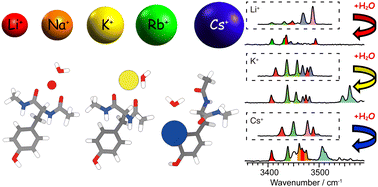
K+ channels allow selective permeation of K+, but not physiologically abundant Na+, at almost diffusion limit rates. The conduction mechanism of K+ channels is still controversial, with experimental and computation studies supporting two distinct conduction mechanisms: either with or without water inside the channel. Here, we employ a bottom-up approach on hydrated alkali metal complexes of a model peptide of K+ channels, Ac-Tyr-NHMe, to characterize metal–peptide, metal–water, and water–peptide interactions that govern the selectivity of K+ channels at a molecular level. Both the extension to the series of alkali metal ions and to temperature-dependent studies (approaching physiological values) have revealed the clear difference between permeable and non-permeable ions in the spectral features of the ion complexes. Furthermore, the impact of hydration is discussed in relation to the K+ channels by comparisons of the non-hydrated and hydrated complexes.