Assessing hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents for intramolecular excimer formation†
Abstract
Intramolecular excimer formation by a dipyrenyl probe, 6-(1-pyrenyl)hexyl-11(1-pyrenyl)-undecanoate [1-Py(CH2)10COO(CH2)61-Py], is used to assess hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents (HDESs) for the purpose. n-Decanoic acid (DA), L(−)-menthol (Men) and thymol (Thy) have been utilized to form HDESs with different pairs of constituents in different molar ratios, namely Men : DA (2 : 1, 1 : 1, and 1 : 2), Thy : DA (2 : 1, 1 : 1, and 1 : 2), and Thy : Men (5 : 1, 2 : 1, 1 : 1, 1 : 2, and 1 : 5). The maximum of the excimer-to-monomer emission intensity ratio, (IE/IM)max, is observed at 343.15–353.15 K for all DESs irrespective of the constitution, and it varies in a narrow range exhibiting no correlation with the dynamic viscosity (η) of the DES which varies between 2.05 and 3.56 mPa s. Excited-state intensity decay data reveal excimer dissociation back to the excited monomer to be negligible in all DESs at lower temperatures (T ≤ 323.15 K); the simplistic Birks scheme is followed at higher temperatures (T > 323.15 K). The rate constant for excimer formation/association, ka, ranges from (3.00 ± 0.50) × 106 s−1 to (103 ± 10) × 106 s−1, which is similar to that reported in other media. The temperature-dependence of the equilibrium constant for excimer formation 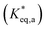 follows the van’t Hoff equation with recovered standard enthalpy (ΔaH*⊖) and standard entropy (ΔaS*⊖) changes, indicating the reversible intramolecular excimer formation to be exothermic and energetically-favorable but entropically unfavorable. A plot of kavs. T/η for all the DES systems investigated exhibits a fairly good linear correlation, indicating the adherence to the Stokes–Einstein formulation within the HDESs further emphasizing the homogeneous nature of the solubilizing media. The work helps to highlight the potential of HDESs for intramolecular excimer formation involving non-polar reactants.
follows the van’t Hoff equation with recovered standard enthalpy (ΔaH*⊖) and standard entropy (ΔaS*⊖) changes, indicating the reversible intramolecular excimer formation to be exothermic and energetically-favorable but entropically unfavorable. A plot of kavs. T/η for all the DES systems investigated exhibits a fairly good linear correlation, indicating the adherence to the Stokes–Einstein formulation within the HDESs further emphasizing the homogeneous nature of the solubilizing media. The work helps to highlight the potential of HDESs for intramolecular excimer formation involving non-polar reactants.



 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...