Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleUncovering ZnS growth behavior and morphology control for high-performance aqueous Zn–S batteries†
Sibo
Wang
a,
Wanlong
Wu
 *b,
Quanwei
Jiang
a,
Chen
Li
a,
Hua-Yu
Shi
*b,
Quanwei
Jiang
a,
Chen
Li
a,
Hua-Yu
Shi
 a,
Xiao-Xia
Liu
a,
Xiao-Xia
Liu
 acd and
Xiaoqi
Sun
acd and
Xiaoqi
Sun
 *ac
*ac
aDepartment of Chemistry, Northeastern University, Shenyang 110819, China. E-mail: sunxiaoqi@mail.neu.edu.cn
bCollege of Chemistry & Chemical Engineering, Yan'an University, Yanan 716000, China. E-mail: wanlongwu@yau.edu.cn
cNational Frontiers Science Center for Industrial Intelligence and Systems Optimization, Northeastern University, 3-11 Wenhua Road, Shenyang, 110819, China
dKey Laboratory of Data Analytics and Optimization for Smart Industry, (Northeastern University), Ministry of Education, 110819, China
First published on 23rd December 2024
Abstract
Aqueous Zn–S batteries provide competitive energy density for large-scale energy storage systems. However, the cathode active material exhibits poor electrical conductivity especially at the discharged state of ZnS. Its morphology generated in cells thus directly determines the cathode electrochemical activity. Here, we reveal the ZnS growth behavior and control its morphology by the anion donor number (DN) of zinc salts in electrolytes. The anion DN affects the salt dissociation degree and furthermore sulfide solubility in electrolytes, which finally determines ZnS growth preference on existing nuclei or carbon substrates. As a result, 3D ZnS is realized from the high DN ZnBr2 electrolyte, whereas a 2D passivation film is formed from low DN Zn(TFSI)2. Thanks to the facile electron paths and abundant reaction sites with 3D morphology, the sulfur cathode reaches a high capacity of 1662 mA h g−1 at 0.1 A g−1 and retains 872 mA h g−1 capacity after 400 cycles at 3 A g−1.
Introduction
Rechargeable aqueous Zn batteries present the advantages of high safety and low cost.1–4 The Zn metal anode delivers high theoretical capacity (820 mA h g−1), low redox potential (−0.76 V vs. standard hydrogen electrode), and good electrochemical reversibility.5–8 The study of cathode materials for Zn batteries has been focused on intercalation-type structures, including oxides,9–14 polyanion compounds,15–17 and organic materials.18–21 Nevertheless, their capacity is limited by the electrochemically inert parts in the structures. In comparison, element materials are composed of fully active sites.22 Sulfur, in particular, is a desired cathode candidate which delivers a high theoretical capacity of 1675 mA h g−1 with the two-electron transfer conversion reaction.23–28 Together with an equilibrium voltage of 0.95 V, the energy density of Zn–S cells greatly exceeds that of other aqueous systems.29–32 Currently, research on aqueous Zn–S batteries is at the early stage, and great challenges have shown up. One key issue is the extremely poor electrical conductivities of both the charged and discharged products of S and ZnS at the cathode, i.e. 10−7 S cm−2 and 10−9 S cm−2, respectively.33,34 This largely limits the reaction kinetics and electrochemical performance of Zn–S cells.A few strategies have been proposed to promote the sulfur redox kinetics in aqueous Zn cells. Iodine components, in the form of I2, ZnI2, or iodinated thiourea, have been shown to catalyze the conversion from ZnS to S during the charging process.35–38 In addition, “cocktail” electrolytes containing the I2 additive in combination with 40% G4 or 10% EG are applied to further facilitate the reaction and enhance the stability.39,40 Zhu et al. also showed that Se doping in the S cathode facilitated iodine catalysis efficiency as well as accelerated the binding between S and Zn2+.41 Besides iodine, Lu et al. demonstrated the promoted cathode reaction activity with a polyaniline doped ferrocyanide redox mediator or atomic Fe site catalyst.33,42 Zhang et al. developed a spatially nano-restricted yolk shell structure with sulfur/nitrogen co-doped carbon nanofibers to accelerate the reaction kinetics of sulfur.43 Mandal et al. proposed a mixed electrolyte with dimethylacetamide co-solvent to reconstruct the Zn2+ solvation shell and facilitate sulfur conversion.44 Despite the above achievements, the electrochemical performance of aqueous Zn–S cells still requires improvement. It is also important to understand the key limitations to propose corresponding solutions.
As mentioned above, both S and ZnS are insulators, and ZnS exhibits two orders of magnitude lower electrical conductivity. This discharged product thus easily passivates the cathode, which is a key obstacle for the high utilization of the active material. Therefore, it is essential to control the growth morphology of ZnS during discharge, in order to enlarge reaction sites and maintain the electron transport network provided by the conductive agent in the cathode. Herein, we show that the anions of zinc salts in electrolytes directly determine the growth behavior of the ZnS product. Experimental and theoretical studies demonstrate that the anion donor number (DN) controls the salt dissociation degree in electrolytes, which further affects sulfide solubilities and finally the growth preference of ZnS on existing ZnS sites or carbon substrates. Among the electrolytes containing Zn(TFSI)2, Zn(OTf)2 or ZnBr2 salt, Br− with the highest DN promotes the 3D growth of ZnS, whereas a 2D passivation film is formed from TFSI− with the lowest DN. OTf− with an intermediate DN results in combined 2D/3D ZnS. In accordance, the sulfur cathode delivers the highest capacity of 1662 mA h g−1 at 0.1 A g−1, which is 99.2% of the theoretical value, together with the lowest overpotential in the Br− containing zinc cells. A good capacity of 872 mA h g−1 is also preserved after 400 cycles at 3 A g−1.
Results and discussion
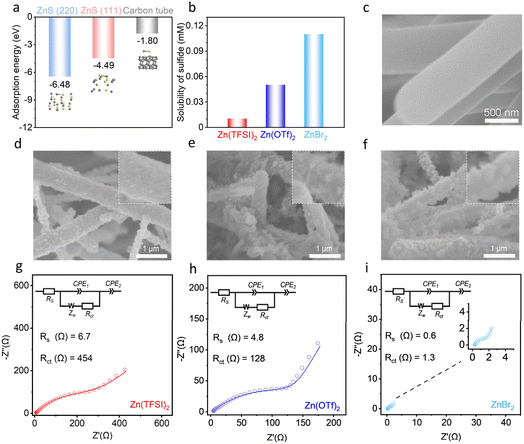
Considering the extremely low electrical conductivity of the discharged product ZnS, i.e., 10−9 S cm−2, the reaction kinetics and electrochemical activity of the cathode in Zn–S cells is highly dependent on its morphology. The morphology is controlled by the growth preference of ZnS. According to theoretical calculations, the adsorption energies of Zn–S on the surface of the (220) and (111) crystal planes of ZnS are −6.48 eV and −4.49 eV, respectively, which are much stronger than the −1.80 eV on conductive carbon (Fig. 1a). This suggests the preferential growth of ZnS on existing ZnS sites. Nevertheless, during electrochemical cathode reactions, S2− is formed after S receives electrons from carbon through a one-step direct reaction,32,33,39 which results in the growth of ZnS on the carbon surface. The above two factors suggest that the solubility of ZnS, or S2− to be more specific considering the abundance of Zn2+ in electrolytes, determines the resulting morphology in Zn–S cells. With low S2− solubilities, ZnS rapidly precipitates in situ on the carbon surface. With sufficient S2− in electrolytes, on the other hand, dissolved anions would migrate to existing ZnS sites which provides larger binding energy.The above hypothesis is examined in the three representative zinc electrolytes of Zn(TFSI)2, Zn(OTf)2 and ZnBr2 (concentration of 1 mol kg−1, m, Table S1†). The sulfide concentrations are measured to be 0.01 mM, 0.05 mM and 0.11 mM, respectively, by inductively coupled plasma (ICP, Fig. 1b). The ZnS growth preference is investigated by discharging the cathode in Zn–S cells, with carbon nanofibers (CNF) applied as the conductive agent to provide enough surface area for active material growth (Fig. S1†). Fig. 1c–f shows the scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images of the resulting ZnS together with the bare CNF substrate. The surface of carbon tubes at the cathode discharged from the Zn(TFSI)2 electrolyte, which provides the lowest sulfide solubility, is fully covered by the laterally deposited ZnS. With the ZnBr2 electrolyte providing the highest sulfide solubility, in contrast, 3D grown ZnS particles on the CNF substrate are obtained. Using the Zn(OTf)2 salt with intermediate sulfide solubility, both 2D and 3D growth behaviors are observed. These ZnS morphologies are in line with the theoretical predictions discussed above.
The influence of ZnS morphology on the electrochemical activity of the cathode is studied by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS). Measurements were conducted at the half/fully discharged states in the three electrolytes when ZnS is generated. The Nyquist plots were fitted with the typical equivalent circuit shown in the insets. As presented in Fig. 1g–i and S2,† the resistance decreases in the order of Zn(TFSI)2, Zn(OTf)2 and ZnBr2 at both states. Specifically, low Rs and Rct values of 0.6 Ω and 1.3 Ω, respectively, are obtained in the ZnBr2 electrolyte at the fully discharged state. These small values correspond to fast reaction kinetics at the cathode, thanks to the 3D morphology of ZnS which provides abundant reaction sites and preserves electron transport paths within the electrode. In the Zn(TFSI)2 electrolyte, in contrast, the 2D passivated ZnS film on the conductive agent hinders electron transport and leads to sluggish reaction kinetics.
The above analysis demonstrates that the morphology of ZnS and electrochemical activity in Zn–S cells are controlled by sulfide solubilities in electrolytes. With salt anions as the variables in these three systems, their fundamental effects are studied. The dissolution equilibrium of ZnS is expressed by eqn (1), and the concentrations of S2− and Zn2+ are further affected by the dissociation of zinc salts according to eqn (2):
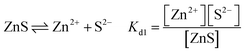 | (1) |
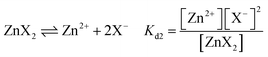 | (2) |
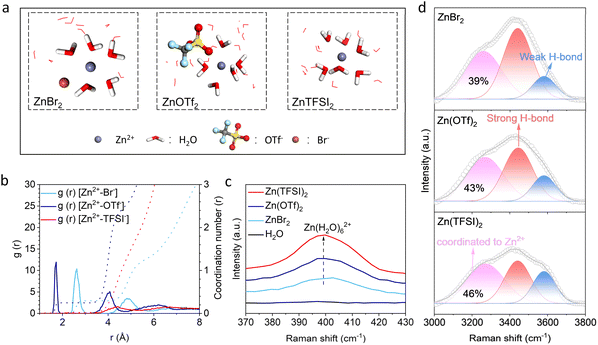
The three electrolyte structures are examined by molecular dynamics (MD) simulations (Fig. 2a and S3†). According to the radial distribution functions (RDFs, Fig. 2b), the first obvious Zn2+–TFSI−(O) peak is found at around 4.2 Å in Zn(TFSI)2, the distance of which corresponds to the second cation solvation shell. This suggests that TFSI− anions do not enter the inner solvation shell of Zn2+, demonstrating a high degree of salt dissociation. In Zn(OTf)2, on the other hand, the first Zn2+–OTf−(O) peak at 1.7 Å is attributed to the anions in the first solvation shell, and the coordination number is calculated to be 0.23. Finally, in the ZnBr2 solution, the first Zn2+–Br− peak is found at 2.6 Å. This also corresponds to the first solvation shell considering the larger size of Br−. A highest coordination number of 0.29 is obtained. The above weakened salt dissociation in the trend of Zn(TFSI)2, Zn(OTf)2 and ZnBr2 is in line with the increase of S2− concentrations.
The electrolyte structures are further confirmed by Raman spectroscopy. We first focus on the low Raman shift region (Fig. 2c), where a clear band is identified at around 400 cm−1 for the Zn(TFSI)2 solution. This is assigned to the Zn(H2O)62+ structure,45 resulting from the full dissociation of Zn2+ and TFSI− in the electrolyte. This band diminishes in the other two solutions. It suggests the entrance of anions in the first solvation shells, which weakens water solvation. In the high Raman shift region, a broad band above 3000 cm−1 is noted (Fig. 2d). This is attributed to the O–H vibration of water, the Raman shift of which depends on the O–H bond strength. For instance, the bond becomes weaker when the oxygen site is coordinated to other species, resulting in a redshift of peak position. In zinc aqueous solutions, the strongest coordination of water results from its entrance into the first solvation shell of Zn2+, and the interaction strength diminishes in strong hydrogen bonding and furthermore in weak hydrogen bonding. Therefore, we further fitted the O–H band with the above three water environments with the increase of Raman shift in sequence. The results show that the percentage of water coordinated with Zn2+ decreases from 46% in the Zn(TFSI)2 solution to 39% in ZnBr2, which is in the same trend of weakened salt dissociation. The above spectroscopy analysis agrees well with MD simulations. Notably, the salt dissociation degrees are determined by the DN of anions, with larger ones providing stronger interactions with Zn2+. The TFSI−, OTf− and Br− anions exhibit the DN of 5.4, 16.9 and 33.7, respectively.26,46 According to eqn (1) and (2), the Br− anion with the largest DN corresponds to the smallest dissociation degree of zinc salt and highest solubility of S2−. It therefore promotes the 3D growth behavior of ZnS.
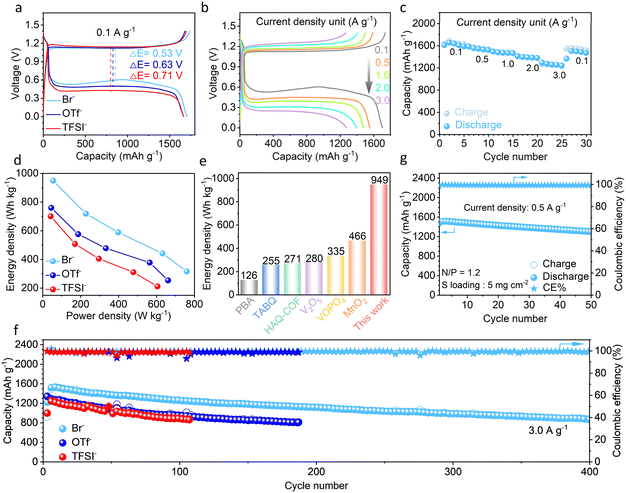
The influence of electrolyte anions on the electrochemical performance of Zn–S cells is studied. In addition to the 1 m ZnBr2, Zn(OTf)2 or Zn(TFSI)2 salts, 0.1 m ZnI2 additive is introduced in electrolytes, in order to further facilitate the oxidation process (electrolytes labelled as Br−, OTf− and TFSI−, respectively).32,36 The cathodes are obtained by mixing the sulfur active material with sodium alginate binder and KB carbon (sulfur loading around 1.8 mg cm−2, Fig. S4 and S5†). Fig. 3a shows the charge–discharge and differential capacity curves of Zn–S batteries with the three electrolytes at 0.1 A g−1. The charge plateaus appear at a similar voltage of around 1.13 V, suggesting the same effect of ZnI2 additive in combination with different zinc salts. Notably, the discharge voltage rises with the increase of anion DN. It results in the decrease of overpotential from 0.71 V in the TFSI− containing electrolyte, to 0.63 V with OTf− and finally down to 0.53 V with Br−. Meanwhile, the sulfur cathode also reaches the highest discharge capacity of 1662 mA h g−1 in the Br− electrolyte (after excluding the capacity contribution from iodine above 1 V, the same treatment for all following conditions). This is 99.2% of the theoretical value. The results confirm that the 3D grown ZnS in the presence of the high DN Br− anion ensures the best electrochemical activity of the cathode in Zn–S cells.
The electrochemical performance of Zn–S cells is further evaluated. Fig. 3b and c display the rate performance in the Br− containing electrolyte. The sulfur cathode achieves the high discharge capacities of 1557, 1474, 1398 and 1286 mA h g−1 at 0.5, 1, 2 and 3 A g−1, respectively. When the current density returns to 0.1 A g−1, the cell still preserves a high capacity of 1455 mA h g−1. The good rate capability further confirms the fast redox kinetics of the sulfur cathode in the Br− electrolyte. In comparison, the capacity and discharge voltage plateaus in the OTf− and TFSI− containing electrolytes are lower at the corresponding current densities (Fig. S6†). As a result, the cathode presents the best energy and power densities in the Br− electrolyte as compared in the Ragone plots (Fig. 3d, calculated by sulfur mass). Notably, its highest energy density of 949 W h kg−1 exceeds that of intercalation-type cathode materials in zinc cells (Fig. 3e)9,11,15,18,19,47 thanks to the capacity superiority of conversion-type materials. The electrochemical performance of our system is also better than that of recently reported Zn–S cells (Fig. S7†).
The cycling performance of the Zn–S cells is tested, with a piece of Zn2+ exchanged Nafion film applied as the separator. The cathode retains 872 mA h g−1 capacity after 400 cycles at the current density of 3 A g−1 in the Br− containing electrolyte (Fig. 3f). In the other two electrolytes with lower DN anions, in contrast, the cathode delivers lower capacity and poorer capacity retention over cycling. For instance, the capacities of 807 mA h g−1 at the 185th cycle and 862 mA h g−1 at the 107th cycle, respectively, are obtained with the OTf− and TFSI− electrolytes. To further evaluate the applicability of our system, we increased the sulfur loading to 5 mg cm−2 and assembled cells with a limited anode of N/P = 1.2. The cathode still delivers a high discharge capacity of 1514 mA h g−1 at 0.5 A g−1 in the Br− containing electrolyte and retains 1299 mA h g−1 after 50 cycles (Fig. 3f and S8†). These results confirm that zinc salts with high DN anions in electrolytes effectively ensure the excellent electrochemical activity of the sulfur cathode.
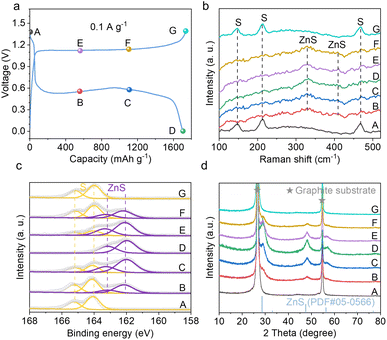
The energy storage mechanism of the sulfur cathode in the Br− electrolyte is investigated. We carried out galvanostatic charge–discharge at 0.1 A g−1 and performed ex situ Raman, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and X-ray diffraction (XRD) characterizations at the marked points shown in Fig. 4a. In the Raman spectrum of the pristine cathode, peaks at 147, 213 and 466 cm−1 are observed, which are attributed to elemental sulfur (Fig. 4b).48 Upon discharge, these sulfur signals gradually disappear and new peaks at around 330 and 414 cm−1 show up. The latter correspond to ZnS, suggesting the reduction process of sulfur. Upon the subsequent charging process, the ZnS peaks diminish and the peaks from sulfur re-appear. This demonstrates the highly reversible conversions between ZnS and S. The same change is observed in XPS analysis. As shown in Fig. 4c, the S 2p spectrum of the pristine cathode is fitted with two peaks at 164.1 eV and 165.2 eV, corresponding to the 2p3/2 and 2p1/2 splitting peaks of sulfur. During discharge, new peaks at 162.1 eV and 163.2 eV appear and gradually grow, which are attributed to ZnS. The spectrum of the fully discharged cathode is fitted with ZnS only. A reversible change is noted upon subsequent charging, showing the gradual diminishing of ZnS peaks and increase of sulfur peaks. The re-charged cathode only shows peaks from sulfur. Fig. 4d presents the evolution of XRD patterns. No diffraction peaks except for the ones from the graphite substrate are observed in the pristine cathode, suggesting the amorphous nature of sulfur. During discharge, three diffraction peaks at 28.6°, 47.5° and 56.3° gradually show up and the intensities reach the highest at the fully discharged state, which corresponds to the ZnS structure (PDF #05-0566). During the subsequent charging process, these peaks gradually diminish and disappear completely after full charging. No peaks attributed to sulfur appear either, which suggests the re-formation of amorphous sulfur. The above analysis confirms the reversible cathode conversion reaction between S and ZnS during discharge and charge in zinc cells. Besides, no signals assigned to polysulfides are identified at any state, demonstrating the direct one-step reactions.
Conclusions
In summary, we present a salt anion dependent growth behavior of the ZnS discharged product in aqueous Zn–S batteries. ZnS exhibits extremely low electrical conductivity, and thus its morphology is a key limiting factor for cathode electrochemical activity. Experimental analysis and theoretical calculations demonstrate that ZnS growth preference is linked to the solubility of S2−, which is related to the dissociation degrees of zinc salts in electrolytes and fundamentally by the DN of anions. Accordingly, the 3D growth of ZnS is realized in a ZnBr2 containing electrolyte with a high DN anion. It presents largely enhanced electrochemical activity in comparison to the 2D passivation film formed with the low DN anion of Zn(TFSI)2. Therefore, the sulfur cathode achieves a high capacity of 1662 mA h g−1 with a low overpotential of 0.53 V at 0.1 A g−1 in the Br− containing electrolyte. It also preserves 872 mA h g−1 capacity after 400 cycles at the high current density of 3 A g−1. Mechanism studies confirm the reversible one-step conversion reaction between S and ZnS at the cathode during discharge and charge. Overall, this study proposes the strategy of regulating the growth behavior of ZnS to improve the electrochemical performance of aqueous Zn–S batteries. It not only presents solutions to aqueous Zn–S systems, but would also be applicable to other electrode materials with conductivity issues.Data availability
The data supporting this article have been included in the main text and the ESI.†Author contributions
S. W., W. W. and X. S. conceived and designed this work. S. W. carried out the synthesis and electrochemical measurements. All authors participated in the analysis of the data, discussed and revised the manuscript.Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.Acknowledgements
This work was supported by The National Natural Science Foundation of China (52174276, 52304322, 51974070), the Doctoral Startup Foundation of Liaoning (2023-BS-055), and the 111 Project (B16009).References
- X. Jia, C. Liu, Z. G. Neale, J. Yang and G. Cao, Active Materials for Aqueous Zinc Ion Batteries: Synthesis, Crystal Structure, Morphology, and Electrochemistry, Chem. Rev., 2020, 120, 7795–7866 CrossRef CAS.
- G. Ma, L. Miao, W. Yuan, K. Qiu, M. Liu, X. Nie, Y. Dong, N. Zhang and F. Cheng, Non-flammable, dilute, and hydrous organic electrolytes for reversible Zn batteries, Chem. Sci., 2022, 13, 11320–11329 RSC.
- Y. Chai, X. Xie, Z. He, G. Guo, P. Wang, Z. Xing, B. Lu, S. Liang, Y. Tang and J. Zhou, A smelting–rolling strategy for ZnIn bulk phase alloy anodes, Chem. Sci., 2022, 13, 11656–11665 RSC.
- J. Shin, J. Lee, Y. Park and J. W. Choi, Aqueous zinc ion batteries: focus on zinc metal anodes, Chem. Sci., 2020, 11, 2028–2044 RSC.
- Y. Dong, L. Miao, G. Ma, S. Di, Y. Wang, L. Wang, J. Xu and N. Zhang, Non-concentrated aqueous electrolytes with organic solvent additives for stable zinc batteries, Chem. Sci., 2021, 12, 5843–5852 RSC.
- C. Li, S. Jin, L. A. Archer, L. F. Nazar, D. Prendergast and L. F. Nazar, Toward practical aqueous zinc-ion batteries for electrochemical energy storage, Joule, 2022, 6, 1733–1738 CrossRef.
- K. Wang, T. Qiu, L. Lin, H. Zhan, X. Liu and X. Sun, Solvation Sheath Regulation to Induce Sulfide Solid-Electrolyte Interphase on Zn Metal, ACS Energy Lett., 2024, 9, 1000–1007 CrossRef CAS.
- N. Dong, F. Zhang and H. Pan, Towards the practical application of Zn metal anodes for mild aqueous rechargeable Zn batteries, Chem. Sci., 2022, 13, 8243–8252 RSC.
- D. Kundu, B. D. Adams, V. Duffort, S. H. Vajargah and L. F. Nazar, A high-capacity and long-life aqueous rechargeable zinc battery using a metal oxide intercalation cathode, Nat. Energy, 2016, 1, 16119 CrossRef CAS.
- Z. Li, Y. Ren, L. Mo, C. Liu, K. Hsu, Y. Ding, X. Zhang, X. Li, L. Hu, D. Ji and G. Cao, Impacts of Oxygen Vacancies on Zinc Ion Intercalation in VO2, ACS Nano, 2020, 14, 5581–5589 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Liu, K. Wang, X. Yang, J. Liu, X. Liu and X. Sun, Enhancing Two-Electron Reaction Contribution in MnO2 Cathode Material by Structural Engineering for Stable Cycling in Aqueous Zn Batteries, ACS Nano, 2023, 17, 14792–14799 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- V. Mathew, B. Sambandam, S. Kim, S. Kim, S. Park, S. Lee, M. H. Alfaruqi, V. Soundharrajan, S. Islam, D. Y. Putro, J. Hwang, Y. Sun and J. Kim, Manganese and vanadium oxide cathodes for aqueous rechargeable zinc-ion batteries: A focused view on performance, mechanism, and developments, ACS Energy Lett., 2020, 5, 2376–2400 CrossRef CAS.
- N. Zhang, F. Cheng, Y. Liu, Q. Zhao, K. Lei, C. Chen, X. Liu and J. Chen, Cation-Deficient Spinel ZnMn2O4 Cathode in Zn(CF3SO3)2 Electrolyte for Rechargeable Aqueous Zn-Ion Battery, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2016, 138, 12894–12901 CrossRef CAS.
- N. Zhang, M. Jia, Y. Dong, Y. Wang, J. Xu, Y. Liu, L. Jiao and F. Cheng, Hydrated Layered Vanadium Oxide as a Highly Reversible Cathode for Rechargeable Aqueous Zinc Batteries, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2019, 29, 1807331 CrossRef.
- H. Shi, Y. Song, Z. Qin, C. Li, D. Guo, X. Liu and X. Sun, Decomposition and Dissolution in Rechargeable Aqueous Zinc Batteries to Promote Voltage and Capacity Stabilities, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2019, 58, 16057–16061 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- F. Wang, W. Sun, Z. Shadike, E. Hu, X. Ji, T. Gao, X. Yang, K. Xu and C. Wang, How Water Accelerates Bivalent Ion Diffusion at the Electrolyte/Electrode Interface, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2018, 57, 11978–11981 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Li, R. Kingsbury, L. Zhou, A. Shyamsunder, K. A. Persson and L. F. Nazar, Tuning the solvation structure in aqueous zinc batteries to maximize Zn-ion intercalation and optimize dendrite-free zinc plating, ACS Energy Lett., 2022, 7, 533–540 CrossRef CAS.
- Z. Lin, H. Shi, L. Lin, X. Yang, W. Wu and X. Sun, A high capacity small molecule quinone cathode for rechargeable aqueous zinc-organic batteries, Nat. Commun., 2021, 12, 4424 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- W. Wang, V. S. Kale, Z. Cao, Y. Lei, S. Kandambeth, G. Zou, Y. Zhu, E. Abouhamad, O. Shekhah, L. Cavallo, M. Eddaoudi and H. N. Alshareef, Molecular Engineering of Covalent Organic Framework Cathodes for Enhanced Zinc-Ion Batteries, Adv. Mater., 2021, 33, 2103617 CrossRef CAS.
- D. Kundu, P. Oberholzer, C. Glaros, A. Bouzid, E. Tervoort, A. Pasquarello and M. Niederberger, Organic Cathode for Aqueous Zn-Ion Batteries: Taming a Unique Phase Evolution toward Stable Electrochemical Cycling, Chem. Mater., 2018, 30, 3874–3881 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Qiu, J. Xu, K. Zhou, X. Huang, M. Liao, Y. Cao, G. Zhou, P. Wei and Y. Wang, Molecular Tailoring of p–type Organics for Zinc Batteries with High Energy Density, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2023, 62, e202304036 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- W. Li and D. Wang, Conversion-Type Cathode Materials for Aqueous Zn Metal Batteries in Nonalkaline Aqueous Electrolytes: Progress, Challenges, and Solutions, Adv. Mater., 2023, 436, 2304983 CrossRef PubMed.
- Q. Pang, J. Meng, S. Gupta, X. Hong, C. Y. Kwok, J. Zhao, Y. Jin, L. Xu, O. Karahan, Z. Wang, S. Toll, L. Mai, L. F. Nazar, M. Balasubramanian, B. Narayanan and D. R. Sadoway, Fast-charging aluminium–chalcogen batteries resistant to dendritic shorting, Nature, 2022, 608, 704–711 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Li and S. Guo, Material design and structure optimization for rechargeable lithium-sulfur batteries, Matter, 2021, 4, 1142–1188 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Liang, A. Garsuch and L. F. Nazar, Sulfur Cathodes Based on Conductive MXene Nanosheets for High-Performance Lithium–Sulfur Batteries, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2015, 54, 3907–3911 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Chu, H. Noh, Y. Kim, S. Yuk, J. Lee, J. Lee, H. Kwack, Y. Kim, D. Yang and H. Kim, Achieving three-dimensional lithium sulfide growth in lithium-sulfur batteries using high-donor-number anions, Nat. Commun., 2019, 10, 188 CrossRef.
- X. Ji, K. T. Lee and L. F. Nazar, A highly ordered nanostructured carbon–sulphur cathode for lithium–sulphur batteries, Nat. Mater., 2009, 8, 500–506 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Ye, D. Chao, J. Shan, H. Li, K. Davey and S. Qiao, Unveiling the Advances of 2D Materials for Li/Na-S Batteries Experimentally and Theoretically, Matter, 2009, 2, 323–344 CrossRef.
- J. Liu, W. Zhou, R. Zhao, Z. Yang, W. Li, D. Chao and S. Qiao, Sulfur-Based Aqueous Batteries: Electrochemistry and Strategies, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2021, 143, 15475–15489 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Zhao, D. Wang, X. Li, Q. Yang, Y. Guo, F. Mo, Q. Li, C. Peng, H. Li and C. Zhi, Initiating a Reversible Aqueous Zn/Sulfur Battery through a “Liquid Film”, Adv. Mater., 2020, 32, 2003070 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Amiri, R. Sellers, M. Naraghi and A. A. Polycarpou, Multifunctional Quasi-Solid-State Zinc–Sulfur Battery, ACS Nano, 2022, 17, 1217–1228 CrossRef.
- W. Wu, S. Wang, L. Lin, H. Shi and X. Sun, A dual-mediator for a sulfur cathode approaching theoretical capacity with low overpotential in aqueous Zn–S batteries, Energy Environ. Sci., 2023, 16, 4326–4333 RSC.
- H. Zhang, Z. Shang, G. Luo, S. Jiao, R. Cao, Q. Chen and K. Lu, Redox Catalysis Promoted Activation of Sulfur Redox Chemistry for Energy-Dense Flexible Solid-State Zn–S Battery, ACS Nano, 2021, 16, 7344–7351 CrossRef PubMed.
- M. Abdulkhadar and B. Thomas, Dc conductivity of nanoparticles of Cds and ZnS, Nanostruct. Mater., 1998, 10, 593–600 CrossRef CAS.
- W. Li, K. Wang and K. Jiang, A Low Cost Aqueous Zn–S Battery Realizing Ultrahigh Energy Density, Adv. Sci., 2020, 7, 2000761 CrossRef CAS.
- P. Hei, Y. Sai, C. Liu, W. Li, J. Wang, X. Sun, Y. Song and X. Liu, Facilitating the Electrochemical Oxidation of ZnS through Iodide Catalysis for Aqueous Zinc-Sulfur Batteries, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2024, 63, e202316082 CrossRef PubMed.
- Y. Guo, R. Chua, Y. Chen, Y. Cai, E. J. J. Tang, J. J. N. Lim, T. H. Tran, V. Verma, M. W. Wong and M. Srinivasan, Hybrid Electrolyte Design for High-Performance Zinc–Sulfur Battery, Small, 2023, 19, 2207133 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. Liu, B. He, Y. Zhong, J. Chen, L. Yuan, Z. Li and Y. Huang, A durable ZnS cathode for aqueous Zn–S batteries, Nano Energy, 2022, 101, 107474 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Yang, Z. Yan, J. Xiao, W. Xin, L. Zhang, H. Peng, Y. Geng, J. Li, Y. Wang, L. Liu and Z. Zhu, Boosting Cathode Activity and Anode Stability of Zn-S Batteries in Aqueous Media Through Cosolvent-Catalyst Synergy, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2022, 61, e202212666 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Mehta, S. Kaur, M. Singh, M. Kumar, K. Kumar, S. K. Meena and T. C. Nagaiah, Unleashing Ultrahigh Capacity and Lasting Stability: Aqueous Zinc-Sulfur Batteries, Adv. Energy Mater., 2024, 2401515 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Zhang, M. Yang, J. Xiao, Z. Wu, W. Xin, X. Xiao, M. Niu, Z. Yan and Z. Zhu, Internal Electron Donor Accelerated Sulfur Redox for Aqueous Zn–S Batteries, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2024, 2406125 CrossRef CAS.
- W. Zhang, M. Wang, J. Ma, H. Zhang, L. Fu, B. Song, S. Lu and K. Lu, Bidirectional Atomic Iron Catalysis of Sulfur Redox Conversion in High-Energy Flexible Zn–S Battery, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2023, 33, 2210899 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Li, J. Liu, F. Xie, R. Bi and L. Zhang, Electrocatalysis and Spatial Nanoconfinement toAccelerate Sulfur Conversion Kinetics in Aqueous Zn–S Battery, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2024, 63, e202406126 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. S. Thomas, A. P. Sinha and D. Mandal, Modulating electrolyte solvation for high-performance aqueous zinc–sulfur batteries, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2024, 12, 21350 RSC.
- L. Sun, Y. Yao, L. Dai, M. Jiao, B. Ding, Q. Yu, J. Tang and B. Liu, Sustainable and high-performance Zn dual-ion batteries with a hydrogel-based water-in-salt electrolyte, Energy Storage Mater., 2022, 47, 187–194 CrossRef.
- W. Linert, A. Camard, M. Armand and C. Michot, Anions of low Lewis basicity for ionic solid state electrolytes, Coord. Chem. Rev., 2002, 226, 137–141 CrossRef CAS.
- Q. Yang, F. Mo, Z. Liu, L. Ma, X. Li, D. Fang, S. Chen, S. Zhang and C. Zhi, Activating C-Coordinated Iron of Iron Hexacyanoferrate for Zn Hybrid-Ion Batteries with 10 000-Cycle Lifespan and Superior Rate Capability, Adv. Mater., 2019, 31, 1901521 CrossRef.
- T. Zhou, H. Wan, M. Liu, Q. Wu, Z. Fan and Y. Zhu, Regulating uniform nucleation of ZnS enables low-polarized and high stable aqueous Zn–S batteries, Mater. Today Energy, 2022, 27, 101025 CrossRef CAS.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available. See DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/d4sc07285e |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2025 |