Influence of Al2O3 nanoparticle doping on depolarization temperature, and electrical and energy harvesting properties of lead-free 0.94(Bi0.5Na0.5)TiO3–0.06BaTiO3 ceramics
Abstract
In this research article, the effects of Al2O3 nanoparticles (0–1.0 mol%) on the phase formation, microstructure, dielectric, ferroelectric, piezoelectric, electric field-induced strain and energy harvesting properties of the 0.94(Bi0.5Na0.5)TiO3–0.06BaTiO3 (BNT–6BT) ceramic were investigated. All ceramics have been synthesized by a conventional mixed oxide method. The XRD and Raman spectra showed coexisting rhombohedral and tetragonal phases throughout the entire compositional range. An increase of the grain size, TF–R, Tm, εmax and δA values was noticeable when Al2O3 was added. Depolarization temperature (Td), which was determined by the thermally stimulated depolarization current (TSDC), tended to increase with Al2O3 content. The good ferroelectric properties (Pr = 32.64 μC cm−2, Ec = 30.59 kV cm−1) and large low-field d33 (205 pC N−1) values were observed for the 0.1 mol% Al2O3 ceramic. The small Al2O3 additive improved the electric field-induced strain (Smax and 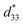 ). The 1.0 mol% Al2O3 ceramic had a large piezoelectric voltage coefficient (g33 = 32.6 × 10−3 Vm N−1) and good dielectric properties (εr,max = 6542, Td = 93 °C, TF–R = 108 °C, Tm = 324 °C and δA = 164 K). The highest off-resonance figure of merit (FoM) for energy harvesting of 6.36 pm2 N−1 was also observed for the 1.0 mol% Al2O3 ceramic, which is suggesting that this ceramic has potential to be one of the promising lead-free piezoelectric candidates for further use in energy harvesting applications.
). The 1.0 mol% Al2O3 ceramic had a large piezoelectric voltage coefficient (g33 = 32.6 × 10−3 Vm N−1) and good dielectric properties (εr,max = 6542, Td = 93 °C, TF–R = 108 °C, Tm = 324 °C and δA = 164 K). The highest off-resonance figure of merit (FoM) for energy harvesting of 6.36 pm2 N−1 was also observed for the 1.0 mol% Al2O3 ceramic, which is suggesting that this ceramic has potential to be one of the promising lead-free piezoelectric candidates for further use in energy harvesting applications.



 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...