Nonisothermal decomposition and safety parameters of HNIW/TNT cocrystal
Abstract
To explore the thermal decomposition behavior and evaluate the thermal safety of the cocrystal 2,4,6,8,10,12-hexanitrohexaazaisowurtzitane (HNIW)/2,4,6-trinitrotoluene (TNT), its thermal and kinetic behaviors were studied by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) technique. With the help of onset temperature (Te) and maximum peak temperature (Tp) from the non-isothermal DSC curves of HNIW/TNT cocrystal at different heating rates (β), the following were calculated: the value of specific heat capacity (Cp) and the standard molar enthalpy of formation 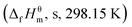 , the apparent activation energy (EK and EO) and pre-exponential constant (AK) of thermal decomposition reaction obtained by Kissinger's method and Ozawa's method, density (ρ) and thermal conductivity (λ), the decomposition heat (Qd, as half-explosion heat), Zhang–Hu–Xie–Li's formula, Smith's equation, Friedman's formula, Bruckman–Guillet's formula, Frank-Kamenetskii's formula and Wang–Du's formulas, the values (Te0 and Tp0) of Te and Tp corresponding to β → 0, thermal explosion temperature (Tbe and Tbp), adiabatic time-to-explosion (ttiad), 50% drop height (H50) for impact sensitivity, critical temperature of hot-spot initiation (Tcr), thermal sensitivity probability density function [S(T)] vs. temperature (T) relation curves with radius of 1 m and ambient temperature of 300 K, the peak temperature corresponding to the maximum value of S(T) vs. T relation curve (TS(T)max), safety degree (SD) and critical ambient temperature (Tacr) of thermal explosion. Results show that the kinetic equation describing the exothermic decomposition reaction of HNIW/TNT cocrystal is
, the apparent activation energy (EK and EO) and pre-exponential constant (AK) of thermal decomposition reaction obtained by Kissinger's method and Ozawa's method, density (ρ) and thermal conductivity (λ), the decomposition heat (Qd, as half-explosion heat), Zhang–Hu–Xie–Li's formula, Smith's equation, Friedman's formula, Bruckman–Guillet's formula, Frank-Kamenetskii's formula and Wang–Du's formulas, the values (Te0 and Tp0) of Te and Tp corresponding to β → 0, thermal explosion temperature (Tbe and Tbp), adiabatic time-to-explosion (ttiad), 50% drop height (H50) for impact sensitivity, critical temperature of hot-spot initiation (Tcr), thermal sensitivity probability density function [S(T)] vs. temperature (T) relation curves with radius of 1 m and ambient temperature of 300 K, the peak temperature corresponding to the maximum value of S(T) vs. T relation curve (TS(T)max), safety degree (SD) and critical ambient temperature (Tacr) of thermal explosion. Results show that the kinetic equation describing the exothermic decomposition reaction of HNIW/TNT cocrystal is 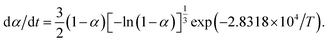 The following thermal safety parameters for the HNIW/TNT cocrystal are obtained: Te0 = 464.45 K; Tp0 = 477.55 K; Tbe = 472.82 K; Tbp = 485.89 K; ttiad = 4.40 s, 4.42 s, and 4.43 s for n = 0, 1, and 2, respectively; Tcr = 531.90 K; H50 = 19.46 cm; and the values of Tacr, TS(T)max, SD and PTE are 469.69 K, 470.58 K, 78.57% and 21.43% for sphere; 465.70 K, 470.58 K, 78.17% and 21.83% for infinite cylinder; and 459.39 K, 464.26 K, 77.54% and 22.46% for infinite flat.
The following thermal safety parameters for the HNIW/TNT cocrystal are obtained: Te0 = 464.45 K; Tp0 = 477.55 K; Tbe = 472.82 K; Tbp = 485.89 K; ttiad = 4.40 s, 4.42 s, and 4.43 s for n = 0, 1, and 2, respectively; Tcr = 531.90 K; H50 = 19.46 cm; and the values of Tacr, TS(T)max, SD and PTE are 469.69 K, 470.58 K, 78.57% and 21.43% for sphere; 465.70 K, 470.58 K, 78.17% and 21.83% for infinite cylinder; and 459.39 K, 464.26 K, 77.54% and 22.46% for infinite flat.



 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...