Pressure enhanced negative thermal expansion in 2H CuScO2 from first-principles calculations
Abstract
Finding materials with negative thermal expansion (NTE) property is challenging. Tuning NTE is of fundamental and technological importance. Pressure enhanced negative thermal expansion behavior in 2H CuScO2 is found and expounded using density functional theory (DFT) and quasi-harmonious approximation (QHA). The frequencies of low energy modes and Grüneisen parameters decrease under pressure, but the bulk modulus increases with pressure. The transverse vibration of Cu atoms becomes stronger under pressure and the materials undergo thermal softening. These factors including thermal softening, pressure induced decrease of Grüneisen parameters and pressure induced strengthening of transverse vibration of Cu atoms all contribute to the enhanced negative thermal expansion property in 2H CuScO2 in view of the thermodynamic relationship 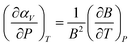 , Grüneisen's theory of thermal expansion
, Grüneisen's theory of thermal expansion 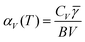 and the mechanism of NTE, respectively.
and the mechanism of NTE, respectively.



 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...