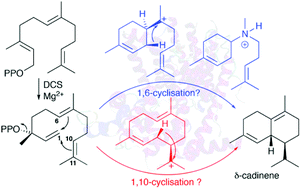
δ-Cadinene synthase (DCS) is a high-fidelity sesquiterpene synthase that generates δ-cadinene as the sole detectable organic product from its natural substrate (E,E)-FDP. Previous work with this enzyme using substrate analogues revealed the ability of DCS to catalyse both 1,10- and 1,6-cyclisations of substrate analogues. To test whether this apparent promiscuity was an artefact of alternate substrate use or an inherent property of the enzyme, aza analogues of the proposed α-bisabolyl cation intermediate were prepared since this cation would be formed after an initial 1,6-cyclisation of FDP. In the presence of 250 μM inorganic disphosphate both (R)- and (S)-aza-bisaboyl cations were potent competitive inhibitors of DCS (Ki = 2.5 ± 0.5 mM and 3.44 ± 1.43 μM, respectively). These compounds were also shown to be potent inhibitors of the 1,6-cyclase amorpha-4,11-diene synthase but not of the 1,10-cyclase aristolochene synthase from Penicillium roquefortii, demonstrating that the 1,6-cyclase activity of DCS is most likely an inherent property of the enzyme even when the natural substrate is used and not an artefact of the use of substrate analogues.