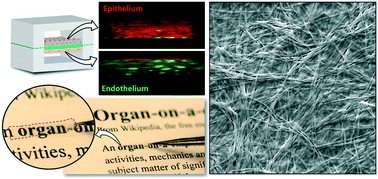
Semipermeable cell culture membranes are commonly used in multilayered microfluidic devices to mimic the basement membrane in vivo and to create compartmentalized microenvironments for physiological cell growth and differentiation. However, existing membranes are predominantly made up of synthetic polymers, providing limited capacity to replicate cellular interactions with native extracellular matrices that play a crucial role in the induction of physiological phenotypes. Here we describe a new type of cell culture membranes engineered from native extracellular matrix (ECM) materials that are thin, semipermeable, optically transparent, and amenable to integration into microfluidic cell culture devices. Facile and cost-effective fabrication of these membranes was achieved by controlled sequential steps of vitrification that transformed three-dimensional (3D) ECM hydrogels into structurally stable thin films. By modulating the composition of the ECM, our technique provided a means to tune key membrane properties such as optical transparency, stiffness, and porosity. For microfluidic cell culture, we constructed a multilayered microdevice consisting of two parallel chambers separated by a thin membrane insert derived from different types of ECM. This study showed that our ECM membranes supported attachment and growth of various types of cells (epithelial, endothelial, and mesenchymal cells) under perfusion culture conditions. Our data also revealed the promotive effects of the membranes on adhesion-associated intracellular signaling that mediates cell–ECM interactions. Moreover, we demonstrated the use of these membranes for constructing compartmentalized microfluidic cell culture systems to induce physiological tissue differentiation or to replicate interfaces between different tissue types. Our approach provides a robust platform to produce and engineer biologically active cell culture substrates that serve as promising alternatives to conventional synthetic membrane inserts. This strategy may contribute to the development of physiologically relevant in vitro cell culture models for a wide range of applications.