Engineered protein–iron oxide hybrid biomaterial for MRI-traceable drug encapsulation†
Abstract
Labeled protein-based biomaterials have become popular for various biomedical applications such as tissue-engineered, therapeutic, and diagnostic scaffolds. Labeling of protein biomaterials, including with ultrasmall superparamagnetic iron oxide (USPIO) nanoparticles, has enabled a wide variety of imaging and therapeutic techniques. These USPIO-based biomaterials are widely studied in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), thermotherapy, and magnetically-driven drug delivery, which provide a method for direct and non-invasive monitoring of implants or drug delivery agents. Where most developments have been made using polymers or collagen hydrogels, shown here is the use of a rationally designed protein as the building block for a meso-scale fiber. While USPIOs have been chemically conjugated to antibodies, glycoproteins, and tissue-engineered scaffolds for targeting or improved biocompatibility and stability, these constructs have predominantly served as diagnostic agents and often involve harsh conditions for USPIO synthesis. Here, we present an engineered protein–iron oxide hybrid material comprised of an azide-functionalized coiled-coil protein with small molecule binding capacity conjugated via bioorthogonal azide–alkyne cycloaddition to an alkyne-bearing iron oxide templating peptide, CMms6, for USPIO biomineralization under mild conditions. The coiled-coil protein, dubbed Q, has been previously shown to form nanofibers and, upon small molecule binding, further assembles into mesofibers via encapsulation and aggregation. The resulting hybrid material is capable of doxorubicin encapsulation as well as sensitive 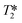 -weighted MRI darkening for strong imaging capability that is uniquely derived from a coiled-coil protein.
-weighted MRI darkening for strong imaging capability that is uniquely derived from a coiled-coil protein.



 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...
