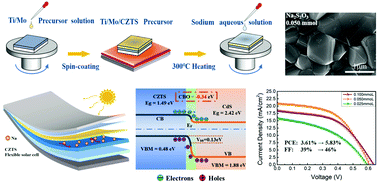
Treating kesterite layers with sodium has been proved to be an effective way to improve the photovoltaic performance of Cu2ZnSnS4 (CZTS) solar cells. However, elemental diffusion effects inside the film and heterojunction energy band matching on the performance of flexible solar cells are rarely reported. In this work, flexible CZTS solar cells were doped with various sodium sources using a simple solution spin-coating post-treatment method. The research results demonstrated that films prepared by Na2S2O3 solution doping exhibit improved crystalline quality and photoelectric properties, while also inhibiting the growth of impurity defects within the films. Further optimization of the doping concentration of post-treatment solution showed that when the doping ratio was 0.05 mmol mL−1, the grain growth of the prepared film was larger, and adhesion between the film layers was enhanced. The energy band bending of the CZTS/CdS heterojunction exhibited a “cliff” arrangement when the conduction band offset (CBO) value was −0.34 eV, facilitating carrier transport in the space charge region and enhancing the collection of photogenerated carriers. The flexible CZTS solar cell constructed on this basis exhibited excellent bending resistance and a maximum photoelectric conversion efficiency (PCE) of 5.83% with an open-circuit voltage (Voc) of 609 mV.