. M. Benedetti, Q. Zhang and C. J. C. E. Su, Carbon Energy, 2023, 5, e295 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Sheng, X. Bin, Y. Yang, Y. Tang and W. Que, Small, 2022, 18, 2203471 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Zhu, S. Zhu, Z. Cui, Z. Li, S. Wu, W. Xu, T. Ba, Y. Liang and H. Jiang, Energy Storage Mater., 2024, 70, 103503 CrossRef.
- D. Wang, C. Zhou, A. S. Filatov, W. Cho, F. Lagunas, M. Wang, S. Vaikuntanathan, C. Liu, R. F. Klie and D. V. Talapin, Science, 2023, 379, 1242–1247 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Li, Z. Wei, Y. Wang, Y. Zhang, M. Wang, H. Zhang, Y. Ma, C. Liu, J. Zou, B. Ge, F. Cheng and Y. Yue, Chem. Eng. J., 2023, 457, 141339 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Chen, J. Wang, D. Liu, C. Yang, Y. Liu, R. S. Ruoff and W. Lei, Nat. Commun., 2018, 9, 1902 CrossRef PubMed.
- H. Park, K. H. Lee, Y. B. Kim, S. B. Ambade, S. H. Noh, W. Eom, J. Y. Hwang, W. J. Lee, J. Huang and T. H. Han, Sci. Adv., 2018, 4, eaau2104 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Jiang, C. Wu, X. Li, Y. Yao, L. Lan, F. Zhao, Z. Ye, Y. Ying and J. Ping, Nano Energy, 2019, 59, 268–276 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Inman, T. Hryhorchuk, L. Bi, R. Wang, B. Greenspan, T. Tabb, E. M. Gallo, A. VahidMohammadi, G. Dion, A. Danielescu and Y. Gogotsi, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2023, 11, 3514–3523 RSC.
- J. Wang, X. Ma, J. Zhou, F. Du and C. Teng, ACS Nano, 2022, 16, 6700–6711 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Wang, Y. Liu, Z. Cheng, Z. Xie, L. Yin, W. Wang, Y. Song, H. Zhang, Y. Wang and Z. Fan, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2020, 59, 14029–14033 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. Hantanasirisakul, M.-Q. Zhao, P. Urbankowski, J. Halim, B. Anasori, S. Kota, C. E. Ren, M. W. Barsoum and Y. Gogotsi, Adv. Electron. Mater., 2016, 2, 1600050 CrossRef.
- S. Wan, Y. Chen, C. Huang, Z. Huang, C. Liang, X. Deng and Q. Cheng, Nature, 2024, 634, 1103–1110 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Zhang, N. Kong, S. Uzun, A. Levitt, S. Seyedin, P. A. Lynch, S. Qin, M. Han, W. Yang, J. Liu, X. Wang, Y. Gogotsi and J. M. Razal, Adv. Mater., 2020, 32, 2001093 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- I. Persson, J. Halim, T. W. Hansen, J. B. Wagner, V. Darakchieva, J. Palisaitis, J. Rosen and P. O. Å. Persson, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2020, 30, 1909005 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Liao, D. Jiang, K. Zheng, M. Zhang and J. Liu, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2021, 31, 2103960 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Zhang, N. Kong, S. Uzun, A. Levitt, S. Seyedin, P. A. Lynch, S. Qin, M. Han, W. Yang, J. Liu, X. Wang, Y. Gogotsi and J. M. Razal, Adv. Mater., 2020, 32, 2001093 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. H. Kim, G. S. Park, Y.-J. Kim, E. Choi, J. Kang, O. Kwon, S. J. Kim, J. H. Cho and D. W. Kim, ACS Nano, 2021, 15, 8860–8869 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M.-Q. Zhao, N. Trainor, C. E. Ren, M. Torelli, B. Anasori and Y. Gogotsi, Adv. Mater. Technol., 2019, 4, 1800639 CrossRef.
- W. Zhu, Y. Zhuang, J. Weng, Q. Huang, G. Lai, L. Li, M. Chen, K. Xia, Z. Lu, M. Wu and Z. Zou, Adv. Mater., 2024, 2407138 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- W. Yu, Y. Yang, Y. Wang, L. Hu, J. Hao, L. Xu and W. Liu, Nano–Micro Lett., 2024, 16, 94 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- G. Ge, Y.-Z. Zhang, W. Zhang, W. Yuan, J. K. El-Demellawi, P. Zhang, E. Di Fabrizio, X. Dong and H. N. Alshareef, ACS Nano, 2021, 15, 2698–2706 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Jiang, W. Zhao and L. Zhao, Nano Lett., 2024, 24, 3196–3203 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Naguib, O. Mashtalir, J. Carle, V. Presser, J. Lu, L. Hultman, Y. Gogotsi and M. W. Barsoum, ACS Nano, 2012, 6, 1322–1331 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- N. Thakur, P. Kumar and P. Sharma, in Age of MXenes, Volume 3. Applications in Energy Storage: Batteries and Supercapacitors, American Chemical Society, 2023, vol. 1444, ch. 1, pp. 1–25 Search PubMed.
- S. Jangra, B. Kumar, J. Sharma, S. Sengupta, S. Das, R. K. Brajpuriya, A. Ohlan, Y. K. Mishra and M. S. Goyat, J. Energy Storage, 2024, 101, 113810 CrossRef.
- M. Naguib, V. N. Mochalin, M. W. Barsoum and Y. Gogotsi, Adv. Mater., 2014, 26, 992–1005 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Ghidiu, M. R. Lukatskaya, M. Q. Zhao, Y. Gogotsi and M. W. Barsoum, Nature, 2014, 516, 78–81 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Xie, Y. Dall'Agnese, M. Naguib, Y. Gogotsi, M. W. Barsoum, H. L. Zhuang and P. R. Kent, ACS Nano, 2014, 8, 9606–9615 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Wang and Y. Zhou, J. Mater. Chem., 2002, 12, 2781–2785 RSC.
- M. Zhang, F. Héraly, M. Yi and J. Yuan, Cell Rep. Phys. Sci., 2021, 2, 100449 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Zhao, H. Cao, B. J. Coleman, Z. Tan, I. J. Echols, E. B. Pentzer, J. L. Lutkenhaus, M. Radovic and M. J. Green, Adv. Mater. Interfaces, 2022, 9, 2200480 CrossRef CAS.
- T. S. Mathis, K. Maleski, A. Goad, A. Sarycheva, M. Anayee, A. C. Foucher, K. Hantanasirisakul, C. E. Shuck, E. A. Stach and Y. Gogotsi, ACS Nano, 2021, 15, 6420–6429 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Shayesteh Zeraati, S. A. Mirkhani, P. Sun, M. Naguib, P. V. Braun and U. Sundararaj, Nanoscale, 2021, 13, 3572–3580 RSC.
- P. A. Shinde, A. M. Patil, S. Lee, E. Jung and S. Chan Jun, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2022, 10, 1105–1149 RSC.
- X. Wang, S. Kajiyama, H. Iinuma, E. Hosono, S. Oro, I. Moriguchi, M. Okubo and A. Yamada, Nat. Commun., 2015, 6, 6544 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Naguib, M. Kurtoglu, V. Presser, J. Lu, J. Niu, M. Heon, L. Hultman, Y. Gogotsi and M. W. Barsoum, Adv. Mater., 2011, 23, 4248–4253 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Zhang, S. Pinilla, N. McEvoy, C. Cullen, B. Anasori, E. Long, S. H. Park, A. Seral-Ascaso, A. Shmeliov, D. Krishnan, C. Morant, X. Liu, G. Duesberg, Y. Gogotsi and V. Nicolosi, Chem. Mater., 2017, 29, 4848–4856 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Alhabeb, K. Maleski, B. Anasori, P. Lelyukh, L. Clark, S. Sin and Y. Gogotsi, Chem. Mater., 2017, 29, 7633–7644 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Q. Long, K. K. Tang, J. Xiao, J. Y. Li, J. Chen, H. Gao, W. H. Chen, C. T. Liu and H. Liu, Mater. Today Sustain., 2022, 19, 100163 Search PubMed.
- J. Halim, M. R. Lukatskaya, K. M. Cook, J. Lu, C. R. Smith, L.-Å. Näslund, S. J. May, L. Hultman, Y. Gogotsi, P. Eklund and M. W. Barsoum, Chem. Mater., 2014, 26, 2374–2381 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Sarycheva, T. Makaryan, K. Maleski, E. Satheeshkumar, A. Melikyan, H. Minassian, M. Yoshimura and Y. Gogotsi, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2017, 121, 19983–19988 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Ghidiu, M. Naguib, C. Shi, O. Mashtalir, L. M. Pan, B. Zhang, J. Yang, Y. Gogotsi, S. J. L. Billinge and M. W. Barsoum, Chem. Commun., 2014, 50, 9517–9520 RSC.
- P. Lakhe, E. M. Prehn, T. Habib, J. L. Lutkenhaus, M. Radovic, M. S. Mannan and M. J. Green, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2019, 58, 1570–1579 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Li, L. Yao, Q. Liu, J. Gu, R. Luo, J. Li, X. Yan, W. Wang, P. Liu, B. Chen, W. Zhang, W. Abbas, R. Naz and D. Zhang, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2018, 57, 6115–6119 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- O. Mashtalir, M. Naguib, V. N. Mochalin, Y. Dall'Agnese, M. Heon, M. W. Barsoum and Y. Gogotsi, Nat. Commun., 2013, 4, 1716 CrossRef PubMed.
- J. Li, H. Liu, X. Shi, X. Li, W. Li, E. Guan, T. Lu and L. Pan, J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2024, 658, 425–440 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- B. Anasori, Y. Xie, M. Beidaghi, J. Lu, B. C. Hosler, L. Hultman, P. R. Kent, Y. Gogotsi and M. W. Barsoum, ACS Nano, 2015, 9, 9507–9516 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Shuck, K. Ventura-Martinez, A. Goad, S. Uzun, M. Shekhirev and Y. Gogotsi, ACS Chem. Health Saf., 2021, 28, 326–338 CrossRef CAS.
- I. A. Vasyukova, O. V. Zakharova, D. V. Kuznetsov and A. A. Gusev, Nanomaterials, 2022, 12, 1797 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Pogorielov, K. Smyrnova, S. Kyrylenko, O. Gogotsi, V. Zahorodna and A. Pogrebnjak, Nanomaterials, 2021, 11, 3412 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Sun and Y. Li, Chemosphere, 2021, 271, 129578 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Iqbal, J. Hong, T. Y. Ko and C. M. Koo, Nano Convergence, 2021, 8, 9 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Jolly, M. P. Paranthaman and M. Naguib, Mater. Today Adv., 2021, 10, 100139 CrossRef CAS.
- L.-Y. Xiu, Z.-Y. Wang and J.-S. Qiu, Rare Met., 2020, 39, 1237–1238 CrossRef CAS.
- Z. Huang, J. Qin, Y. Zhu, K. He, H. Chen, H. Hoh, M. Batmunkh, T. Benedetti, Z. Qitao, C. Su, S. Zhang and Y. L. Zhong, A green and scalable electrochemical route for cost-effective mass production of MXenes, 2022 Search PubMed.
- M. Ghidiu, M. R. Lukatskaya, M.-Q. Zhao, Y. Gogotsi and M. W. Barsoum, Nature, 2014, 516, 78–81 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. M. Viculis, J. J. Mack and R. B. Kaner, Science, 2003, 299, 1361 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. Tan, M. Zaed, S. Rahman, N. Abdullah, N. Ishak and J. Cherusseri, E3S Web Conf., 2024, 488, 01003 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Amrillah, C. A. Abdullah, A. Hermawan, F. N. Sari and V. N. Alviani, Nanomaterials, 2022, 12, 4280 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Shuck, A. Sarycheva, M. Anayee, A. Levitt, Y. Zhu, S. Uzun, V. Balitskiy, V. Zahorodna, O. Gogotsi and Y. Gogotsi, Adv. Eng. Mater., 2020, 22, 1901241 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Mim, K. Habib, S. N. Farabi, S. A. Ali, M. A. Zaed, M. Younas and S. Rahman, ACS Omega, 2024, 9, 32350–32393 CAS.
- O. Gogotsi, V. Zahorodna, A. Serhiienko, I. Hryshko, Y. Zozulya, V. Balitskyi, M. Seredych, B. Anasori and Y. Gogotsi, Scale-up of MXene Synthesis, 2018 Search PubMed.
- S. Seyedin, J. Zhang, K. A. S. Usman, S. Qin, A. M. Glushenkov, E. R. S. Yanza, R. T. Jones and J. M. Razal, Global Chall., 2019, 3, 1900037 CrossRef PubMed.
- R. A. Soomro, P. Zhang, B. Fan, Y. Wei and B. Xu, Nano–Micro Lett., 2023, 15, 108 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- F. Xia, J. Lao, R. Yu, X. Sang, J. Luo, Y. Li and J. Wu, Nanoscale, 2019, 11, 23330–23337 RSC.
- J. Palisaitis, I. Persson, J. Halim, J. Rosen and P. O. Å. Persson, Nanoscale, 2018, 10, 10850–10855 RSC.
- S. Sunderiya, S. Suragtkhuu, S. Purevdorj, T. Ochirkhuyag, M. Bat-Erdene, P. Myagmarsereejid, A. D. Slattery, A. S. R. Bati, J. G. Shapter, D. Odkhuu, S. Davaasambuu and M. Batmunkh, J. Energy Chem., 2024, 88, 437–445 CrossRef CAS.
- Z. Li, L. Wang, D. Sun, Y. Zhang, B. Liu, Q. Hu and A. Zhou, Mater. Sci. Eng., B, 2015, 191, 33–40 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Huang and V. N. Mochalin, Inorg. Chem., 2019, 58, 1958–1966 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. He, X.-X. Wang, Y.-Z. Cai, J.-C. Shu, Q.-L. Zhao, J. Yuan and M.-S. Cao, Nanoscale, 2019, 11, 6080–6088 RSC.
- B. Soundiraraju and B. K. George, ACS Nano, 2017, 11, 8892–8900 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Aleksandrova, N. Kurtev and I. Pandiev, Appl. Sci., 2024, 14, 2452 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Jiang, S. Bai, J. Zou, S. Liu, J.-P. Hsu, N. Li, G. Zhu, Z. Zhuang, Q. Kang and Y. Zhang, Nano Res., 2022, 15, 6551–6567 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Nahirniak, A. Ray and B. Saruhan, Batteries, 2023, 9, 126 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Melethil, M. S. Kumar, C. M. Wu, H. H. Shen, B. Vedhanarayanan and T. W. Lin, Nanomaterials, 2023, 13, 1257 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Liu, J. Yu, G. Dongfang, Z. Li and Y. Su, J. Alloys Compd., 2019, 815, 152403 CrossRef.
- H. Tariq, U. Nisar, J. James Abraham, Z. Ahmad, S. Al-Qaradawi, R. Kahraman and R. Shakoor, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2022, 583, 152441 CrossRef.
- M. H. Hossain, M. A. Chowdhury, N. Hossain, M. A. Islam and M. H. Mobarak, Chem. Eng. J. Adv., 2023, 16, 100569 CrossRef.
- S. Zhang, H. Ying, P. Huang, J. Wang, Z. Zhang, T. Yang and W.-Q. Han, ACS Nano, 2020, 14, 17665–17674 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. R. Lukatskaya, S. Kota, Z. Lin, M.-Q. Zhao, N. Shpigel, M. D. Levi, J. Halim, P.-L. Taberna, M. W. Barsoum, P. Simon and Y. Gogotsi, Nat. Energy, 2017, 2, 17105 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Li, B. Ding, J. Wang, Z. Qin, J. F. S. Fernando, Y. Bando, A. K. Nanjundan, Y. V. Kaneti, D. Golberg and Y. Yamauchi, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2020, 12, 14993–15001 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Z. Zhang, H. Ying, P. Huang, S. Zhang, Z. Zhang, T. Yang and W.-Q. Han, Chem. Eng. J., 2023, 451, 138785 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Lv, Z. Deng, M. Wang and J. Deng, J. Alloys Compd., 2022, 918, 165697 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Xu, K. Feng, X. Yang, Y. Cheng, X. Zhao, L. Yang and S. Yin, J. Energy Storage, 2023, 69, 107888 CrossRef.
- M. N. Chy, M. A. Rahman, J.-H. Kim, N. Barua and W. A. Dujana, Nanomaterials, 2024, 14, 616 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Zheng, Y. Shen, J. Guo, J. Li, J. Wang, D. Ning, Y. Liu, Y. Huang, Y. Tang, Y. Deng, H. Yan and H. Shao, Nano Res. Energy, 2024, 3, e9120118 CrossRef.
- J.-L. Yang, Y. Qian, K. Wang, H.-D. Yuan, J.-W. Nai, Y.-J. Liu, Y. Wang, J.-M. Luo and X.-Y. Tao, New Carbon Mater., 2023, 38, 659–673 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Luo, W. Zhang, H. Yuan, C. Jin, L. Zhang, H. Huang, C. Liang, Y. Xia, J. Zhang, Y. Gan and X. Tao, ACS Nano, 2017, 11, 2459–2469 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Luo, W. Zhang, H. Yuan, C. Jin, L. Zhang, H. Huang, C. Liang, Y. Xia, J. Zhang, Y. Gan and X. Tao, ACS Nano, 2017, 11, 2459–2469 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. Zhao, M. Clites, G. Ying, S. Kota, J. Wang, V. Natu, X. Wang, E. Pomerantseva, M. Cao and M. W. Barsoum, Chem. Commun., 2018, 54, 4533–4536 RSC.
- M. Mozafari and M. Soroush, Mater. Adv., 2021, 2, 7277–7307 RSC.
- T. Yuan, Z. Zhang, Q. Liu, X. T. Liu, Y. N. Miao and C. L. Yao, Carbohydr. Polym., 2023, 304, 120519 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Wen, T. Rufford, X. Chen, N. Li, M. Lyu, L. Dai and L. Wang, Nano Energy, 2017, 38, 368–376 CrossRef CAS.
- R. Wang, W. Young Jang, W. Zhang, C. Venkata Reddy, R. R. Kakarla, C. Li, V. K. Gupta, J. Shim and T. M. Aminabhavi, Chem. Eng. J., 2023, 472, 144913 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Wang, D. Li, H. Xu, L. Wang, Y. Li, G. Li, J. Li and W. Han, Small, 2024, 20, 2305530 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Wang, N. Chen, B. Zhou, X. Zhou, B. Pu, J. Bai, Q. Tang, Y. Liu and W. Yang, Nano–Micro Lett., 2023, 15, 231 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Xu, Y. Li, K. Quan, G. Wei, T. Mo, D. Huang, H. Huang, X. Liang and Y. Yang, Energy Storage Mater., 2024, 72, 103721 CrossRef.
- M. A. Tekalgne, H. H. Do, T. V. Nguyen, Q. V. Le, S. H. Hong, S. H. Ahn and S. Y. Kim, ACS Omega, 2023, 8, 41802–41808 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. A. Tekalgne, H. H. Do, T. V. Nguyen, Q. V. Le, S. H. Hong, S. H. Ahn and S. Y. Kim, ACS Omega, 2023, 8, 41802–41808 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Z. Lu, W. Xu, W. Zhu, Q. Yang, X. Lei, J. Liu, Y. Li, X. Sun and X. Duan, Chem. Commun., 2014, 50, 6479–6482 RSC.
- J. K. Im, E. J. Sohn, S. Kim, M. Jang, A. Son, K.-D. Zoh and Y. Yoon, Chemosphere, 2021, 270, 129478 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Q. Liu, L. Ai and J. Jiang, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2018, 6, 4102–4110 RSC.
- Y. Xu, S. Wang, J. Yang, B. Han, R. Nie, J. Wang, Y. Dong, X. Yu, J. Wang and H. Jing, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2018, 6, 15213–15220 RSC.
- X. An, W. Wang, J. Wang, H. Duan, J. Shi and X. Yu, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2018, 20, 11405–11411 RSC.
- X. Huang, C. L. Tan, Z. Y. Yin and H. Zhang, Adv. Mater., 2014, 26, 2185 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Xie, N. Zhang, Z.-R. Tang, M. Anpo and Y.-J. Xu, Appl. Catal., B, 2018, 237, 43–49 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Sun, X. Meng, Y. Dall'Agnese, C. Dall'Agnese, S. Duan, Y. Gao, G. Chen and X.-F. Wang, Nano–Micro Lett., 2019, 11, 79 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Ye, X. Wang, E. Liu, J. Ye and D. Wang, ChemSusChem, 2018, 11, 1606–1611 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Ran, G. Gao, F.-T. Li, T.-Y. Ma, A. Du and S.-Z. Qiao, Nat. Commun., 2017, 8, 13907 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Peng, X. Yang, Y. Li, H. Yu, H. Wang and F. Peng, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2016, 8, 6051–6060 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Wang, J. Yu, W. Xiao and Q. Li, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2014, 2, 3847–3855 RSC.
- H. Wang, Y. Wu, T. Xiao, X. Yuan, G. Zeng, W. Tu, S. Wu, H. Y. Lee, Y. Z. Tan and J. W. Chew, Appl. Catal., B, 2018, 233, 213–225 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Huang, Y. Song, N. Li, D. Chen, Q. Xu, H. Li, J. He and J. Lu, Appl. Catal., B, 2019, 251, 154–161 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Cao, B. Shen, T. Tong, J. Fu and J. Yu, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2018, 28, 1800136 CrossRef.
- X. Cheng, L. Zu, Y. Jiang, D. Shi, X. Cai, Y. Ni, S. Lin and Y. Qin, Chem. Commun., 2018, 54, 11622–11625 RSC.
- J. Li, S. Wang, Y. Du and W. Liao, Ceram. Int., 2018, 44, 7042–7046 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Iravani and R. S. Varma, Molecules, 2022, 27, 8830 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Li, X. Deng, J. Tian, Z. Liang and H. Cui, Appl. Mater. Today, 2018, 13, 217–227 CrossRef.
- S. Iravani and R. S. Varma, Molecules, 2022, 27, 8830 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. Kuang, J. Low, B. Cheng, J. Yu and J. Fan, J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2020, 56, 18–44 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Khatami, P. Iravani, G. Jamalipour Soufi and S. Iravani, Mater. Technol., 2022, 37, 1890–1905 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Khatami and S. Iravani, Comments Inorg. Chem., 2021, 41, 213–248 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Zhang, M. Li, C. Zhu, Q. Tang, P. Kang and J. Cao, Ceram. Int., 2020, 46, 81–88 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Lv, K. Wang, D. Li, P. Li, X. Chen and W. Han, Chem. Phys., 2022, 560, 111591 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Kumar, P. Majithia, P. Choudhary, I. Mabbett, M. F. Kuehnel, S. Pitchaimuthu and V. Krishnan, Chemosphere, 2022, 308, 136297 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2025 |
