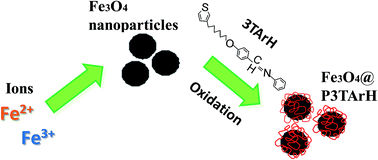
Core–shell magnetic nanoparticles have received significant attention and are actively explored due to their prospective applications. In the current study, superparamagnetic nanosorbent poly(phenyl(4-(6-thiophen-3-yl-hexyloxy)-benzylidene)-amine)/Fe3O4 nanoparticles (Fe3O4@P3TArH) was successfully synthesized via a simplistic method for the enhanced extraction of a potent endocrine disruptor, di-(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate (DEHP). The synthesized materials were characterized by Fourier transform infra-red (FTIR), X-ray diffractometry (XRD), Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) surface area analysis, field emission scanning electron microscope (FESEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), and vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM). The extraction efficiencies of the synthesized sorbent materials were evaluated by monitoring the extraction of DEHP from aqueous solution. Removal of DEHP using Fe3O4@P3TArh was found to be pH and temperature dependent with a maximum adsorption capacity found to be at 298.15 K at pH 7 and the adsorption kinetics followed a pseudo second-order kinetics model. Thermodynamic studies revealed that adsorption occurred heterogeneously on the adsorption sites, and adsorption of di-(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate onto Fe3O4@P3TArh was found to be spontaneous, feasible, ordered, and exothermic. The activation energy was determined to be −40.6 kJ mol−1, which indicated the adsorption process was physisorption.