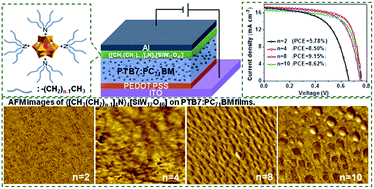
In this study, we synthesized four alcohol-soluble surfactant-encapsulated polyoxometalate complexes (SEPCs) containing four tetra-n-alkyl ammonium groups, namely {[CH3(CH2)n−1]4N}4[SiW12O40] (TA-SiW12, n = 2, 4, 8, and 10), and investigated the effect of the alkyl chain length of TA-SiW12 as a cathode interlayer (CIL) on the performance of polymer solar cells (PSCs). Different alkyl chain lengths in the four TA-SiW12s resulted in different device performances. Highest power conversion efficiency (9.15%) was achieved for the PTB7:PC71BM-based PSC with TA-SiW12 (n = 8) due to its highest open circuit voltage (VOC), short circuit current (JSC), and fill factor (FF). Combined measurements of the capacitance–voltage characteristics, charge carrier mobility, and photocurrent density-effective voltage characteristics demonstrated that incorporation of TA-SiW12 (n = 8) resulted in higher built-in potential, charge carrier density, and mobility, and better charge carrier extraction as compared to that of other TA-SiW12 (n = 2, 4, and 10) in the PSCs. AFM images showed that only TA-SiW12 (n = 8) formed homogeneous, closely packed, and well-distributed grain clusters with a quasi-periodic structure on the active layer, which explains the higher JSC and FF of the PSC with TA-SiW12 (n = 8).