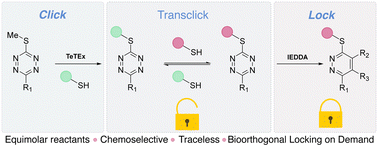
The late-stage functionalisation and diversification of complex structures including biomolecules is often achieved with the help of click chemistry. Besides employing irreversible click-like reactions, many synthetic applications benefit from reversible click reaction strategies, so called de-/trans-click approaches. Yet, the combination of both, reversible and irreversible click chemistry – while still respecting the stringent criteria of click transformations – remains so far elusive for modifications of biomolecular structures. Here, we report click’n lock as a concept that enables reversible click reactions and on-demand locking of chemical entities, thus switching from reversible to irreversible modifications of complex biomolecules. For this purpose, we employ the tetrazine–thiol exchange (TeTEx) reaction as a fully traceless click reaction with second order rate constants k2 higher than 2 M−1 s−1 within aqueous environments. Employing TeTEx as a reversible click reaction for the chemoselective modification of biomolecules is made possible by the use of 3,6-disubstituted 1,2,4,5-tetrazines bearing a single sulfide residue. The inherent reactivity of tetrazines towards inverse electron demand Diels–Alder (IEDDA) reactions allows to stabilize the clicked structure, switching from reversible to irreversible systems (click’n lock).