Topological phase transition and skyrmions in a Janus MnSbBiSe2Te2 monolayer†
Abstract
Using first-principles calculations and micro-magnetic simulations, we propose a Janus MnSbBiSe2Te2 (MSBST) monolayer derived from the MnBi2Te4 (MBT) ferromagnet and investigate the influence of biaxial strain on the electronic structures, topological characteristics and spin textures. Different from pristine MBT with an out-of-plane easy axis, the anisotropy of MSBST prefers an in-plane direction. Intriguingly, switching the easy axis direction of MSBST will significantly modify the band structure. Topological phase transition can be achieved by applying a compressive strain, making MSBST become a topological insulator with 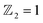 . Moreover, due to the inherent inversion asymmetry of Janus MSBST, a large Dzyaloshinskii–Moriya interaction (DMI) is induced for generating and stabilizing skyrmions. By micro-magnetic simulations, the results of spin textures show that the skyrmions phase can be achieved in MSBST with an external magnetic field of 0.8 T. Our findings provide guidelines for the development and application of spintronic devices with nontrivial topological properties and a large DMI.
. Moreover, due to the inherent inversion asymmetry of Janus MSBST, a large Dzyaloshinskii–Moriya interaction (DMI) is induced for generating and stabilizing skyrmions. By micro-magnetic simulations, the results of spin textures show that the skyrmions phase can be achieved in MSBST with an external magnetic field of 0.8 T. Our findings provide guidelines for the development and application of spintronic devices with nontrivial topological properties and a large DMI.



 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...