Enhanced thermal stability by short-range ordered ferroelectricity in K0.5Na0.5NbO3-based piezoelectric oxides†
Abstract
Industrial application of lead-free piezoelectric ceramics is prevented by intrinsic thermal instability. Herein, we propose a method to achieve outstanding thermal stability of converse piezoelectric constant (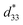 ) in lead-free potassium sodium niobate (KNN)-based ceramics by inducing a synergistic interaction between the grain size and polar configuration. Based on computational methods using phase-field simulations and first-principles calculations, the relationship between the grain size and polar configuration is demonstrated, and the possibility of achieving improved thermal stability in fine grains is suggested. A set of KNN systems is presented with meticulous dopant control near the chemical composition at which the grain size changes abnormally. Comparing the two representative samples with coarse and fine grains, significant enhancement in the thermal stability of
) in lead-free potassium sodium niobate (KNN)-based ceramics by inducing a synergistic interaction between the grain size and polar configuration. Based on computational methods using phase-field simulations and first-principles calculations, the relationship between the grain size and polar configuration is demonstrated, and the possibility of achieving improved thermal stability in fine grains is suggested. A set of KNN systems is presented with meticulous dopant control near the chemical composition at which the grain size changes abnormally. Comparing the two representative samples with coarse and fine grains, significant enhancement in the thermal stability of 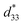 is exhibited up to 300 °C in the fine grains. The origin of the thermal superiority in fine-grained ceramics is identified through an extensive study from a microstructural perspective. The thermal stability is realized in a device by successfully demonstrating the temperature dependence of piezoelectricity. It is notable that this is the first time that lead-free piezoelectric ceramics are able to achieve exceptionally stable piezoelectricity up to 300 °C, which actualizes their applicability as piezoelectric devices with high thermal stability.
is exhibited up to 300 °C in the fine grains. The origin of the thermal superiority in fine-grained ceramics is identified through an extensive study from a microstructural perspective. The thermal stability is realized in a device by successfully demonstrating the temperature dependence of piezoelectricity. It is notable that this is the first time that lead-free piezoelectric ceramics are able to achieve exceptionally stable piezoelectricity up to 300 °C, which actualizes their applicability as piezoelectric devices with high thermal stability.



 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...