Concentration dependence of resistance components in solutions containing dissolved Fe2+/Fe3+
Abstract
Electrolyte solutions containing Fe2+/Fe3+ are suitable for liquid thermoelectric conversion devices (LTEs), because they are inexpensive materials and exhibit a high electrochemical Seebeck coefficient α. Here, we investigated the concentration (c) dependence of resistance components, i.e., solvent (Rs), charge-transfer (Rct), and diffusion (Rdif) resistances, of dissolved-Fe2+/Fe3+-containing aqueous, methanol (MeOH), acetone, and propylene carbonate (PC) solutions. We found that the c dependence of Rs and Rdif are well reproduced by empirical formulas, 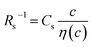 and
and 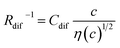 , where η(c) is viscosity at c. We further found that the magnitudes of Cs and Cdif are nearly independent of solvent, suggesting that η is one of the significant solution parameters that determine Rs and Rdif.
, where η(c) is viscosity at c. We further found that the magnitudes of Cs and Cdif are nearly independent of solvent, suggesting that η is one of the significant solution parameters that determine Rs and Rdif.



 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...