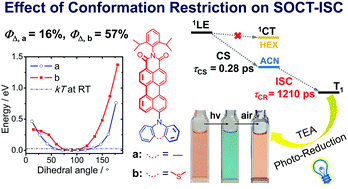
Perylenemonoimide (PMI)–carbazole (Cz) compact electron donor/acceptor dyads were prepared to study the relationship between the mutual orientation of the electron donor/acceptor in the dyads and the spin–orbit charge transfer intersystem crossing (SOCT-ISC) efficiency. The PMI and the Cz units are connected via either a C–C or C–N bond, or with an intervening phenyl moiety. The photophysical properties of the dyads were studied with steady state and time-resolved optical spectroscopies. The fluorescence of the PMI unit in the dyads was generally quenched, due to photo-induced electron transfer, especially in polar solvents (the fluorescence has a biexponential decay in acetonitrile, τF = 1.4 ns/population ratio: 98.9%, and 9.6 ns/population ratio: 1.1%). The triplet state (lifetime τT = 14.7 μs) formation of the dyads is dependent on the solvent polarity, which is characteristic for SOCT-ISC. Femtosecond transient absorption spectra show that the charge separation takes 0.28 ps and the charge recombination takes 1.21 ns. Reversible photo-reduction of the PMI–Cz dyads and generation of the near IR-absorbing (centered at 604 nm and 774 nm) PMI radical anion (PMI−˙) were observed in the presence of a sacrificial electron donor (triethylamine). These results are useful for study of the fundamental photochemistry of compact electron donor/acceptor dyads and for design of new heavy atom-free triplet photosensitizers.