Multi-domain BNiT modification enhanced the piezoelectric properties of BNT-based lead-free thin films†
Abstract
From the perspectives of environmental protection and health, new lead-free piezoelectric materials have become a research hotspot in the field of materials science. In domain structure engineering, a higher domain wall density stores a higher density of mechanical energy, which is beneficial for the enhancement of piezoelectric properties. Based on this multi-domain structure strategy to improve piezoelectric performance, we introduced BNiT with a multi-domain structure into BNT-based thin films, and constructed (1 − x)(0.94Bi0.5Na0.5TiO3–0.06BaTiO3)–xBi(Ni0.50Ti0.5)O3 (BNT–BT–xBNiT) ternary composite lead-free piezoelectric thin films on Pt(111)/Ti/SiO2/Si(100) substrates via a sol–gel method. Through structural analysis, such as XRD, SEM, Raman and XPS analysis, it was proven that the introduction of BNiT is accompanied by lattice expansion and relaxation characteristics, and the resulting defect dipoles 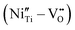 can reduce oxygen vacancies
can reduce oxygen vacancies 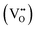 . In particular, the domain structure and phase changes in local regions under different electric fields were characterized by PFM, which proved that the multi-domain structure plays an important role in improving the piezoelectric properties of the thin films. Under the same conditions, the converse piezoelectric coefficient of the BNT–BT–0.02BNiT thin film is about 3.2 times that of the BNT–BT thin film. It is expected that this research can provide a theoretical and experimental basis for the domain structure modification of high-performance lead-free piezoelectric thin films for potential micro-electromechanical system (MEMS) applications.
. In particular, the domain structure and phase changes in local regions under different electric fields were characterized by PFM, which proved that the multi-domain structure plays an important role in improving the piezoelectric properties of the thin films. Under the same conditions, the converse piezoelectric coefficient of the BNT–BT–0.02BNiT thin film is about 3.2 times that of the BNT–BT thin film. It is expected that this research can provide a theoretical and experimental basis for the domain structure modification of high-performance lead-free piezoelectric thin films for potential micro-electromechanical system (MEMS) applications.



 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...