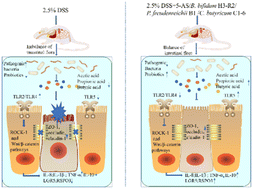
Probiotics have long been shown to modulate inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) in a variety of ways, and their major metabolites, short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), have been shown to play a role in the alleviation of ulcerative colitis (UC). In the present study, DSS-treated C57BL/6J mice were gavaged with Bifidobacterium bifidum H3-R2, Propionibacterium freudenreichii B1 and Clostridium butyricum C1-6, which are capable of high production of acetic acid, propionic acid and butyric acid, respectively. We measured the effects of these three strains on inflammatory factors, intestinal barrier function, colitis-related signalling pathways, intestinal microbiome composition, and SCFA content in intestinal contents. The results of the experiment showed that all three strains differentially increased the colon length; reduced weight loss; decreased the splenic index; decreased the DAI scores and MPO activity; decreased proinflammatory factor levels (IL-8, IL-1β and TNF-α); increased anti-inflammatory factor production (IL-10); and enhanced tight junction protein expression (ZO-1, occludin, and claudin-1). Moreover, Bifidobacterium bifidum H3-R2 and Propionibacterium freudenreichii B1 played crucial roles through TLRs/RHO kinase (ROCK1) and Wnt/β-catenin pathways in these protective effects. In addition, three strains improved the composition of the intestinal flora and increased the production of SCFAs; notably, Propionibacterium freudenreichii B1 had the best effect. This study provides a scientific basis for the further application of probiotics in the treatment of UC in the future.