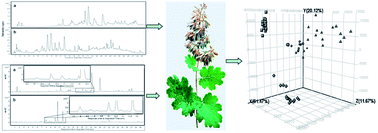
In this study, an improved separation method for the metabolomic study of polar and basic secondary metabolites by high-performance liquid chromatography-quadrupole-time-of-flight-mass spectrometry (HPLC-Q-TOF-MS) using an “Xcharge C18” column has been developed. Good retention for the polar compound and perfect peak shape for basic components was achieved. Classification of four different major origins of Macleaya cordata, which is a traditional folk medicine mainly used as a popular natural feed additive (e.g. Sangrovit®) in Europe and Asia since 2002, was performed by principal component analysis (PCA) and partial least square-discriminant analysis (PLS-DA). PCA data showed a clear separation among four different geographical origins. Biomarkers such as N-methyl-7-demethoxylhydrocotarnine and 13-methylcryptopine accountable for variation were tentatively identified by their tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS) fragmentation behaviors. The proposed analytical method was shown to be a useful tool for the metabolomic study of polar compound and alkaloid containing plants.