Designing inorganically functionalized magic-size II–VI clusters and unraveling their surface states†
Abstract
Surface engineering is a critical step in the functionalization of nanomaterials to improve their optical and electrochemical properties. However, this process remains a challenge in II–VI magic-size clusters (MSCs) due to their high sensitivity to the environment. Herein, we developed a general surface modification strategy to design all-inorganic MSCs by using certain metal salts (cation = Zn2+, In3+; Anion = Cl−, NO3−, OTf−) and stabilized (CdS)34, (CdSe)34 and (ZnSe)34 MSCs in polar solvents. We further investigated the surface states of II–VI MSCs using electrochemiluminescence (ECL). The mechanism study revealed that the ECL emission was attributed to 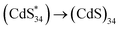 . Two ECL emissions at 556 nm and 530 nm demonstrated two surface passivation modes on (CdS)34 MSCs, which can be tuned by the surface ligands. The achievement of surface engineering opens a new design space for functional MSC compounds.
. Two ECL emissions at 556 nm and 530 nm demonstrated two surface passivation modes on (CdS)34 MSCs, which can be tuned by the surface ligands. The achievement of surface engineering opens a new design space for functional MSC compounds.



 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...